Joints - LCC
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Synovial Joint
a freely movable joint
Types
pivot
hinge
condyloid
saddle
plane
ball-and socket-joints
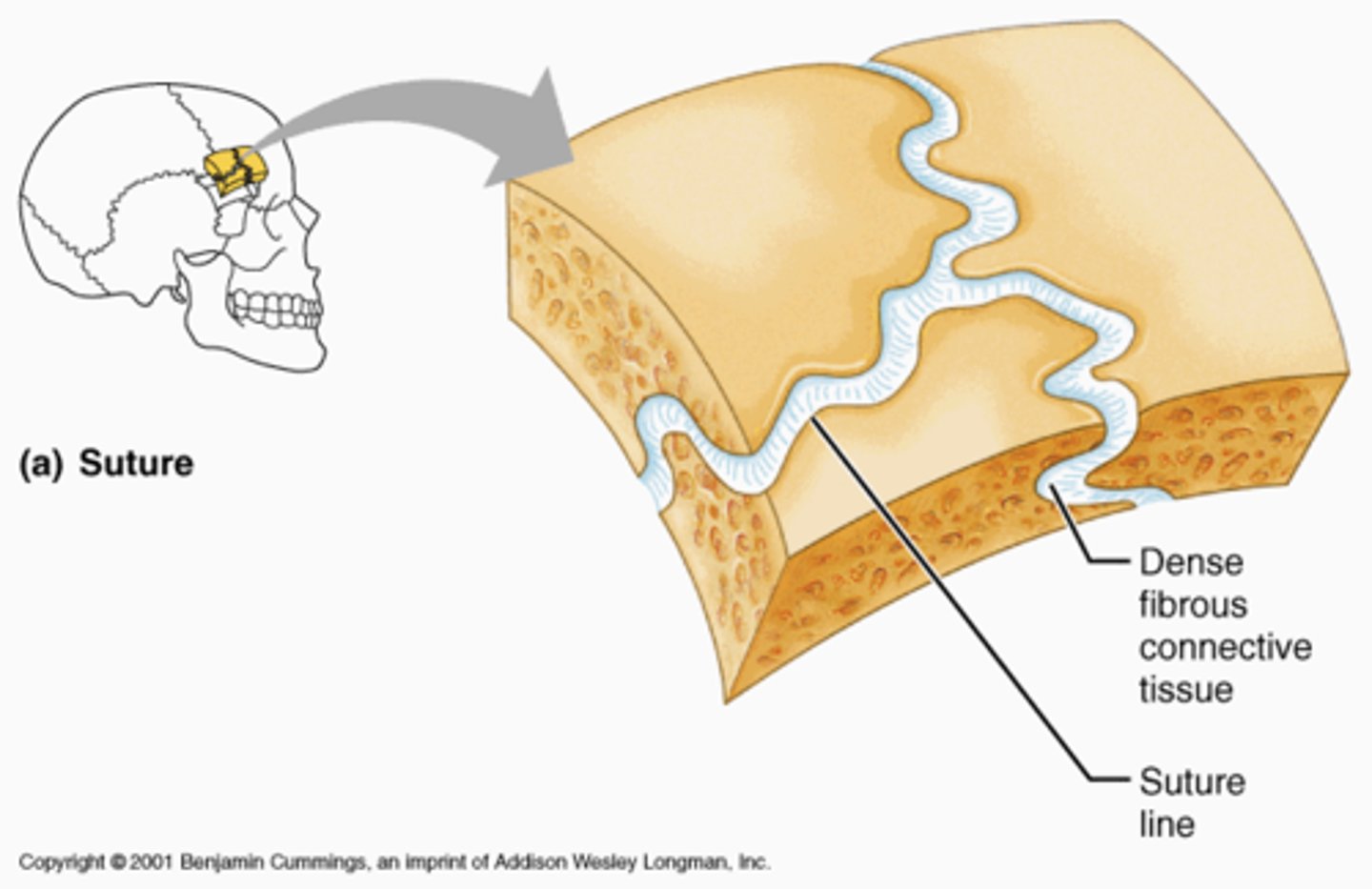
Fibrous Joint
immovable joint
Types:
Suture
Syndesmosis
Gomphosis
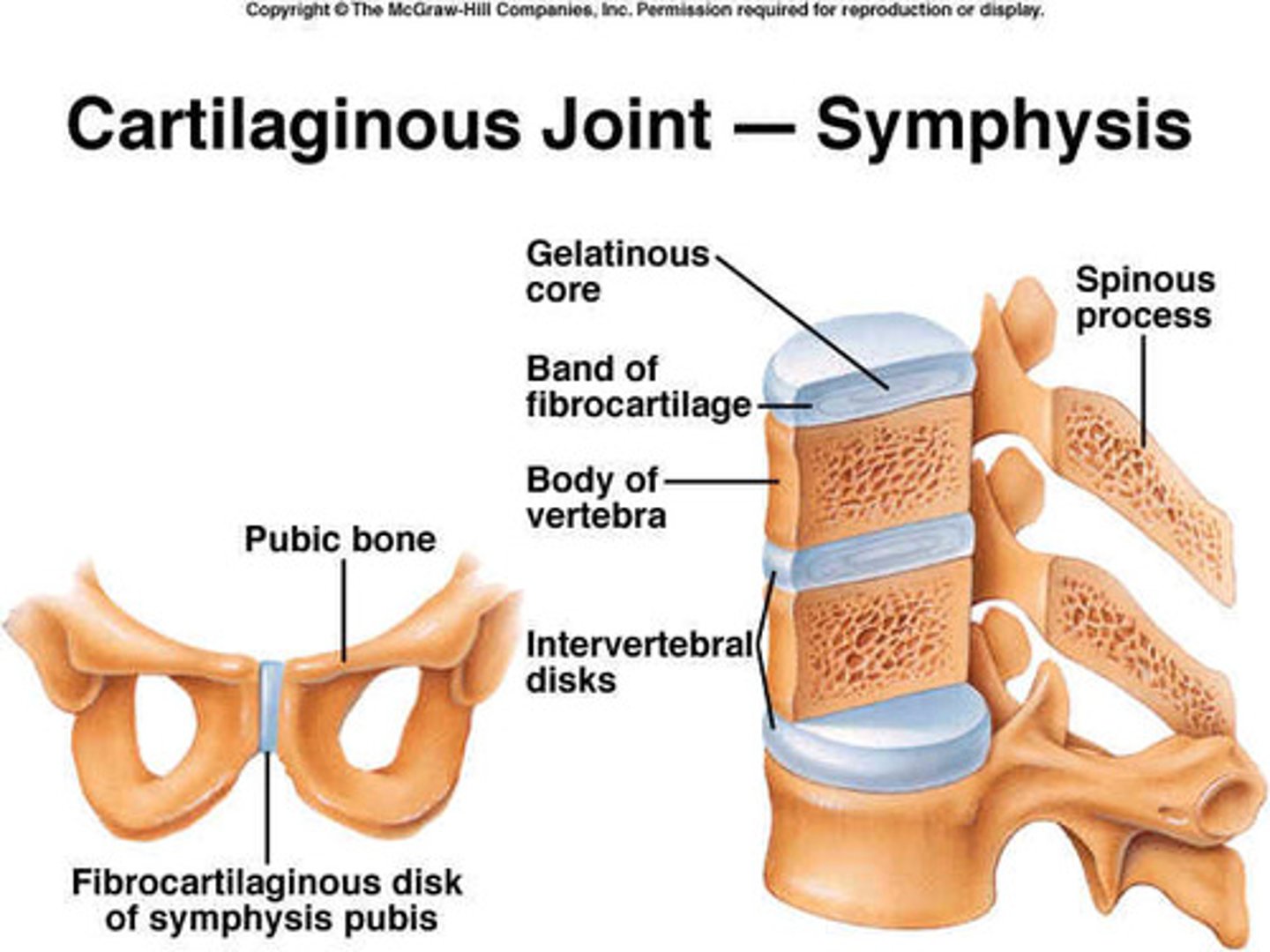
Cartilaginous Joint
allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage
Types:
Synchondrosis
Symphosis
Articulation
site where two or more bones meet (synonymous with "joint")
Synarthrosis
Provides strong support but no or very little mobility. Most fibrous joints fall into this functional category.
