Module 5: Special Senses
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
What are the three tunic layers in the eye
fibrous, vascular, sensorineural
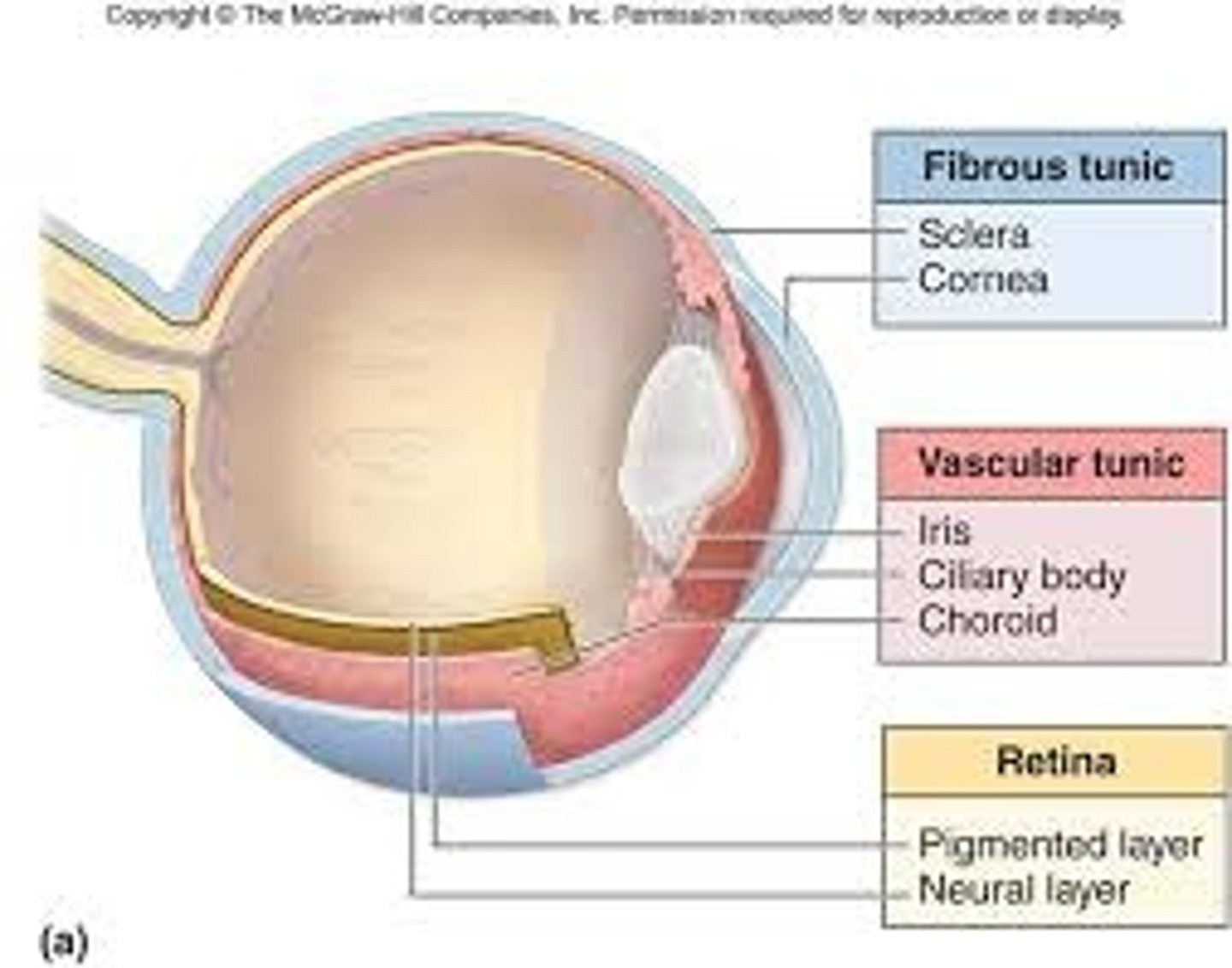
What is the superficial layer in the eye
fibrous layer
What is the deep layer in the eye
sensorineural
What is the sclera
dense C.T. that helps give the eye shape
What is the cornea
continuous with sclera, only present on the anterior surface of the eye; allows light to pass through but upon hitting the light waves are refracted
What makes up the vascular tunic
choroid, ciliary body, iris
What is the fibrous tunic made up of
sclera and cornea
What is the retina made up of
pigmented and neural layer
What does the choroid do
highly pigmented area that lies against the sclera. highly vascularized and supplies nutrients to retina
What does stray light lead to
"noise" and causes a blurred image
What is a ciliary body
continuous with choroid, smooth muscle, connected to suspensory ligaments that connect to lens.
