The Human Body: chapter 1
1/67
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering key terms and definitions from the anatomy & physiology lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of body parts and their relationships; how things look.
Physiology
The study of the function of the body's structures; how things work.
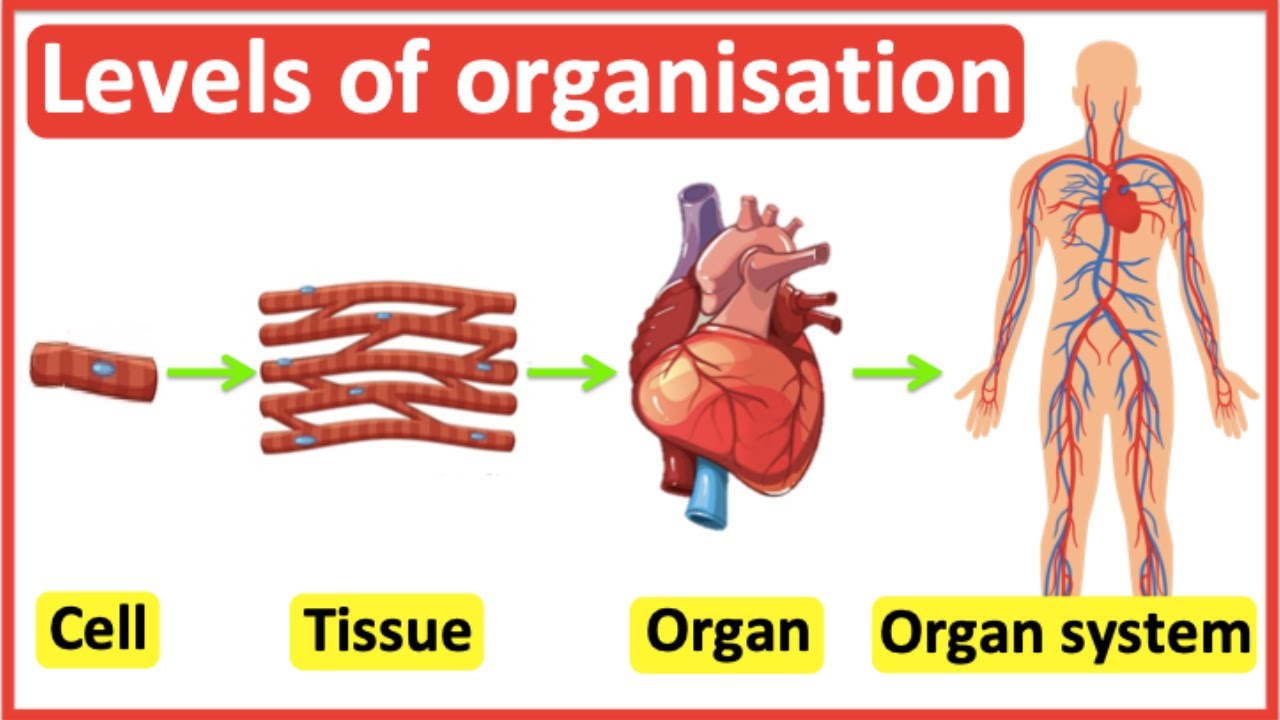
Gross (Macroscopic) Anatomy
Anatomy visible to the naked eye:
external body parts(head, hand, eye…)
Internal organs (heart, lungs,liver…)
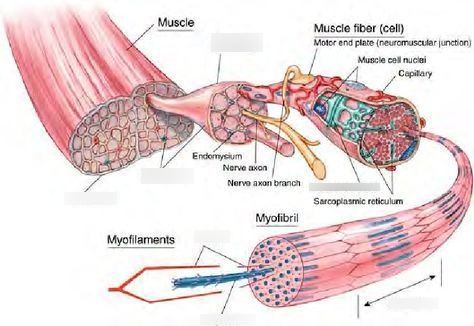
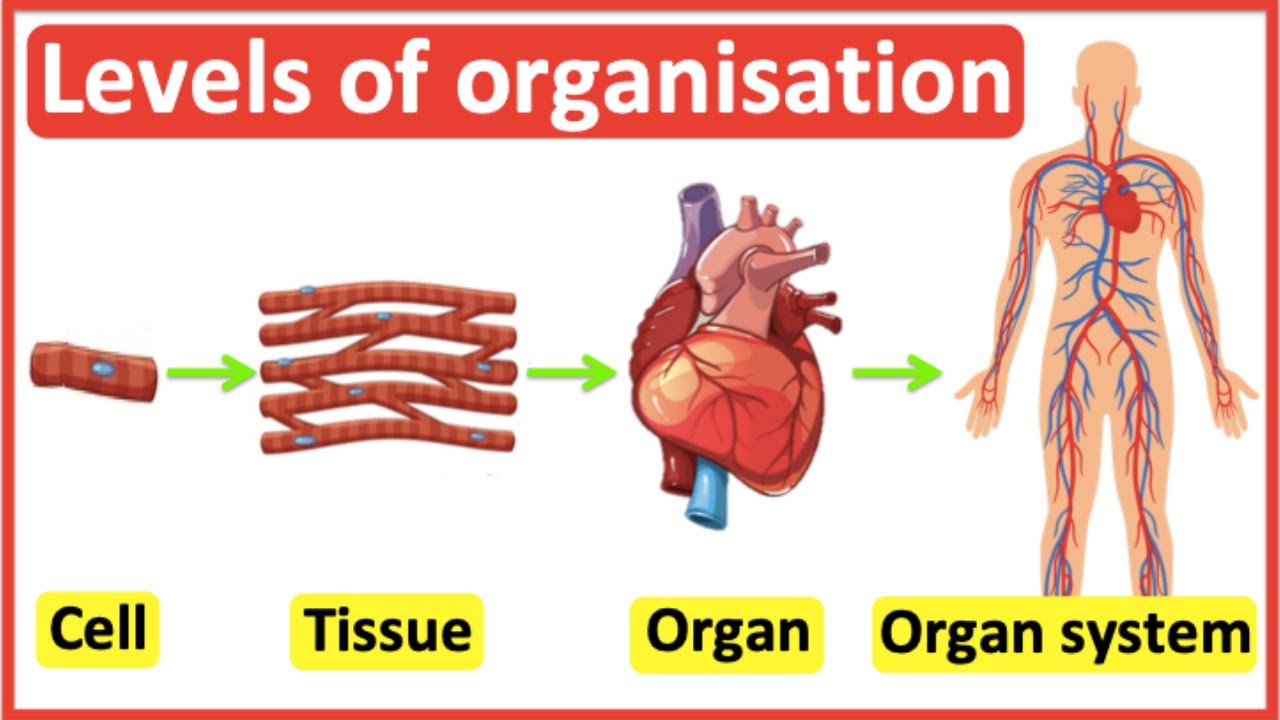
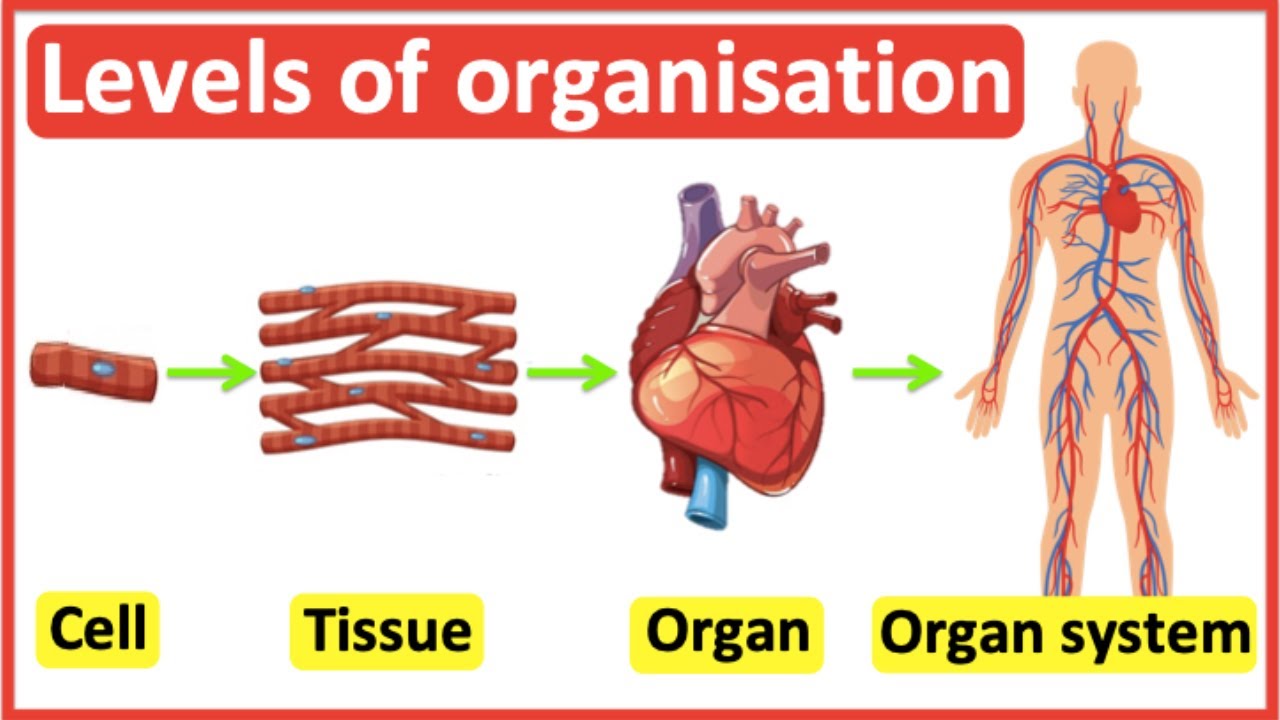
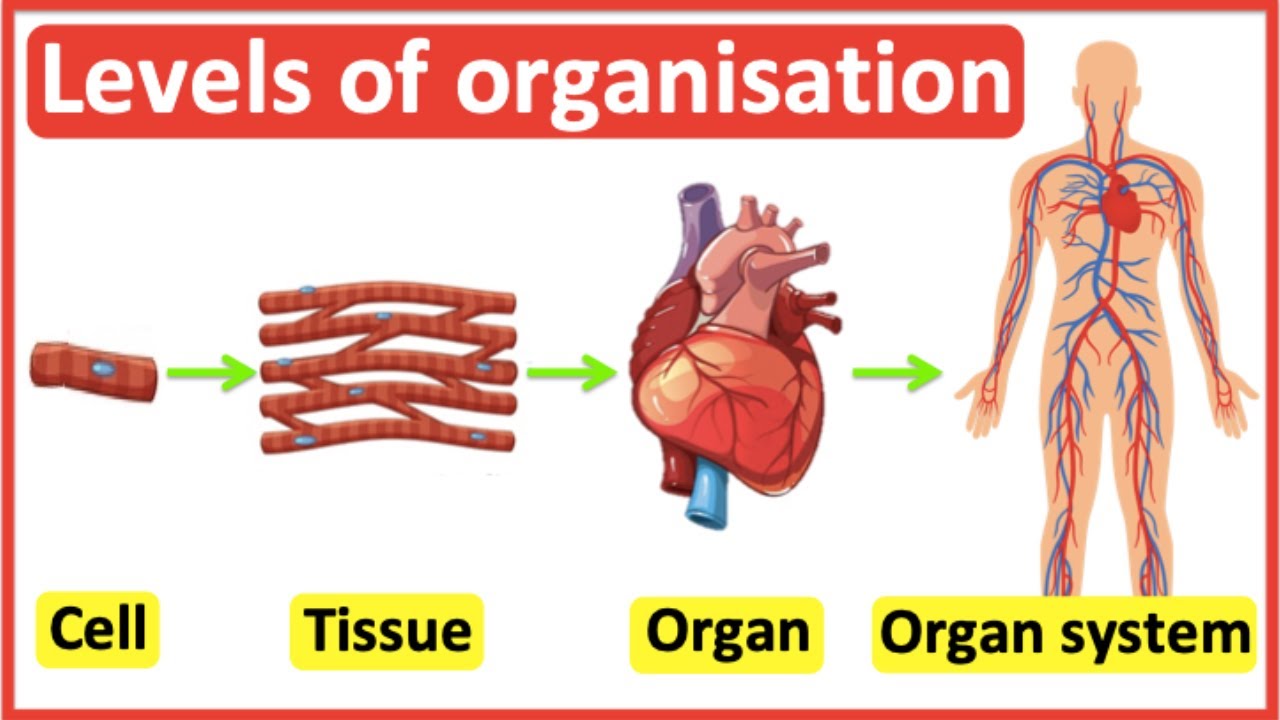
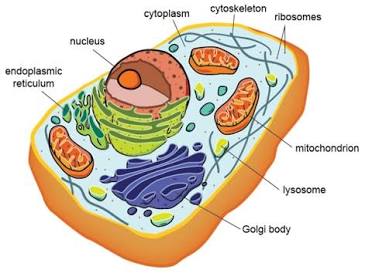
Microscopic Anatomy
Anatomy seen with a microscope (cells and tissues).
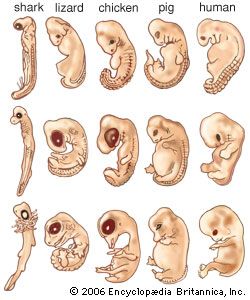
Developmental Anatomy
How the structure of the body changes as it grows.
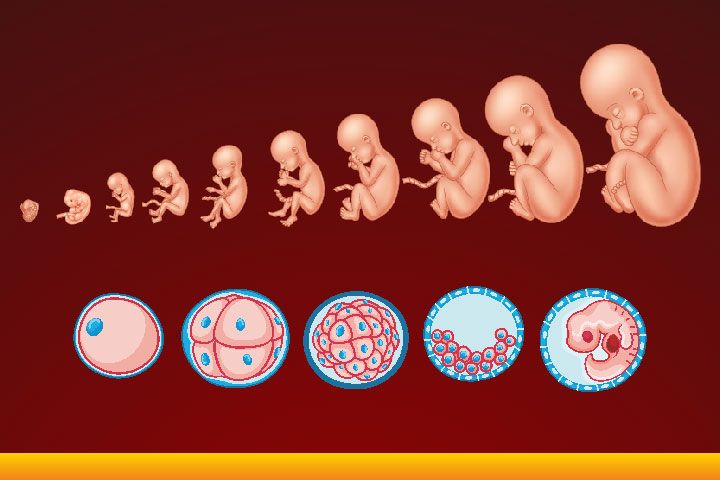
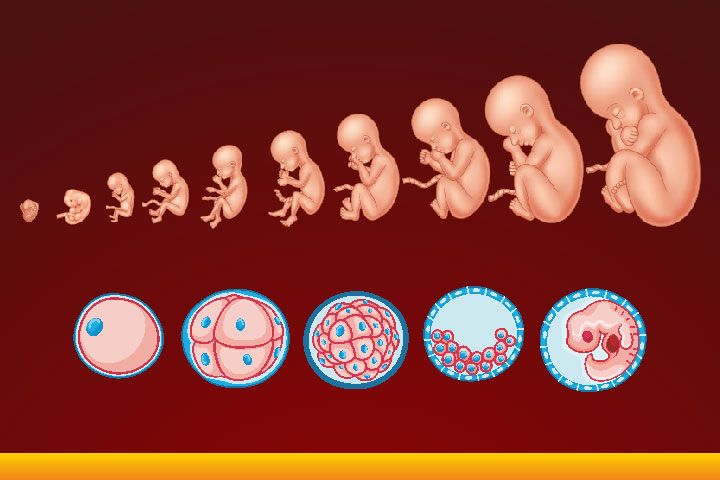
Embryology
Developmental changes of the body before birth.
Cytology
Study of the cell.
Histology
Study of tissues.
Pathology
Study of diseases and the structural changes they cause.
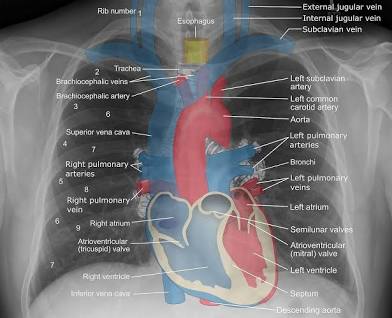
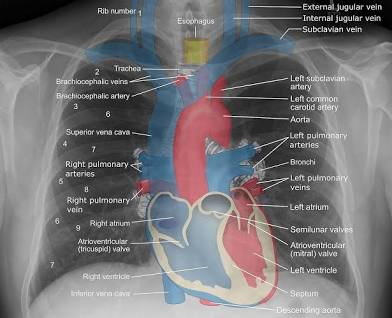
Radiographic Anatomy
Internal structures visualized by X-rays or other imaging methods.
