Quality Control and Assurance
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Gaussian Distribution
Normal, symmetrical distribution around the mean
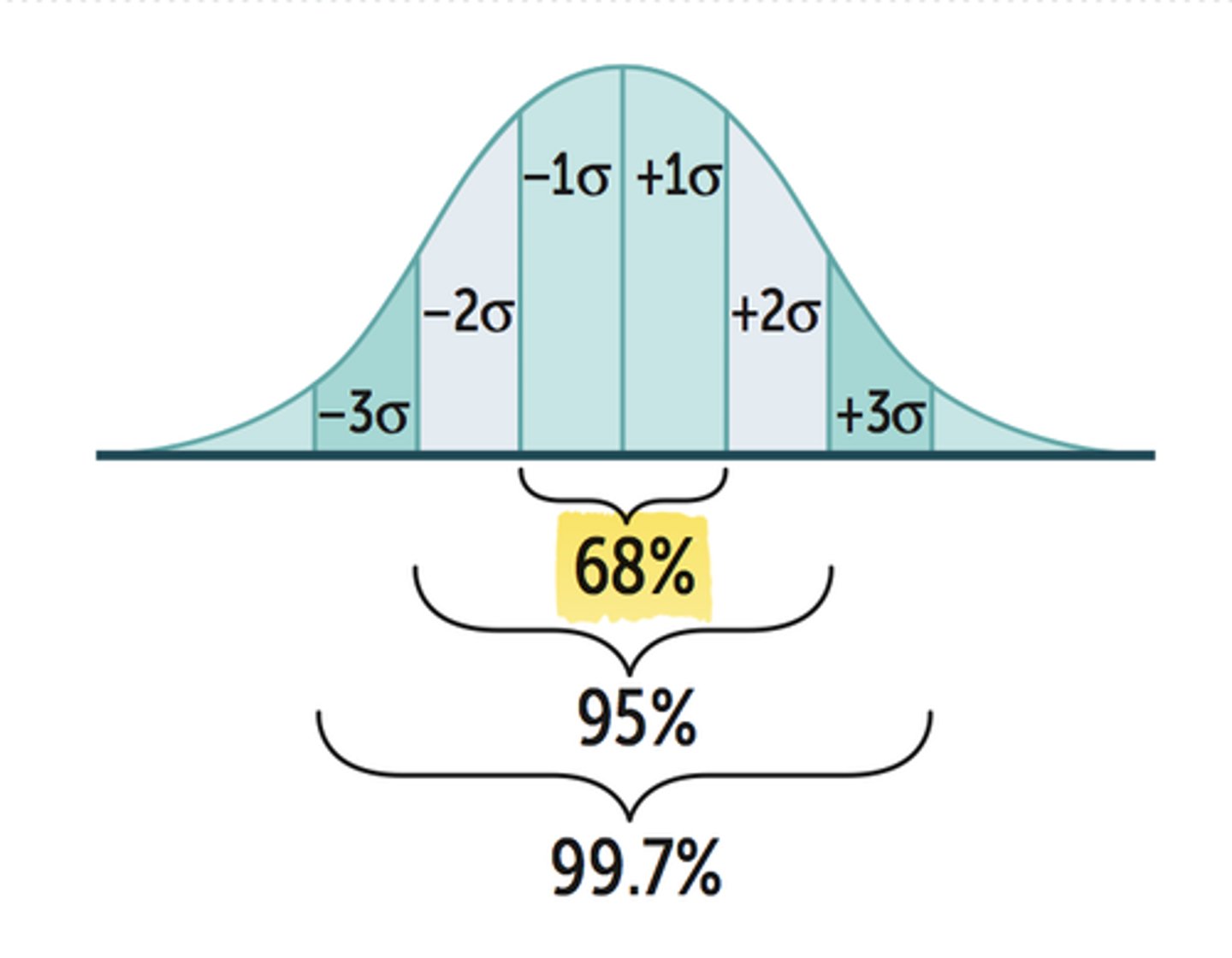
Gaussian distribution is assumed for all ______ statistics.
quality control
Confidence intervals are the limits between we expect a specified ______ of a population to lie.
proportion
The percent coefficient of variation (%CV) is ______ expressed as a percent.