What does changing the lens do
changes the degree of refraction
What is the iris
continuous with ciliary body and is muscle tissue found between cornea and lens. Hole in middle (pupil).
contraction of circular smooth muscle =pupil decreasing in size
contraction of radial muscle: results in pupil increasing in size
What does the size of the pupil control
how much light enters the eye
When the lens becomes more bulbous...
the iris blocks stray light from hitting the retina
What is the retina
deepest tunic and contains nervous tissue; continuous with optic nerve through axon projections
What is a focal point
where the lens converges as a single point
What is the lens
made up of rings of protein, biconvex, shape of lens is controlled by ciliary body and suspensory ligaments
For a closer object you want the lens to be
bulbous
For an object further away, you want the lens to be
elongated
Vision physiology: what is vision controlled by
light and it's reflection off an object
What do the light rays come into contact with first
cornea which refracts light towards the lens
Process of vision physiology
1. light hits object and is reflected
2. light reaches cornea which refracts the light towards the lens
3. light hits lens and is refracted again to converge on a single point on the retina
4. light converges at focal point via exiting the lens through the posterior side
Ideally, where is the focal point
on the retina
If an object moves closer, where does the focal point go
behind/posterior to the retina
If an object moves further away, where does the focal point go
in front of the retina
What happens when light hits the retina without passing through the lens
light would be unrefracted and does not converge with other light rays. This creates "noise" and the image is blurred.
When does the iris contract
the same time the lens changes shape in order to block the light ways that won't converge
When don't light rays need to be refracted as much
if object moves further away because the light rays are more parallel. this allows the curvature of the biconvex lens to decrease and light is refracted less
In the lens, objects in the superior visual field are focused on
the inferior portion of the retina
In the lens, objects in the inferior visual field are focused on
superior portion of the retina
Projection of the image is
inverted
Where are photoreceptors
located in the retina
What are the other neurons in the retina called
Bipolar cells and ganglion cells
Which retina neuron is tertiary
ganglion
Which retina neuron is secondary
bipolar
Which cell axons group together to form the optic nerve
ganglion cells; transmits signals to the brain
What are the layers in the retina
inner plexiform, inner nuclear, outer plexiform, outer nuclear, and rod/con layer
What does the deepest layer of the retina contain
rods/cones
What are rods/cones stimulated by
light
What are the two types of photoreceptors
cones/rods
Rods
extremely sensitive to light, insensitive to the wavelength
Cones
not as sensitive to light, very sensitive to wavelngths
Which photoreceptor are responsible for color vision
cones
Why don't you see color at night
b/c cones require much more light to be stimulated
Multiple rods synapse with
a single bipolar cell
a single cone synapses with
a single bipolar cell
Why are cones better at resolving detail
because multiple rods synapse with a single bipolar cell while a single cone synapses with a single bipolar cell
What are the three types of cones
red, green, blue
What cones does yellow light stimulate
green and red
What cones does cyan light stimulate
blue and green
What happens when light hits rhodopsin
rhodophsin changes shape by alterining retinal.
