operative dentistry
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
main goals of operative dentistry
1. Diagnosis
2. Prevention
3. Treatment
diagnosis
the use of various aids (such as radiographs, instruments, medical history, dental history) to determine etiology and appropriate treatment
primary prevention
prevention of the disease prior to evidence of its occurance
secondary prevention
prevention of a recurrence of the disease or an incipient lesion from progressing to a more advanced condition
primary goal of dental provider
prevention of lesions (not treatment)
tooth preparation
the mechanical alteration of a defective, injured, or diseased tooth such that the placement of restorative material re-establishes normal form and function including esthetic corrections where indicated
types of tooth preparations
conventional preparations, modified preparations
conventional preparations
precise procedure with specific depths, wall forms, and marginal configurations
- dental amalgams, cast metal restorations, ceramic restorations
modified preparations
less precise design requirements
- composite resins
types of lesions (7)
-caries
-abrasion
-erosion
-attrition
-fracture
-developmental defects
-abfraction
caries
- non-communicable disease that results in the breakdown of enamel and dentin due to bacterial invasion
- most common type of lesion
etiologic factors of caries
- acid producing microbes (lactic acid)
- susceptible tooth structure
- carb rich diet
abrasion
- pathogenic wearing of tooth structure via abrasive agents like excessive toothbrushing
- usually produces a V shaped defect
- surrounding gingival tissues are usually healthy
erosion
chemical dissolution of tooth structure
- most common on facial surface in gingival third
- usually not associated with caries
- produces a rounded or saucered defect
- surrounding gingival tissues usually healthy
attrition
physiologic wear, generally due to occlusal forces
- affects occlusal and proximal surfaces
fracture
usually due to trauma
- may be caused by excessive or improperly directed occlusal forces
developmental defects
restored to remove caries, to prevent carious involvement or for esthetic considerations
abfration
non-carious lesions thought to have a combined cause of abrasion and occlusally induced tooth flexure
objectives of tooth preparation
- remove defects/ faults/ carious structure (+unsupported enamel)
- pulpal protection
- extend as conservatively as possible
- protect the restoration and remaining tooth structure
- esthetics and function
primary caries
original carious lesion of the tooth
secondary caries
Occurs at the junction of a restoration & tooth... often progresses under the restoration
residual caries
Caries that remain in a completed tooth preparation
incipient caries
Reversible, enamel surface is intact
cavitated caries
Irreversible, enamel surface is broken
Armamentarium
a collection of resources available or utilized for an undertaking or field of activity; especially the equipment, methods, and pharmaceuticals used in medicine
electric rotary instrument
- 200,000 RPM
- increased torque (little or no slowing as load is increased)
air driven rotary instrument
- 400,000 RPM
- decreased torque (may slow and/or stop if load is increased)
uses for slow speed
- finishing and polishing restorations/ teeth
- prophylaxis
- caries excavations close to pulp
- lab procedures
High speed handpiece
- 200k-500k rpm
- increaed cutting efficiency
- decreased vibration
- fiber optic lighting
- water spray
uses for high speed
cutting enamel and dentin
removing old restorations
why not only use slow speed?
- it is not as efficient
- not as comfy for patient or operator
- needs a heavy hand
- excessive vibration
bur shank
fits into handpiece, can be latch or friction grip
carbide bur
blade cutting
- better for end cutting, produce lower heat, and have more blade edges for cutting
diamond bur
more effective than carbides for intracoronal and extracoronal tooth preparations, beveling enamel margins, and enamelplasty
how carbides cut
shear off or cause brittle fracture of tooth structure
- blade edges fracture off pieces of the surface being cut
how diamonds cut
abrade away tooth structure
- hard particles repeatedly scratch the surface deforming it, work hardening or weakening it, and finally wearing it away
concentricity
symmetry of bur head and preciseness of spin
run out
center of rotation of bur head is not symmetrical
- caused by bur head that is off center, bent bur neck/ shank or defective handpiece
- produces vibration and lack of cutting control
rake face
toward the direction of cutting
clearance face
facing away from direction of cutting
flutes
spaces between blades, remove debris
- increases cutting efficiency by removing debris
rake angle
MOST IMPORTANT
-negative rake angles allow cutting edge to sweep across surfaces without "digging in" minimizing fracture of the bur
- the rake angle is said to be "negative" when the rake face is ahead of the radius from the cutting edge to the axis of the bur
edge angle
Larger edge angles provide more bulk behind the cutting edge minimizing fracture of bur, usually 90 degrees on carbide burs
increased clearance angle…
Increased clearance angle causes a decreased edge angle
Increased clearance angle decreases friction on tooth and facilitates cleaning away of tooth debris
Need for restorative Summary:
