SPDI WEEK 2
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
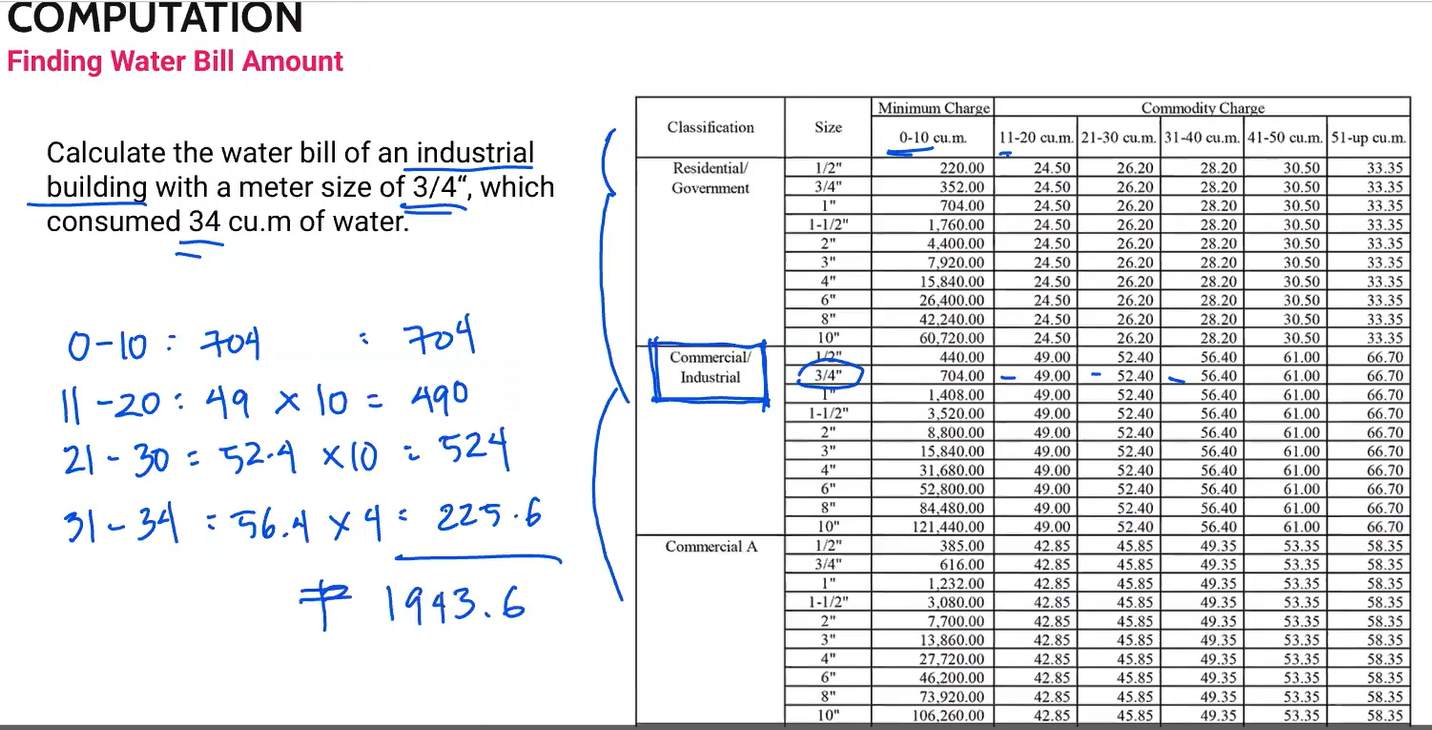
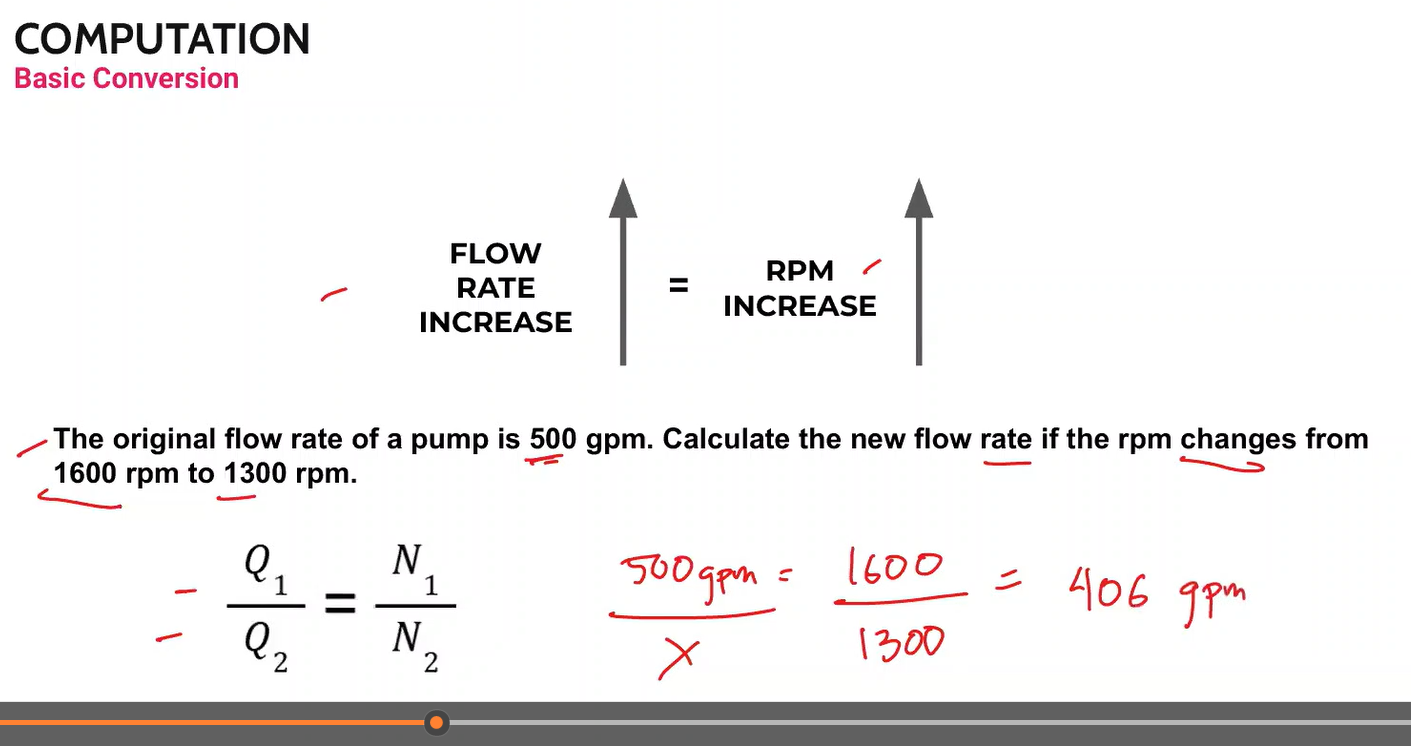
Calculate the water bill of an industrial building with a meter size of 3/4”, which consumed 34 cu. m. of water.

minimum 1/2” in diameter'
Galvanized steel or Black steel pipe
Piping outlet for gas appliance
Material type is Type K or L in drawn tube only
-Comes in green or blue color
-surface of copper itself is antimicrobial and can effectively kill the most toxic bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Medical Gas Tube
Vents suitable only for listed, draft-hood equipped, gas-fired appliances, including most domestic heating and hot water systems.
-factory built double wall vent pipes that are only used to for venting gas
Type B gas vent

For venting listed gas-fired vented wall furnaces or gas-fired vented recessed heaters
Type BW

Use only for positive or negative pressure venting gas appliances producing flue gasses at Class I (up to 245°C) or Class II (up to 135°C) temperatures
Type BH

Designed for venting approved oil-fired and natural-gas appliances that produce draft hood flue gasses that do not exceed a temperature of 570 °F (299°C) or 926 °F for 10 minutes in an over-fire situation
-can be a vent or connect; made to vent oil
-includes pellet vent
Type L

used only as connectors; used only for venting gas or oil
Type C
not less than 16oz. sheet copper, or No. 20 galvanized sheet gauge steel, or of other equivalent noncombustible corrosion resistive material
single-wall metal vents

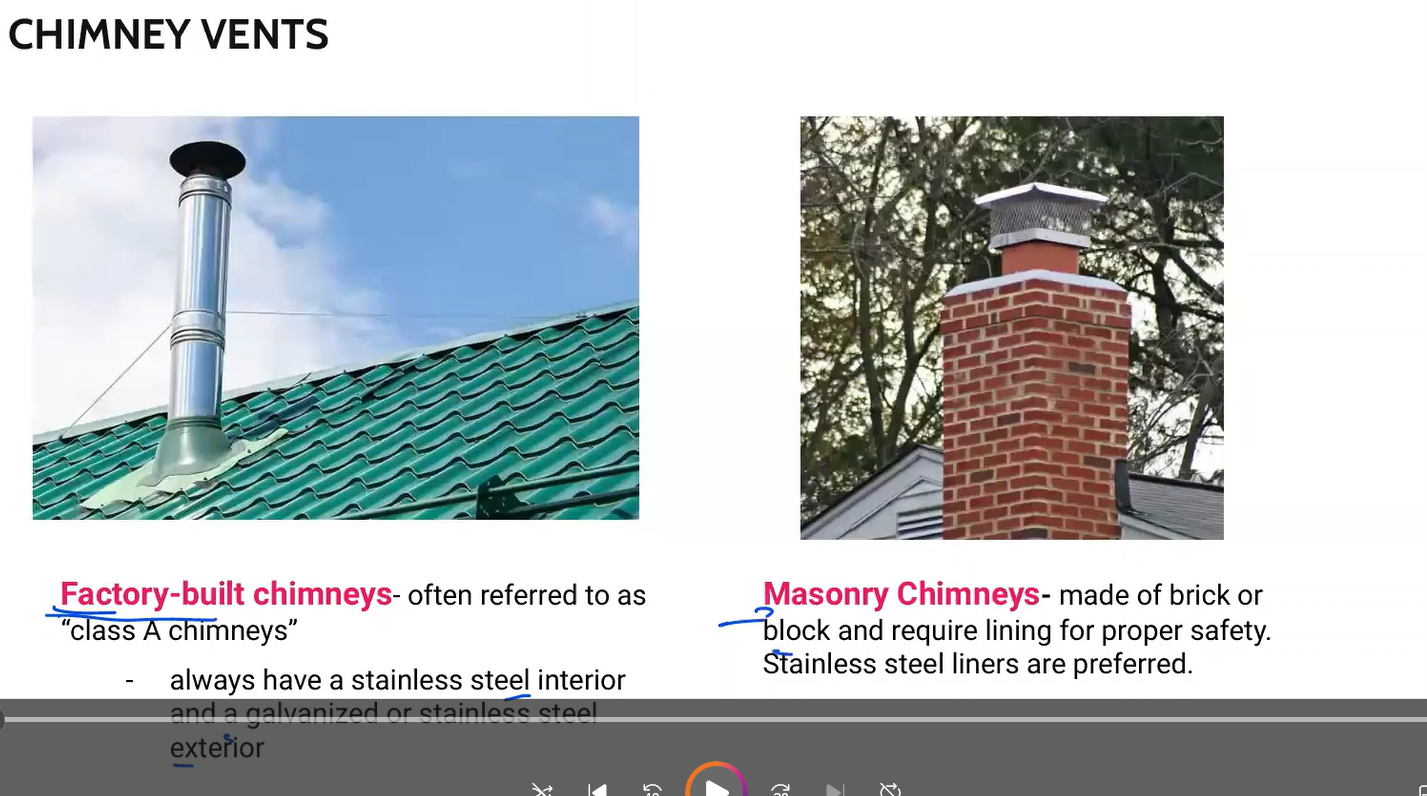
often referred to as “Class A chimneys”
always have a stainless steel interior and a galvanized or stainless steel exterior
Factory-built chimneys
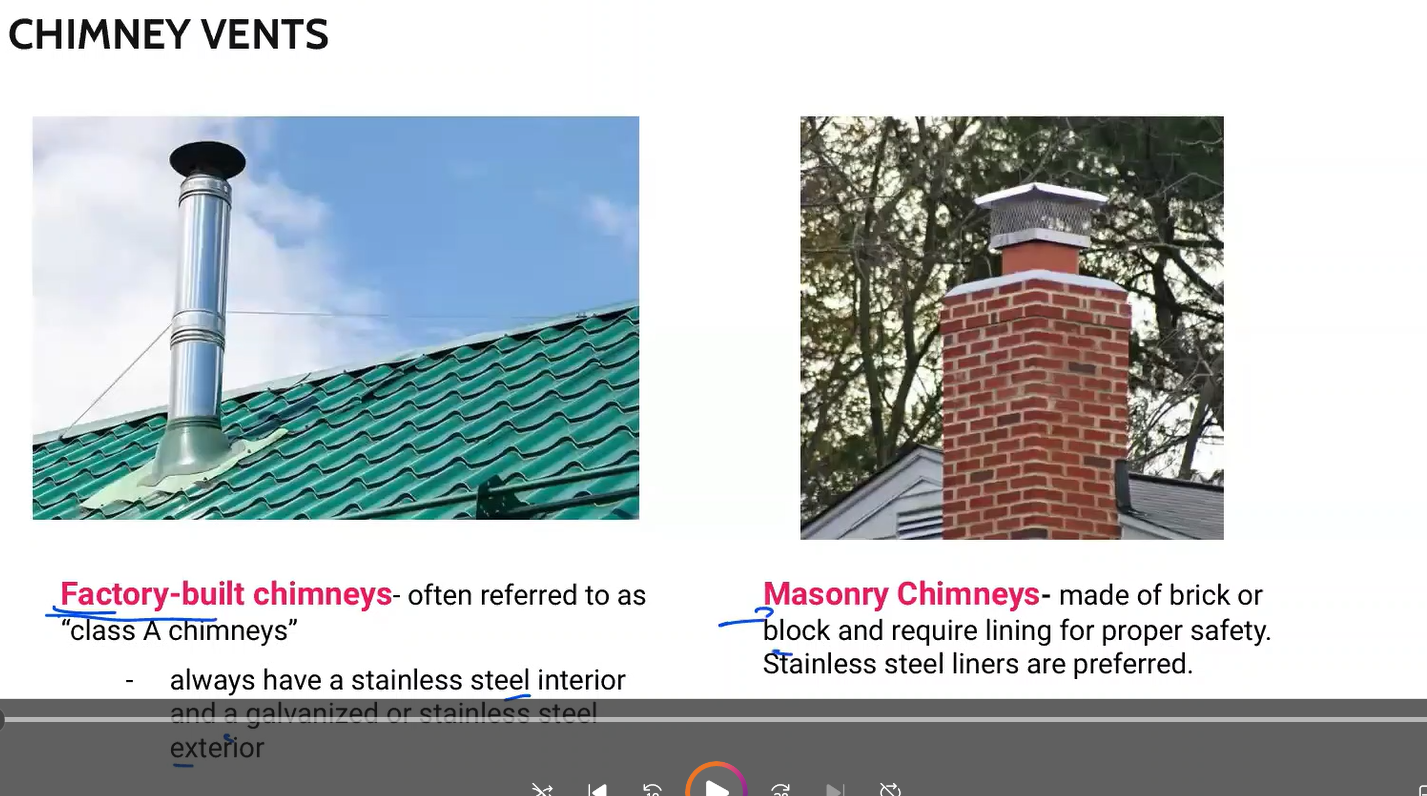
Made of brick or block and require lining for proper safety. Stainless steel liners are preferred.
Masonry Chimneys
Pipe Colors
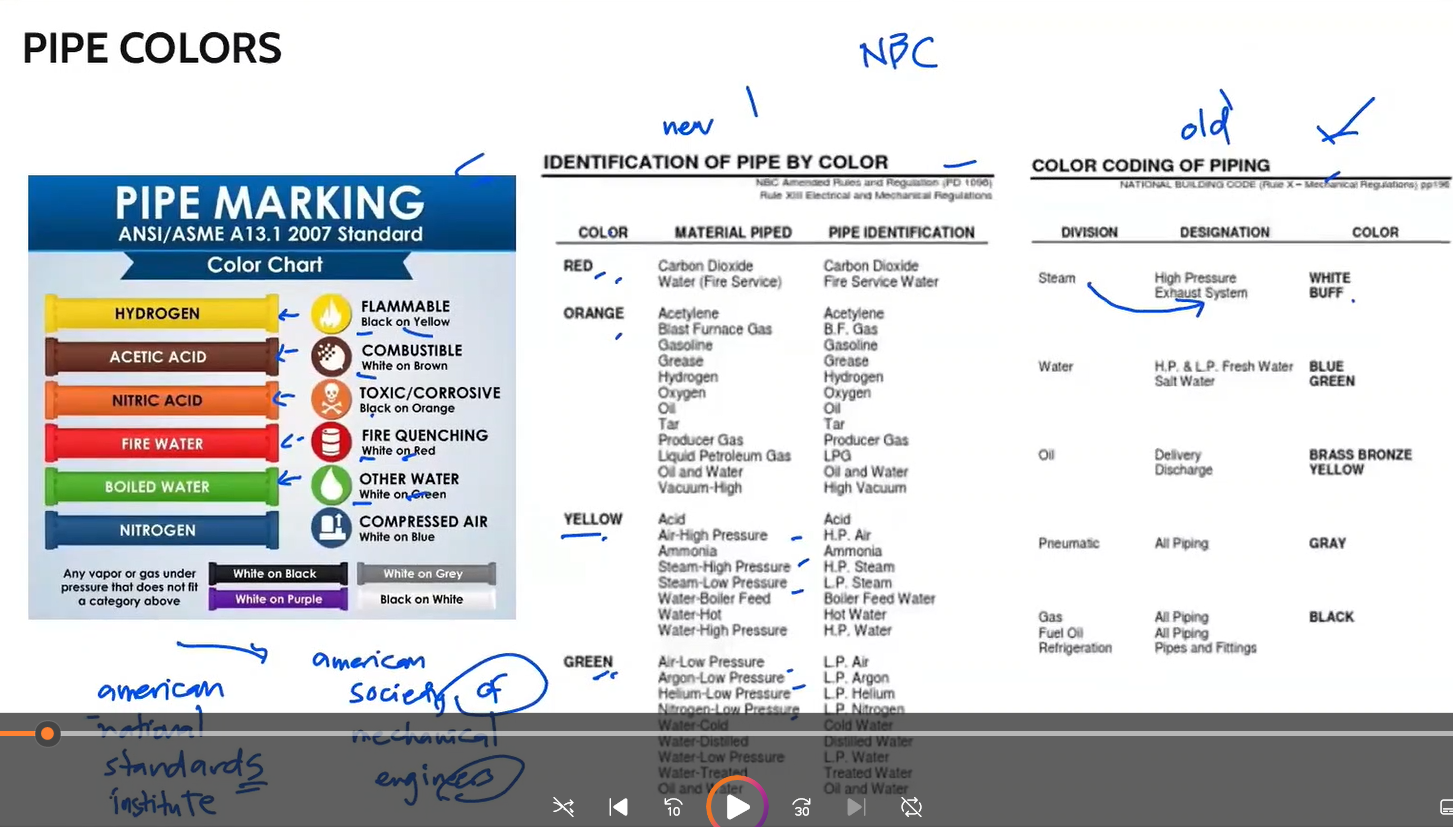
Pipe colors for gas pipe
a. yellow
b. black
c. Violet
d. Blue
a. yellow

The common pipe material used for in-house water system.
a. BI pipe
b. CI pipe
c. GI pipe
d. AC pipe
c. GI pipe

A red spiral line painted on a pipe section identifies the pipe as______.
a. PPR
b. Wrought Iron Pipe
c. Copper Pipe
d. Asbestos Cement Pipe
b. Wrought Iron Pipe

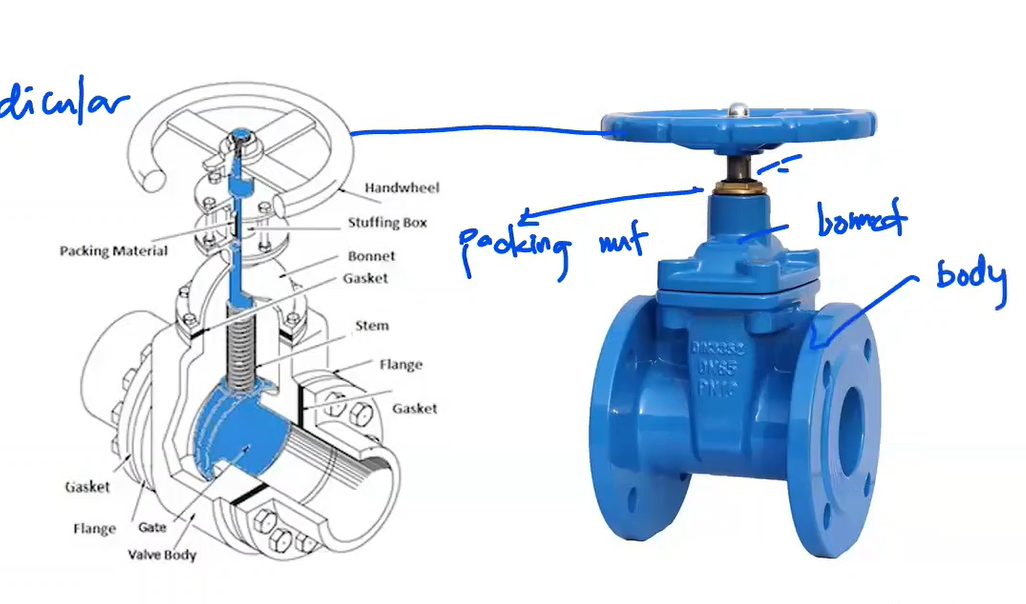
used to completely close or completely open the line but not to control the flow
Gate Valve
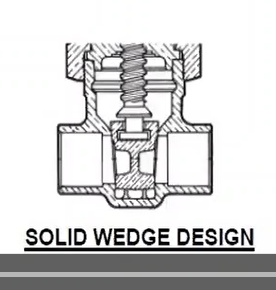
Type of gate valve: a single tapered disc thin at the bottom and thicker at the top
Solid-wedge
Type of gate valve: closes in the same manner as the wedged type; its parallel faces drop in a vertical position and forced apart by the disc spreader.
Double-disc
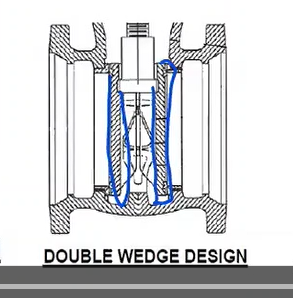
Type of gate valve: a compact design with body guided, two piece gates that provide reliable operation and sealing.
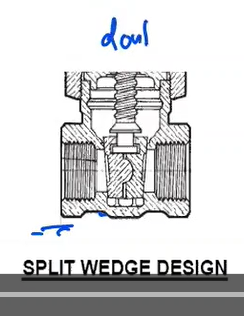
Split-wedge
Actuated by a stem screw, and hand wheel that calls for throttling;
-much more resistant to flow that gate valve
Globe Valve