Amphiarthrosis
Provides strong support with some limited movement. Most cartilaginous joints fall into this functional category.
Diarthrosis
Allows for greater mobility at the expense of structural support. Most synovial joints are in this functional category.
Fibrous membrane
Attaches to the periosteum of articulating bones
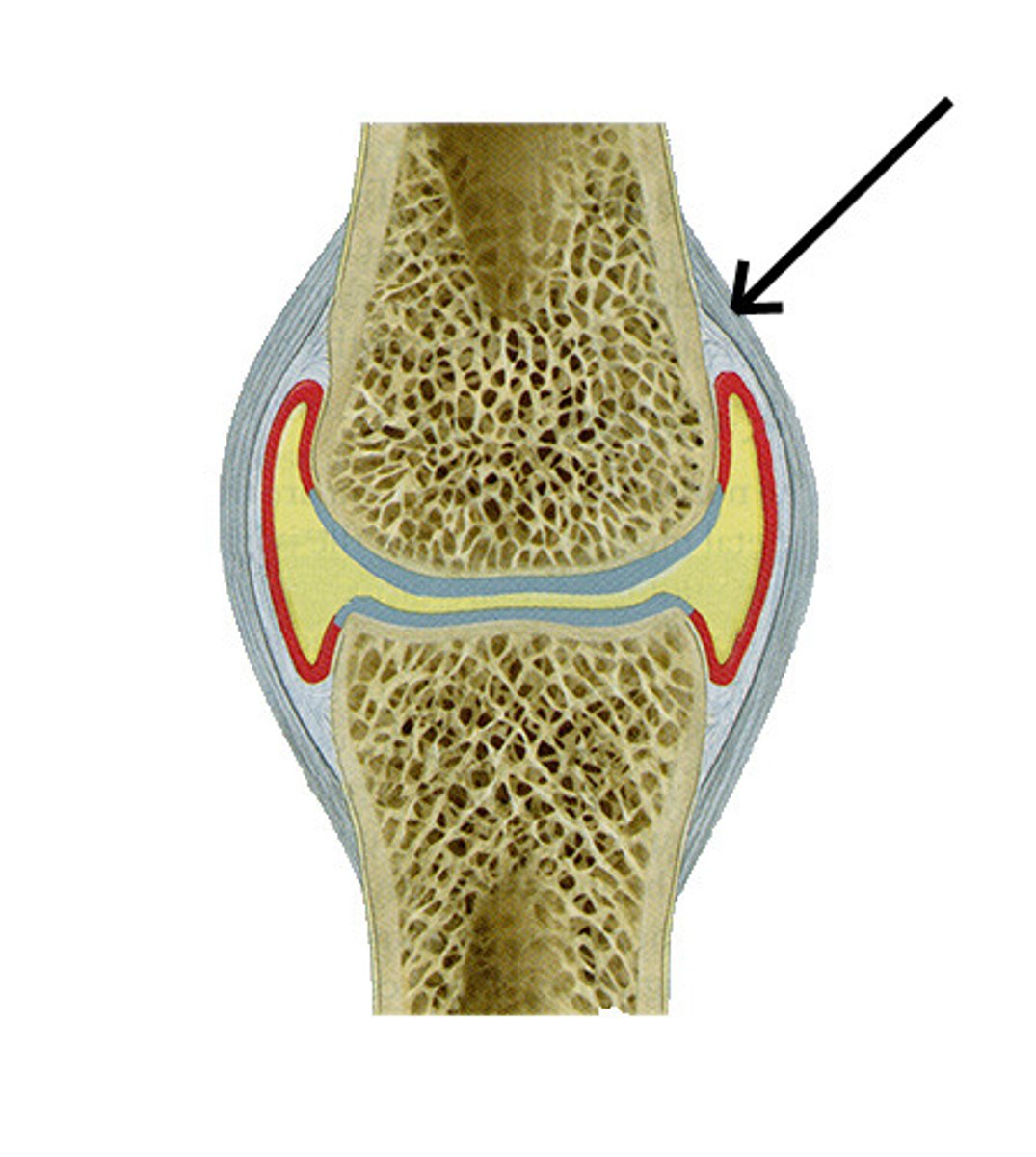
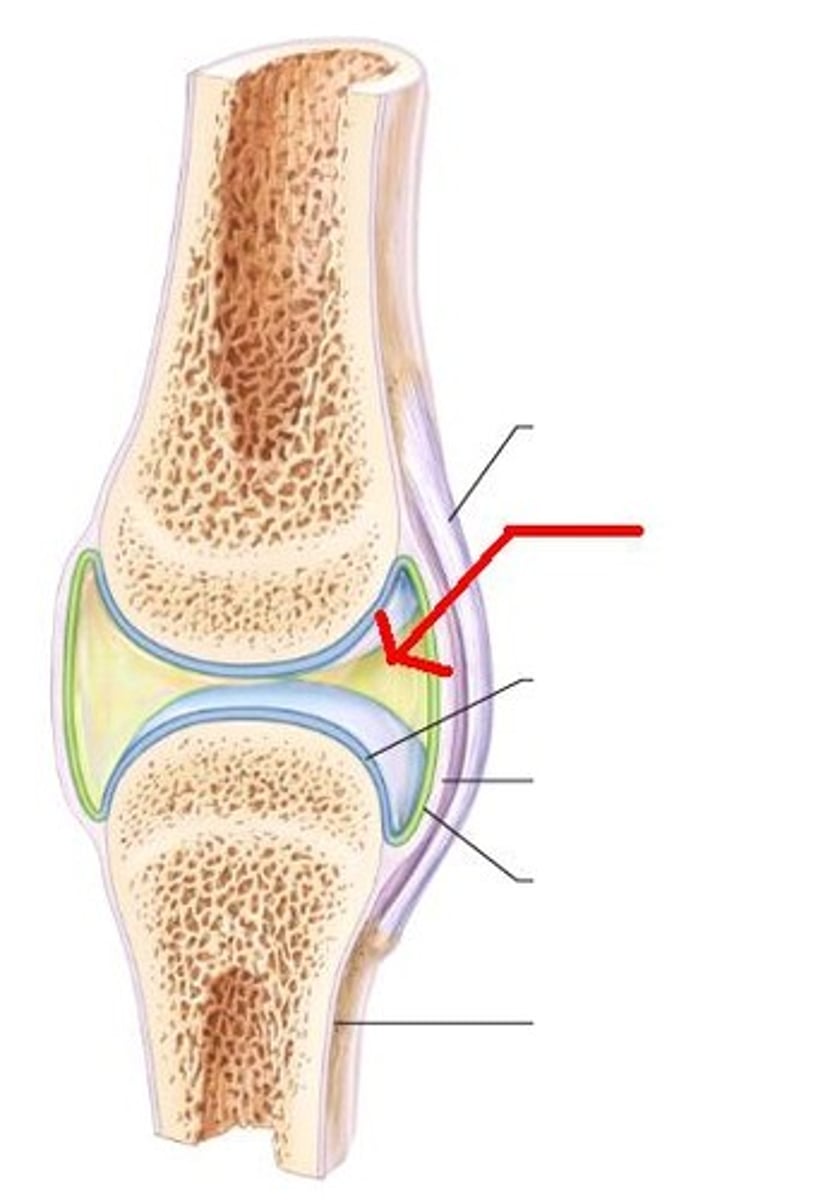
Synovial membrane
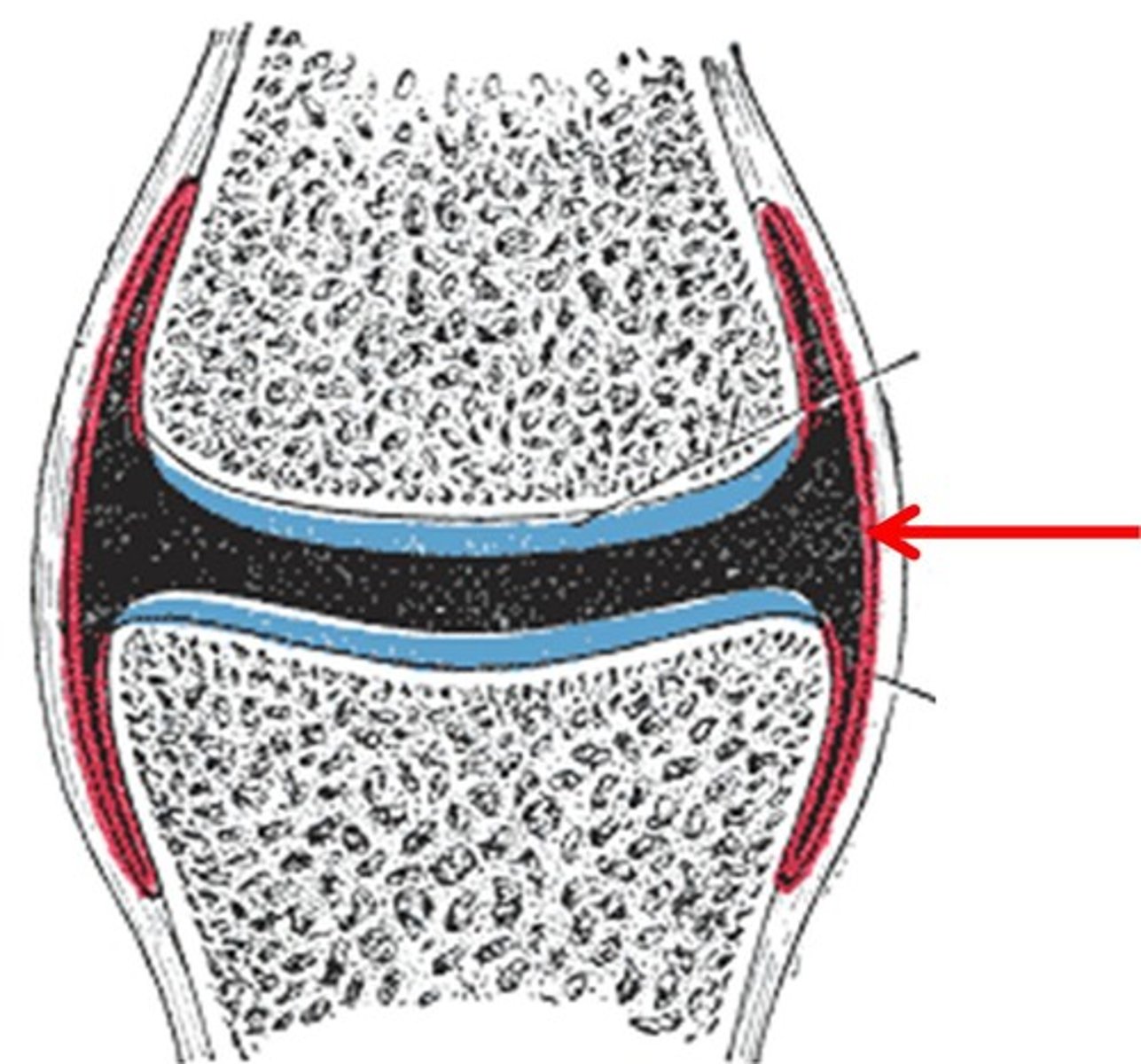
Articular capsule
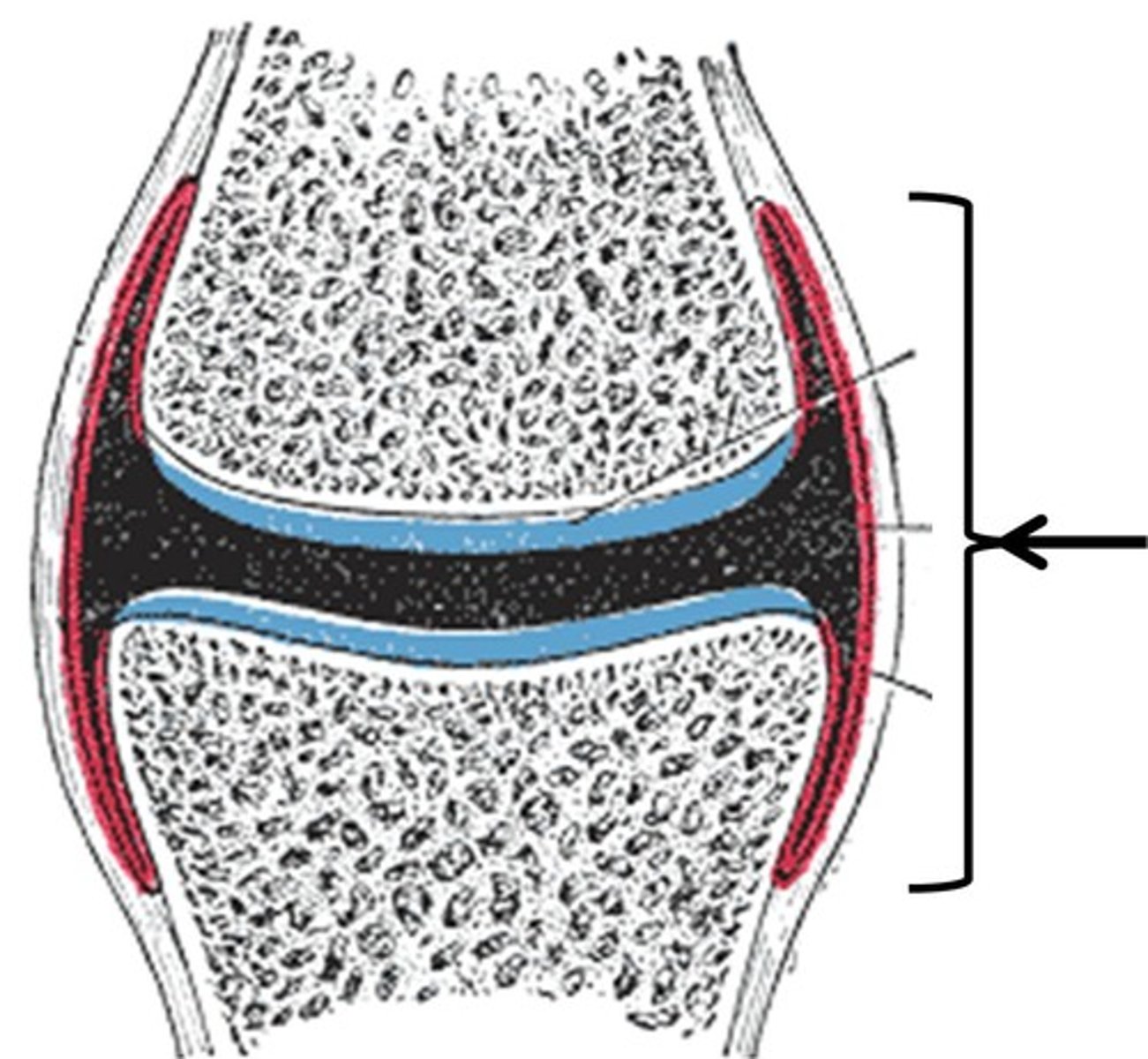
Articular cartilage
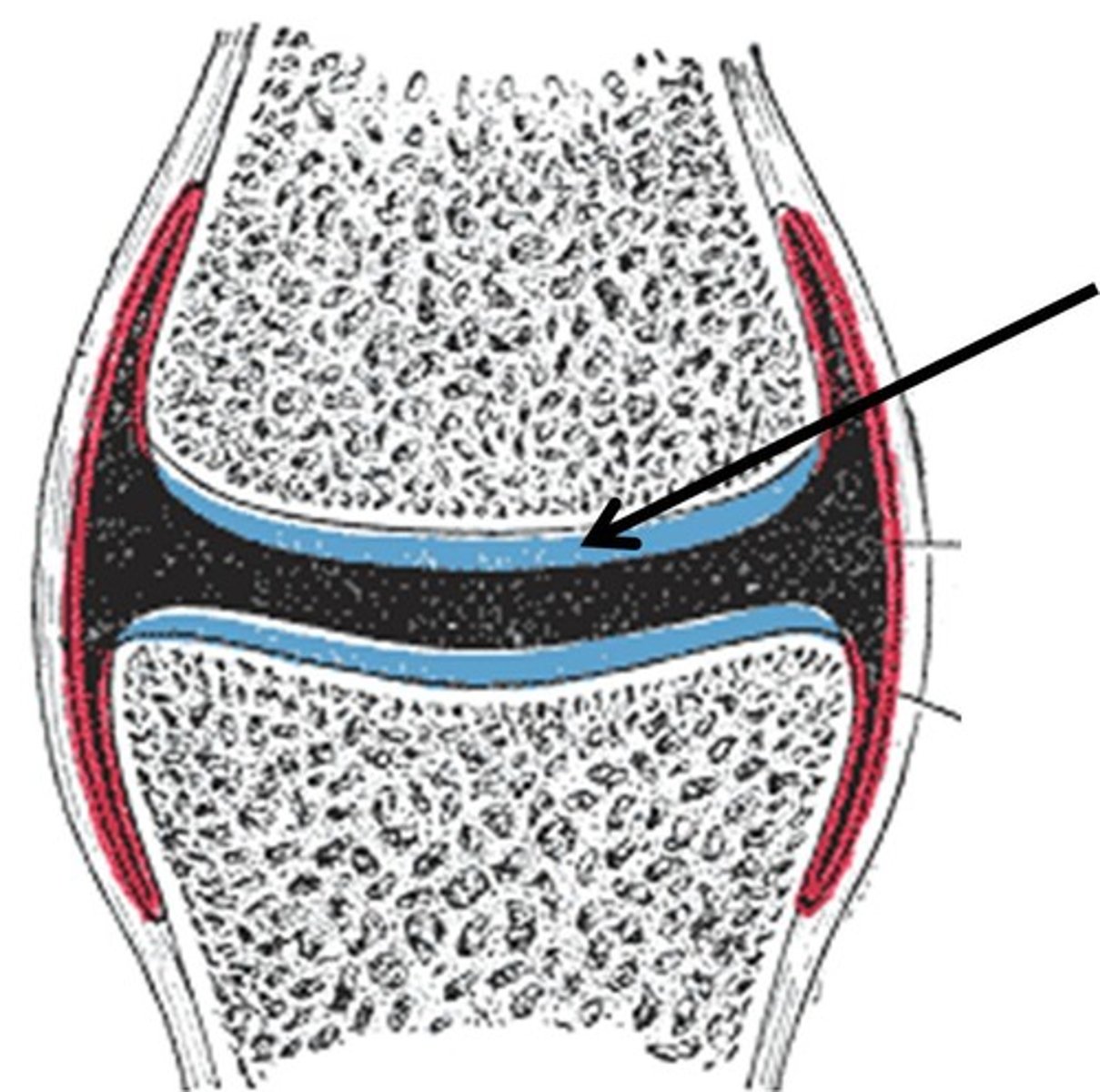