What is the change in retinal
cis-retinal to trans-retinal
When rhodopsin changes shape what does it communicate with
G-protein called transducin
What is activated when rhodopsin joins with transducin
cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase
What does cyclic GMP phosodiesterase do
breaks down cyclic GMP
What do the Na+ channels on the rod cell membranes have
cyclic GMP ligand
Does a photoreceptor generate a "true" action potential
since the cell cannot depolarize it can no longer release the neurotransmitter. The neurotransmitter in rods is glutamate which acts as an inhibitor and inhibits the bipolar cell from generating an action potential
essentialy: if glutamate is present in the synapse, biopolar cell is essentially inactive
If glutamate is not present in the synapse what can happen
the biopolar cell generates an action potential
How does glutamate work
by binding to the dendrite of the bipolar cell and creating an enzyme cascade that closes the Na+ channels on a bipolar cell. This causes Na+ channels on the bipolar cell to close and bipolar cell is unable to depolarize
What do the cones use as a signaling chemical
opsin (red, green, blue_
What is a visual field
everything that is seen by one eye
Binocular visual field
the overlap of each eye's individual field
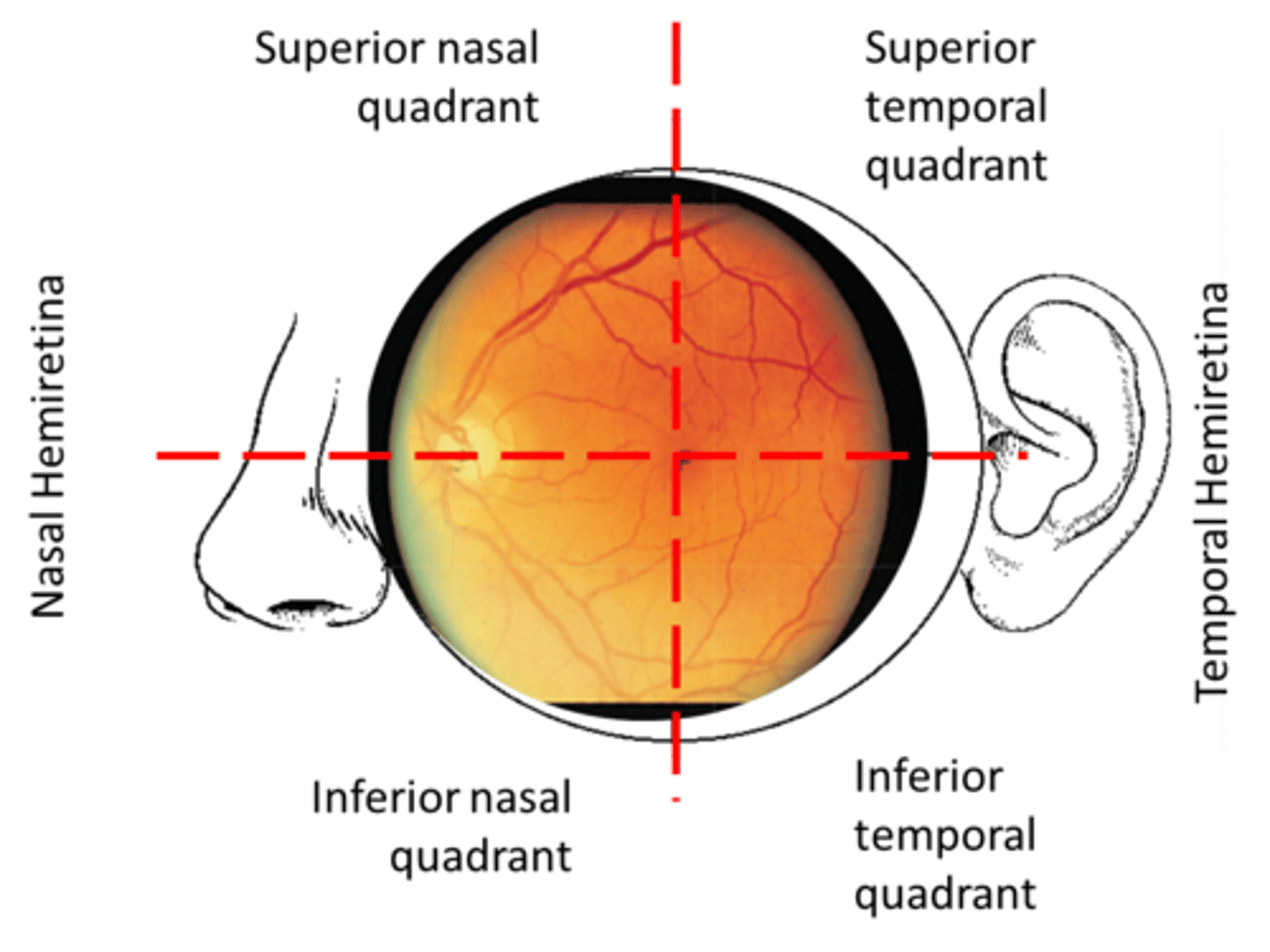
How is the retina divided
four visual quadrants: temporal, nasal, superior, inferior
What is located at the center of the four retina quadrants
fovea centralis of the macula
Where is the sharpest focus located at
fovea centralis of the macula
how does the inversion of an image work
works along the y-axis
how does reversal of the image work
along the x-axis
Where would the reversal of an image in the temporal region be
the nasal portion
Where would the reversal of an image in the inferior region be
the superior region
Picture of the 4 quadrants in retina
What is a nerve pathway