3 types of gate valve
Solid-wedge
Double-disc
Split-wedge
3 types of globe valve
Conventional disc
Plug-type
Composition disc
-has a pressure-tight bearing between the disc and the seat recommended for cold water and any temperature service
-commonly used for low pressure water
Conventional disc (ball disc)
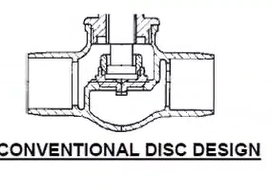
wide bearing surface producing good resistance to the cutting effects of scale, dirt and other kind of foreign matter found inside the pipe.
Plug-type
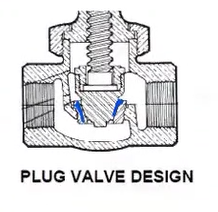
-does not fit into the seat opening, but over it, much as a bottlecap fits over the bottle opening.
-for steam and hot water
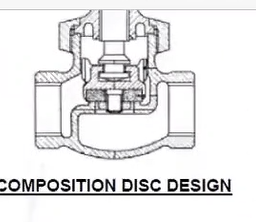
Composition disc
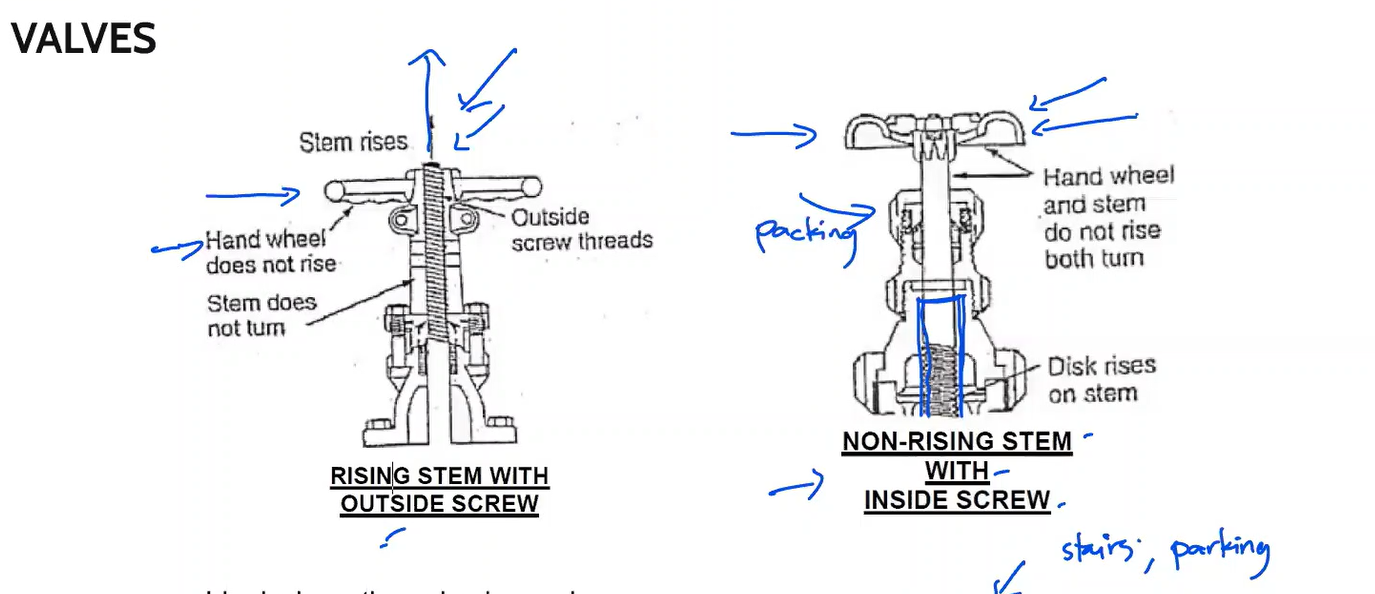
Ideal where the valve is used infrequently and the possibility of sticking constitutes a hazard, such as in a fire protection system.
Rising stem with outside screw
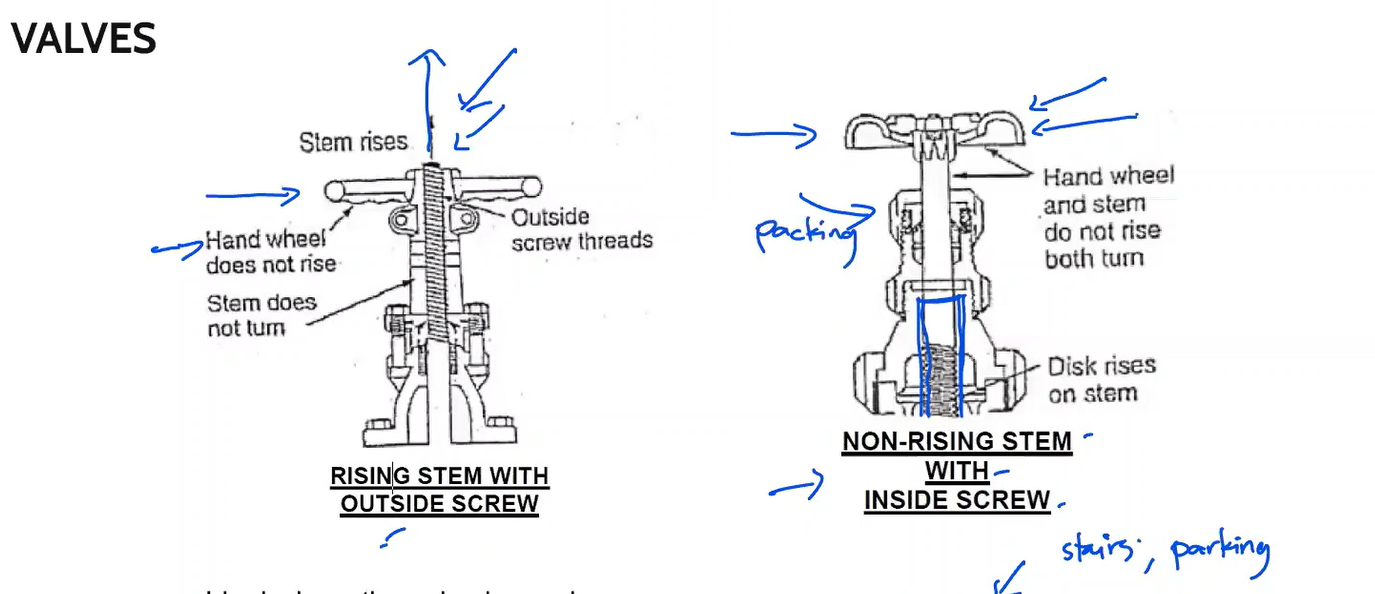
Ideal where headroom is limited. They generally are limited to use with gate valves.
Non-rising stem with inside screw
The simplest and most common stem design for gate, globe, and angle valves.
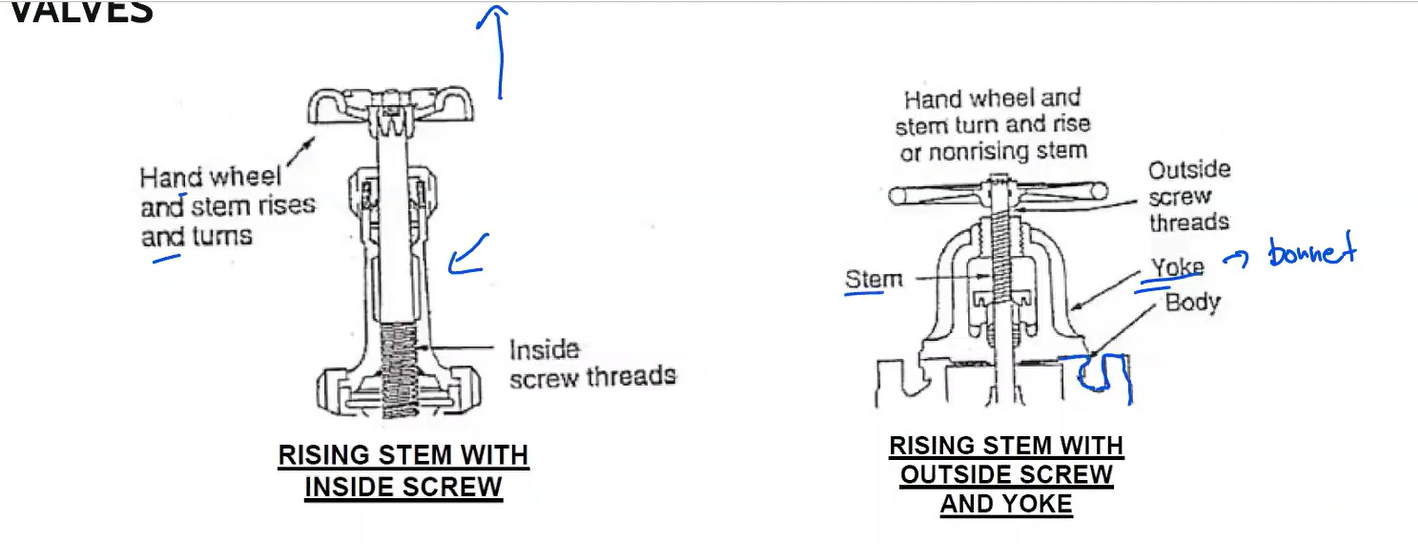
Rising stem with inside screw
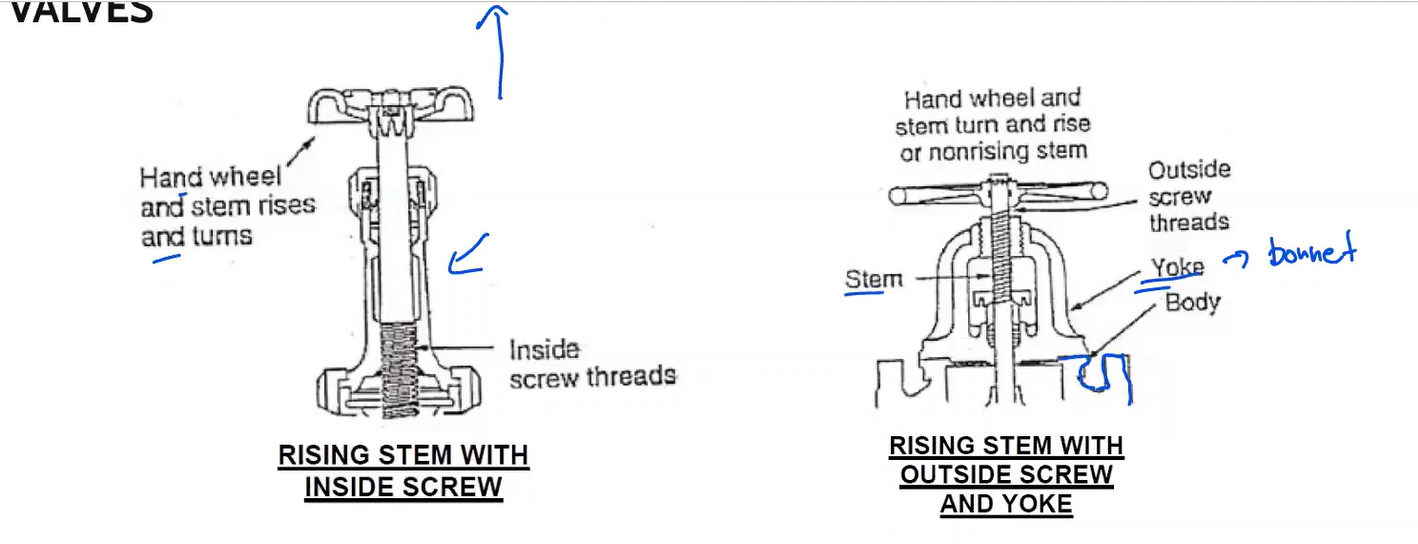
The operating threads of the system are outside the valve housing, where they may be lubricated easily and do not come into contact with the fluid flowing through the valve.
Rising stem with outside screw and yoke
Operates in the same manner as the globe valve; used in making 90° turn in a line to reduce the number of joints.
Angle valve

