Biology Unit 15-Human Body Systems
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
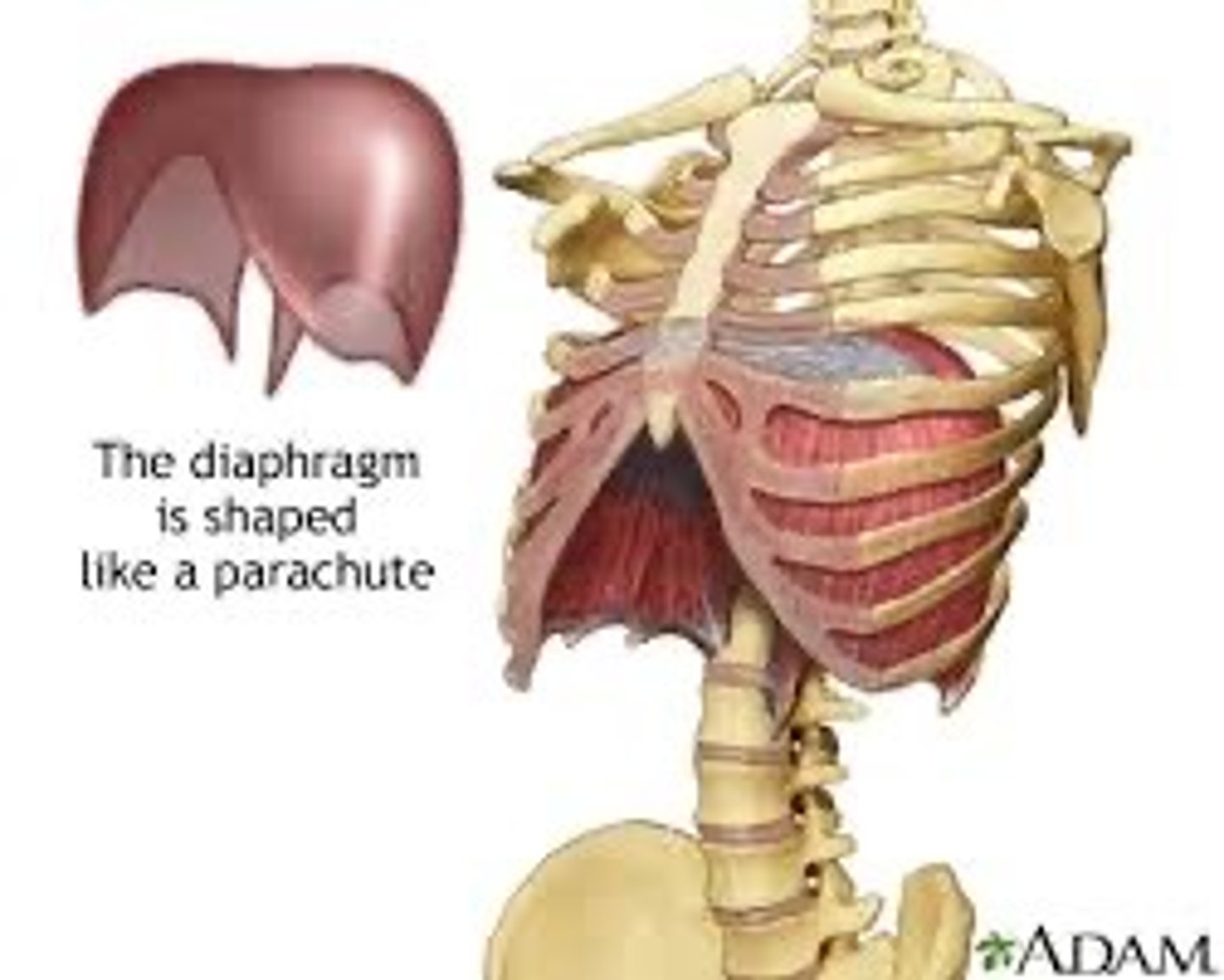
Diaphragm
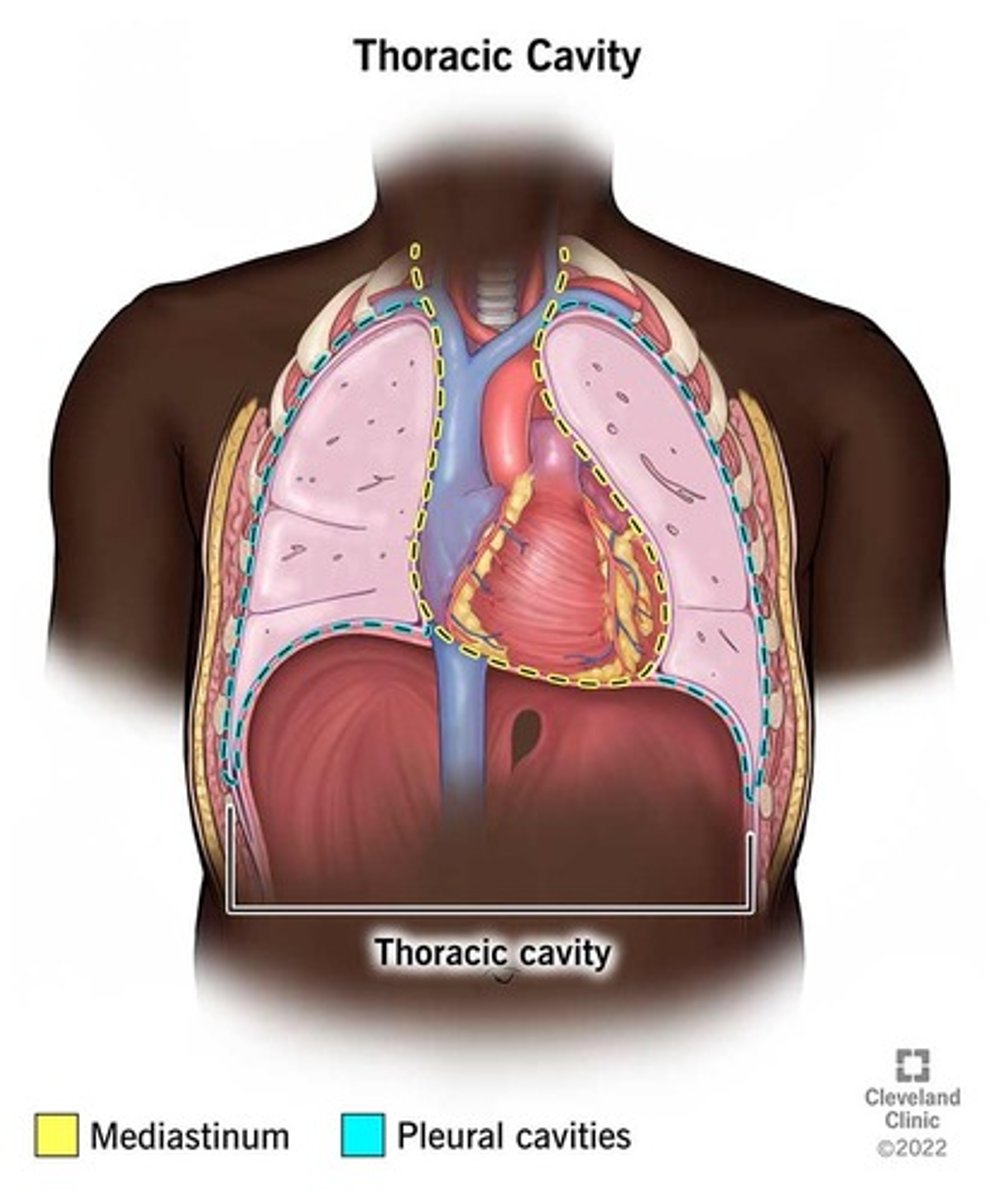
Thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs(main organs).
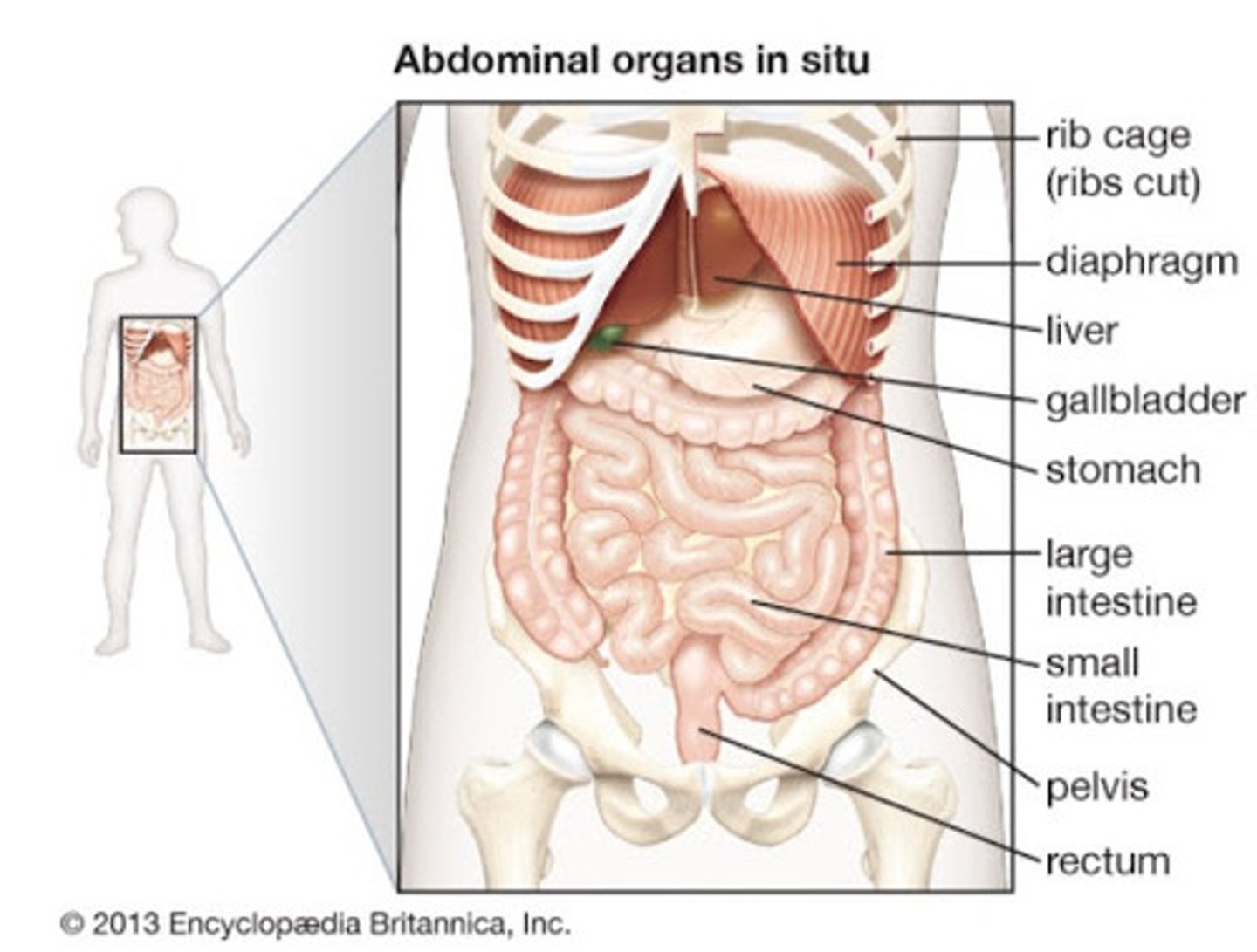
abdominal cavity
Contains stomach, intestines, spleen, and liver, and other organs
Homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as temperature, blood sugar, pH etc.
Anterior side
The head of the pig(the front)
Posterior side
The tail of the pig (the back)
Dorsal side
The top of the pigs back
Ventral side
Opposite from the dorsal side, the stomach/bottom area.
What are the 4 types of tissues in the human body? What do they do?
Epithelial tissue-covers body surfaces (skin)
Connective tissue-supports the body and connects its parts (bone, blood)
Nervous tissue-carries messages throughout the body
Muscle tissue-enables the body to move
Levels of organization
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
Respiratory system
Takes in oxygen and gets rid of carbon dioxide (gas exchange)
The circulatory system
Circulates blood around your body (many purposes)
The digestive system
Breaks down food into usable energy. Cellular respiration (breaks good into energy)
The Urogenital system
Filter waste materials from the blood; store and expel urine
What kind of system is the digestive system?