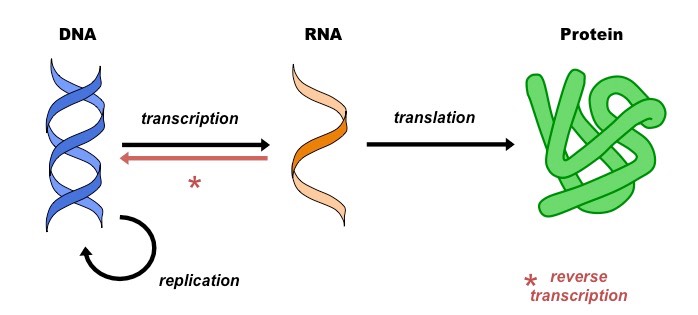
Molecular Biology
Study of anatomical structures at a subcellular level.
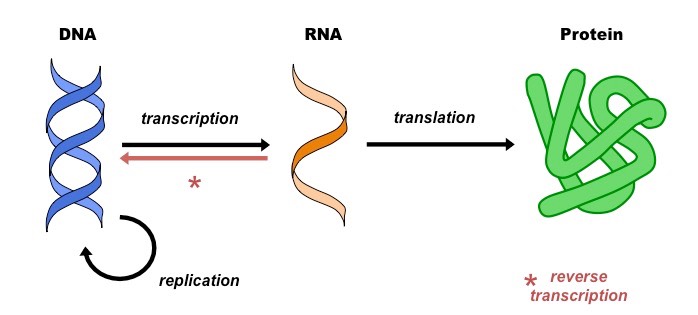
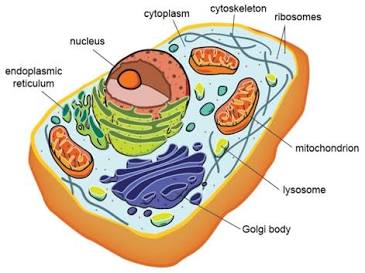
Subcellular
Relating to components smaller than a cell (molecules, organelles).
Regional Anatomy
Study of all structures in one part of the body.
Systemic Anatomy
Study of anatomy by body system.
Surface Anatomy
Study of internal structures as they relate to the overlying skin.
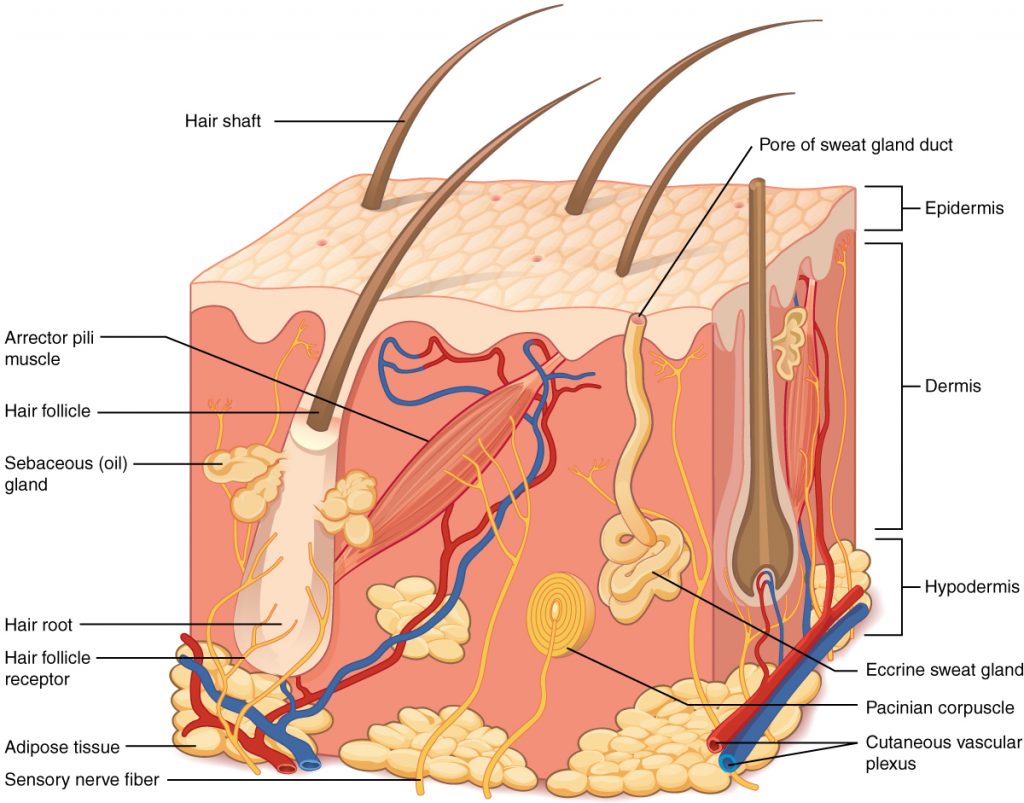
Integumentary System
External body covering (skin, hair, nails, glands) that protects and helps synthesize vitamin D; Dermis is a key skin layer.
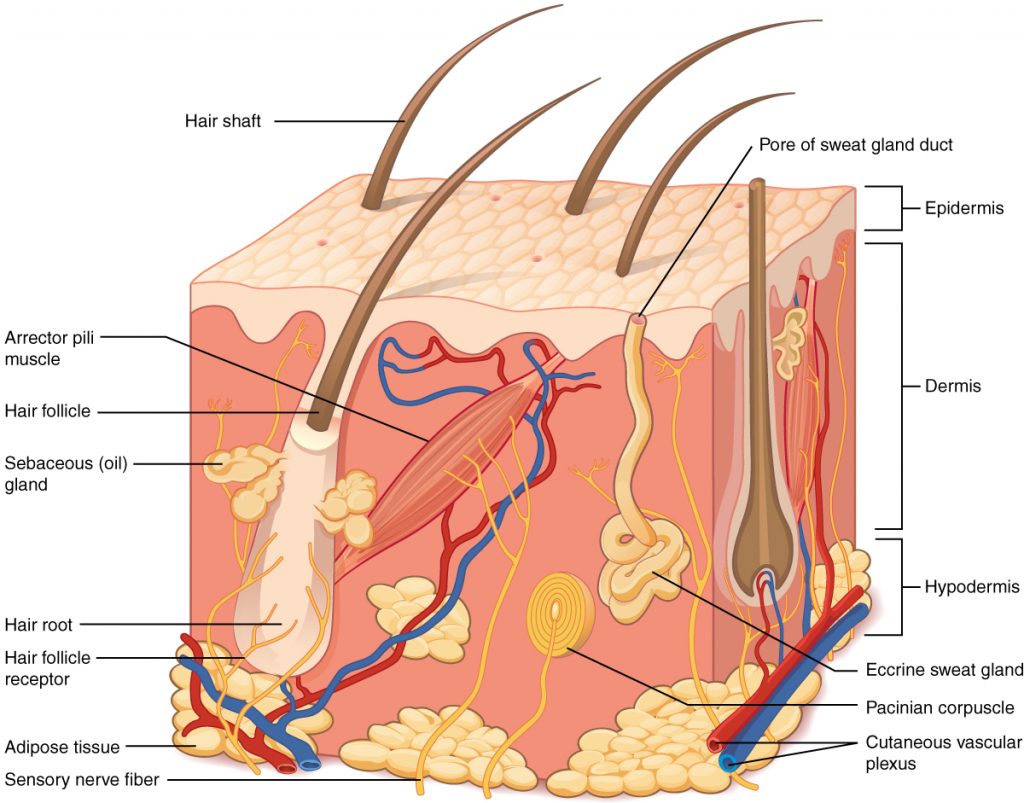
Dermis
The deeper skin layer beneath the epidermis.
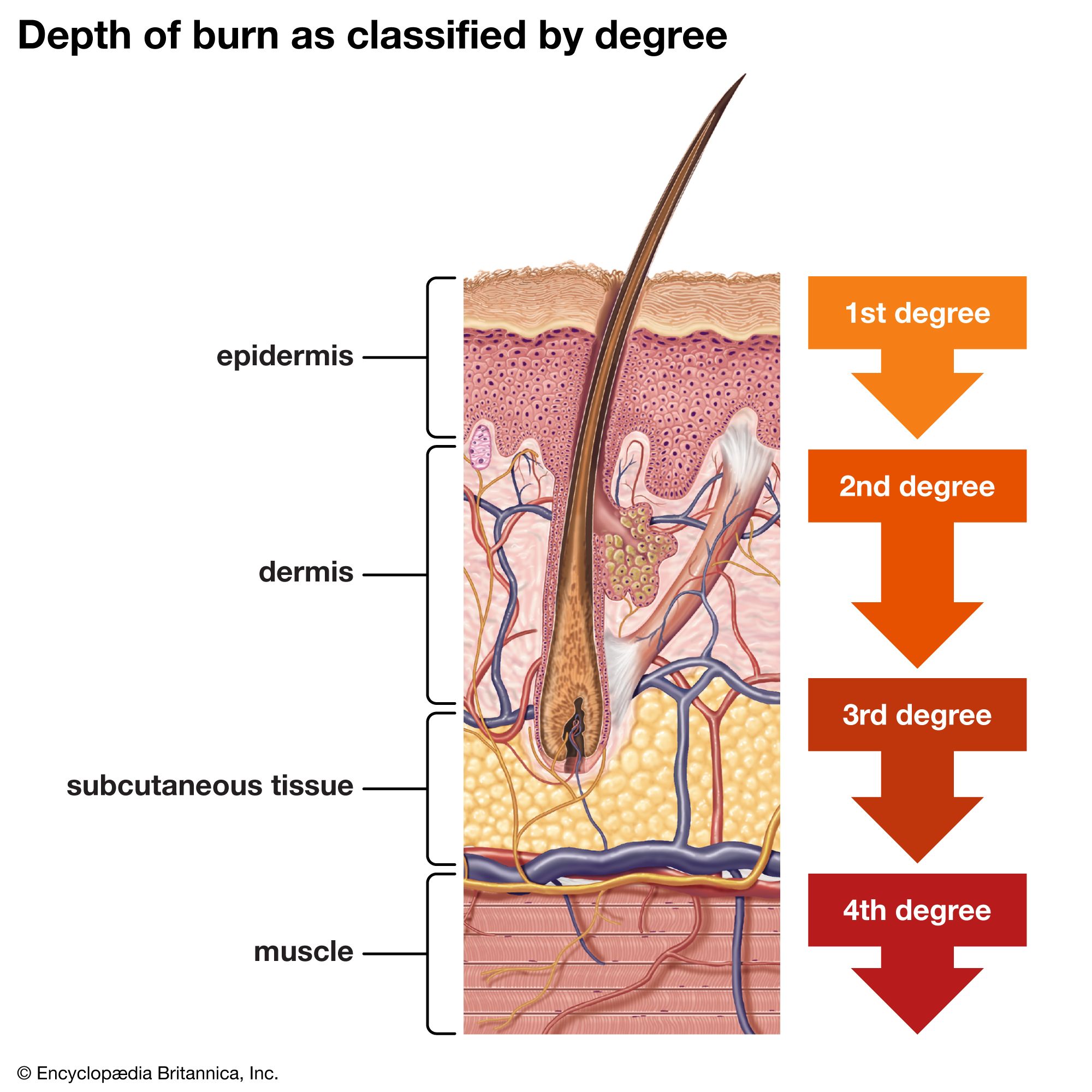
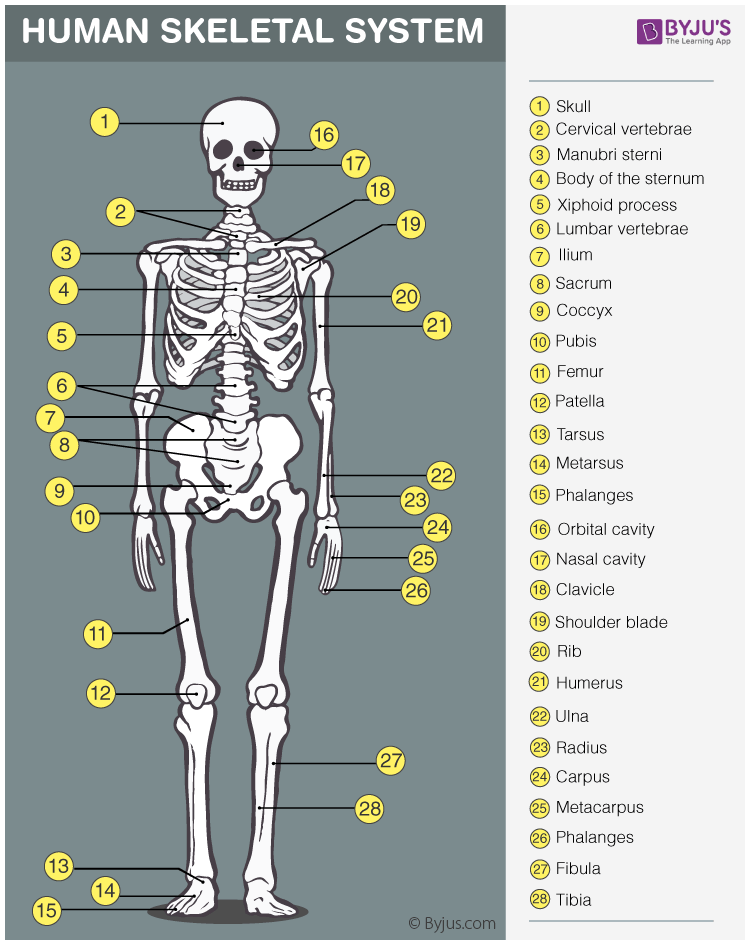
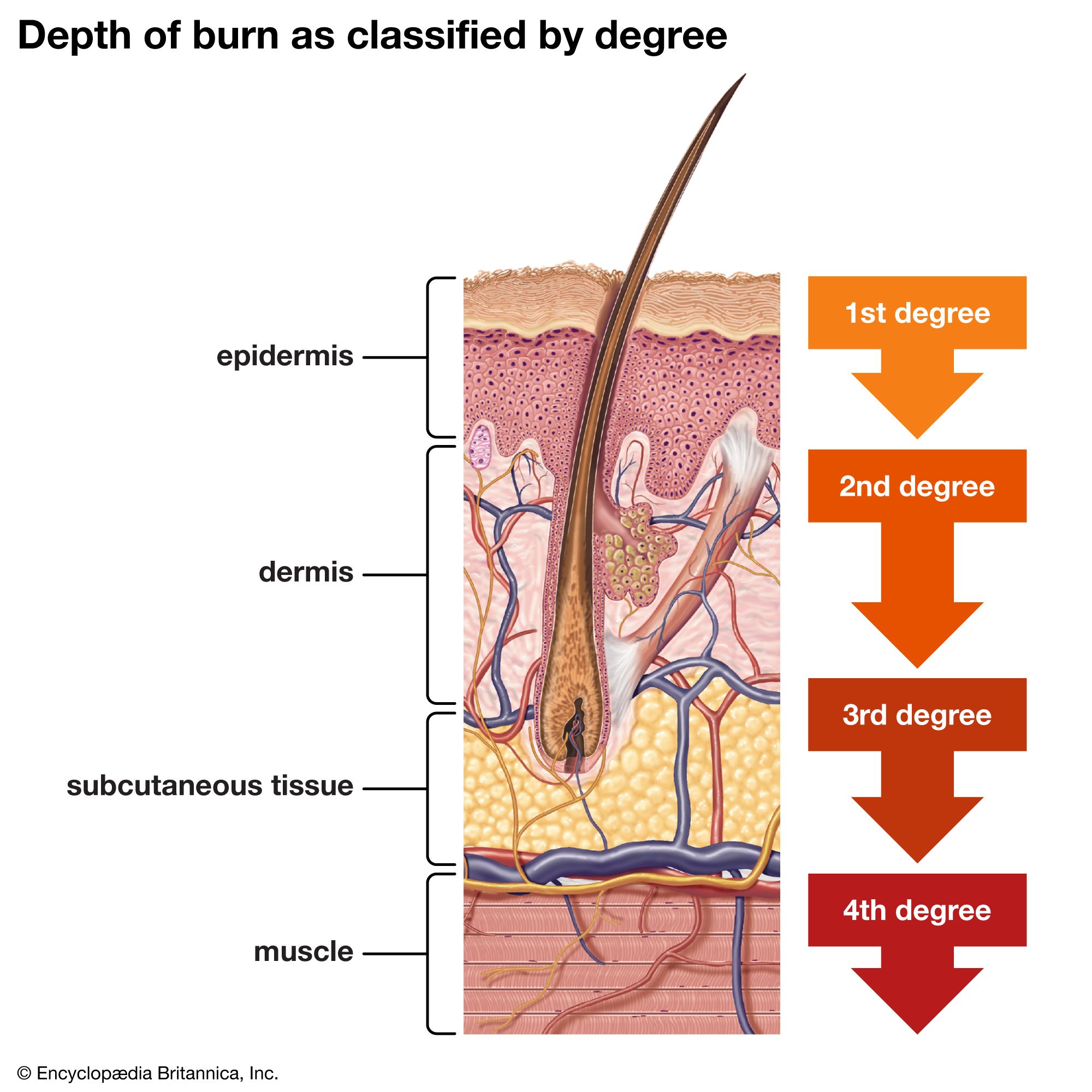
Skeletal System
Bones, cartilage, and ligaments; protects and supports the body; site of blood formation; stores minerals; osteo- means bone.