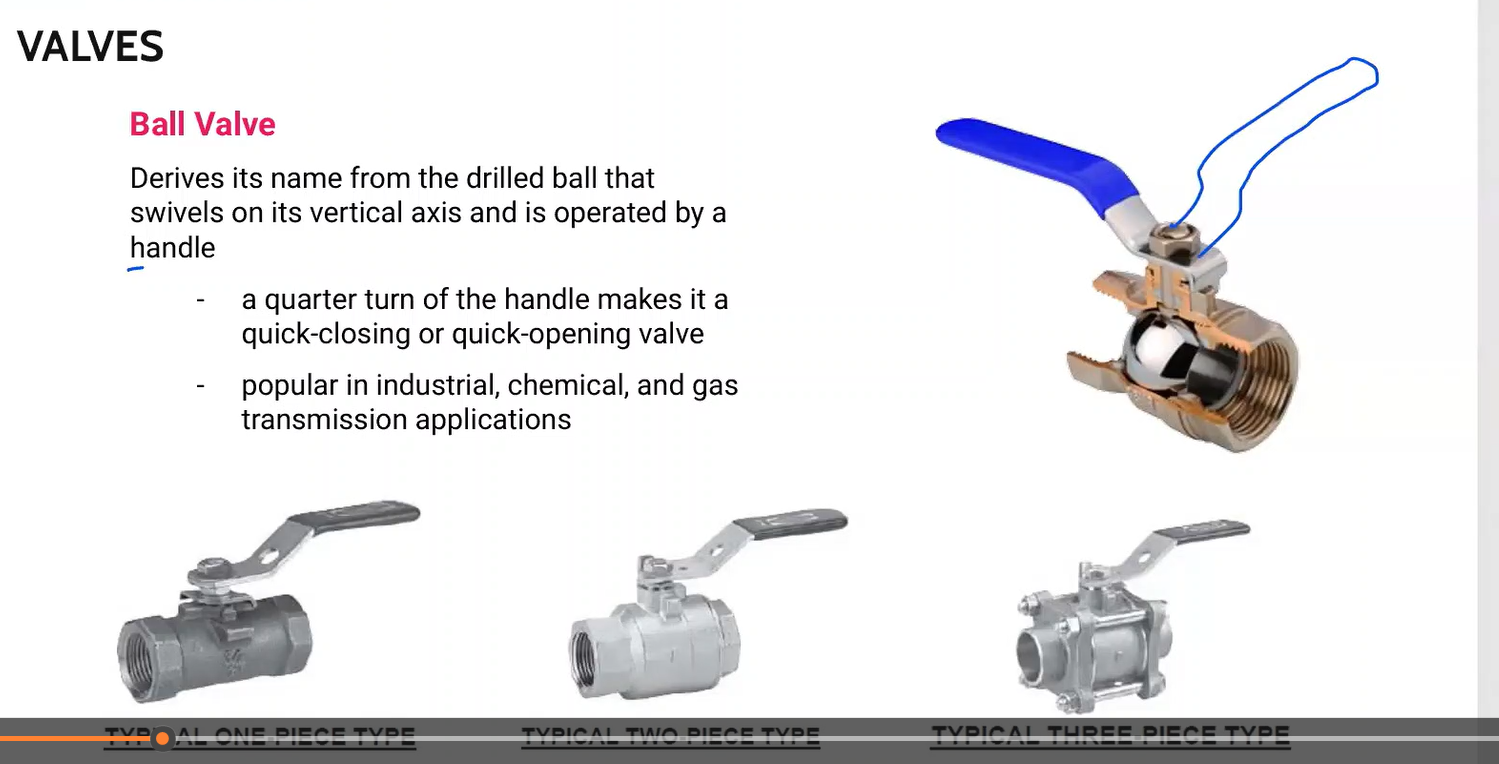
Derives its name from the drilled ball that swivels on its vertical axis and is operated by a handle.
-a quarter turn of the makes it a quick-closing or quick-opening valve
-popular in industrial, chemical, and gas transmission applications
Ball Valve
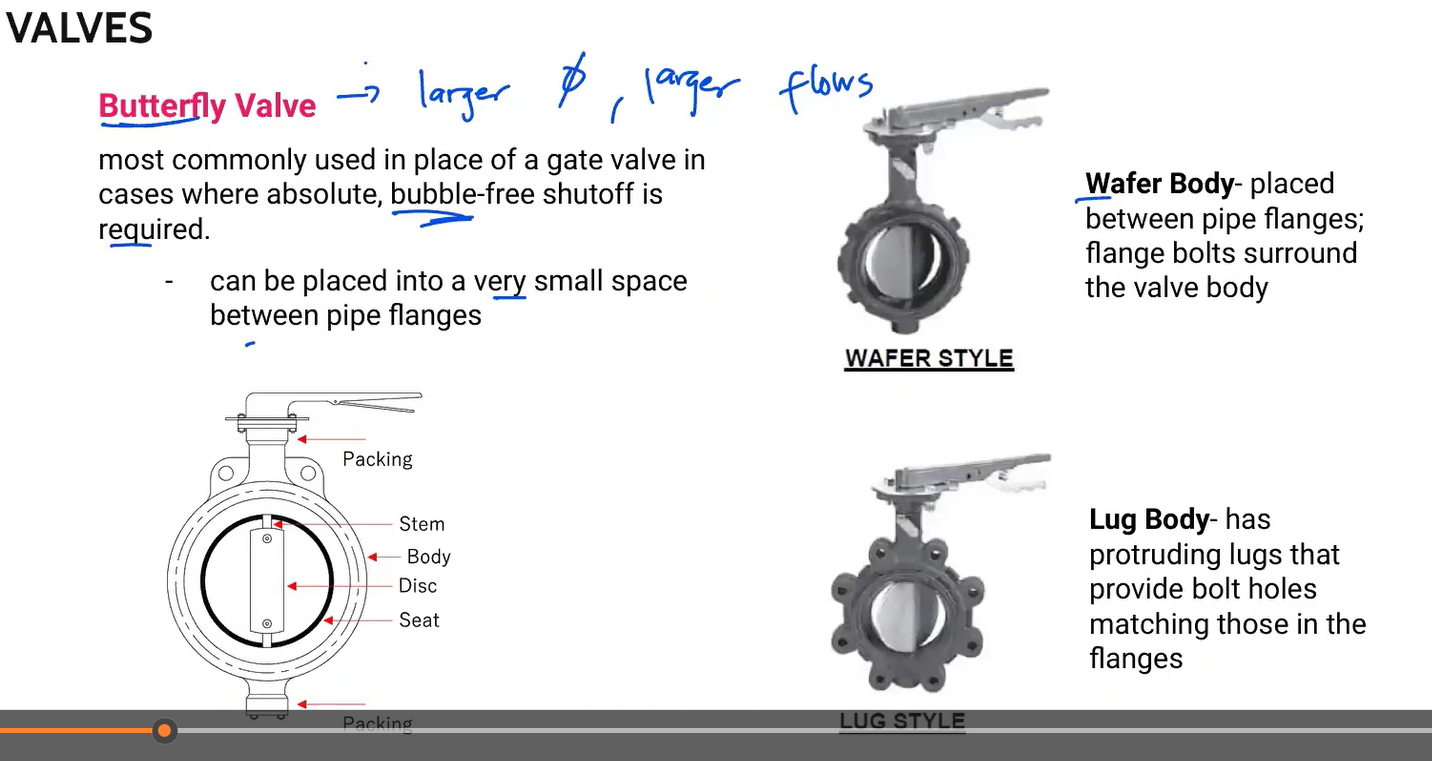
most commonly used in place of a gate valve in cases where absolute, bubble-free shutoff is required.
-can be placed into a very small space between pipe flanges
-for larger diameters and flows; fire pro
Butterfly valve
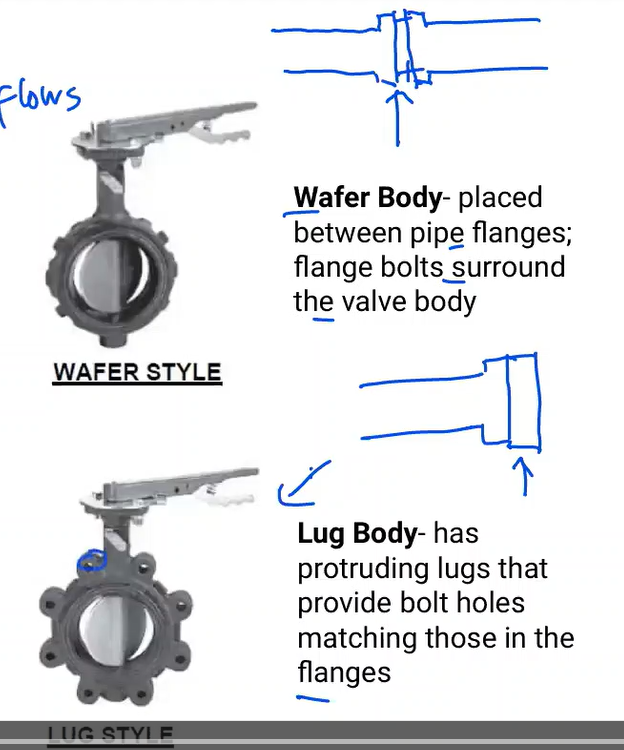
2 designs of butterfly valve
wafer body
Lug body
placed between pipe flanges; flange bolts surround the vave body
Wafer body
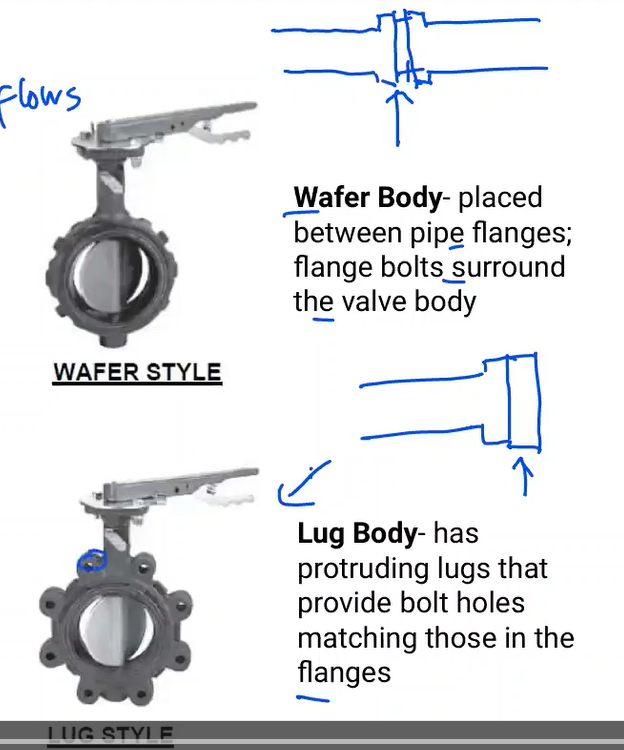
has protruding lugs that provide bolt holes matching those in flanges
Lug Body
quarter-turn design similar to a ball valve, with a ball replaced by a plug
-requires a higher operating torque for closure
Plug valve
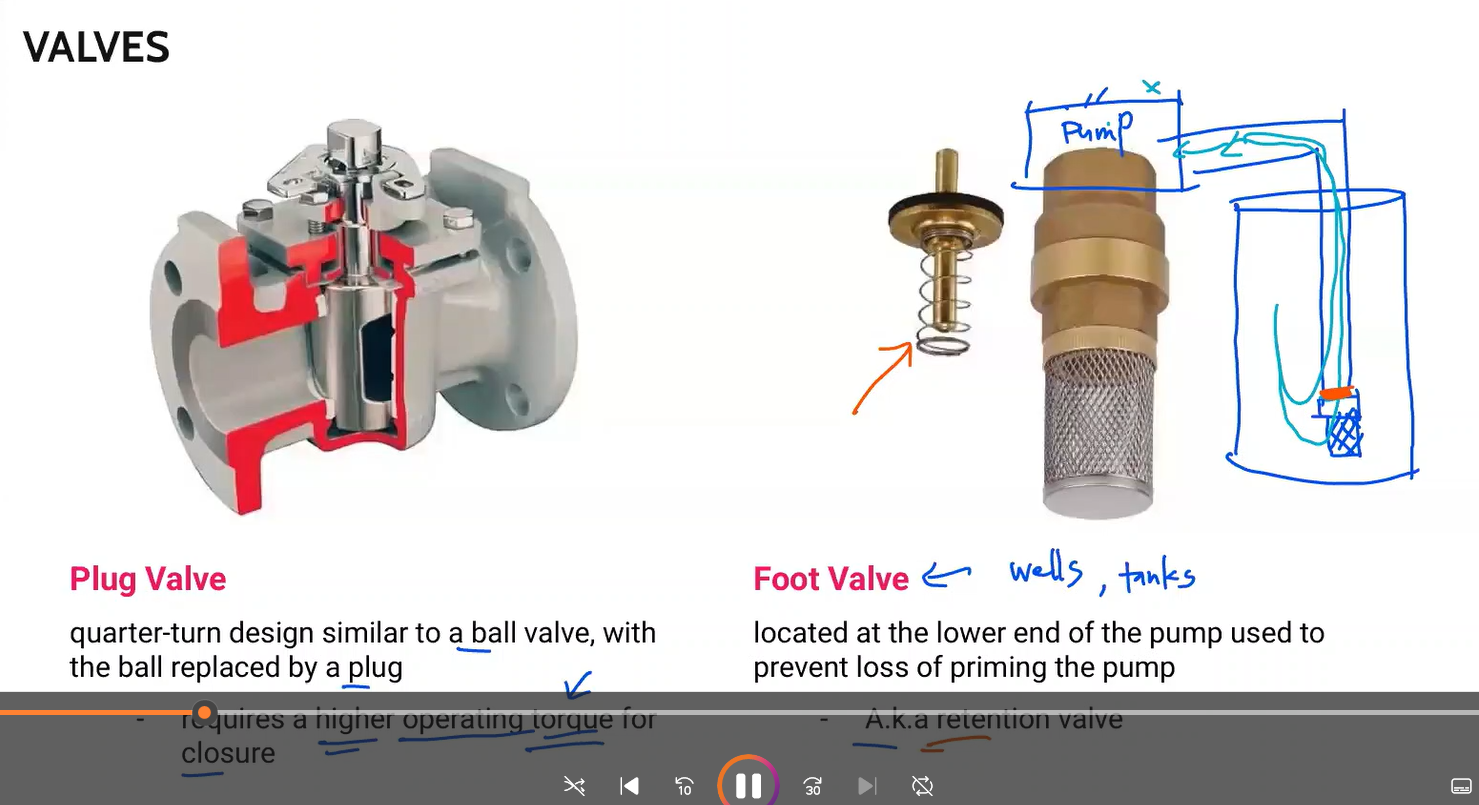
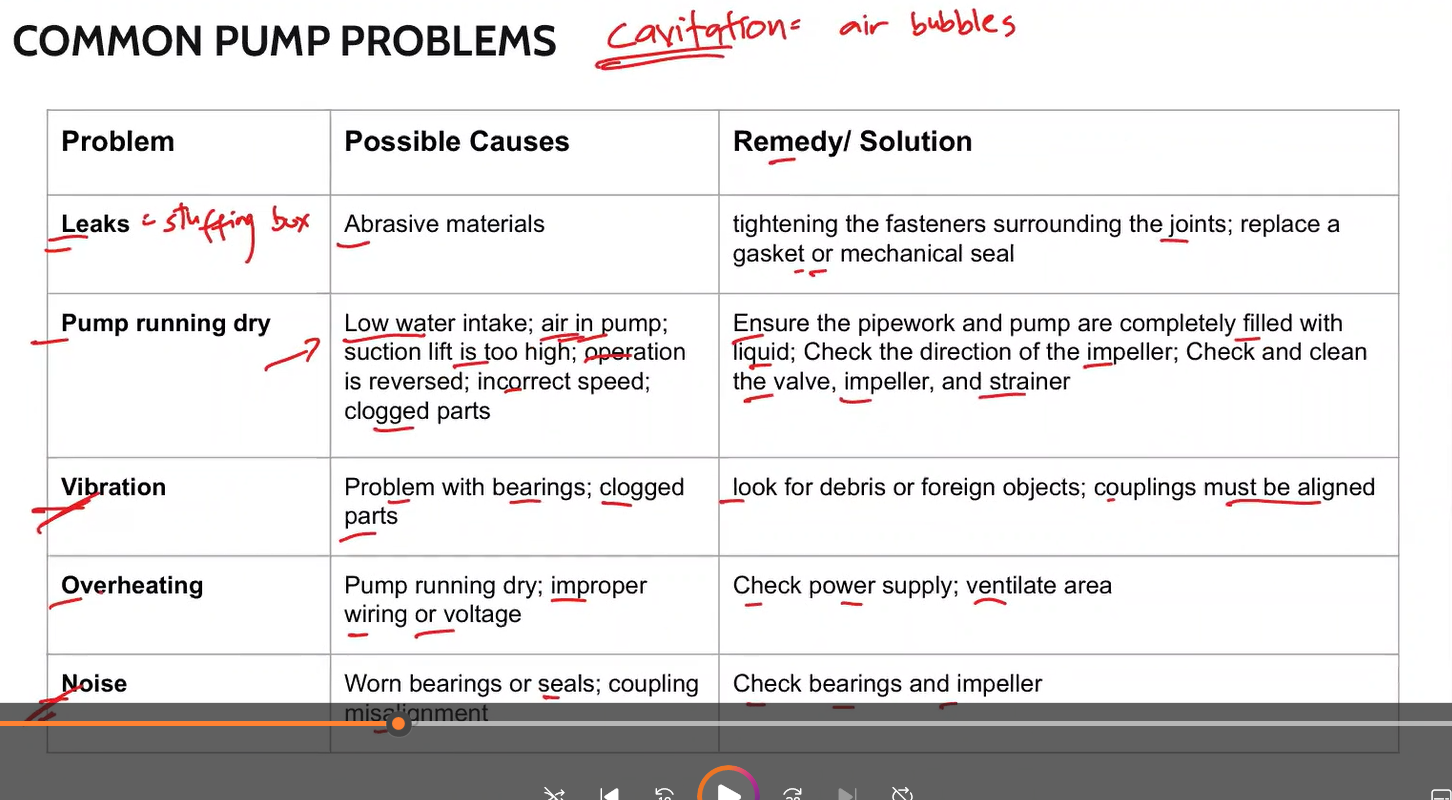
Located at the lower end of the pump used to prevent loss of priming the pump
-aka retention valve
Foot valve

Main function is to prevent the reversal flow of gas or liquid in the line.
-Principally used in industrial piping connections for gas, water, steam, air, and other general vapor services.
Check valve
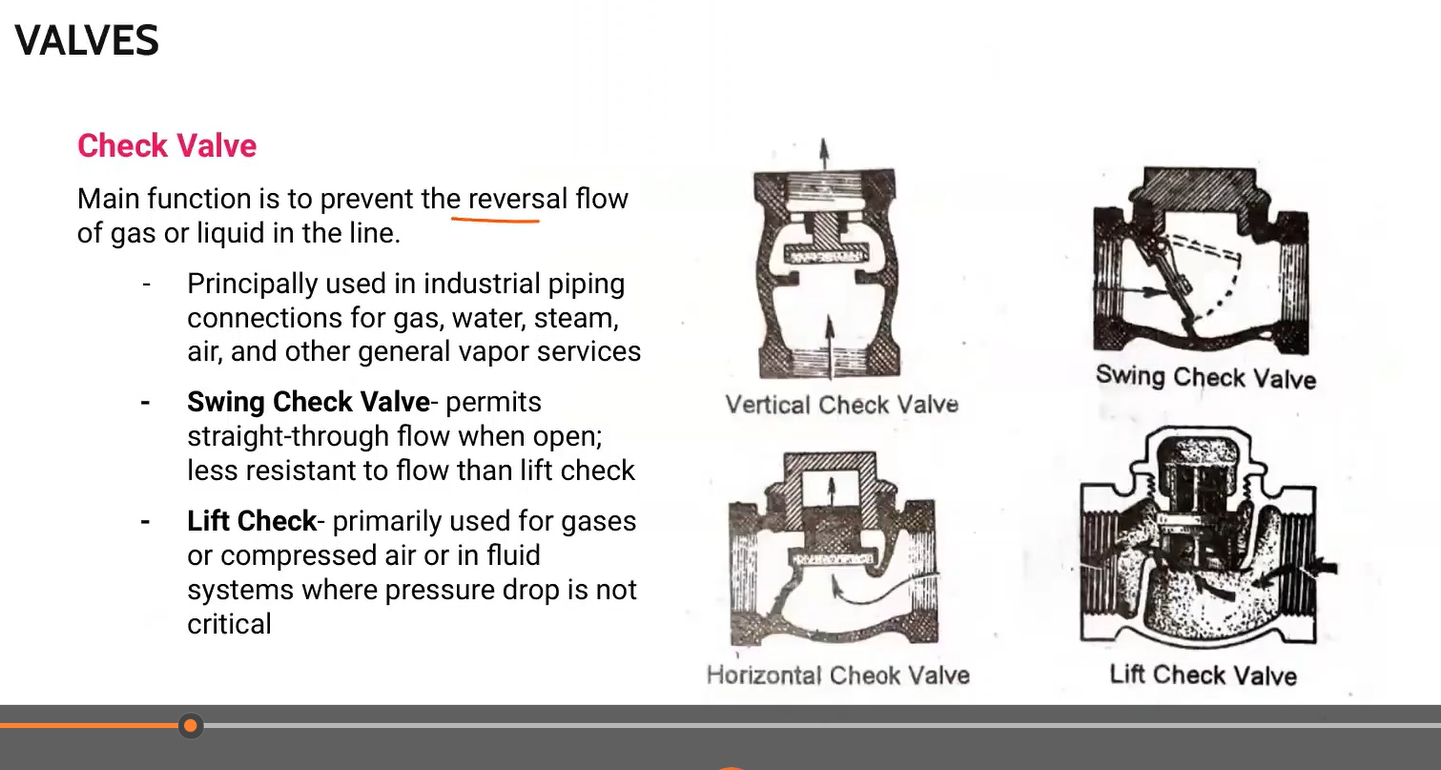
Type of check valve: Permits straight-through flow when open; less resistant to flow than lift check
Swing check valve
Type of check valve: primarily used for gases or compressed air or in fluid systems where pressure drop is not critical.
Lift check
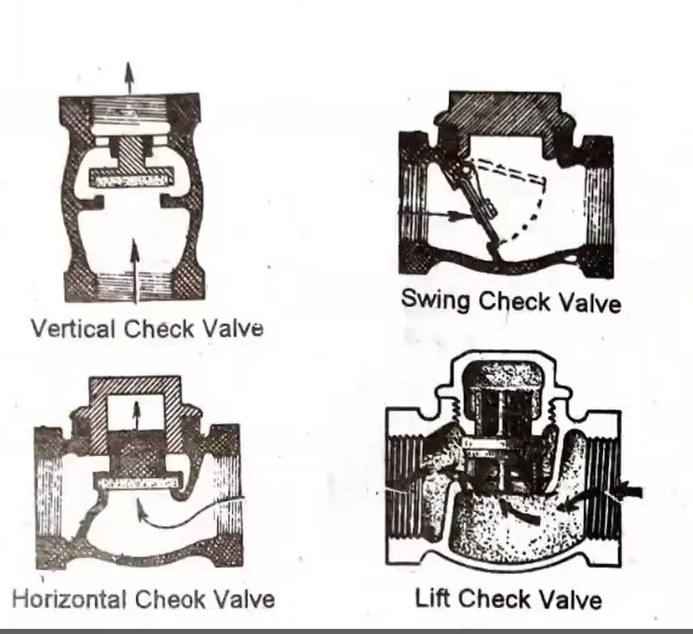

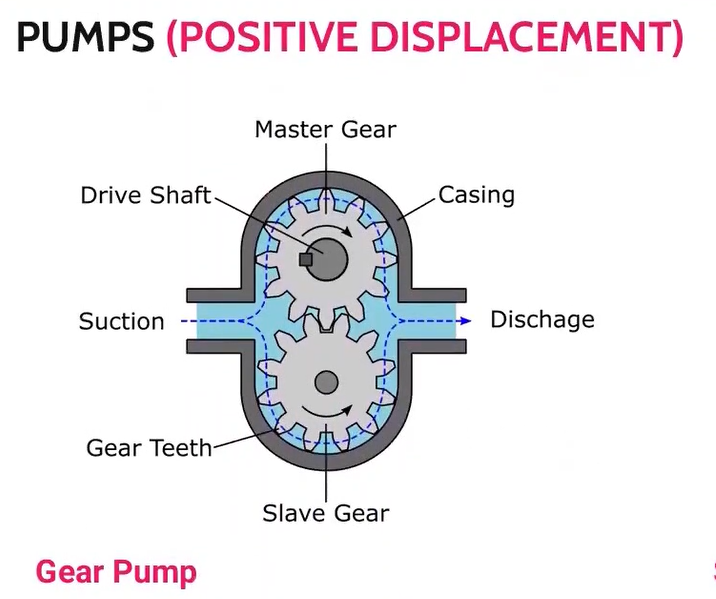
familirize
a simple kind of rotary pump that a pair of gears push the liquid.
-commonly used for piping high viscosity fluids such as oil, paints, resins, or foodstuffs.
Gear Pump
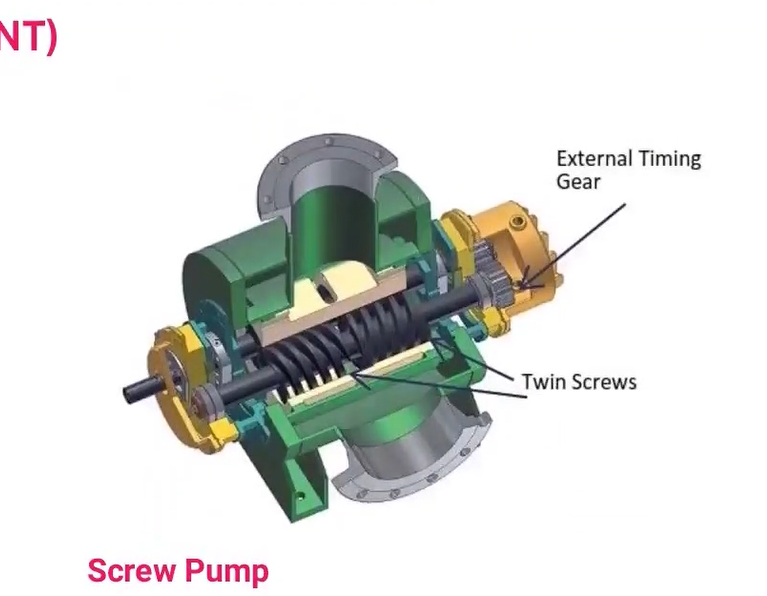
Two screws turning against each other for pumping the liquid.
-use one or several screws to move fluid solids or liquids along the screw(s) axis.
Screw Pump
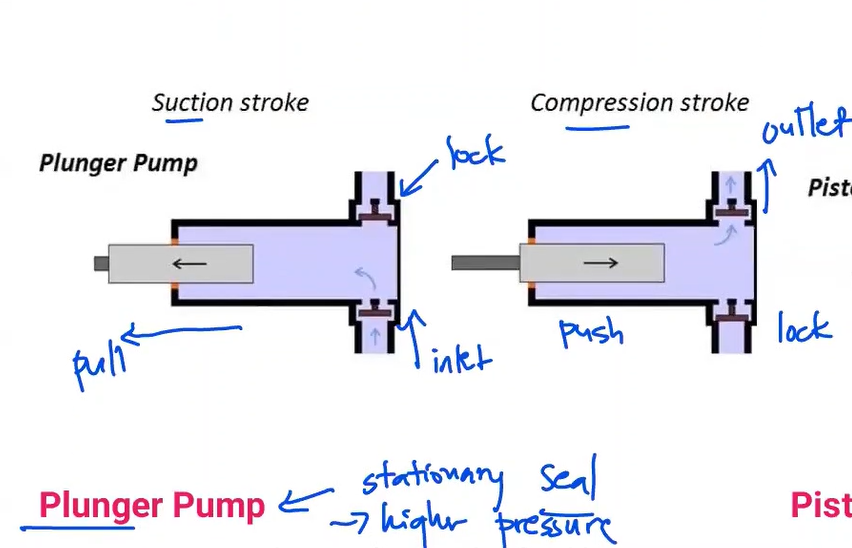
A reciprocating plunger forces the liquid by one or two open valves, blocked by suction on the way back
-have a stationary, high-pressure seal that is attached to the cylinder housing of the pump.
Plunger Pump
Simple tools for pumping small volumes of liquid or gel manually
-seal is connected to the piston
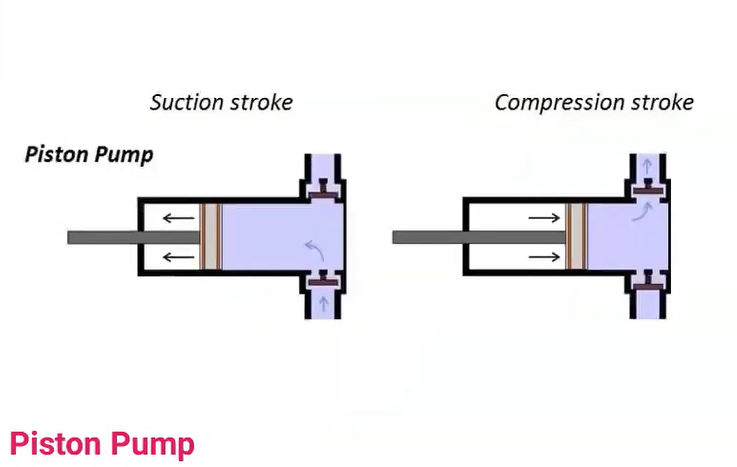
Piston pump