Chemical and mechanical
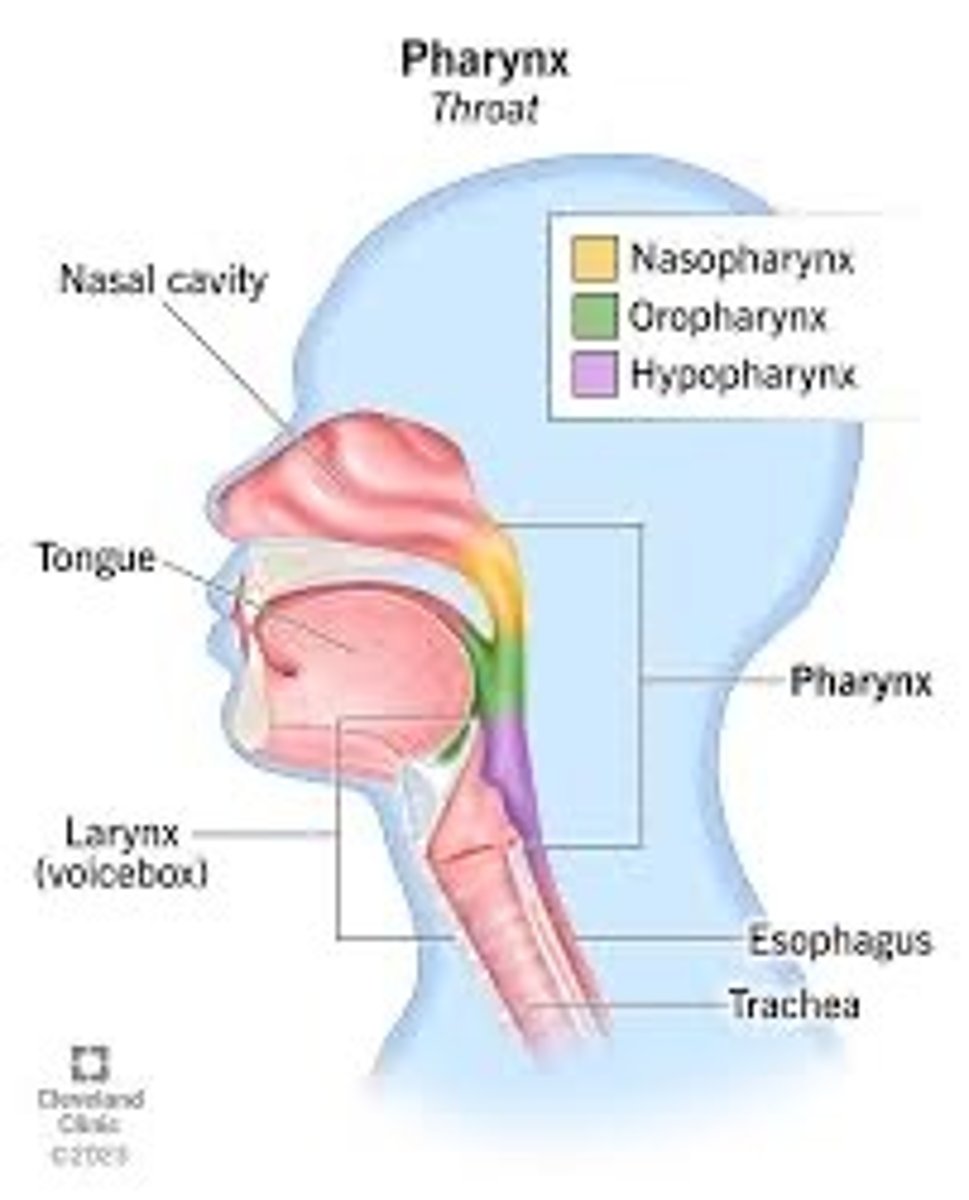
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
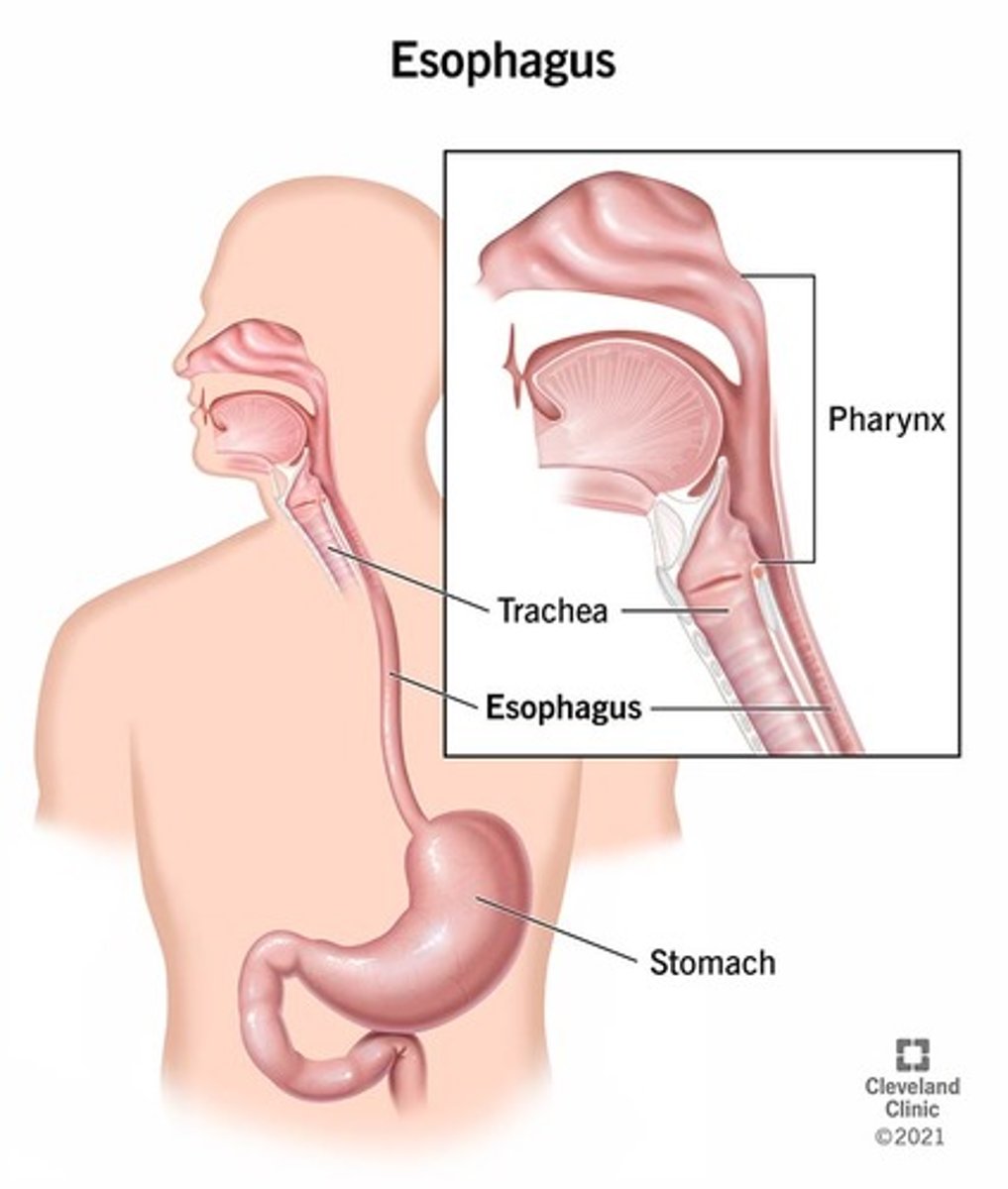
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach.
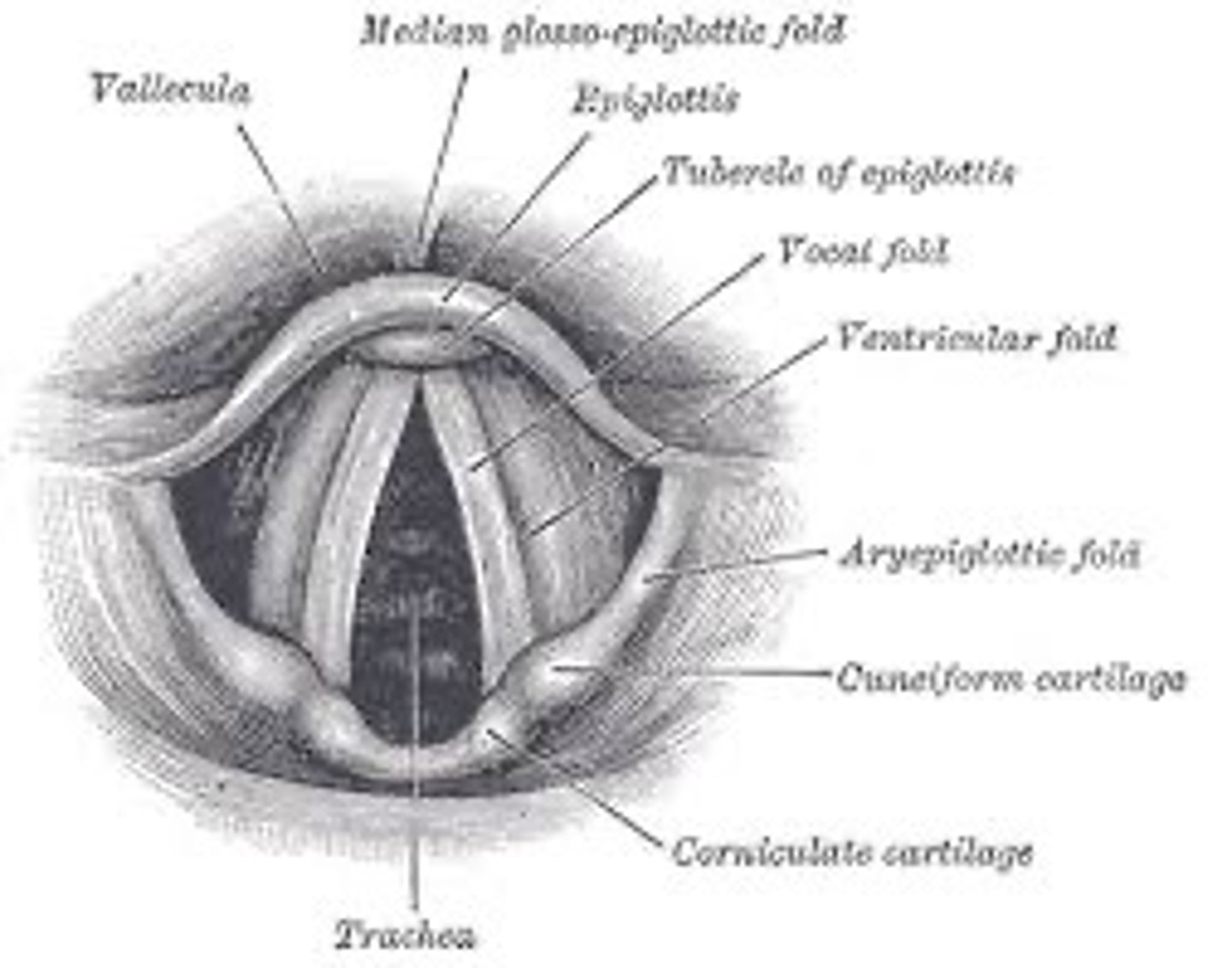
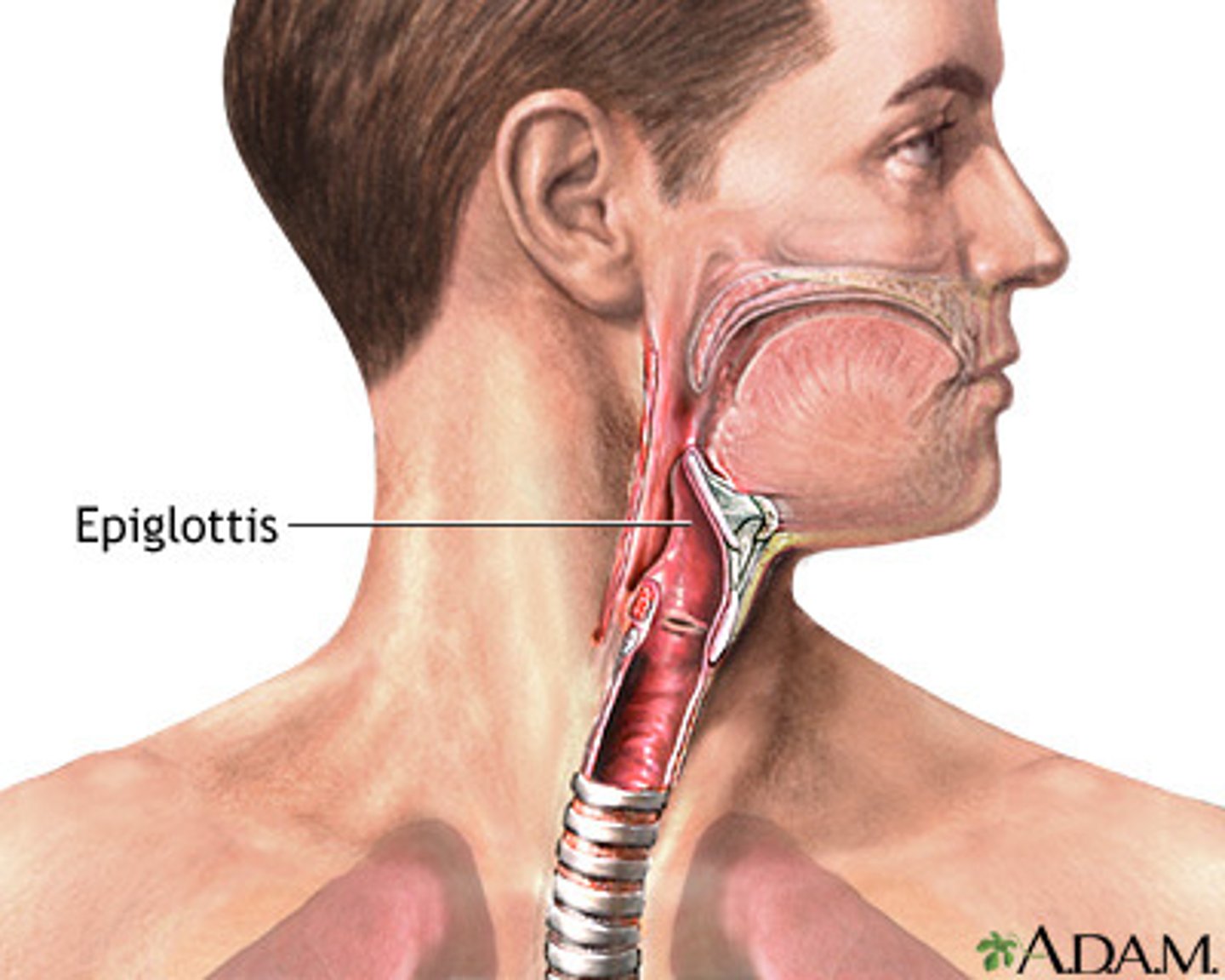
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that seals off the windpipe and prevents food from entering the trachea.