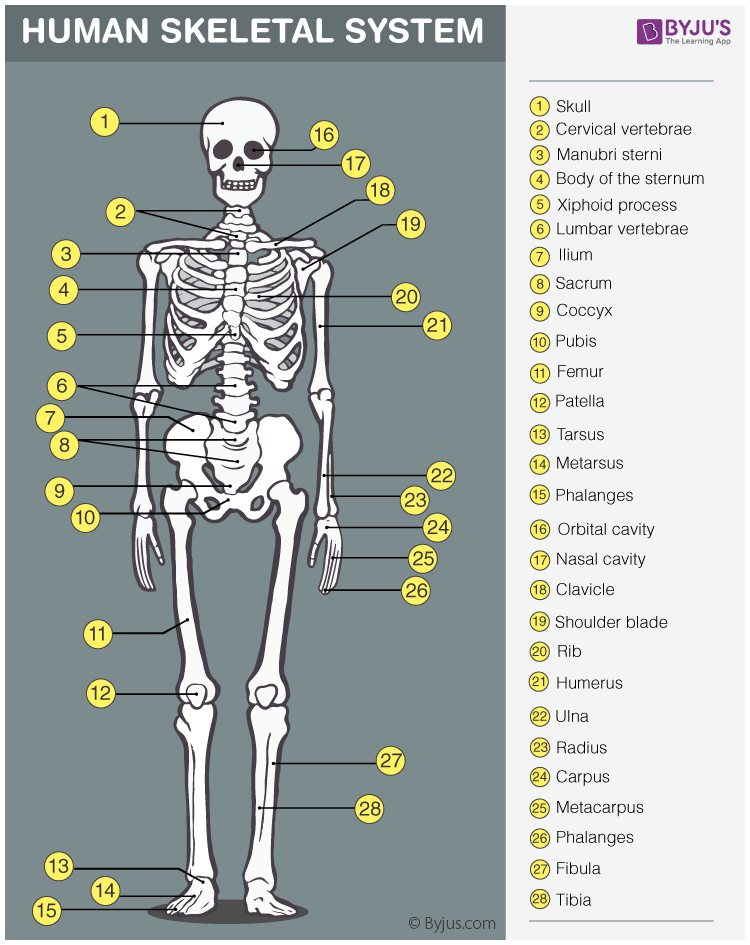
Osteo- (osteo-)
Prefix meaning bone.
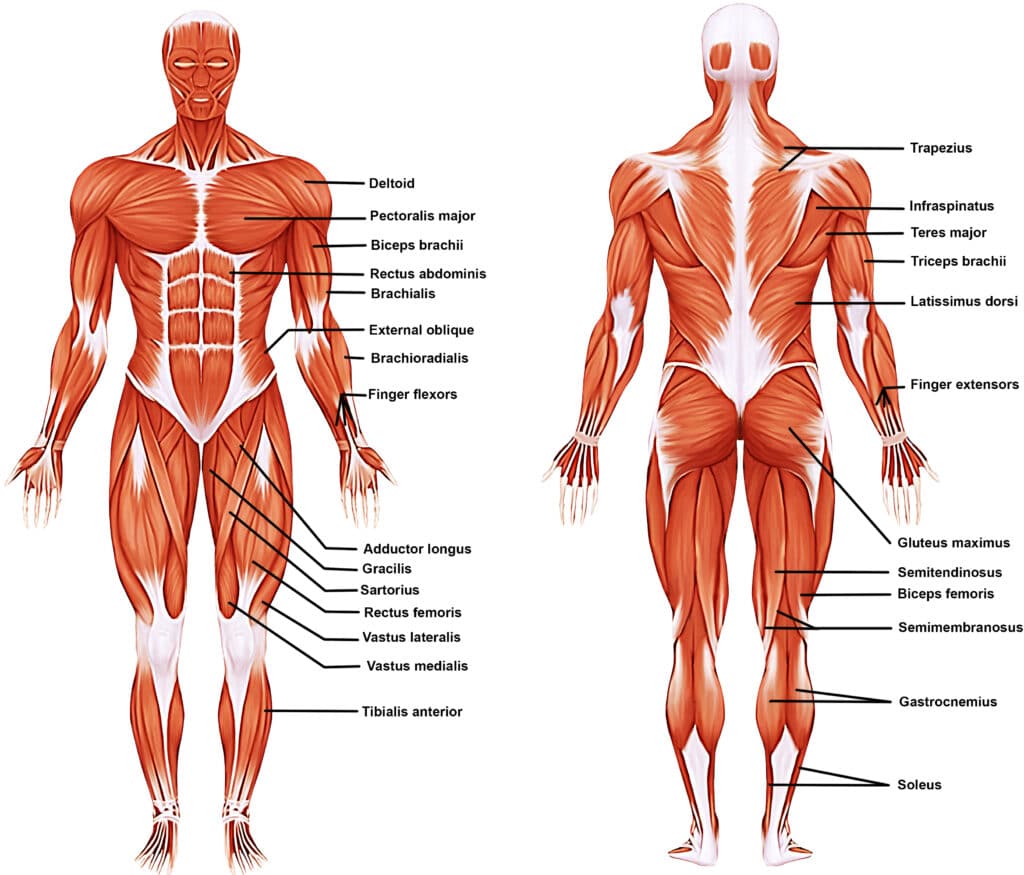
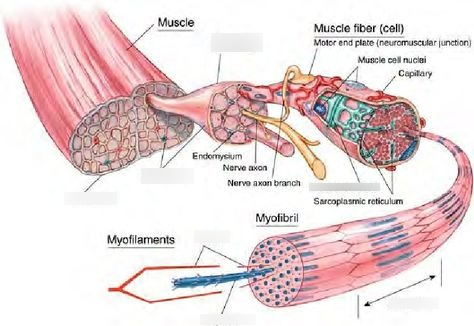
Muscular System
Muscles and tendons; enables movement and generates heat; term roots include myo- and sarco-.
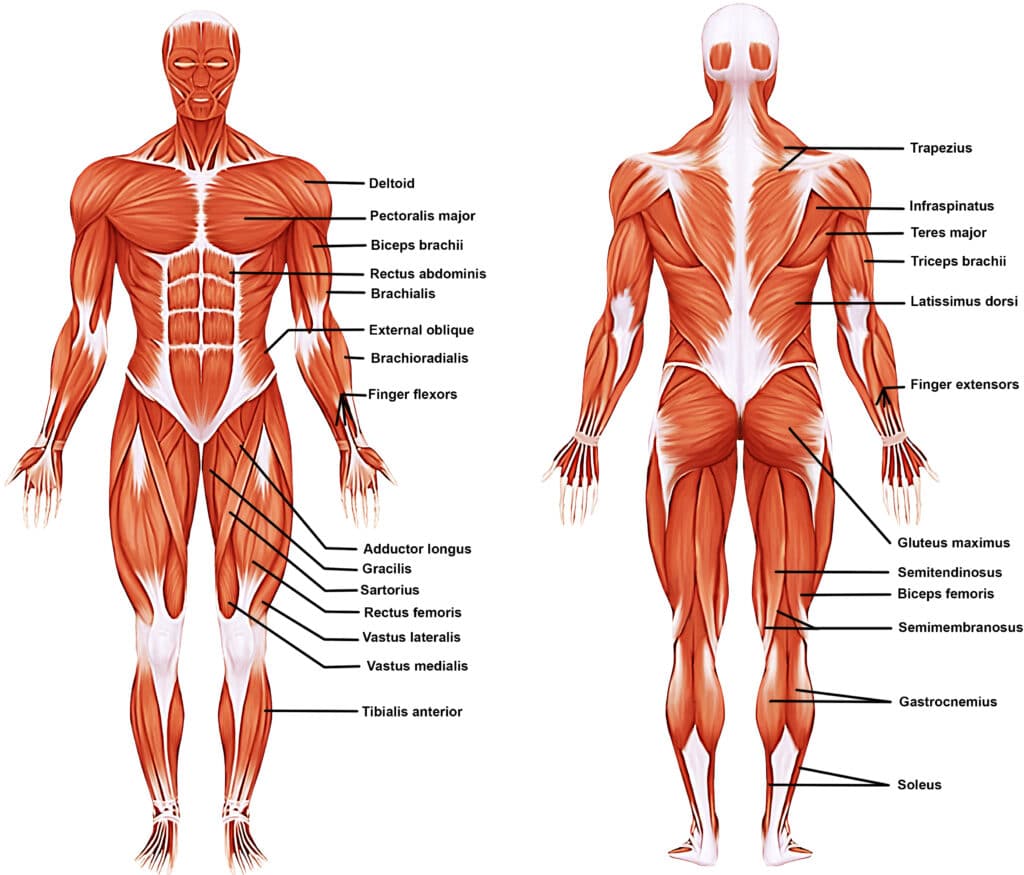
Myo-
Prefix meaning muscle.
Sarco-
Prefix meaning flesh (used in muscle-related terms).
Nervous System
Brain, spinal cord, and nerves; fast-acting control system; neuro- is a root for nerve.
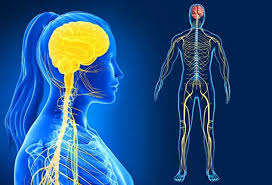
Neuro-
Prefix meaning nerve.
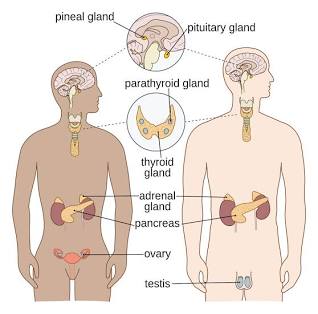
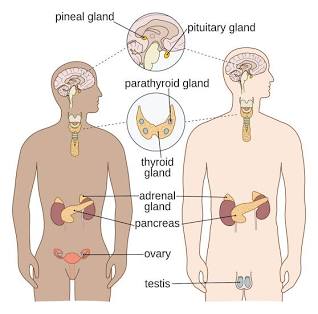
Endocrine System
Glands and hormones that regulate growth, metabolism, and homeostasis.
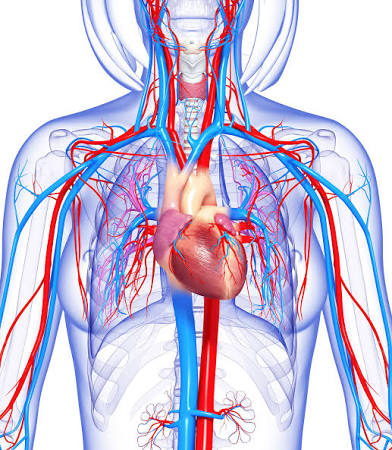
Cardiovascular System
Heart and blood vessels; pumps and transports blood.
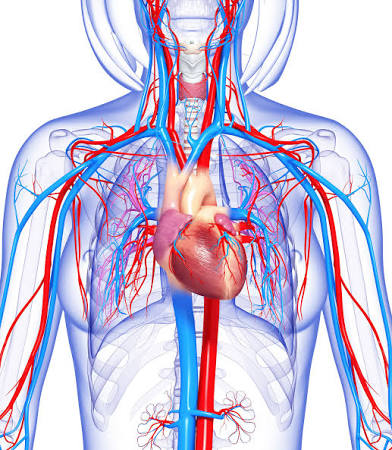
Cardio-
Prefix meaning heart.
Cardiac
Relating to the heart.
Coronary
Relating to the heart's vessels.
Pulmonary/ Pleural
Pulmonary relates to the lungs; Pleural relates to the membranes around the lungs.
Immune/Lymphatic System
Red bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes; returns leaked fluid to blood and supports immunity.
Leuko-
Prefix meaning white (as in leukocytes).
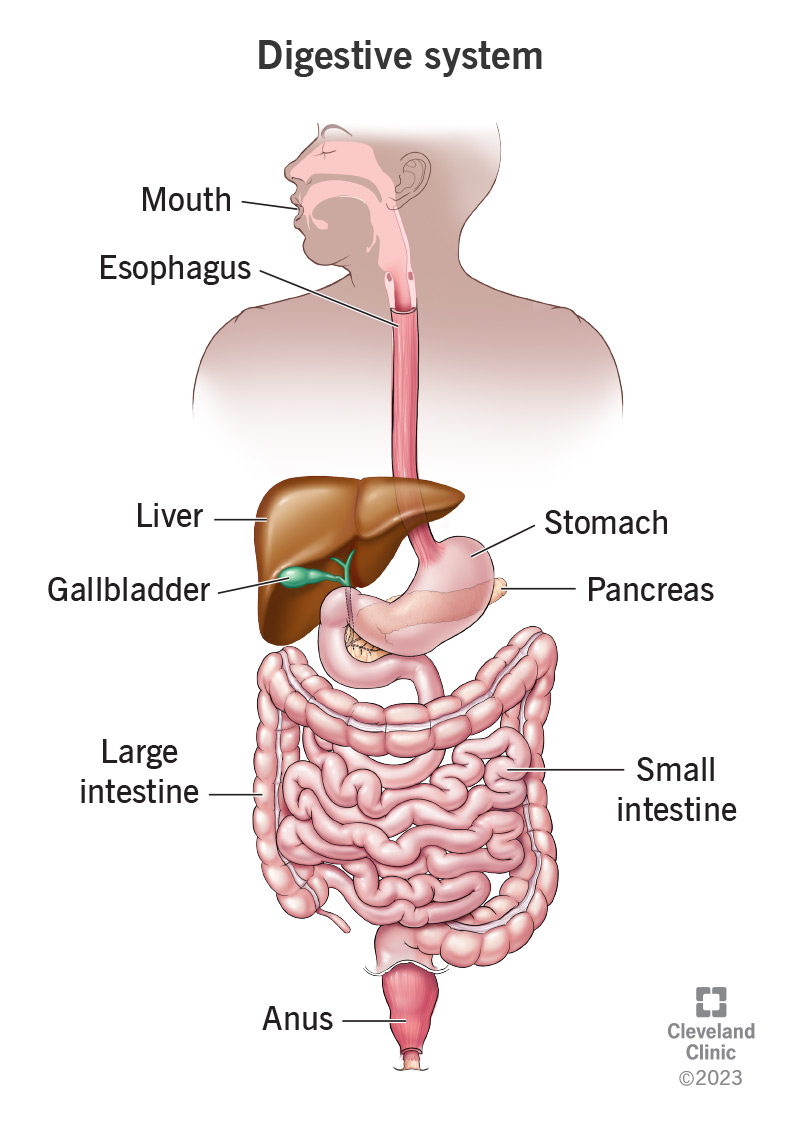
Digestive System
Mouth to anus; breaks down food and absorbs nutrients.
