Greek Architecture
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/122
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
1
New cards
**GEOGRAPHICAL INFLUENCE**
The rugged nature of the Greek Peninsula & its widespread islands, made
communication difficult. It was bounded on two sides by "Black Sea and
the Mediterranean Sea"
communication difficult. It was bounded on two sides by "Black Sea and
the Mediterranean Sea"
2
New cards
Black Sea and the Mediterranean Sea
The rugged nature of the Greek Peninsula & its widespread islands, made
communication difficult. It was bounded on two sides by "____________"
communication difficult. It was bounded on two sides by "____________"
3
New cards
Citadels
GEOGRAPHICAL INFLUENCE: "Athens as its center kingdom contains the upper city known as "________"
4
New cards
Marble
GEOLOGICAL INFLUENCE:
\
the chief building material
\
the chief building material
5
New cards
Stone
GEOLOGICAL INFLUENCE:
\
had an ample supplies of this material.
\
had an ample supplies of this material.
6
New cards
AEGANS
**RELIGIOUS INFLUENCE**
\
worships "nature" and priestesses rather than priest conducted
\
worships "nature" and priestesses rather than priest conducted
7
New cards
GREEKS
**RELIGIOUS INFLUENCE**
\
Represents their deities by large statues. Worships "natural
phenomena
\
Represents their deities by large statues. Worships "natural
phenomena
8
New cards
APHRODITE
goddess of commerce, love and beauty
9
New cards
APOLLO
god of law and reason, art and music and poetry
10
New cards
ARES
god of war
11
New cards
ARTEMIS
goddess of chastity
12
New cards
DEMETER
goddess of earth and agriculture
13
New cards
HERA
wife of Zeus, goddess of marriage
14
New cards
ATHENA
goddess of learning and wisdom
15
New cards
ZEUS
supreme god, ruler of the sky, chief god.
16
New cards
HERMES
messenger of the gods
17
New cards
POSEIDON
god of the sea
18
New cards
***EARLY PERIOD***
***3000BC -700 BC***
\
People on in Greece were Aegans, Minoans, & Myceneans
\
People on in Greece were Aegans, Minoans, & Myceneans
19
New cards
***HELLENIC PERIOD***
Essentially columnar & trabeated in Acropolis which was Crowned by
20
New cards
a. Simplicity and Harmony
\
b. Purity of Lines
\
c. Perfections of Proportions
\
d. Refinement of Details
\
b. Purity of Lines
\
c. Perfections of Proportions
\
d. Refinement of Details
**CHARACTERISTIC OF GREEK ARCH**
21
New cards
**Cyclopean, Polygonal, Rectangular, Inclined Blocks**
***FOUR METHODS OF WALLING SURFACE FINISHES***
22
New cards
CYCLOPEAN
a masonry made up of huge stone blocks laid mortar
23
New cards
POLYGONAL
a masonry which is constructed with stones having polygonal faces.
24
New cards
RECTANGULAR
block of stone cut into rectangular shapes
25
New cards
INCLINED BLOCKS
stones with inclined blocks.
26
New cards
***TWO WAYS OF DESCRIBING TEMPLES***
***(a)*** According to the number of columns on the entrance front
\
***(b)*** by the arrangement of the exterior columns of the temple in relation to naos
\
***(b)*** by the arrangement of the exterior columns of the temple in relation to naos
27
New cards
HENOSTYLE
one column
28
New cards
DISTYLE
two columns
29
New cards
TRISTYLE
three columns
30
New cards
TETRASTYLE
four columns
31
New cards
PENTASTYLE
five columns
32
New cards
HEXASTYLE
six columns
33
New cards
HEPTASYLE
seven columns
34
New cards
OCTASTYLE
eight columns
35
New cards
ENNEASTYLE
nine columns
36
New cards
DECASTYLE
ten columns
37
New cards
DODECASTYLE
twelve columns
38
New cards
**Naos, Pranaos, Epinaos**
***PARTS OF A GREEK TEMPLE***
39
New cards
NAOS
principal chamber containing the statue of the god or goddess with porticoes
40
New cards
PRONAOS
the inner portico in front of naos or cella of the naos.