A variety of reasons
__
__ and or _ of previous ?
__ tooth structure, or _
__ defects: restore _ and/or ? of a ? tooth
In conjunction with other restorative procedures
Caries
Replacement, repair of previous restorations
Missing, fracture
Congenital, form, function, malformed
Need for restorative Dentistry:
Replacement and or repair of previous restorations:
__ _ contacts or poor ?
Gingival __, or _
__ or (?) _
Poor ?
Improper proximal, embrasure forms
Overhangs, ledges
Defective (open) margins
esthetics
5 Factors that affect tooth prep
diagnosis, dental anatomy, patient factors, conservation of tooth structure, restorative material considerations/factors
Preparing a tooth for restoration:
In order to place a restoration, we must first __?
Remove ?
Prepare a proper “__ _,” to retain the restorative (?) ?
Each material has different requirements for ?
Preservation of ?
prepare it
decay
outline form, filling material
prep design
Healthy tooth structure
Caries Definition:
Microbiologic __ that results in ? ?, or ? or ? tissues of the teeth
disease, localized dissolution, destruction, calcified
Episodic caries:
? and ?
Demineralization and remineralization
Hand held instruments are designed to cut ?
They cut __ _ (ie ? or ?)
They cut ___ _ (ie ? ?)
Intraorally
tooth structure, dentin enamel
Restorative materials (carve amalgram)
Basic elements of hand instruments
__: to ?
__ to ?
__ to ?
handle (shaft), to hold
Blade, to cut
Shank: to connect handle to blade
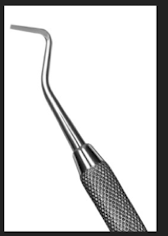
Used to ? Which class?
hatchet: used to plane proximal walls and gingival seats of class II cav preps
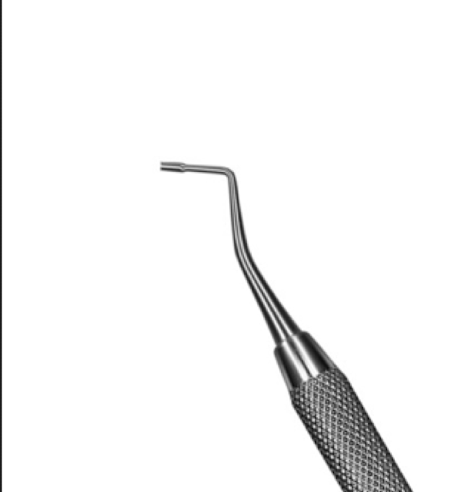
What is it?
used to __ into cavity prep
The part equivalent to the blade is the ?
The end of the ^ is the ?
Plugger/condenser
pack restorative material
nib, face

WHat is it?
Used to __ restorative materials
Ball burnisher, burnish

It is the ___ instrument
Plastic filling: composite resin placement
What cassette do we use in dent disease?
CL-OP (clinical operative cassette)
two alternatives to rotary instrumentation
Laser + air abrasion
One component device is a __ speed, while two+ is?
high, slow
Slow speed Hand-piece
Vibrates more or less than high speed?
better __ than high
Higher or lower RPM
High or low torque?