nerve tract to optic nerve to optic chiasm, crossing of nerve tracts
Where do nerve tracts from the temporal retina cross
nasal field of view, do not cross
What does the brain look for when putting together images
regions of overlap from the right and left field of view
Where do nerve cells in the corpus callosum communicate
with the nuclei of the visual cortex
Where are images in the nasal field of view projected
from the right and onto the temporal portion of the retina
Where are images from the temporal view of the left eye projected
onto the nasal portion of the retina
Which tracts cross at optic chiasm
nasal tracts
Crossing the fibers provides the left side of the brain with
all visual info on the right visual field
vice versa for right side of brain
What is the optic tract
where nerve fibers merge again
travels to lateral geniculate body of thalamus and then to visual core
Where does partial decussation occur
when optic nerve fibers exit the eye at the optic disk and project into the optic chiasm
Steropsis
the process by which the visual cortex combines the differing neural signals caused by binocular disparity, resulting in the perception of depth
What are the three major cell types in the olfactory epithelium
olfactory receptor neurons
sustentacular cells
basal cells
What are bowman's glands
responsible for producing mucus with antibodies to protect against bacteria and viruses
What is the protein complex located on the olfaction's plasma membrane
GOLF
G-protein of OLFaction
What the are units of the G-protein complex
alpha, beta, gamma
What else is located on the plasma membrane of the olfactory
Adenylyl cyclase and cation channels (transmembrane), closed chlorine channels
Generation of Olfactory Action Potential
1. odorant binds to receptor
2. binding of the odorant causes alpha subunit of the G-protein complex dissociates
3. G-protein interacts with adenylyl cyclase
4. GTP binds to alpha G-protein-adenyly cyclase compound