41
New cards
EPINAOS
posticum which serves as the treasury chambers
42
New cards
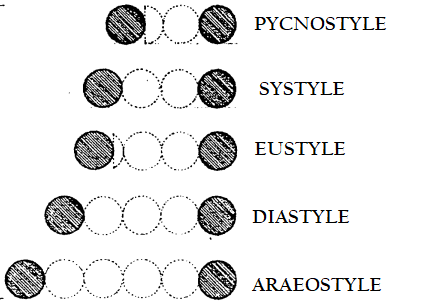
**INTERCOLUMNIATION**
the space between two adjacent columns, usually the clear space between the lower parts of the shafts, measured in diameters. Also, a system for spacing columns in a colonnade based on the measurement
43
New cards
ACCOUPLEMENT
**T**he placement of two columns or pilasters very close to each other is called "___________"
44
New cards
PYCNOSTYLE
Having an intercolumniation of 1 ½ diameters.
45
New cards
SYSTYLE
Having an intercolumniation of 2 diameters
46
New cards
EUSTYLE
Having an intercolumniation of 2 ¼ diameters.
47
New cards
DIASTYLE
Having an intercolumniation of 3 diameters.
48
New cards
ARAEOSTYLE
Having an intercolumniation of 4 diameters.
49
New cards
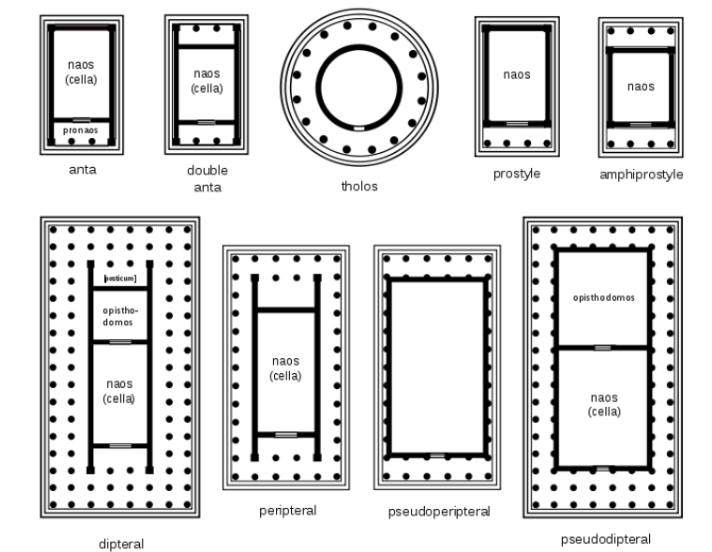
LAYOUT OF GREEK TEMPLES
anta, double anta, amphiprostyle, prostyle, dipteral, pseudodipteral, peripteral, pseudoperipteral
50
New cards
ANTA
temples have one to four columns between antae at the front. Two is the usual number.
51
New cards
DOUBLE ANTA
temples have one to four columns between antae at the front and the rear. Two is the usual number
52
New cards
AMPHIPROSTYLE
temples that have portico of columns at front and rear.
53
New cards
PROSTYLE
temples that have portico of columns at front only.
54
New cards
DIPTERAL
temples that have a double line of columns surrounding on all sides.
55
New cards
PSEUDODIPTERAL
temples that having a double line of columns but the inner range of columns is attached to the naos.
56
New cards
PERIPTERAL
temples that have a single line of columns surrounding on all sides
57
New cards
PSEUDOPERIPTERAL
temples that have flanked of columns attached to the naos.