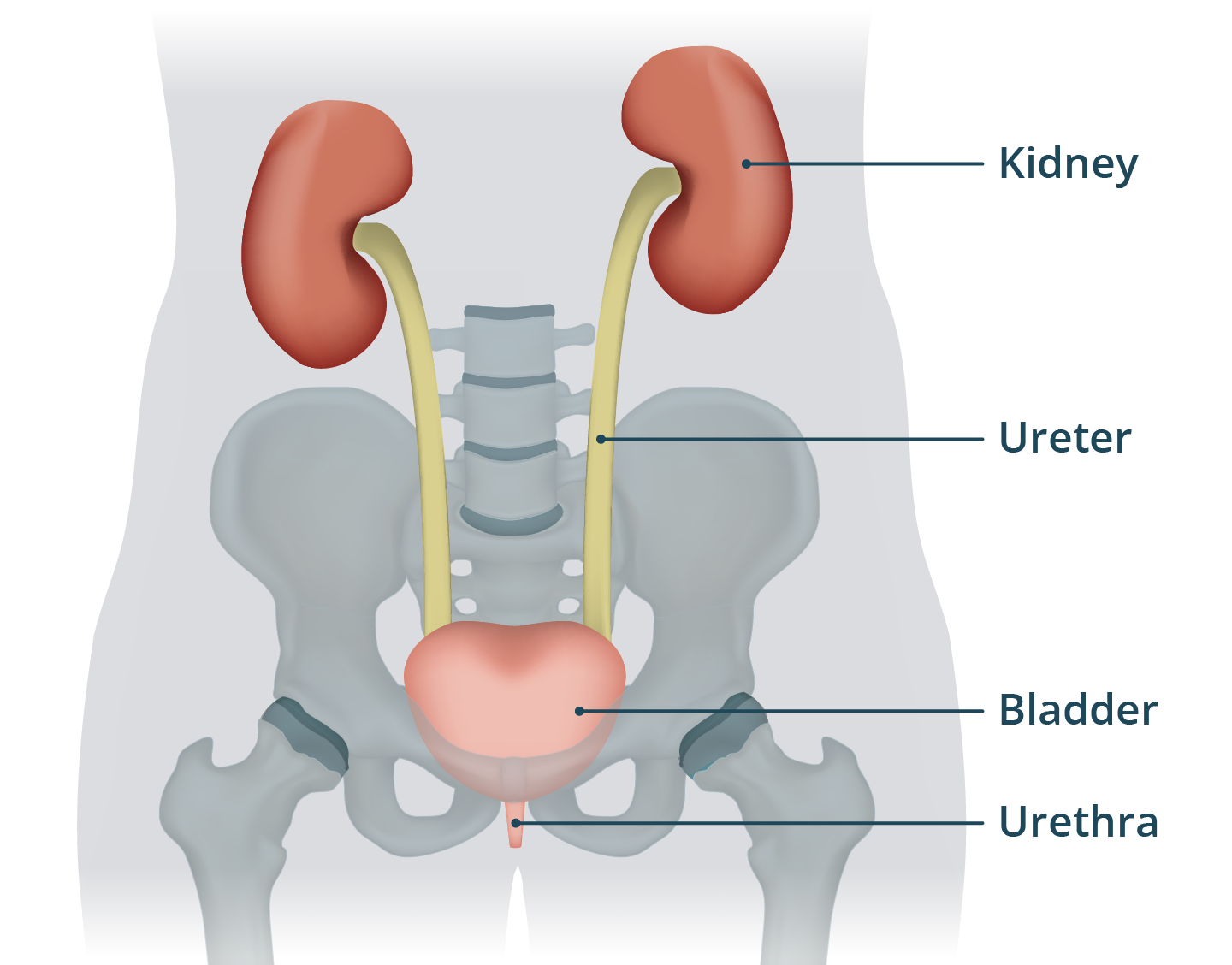
Renal (Urinary) System
Kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra; eliminates wastes and balances fluids and pH.
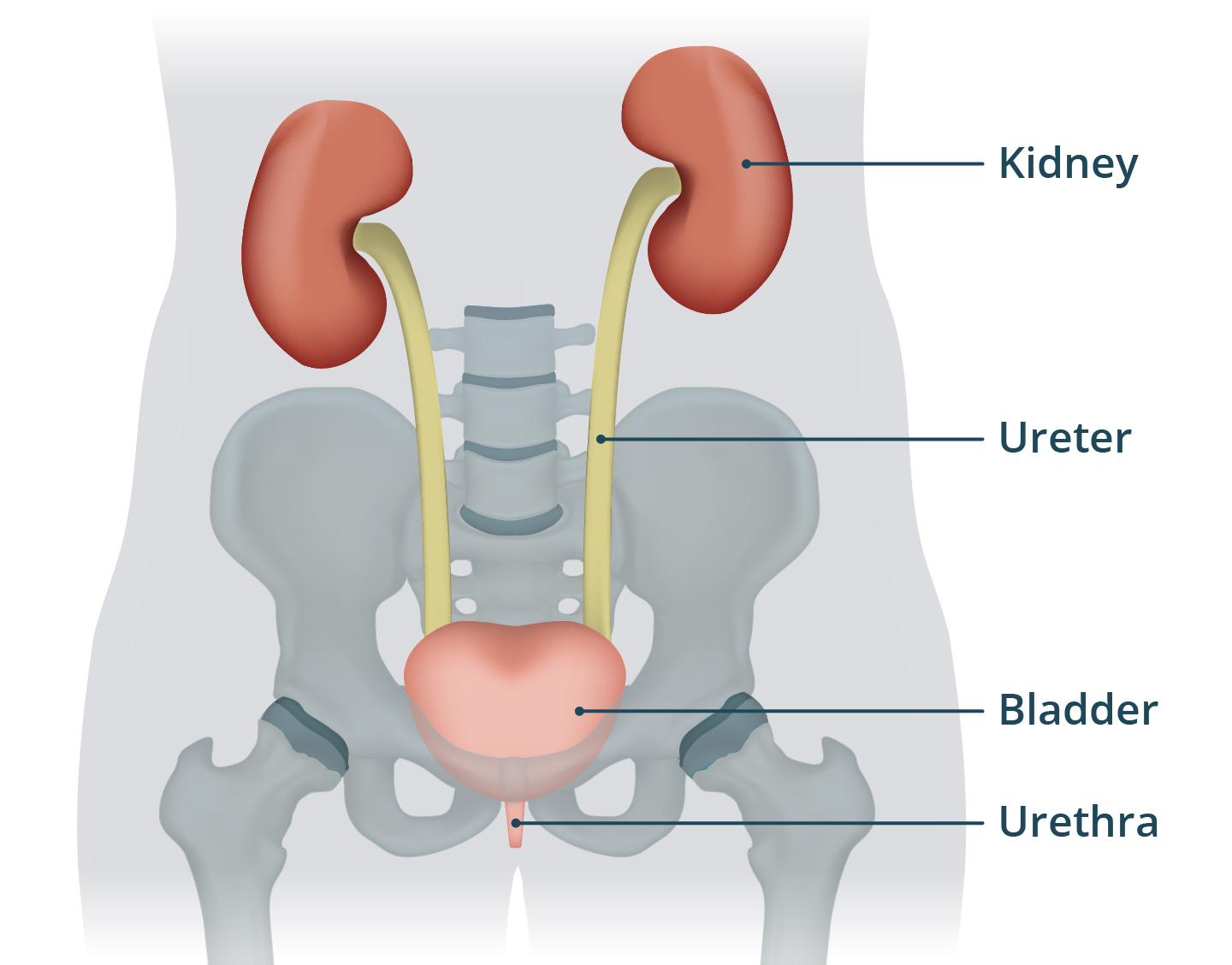
Renal-
Prefix meaning kidney.
Male Reproductive System
Glands and ducts that produce offspring; testes, prostate, penis, etc.
Female Reproductive System
Ovaries, uterus, mammary glands; produces eggs and supports offspring.
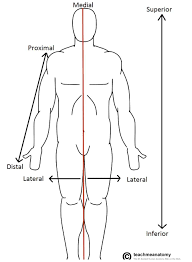
Anatomical Position
Standard body stance: upright, feet together, palms forward, thumbs outward.
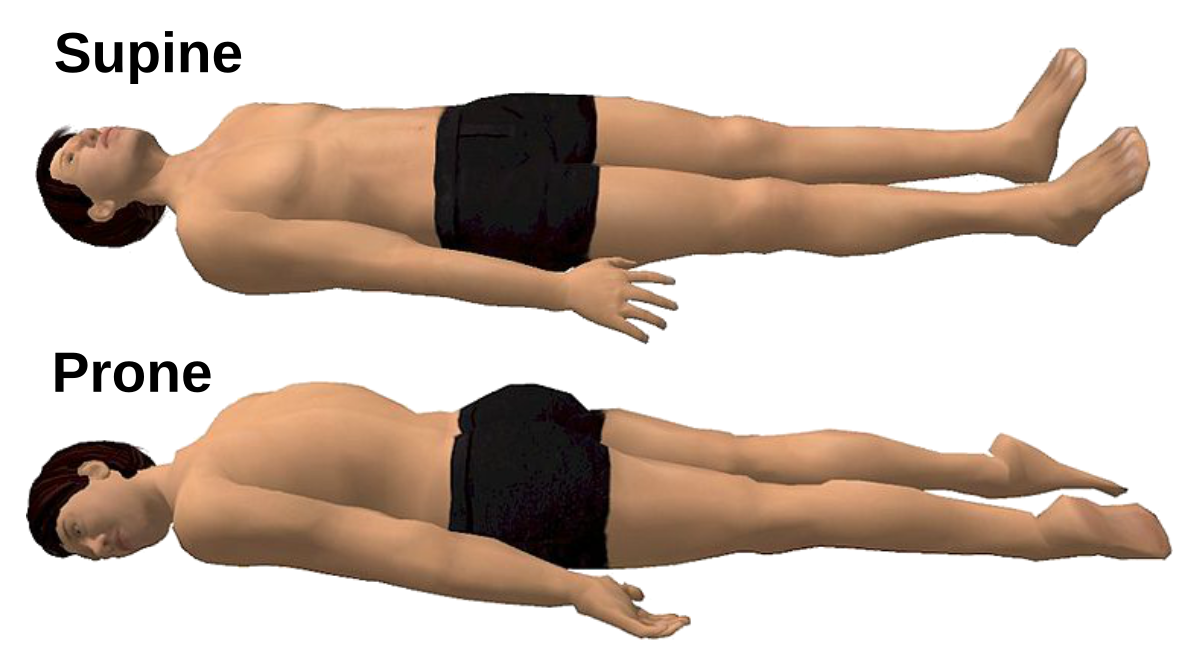
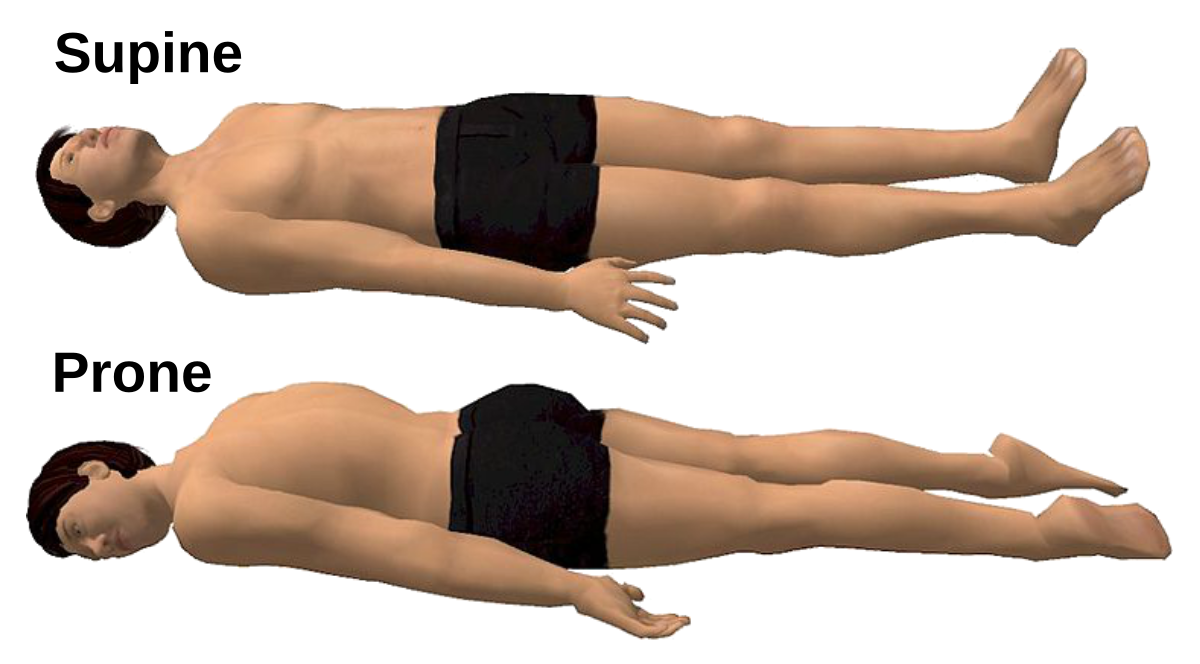
Prone Position
Body lying face down.
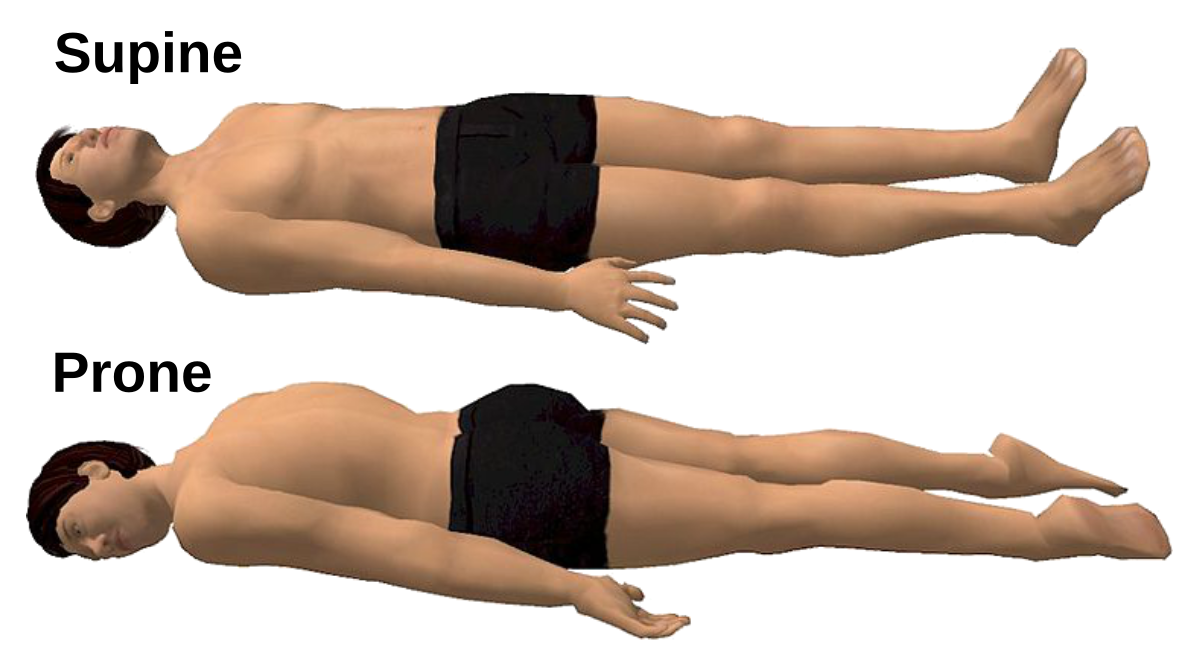
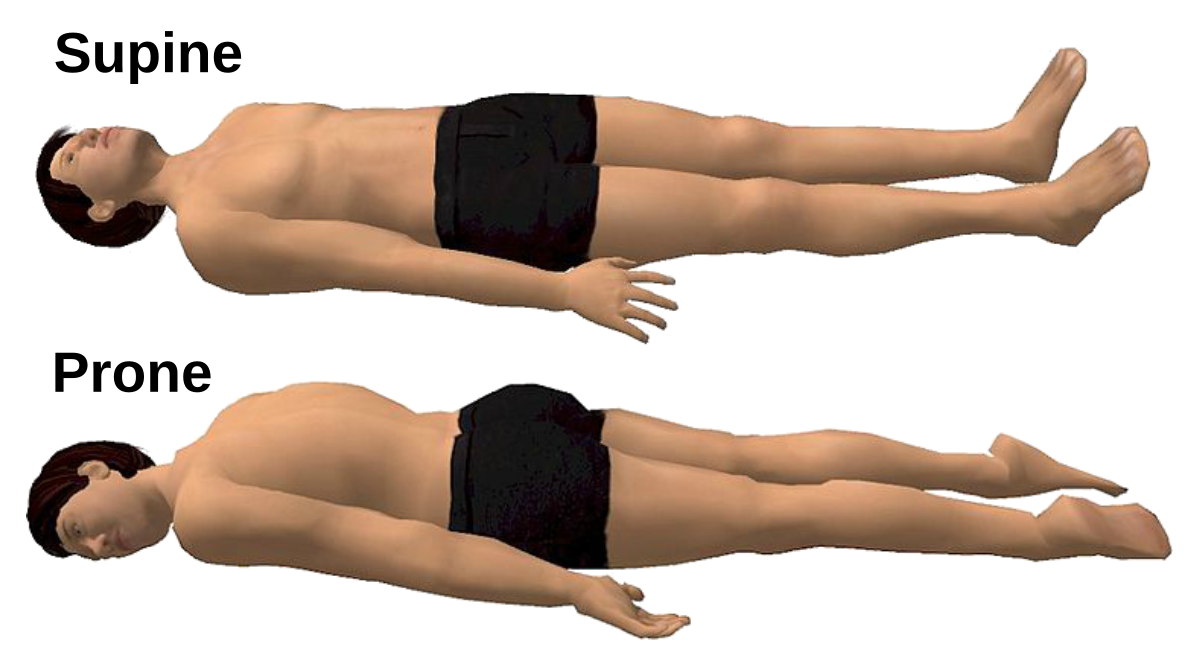
Supine Position
Body lying face up.