Synovial cavity
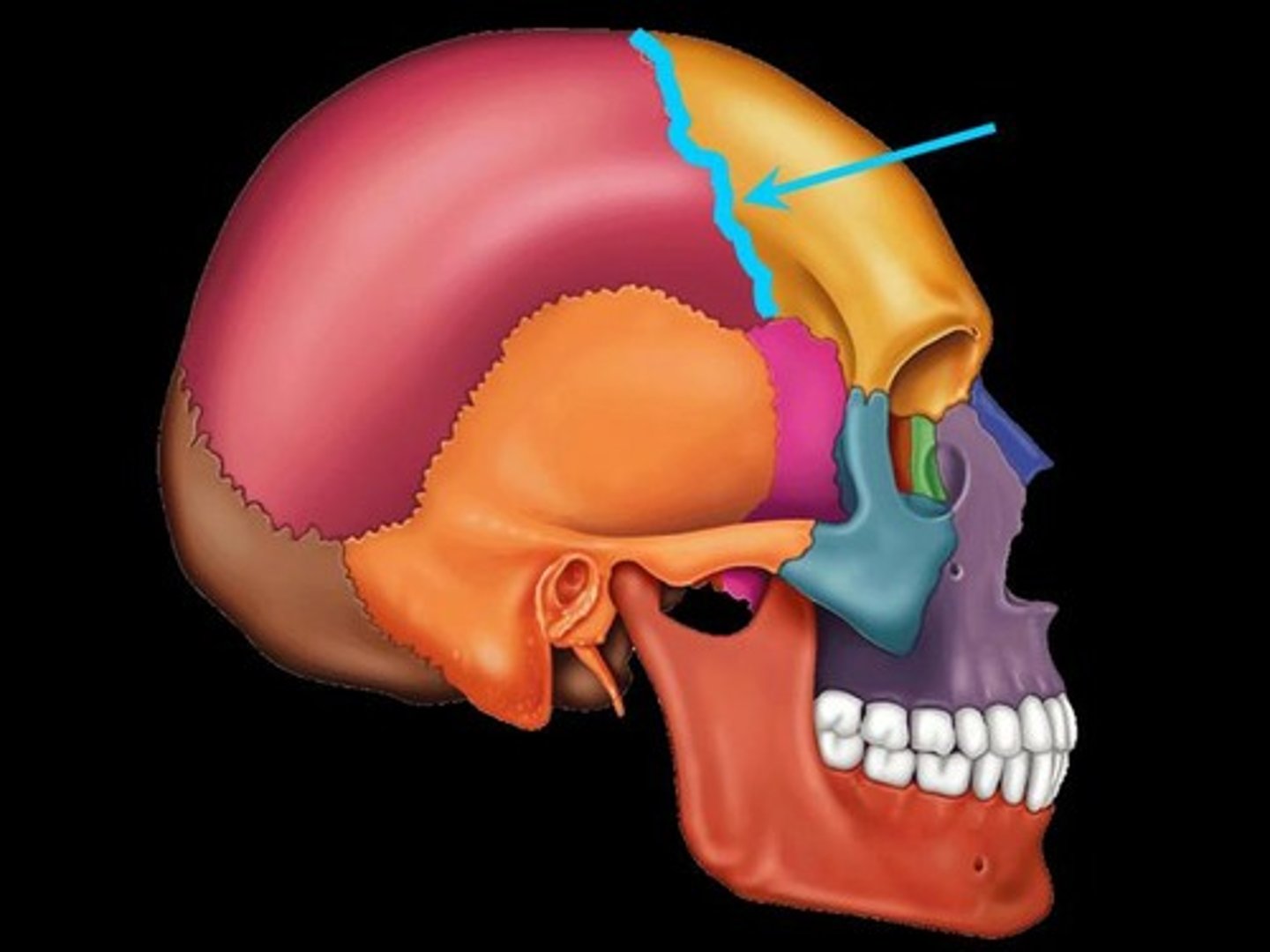
Suture
interlocking line of union between bones
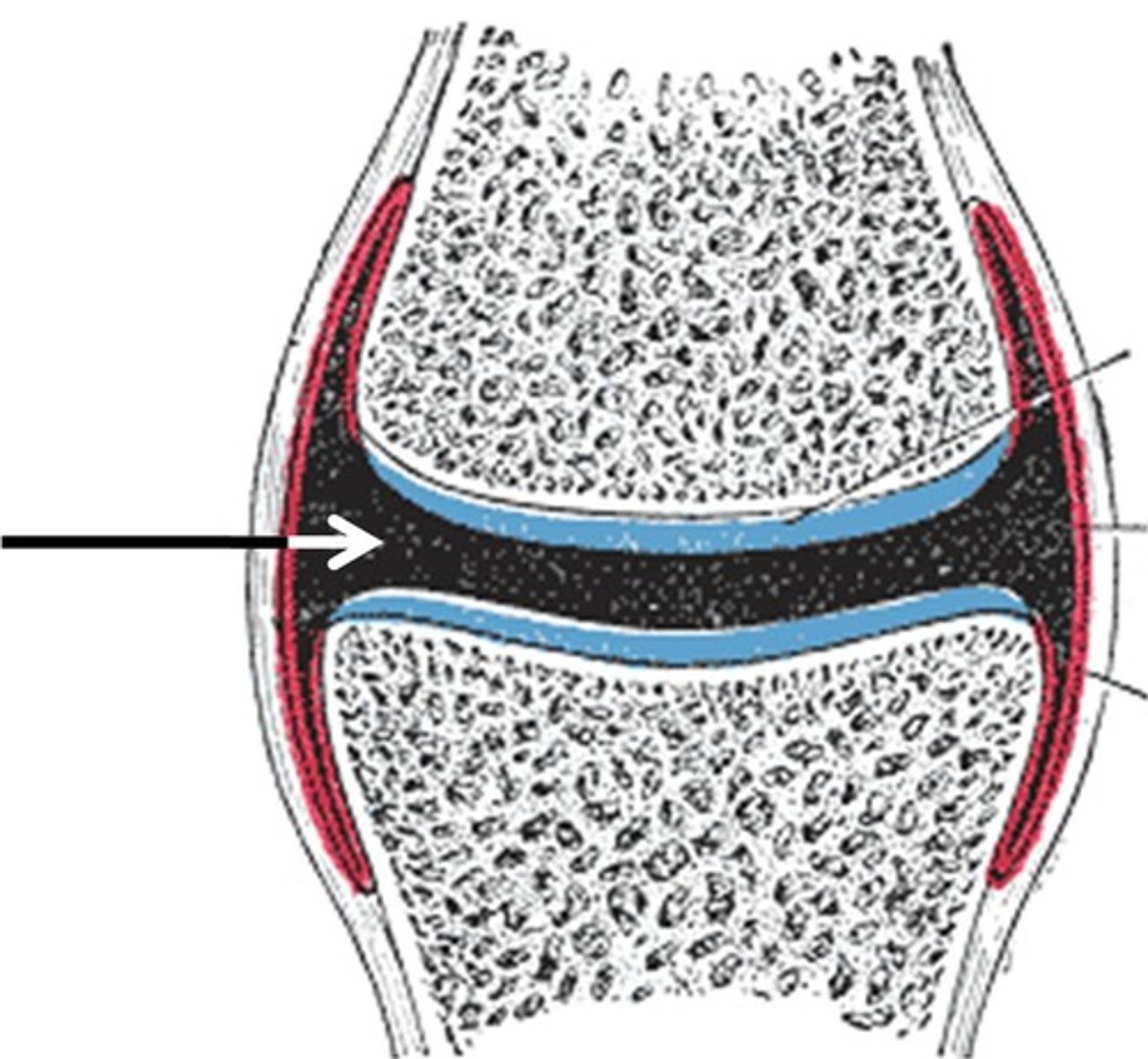
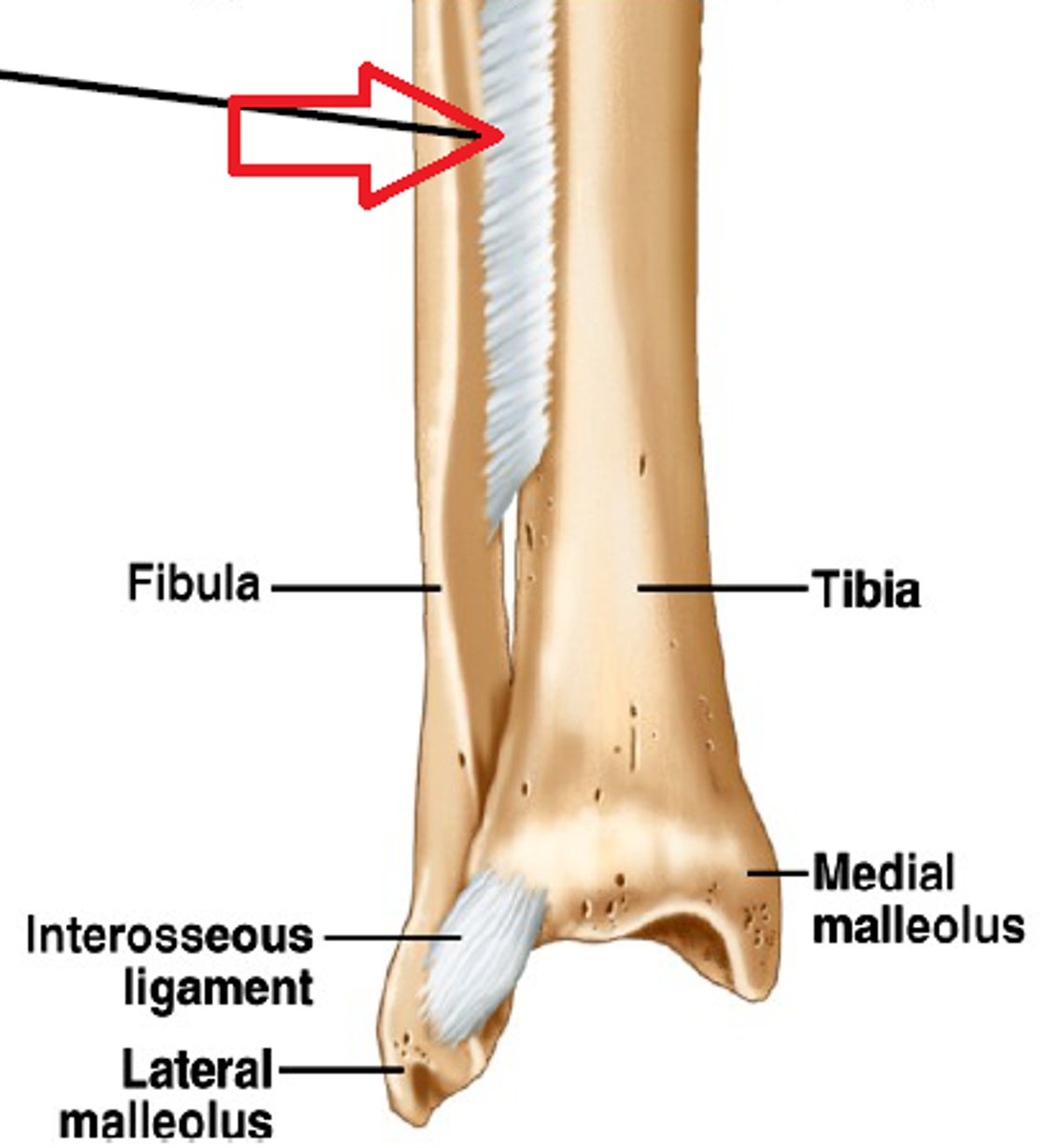
Syndesmosis
bones united by fibrous connective tissue, forming an interosseous membrane or ligament
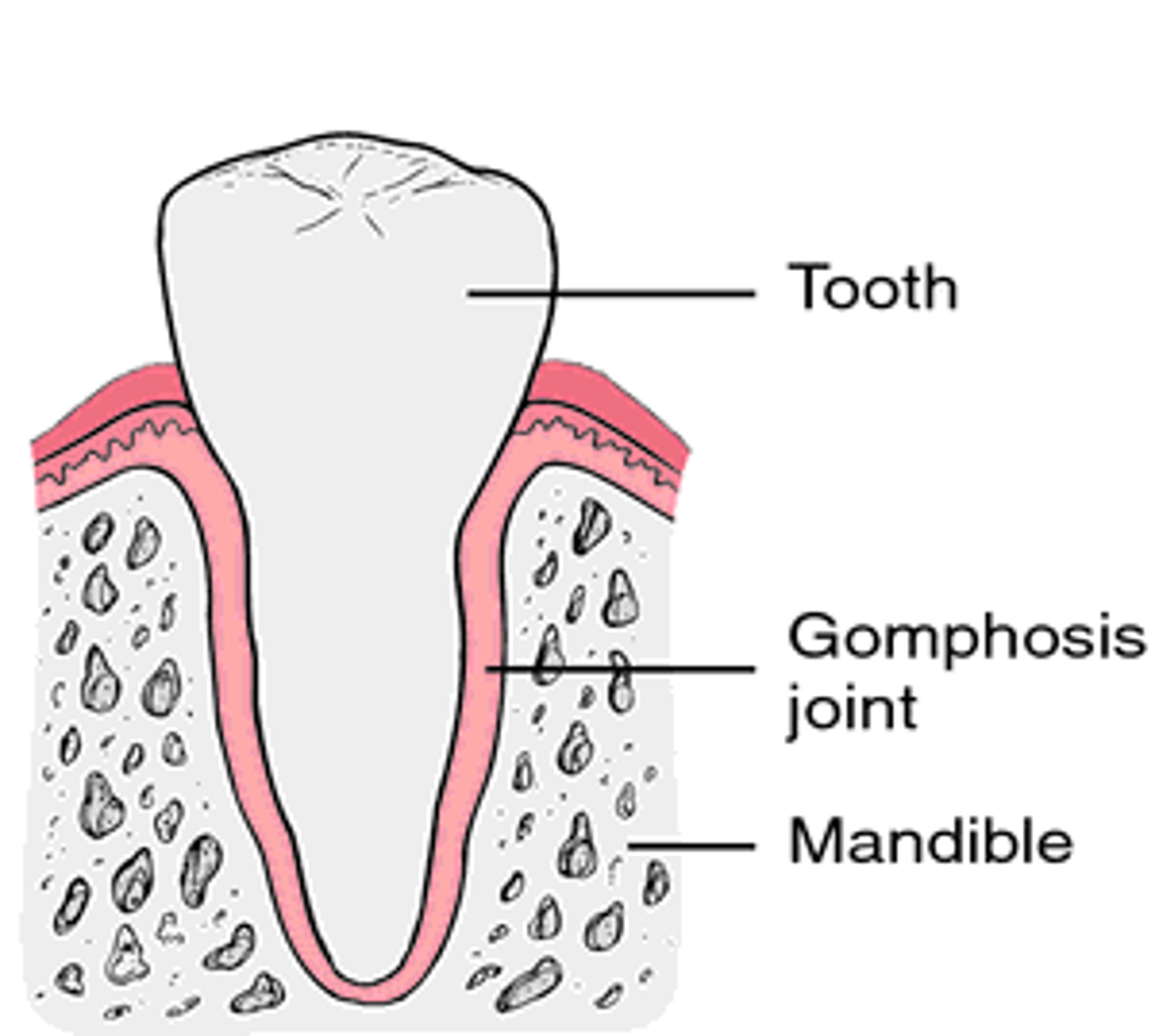
Gomphosis
Fibrous cone shaped joint found in teeth
Symphosis
held by fibrocartilage (pelvic bones)
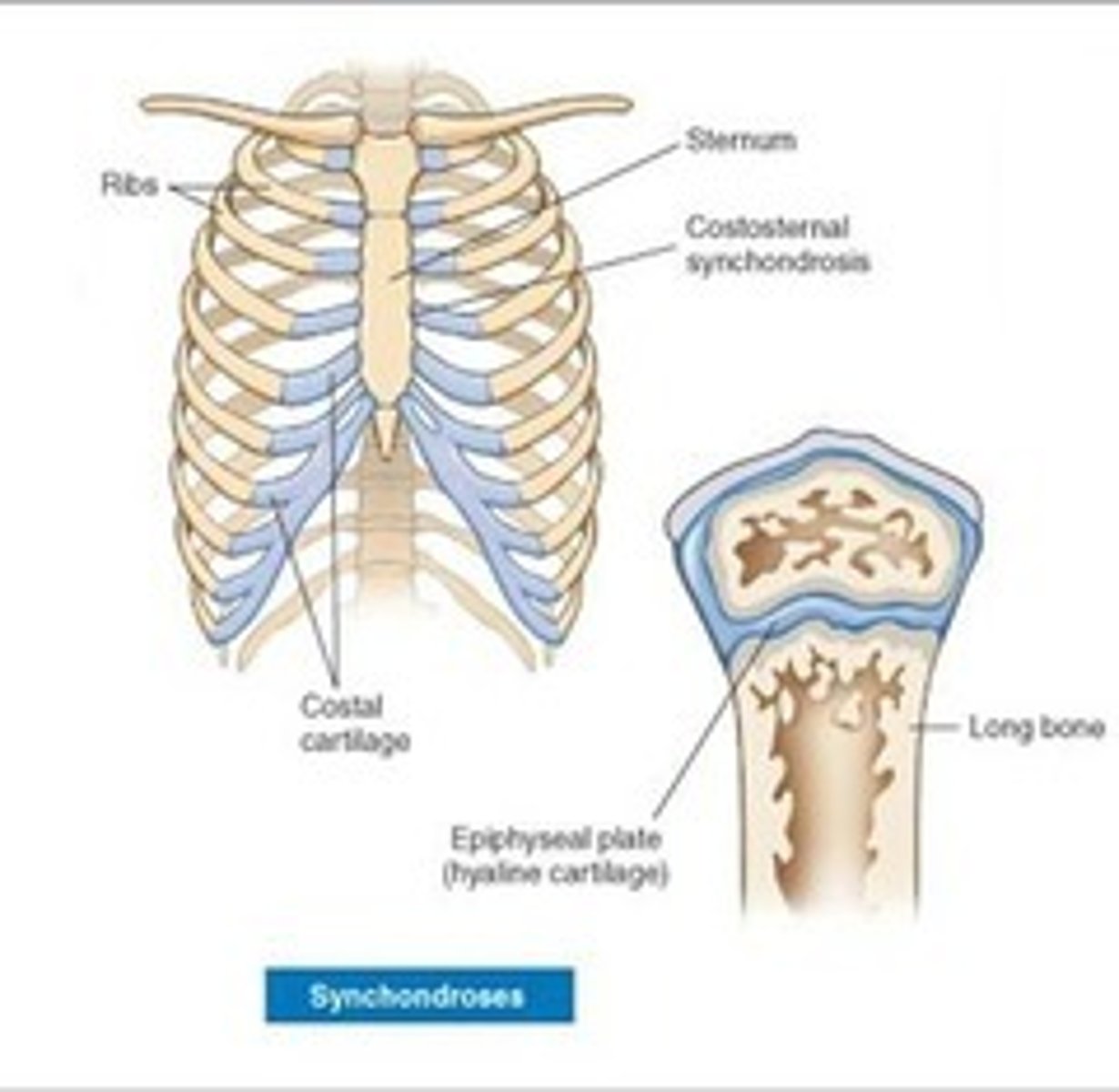
Synchondrosis
bones are bound by hyaline cartilage
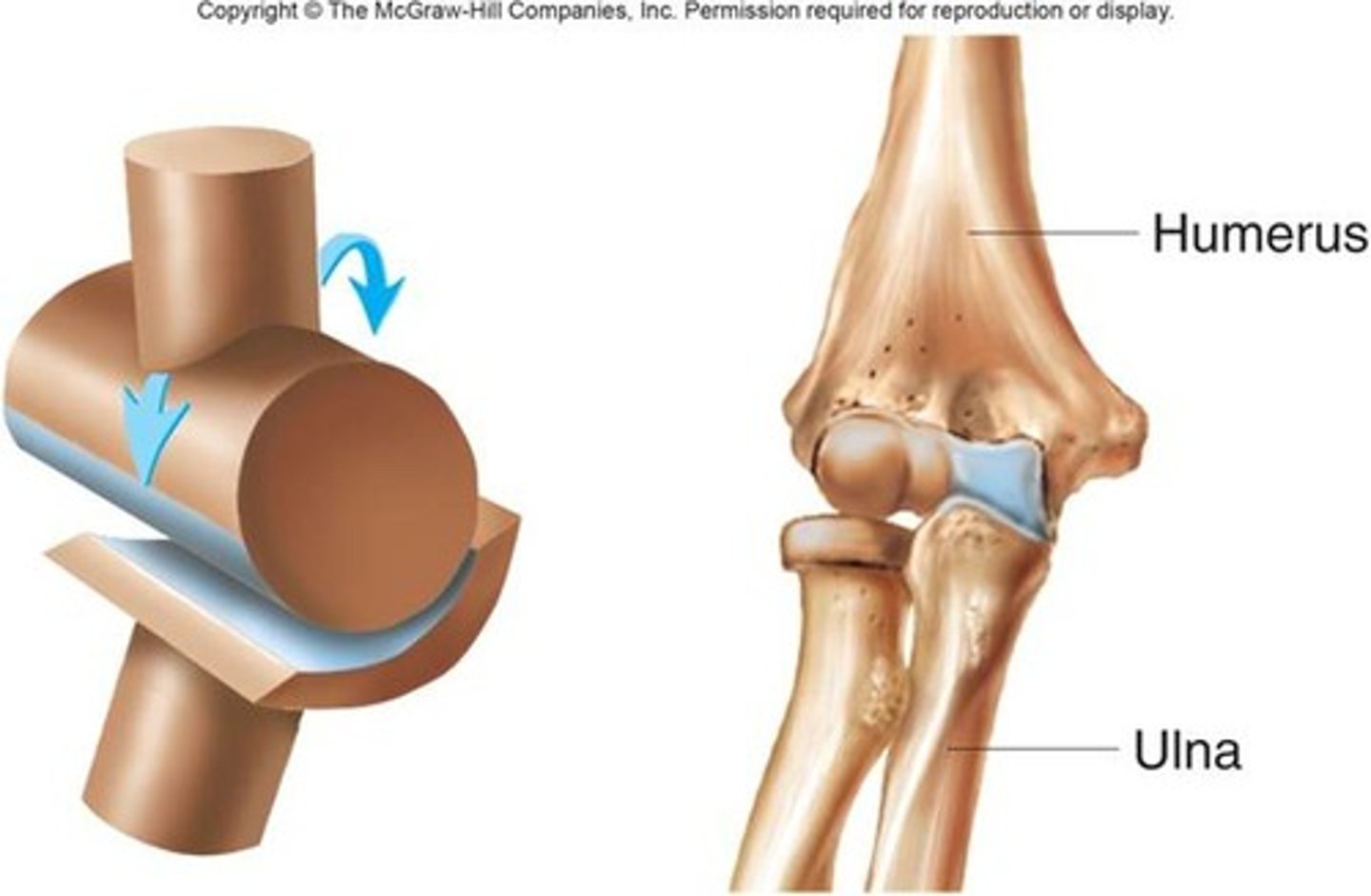
Hinge Joint
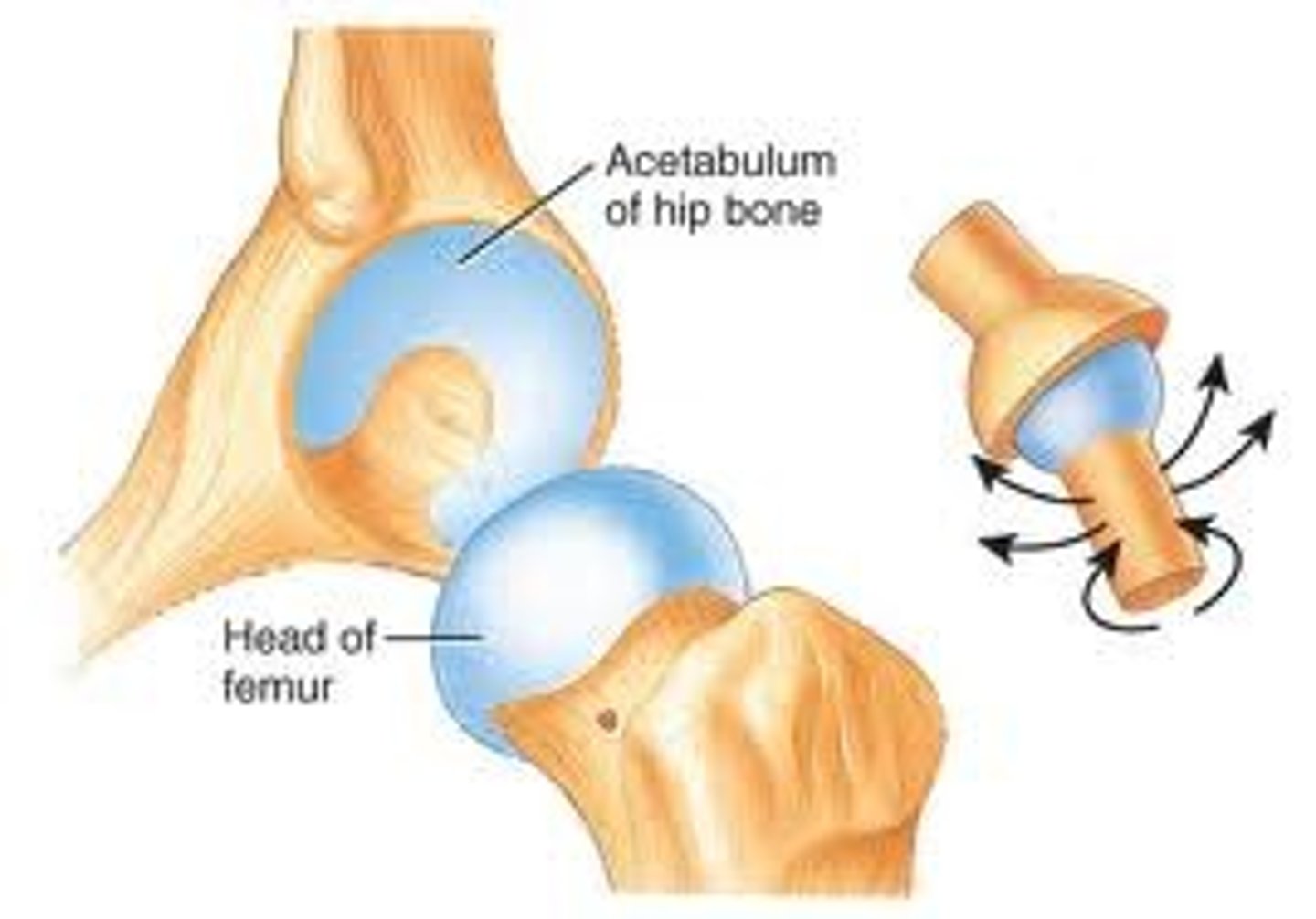