Cardiac sphincter (or esophageal sphincter)
Keeps food in the stomach until it is ready to go to the small intestine.
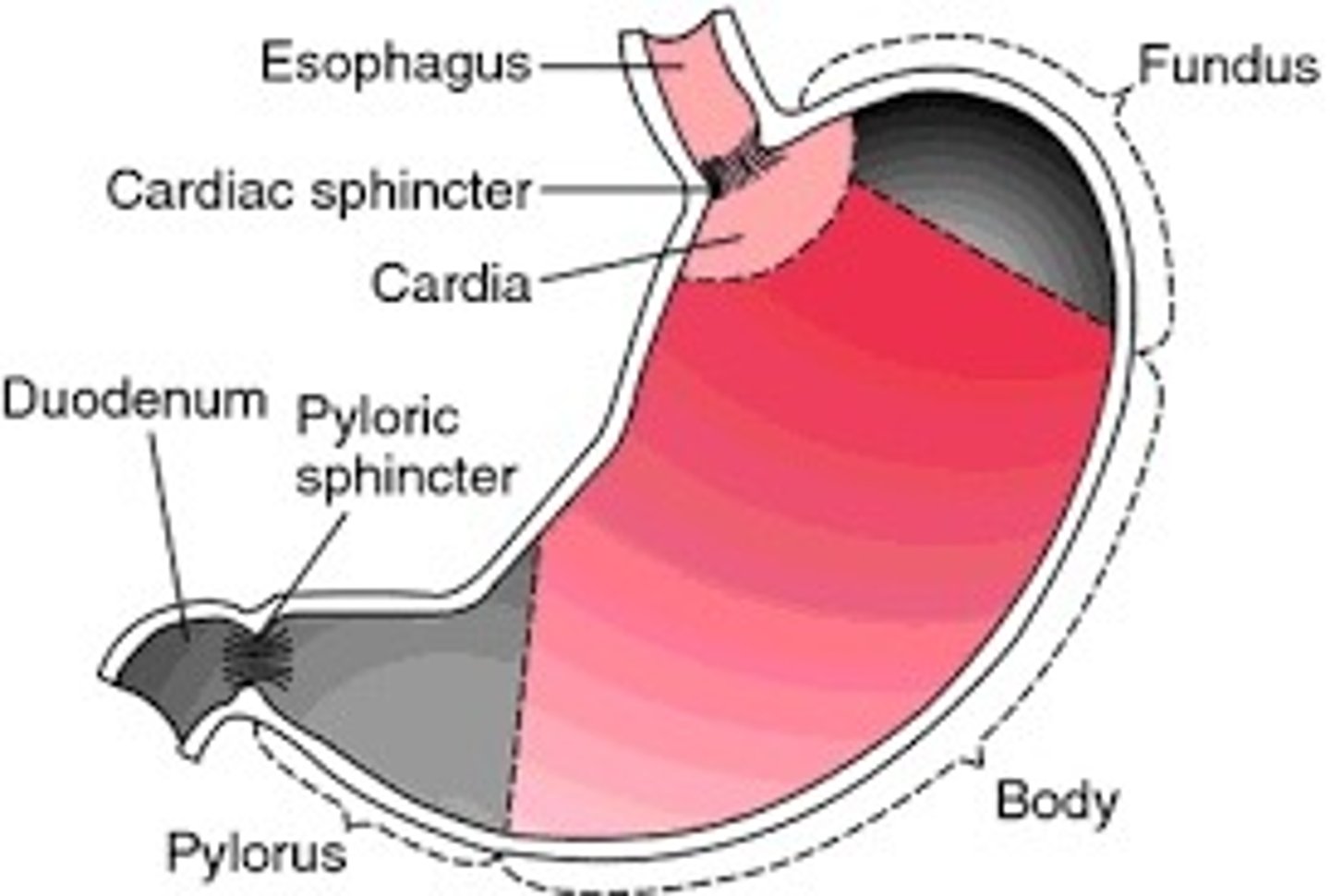
Stomach
Holds the food, contains acid that breaks it down.
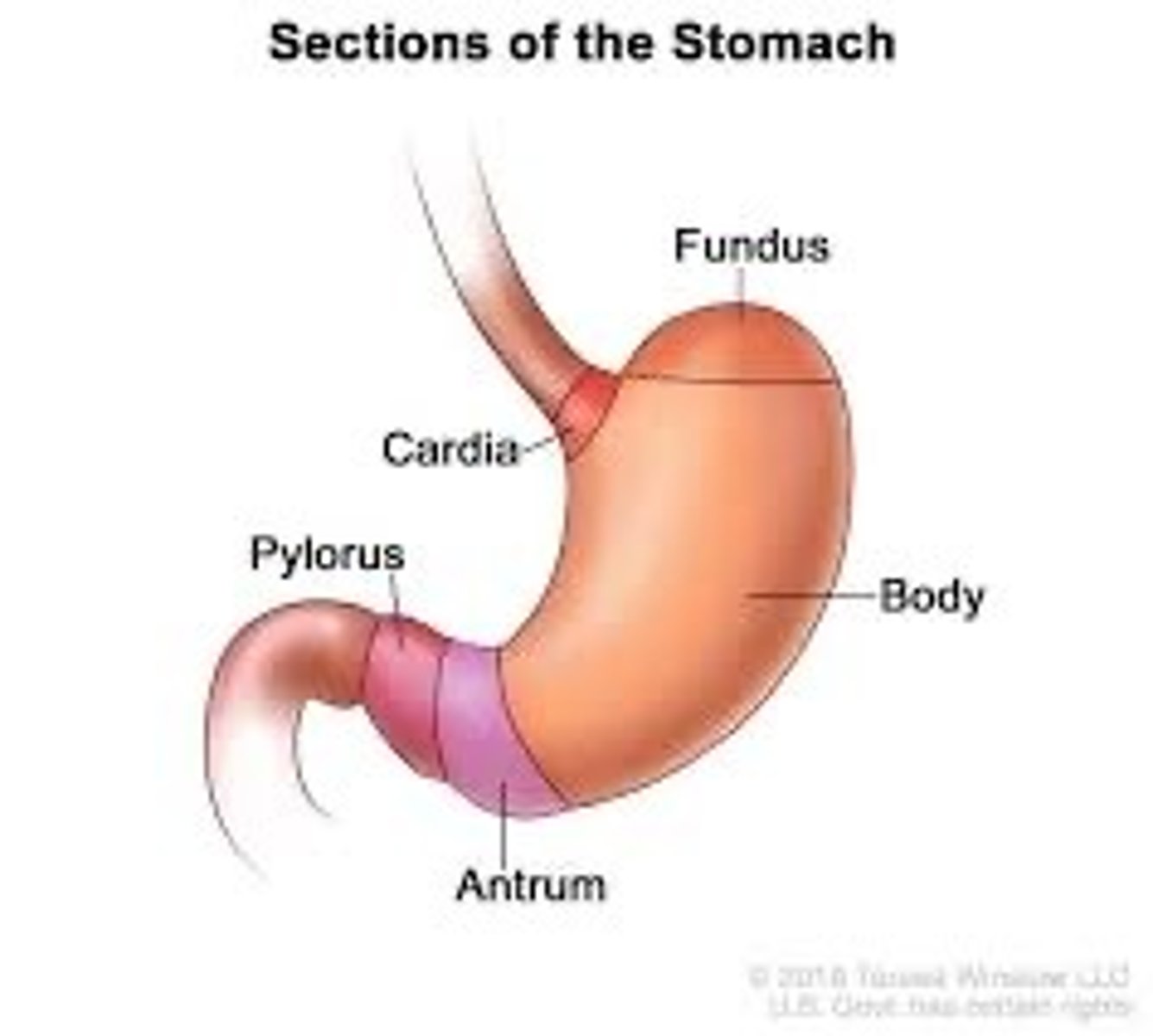
Rugae
Folds in the stomach that increase surface area and allow it to expand
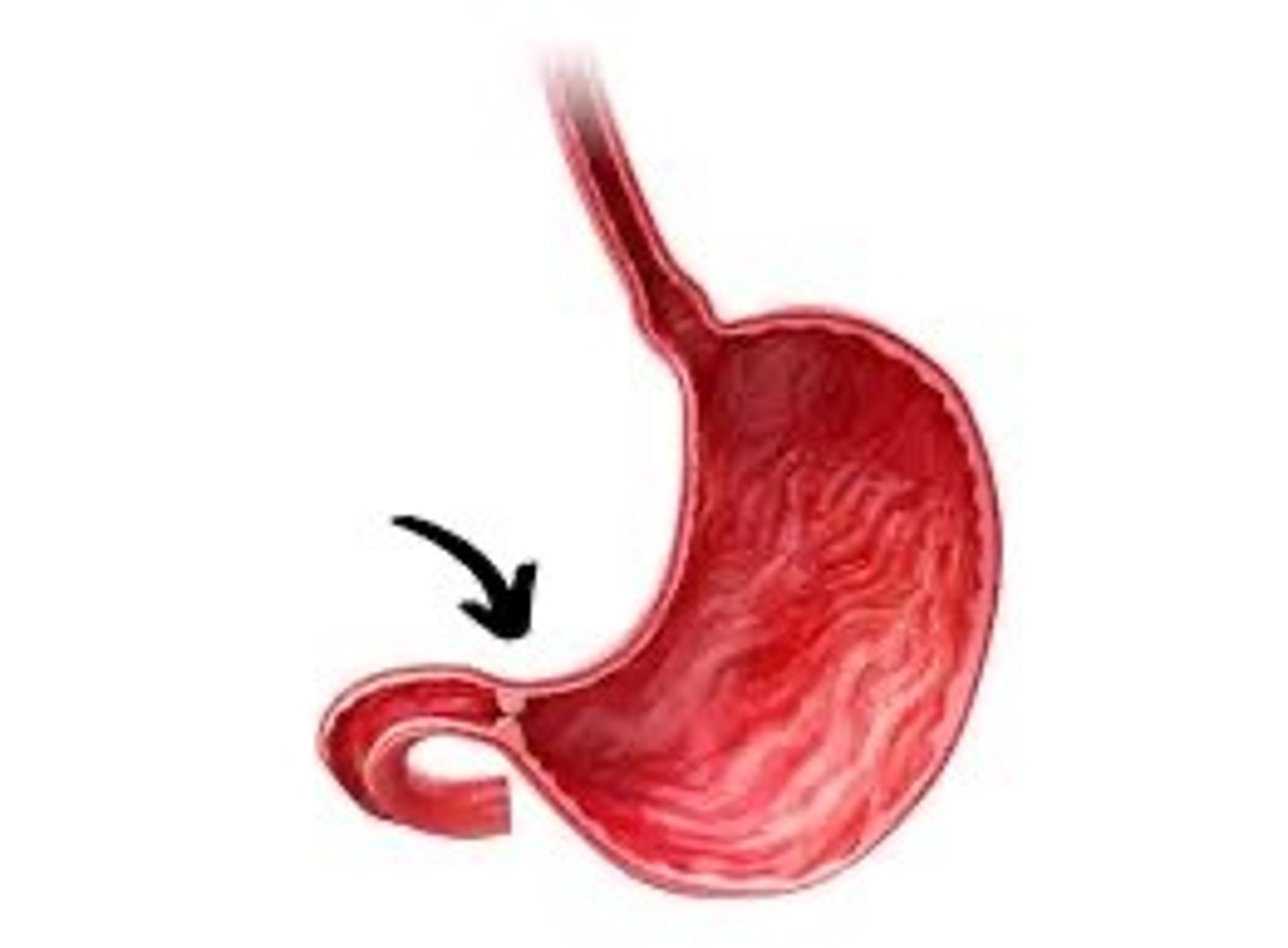
Pyloric Sphincter
Controls passage of food from stomach to small intestine(circular muscle)
Small intestine
Where most of the absorption of nutrients happens (is held together by the mesentery.