Centrifugal pump
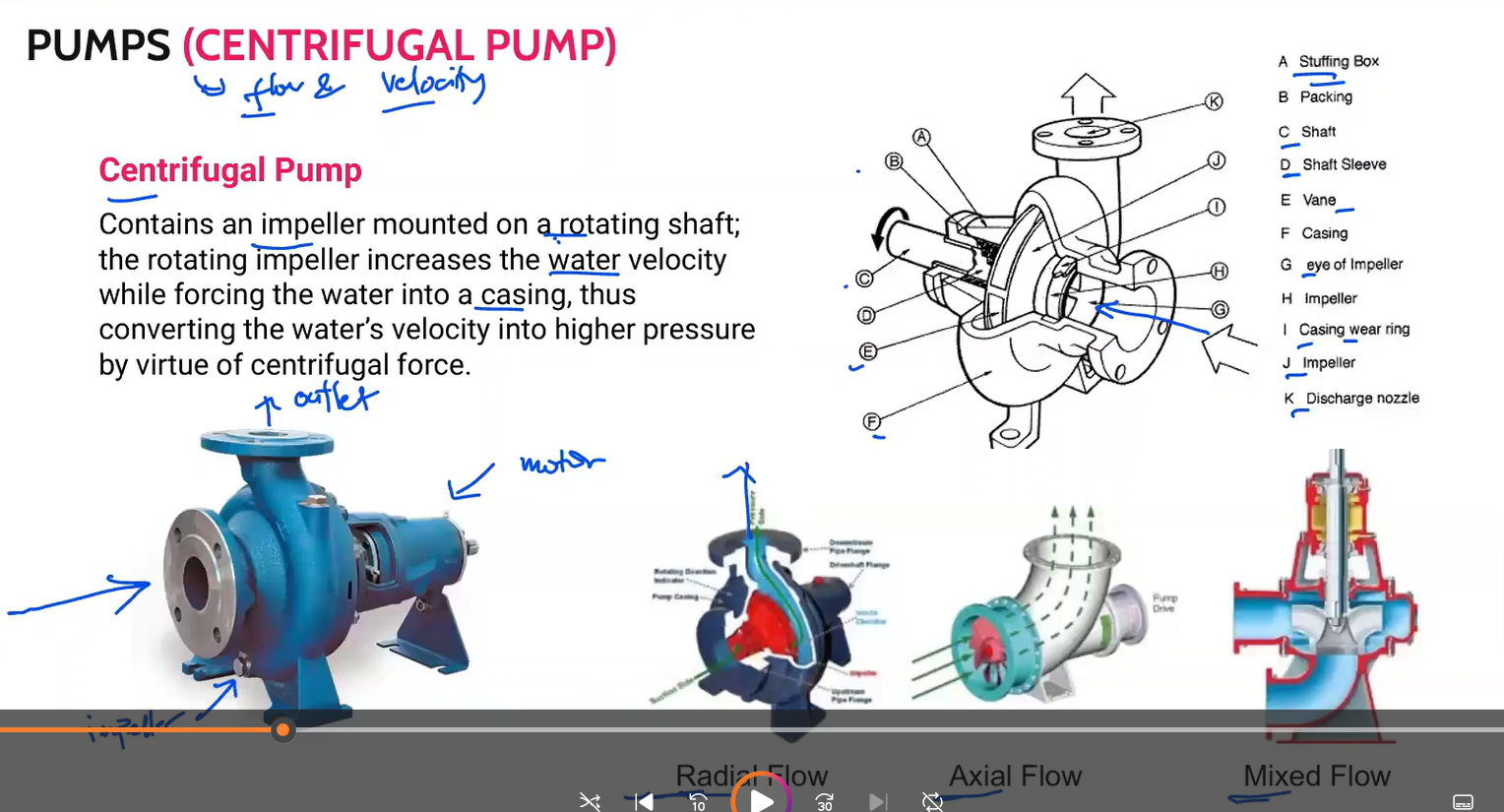
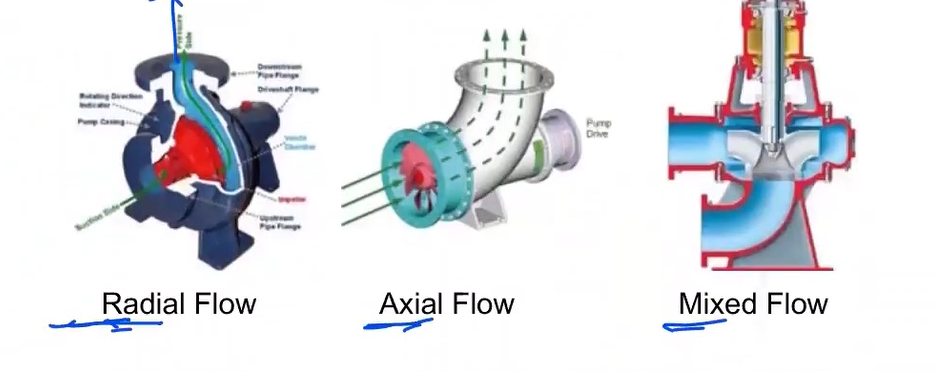
3 types of centrifugal pump
Radial flow
Axial flow
Mixed flow
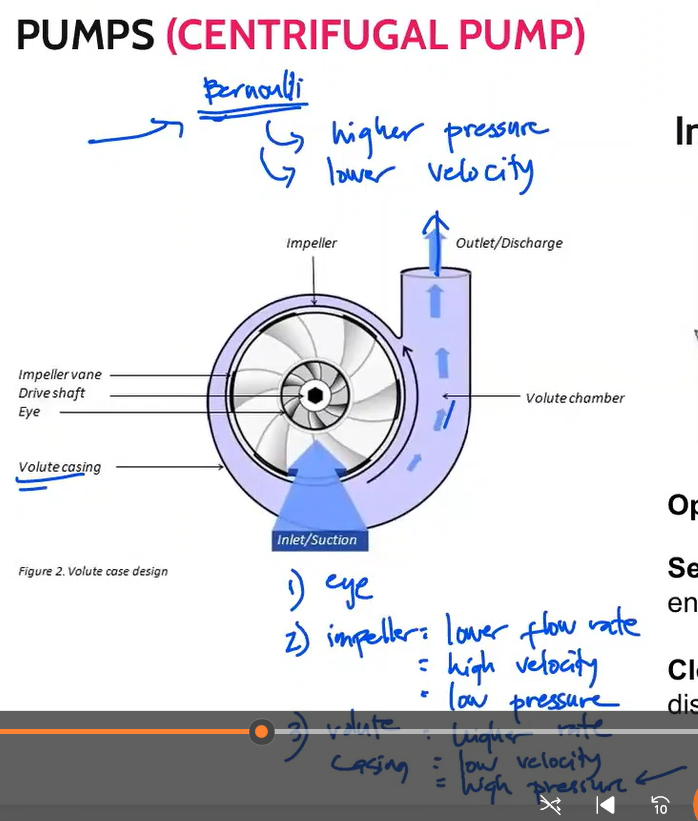
Familiarize impeller
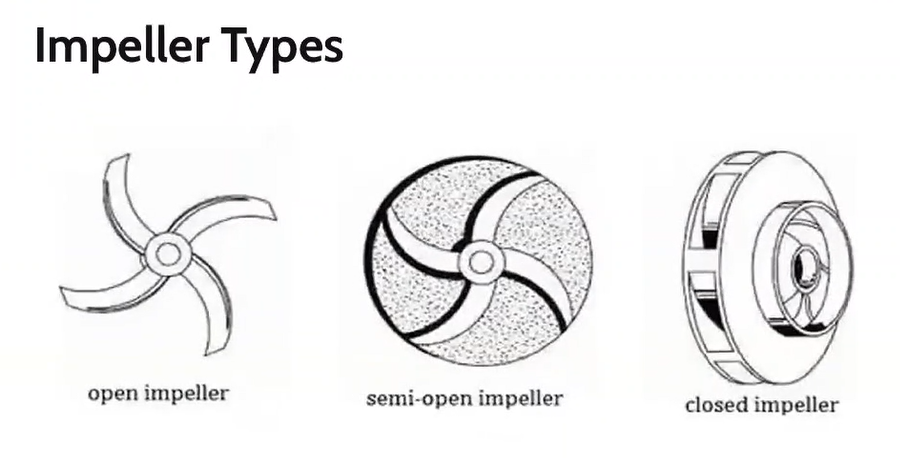
Types of impeller
Open impeller
Semi-open impeller
Closed impeller
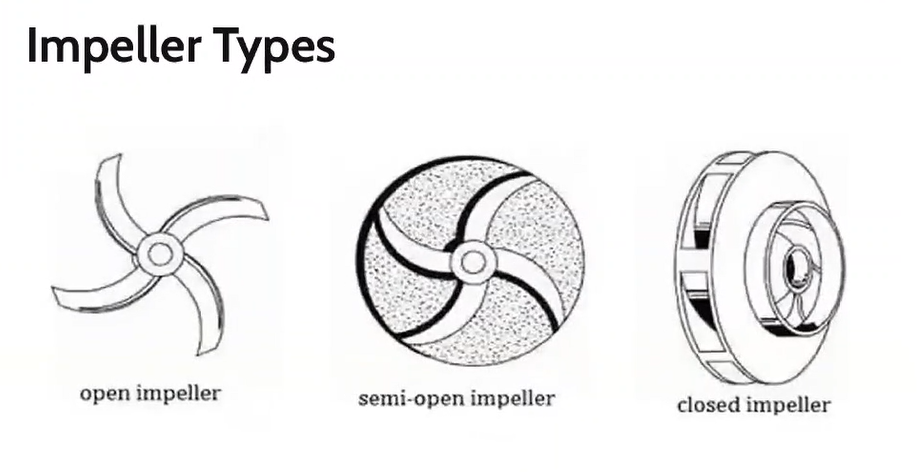
Type of impeller that have the vanes free on both sides
Open impeller
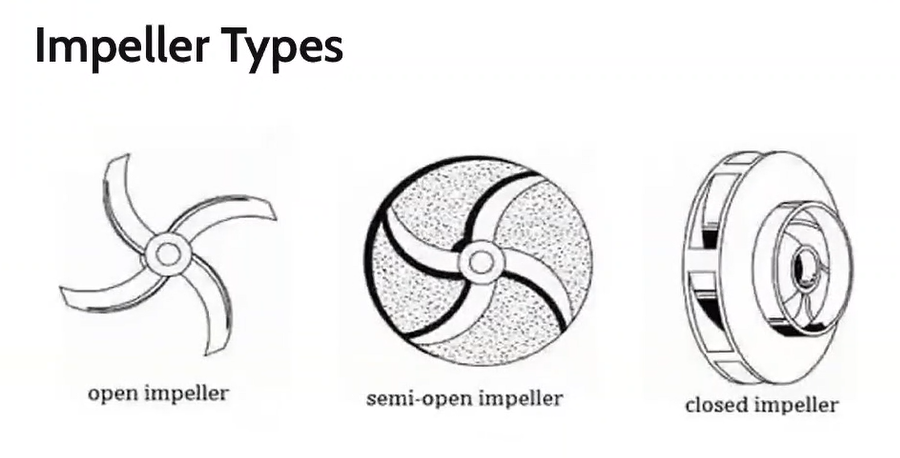
Type of impeller where the vanes are free on one side and enclosed on the other.
Semi-open impeller
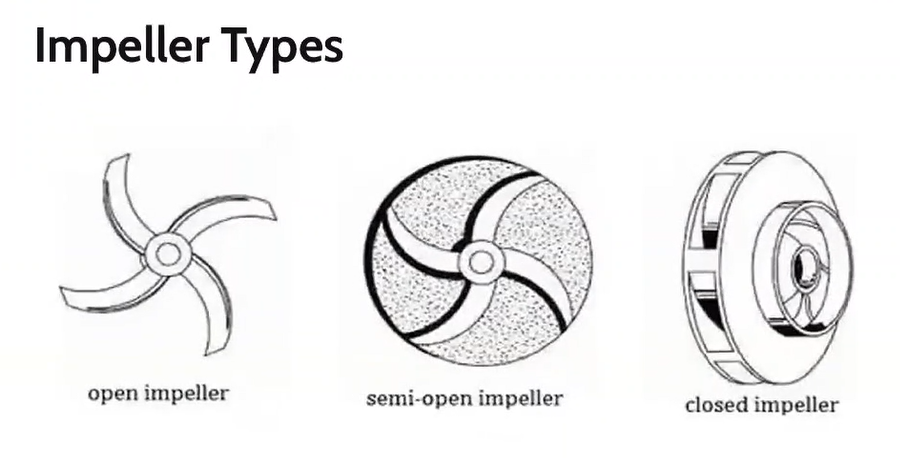
Type of impeller where the vanes are located between the two discs, all in a singe casting.
Closed impeller
centrifugal pumps whose hydraulic components (pump casing, impeller, diffuser element) are flooded by the fluid handled.
-motor runs a series of impellers which drive water up the pipe
Submersible pump

