4.2.1 Absolute & relative poverty & 4.2.2 Inequality/
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Distinction between absolute poverty & relative poverty (very common)
Absolute poverty = when a person’s daily existence is threatened because they have insufficient resources to meet their daily needs or basic necessities to survive
Relative poverty = when a person’s daily existence is relatively poor compared with others in their society/rest of their country
Measures of absolute poverty & relative poverty (very common)
Absolute poverty
World Bank defines extreme poverty / absolute poverty as living less than $3 per day
Relative poverty
For UK / in any country, this is if household has less than 60% of the median household income in their country (31000 pounds for UK)
Causes of changes in absolute poverty & relative poverty
Economic growth rates
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)
= Investment in a firm by another country → create jobs for unskilled workers, bring new technologies to improve quality of services (healthcare, education)
Trade
expand markets & foster growth
Taxation rates
Benefit payments
Asset prices
Distinction between wealth & income inequality
Wealth inequality = Differences between people due to the value of assets that they own (eg. Savings, shares, property)
Income inequality = Differences between people due to their earnings from wages or profit
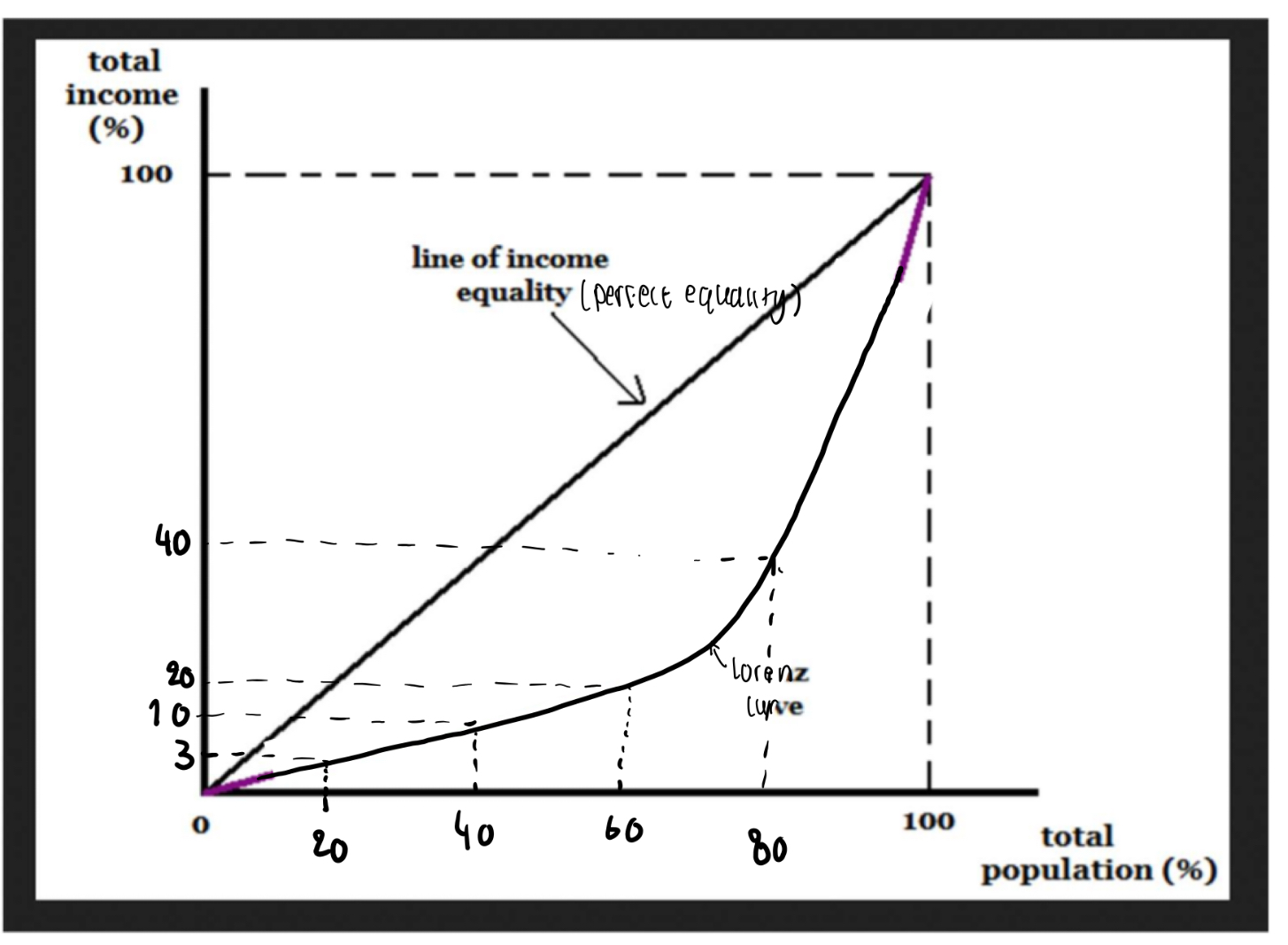
Measurements of income inequality: the Lorenz curve (diagrammatic analysis)
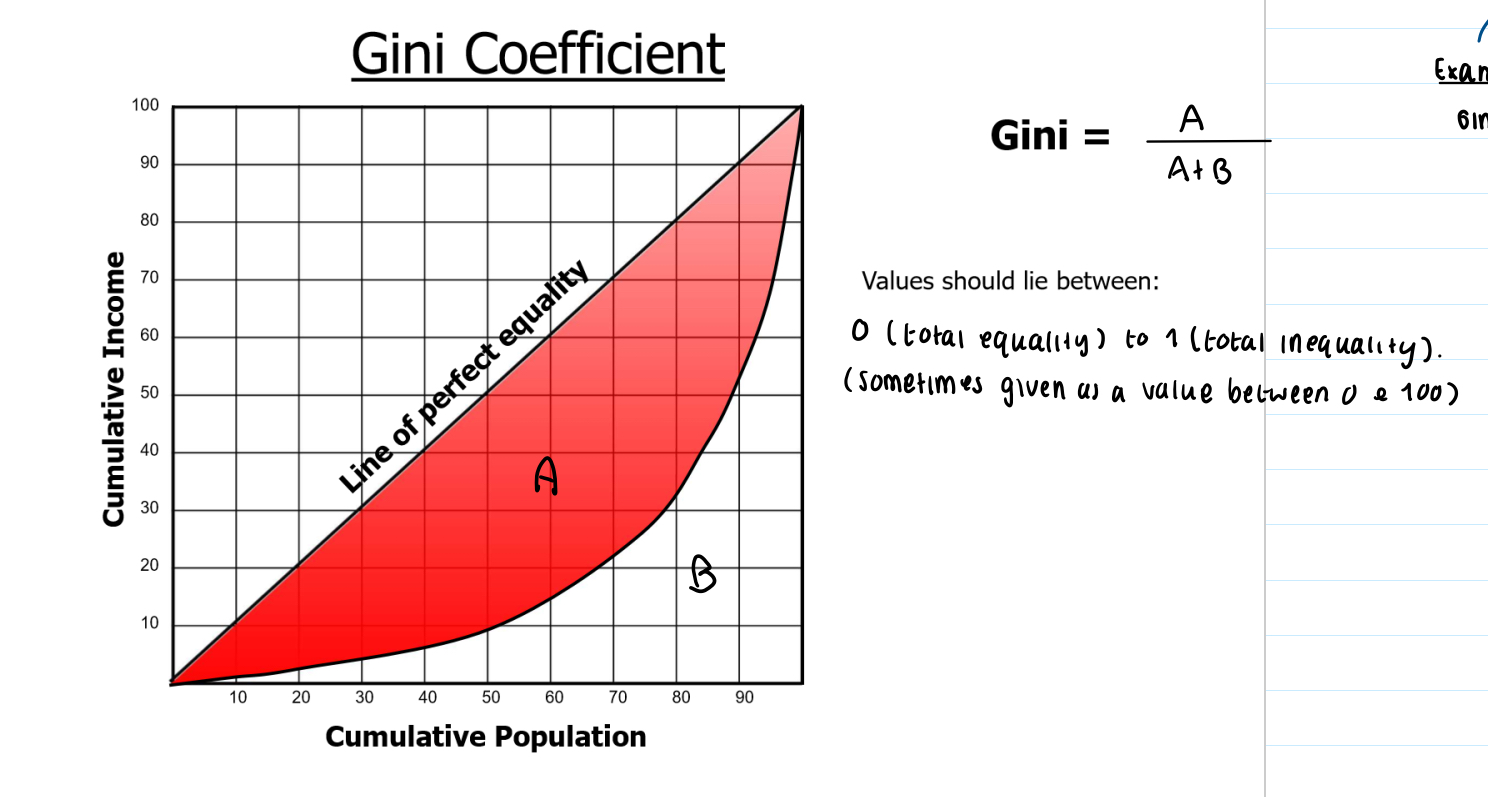
Measurements of income inequality: the Gini coefficient
Causes of income & wealth inequality within countries and between countries
level of education, training & skills
Lack of education - poor education = ppl lack skills to take on higher-paying jobs & these jobs could increase one’s wealth
Wage rates, including minimum wage
Trade union strength
Level of benefit payments
Tax system’s progressiveness
Level of state pension
Family wealth
One likely reason for the change in UK income inequality
May be use to change in government policies / taxation
Ie. An increase in level of benefit payment
Impact of economic change & development on inequality
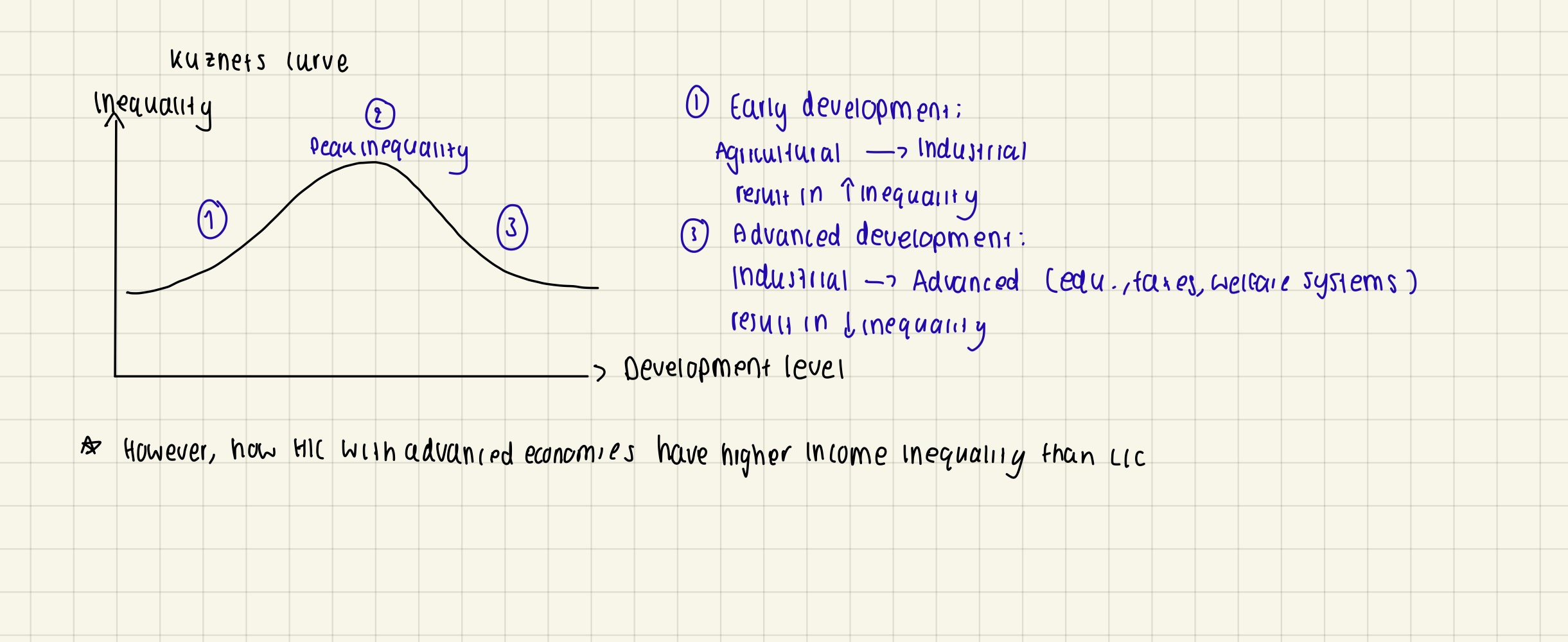
Significance of capitalism for inequality
Capitalistic economic system = a free market economy where resources are owned by private sector & prices are determined by supply & demand
The system is split into 2 parts:
the owners of the resources required for producing & distributing gds
working class who sell their labour to the owners in exchange for wages
Owners will have more wealth & income than workers → inequality
Policies to reduce inequality
Universal Basic Income
when government gives every adult citizen a set amount of money regularly, regardless of their employment status to ensure they meet the basic standard of living
flaws: reduces incentive to work, might be insufficient in expensive cities while being generous in rural areas
Does not cause inflation as money for UBI is redistributed from other areas, not newly printed
Redistribution of income (through taxes & benefits) - taking more from higher earners and distribute it to lower earner
Improve educational training opportunities
Regional assistance (directing funds to areas which needed to improve their infrastructure, create jobs…)
Anti-discrimination laws
Distinction between income & wealth (2)
Income = money received as payment for work (ie. Salaries / wages)
Wealth = total value of assets owned
Explain the distinction between absolute poverty & relative poverty (5) (very common)
Definition of absolute poverty (k)
Definition of relative poverty (k)
Measurement of absolute poverty (application)
Measurement of relative poverty (application)
Quote from extract suggesting absolute poverty is decreasing, relative poverty is rising
Analysis: absolute poverty can decrease at the same time as relative poverty increases