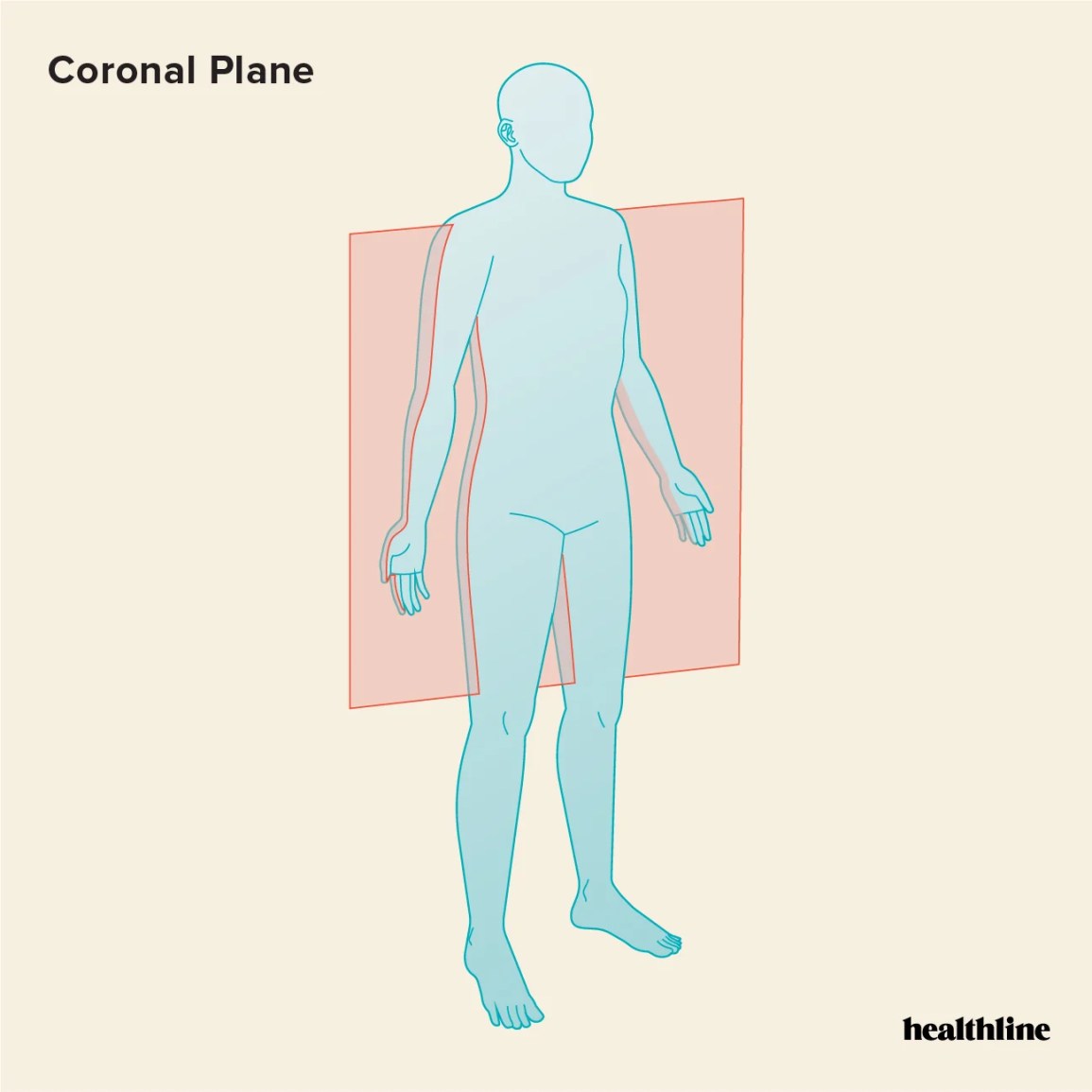
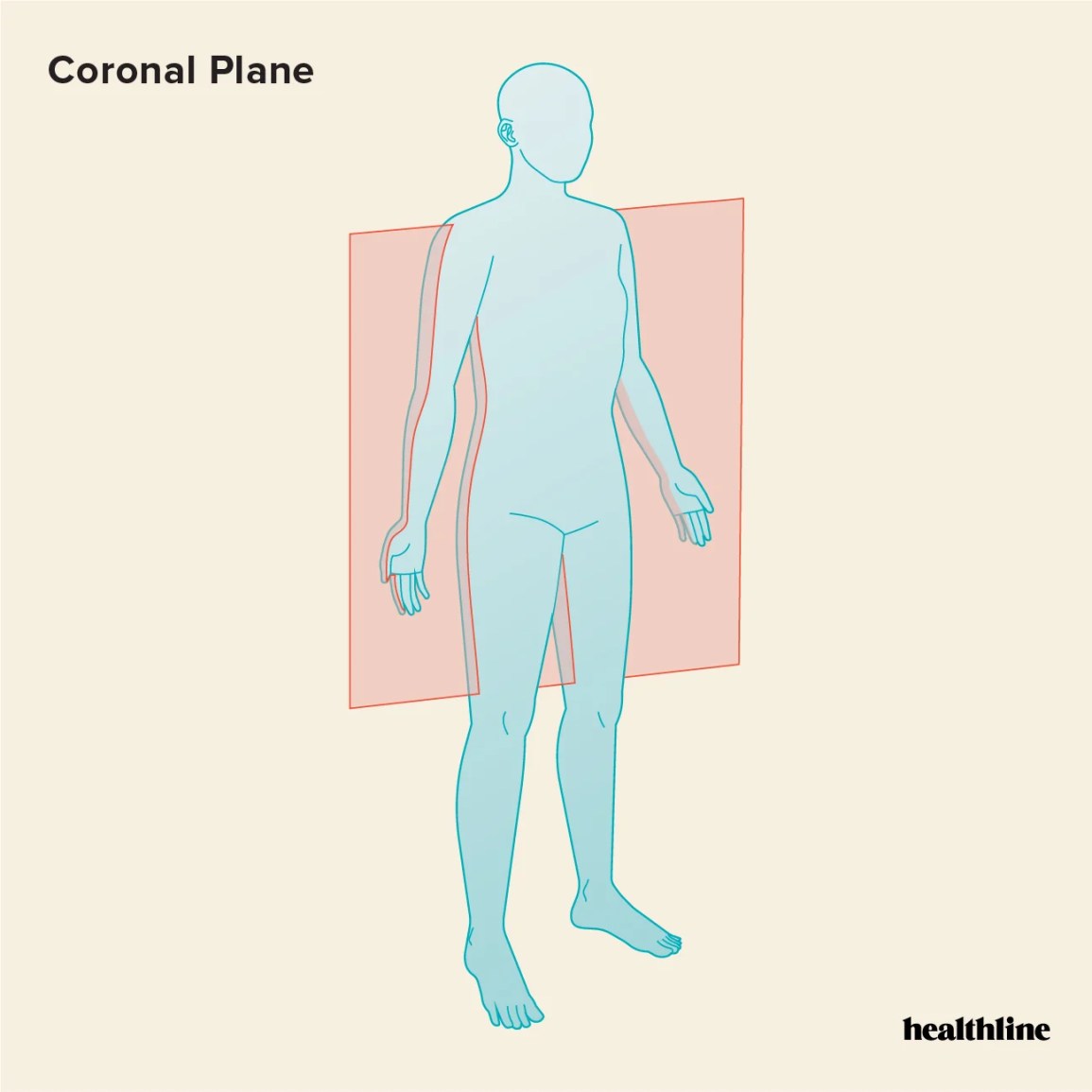
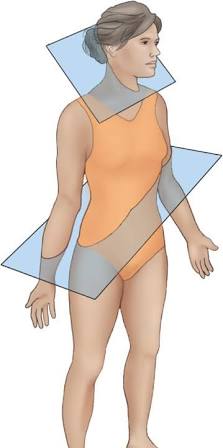
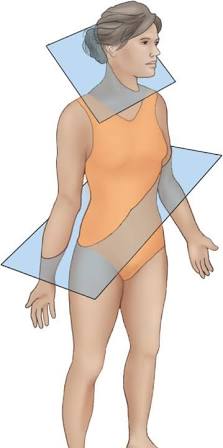
Coronal (Frontal) Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into anterior (front) and posterior (back) parts.
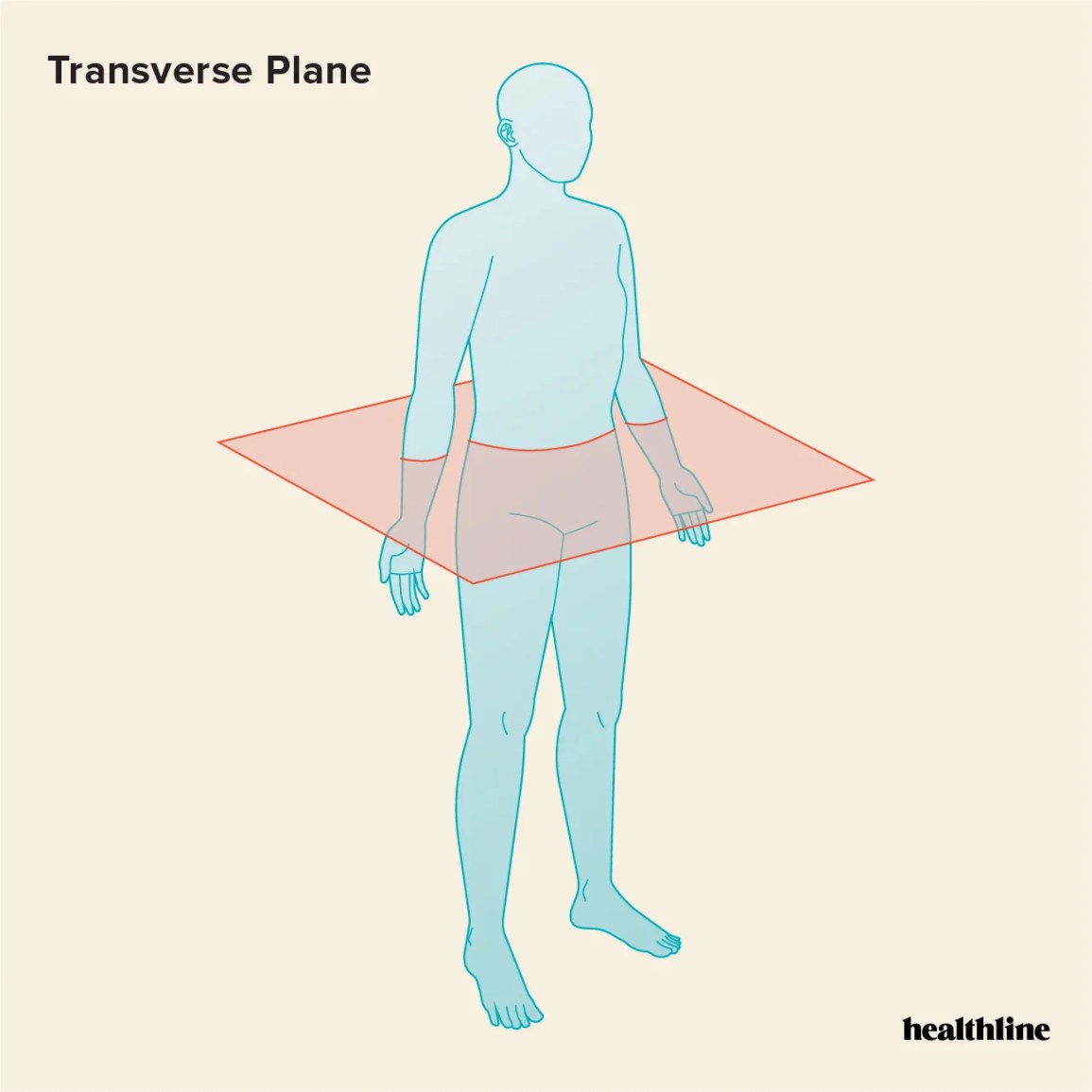
Transverse (Horizontal) Plane
Plane dividing the body into superior (top) and inferior (bottom) parts.
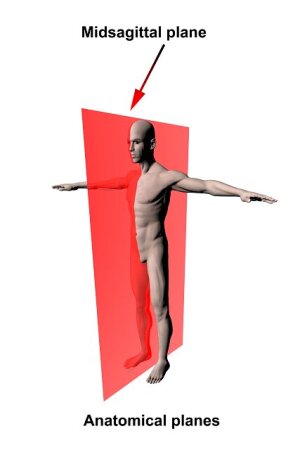
Midsagittal (Median) Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into equal left and right halves.
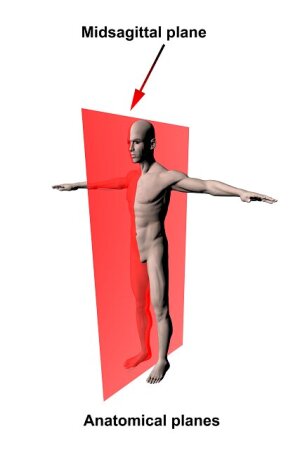
Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane parallel to the midsagittal plane; divides left and right in unequal portions.
Oblique Plane
Plane that passes through the body at an angle.