Villi/microvilli
Folds in the small intestine lining, and the extra folds in the folds of the lining. Increase surface area to help absorption.

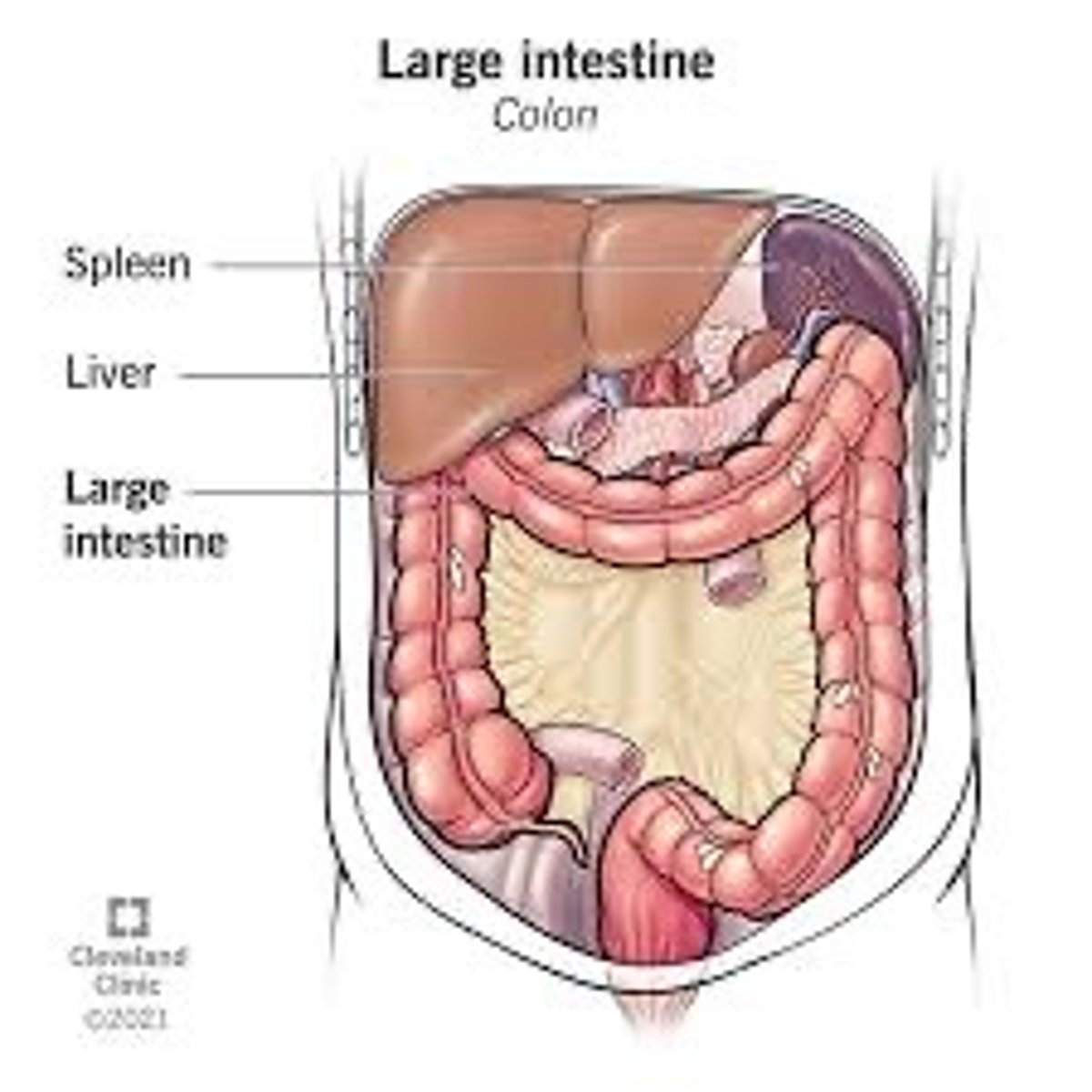
Large Intestine (colon)
Removes waste from the chyme and eliminates water
Chyme
Partially digested, semiliquid food mixed with digestive enzymes and acids in the stomach.
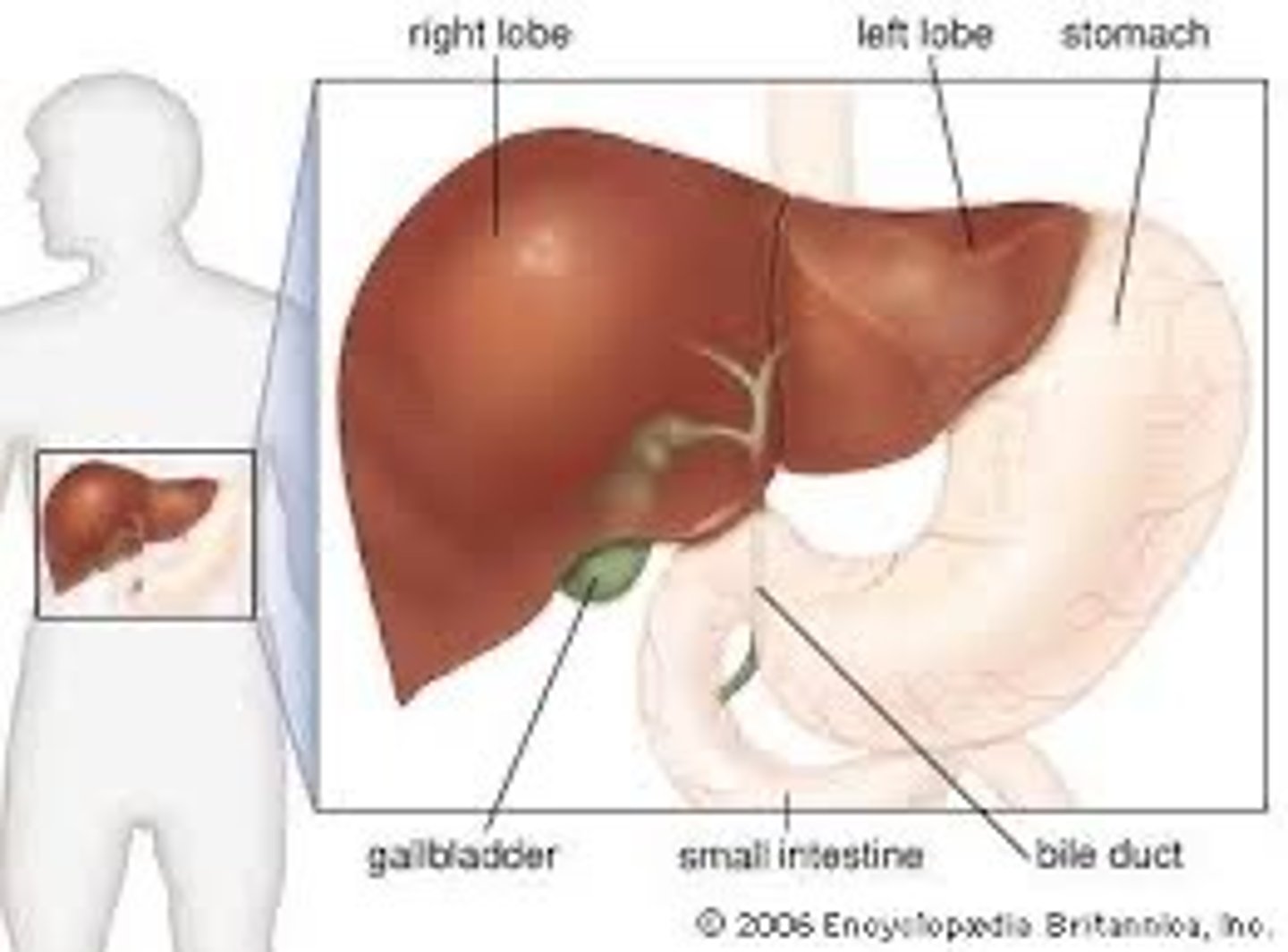
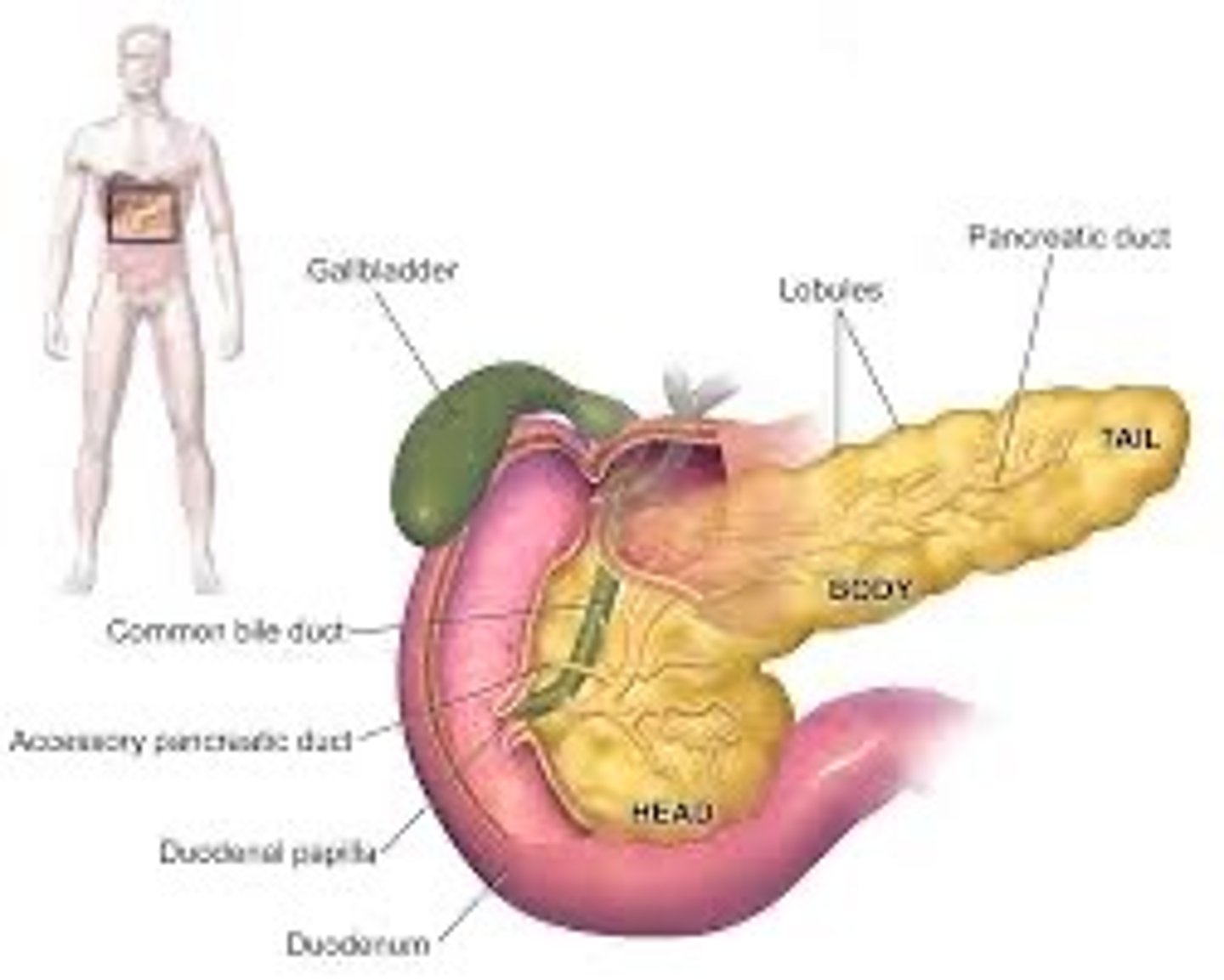
Gallbladder
A muscular sac attached to the liver that secretes bile and stores it until needed for digestion
