Gas exchange in humans.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
what features do gas exchange surfaces have?
large surface area - gives more space for diffusion to take place thereby speeding up the rate of diffusion and maximising gas exchange
thin surface - reduces the diffusion distance across which gases must diffuse
good blood supply - ensures good concentration gradients are always maintained
good ventilation w/ air - this also ensures that a good concentration gradient is maintained
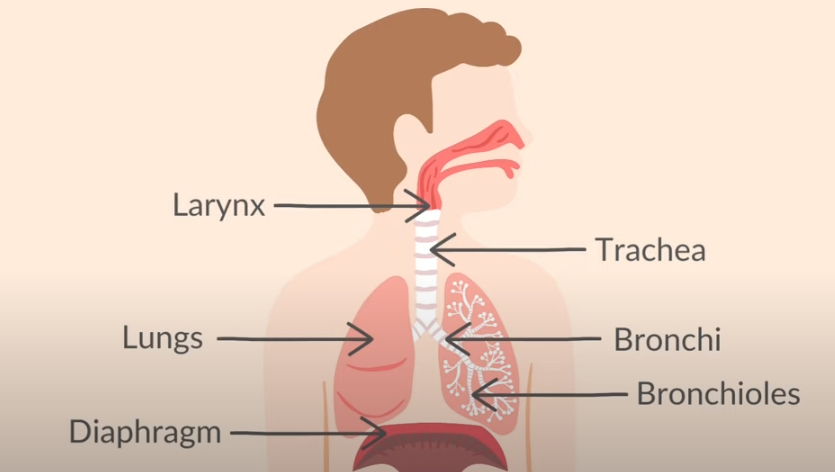
why is the trachea lined with rings of cartilage
keep trachea open
prevent trachea from collapsing
allows flexibility, can breathe even when bent
inspiration
act of breathing in
during inspiration:
the external intercostal muscles contract
the internal intercostal muscles relax
this pulls the ribcage upwards and outwards
diaphragm contracts and moves downwards
volume of thorax increases
air pressure inside lungs decreases
air moves from outside to into the lungs down a pressure gradient
expiration
act of breathing out:
the external intercostal muscles relax
the internal intercostal muscles contract
this pulls the ribcage downwards and inwards
the diaphragm relaxes and moves back upwards
volume of thorax decreases
air pressure inside of lungs increases
air moves from the lungs into the outside down a pressure gradient
composition of expired and inspired air
oxygen - 21% inspired air. 16% expired air.
why: Only 5% of oxygen absorbed. The concentration of oxygen of the blood surrounding the alveoli is lower than the inspired air. Oxygen used in aerobic respiration. Oxygen diffuses through the partially permeable membranes of the alveoli and enters into the bloodstream down a concentration gradient.
----------------------
carbon dioxide - 0.04% inspired. 4% expired - The concentration of carbon dioxide of the blood surrounding the alveoli is higher than the inspired air. carbon dioxide is released by respiration Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the bloodstream through the partially permeable membrane of the alveoli into the outside down a concentration gradient.
-----------------
water vapour - less in inspired. more in expired. - the body’s warmth causes water in the alveoli surface to evaporate into the expired air. water vapour increases, produced in respiration
protecting the breathing system
a thin layer of mucus lines the respiratory tract
this mucus is produced by goblet cells
the mucus traps pathogens and dust particles.
this prevents the entry of pathogens into the lungs
the respiratory tract is also lined with ciliated epithelial cells
these cells have tiny hairs called cilia
the cilia beat and waft the mucus upwards towards the throat, where it can be swallowed