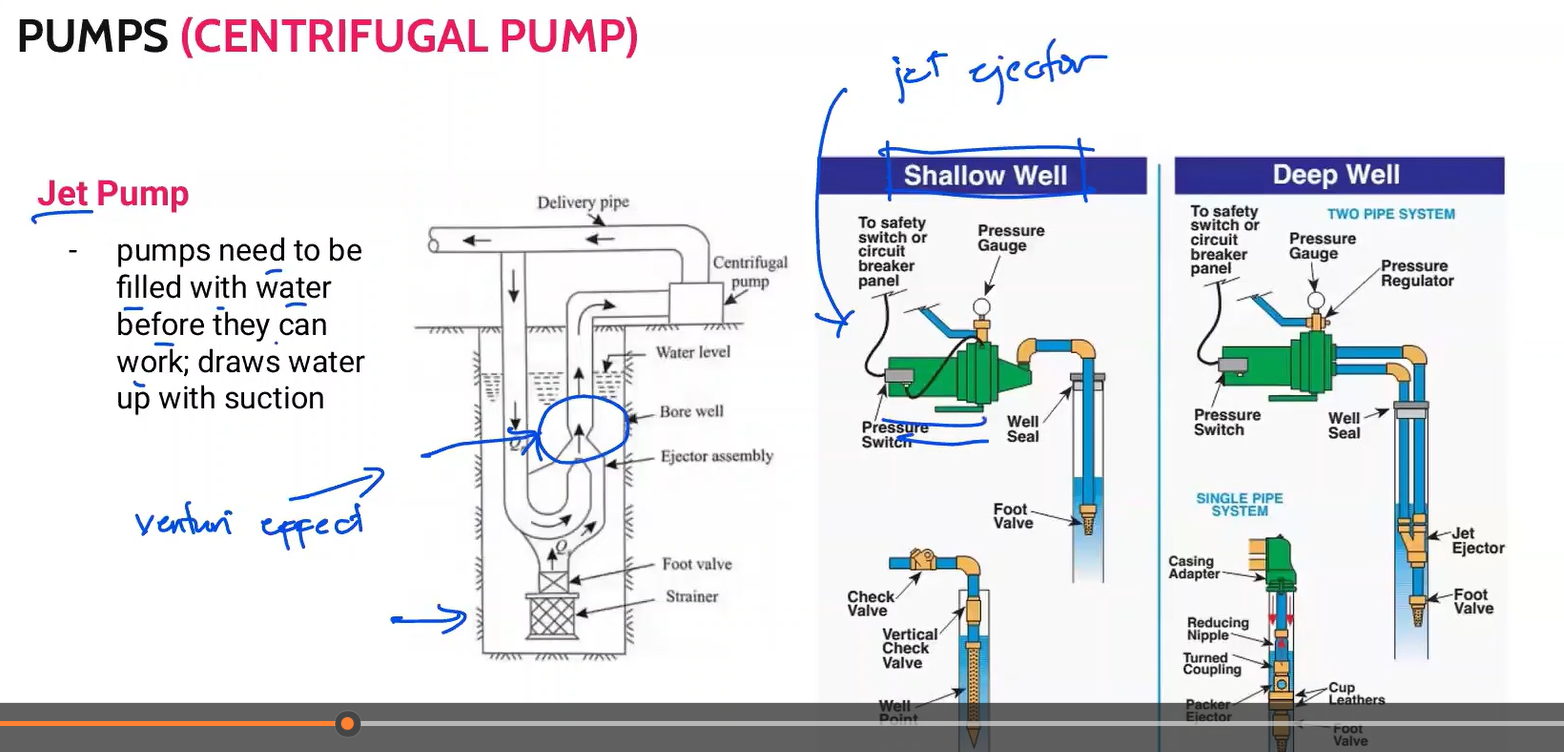
pump needs to be filled with water before they can work; draws water up with suction.
Jet pump
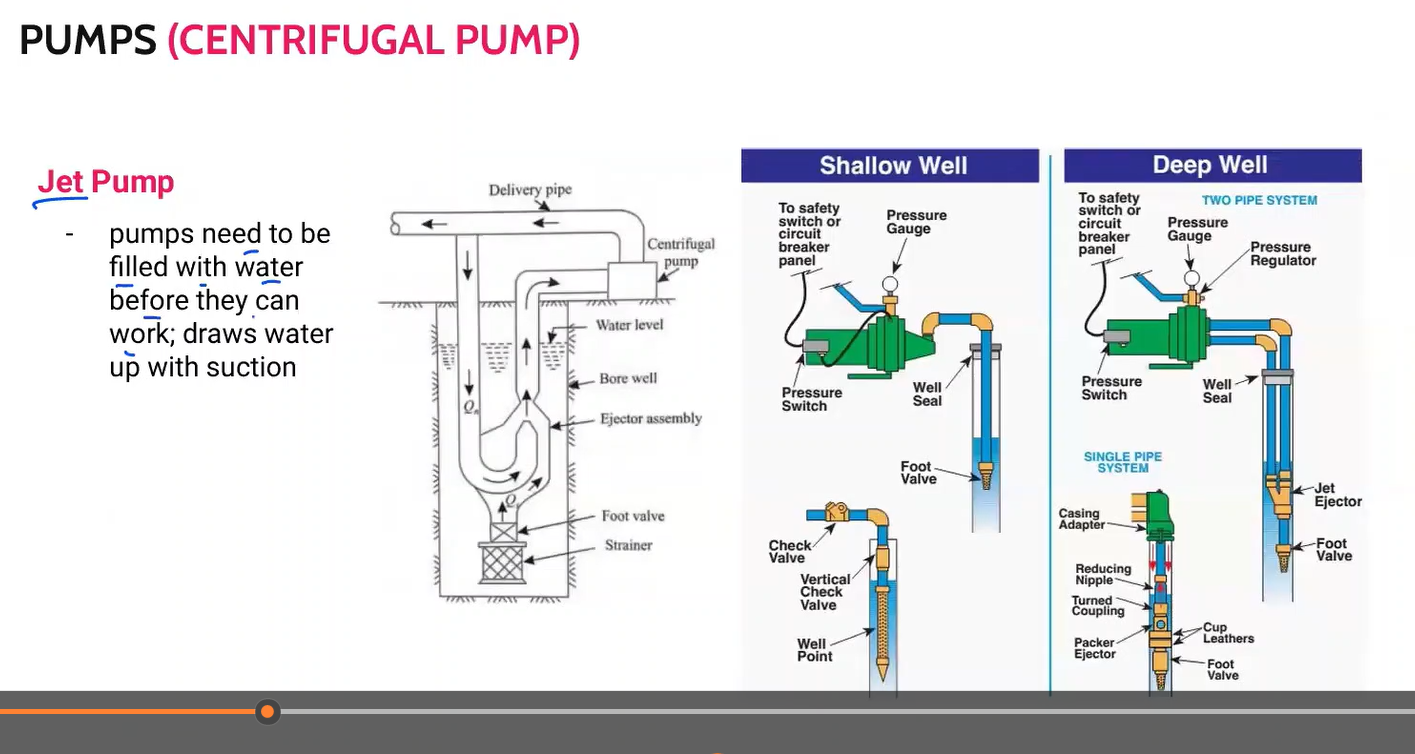
2 applications of jet pump
shallow well
deep well
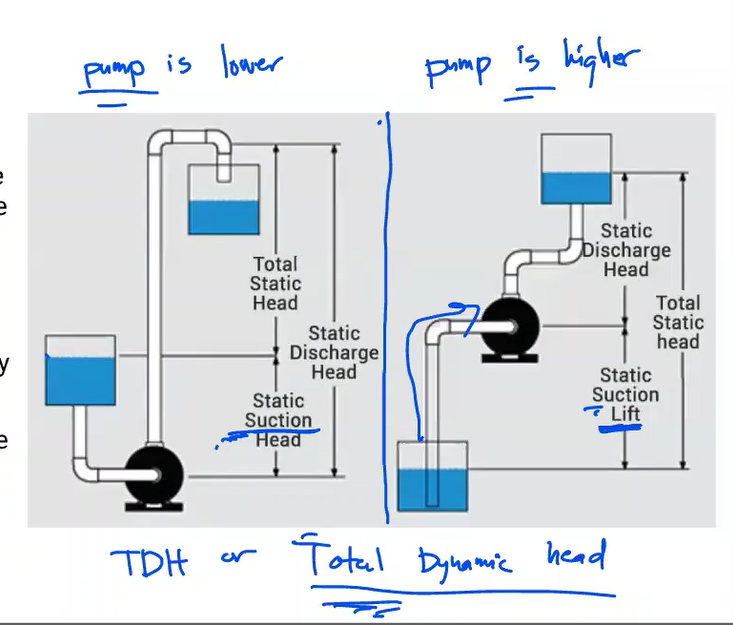
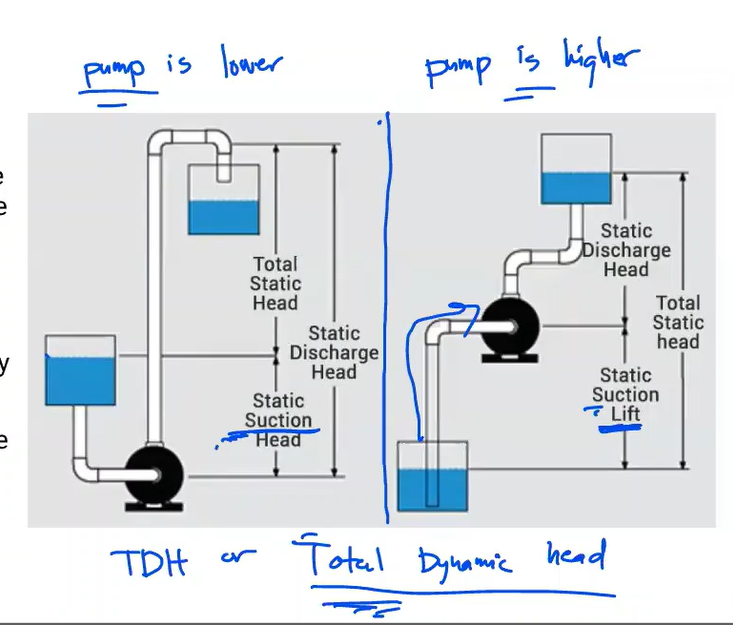
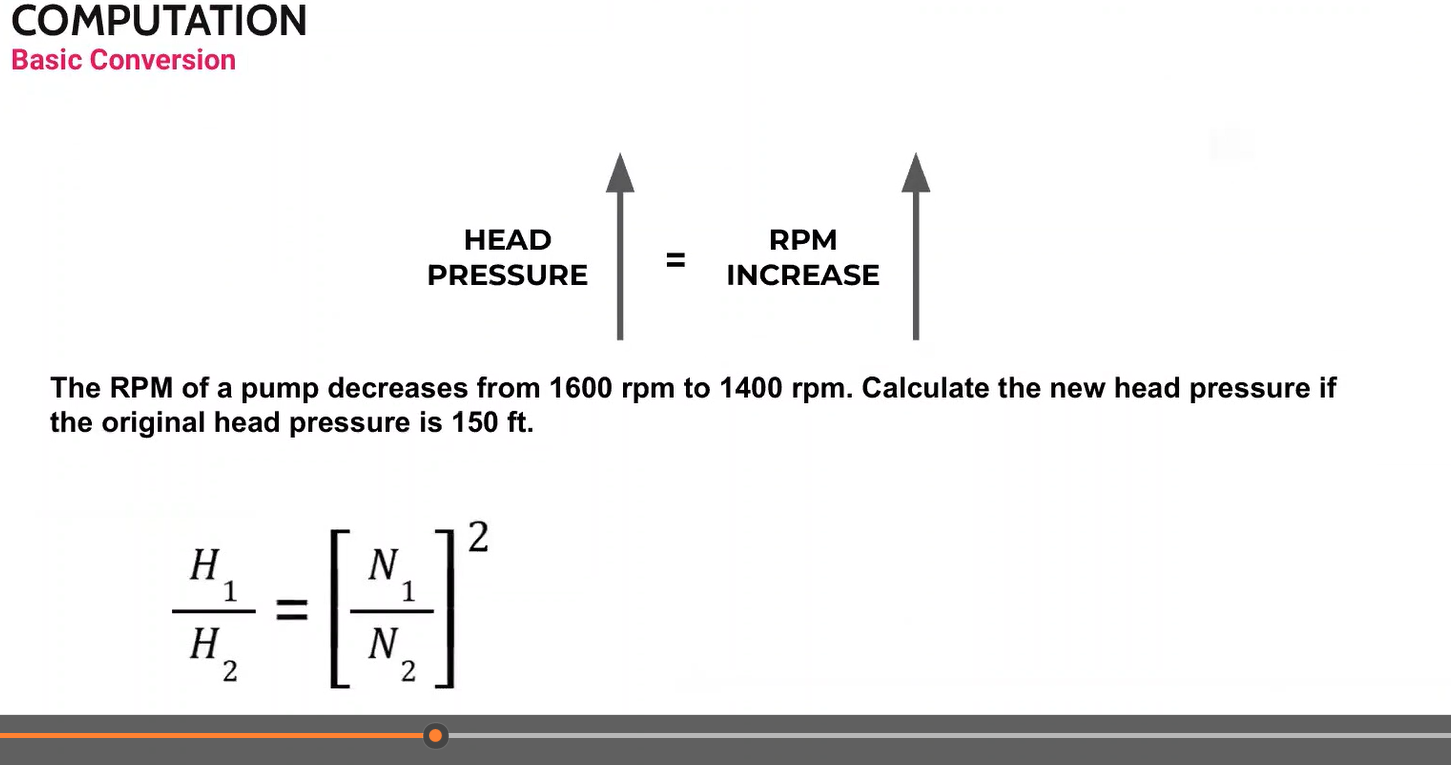
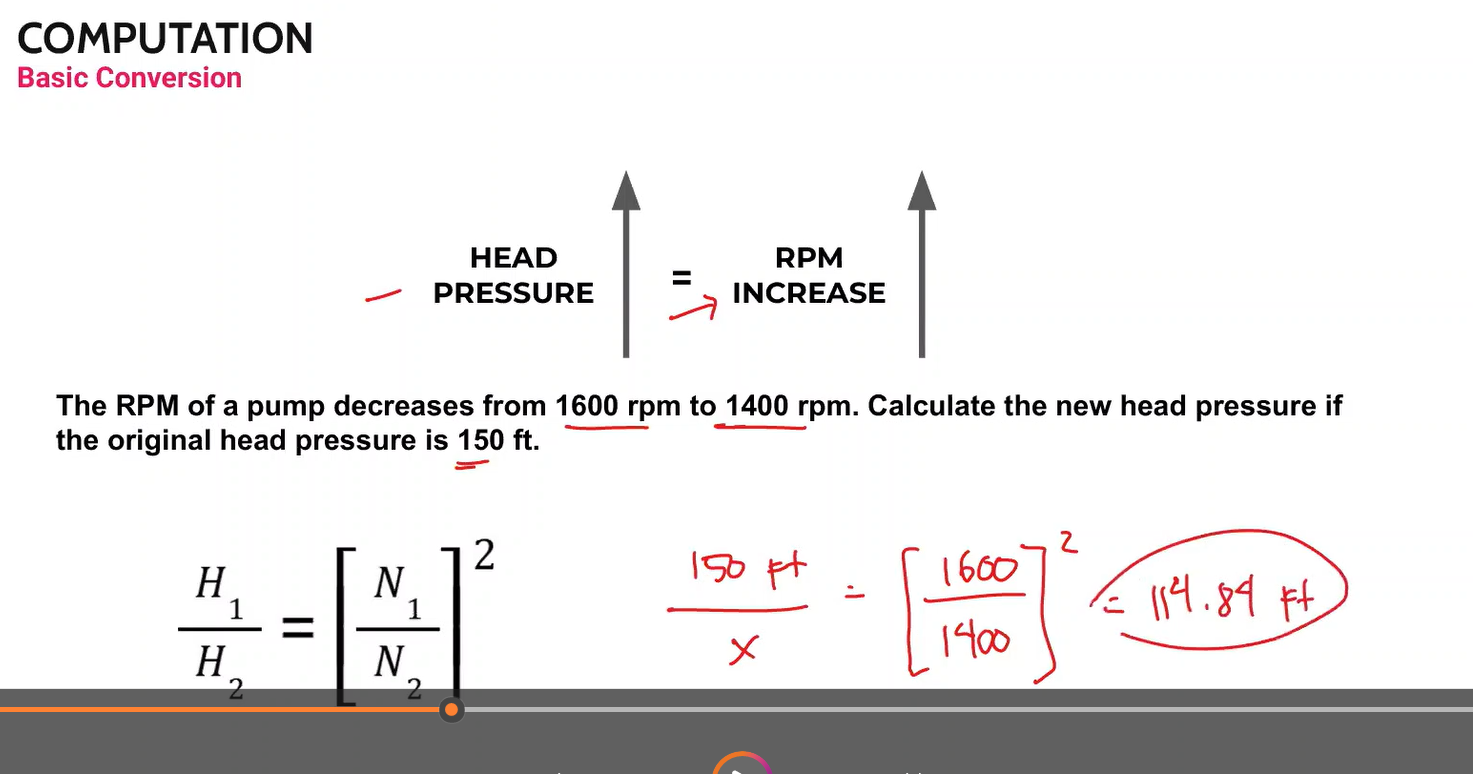
The energy of a fluid at any particular point of a flow stream per weight of the fluid. Units of measurement are generally in feet (meters)
Head
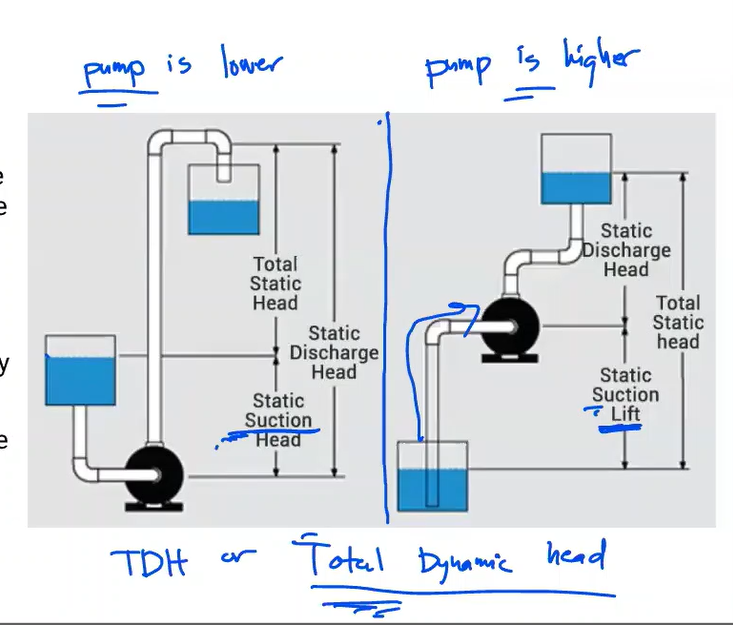
Elevation of water in a standpipe relative to the pipe centerline of a piping system. Any pressure gauge reading can be converted to static head if the density of liquid is known.
Static head
The velocity portion of head with its units converted to an equivalent static head.
Velocity Head
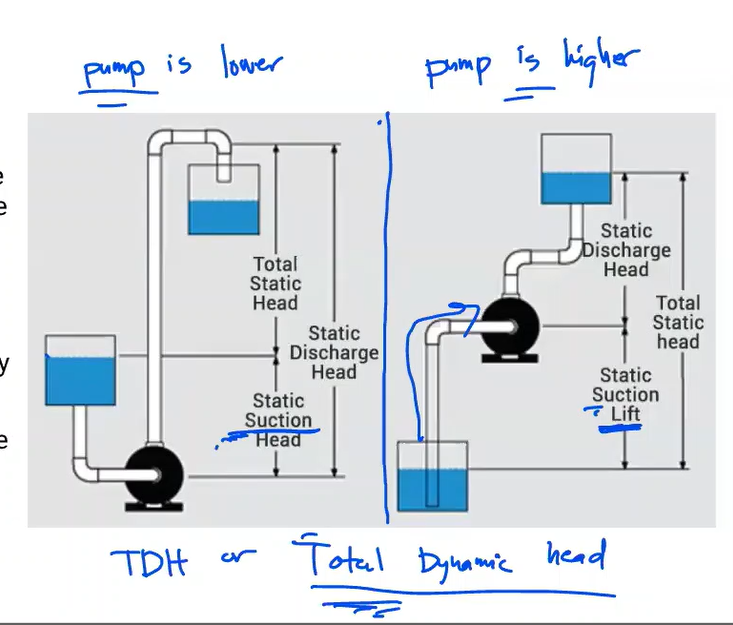
The sum of static head and velocity head at a pump discharge.
Total Discharge Head
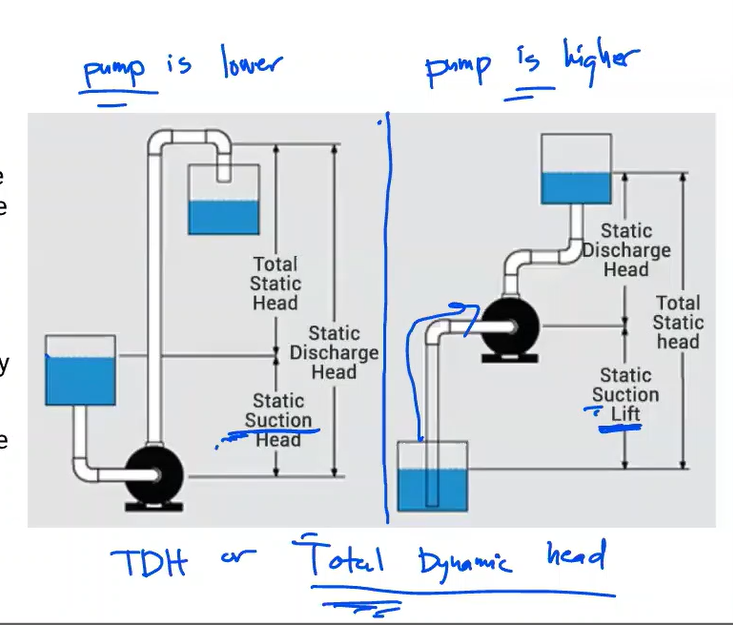
Static head near the inlet of a pump relative to the pump centerline.
Suction Head
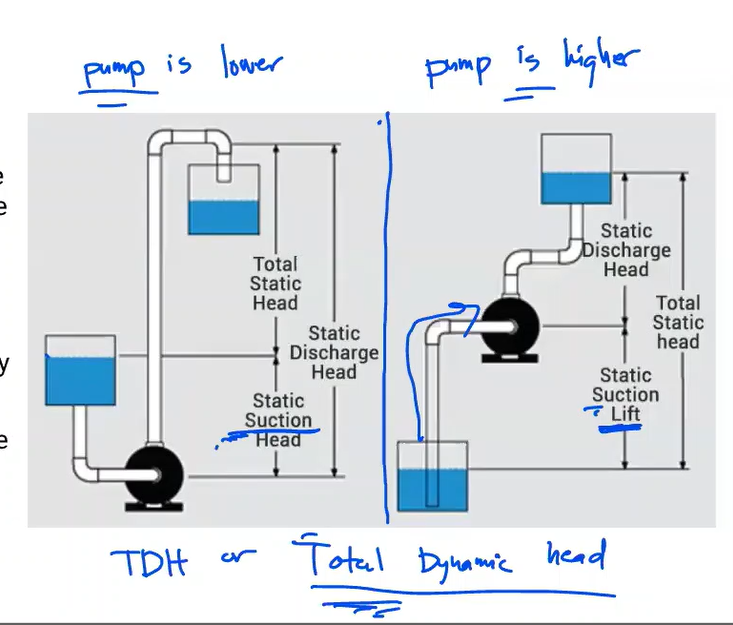
In contrast to suction head, this vertical dimension is between the pump centerline and a liquid’s surface that is below the pump.
Suction Lift
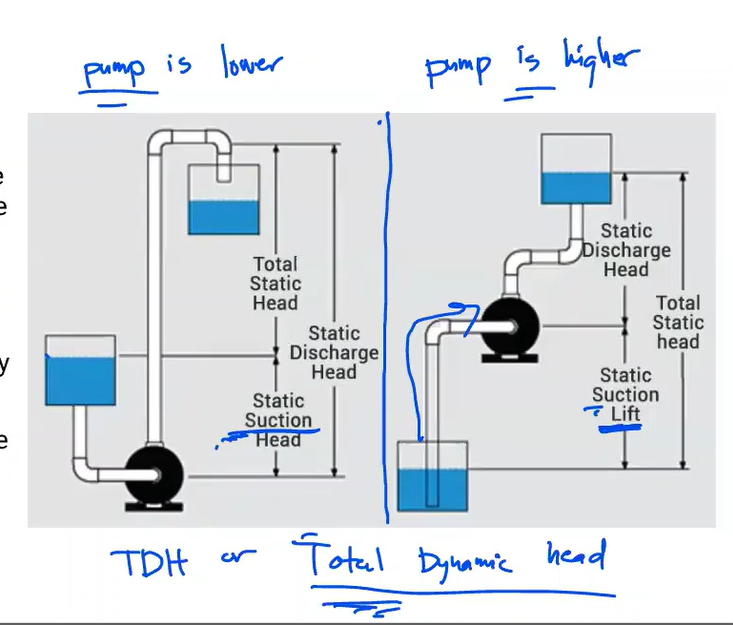
Total head at the pump discharge minus suction head or plus suction lift
Total Head
Familiarize
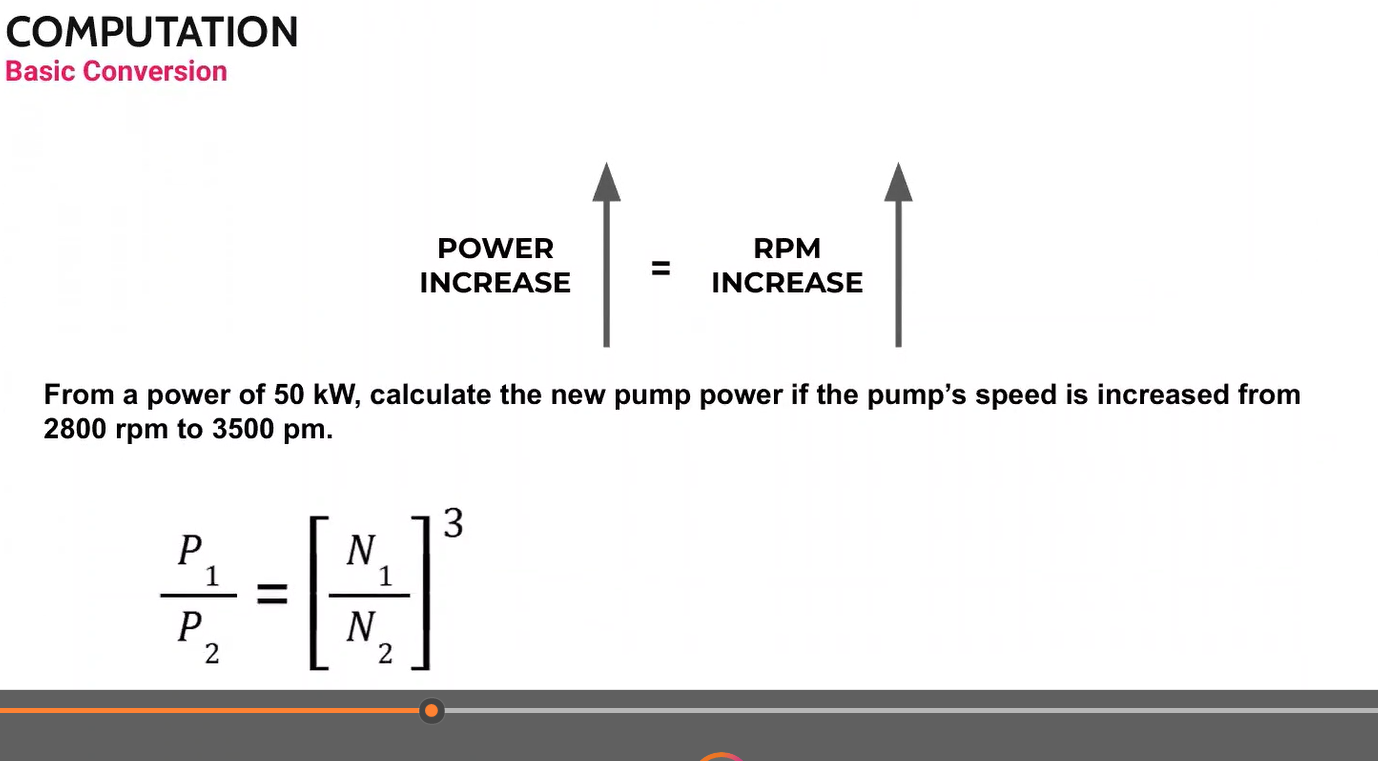
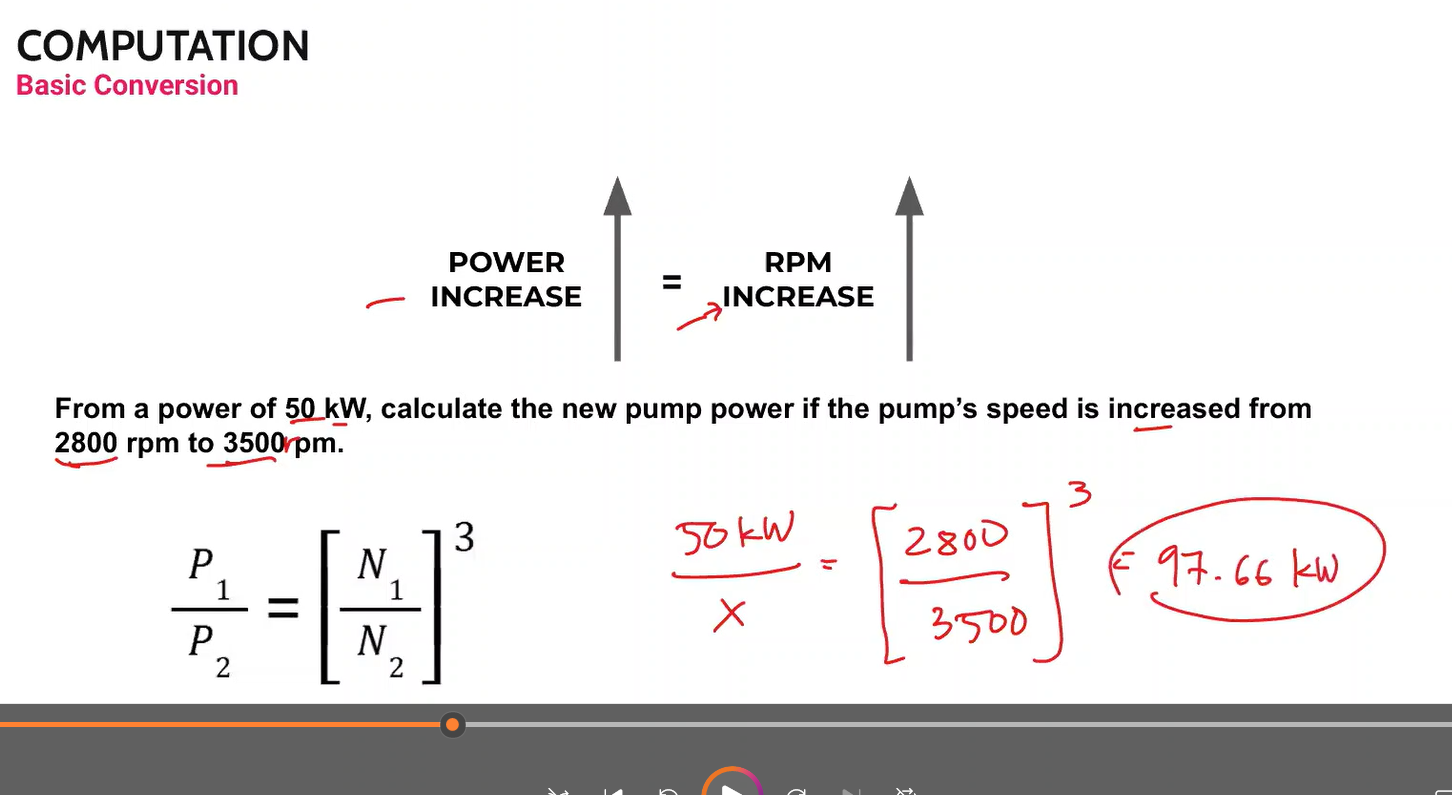
Computation:
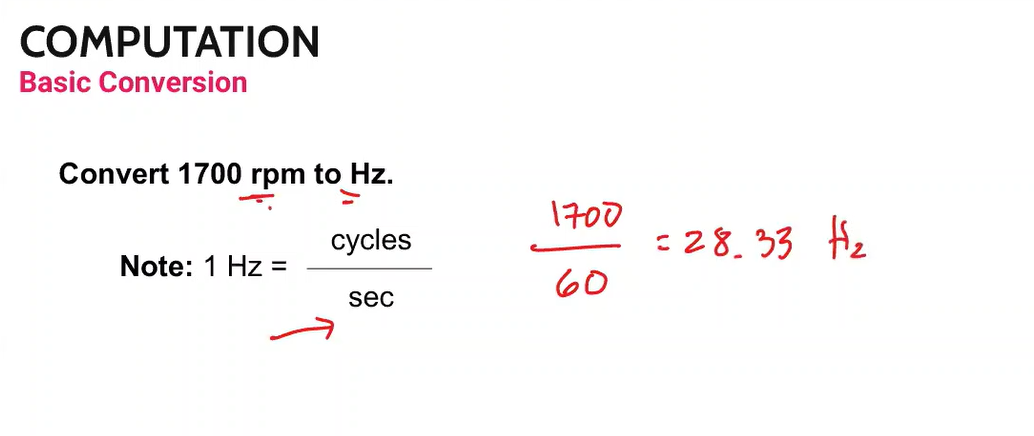
Convert 1700 rpm to Hz
1 Hz = cycles/sec
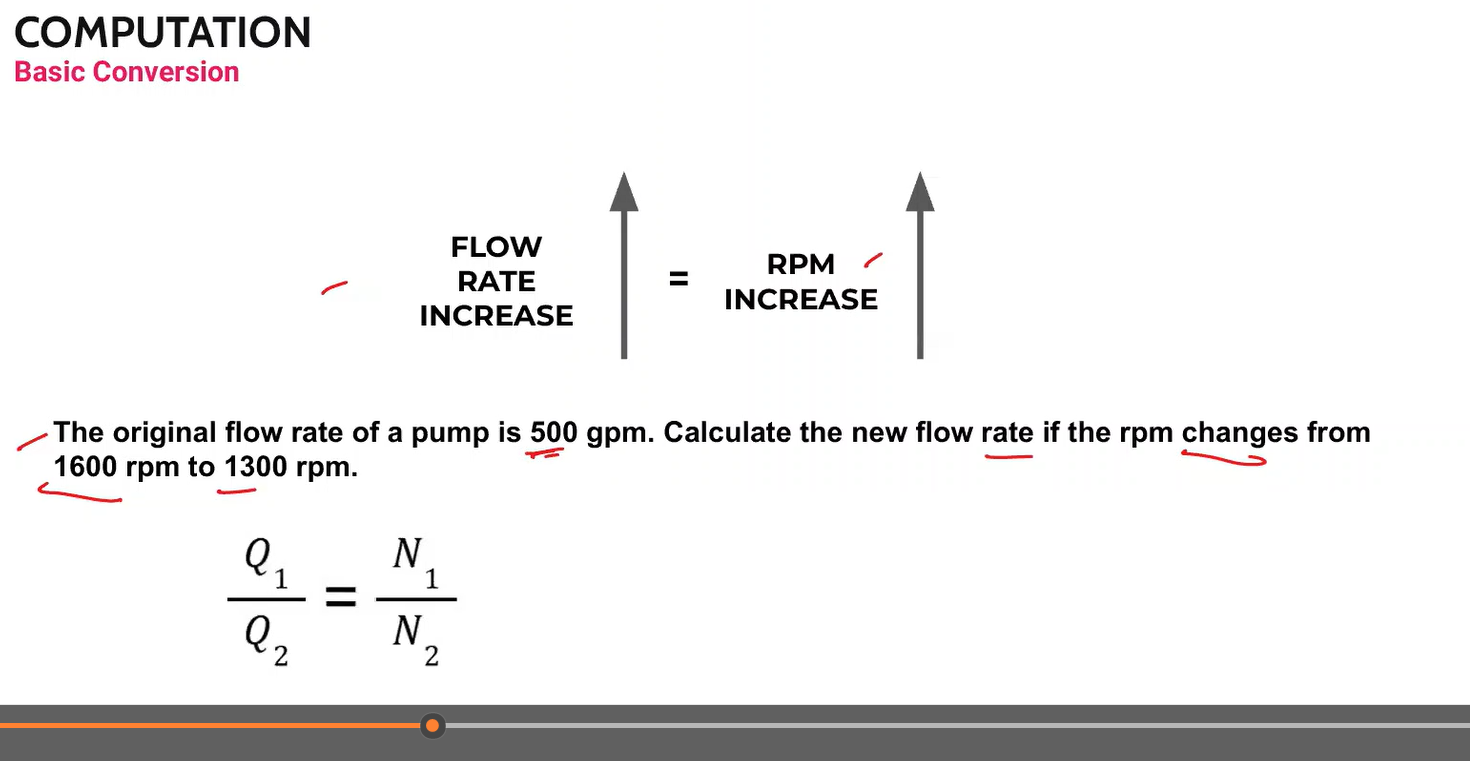
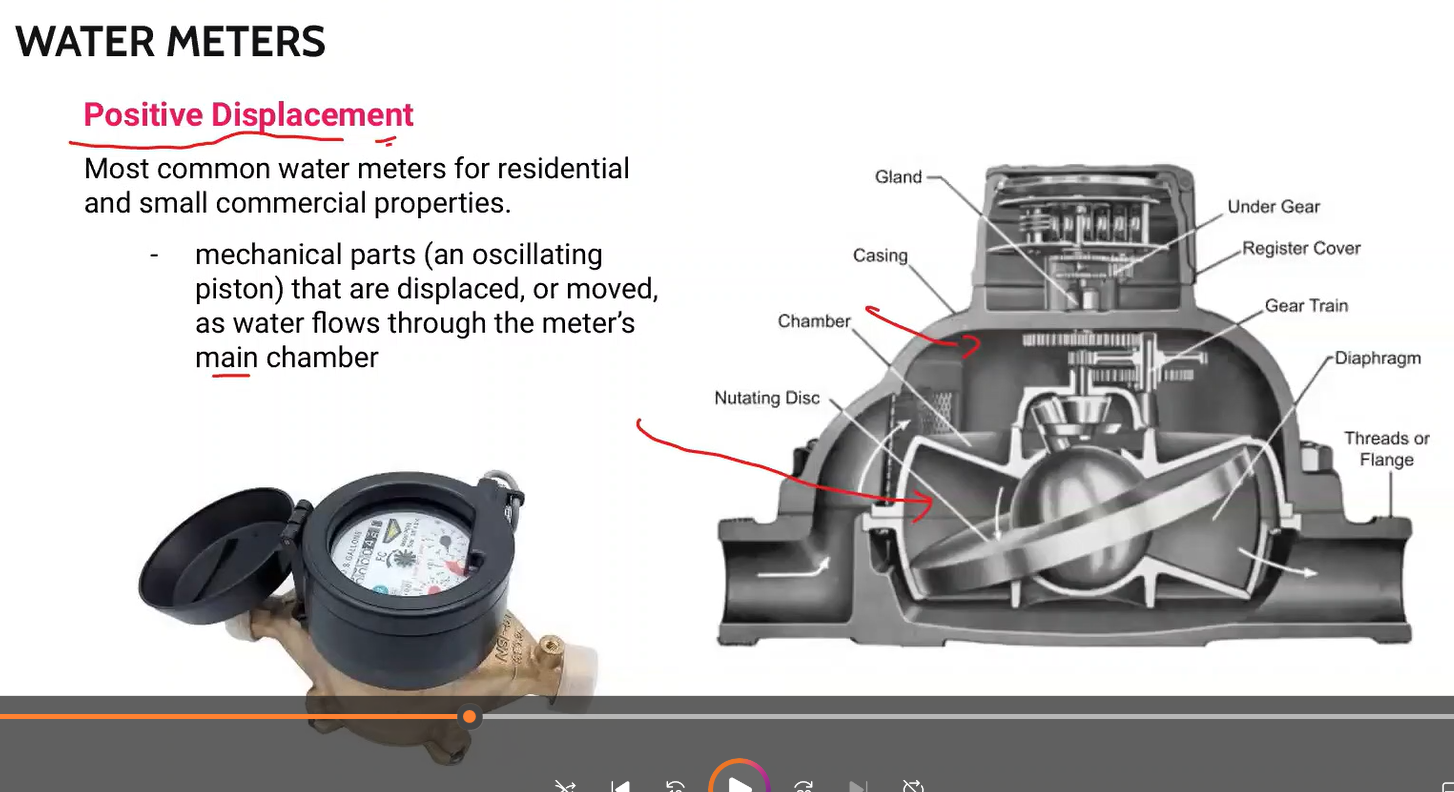
Most common water meters for residential and small commercial properties.
mechanical parts (an oscillating piston) that are displaced, or moved, as water flows through the meter’s main chamber
Positive Displacement
Determines the flow through a meter of known internal capacity. The speed of the flow can then be converted into a volume of flow to determine the usage.
Velocity meters
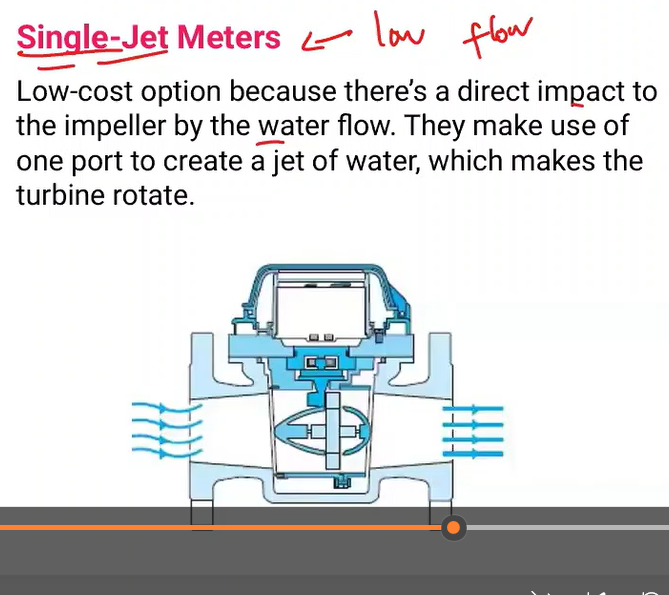
Low-cost option because there’s a direct impact to the impeller by the water flow. They make use of one port to create a jet of water, which makes the turbine rotate.
Single-jet meters
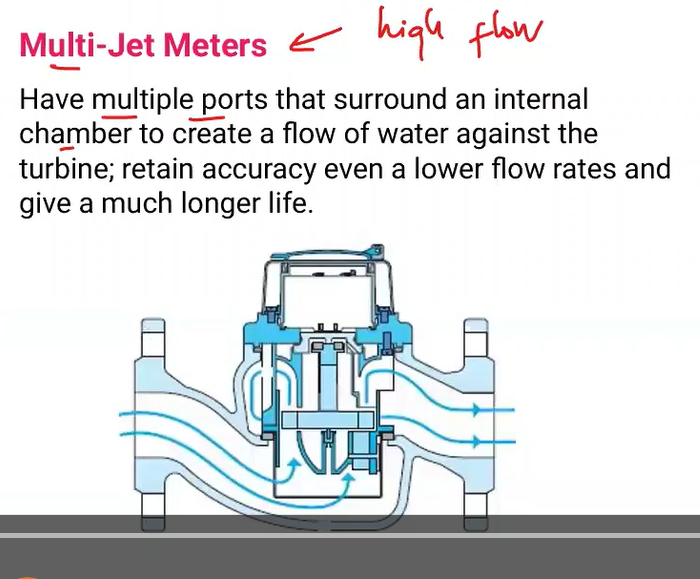
Have multiple ports that surround an internal chamber to create a flow of water against the turbine; retain accuracy even a lower flow rates give a much longer life.
Multi-jet meters
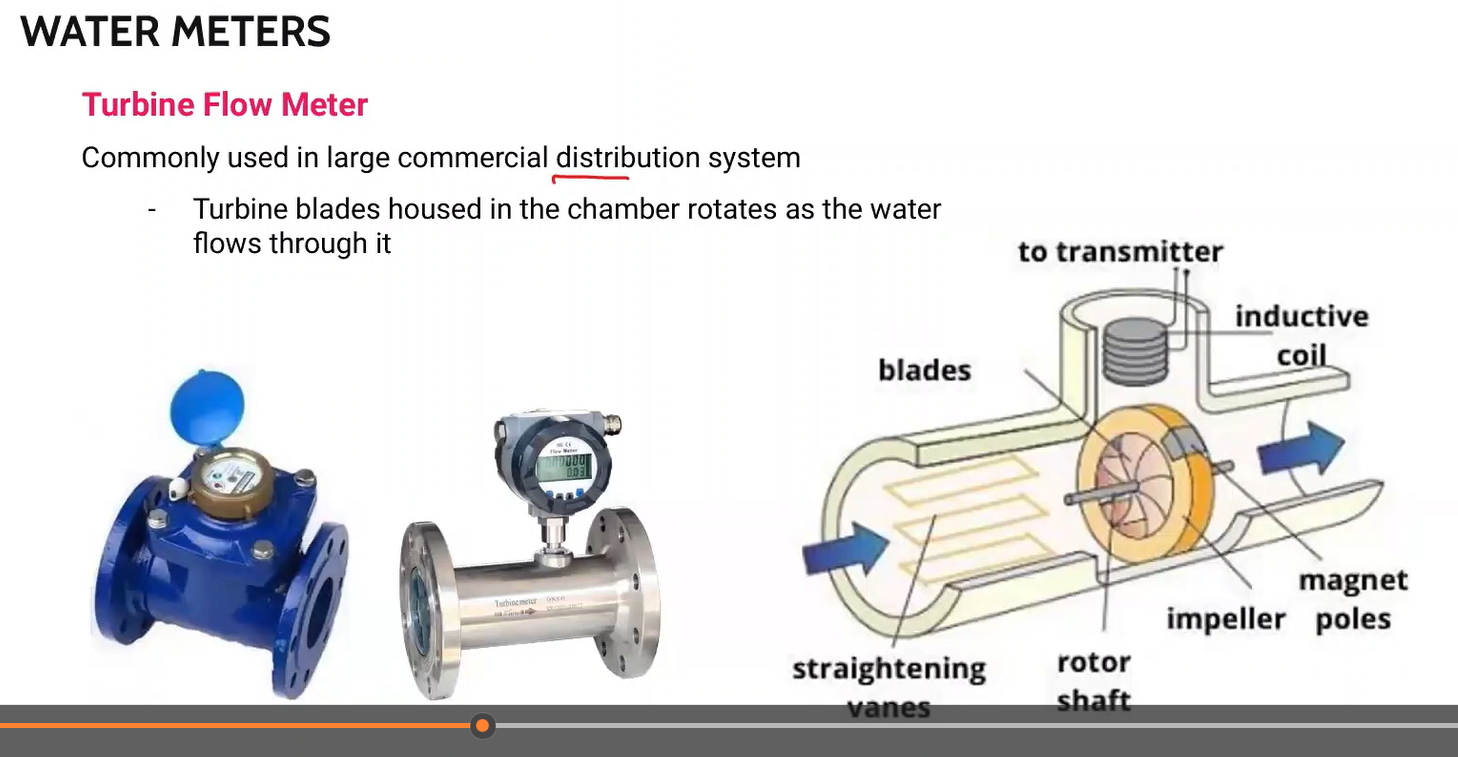
Commonly used in large commercial distribution system
Turbine blades housed in the chamber rotates as the water flows through it
Turbine flow meter
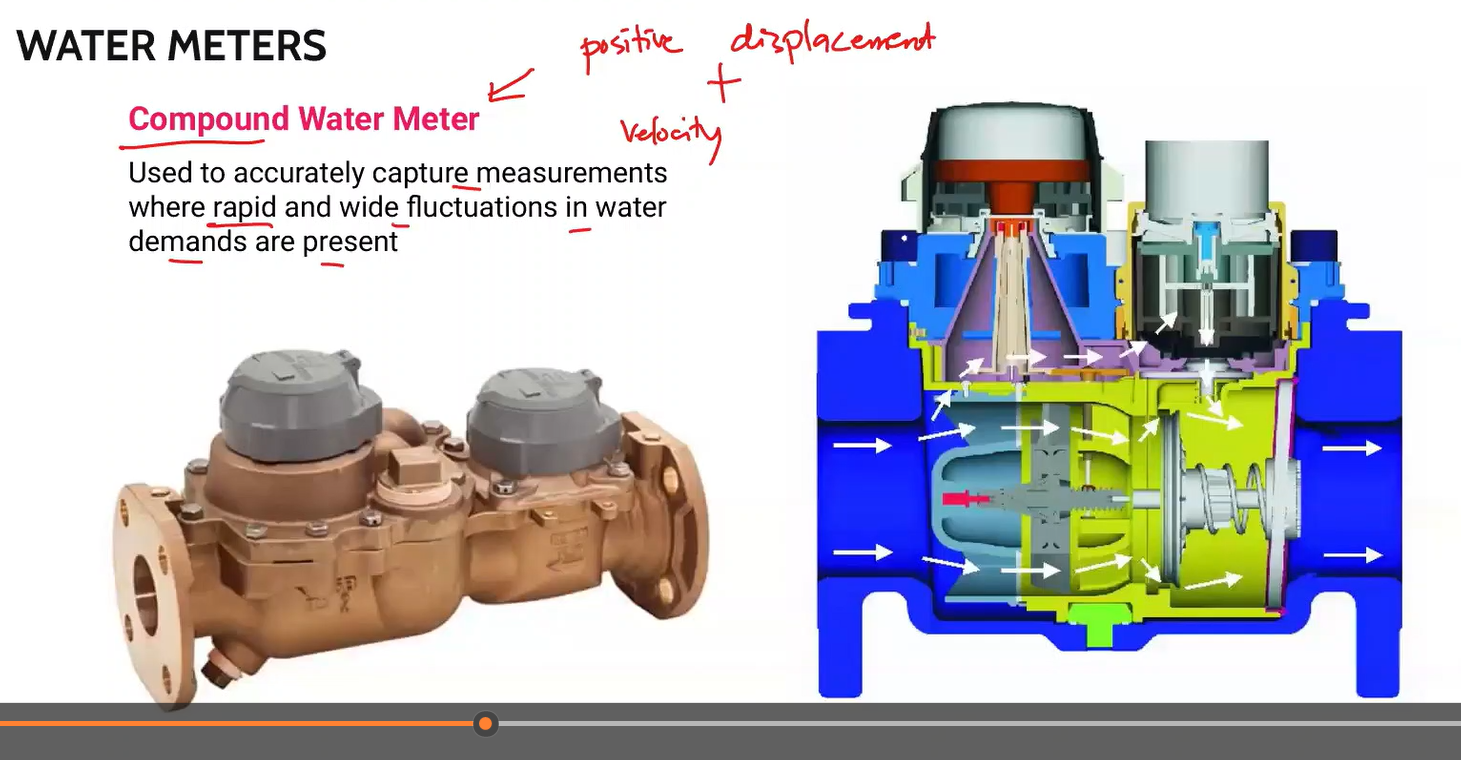
Used to accurately capture measurements where rapid and wide fluctuations in water demands are present.
Compound water meter
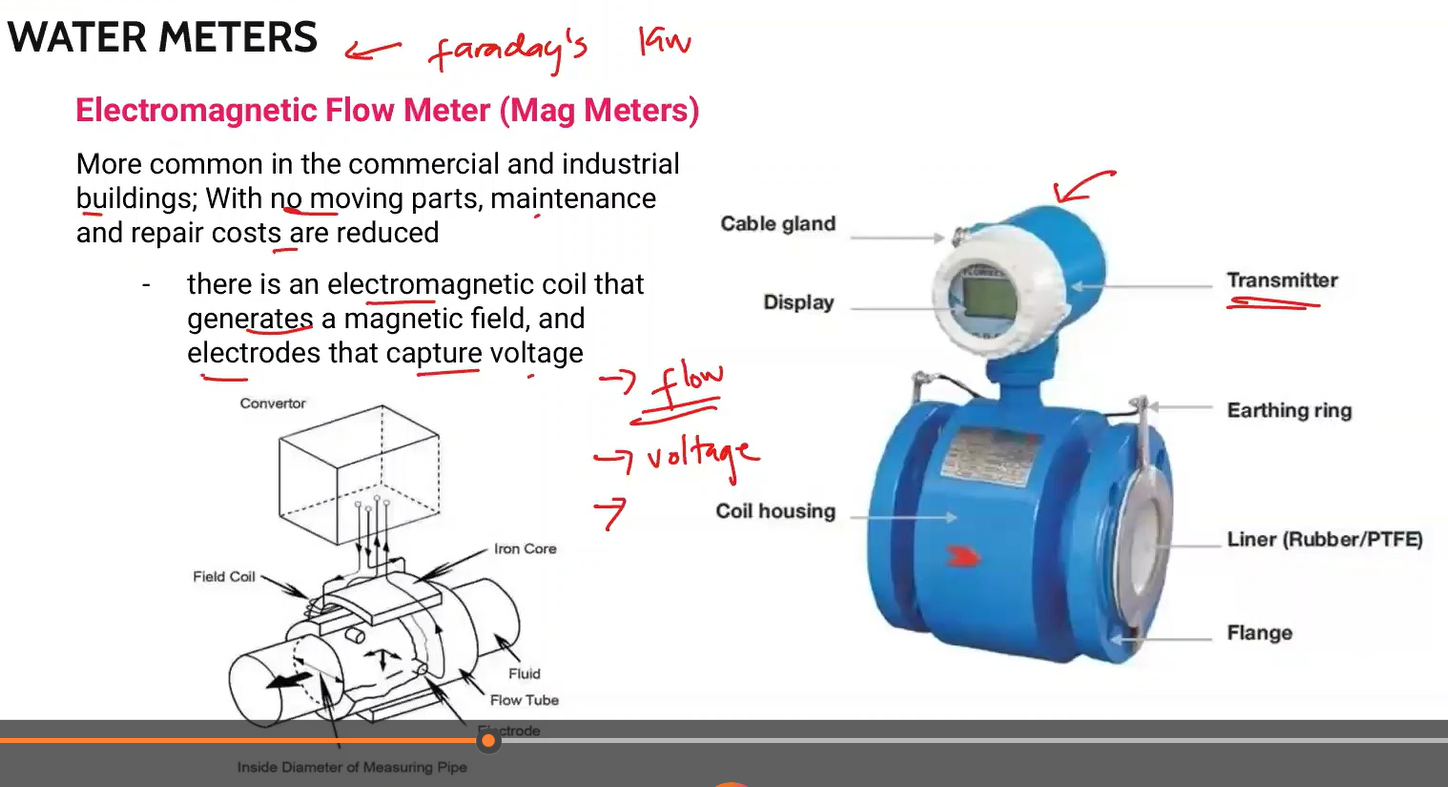
More common in the commercial and and industrial buildings; With no moving parts, maintenance and repair costs are reduced.
there is an electromagnetic coil that generates a magnetic field, and electrodes that capture voltage
Electromagnetic Flow Meter (Mag meters)
Use ultrasound to measure the speed of the fluid. These meters are ideal for wastewater applications or any dirty liquid which is conductive or water based.
Employs doppler effect of an ultrasonic signal when it is reflected by suspended particles or gas bubbles in motion.
Ultrasonic Water Meters