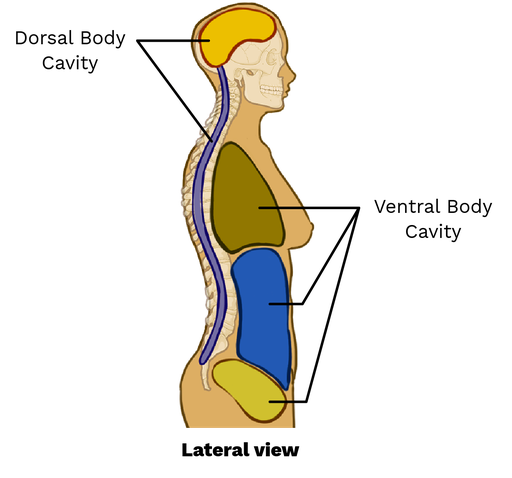
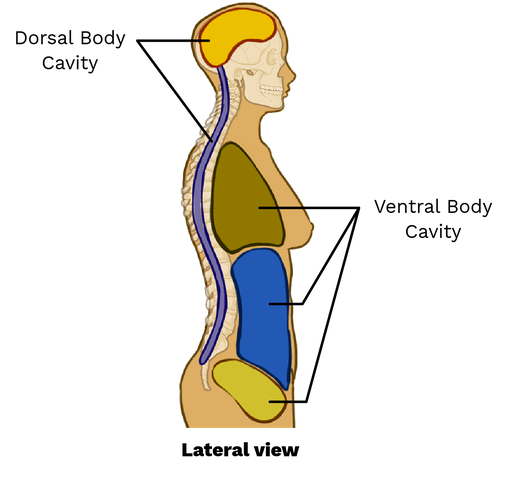
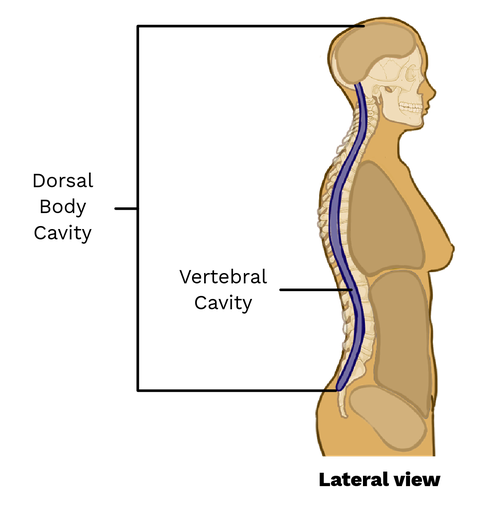
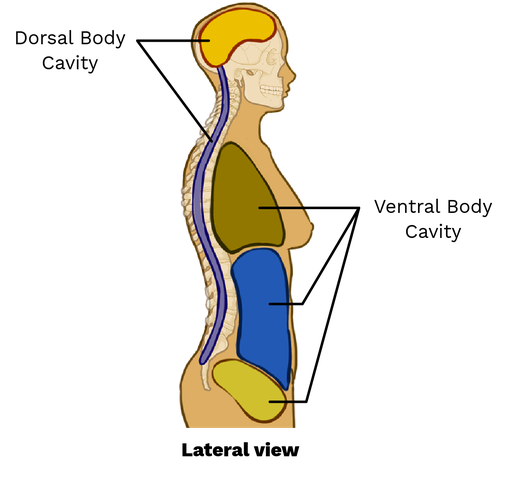
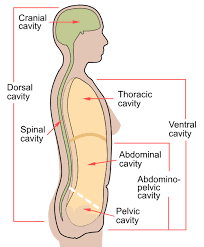
Dorsal Body Cavity
Back (posterior) cavity; includes cranial and vertebral cavities.
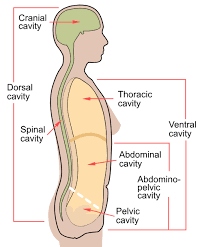
Cranial Cavity
Within the skull; encases the brain.
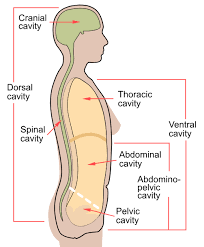
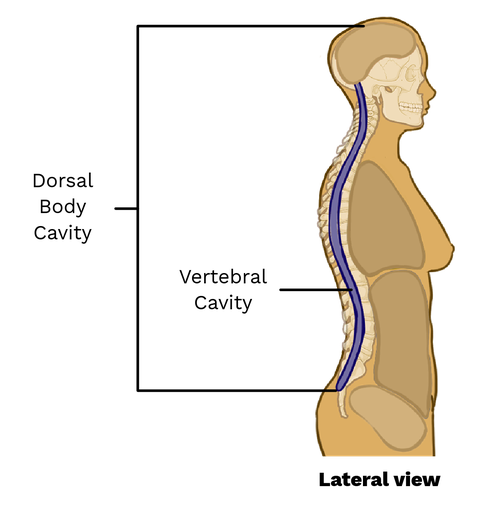
Vertebral Cavity
Runs within the vertebral column; encases the spinal cord.
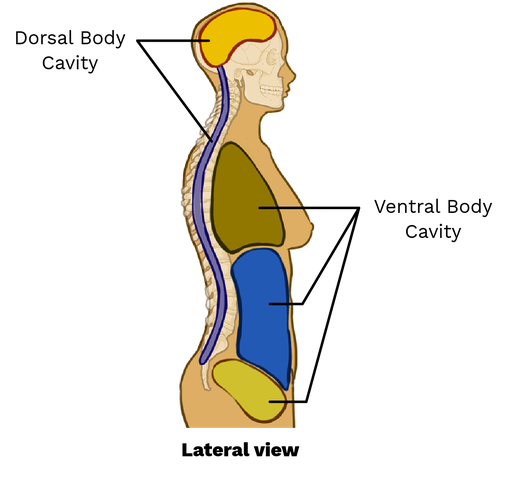
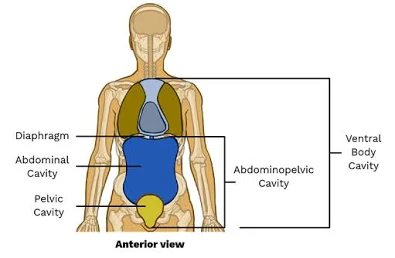
Ventral Body Cavity
Front (anterior) cavity; subdivided into thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
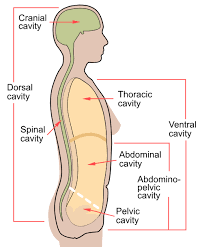
Thoracic Cavity
Subdivided into pleural cavities, mediastinum, and pericardial cavity.
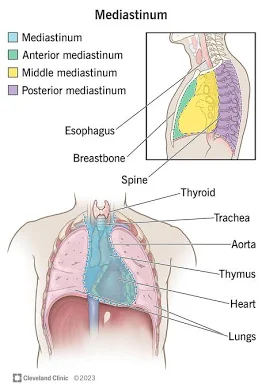
Mediastinum
Central part of the thoracic cavity; contains the heart, thymus, trachea, esophagus; surrounds pericardial cavity.
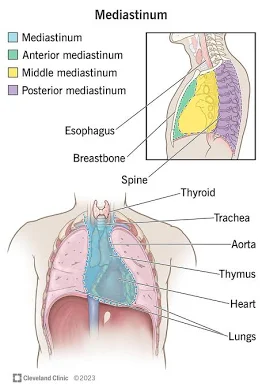
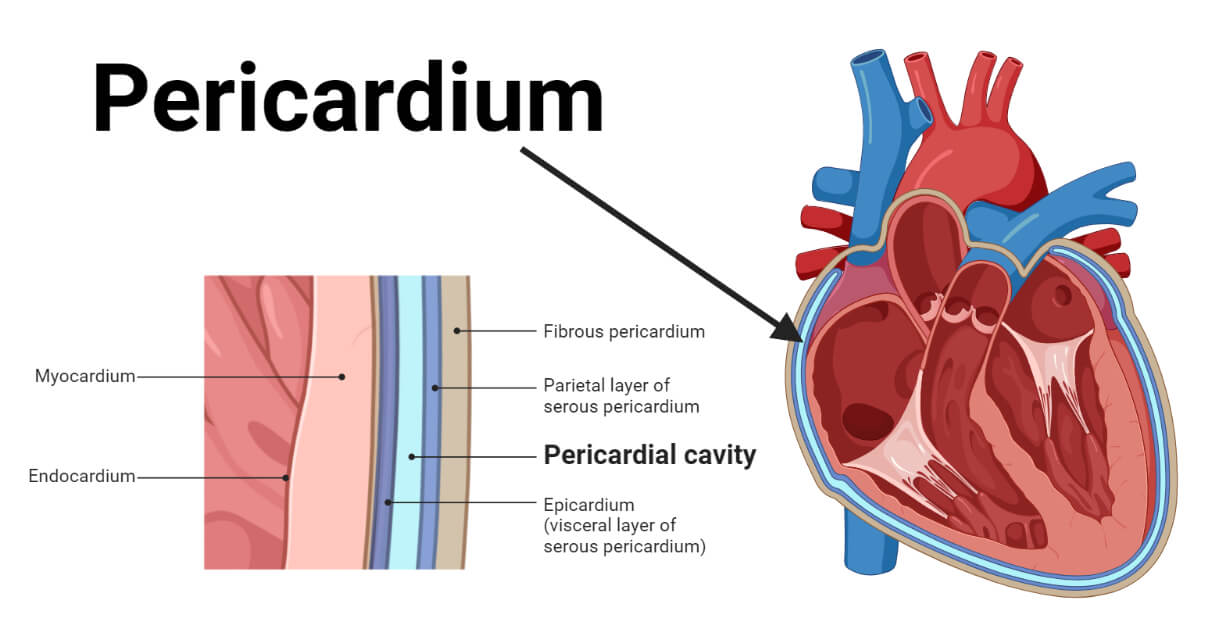
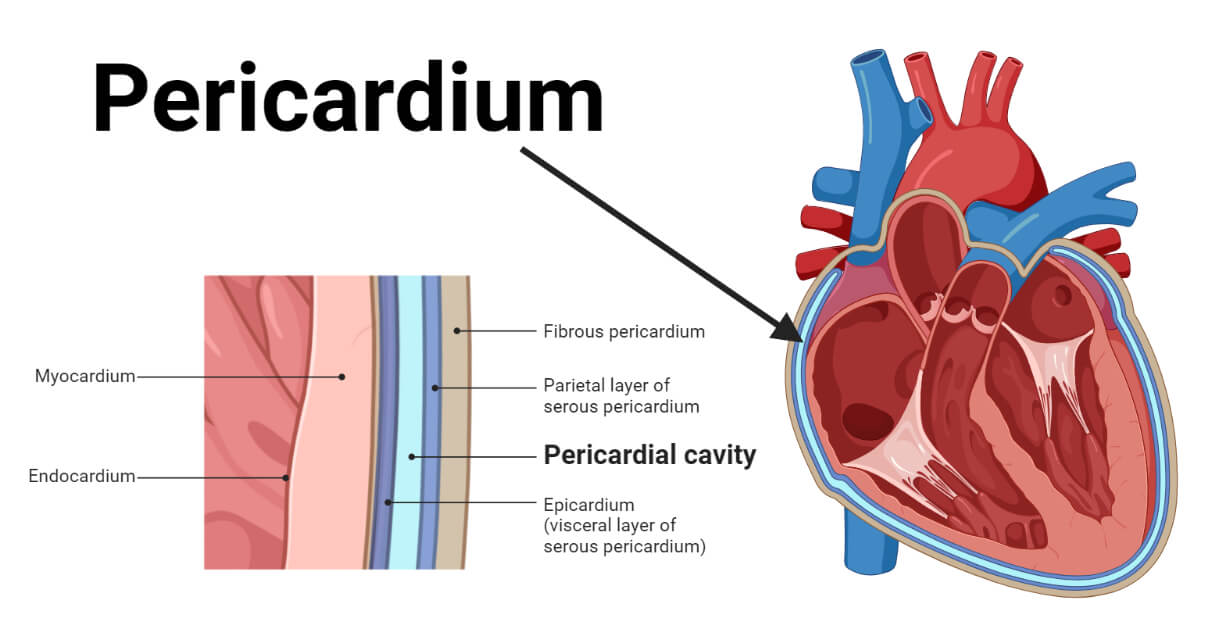
Pericardial Cavity
Encloses the heart.
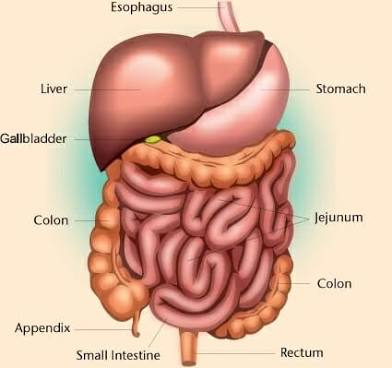
Abdominal Cavity
Contains digestive viscera such as stomach, liver, intestines.
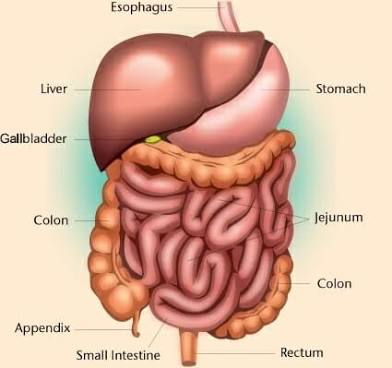
Pelvic Cavity
Contains bladder and reproductive organs; within the pelvis.
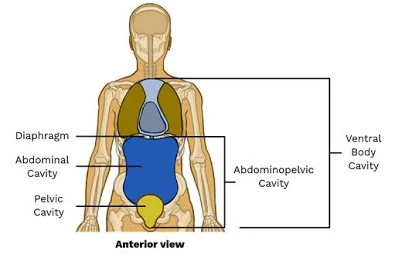
Abdominopelvic Cavity
Combination of the abdominal and pelvic cavities.
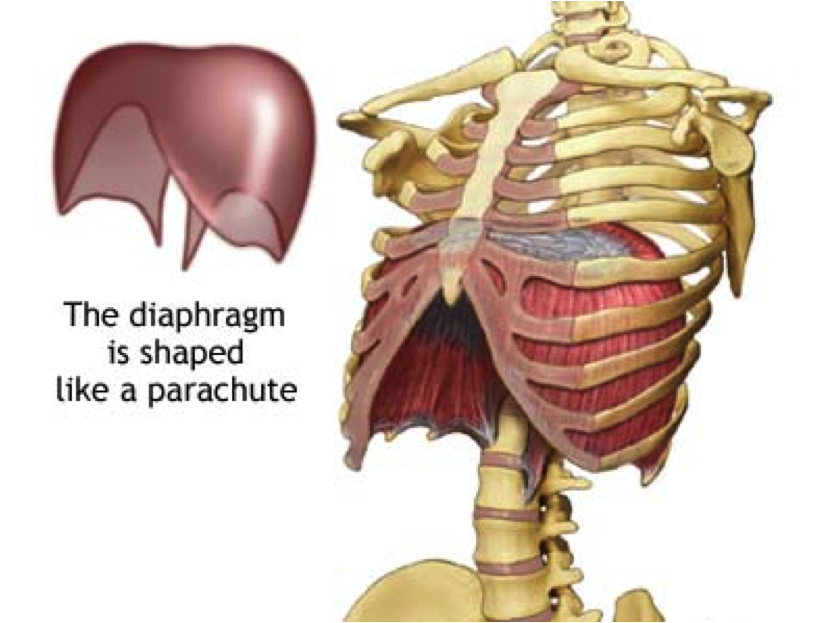
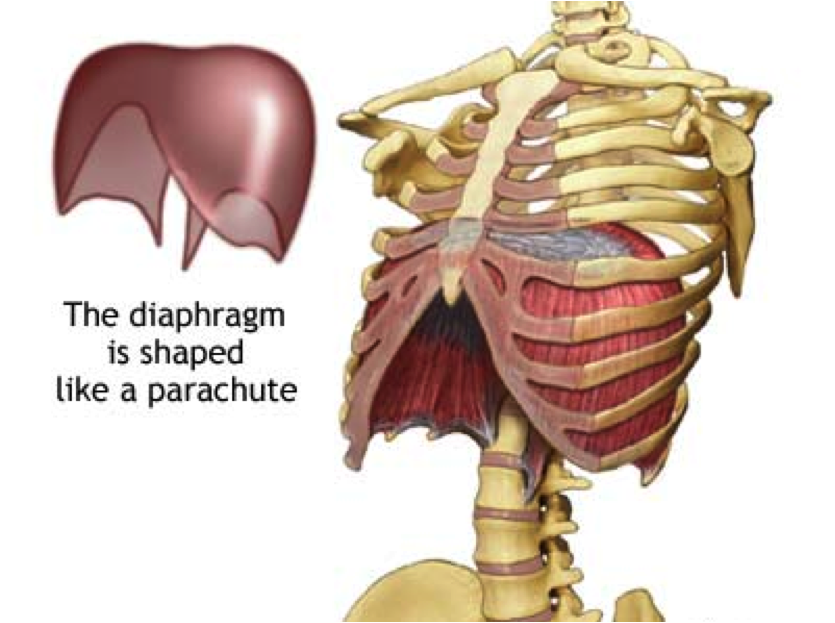
Diaphragm
Dome-shaped muscle that separates the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities.