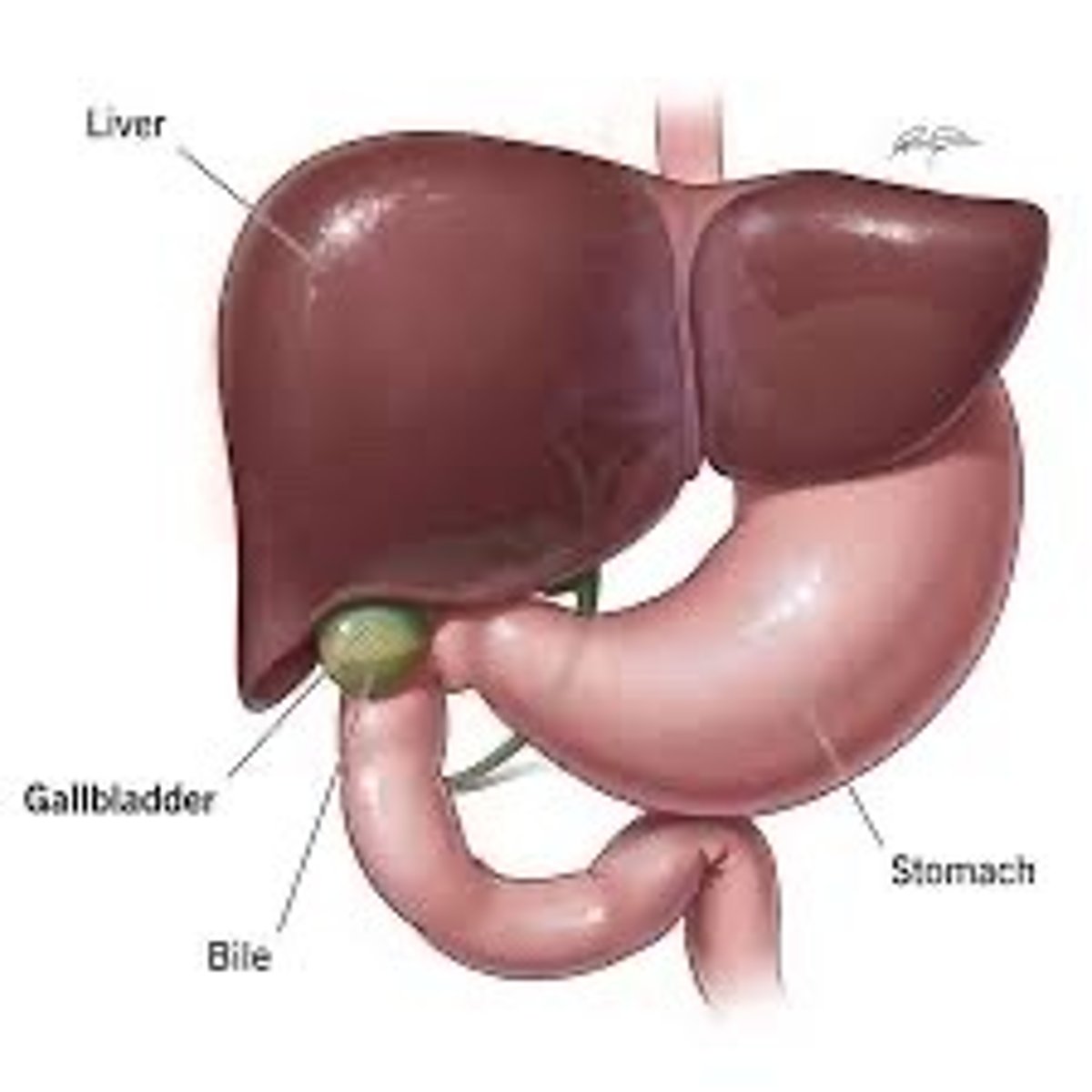
Bile
Made in the liver-breaks down fats
Liver
1. Breaks down toxins 2. Makes bile
Pancreas (endocrine system)
makes insulin and glucagon
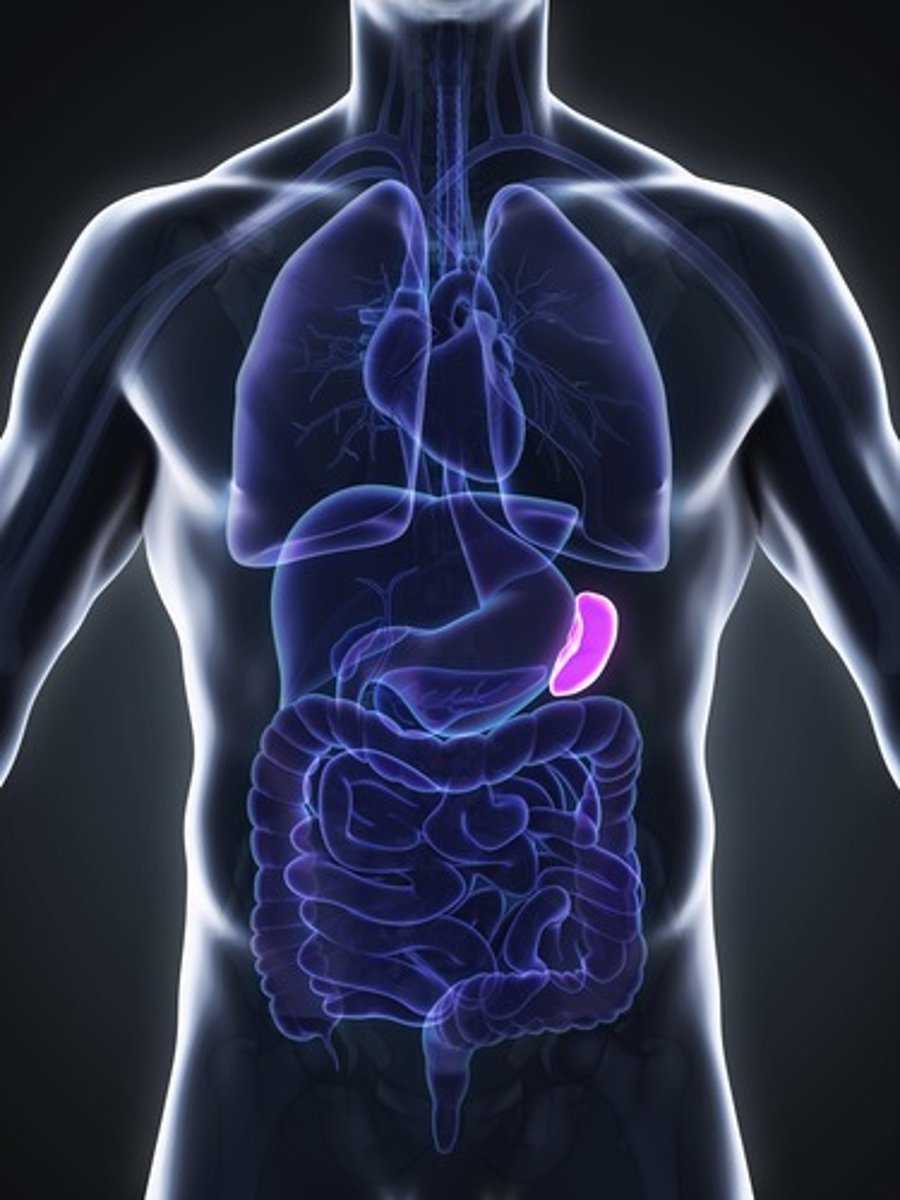
spleen (lymphatic system)
Organ near the stomach that produces, stores, and eliminates blood cells
What is one of the most visible differences between the internal anatomy of a pig and a human?
In the human the large intestine is wrapped around the small intestine.
In the pig the small intestine and large intestine are bundled separately.