Ball and socket joint
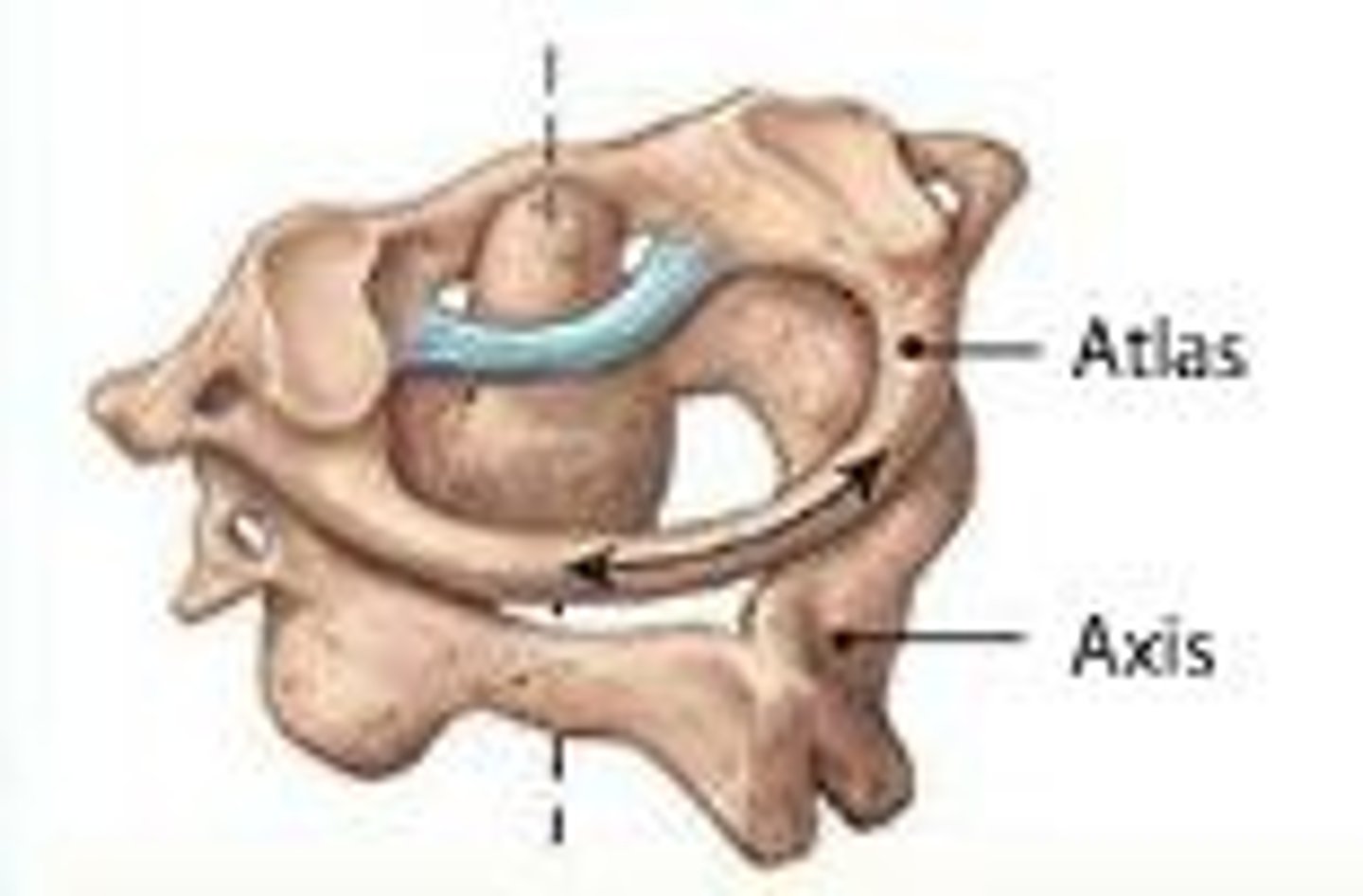
Pivot joint
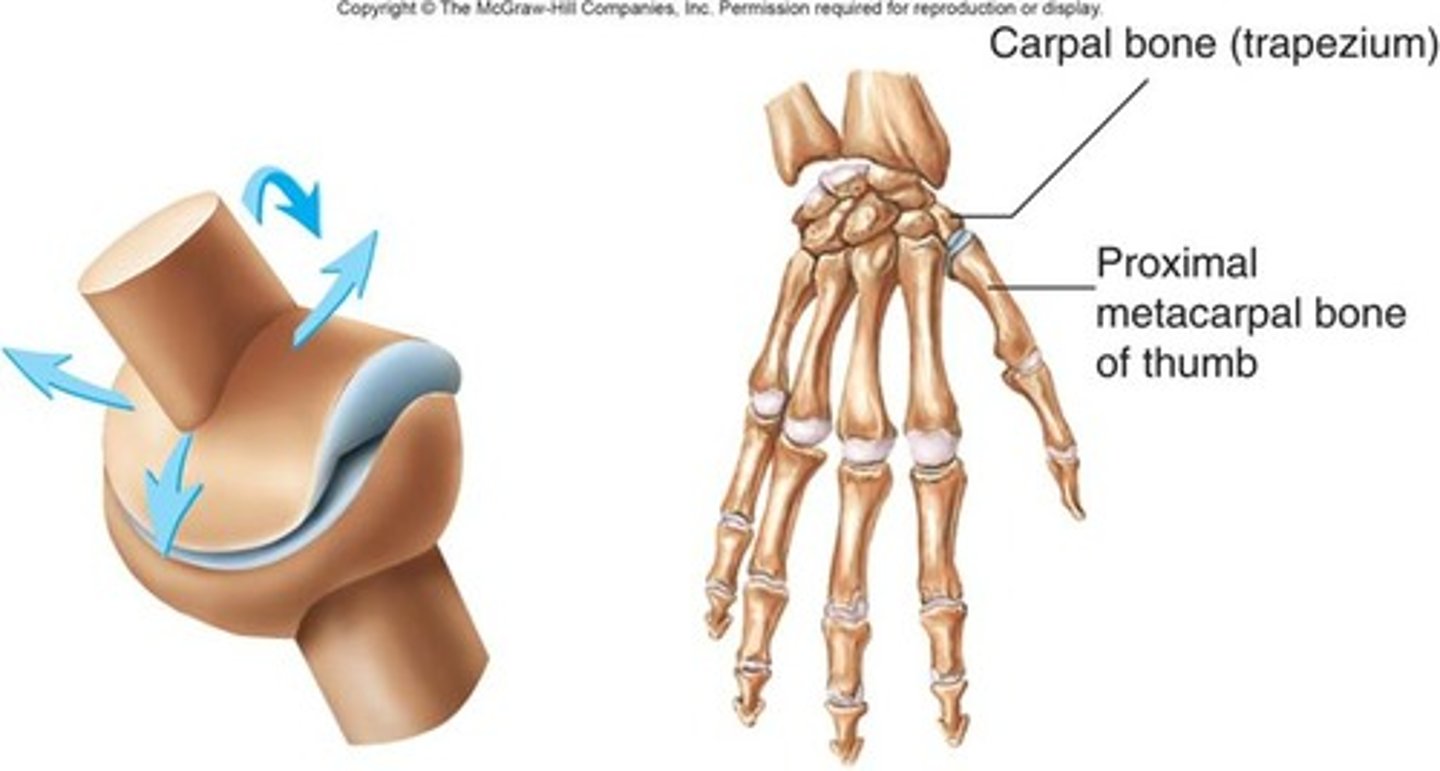
Saddle joint
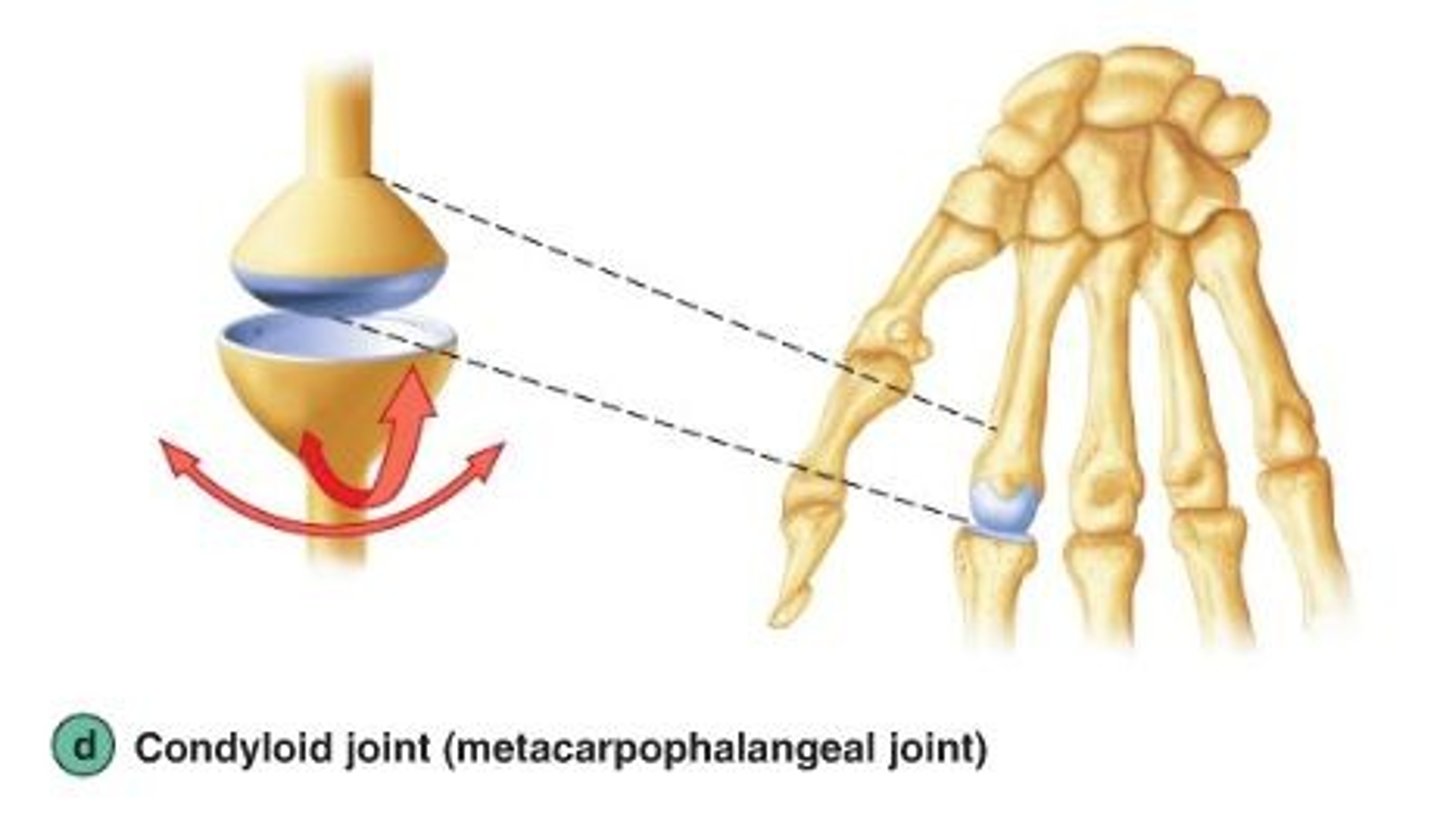
Condyloid joint
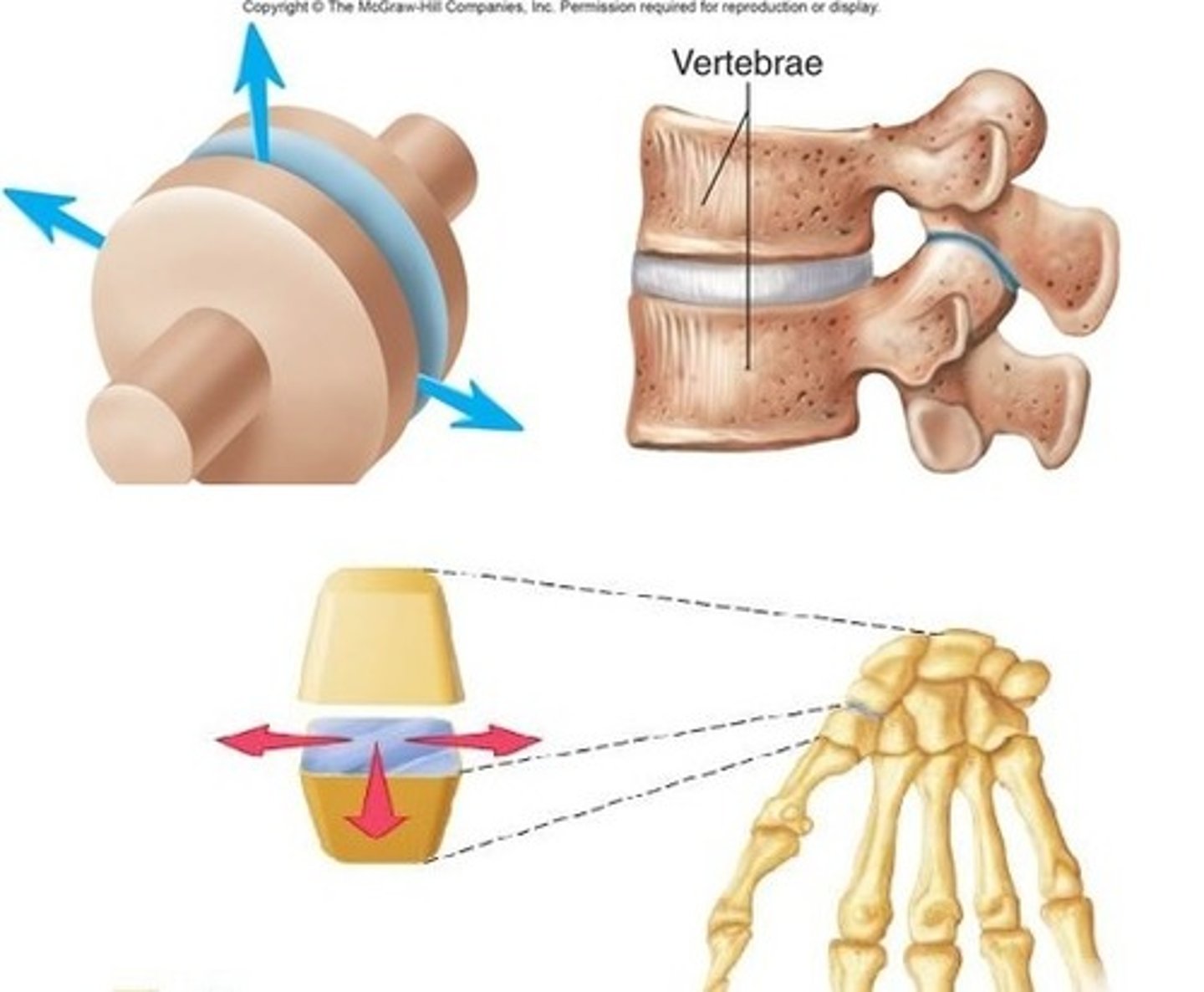
Planar joint
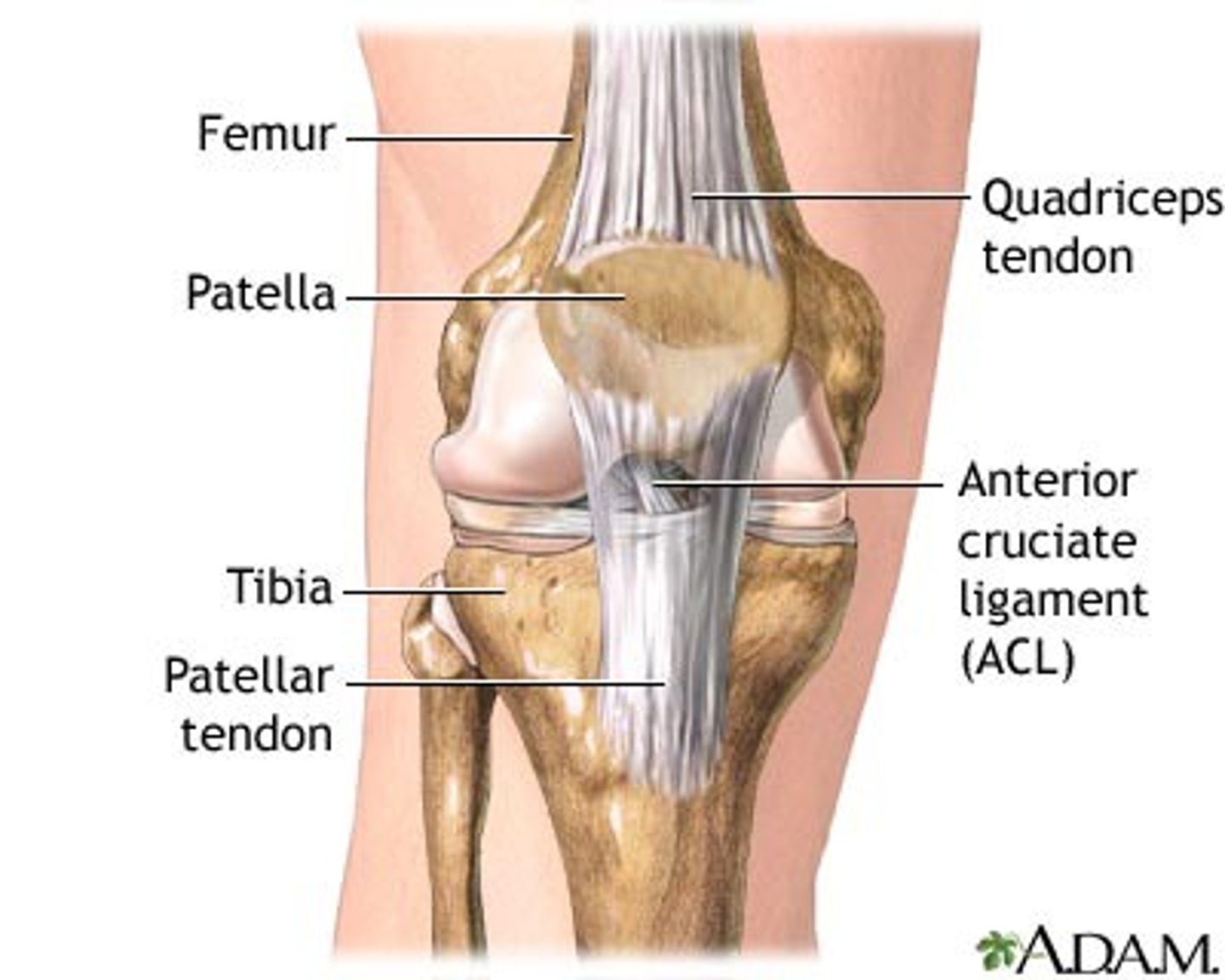
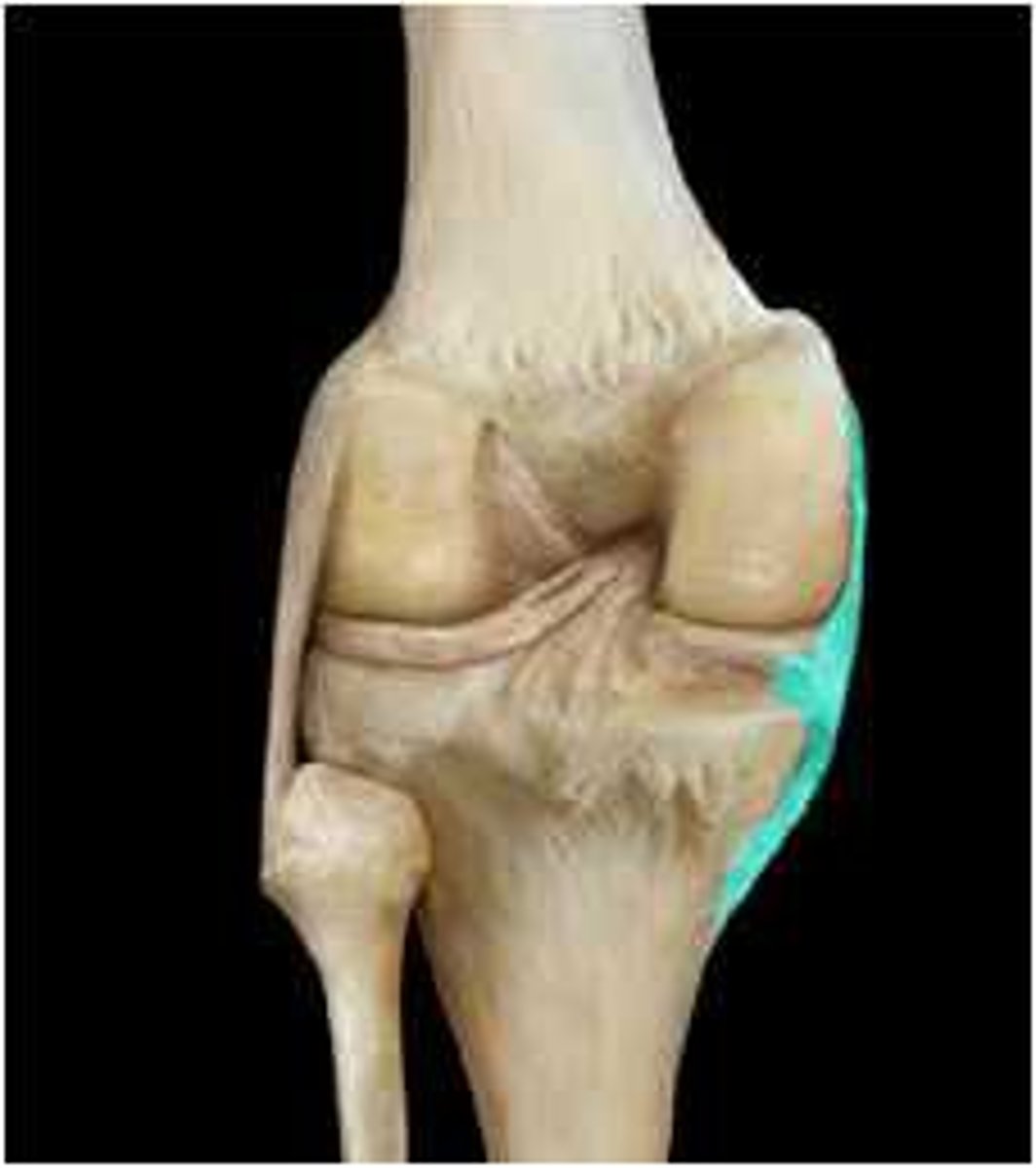
Anterior cruciate ligament
Stabilizes knee in extended position
Prevents hyperextension of knee
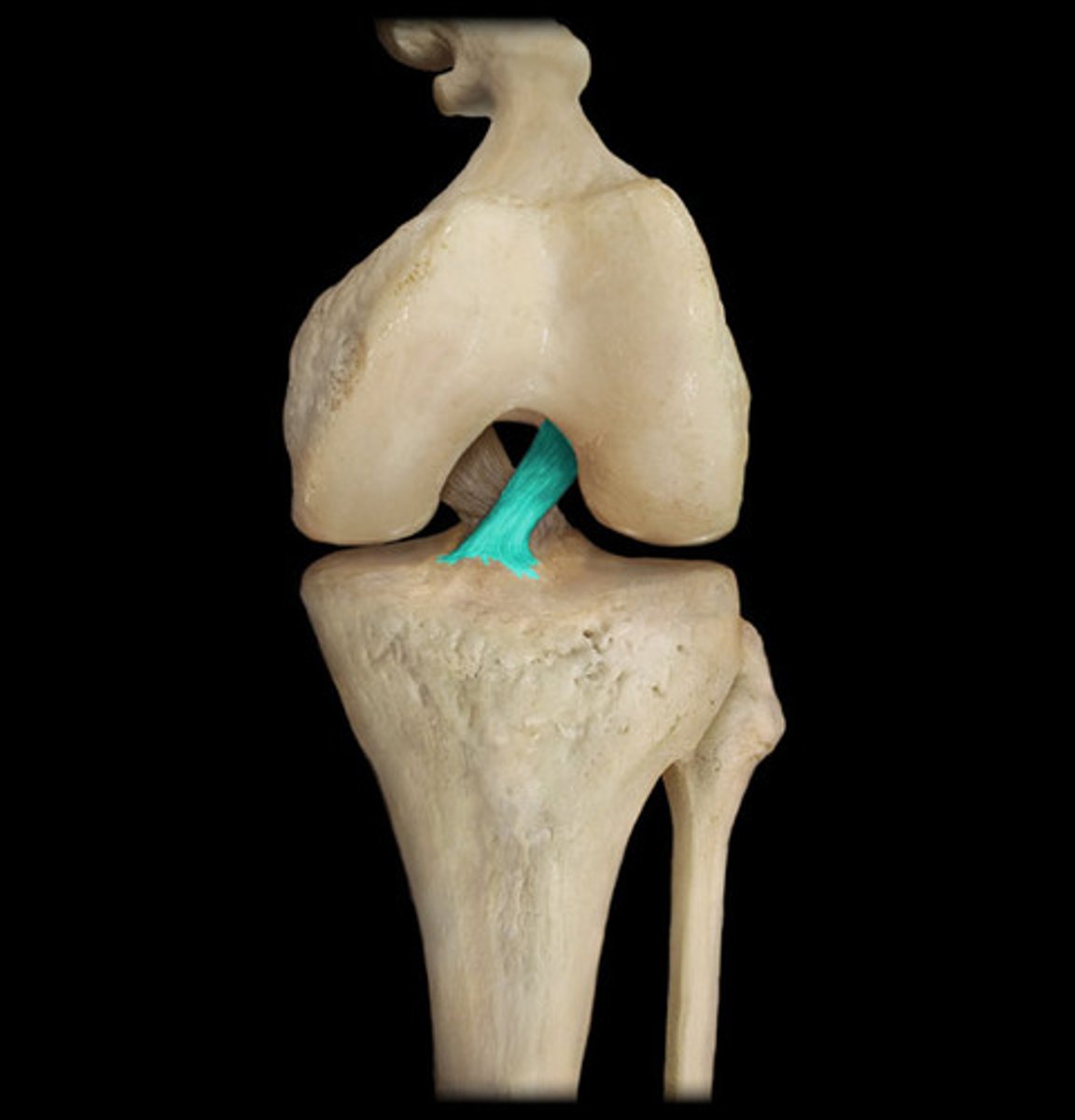
Posterior cruciate ligament
Stabilizes knee in flexed position
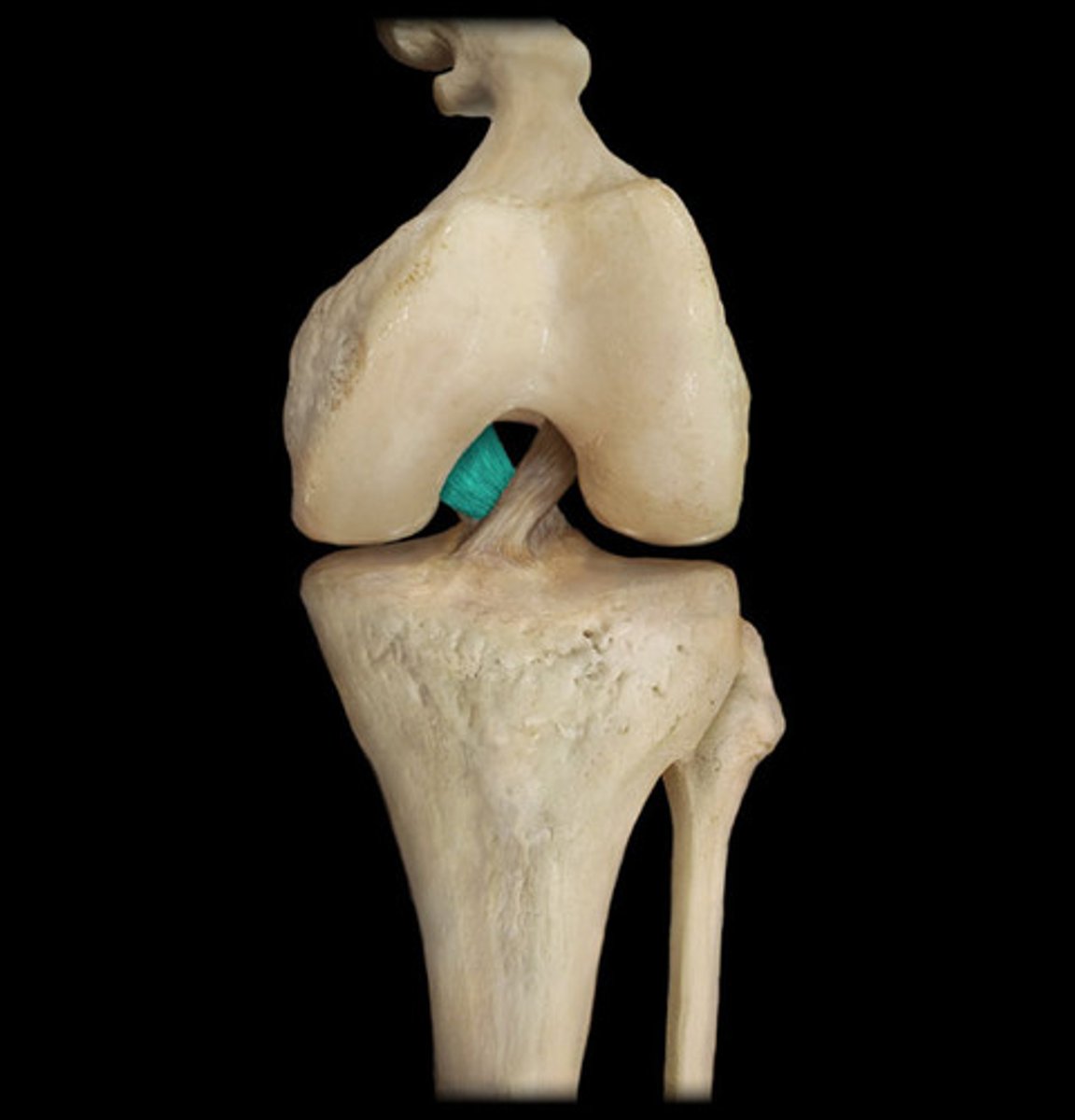
Lateral meniscus