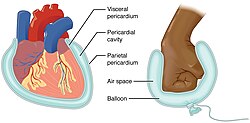
Serous Membranes
A thin tissue that lines body cavities and organs in the chest and abdomen, including the stomach
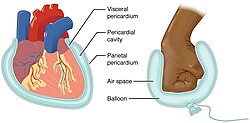
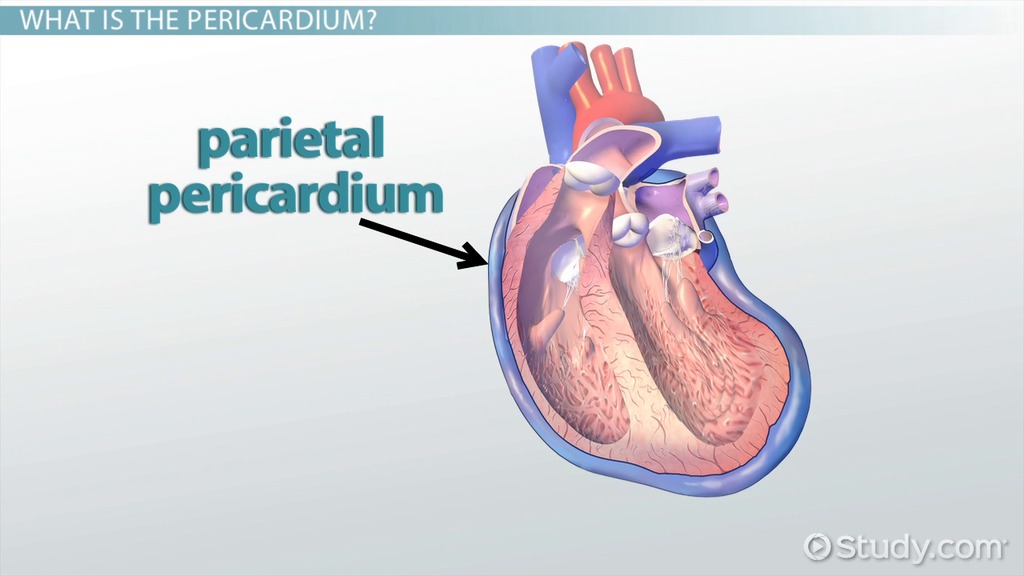
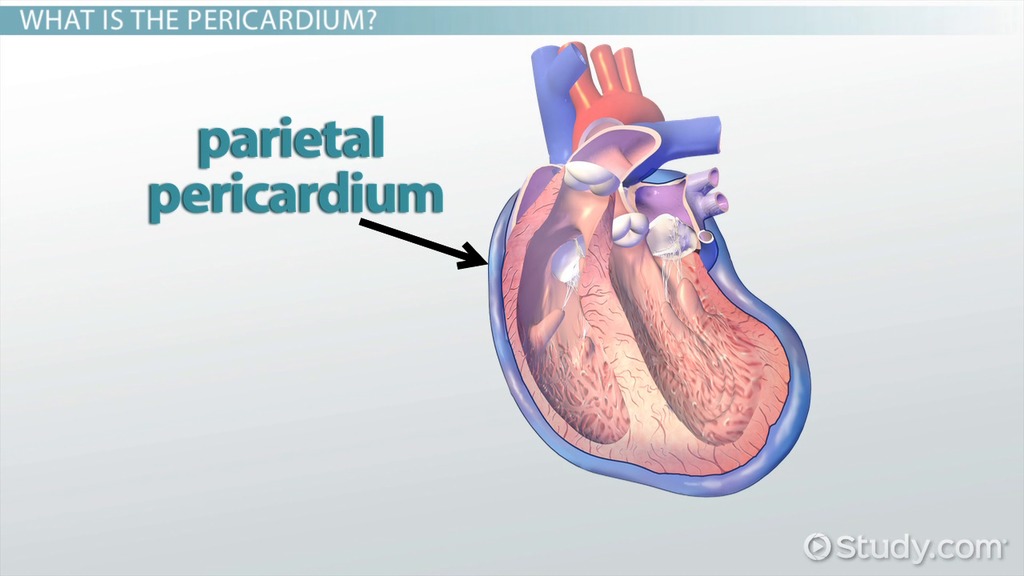
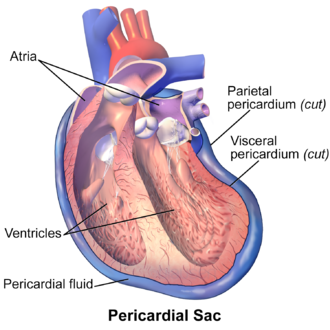
Parietal Pericardium
Parietal serosa lining the pericardial cavity surrounding the heart.
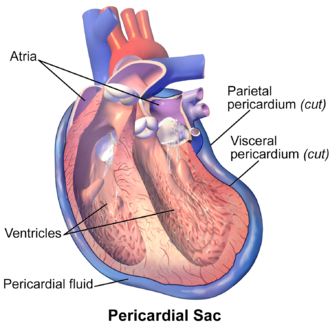
Visceral Pericardium
Serosa covering the heart muscle.
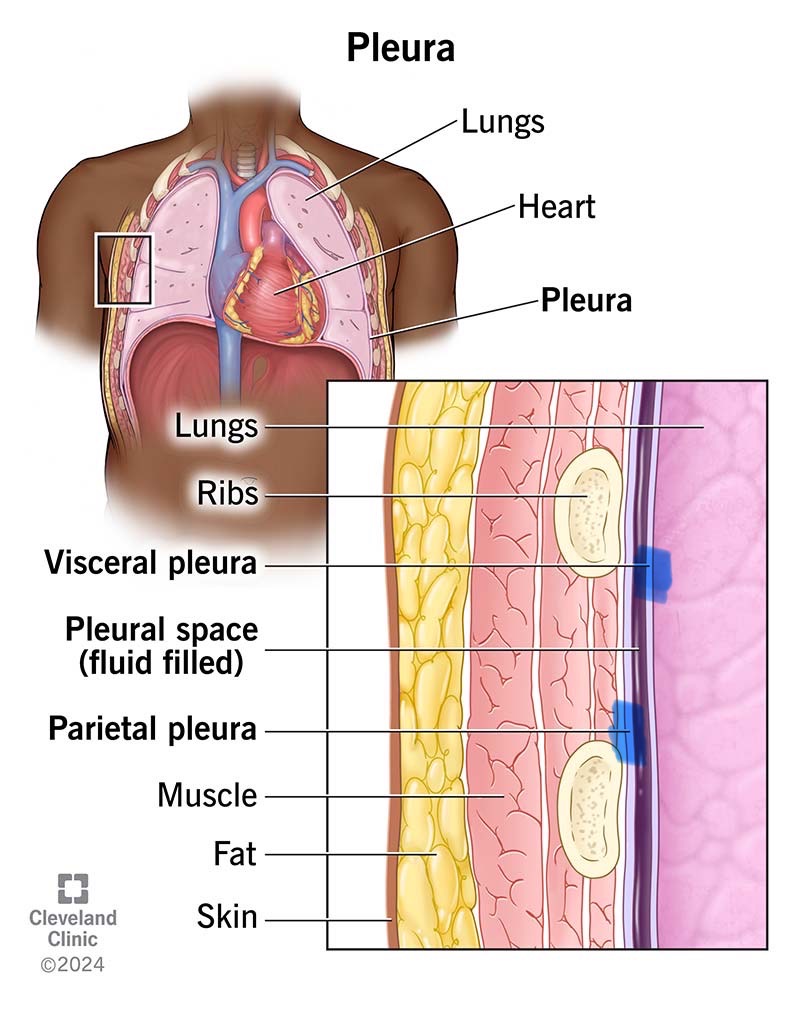
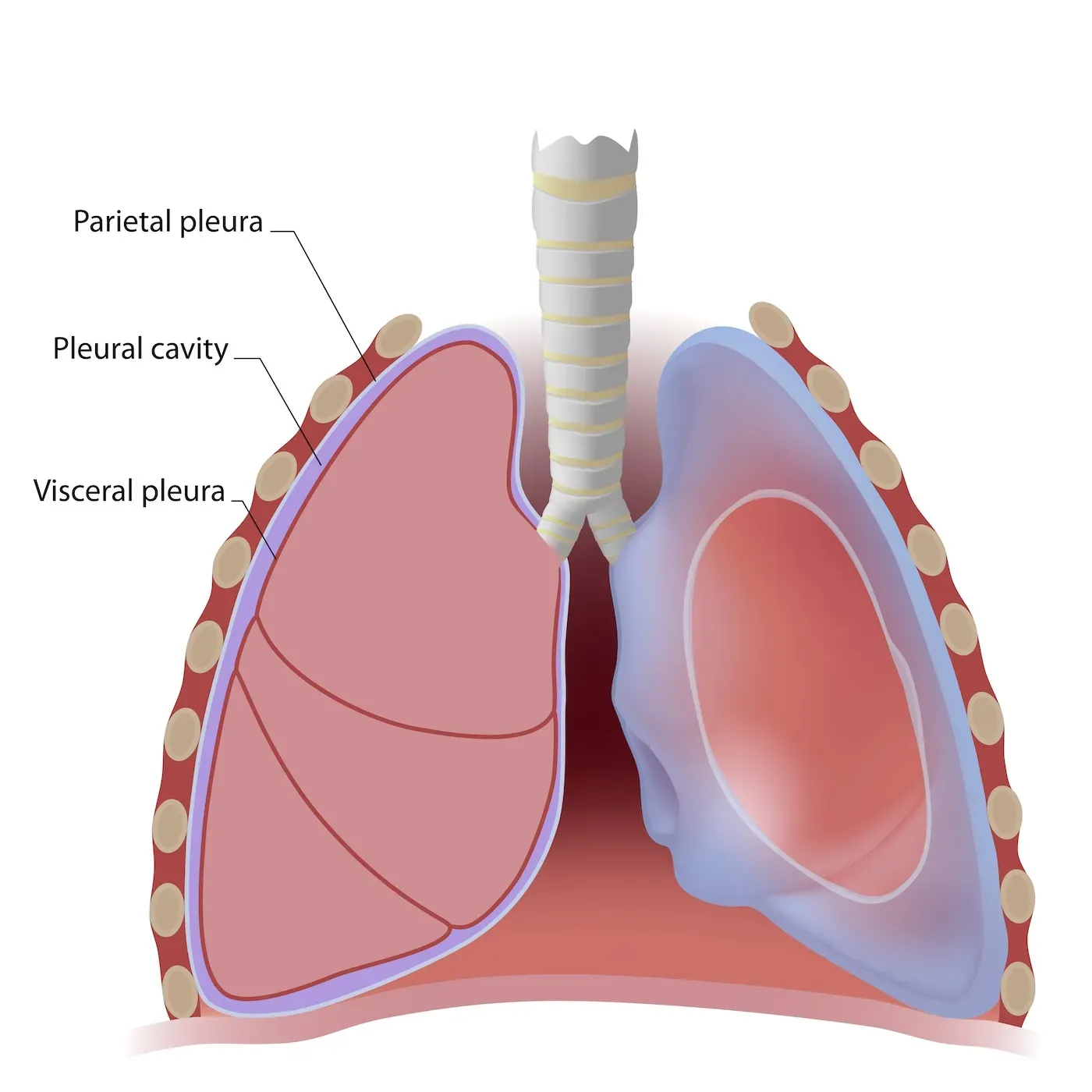
Parietal Pleura
Parietal serosa lining the thoracic wall around the lungs.
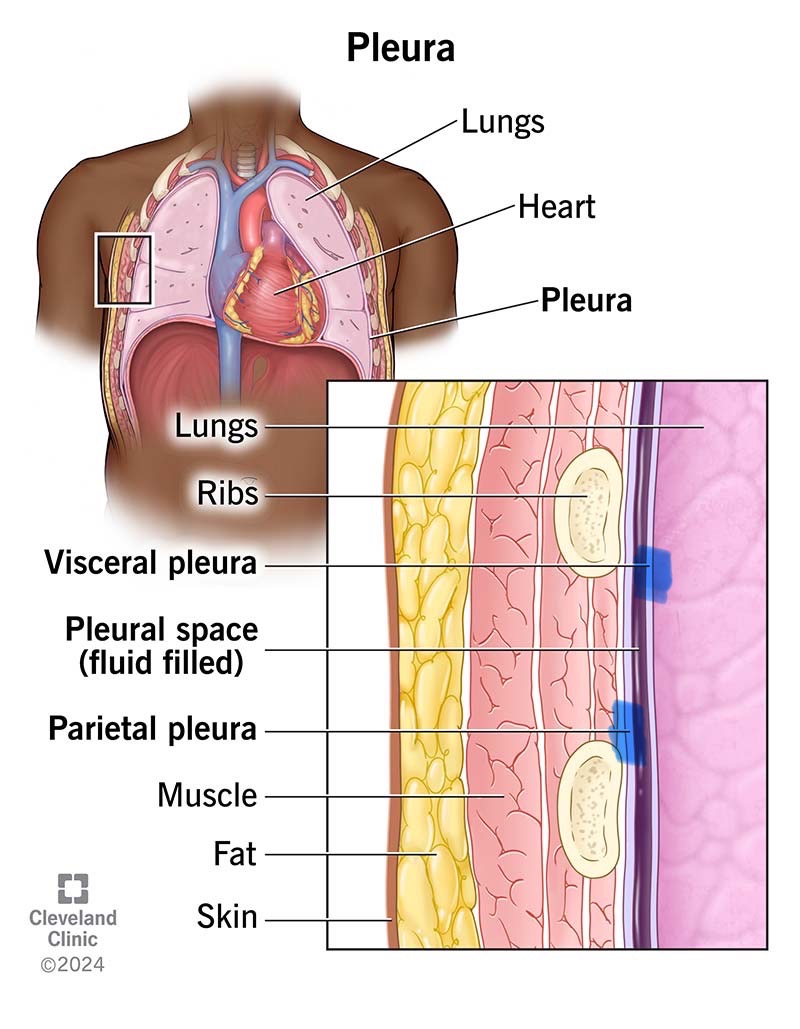
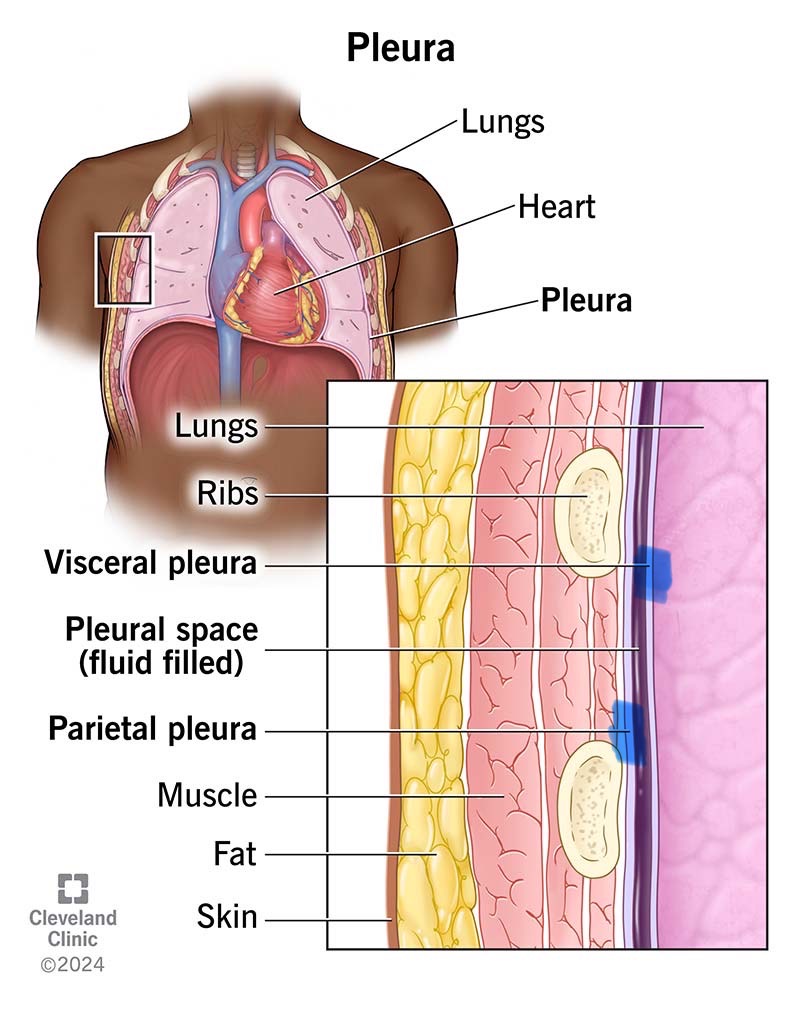
Visceral Pleura
Serosa covering the lungs.