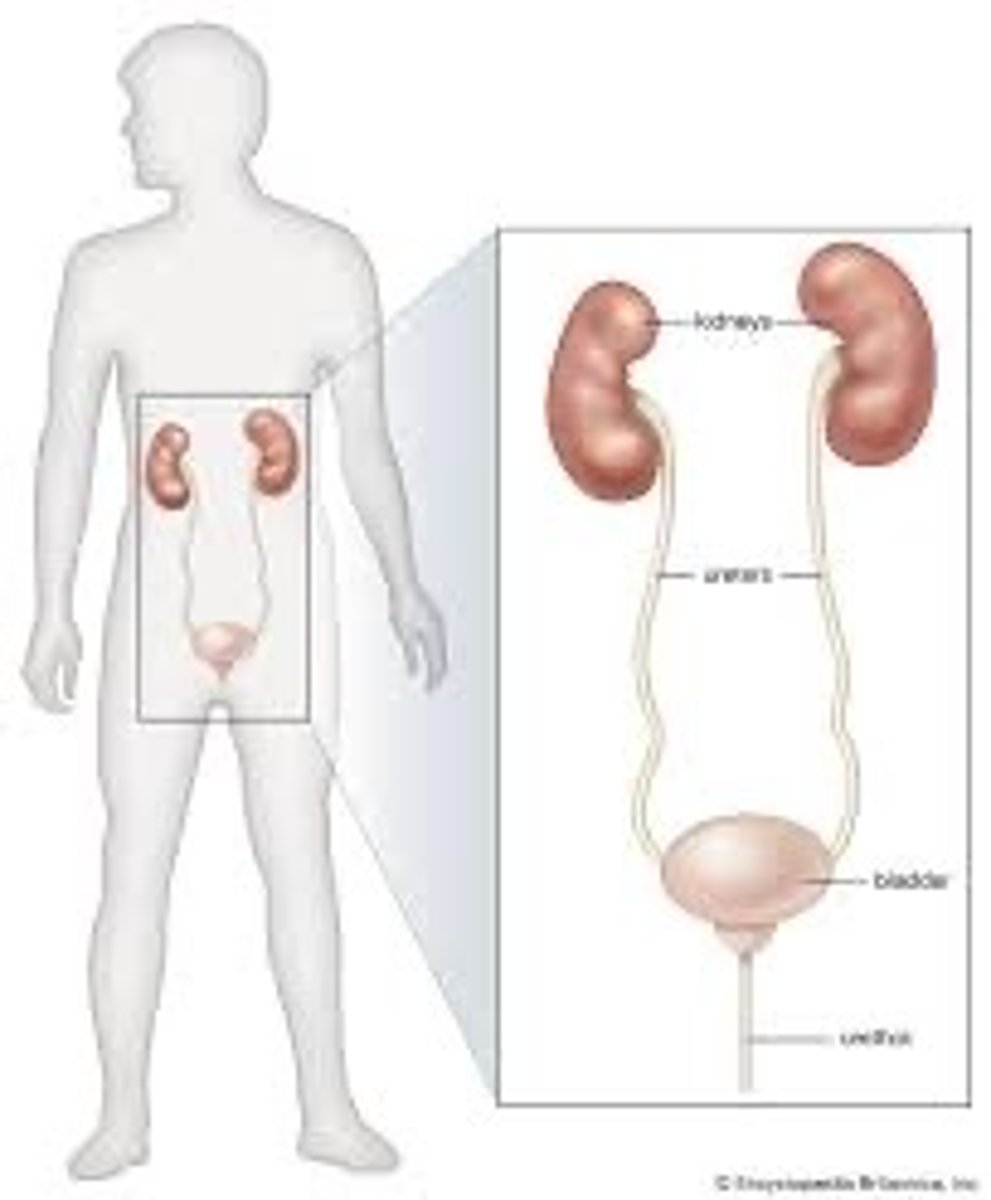
Kidneys
Filters excess water + urea
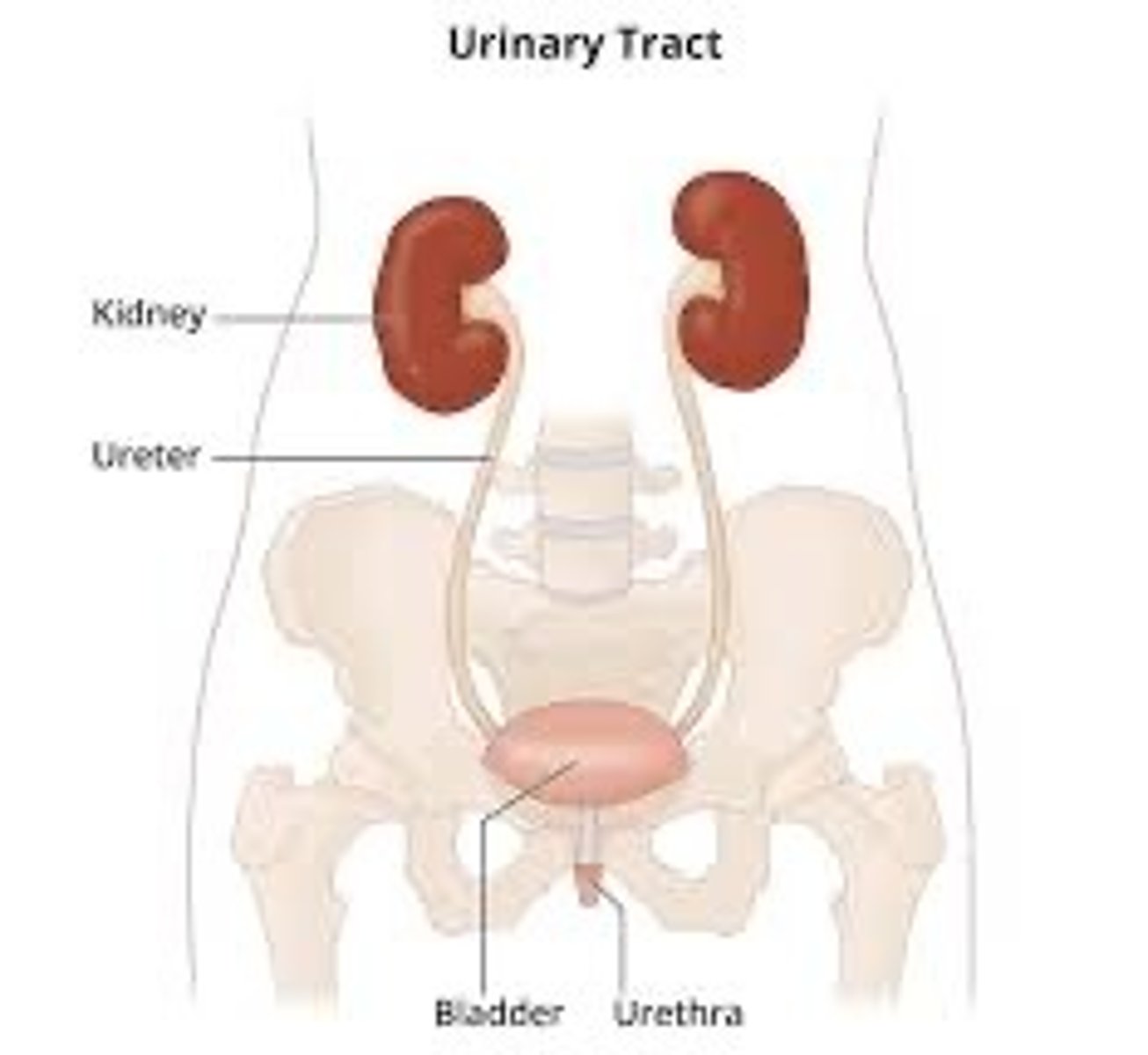
Ureter
Tubes that connect kidneys to the bladder
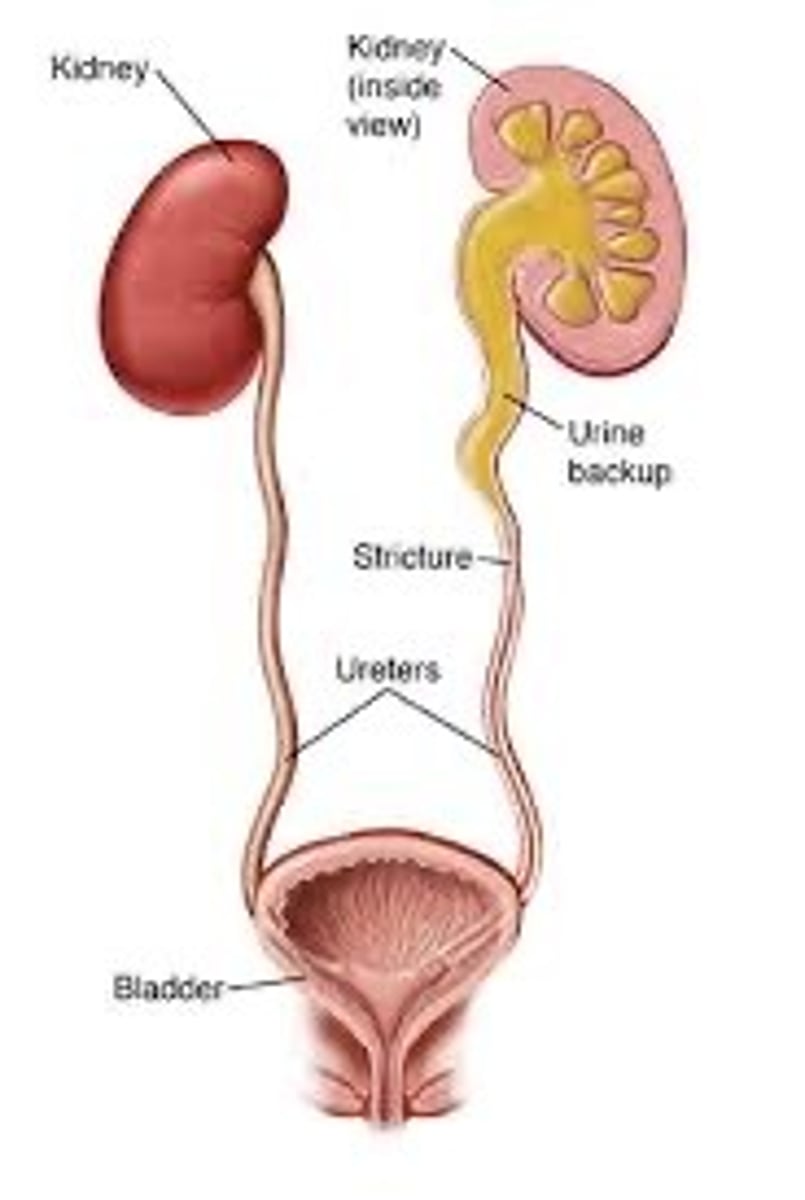
Urinary bladder
Holds urine until it is released from the body
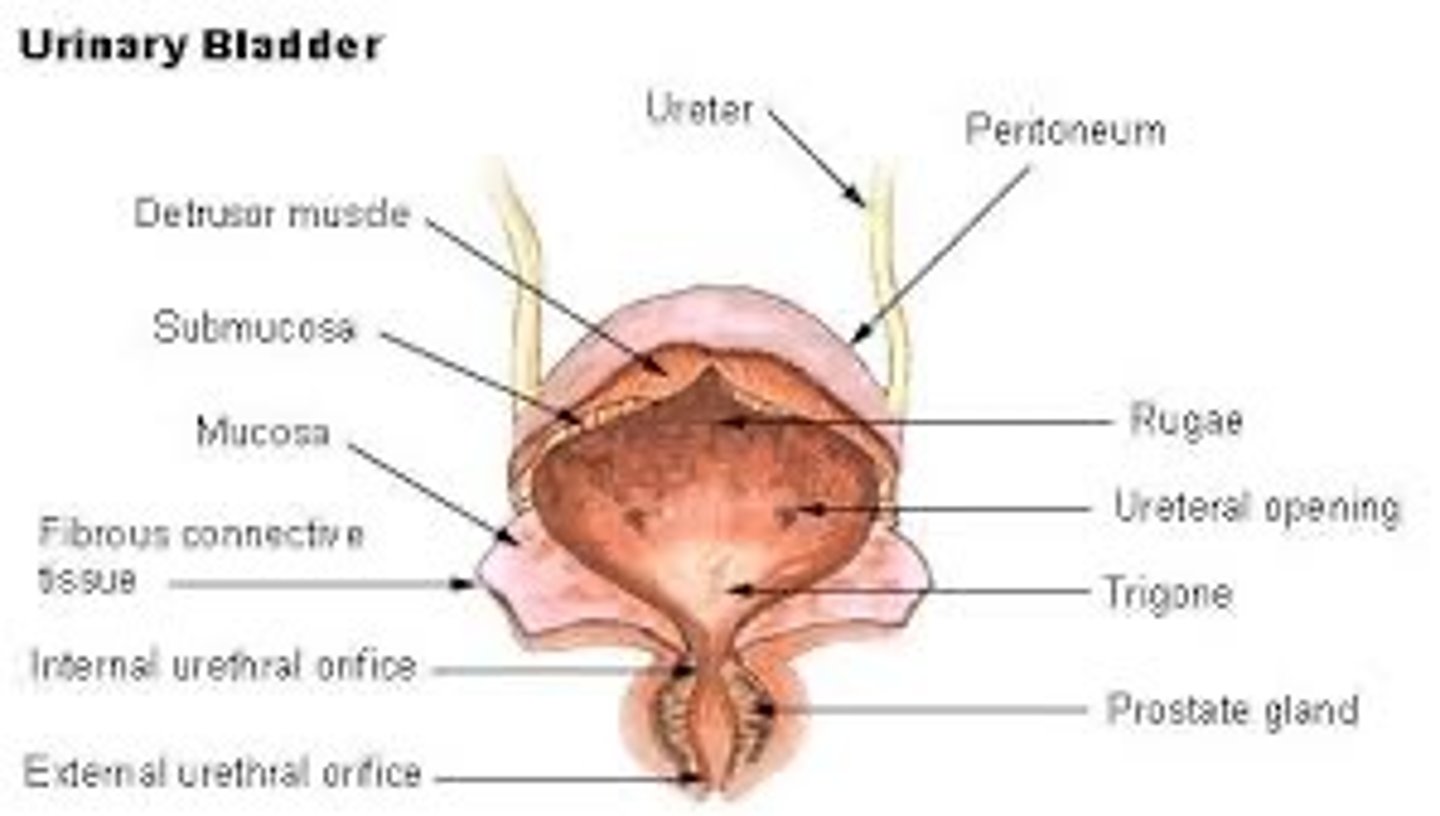
Urethra
Urine is released through this tube
Urea
A waste product (urine + water=urine)
Larynx
Voice box-vocal folds, vocal chords
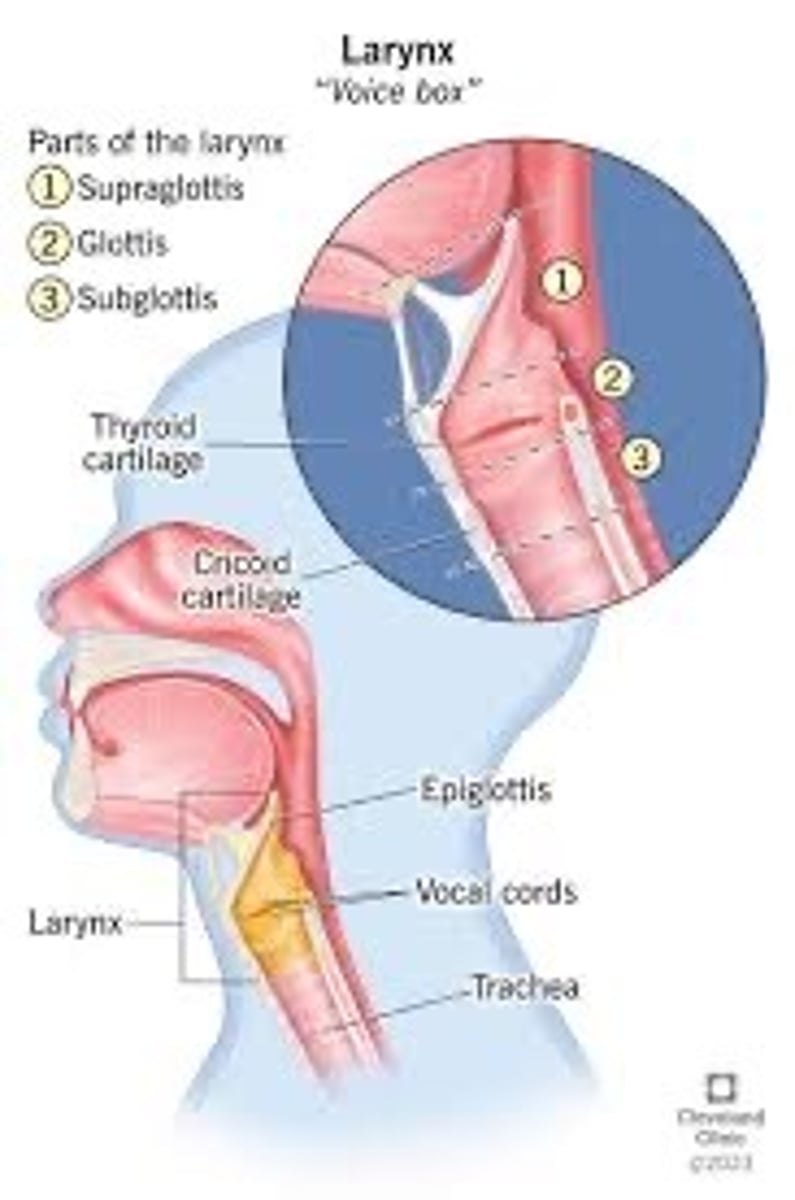
Trachea
Main pipe that goes down into lungs-has cartilage rings.