SD
%CV allows comparison of variation between two sets of data/methods that have different ______.
means
The higher the %CV, the more ______ is expected with those results.
variation
Sensitivity is ______ related to specificity.
inversely
What are the two types of sensitivity?
Analytical and clinical
Analytical sensitivity is the ability of a test to detect the analyte regardless of its ______.
amount (limit of detection)
Clinical sensitivity is the assay's ability to correctly identify patients ______ a disease.
with
Clinical sensitivity is like a ______.
screening
Clinical sensitivity equation
TP/(TP + FN)
Analytical specificity is the ability of a test to detect the ______ analyte.
intended
Clinical specificity is an assay's ability to correctly identify patients ______ as negative.
without
Clinical specificity is like a ______.
confirmation
Clinical specificity equation
TN/(TN + FP)
The prevalence compares what two things?
positive and negative predictive value
Prevalence is dependent on ______.
population
Analytical sensitivity/specificity are both ______ specific.
lab
What are the consequences of a false negative?
- Delay treatment
- Can spread disease
- Worsening disease
What are the consequences of a false positive?
- Stress
- Unnecessary treatment
- Legal action (illegal drug use)
Linearity is the relationship between ______ and ______ values over the range of analytical measurements.
measured, expected
Analytical range of method is the ______ and ______ test results that are reliable and can be reported.
lowest, highest
A control material is run in large batches (50-100 samples) to get a ______.
reference range
Often, a ______ of control material is used for analytical testing.
combination
An analyte standard has a known concentration and is used for ______.
calibration
The ______ of a control is plotted on a chart.
concentration
A known control needs to be determined if it is ______ or ______.
normal, abnormal
If a control is unknown, it will need to be ______.
identified
A ______ is when a patient result is compared to a previous result from the same patient.