58
New cards
GREEK ORDERS
Doric, Ionic, Corinthian
59
New cards
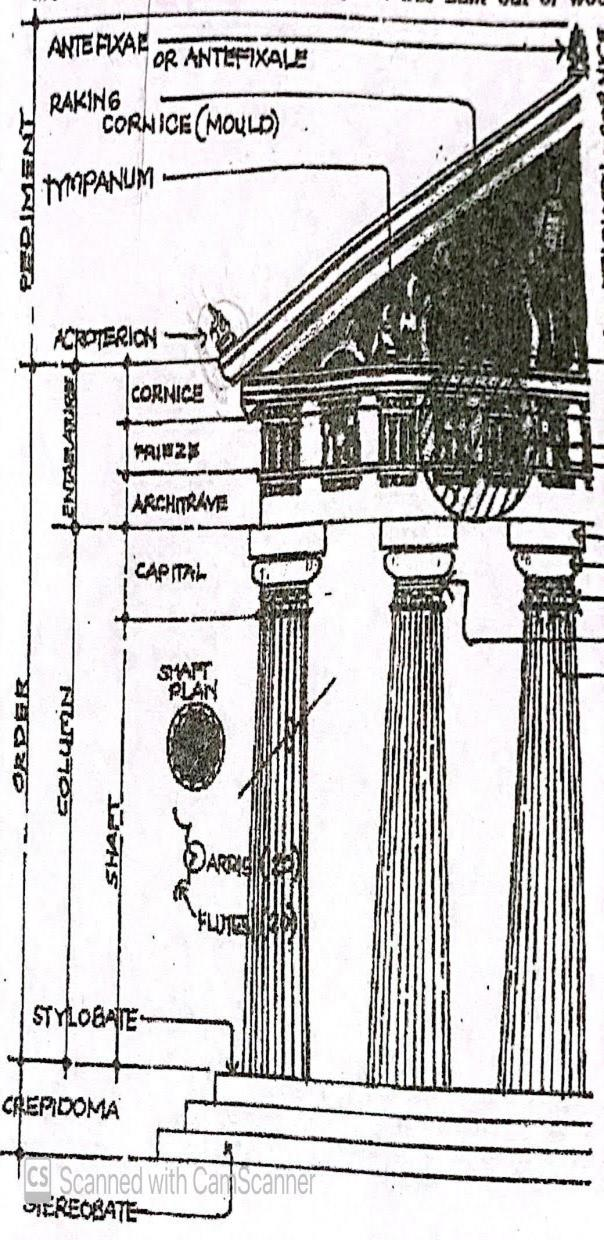
DORIC ORDER
The simplest and the earliest among the five orders.
60
New cards
PEDIMENT PARTS
Antefixae, Tympanum, Acroterion
61
New cards
ANTEFIXAE
an upright ornament at the eaves of a roof concealing the foot of a row of convex tiles that cover the joints of the flat tiles.
62
New cards
TYMPANUM
the triangular space enclosed by the horizontal and raking cornices of a pediment, often
recessed and decorated with sculpture.
recessed and decorated with sculpture.
63
New cards
ACROTERION
a pedestal for a sculpture ornament at the apex or at each of the lower corners of a pediment.
64
New cards
ENTABLATURE PARTS
Cornice, Frieze, Architrave
65
New cards
CORNICE
the uppermost member of an entablature, consisting typically of a cymatium, corona, and bed molding.
66
New cards
FRIEZE
the horizontal part of an entablature between the cornice and architrave, often decorated with sculpture inflow relief.
67
New cards
ARCHITRAVE
the lowermost division of an entablature, resting directly on the column capitals and supporting the frieze.
68
New cards
COLUMN PARTS
Captial, Shaft, Stylobate, Stereobate
69
New cards
CAPITAL
the distinctively treated upper end of a column, pillar, or pier, crowning the shaft and taking the weight of the entablature or architrave.
70
New cards
SHAFT
the central part of a column or pier between the capital and the base.
71
New cards
STYLOBATE
a course of masonry forming the foundation for a row of columns especially the outermost colonnade of a classical temple.
72
New cards
STEREOBATE
a solid mass of masonry visible above ground level and serving as the foundation of a building especially the platform forming the floor and substructure of a classical temple also called as crepidoma.
73
New cards
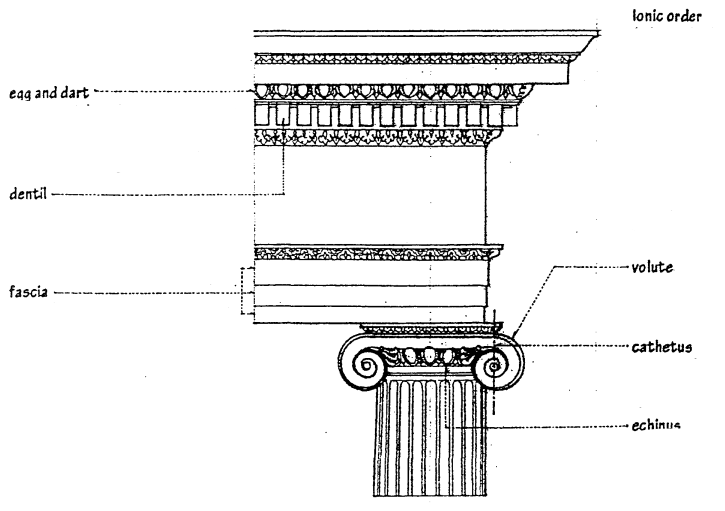
IONIC ORDER
More sophisticated order. Less heavy than the Doric, less elaborated than the Corinthian order.