Lungs
two spongy organs, located in the thoracic cavity enclosed by the diaphragm and rib cage, responsible for respiration, contains alveoli to preform gas exchange
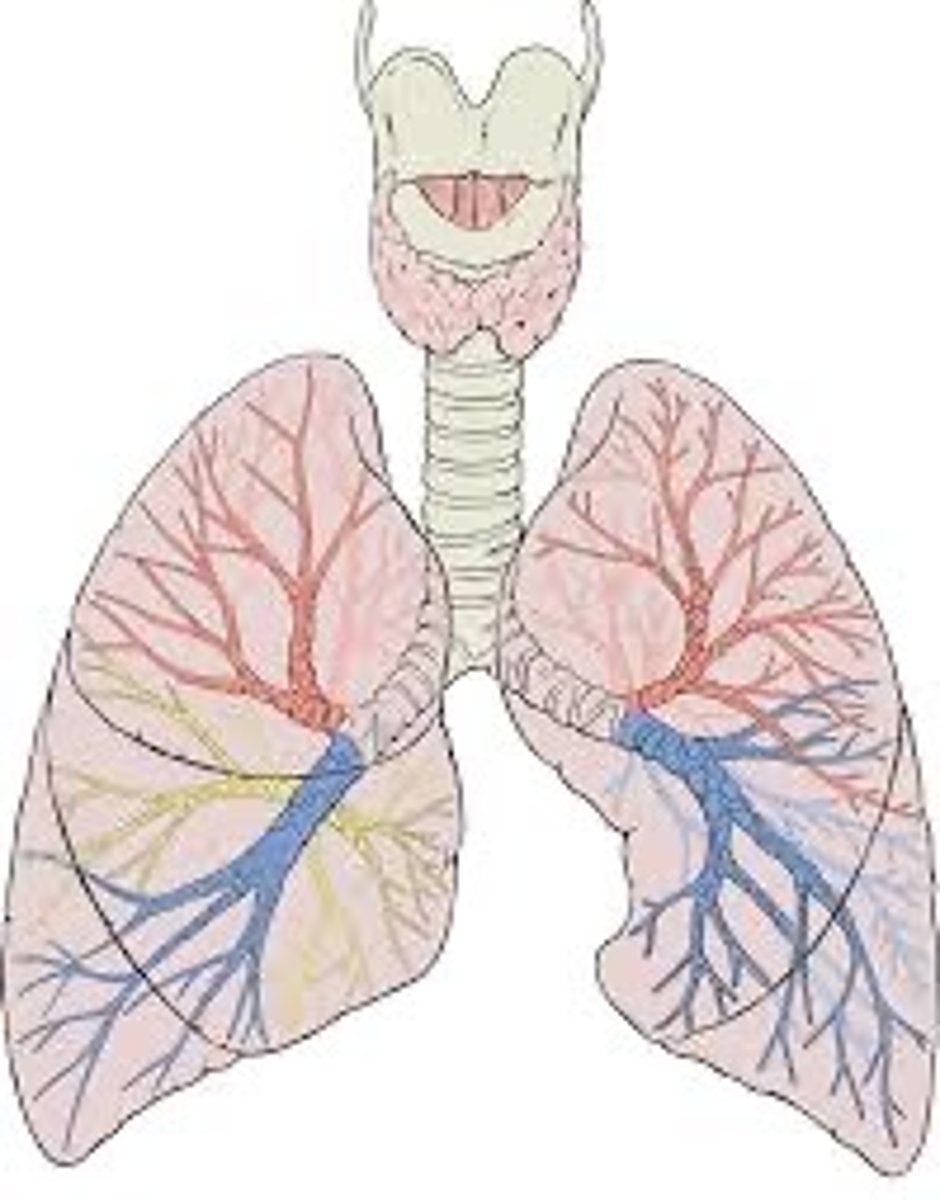
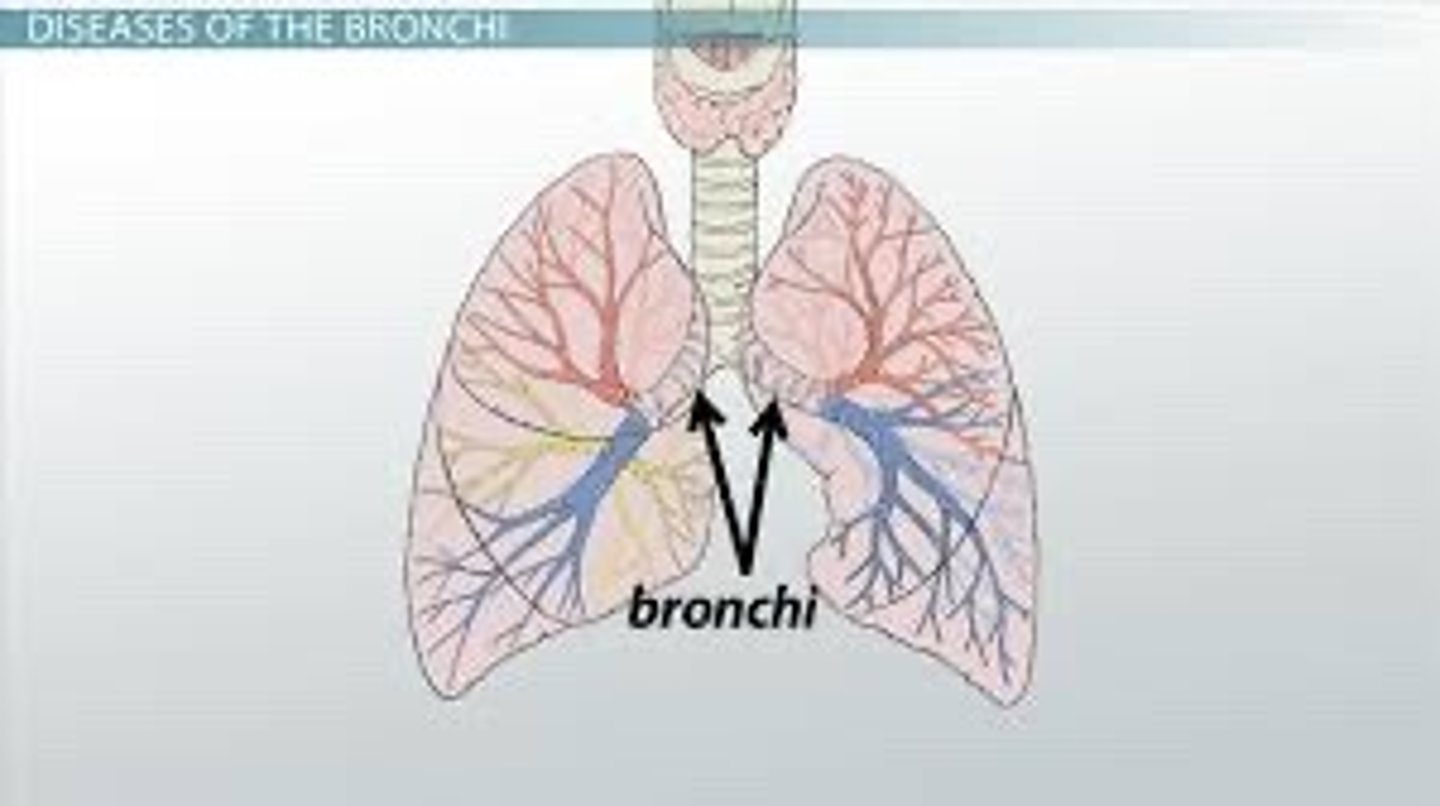
Bronchi/Bronchus
.The trachea splits into these two tubes when they enter the lungs. (Air goes through these into the lungs)
Bronchioles
small branches of the bronchi; carry air in the lungs

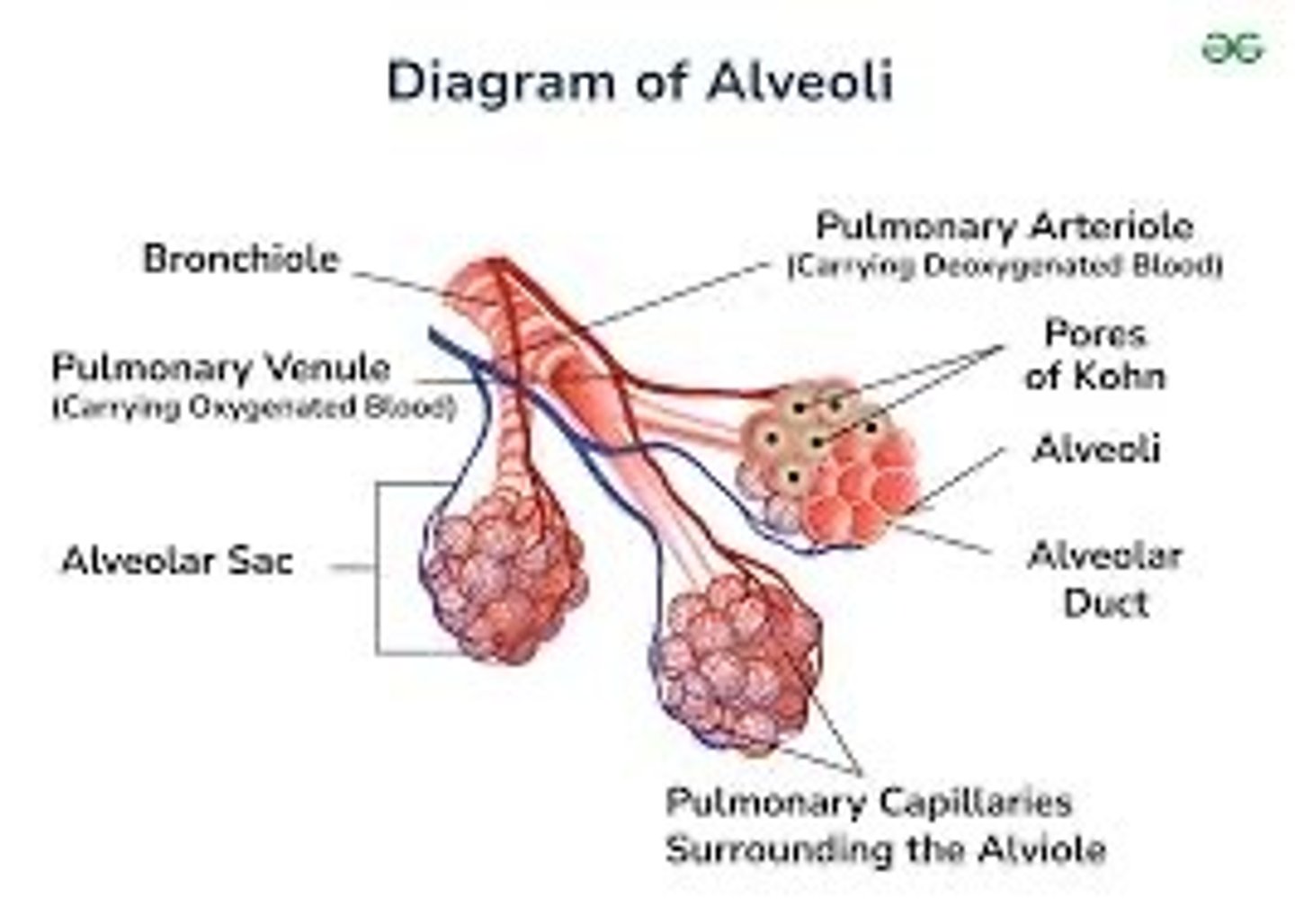
Alveoli/alveolus
Covered in capillaries, add extra surface area for blood to diffuse oxygen (gas exchange)
Heart
A hollow, muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
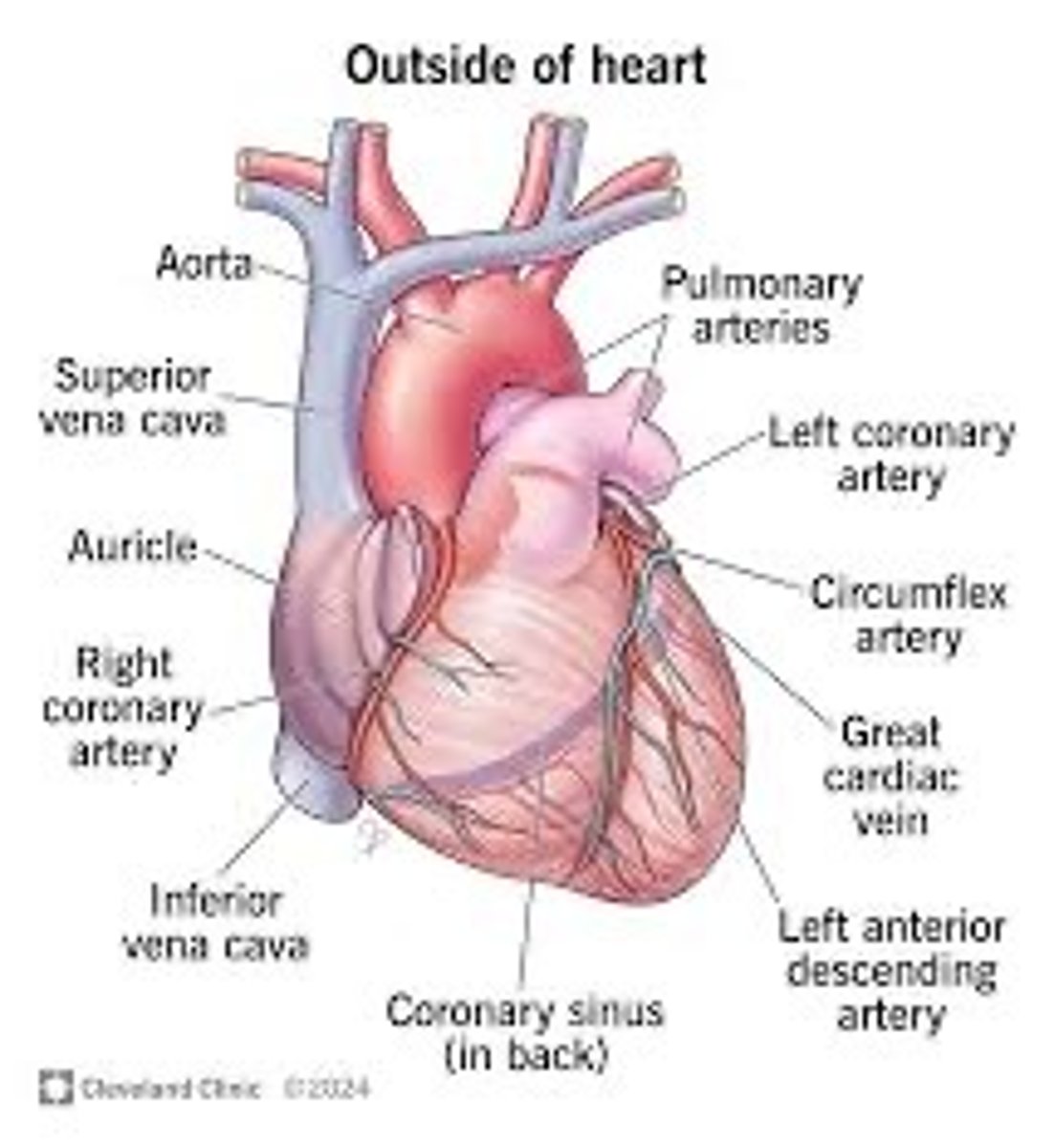
What are the four chambers of the heart?
left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle, right ventricle
Ventricles
the two lower chambers of the heart, and they pump blood out to the lungs and body.