delta check
An analyte used in a delta check should be ______ in healthy individuals.
stable
Delta checks can be reported as an ______ or ______ between values.
absolute number, % change
A Levey-Jennings chart is a visual indication of if a test is ______.
working well
On a Levey-Jenning chart, a perfect control would show 8-9 points between the ______ limits and ______ limits on each side of the mean.
1s, 2s
A ______ is an abrupt change in data pattern.
shift
A ______ is a gradual change in the pattern of data points.
trend
If data is rejected from Westgard rules, the patients results are ______ until the problem is fixed.
not reported
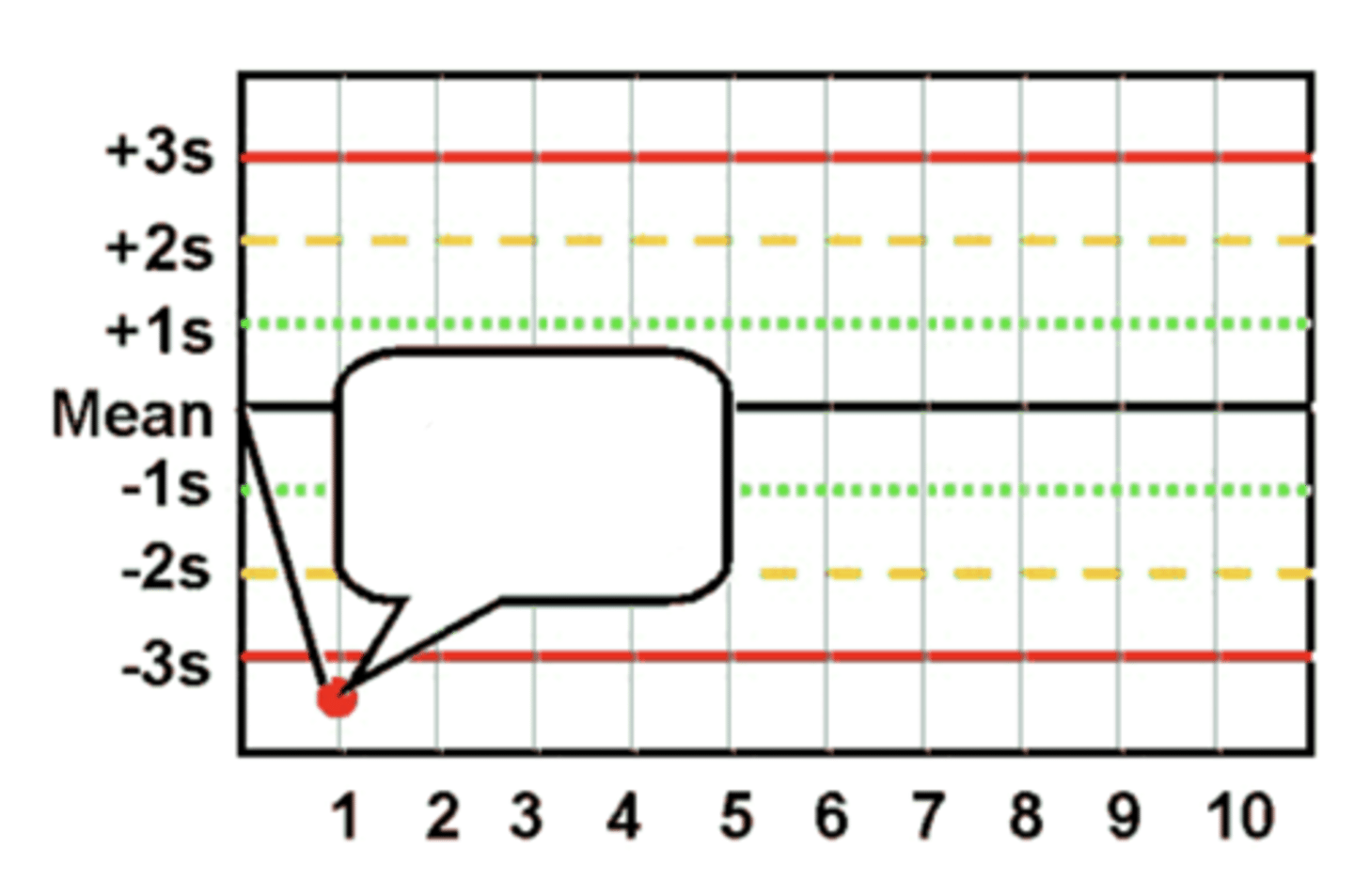
1(2s) Westgard Rule violation
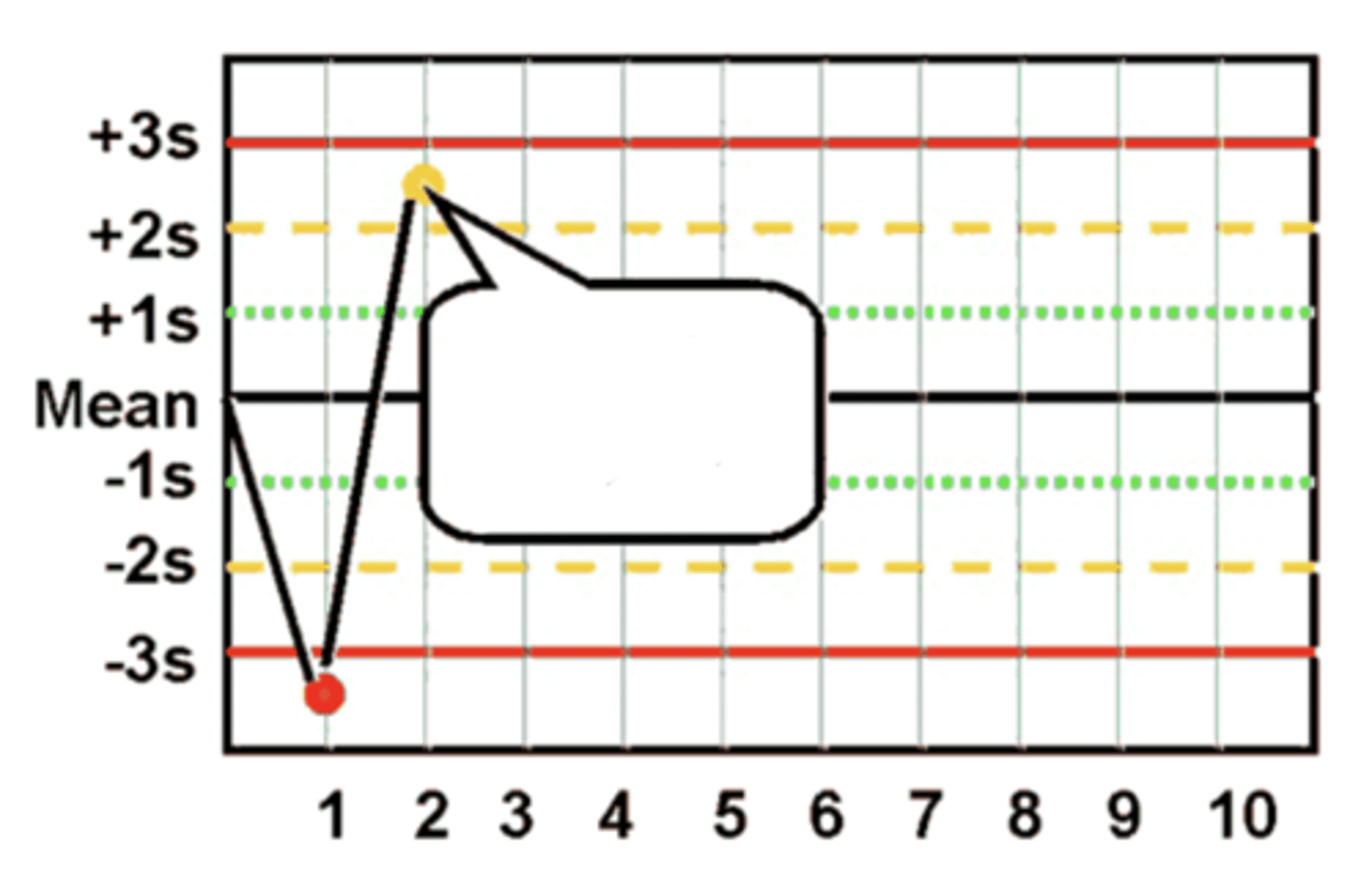
1(3s) Westgard Rule violation
R(4s) Westgard Rule violation
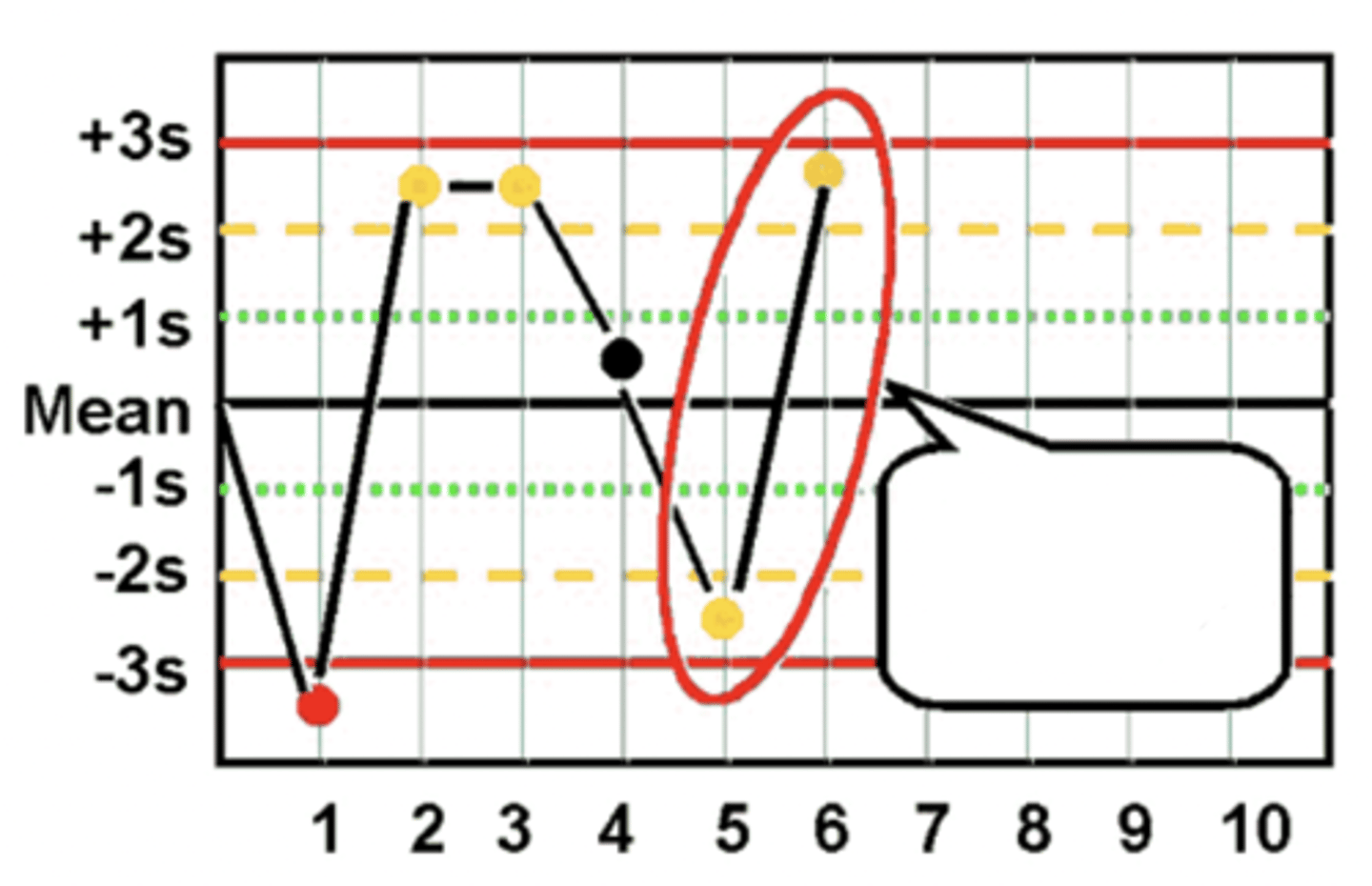
2(2s) Westgard Rule violation
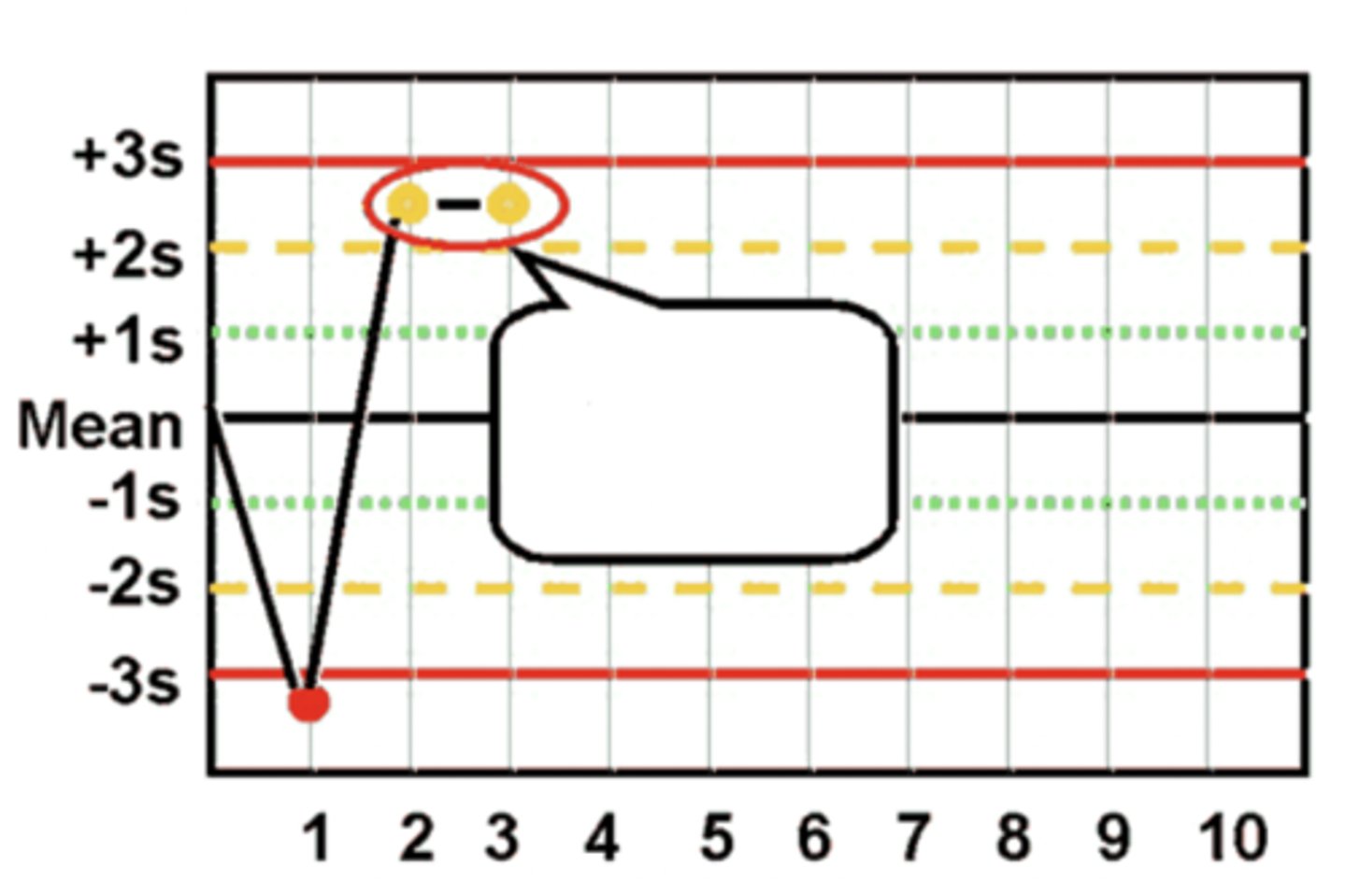
4(1s) Westgard Rule violation
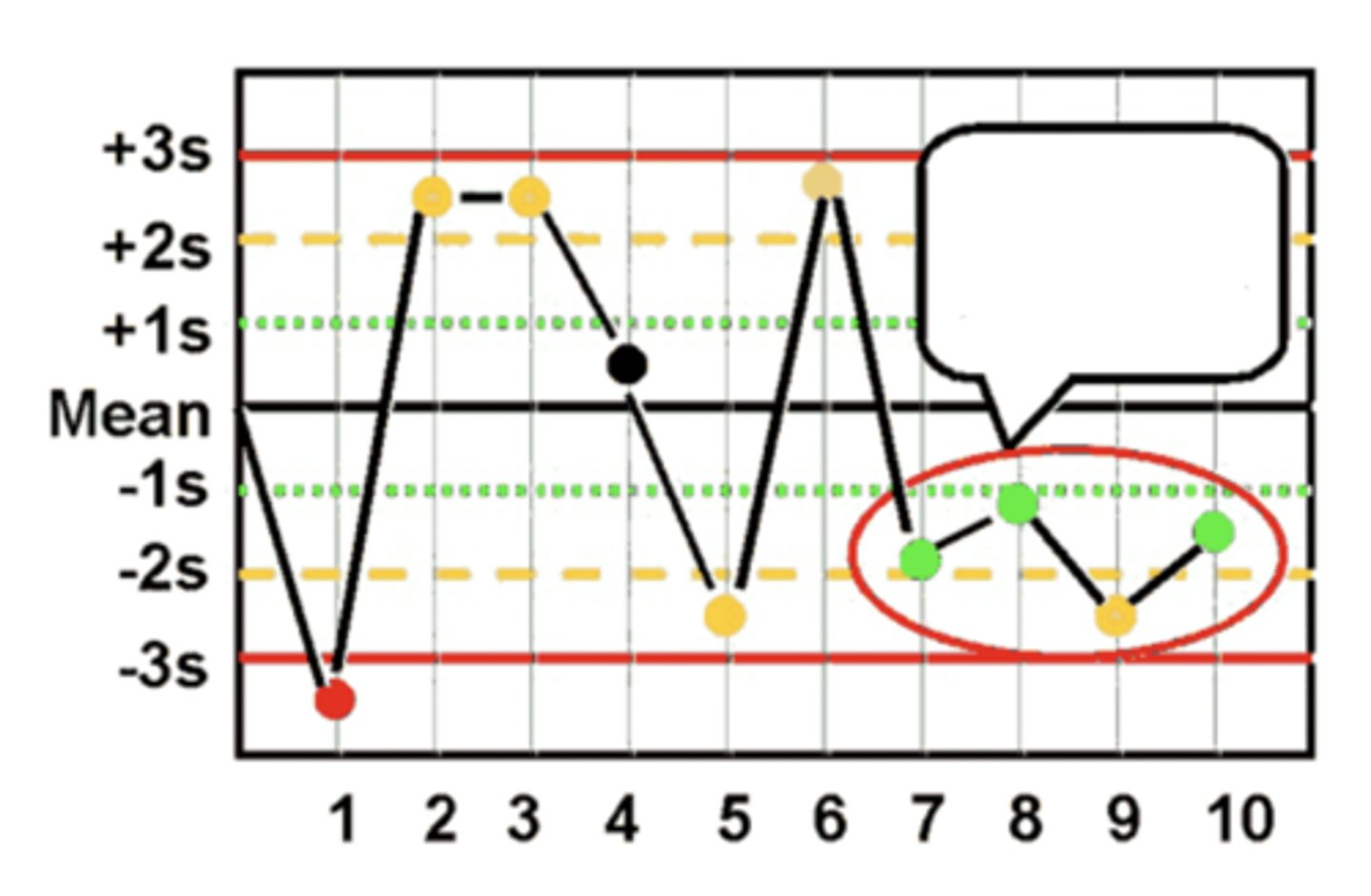
10x Westgard Rule violation
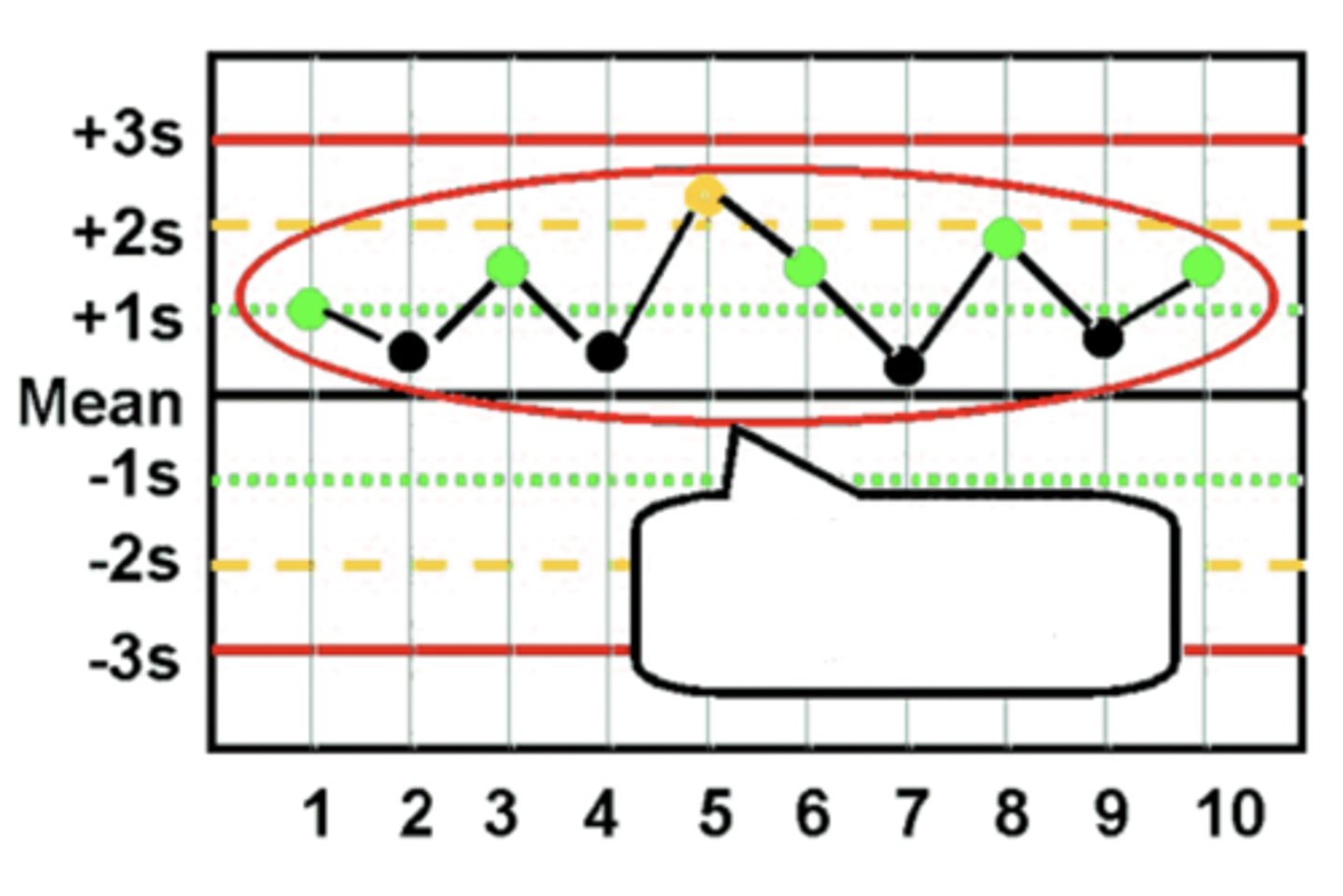
Which Westgard Rule violations are due to random error?
- 1(2s)
- 1(3s)
- R(4s)
Which Westgard Rule violations are due to systematic error?
- 2(2s)
- 4(1s)
- 10x
Accuracy is the ability of an analytical method to obtain true/correct results after a number of ______.
replicates
Precision is the ______ of a method.
reproducibility
The narrower a distribution of results after a number of replicate analyses, the ______ the precision.
better
______ is the amount by which analysis varies from the correct result.
Bias
Example:
Expected value = 50
Result value = 47
Bias = ______.
3 units
What are the 3 types of error in the clinical lab?
Pre-analytical, analytical, post-analytical
Examples of pre-analytic error
Test order entry, pt. identification, specimen collection/transport, etc.
Analytical error is associated with the performance of the ______.
method/instrument
What are the two types of analytical error?
Random and systematic
Random analytical error affects ______ of the result.
reproducibility
What are some causes of random analytical error?
Air bubbles in reagent, improperly mixed reagents, imprecise pipette, etc.
Systematic analytical error causes a shift to the ______ over time.
mean
Systematic analytical error is ...
Constant and porportional
Systematic analytical error is caused frequently by ______.
instrument calibration
What are some examples of systematic analytical error?
Interfering substances, deterioration of reagents/calibrators/photometric light source, etc.
Post-analytical error occurs when the results are ______.
reported/released
What are some examples of post-analytic error?
Transcription mistakes, using wrong units, delays, etc.