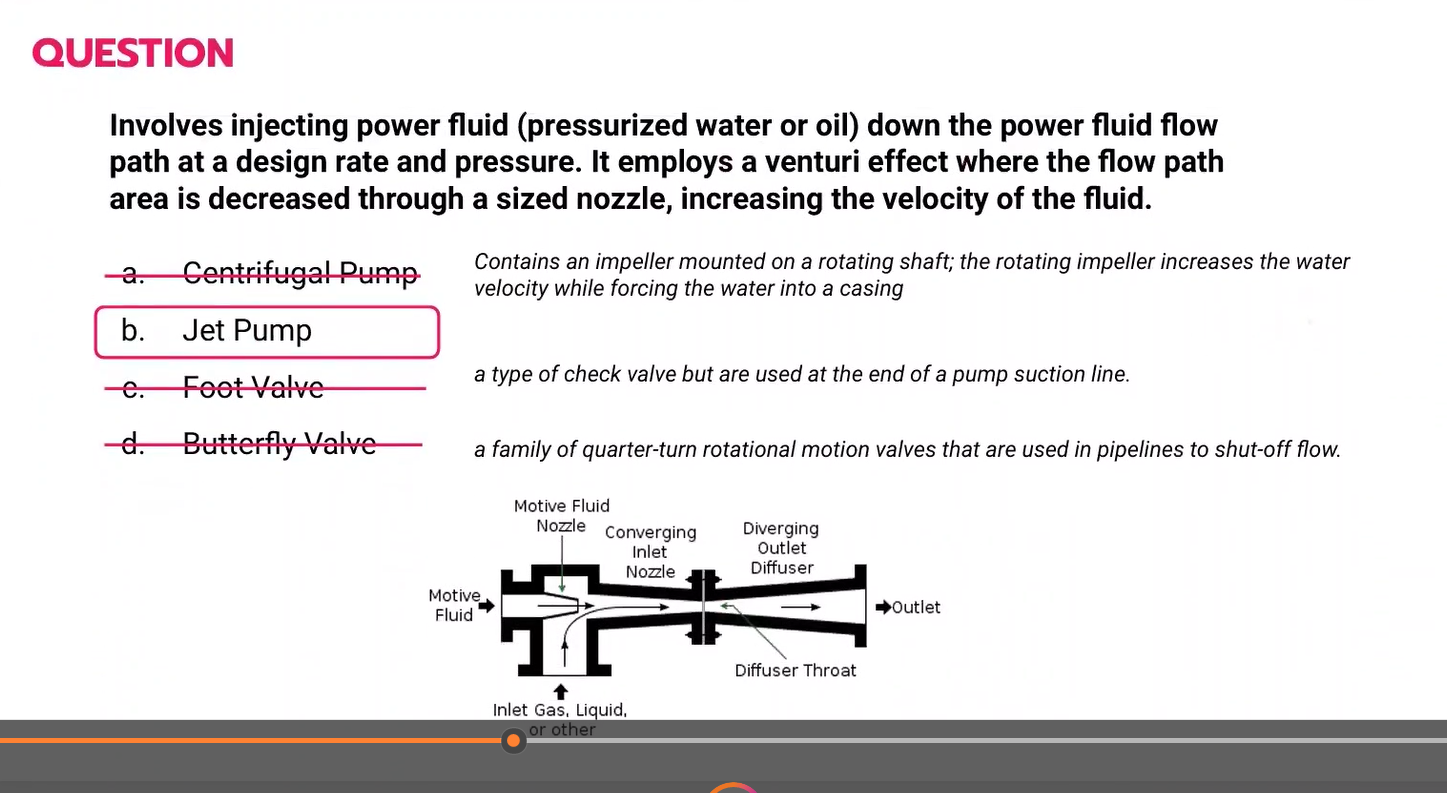
Involves injecting power fluid (pressurized water or oil) down the power fluid flow path at a design rate and pressure. It employs a venturi effect where the flow path area is decreased through a sized nozzle, increasing the velocity of the fluid.
a. Centrifugal pump
b. Jet Pump
c. Foot valve
d. Butterfly valve
b. Jet Pump
An act to enhance the mobility of disabled persons by requiring certain buildings, institutions, establishments, and public utilities to install facilities and other devices.
Batas Pambansa 344