74
New cards
EGG AND DART
an ornamental motif for enriching an ovolo or echinus, consisting of a closely set, alternating series of oval and pointed forms. Also called "egg and tongue"
75
New cards
DENTIL
any of a series of closely spaced, small rectangular blocks forming a molding or projecting beneath the coronas of Ionic cornices.
76
New cards
FASCIA
one of the three horizontal banda making up the architrave in the Ionic order.
77
New cards
VOLUTE
a spiral, scroll like ornament, as on the capitals of the Ionic order.
78
New cards
CATHETUS
the vertical guideline through the eye of a volute in an Ionic capital, from which the spiral forms is determined.
79
New cards
FLEURON, BALTEUS
In Ionic Capital, if there is a central flower, it is called "_______" and "______" if none.
80
New cards
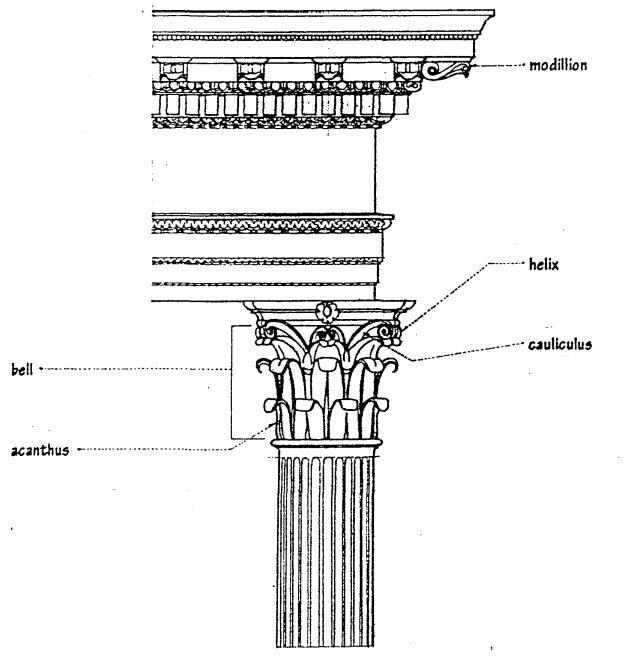
CORINTHIAN ORDER
Most elaborated & most elegant of all the orders. Looks like an "Inverted Bell."
81
New cards
MODILLION
an ornament bracket, usually in the form of a scroll with acanthus, used in series beneath the corona of a Corinthian.
82
New cards
HELIX
a spiral ornament, as any of the volutes issuing from a cauliculus in a Corinthian capital
83
New cards
CAULICULUS
any of the ornamental stalks rising between the acanthus leaves of a Corinthian capital, from which volutes spring.
84
New cards
BELL
the underlying part of a foliated capital, between the abacus and neck molding
85
New cards
ACANTHUS
an ornament, patterened after the large toothed leaves of a Mediterranean plant of the same name.
86
New cards
CARYATIDS
a sculptured female figure used as a column.
87
New cards
CANEPHORAE
a sculptured female supporting baskets on their heads.
88
New cards
ATLAS
a sculptured male kneeling or crouching figure used as a column.
89
New cards
TELAMONES
a sculptured male column in a standing position.
90
New cards
GREEK BASIC BUILDINGS
Propylaea, theater, Public Buildings
91
New cards
PROPYLAEA
entrance gateways which marked the approach to the sacred enclosure in many cities in Greeks.
92
New cards
THEATER
an open air structure, which consisted of orchestra, auditorium or cavea out of the slope of hillside, in or near city.
93
New cards
Entasis
In Architecture, ________is the application of a convex curve to a surface for aesthetic and technical purposes. Their diameter is decreased from the bottom upwards and one-third from the bottom is the thickest point.
94
New cards
AGORA OR TOWN SQUARE
an open air, meeting place for the transaction of business & also market place.
95
New cards
STOA
long colonnaded building which serves to connect public monuments & for shelter.
96
New cards
PRYTANEION
a senate house to the chief dignitaries of the city.
97
New cards
BOULEUTERION
also called council house, covered meeting place of the democratically elected councils.
98
New cards
ASSEMBLY HALLS
used by citizens in general assembly.
99
New cards
ODEION
a theater building used mainly by musicians in the presentation of their works for competition & for public approval.
100
New cards
STADIUM / STADION
foot race course & also used for other athletic performance.