cartilage cushioning the knee joint
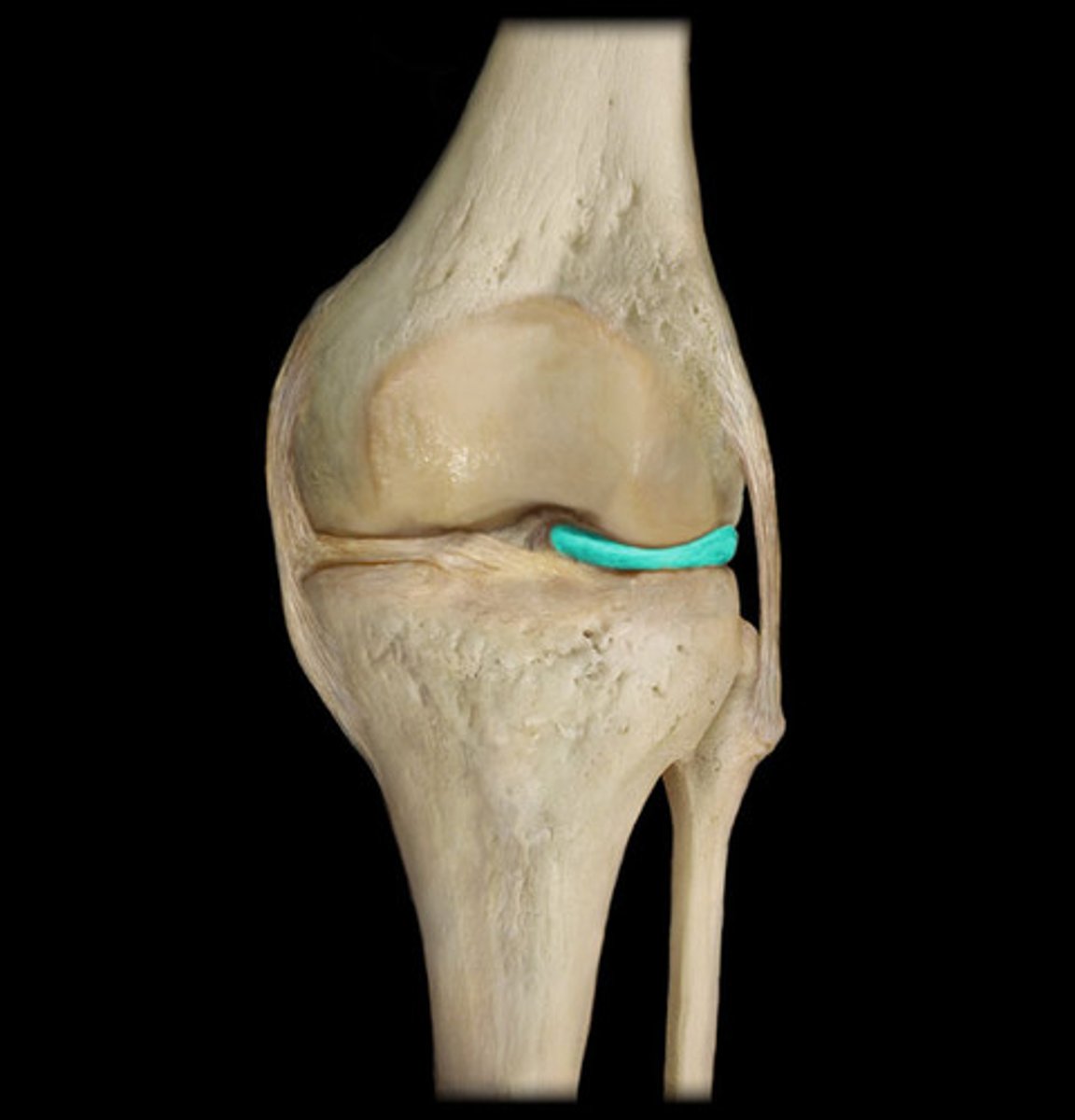
Medial meniscus
Cartilage cushioning the knee joint
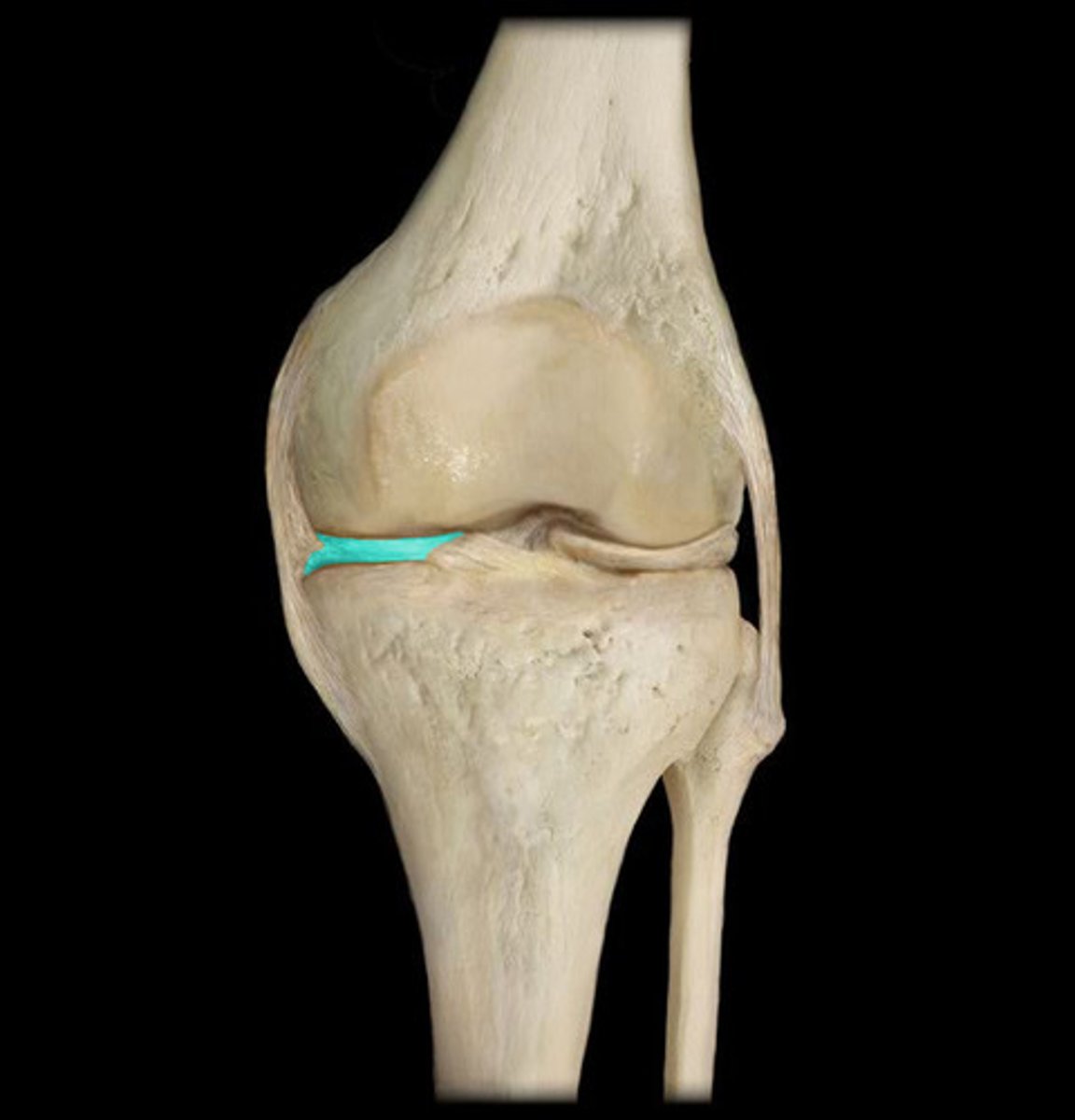
Bursa
enclosed sac filled with viscous fluid located in joint areas of potential friction
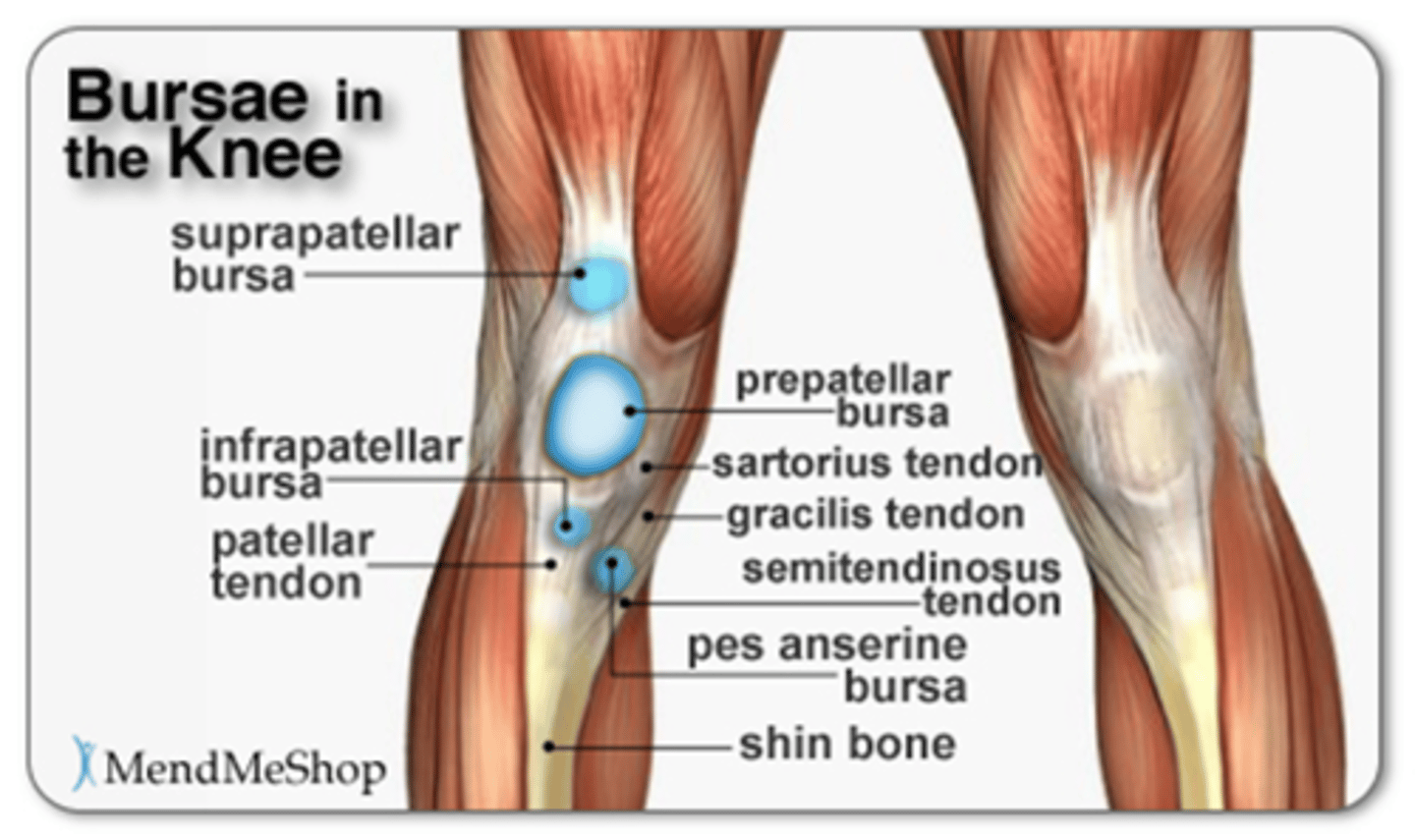
Patellar ligament
connects the tibial tuberosity to the patella; an extension of the rectus femoris tendon
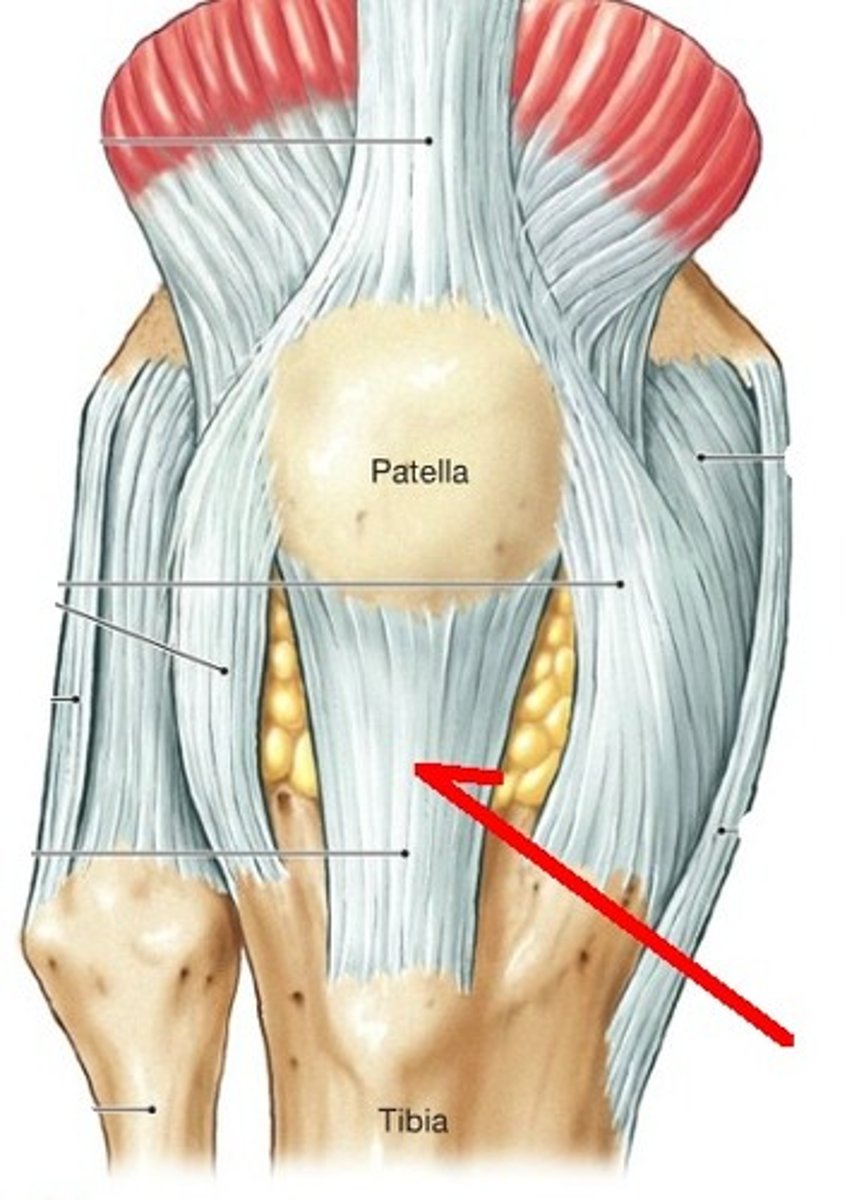
Quadricep tendon
where the 4 quads come together to attach on to the patella
Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