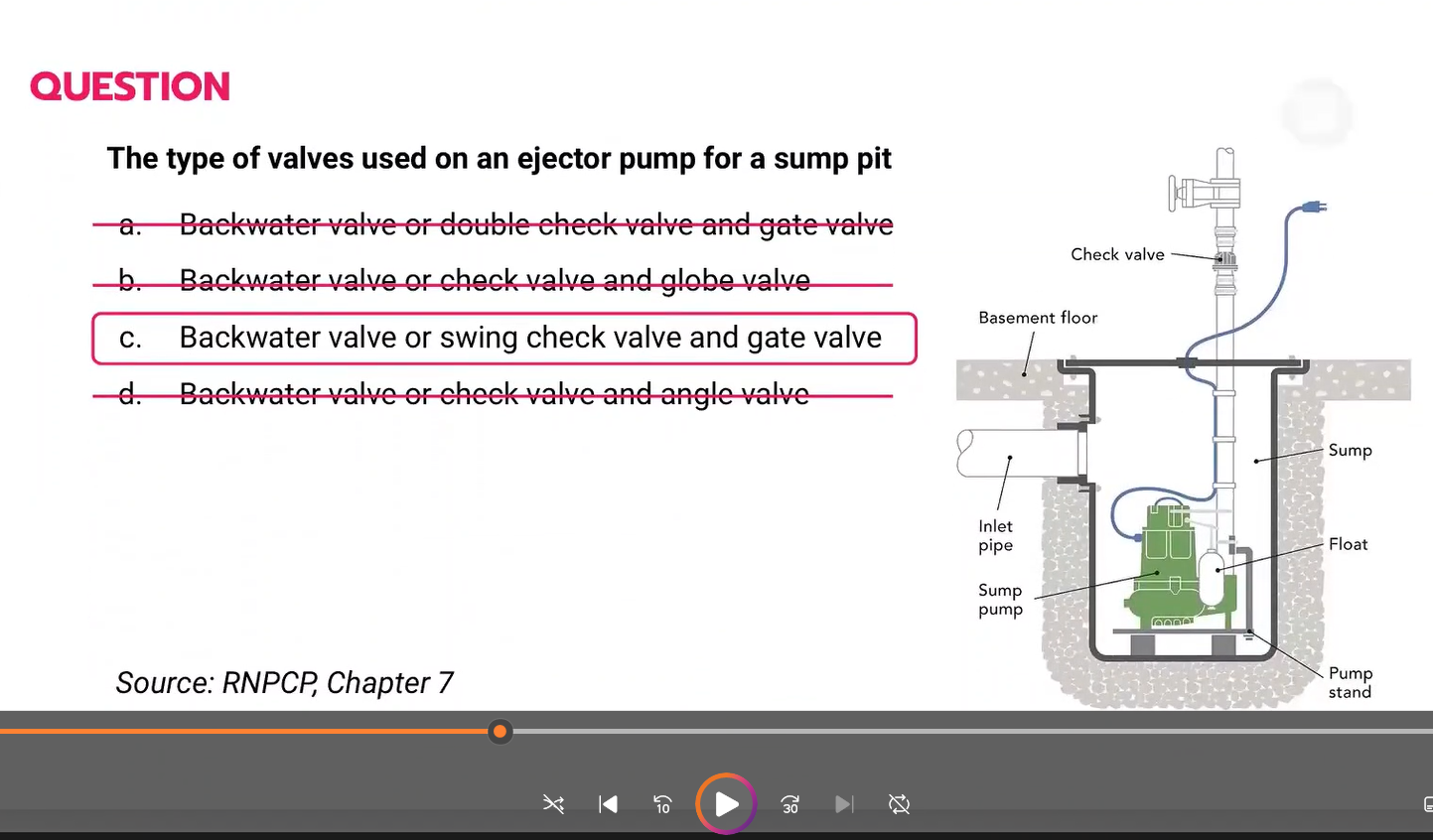
The type of valve used on an ejector pump for a sump pit.
a. Backwater valve or double check valve and gate valve
b. Backwater valve or check valve and globe valve
c. Backwater valve or swing check valve and gate valve
d. Backwater valve or check valve and angle valve
c. Backwater valve or swing check valve and gate valve
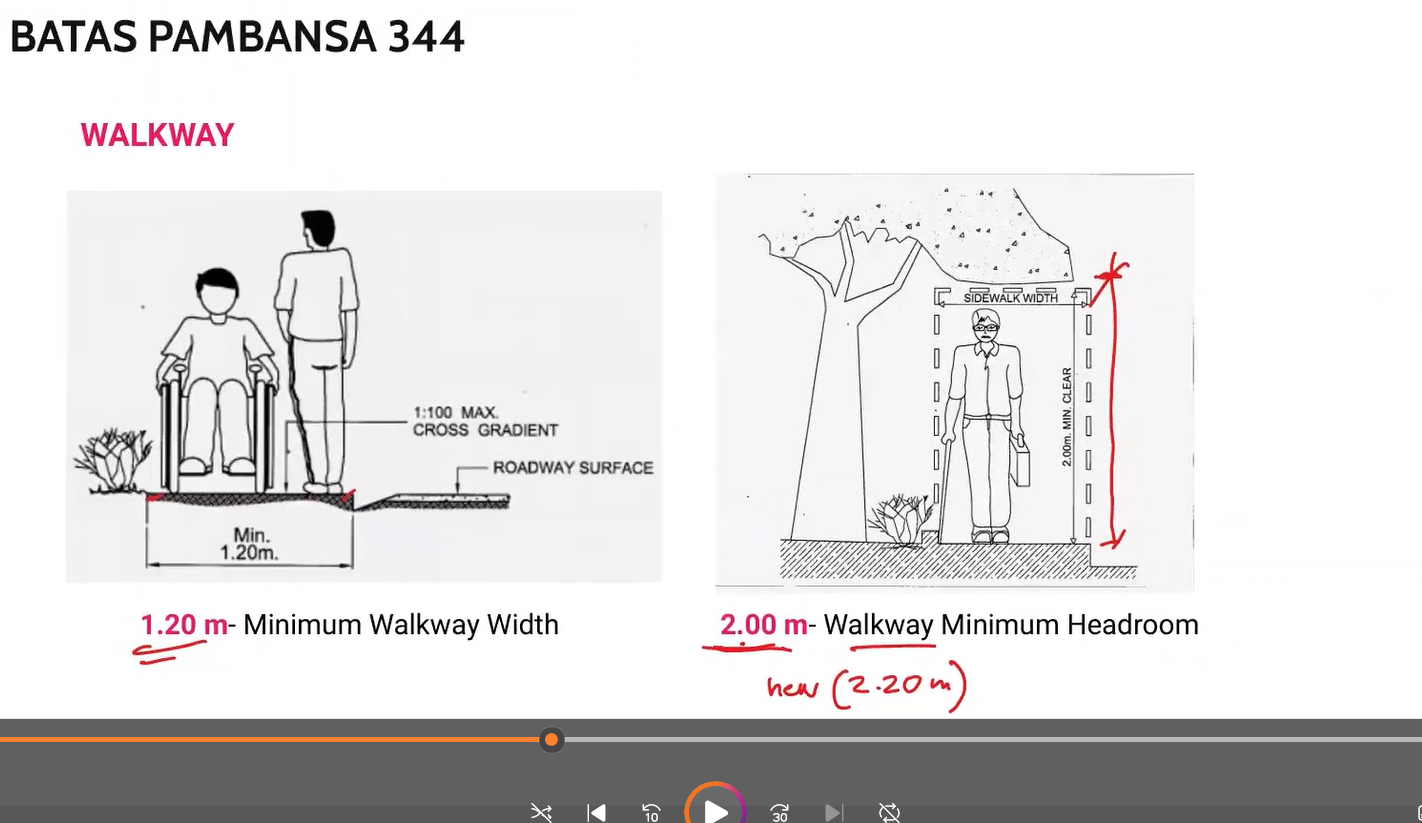
BP 344 Walkway
Old BP 344
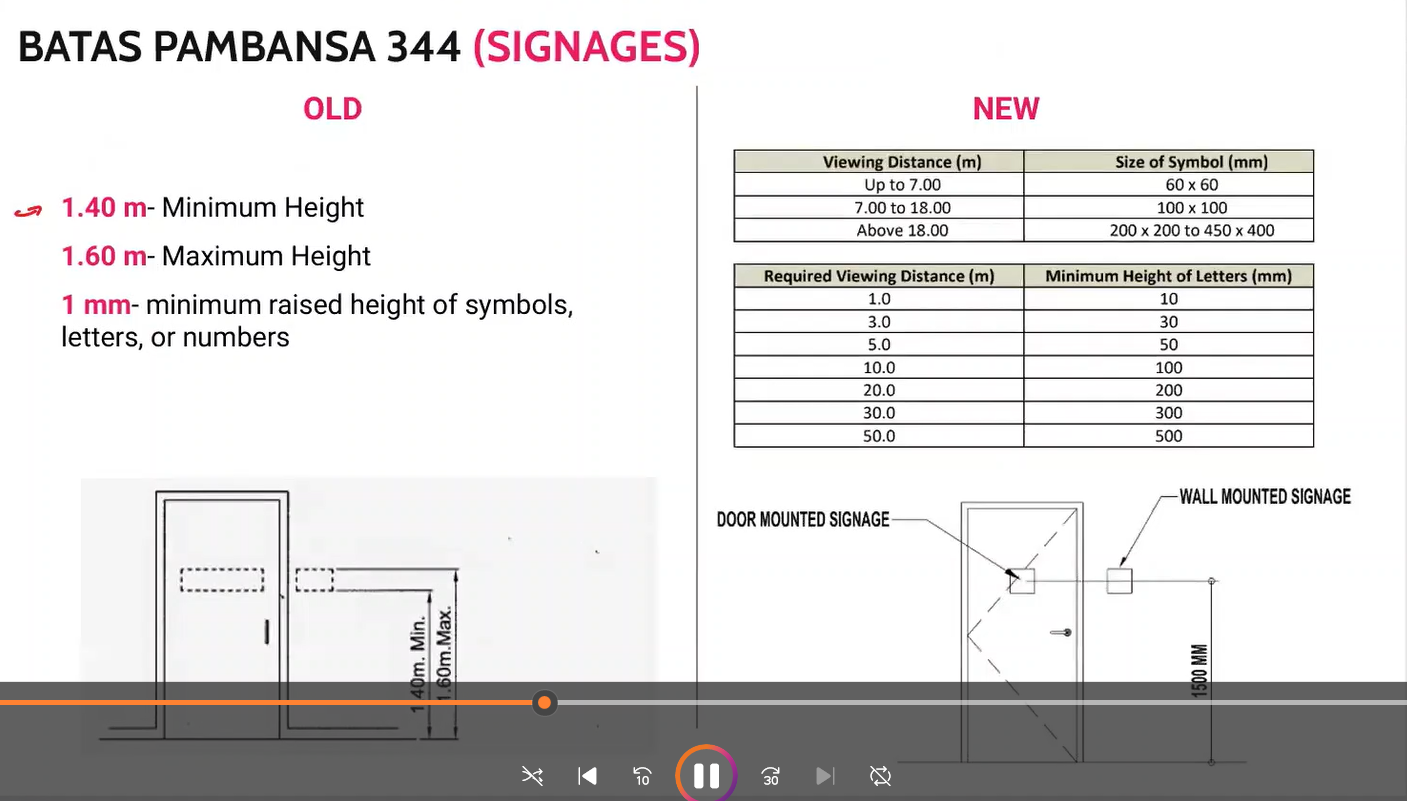
BP 344 Signages
memorize
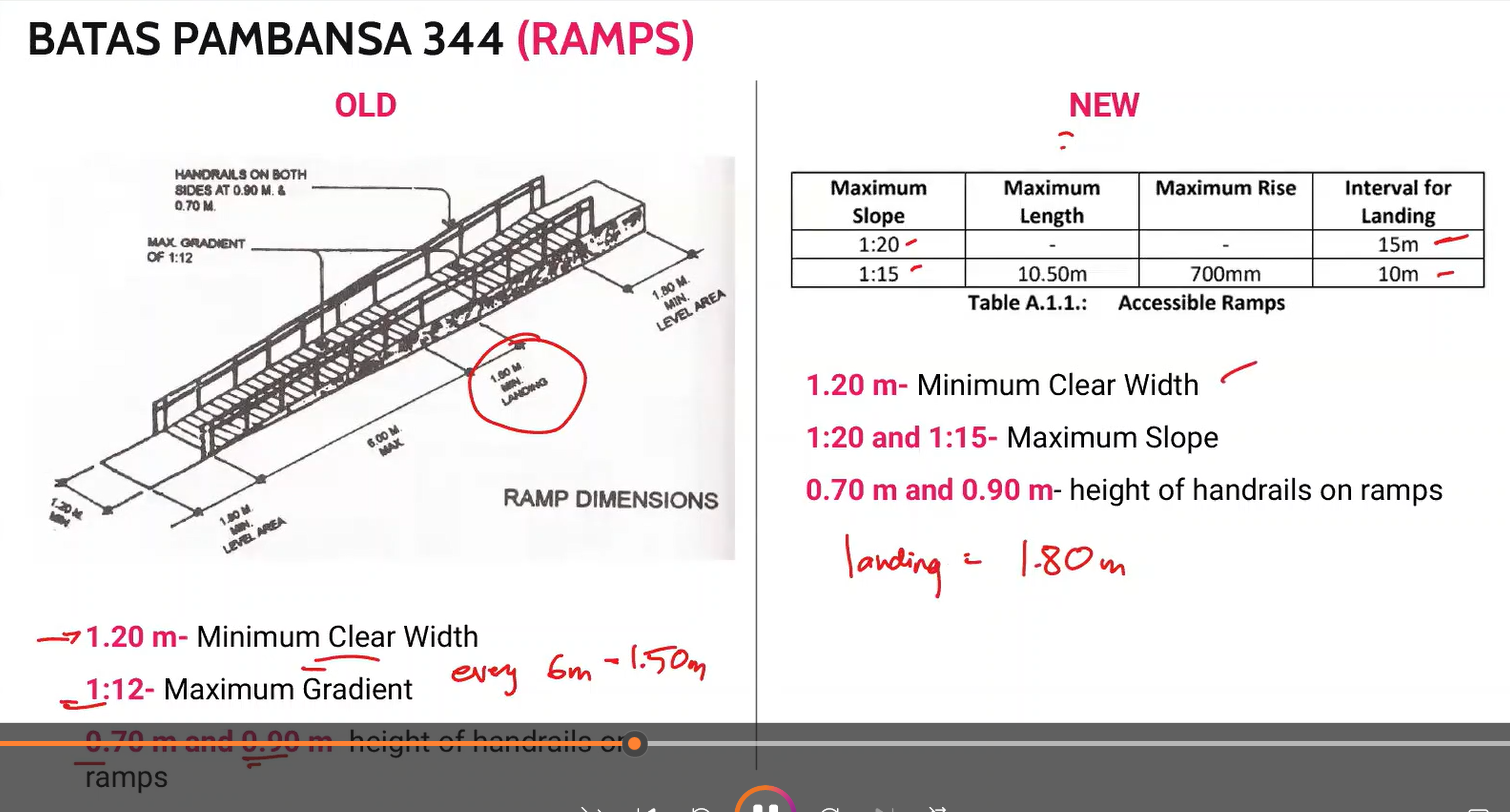
BP 344 Ramps
memorize

