Topic 1: Basic Economics Concept
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Needs
the basic necessities that a person must have in order to survive
eg. food, water, warmth, shelter and clothing
wants
the desire that people have
eg. things that people would like to have, such as bigger homes, iphones
Study of economics
How to meet unlimited needs with scarce resources
Economists study how to meet people’s unlimited wants with scarce, available resources
Scarcity
The excess of wants resulting from having limited resources (land, labor, capital and entrepreneurs) in satisfying the endless wants of people.
It is a universal problem for societies – it is not limited to poor countries.
To the economist, all goods and services that have a price are relatively _____. This means that they are ____ relative to people’s demand for them.
Economics
_____ is classified as social science because it deals with the study of human’s life and how he lives with other men
a social science concerned chiefly with description and analysis of the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services
Applied Economics
is the study of economics in relation to real world situations. It is the application of economic principles and theories, ridiculous situations, and trying to predict what the outcome might be
the study of observing how theories work in practice
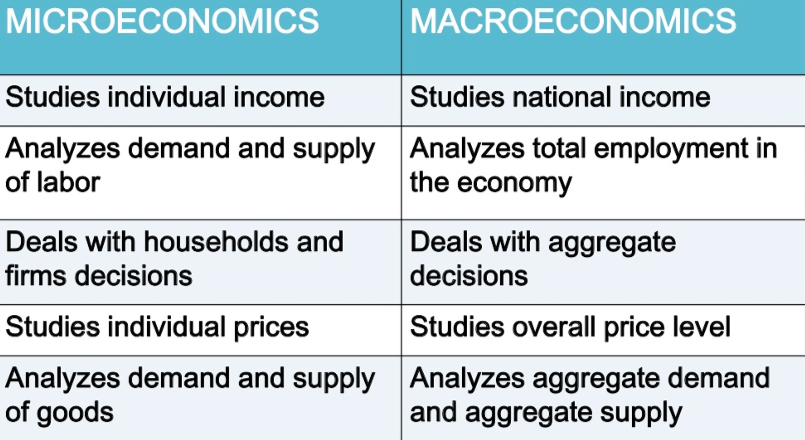
Microeconomics
Macroeconomics
Branches of Economics
Microeconomics
focuses on how decisions are made by individuals and firms and the consequences of those decisions.
examines small economic units, the components of the economy (individuals, households, firms, industries)
Example:
How much it would cost for a university or college to offer a new course ─ the cost of the instructor’s salary, the classroom facilities, the class materials, and so on. Having determined the cost, the school can then decide whether or not to offer the course by weighing the costs and benefits.
Macroeconomics
examines the aggregate behavior of the economy (i.e. how the actions of all the individuals and firms in the economy interact to produce a particular level of economic performance as a whole).
(national output, overall price level, aggregate unemployment)
Example:
Overall level of prices in the economy (how high or how low they are relative to prices last year) rather than the price of a particular good or service.
Microeconomics vs Macroeconomics
Land
Capital
Labor
Enterprise
Factors of Production
Unemployment
Poverty
Poor quality of infrastructure
Income Inequality
Basic Economic Problems
Unemployment
- A situation where a person actively searches for employment, but is unable to find work
- Considered to be a key measure of the health of the economy
Frictional
Cyclical
Structural
Types of Unemployment
Frictional
this occurs naturally when workers are between jobs, or have just graduated and are looking for work for the first time.
Cyclical
The economy regularly goes through ups and downs; When it enters a recession, more people become unemployed.
Structural
When there is a match between the skills People have learned in the skills the job market requires.
Recession
when the economy “shrinks,” businesses struggle, people lose jobs, and money doesn’t circulate as actively as before.