connects the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the fibula
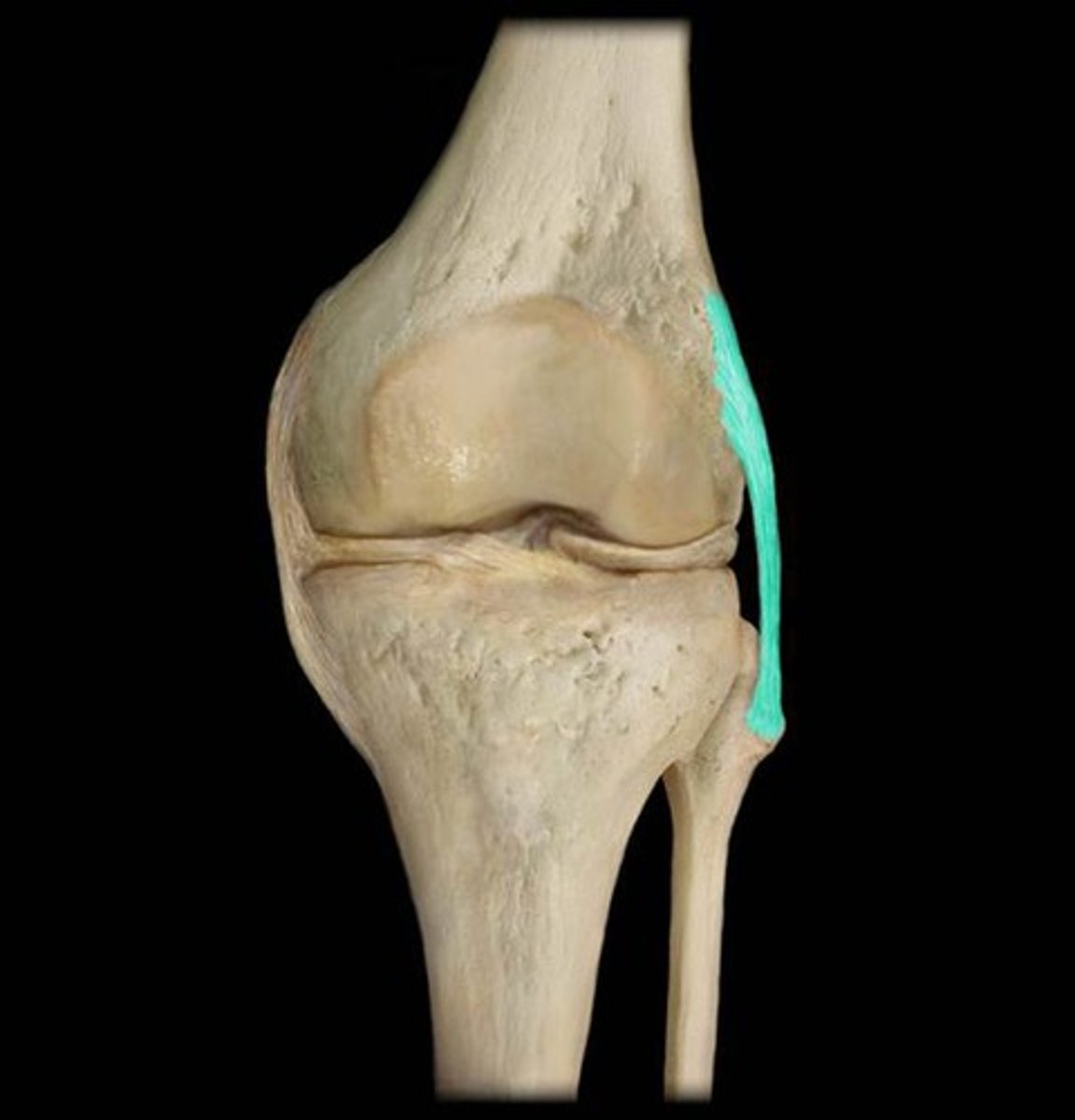
Tibial (medial) collateral ligament
Connects the medial epicondyle of the femur to the tibia
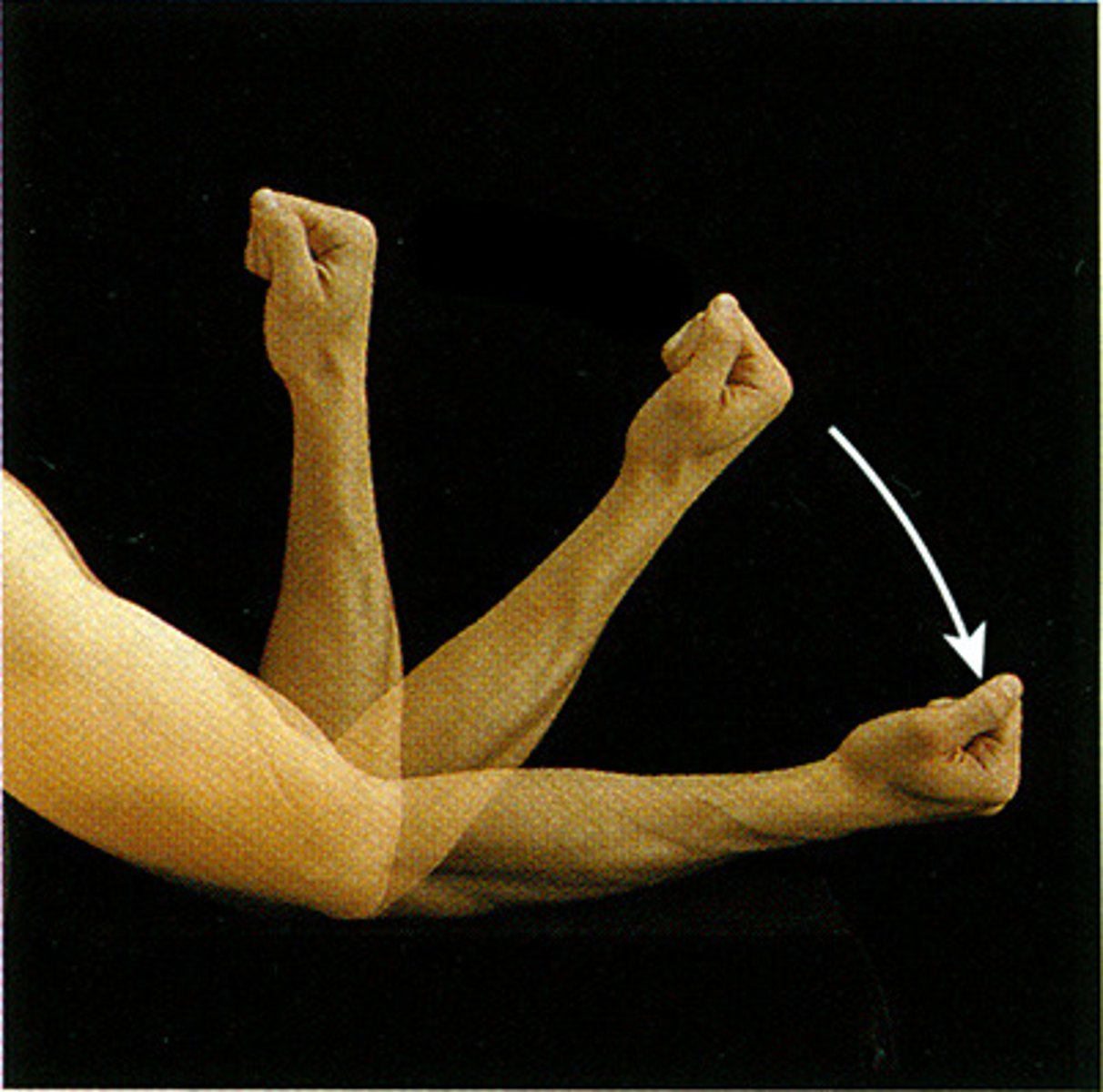
Extension
increases the angle of a joint
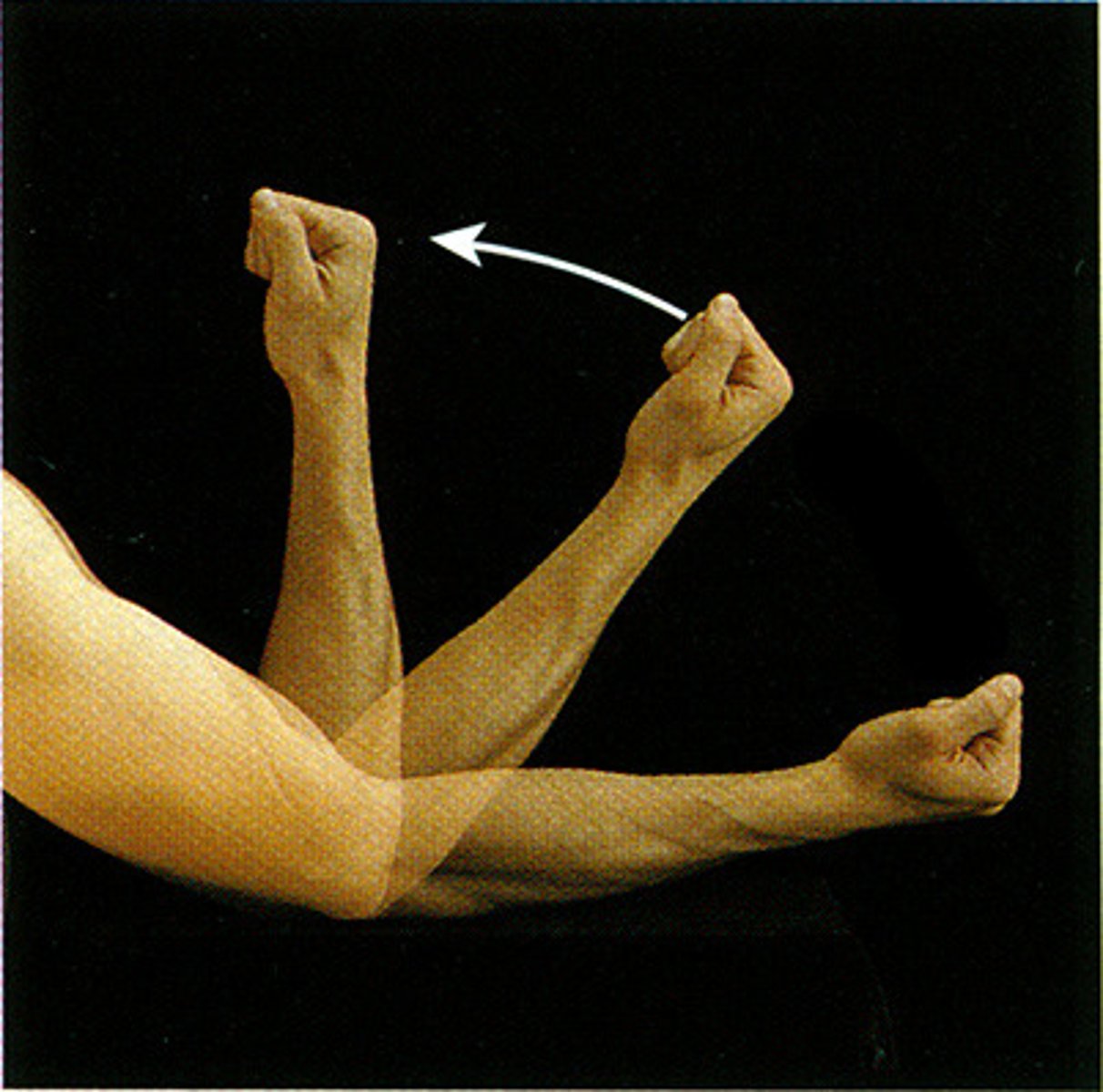
Flexion
decrease the angle of a joint
Supination
the act of rotating the arm so that the palm of the hand is forward or upward
Pronation
turning the hand so that the palm faces downward or backward.
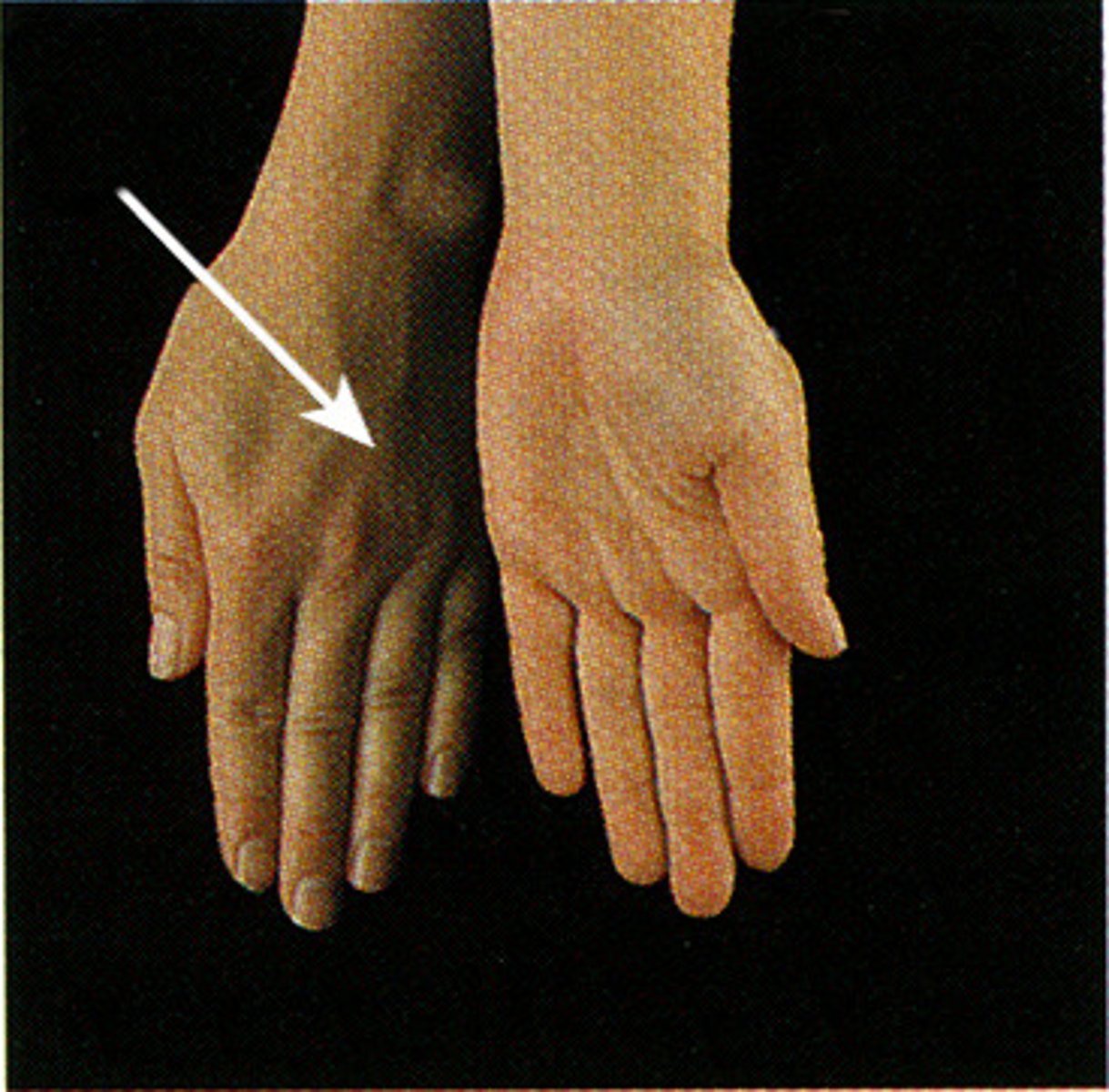
Elevation
Raising a body part parallel to the body's long axis