5. binding of GTP causes adenylyl cyclase to produce cyclic AMP (cAMP)
6. cAMP binds with cation channel and allows Na+ and Ca2+ to enter cell
7. Ca2+ ions enter the cell and bind to closed Cl- channel
8. Cl- channel opens and theres an efflux of Cl- ions
9. Cell becomes more positive (depolarizes)
10. sensory neuron is depolarized and action potential propagates down the sensory neuron
Where are the axon terminals that the sensory receptors respond to located
glomerulus
Give the pathway of what happens after A.P. is generated
1. odorants binds to sensory neurons
2. depolarization of sensory neuron and action potential is generated
3. multiple sensory neurons have the same reaction (many are responsive to same neuron)
4. action potentials propagates down each axon to axon terminal (group at glomerulus)
5. signal is transferred from sensory to secondary neuron (either mitral or tufted cell)
6. Activation of mitral/tufted cell causes activation of interneuron (periglomerular cell)
7. causes inhibition of mitral/tufted cells associated with axon terminal of other chemoreceptors
8. A.P. is sent to olfactory cortex via olfactory tract
9. signal from olfactory cortex is transmitted back through olfactory bulb through centrifugal fibers
10. granular cells are activated
11. granule cells release gamma aminobutryic acid (GABA; inhibitory neurotransmittor)
12. chemoreceptors are inhibited
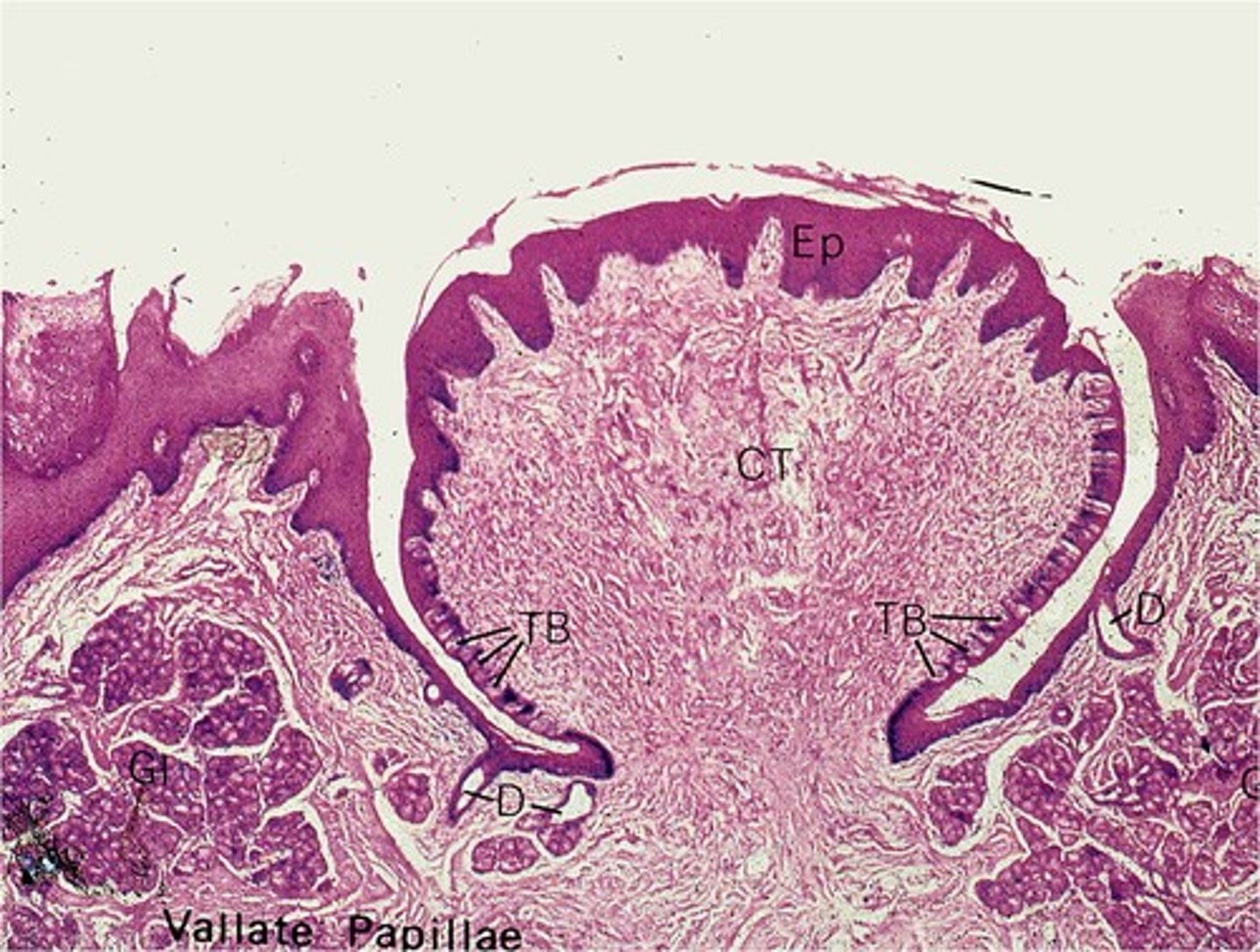
What are the four types of papillae
Filiform, foliate, fungiform, vallate
What is gustation
sense of taste
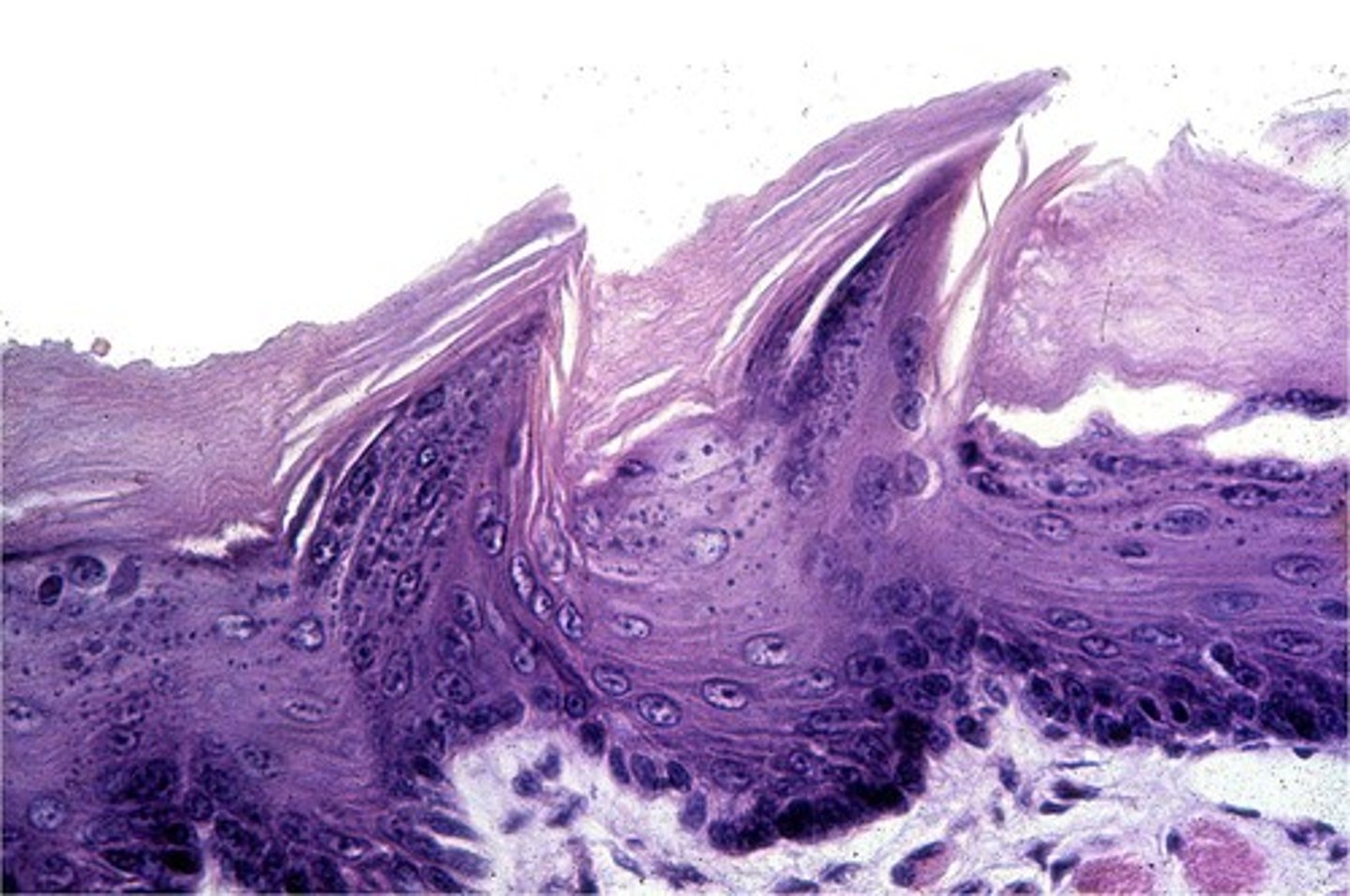
Filiform
filament shaped
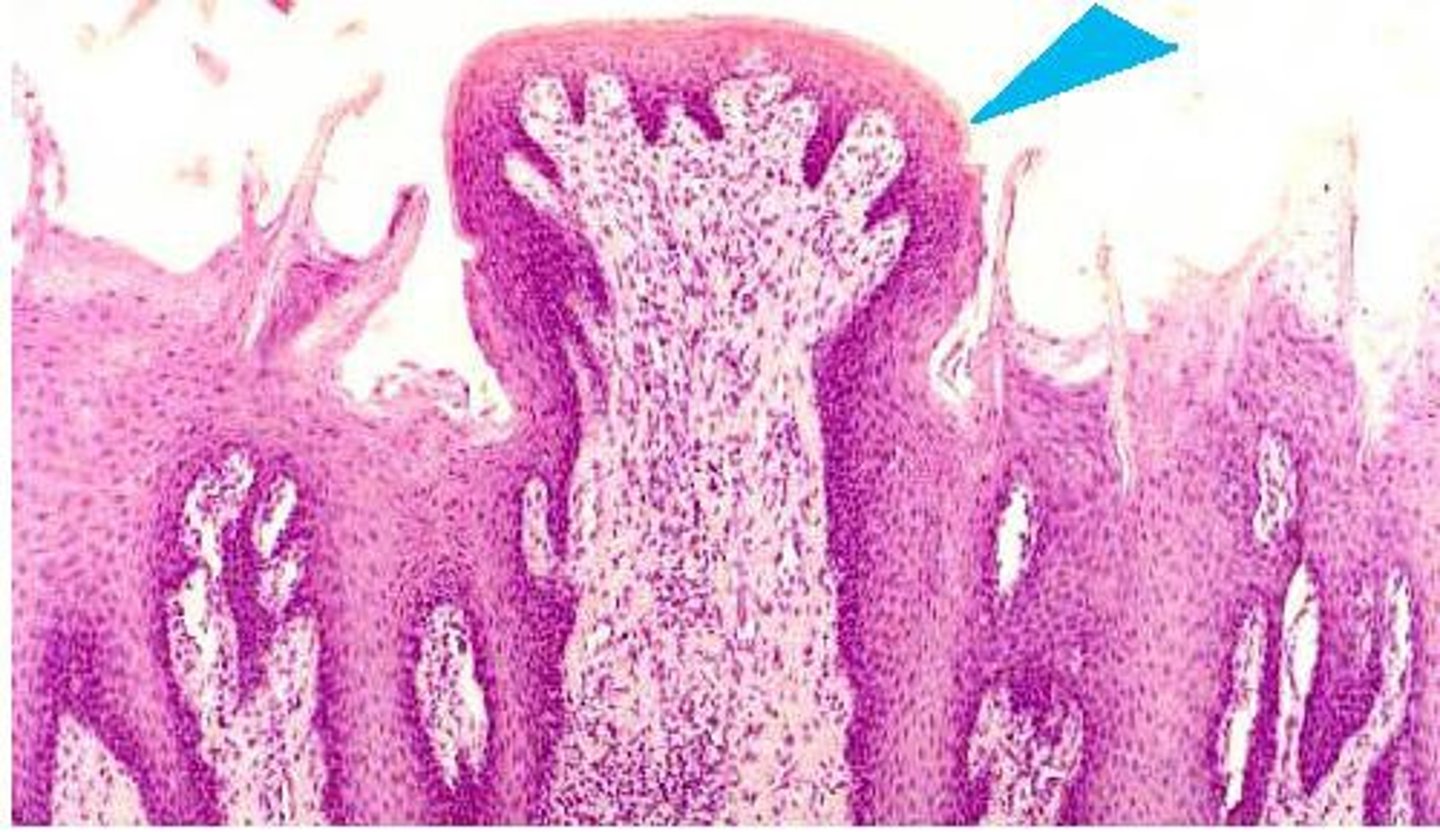
Fungiform
mushroom shaped
Vallate
surrounded by wall
Foliate
leaf shaped
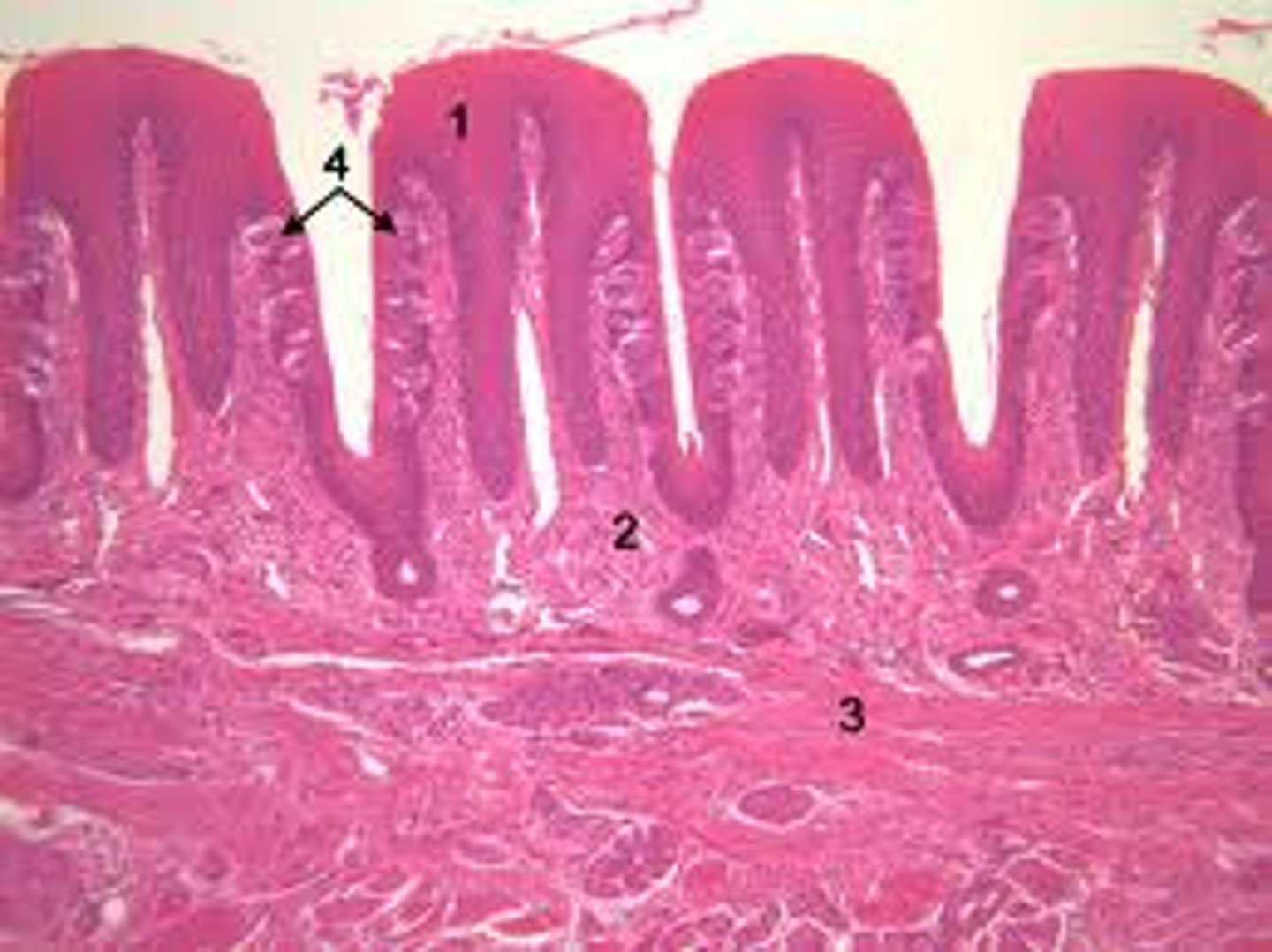
What does the epithelium of the tongue consist of
taste cells, sustentacular cells, basal cells
Taste cells are...
chemical sensory neurons
Sustentacular cells are...
support cells
Basal cells are...
stem cells