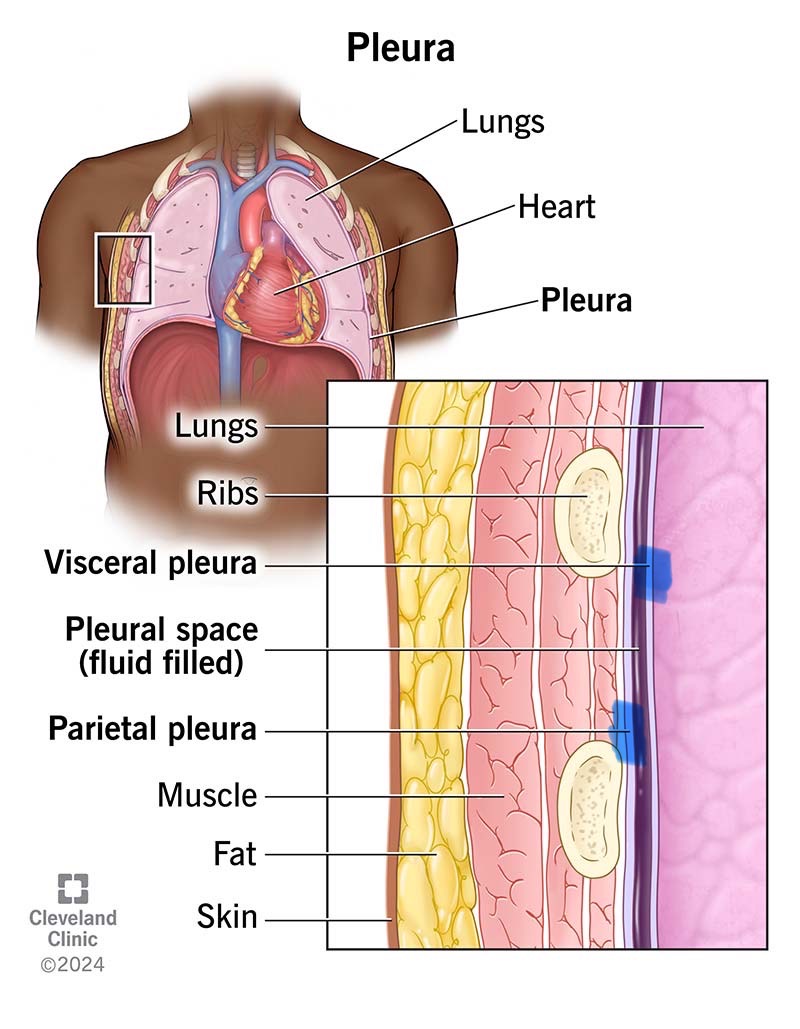
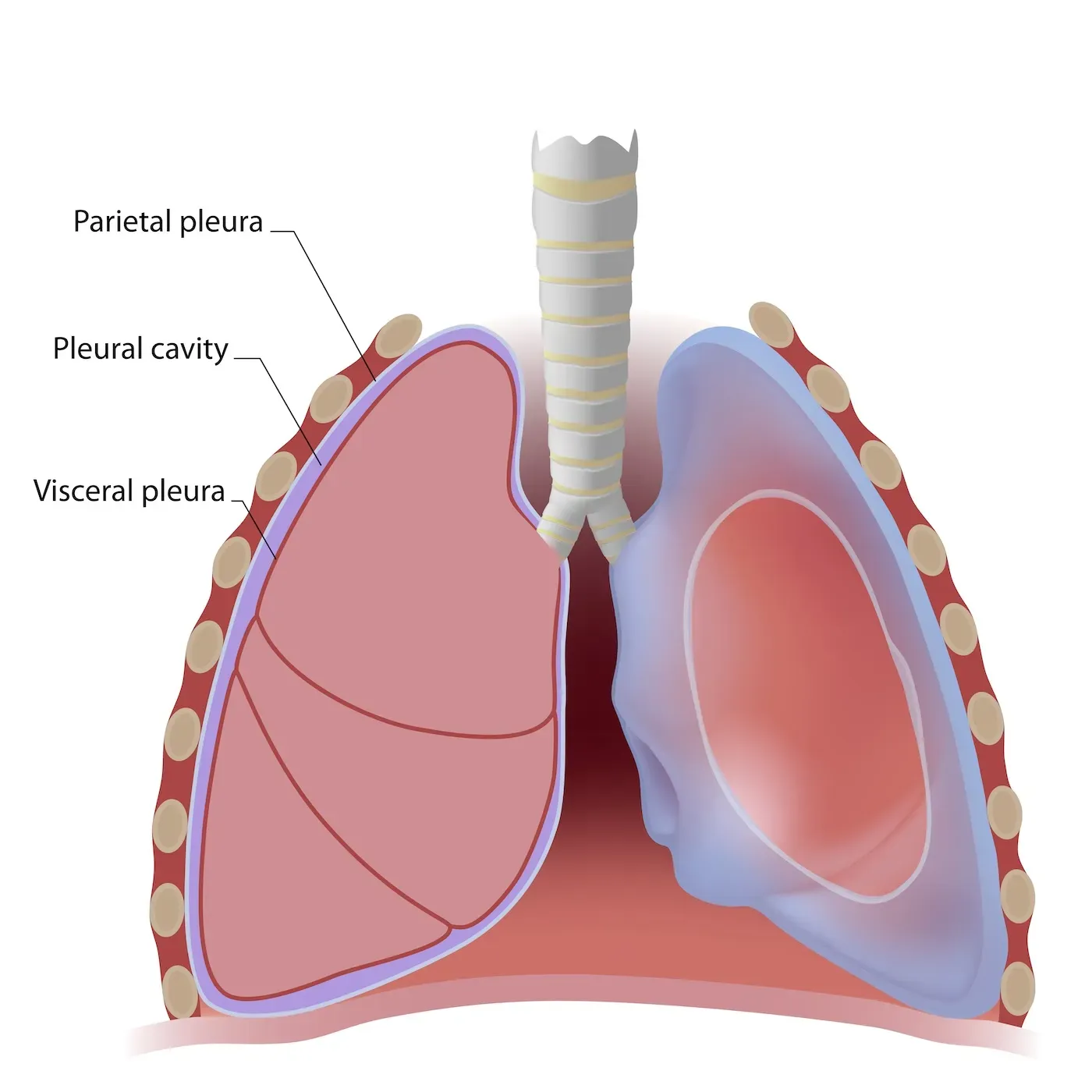
Pleural Cavity
Space between the pleural membranes around each lung, containing serous fluid.
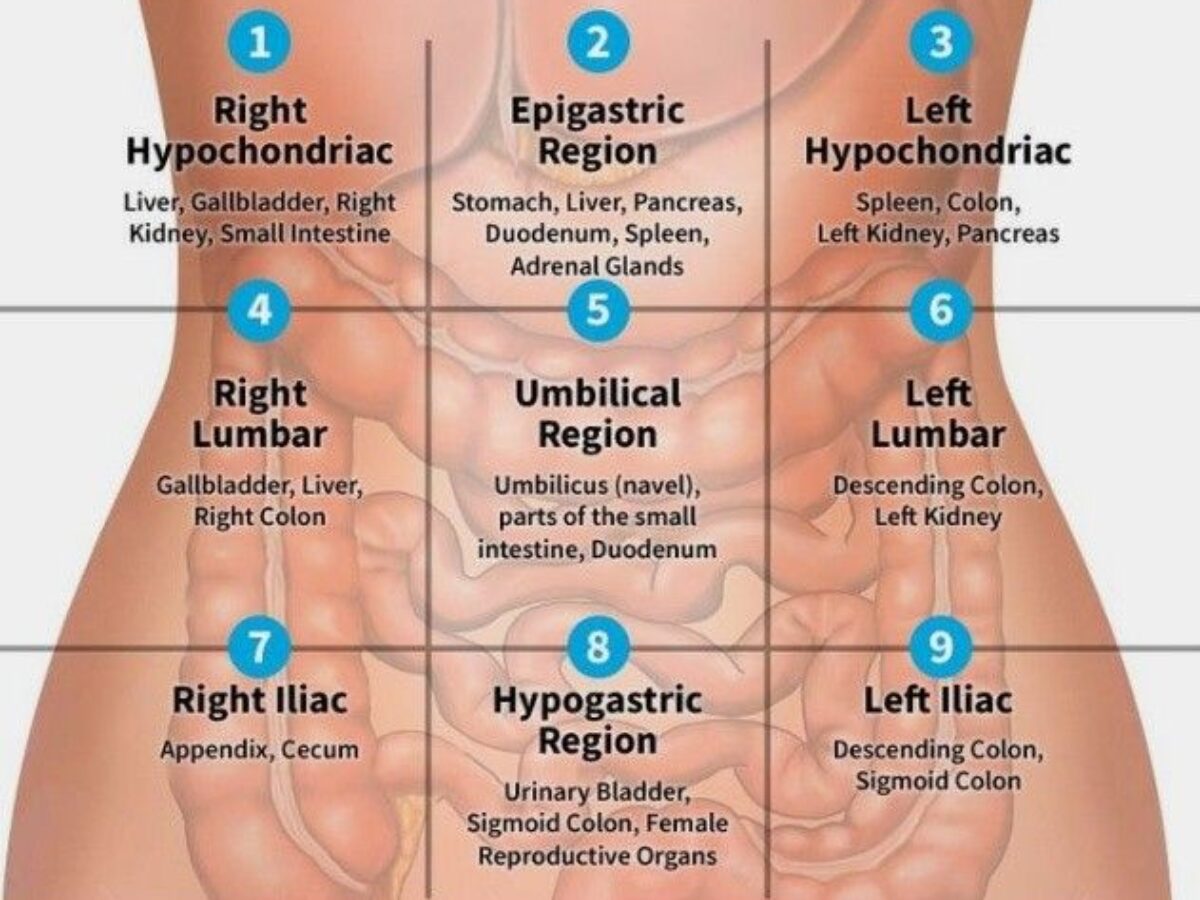
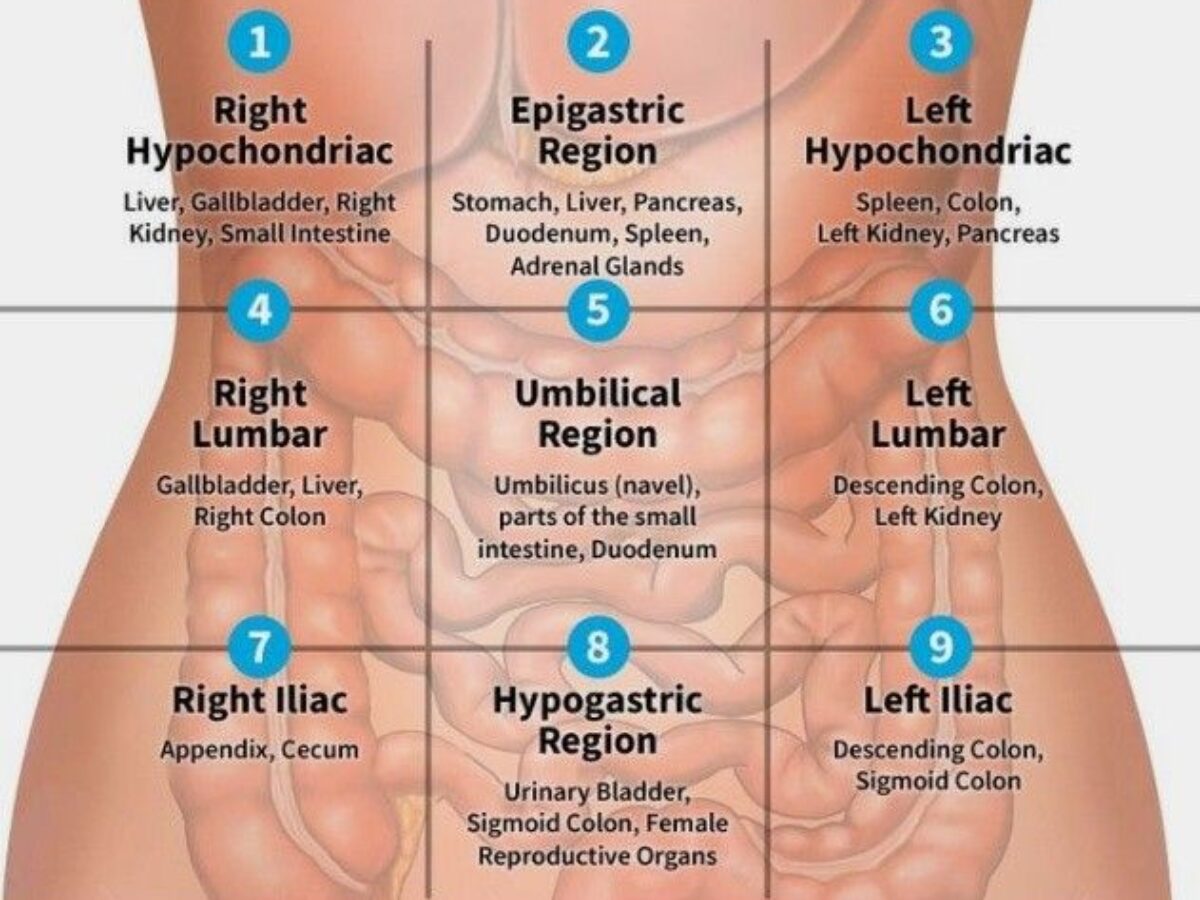
Abdominopelvic Quadrants
Four regions: right upper, left upper, right lower, left lower.
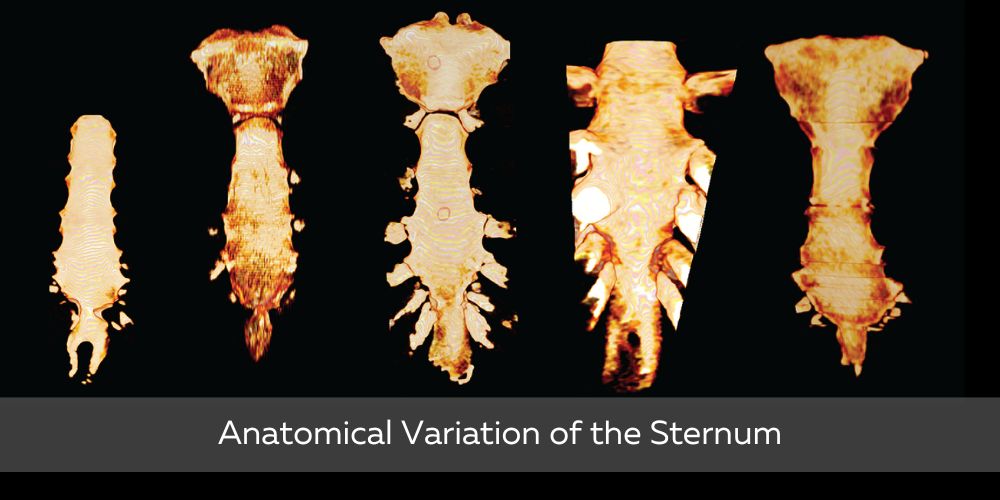
Anatomical Variability
Humans vary slightly in anatomy; most structures match textbook descriptions, with some deviations.
Cephalic Region
Head region; includes facial features such as frontal, orbital, nasal, oral, mental.
Thoracic Region
Chest region; includes axillary and pectoral areas.
Upper Limb Regions
Regions of the arm and hand: deltoid, brachial, antecubital, antebrachial, carpal, palmar, digital.
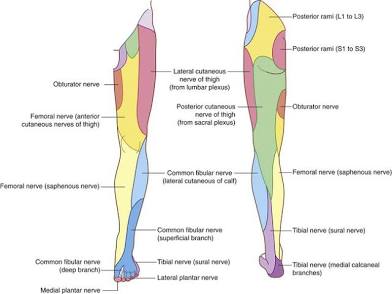
Lower Limb Regions
Regions of the leg and foot: femoral, patellar, popliteal, crural, sural, calcaneal, tarsal, pes, plantar, digital.