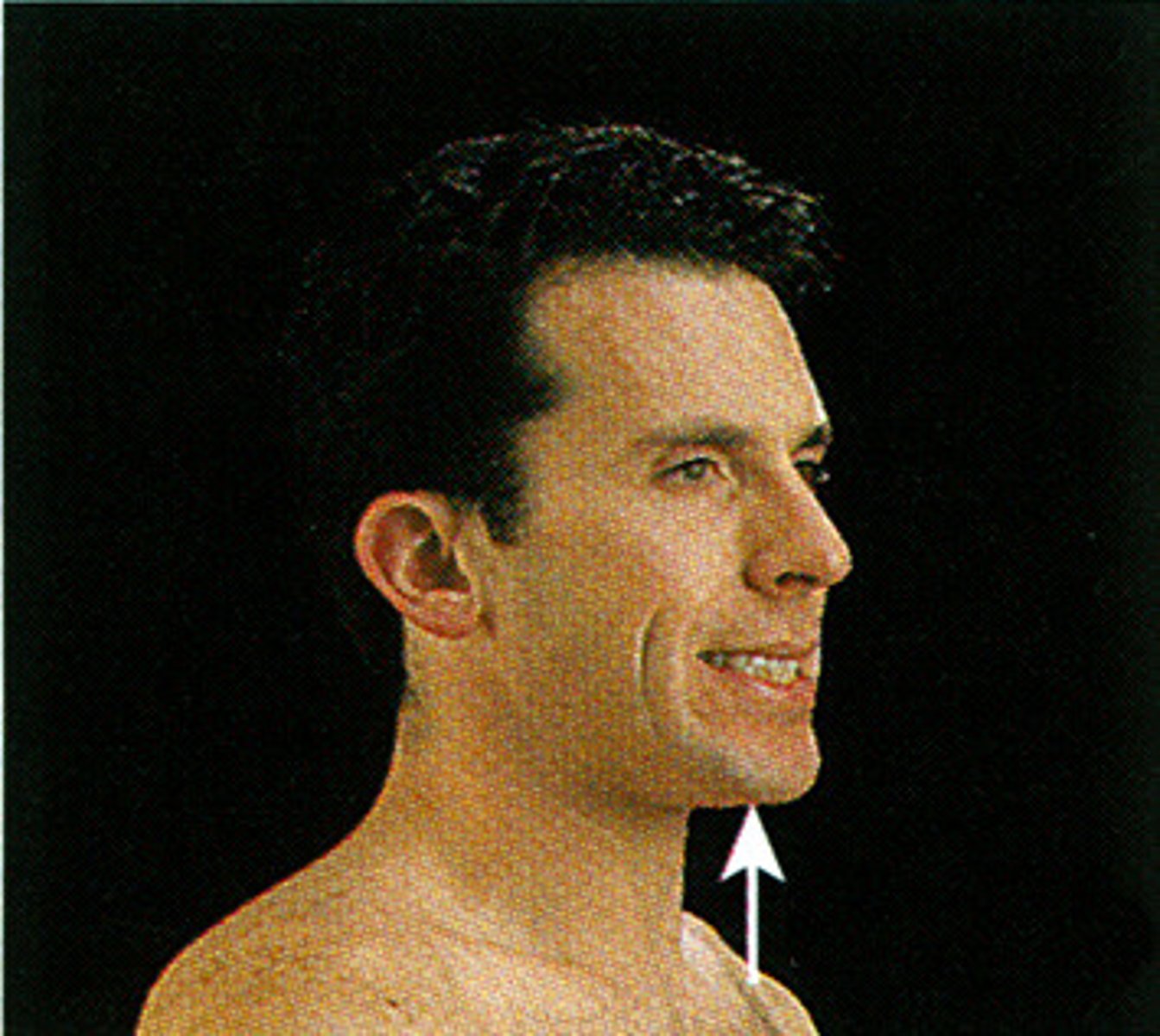
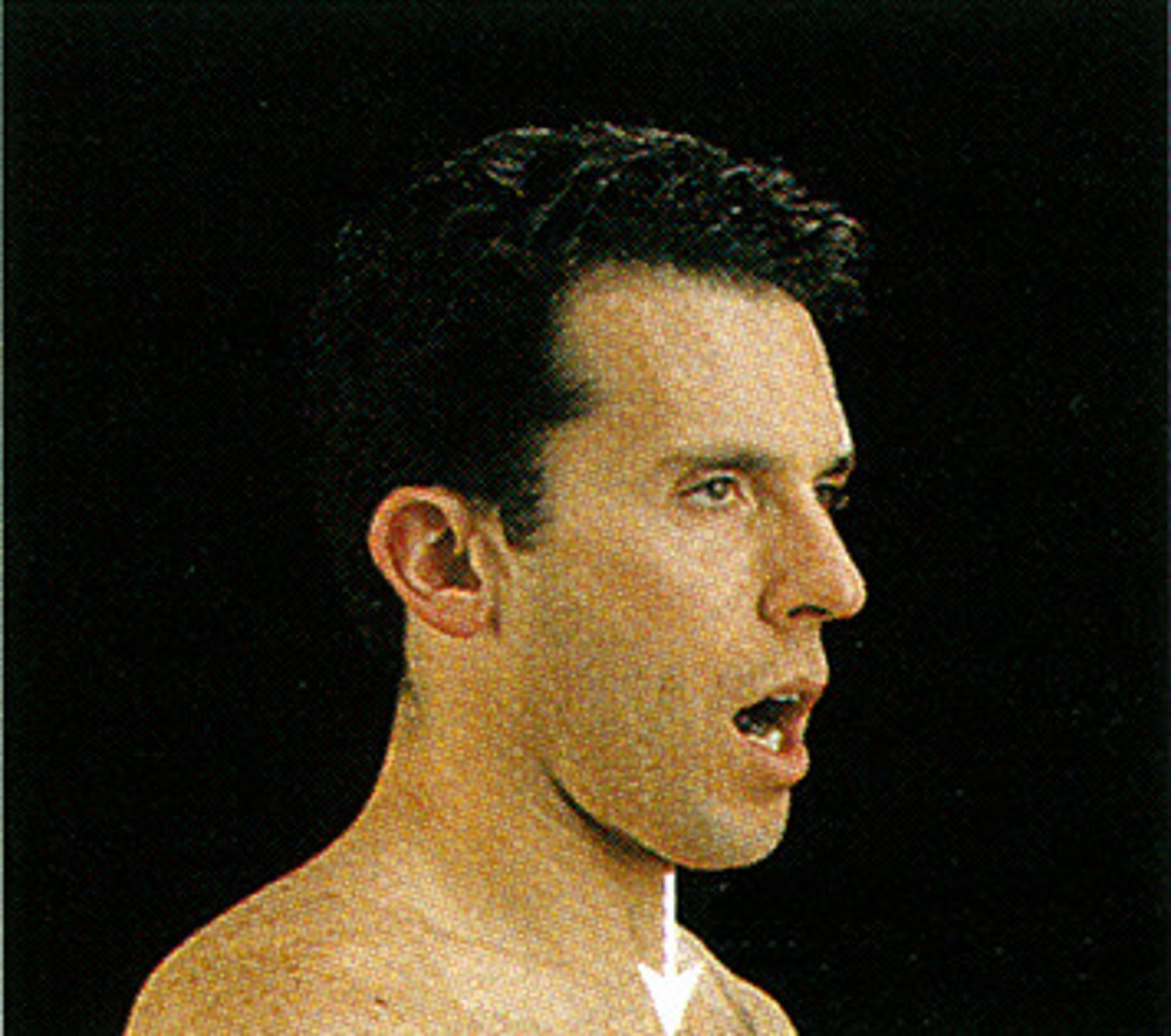
Depression
Lowering a body part parallel to the body's long axis
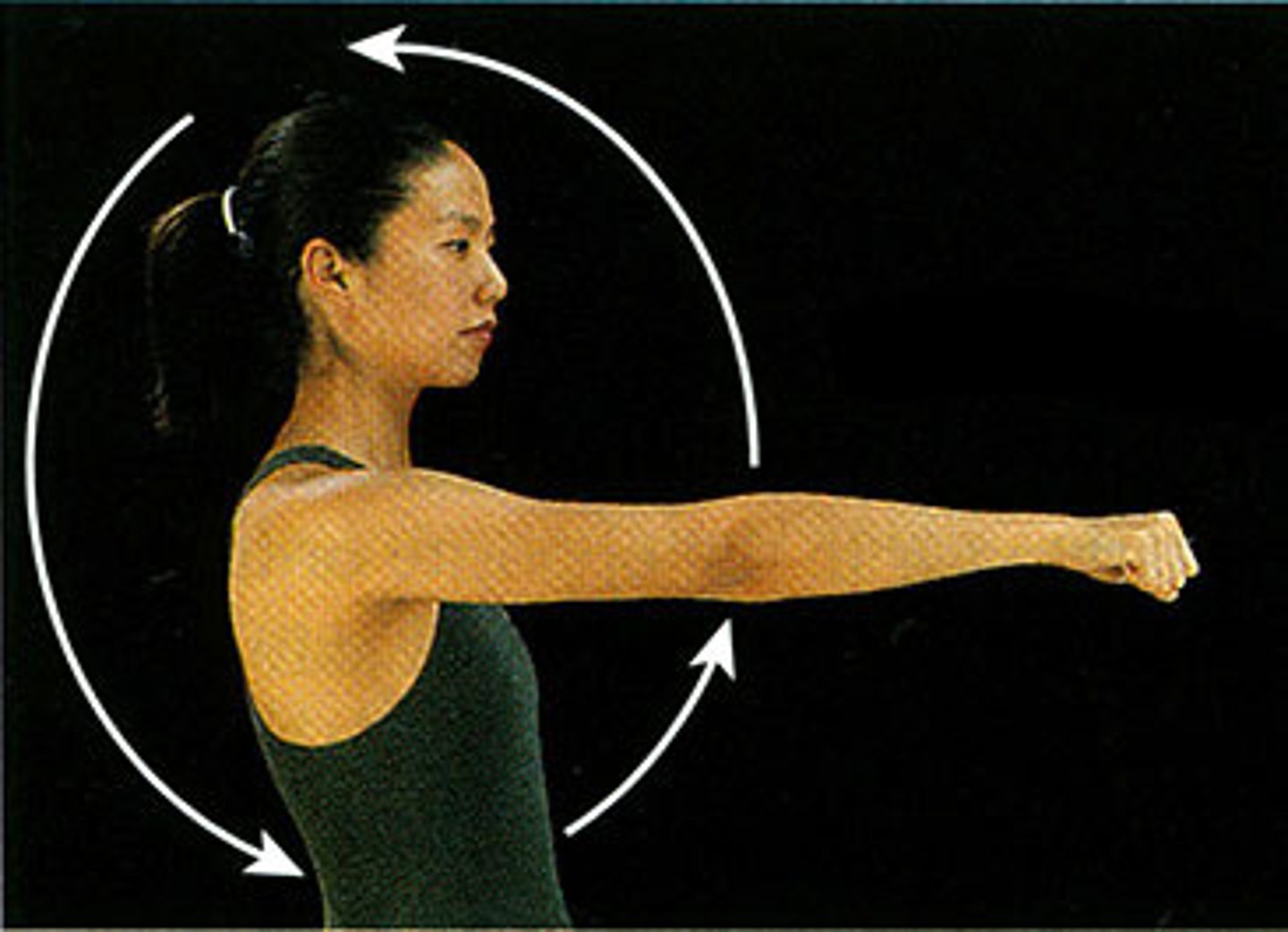
Circumduction
circular movement of a limb at the far end
Dorsiflexion
Bending the foot in the direction of the dorsum (upper surface)
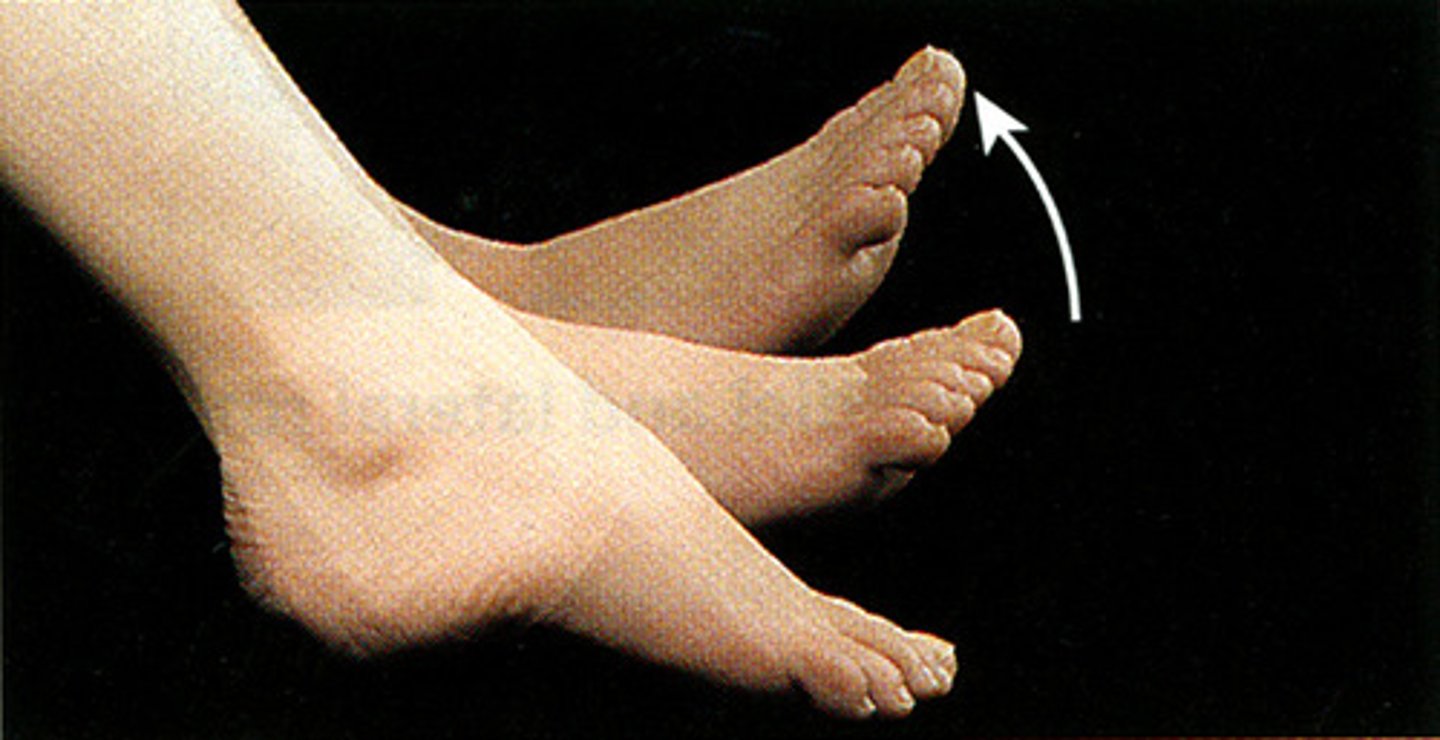
Platarflexion
Foot down
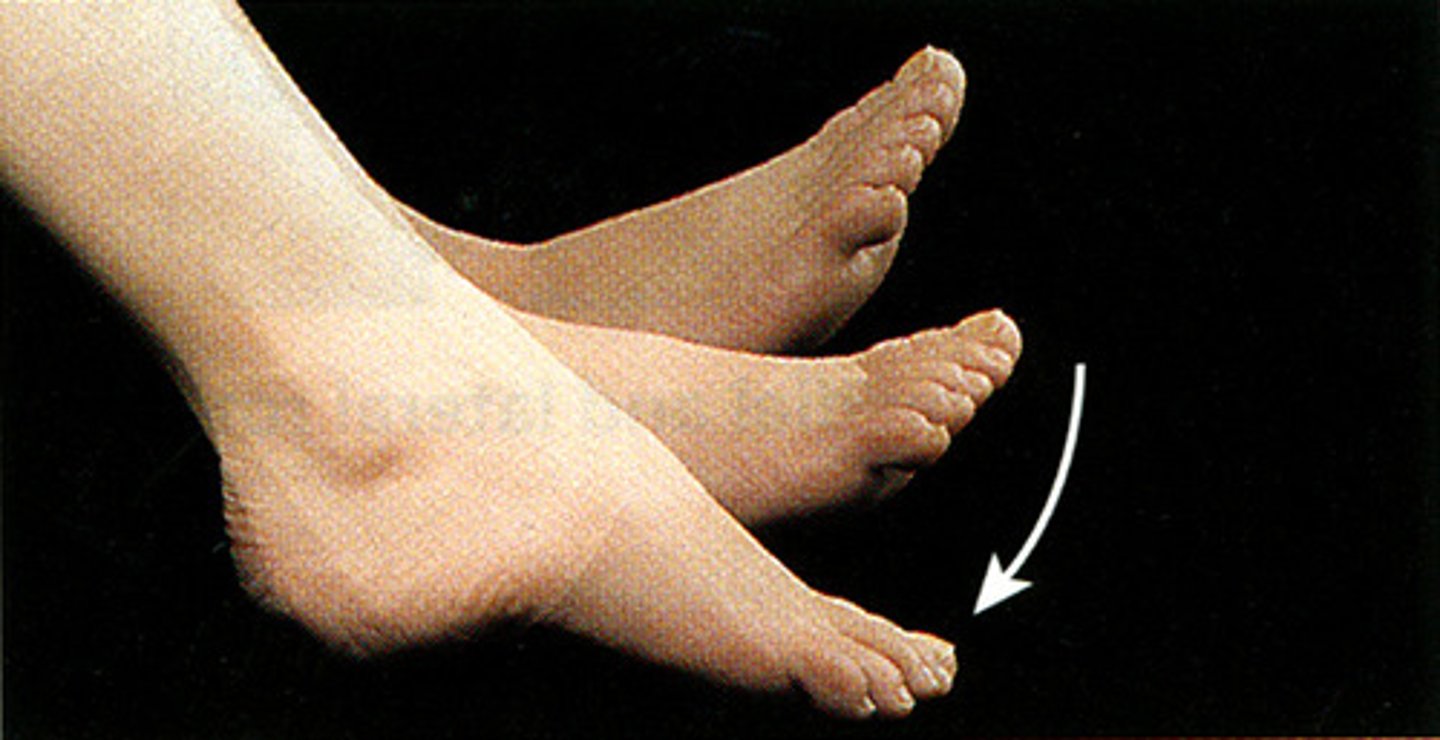
Inversion
turning inward
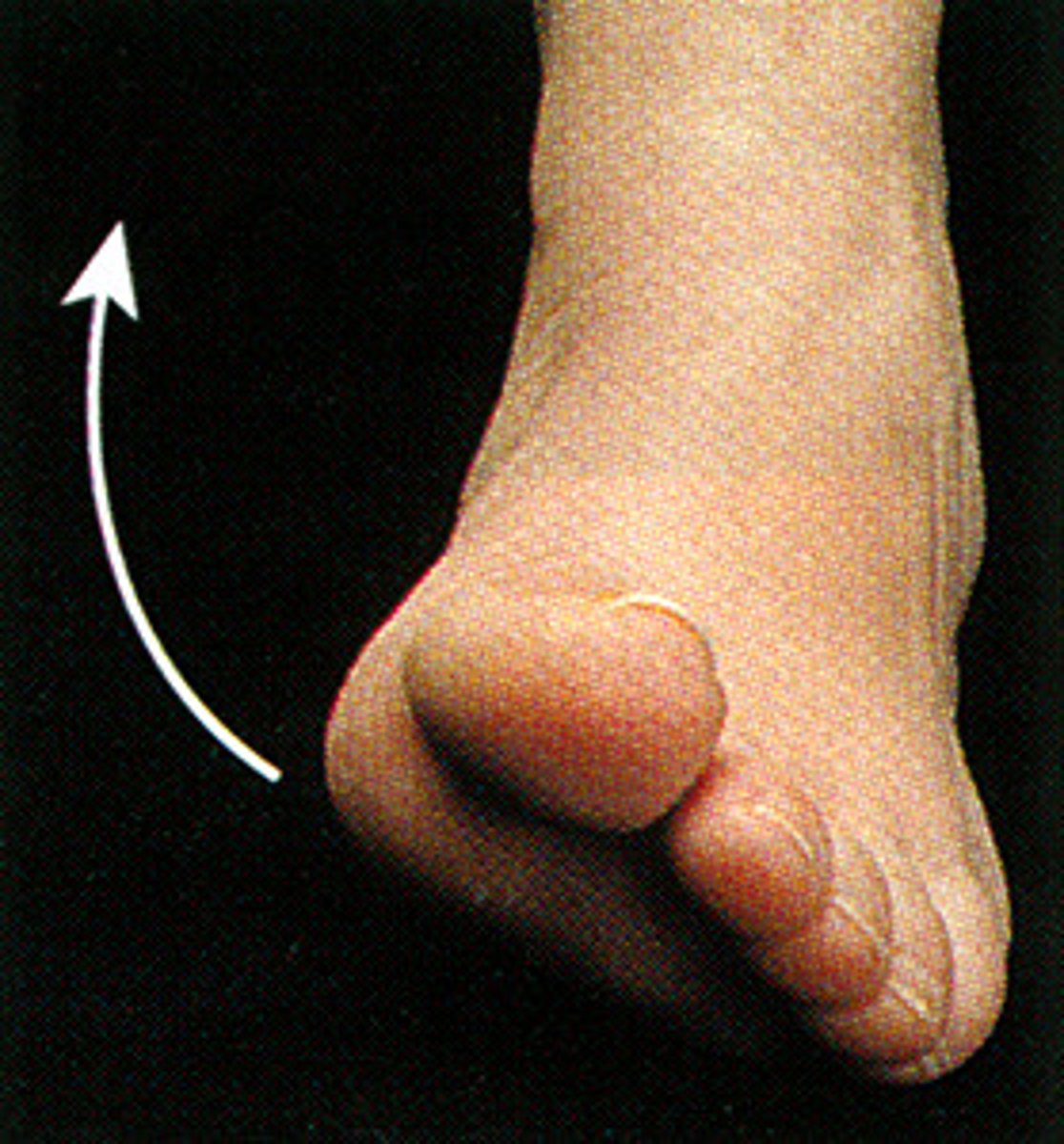
Eversion
turning outward
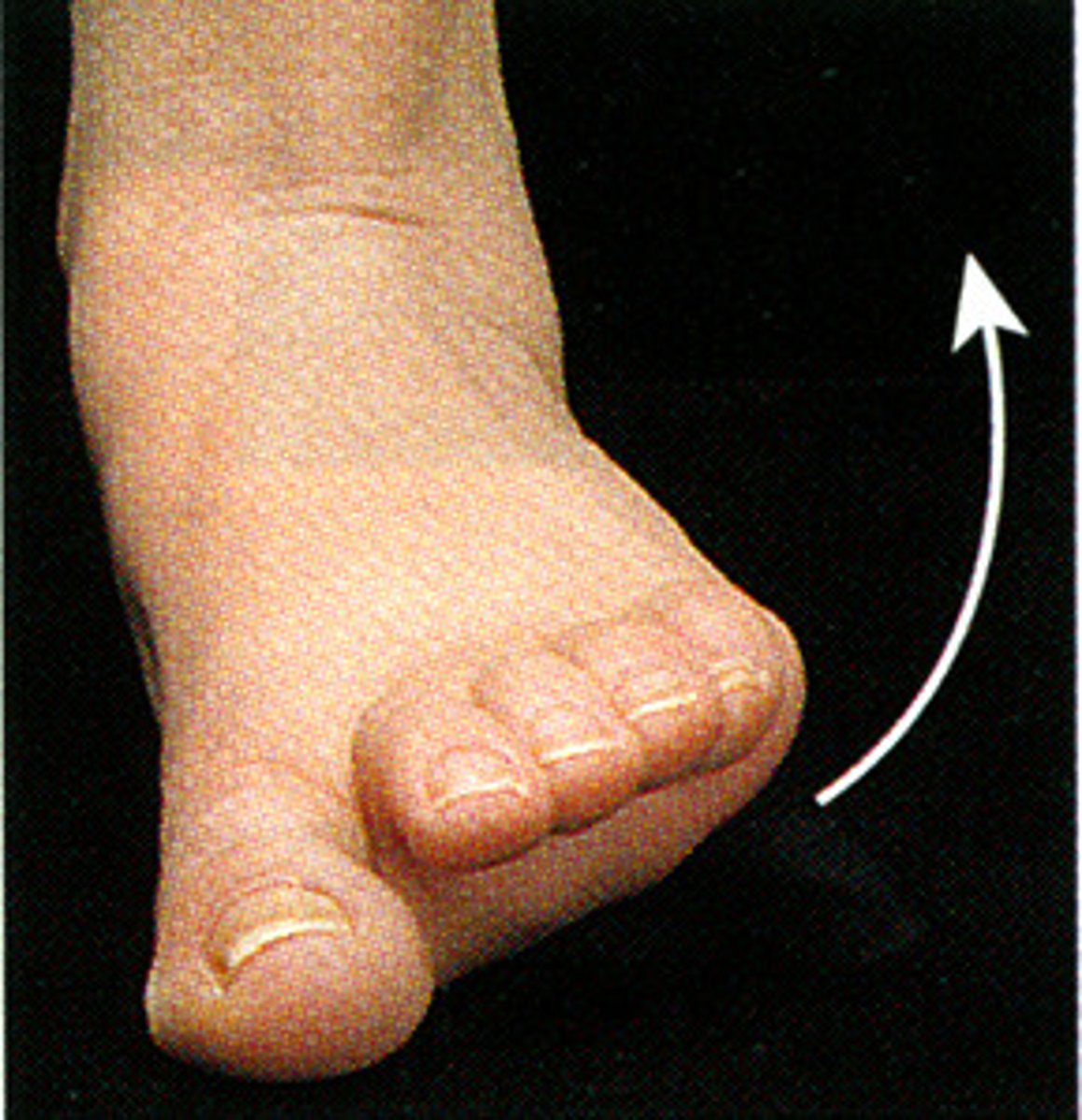
Hyperextension
extension beyond anatomical position