More, tactile, lower, high
Match: Effectiveness, efficiency
Amount of energy utilized in cutting, not wasted as heat or vibration
Amount of structure removed per unit of time
Efficiency
Effectiveness
Carbide burs are made of __ carbide power and _ molded under heat and vacuum in a process called ?
tungsten, pressure, sintering
Match: Round, Inverted, Pear shaped
Placing retentive undercuts in preparations, flattening floors
Initial entry into tooth, extension of prep, prep retentive features, caries removal
Good for amalgam, composite prep, versatile
Inverted
Round
Pear shaped
Amalgam tooth preparations or any prep that requires parallel walls, the __ fissure is used
Indirect restorations and divergent walls: __ fissure
straight, tapered
Each blade has 2 Sides:
__: faces?
__: faces?
Flutes: __ between ?, remove ?
Rake, toward cutting
Clearance: away
Spaces blades, debris
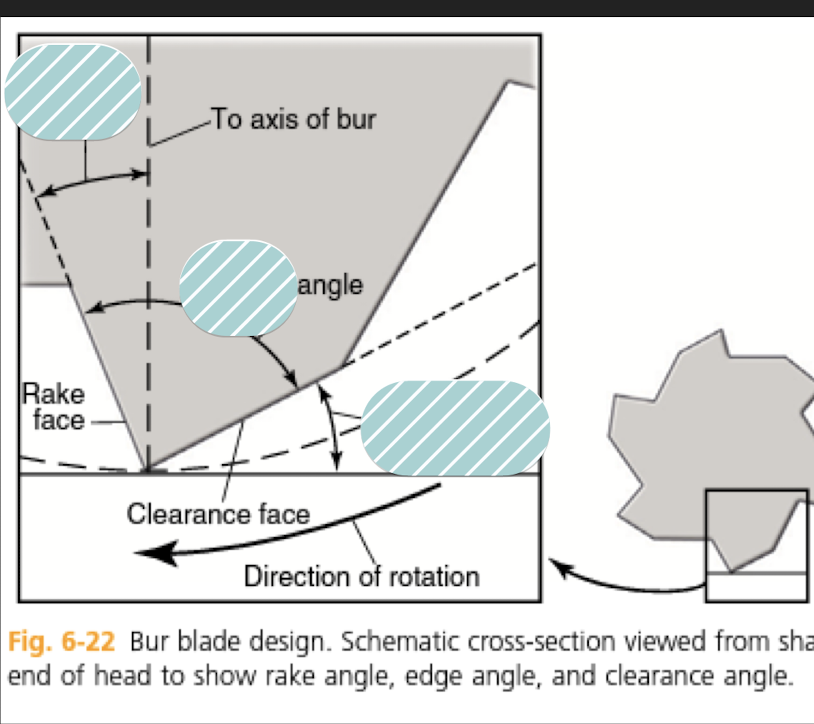
Rake, edge, clearance
The blade __ and _ determines its use and function
shape, design
Match: The bur designs that influence cutting
Spiral Blades, Cross cut blades, flutes, number of blades
larger blade number produces __ surfaces at _ speeds
Increase cutting efficiency at high speeds
Increase cutting efficiency by removing debris
Increase cutting efficiency and increase surface roughness at low speeds
Number of blades: smooth, low
Spiral
Flutes
Cross cut
In addition to the shank, head, and neck, diamond burs consists of three parts
metal blank, powdered diamond abrasive, metallic bonding agent
The ___ __ _ holds the power on the blank of the diamond bur
Metallic bonding agent
Longer lasting: carbide or diamond
More efficient overall for cutting tooth structure: carbide or diamond
In diamond, the cutting effectiveness and applications are determined by the ____ and __ of diamond _
Diamond, diamond, size, spacing, particles
Diamond:
__ determines amount and pressure of particles in contact with surfaces to be cut
The particles __ _ structure to remove tooth structure
spacing, dig into
The ___ the particles of diamond, the ___ the prep
Which is Smaller? carbide or diamond?
Which has more shapes?
finer, smoother
Carbides
Diamonds