Atrium
Each of the two upper chambers of the heart that receives blood that comes into the heart
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart
Veins
Carry blood to the heart
Aorta
The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body.
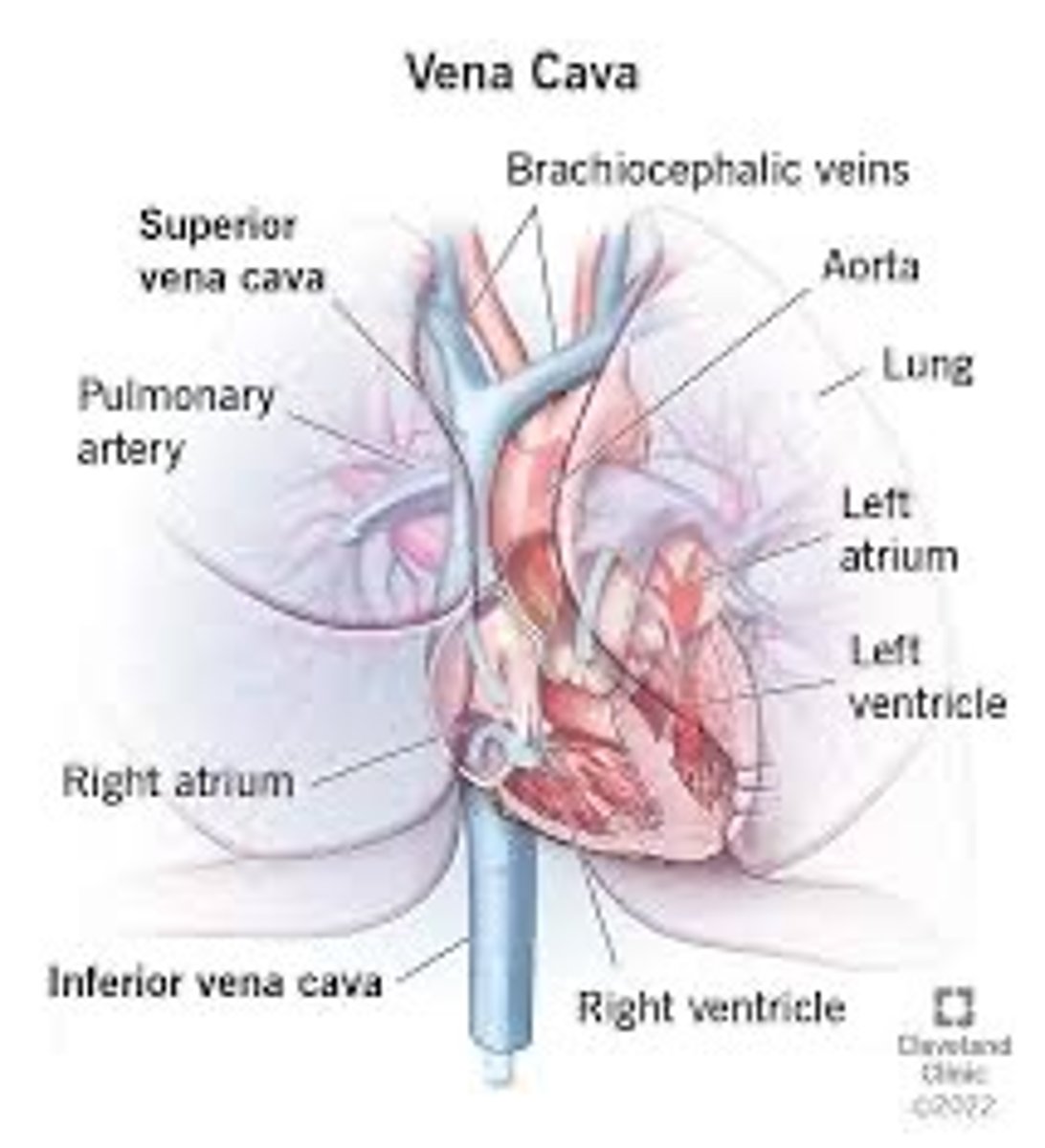
vena cava (superior and inferior)
These two major veins return blood from the body to the right atrium
Capillaries
Smallest blood vessels where gas exchange takes place
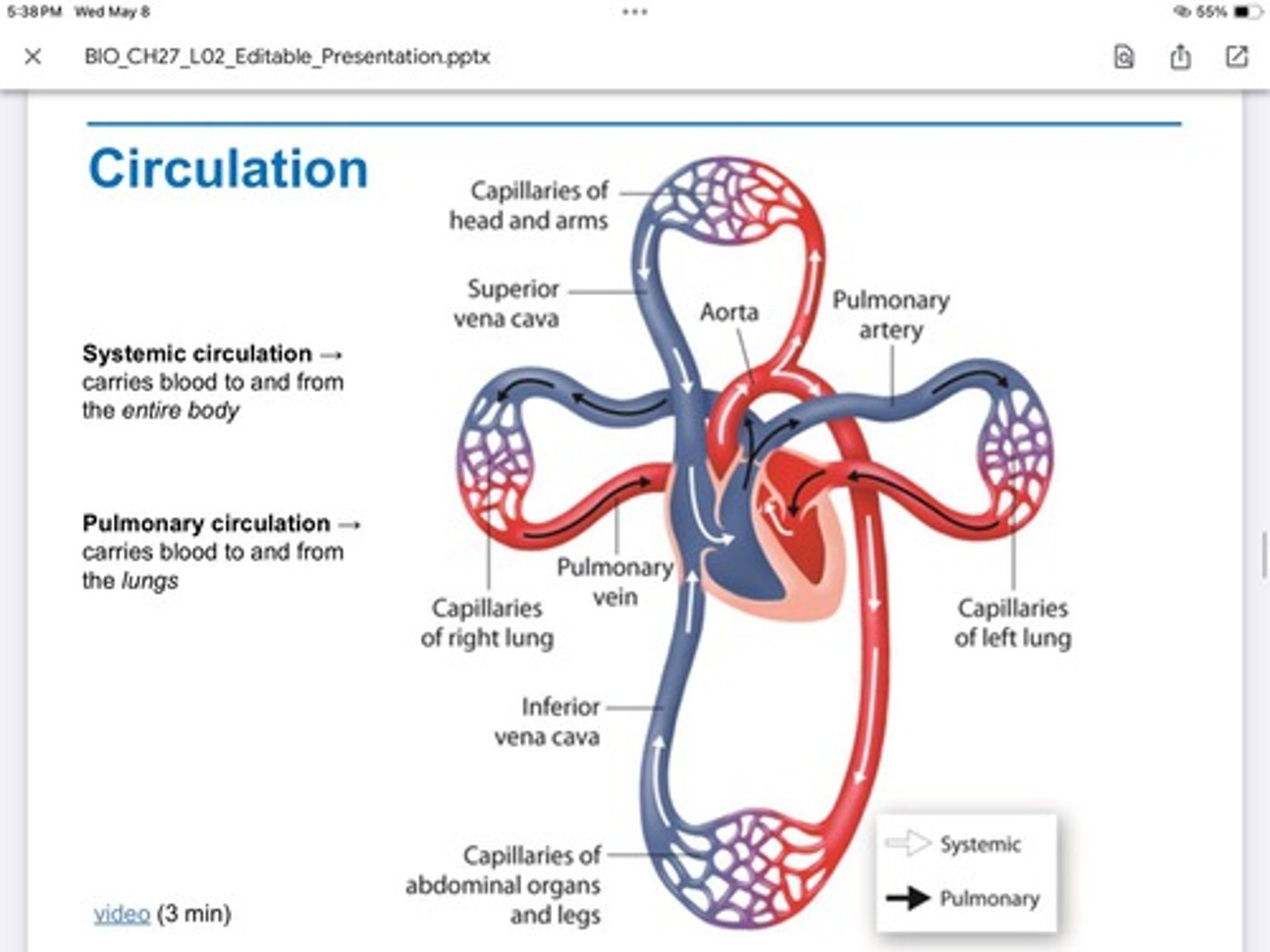
Pulmonary circulation
Carries blood to and from the lungs
systemic circulation
Carries blood to and from the entire body
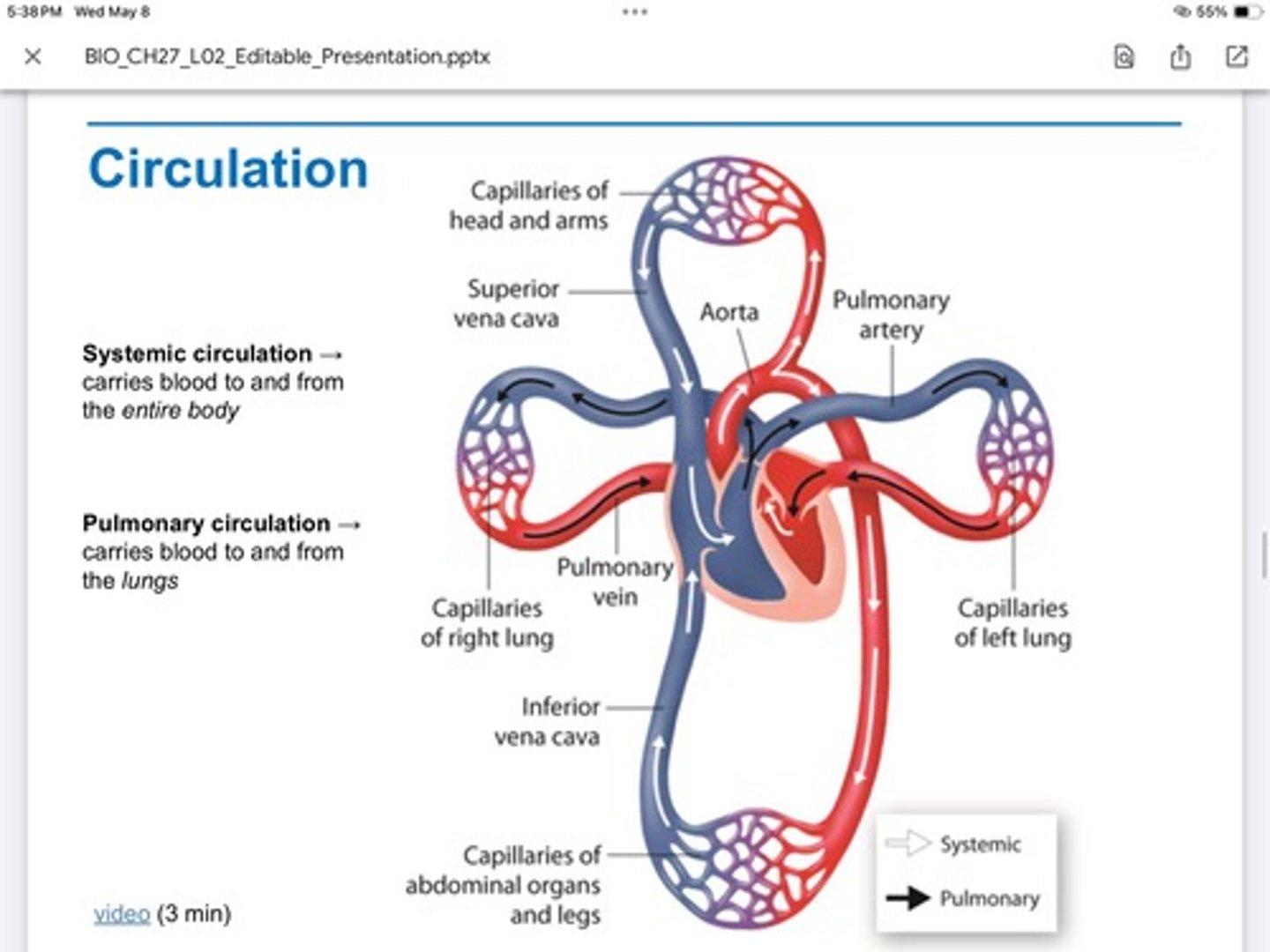
Coronary Circulation
Part of the systemic circulation—> can cause a heart attack if veins and arteries get clogged—> circulation that feeds the heart
What are the four components of blood?
1. Plasma (more then half 55%)
2. Red blood cells—>oxygen
3. White blood cells—->pathogens
4. Platelets—> helps blood clot (only good for blood to clot outside of the body)
What is the purpose of blood?
Fights, diseases, pathogens, HELPS MAINTAIN HOMEOSTASIS, carries oxygen and nutrients to places, helps the body heal.
Make sure to...
Look at the images in the Quizlet to identify the location of each body part.
Study your..
Notes from class and the slides in google classroom.
Vocal Folds
Two elastic bands of muscle tissue located in the larynx directly above the trachea. When you breathe your vocal folds remain apart and when you swallow, they are tightly closed. When you use your voice air from lungs causes your vocal folds to vibrate between open and closed positions.