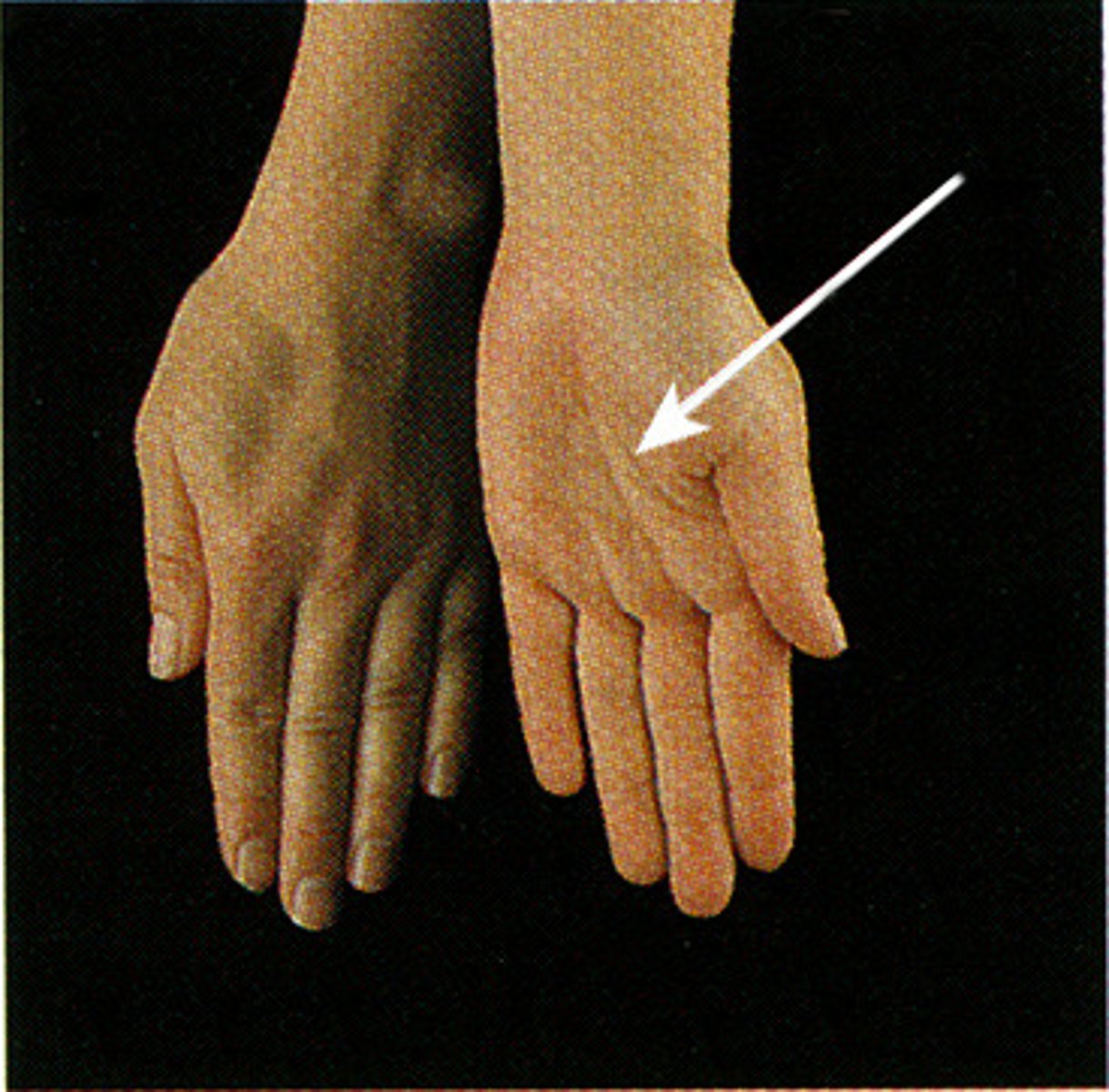
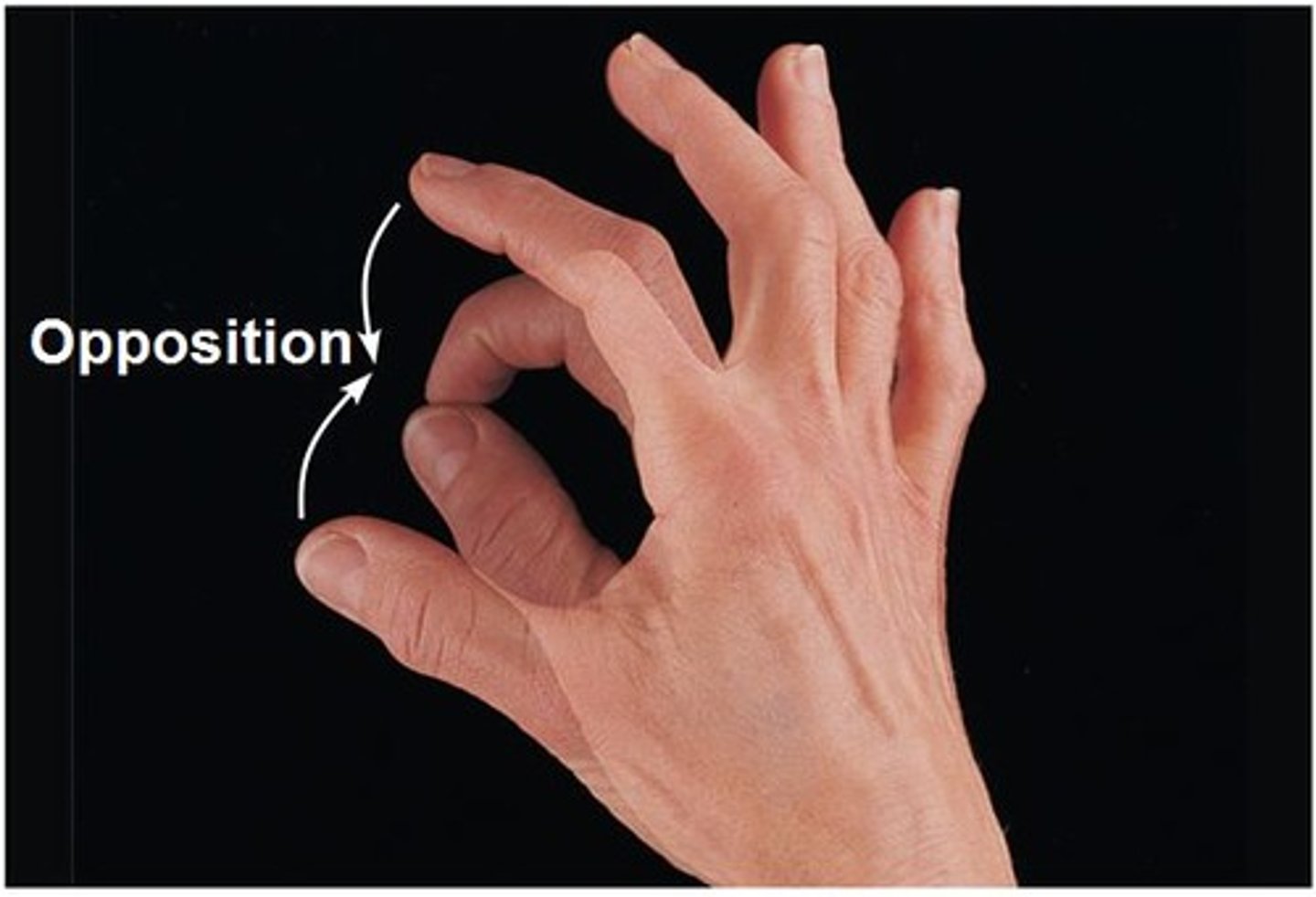
Opposition
Touching the thumb to any other finger
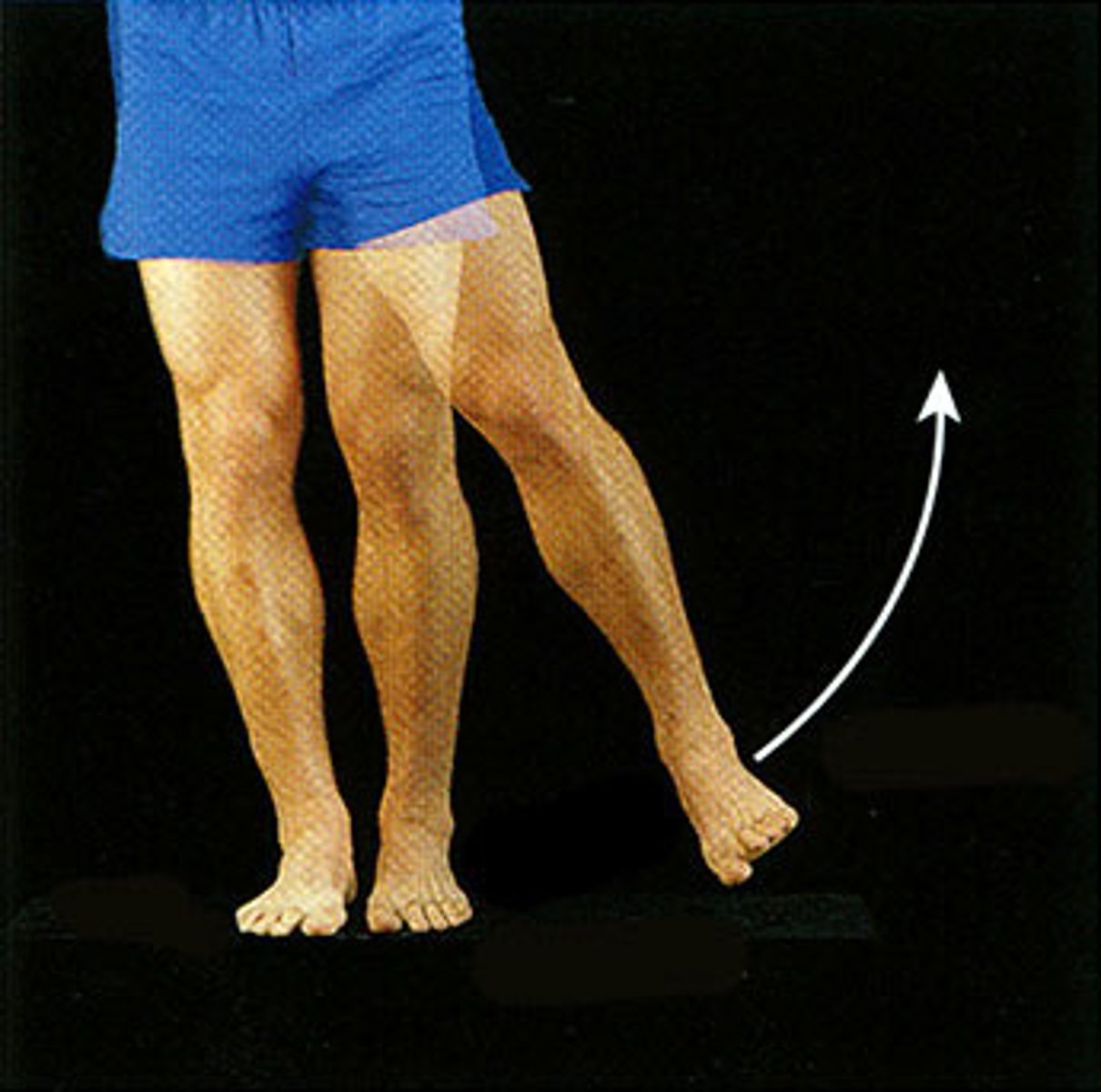
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
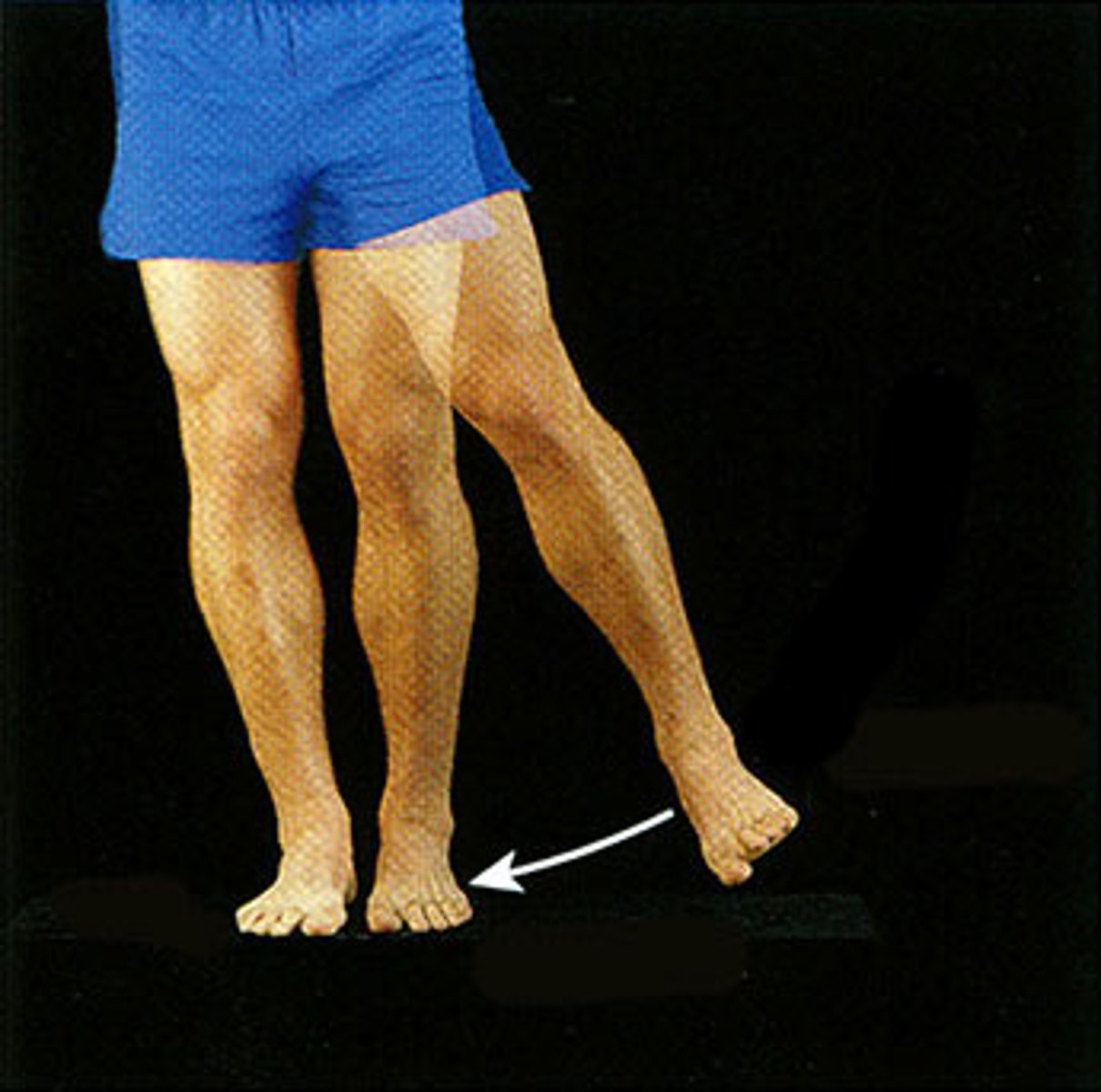
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
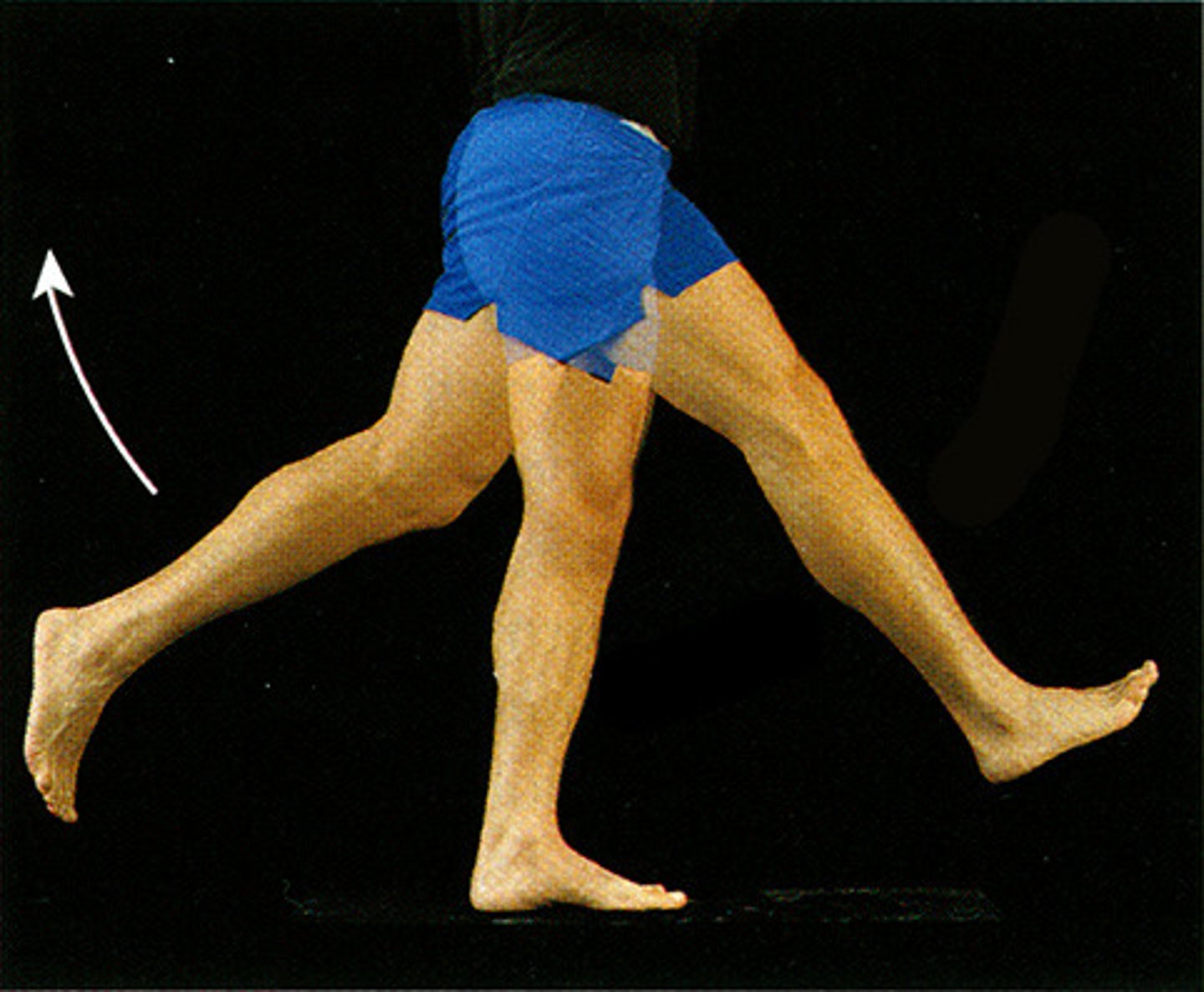
Rotation
Turning around an axis or center point.
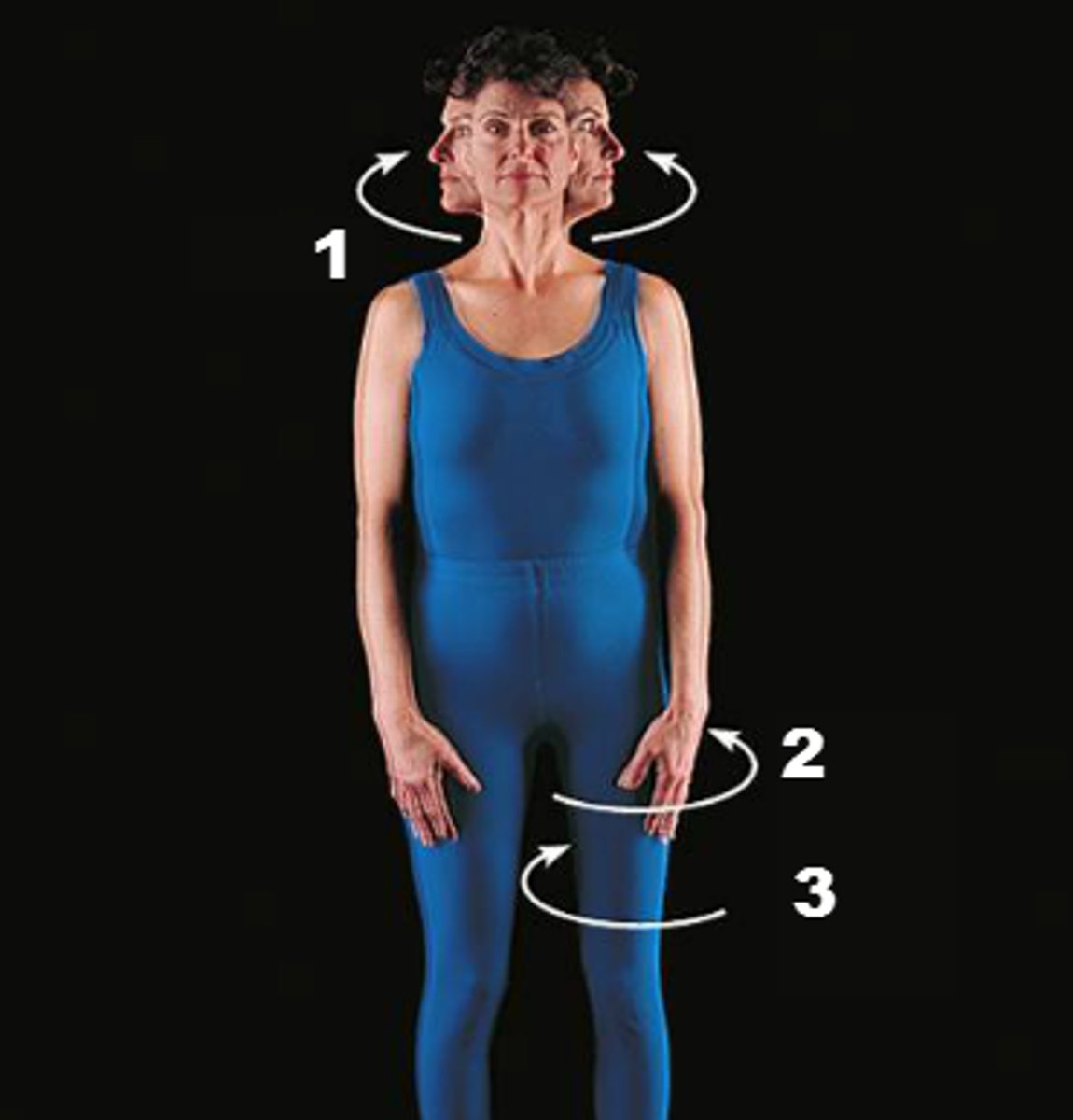
Protraction
moving a body part forward and parallel to the ground

Retraction
moving a body part backward and parallel to the ground