BP 344 Toilets
memorize
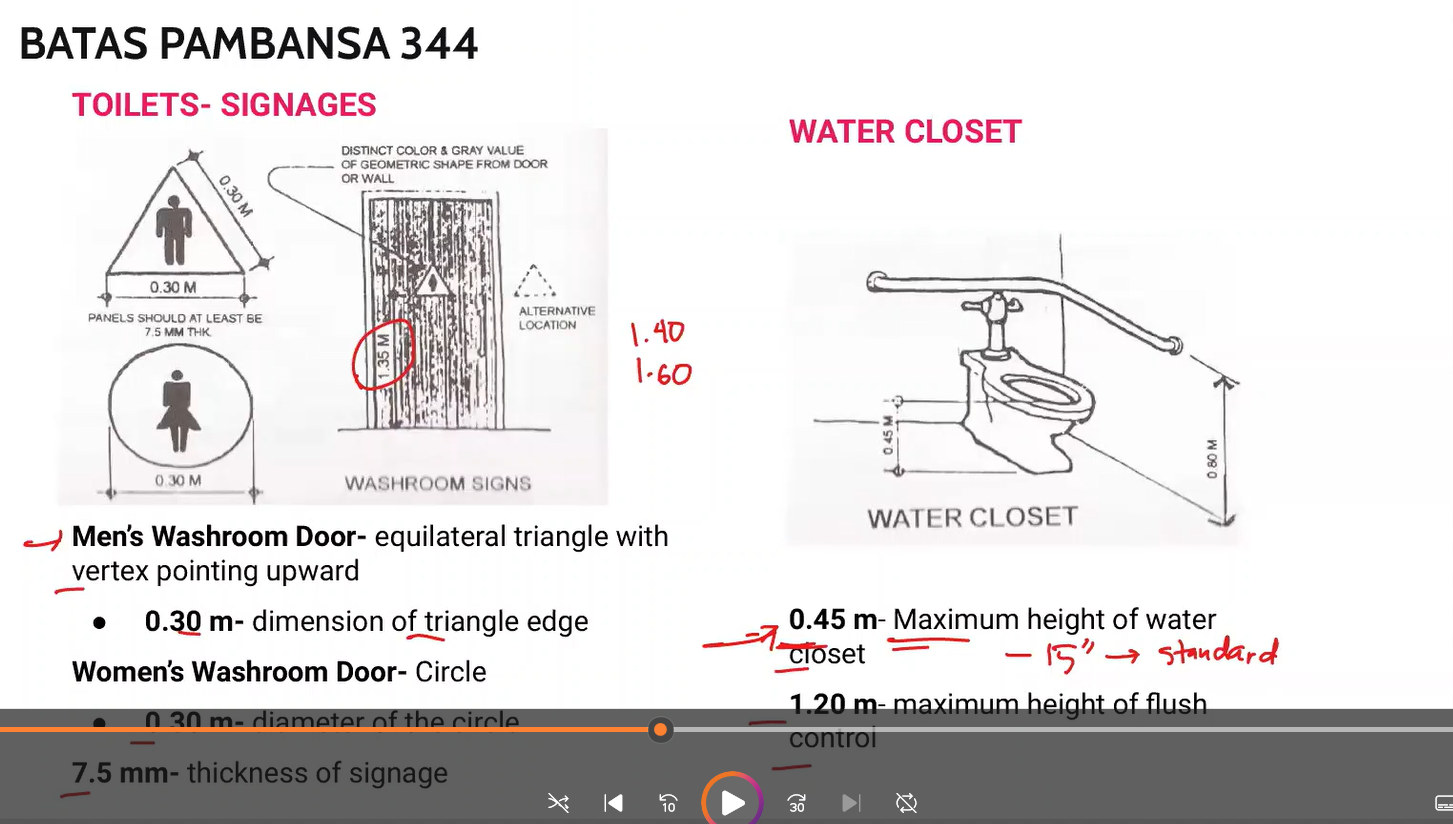
BP 344 Toilet Signages and water closet
memorize
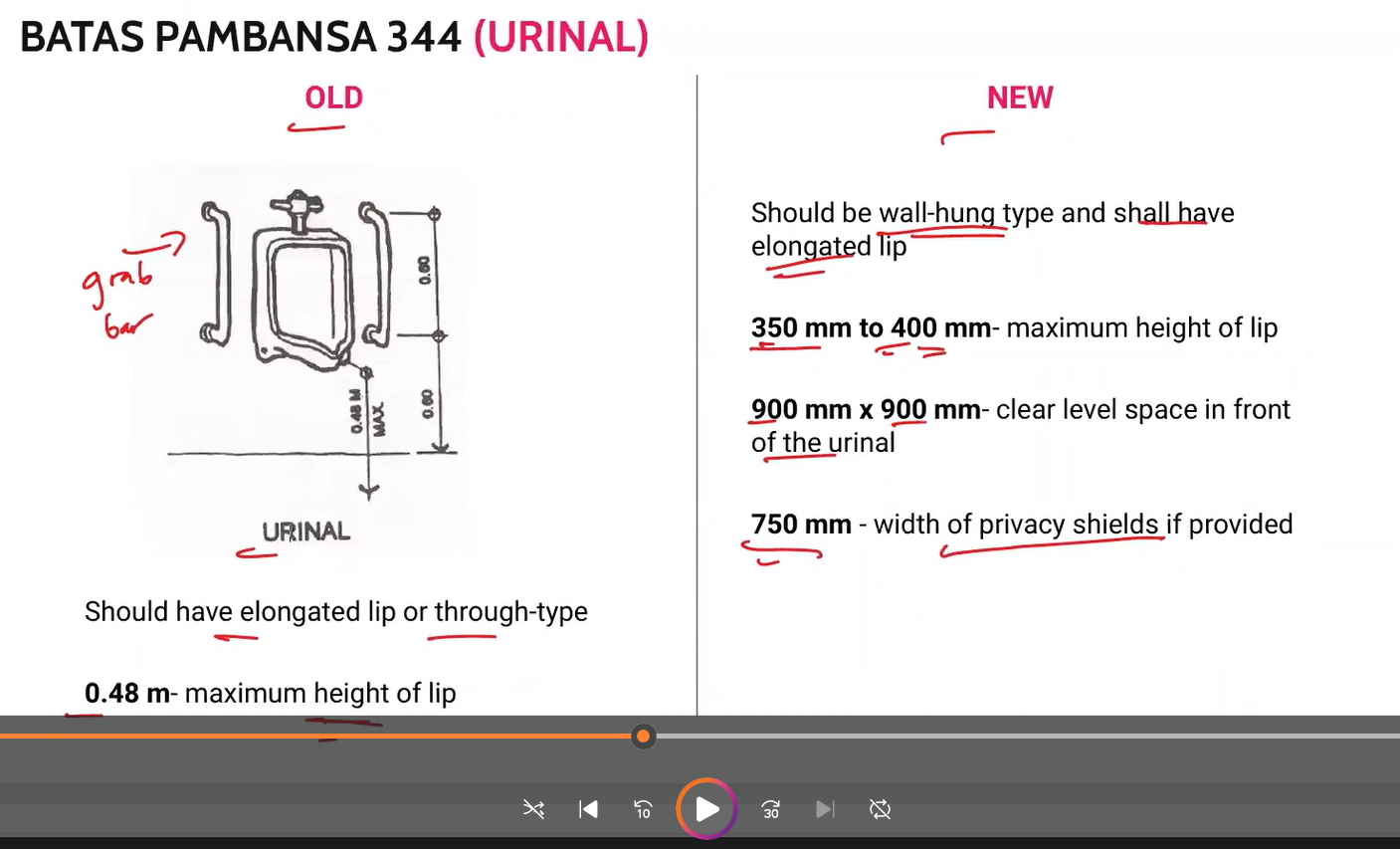
BP 344 Urinal
memorize
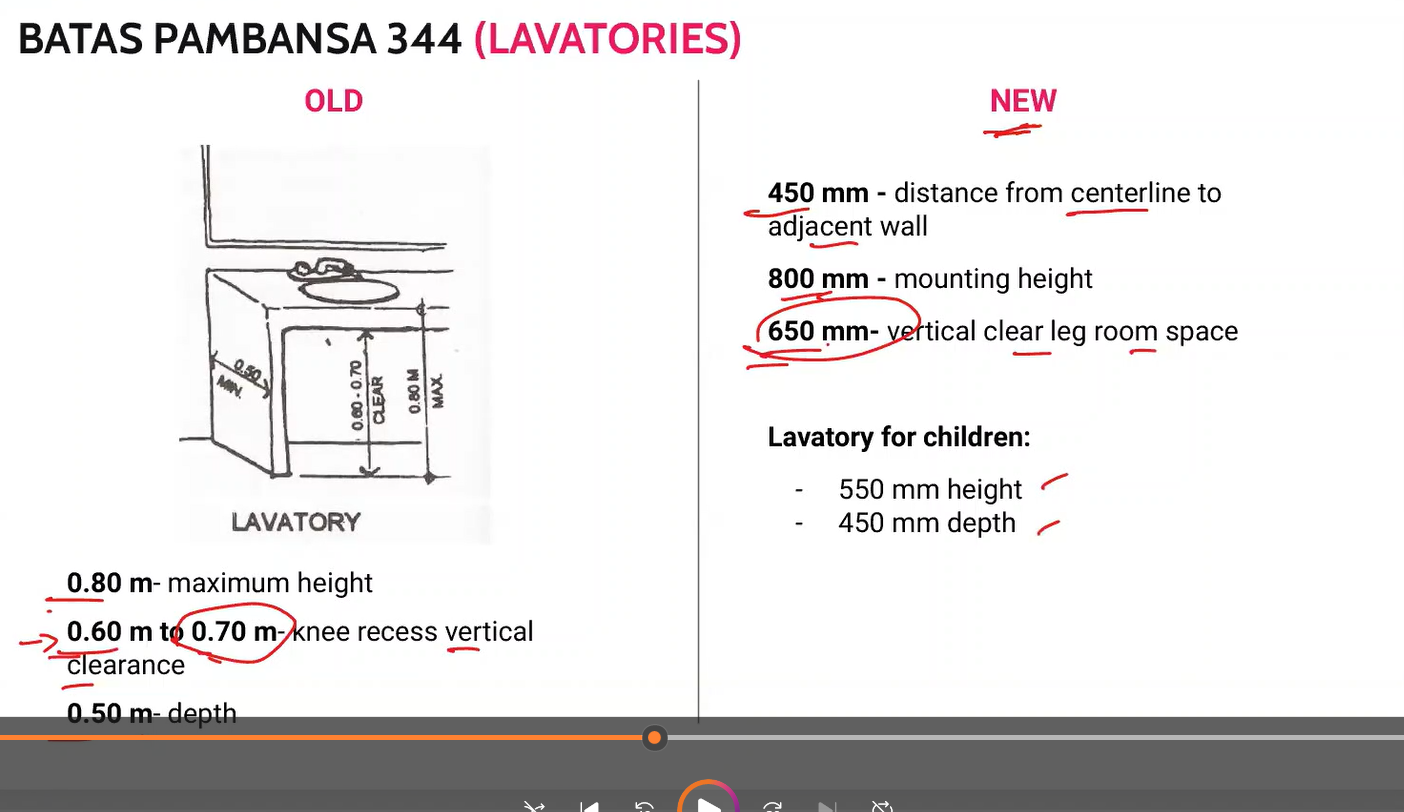
BP 344 Lavatory
memorize

BP 344 Water Fountains
Memorize
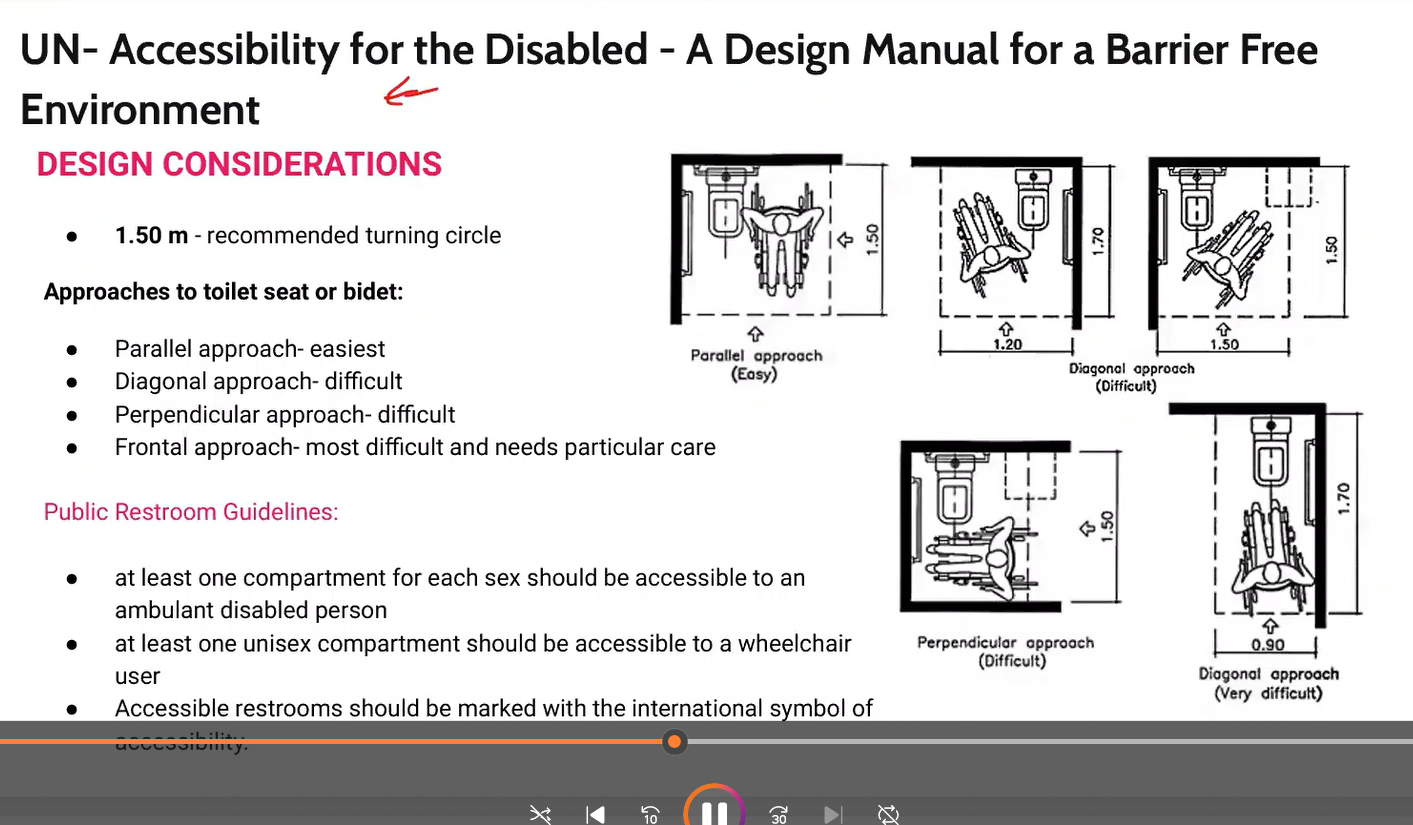
Memorize

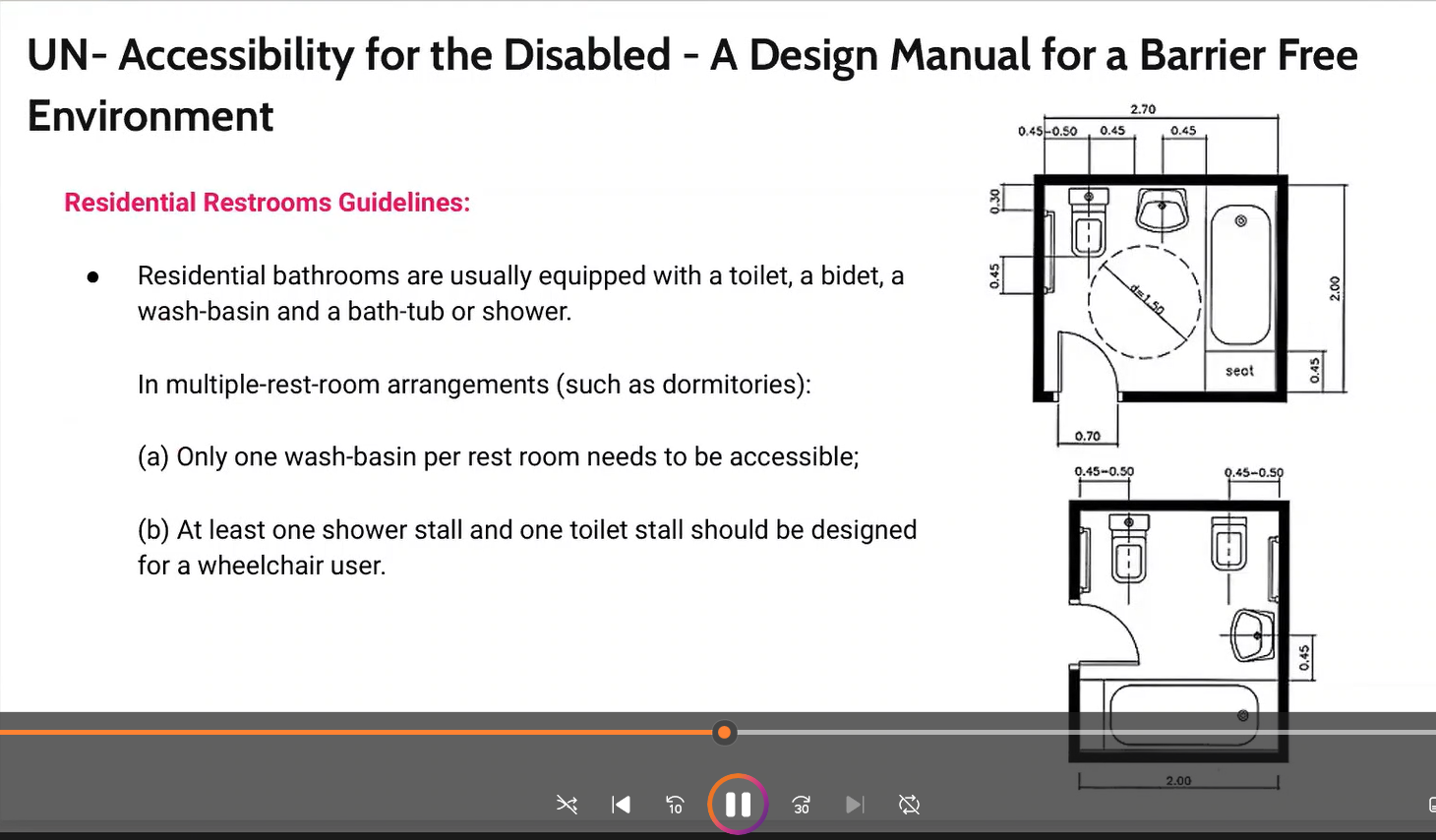
memorize
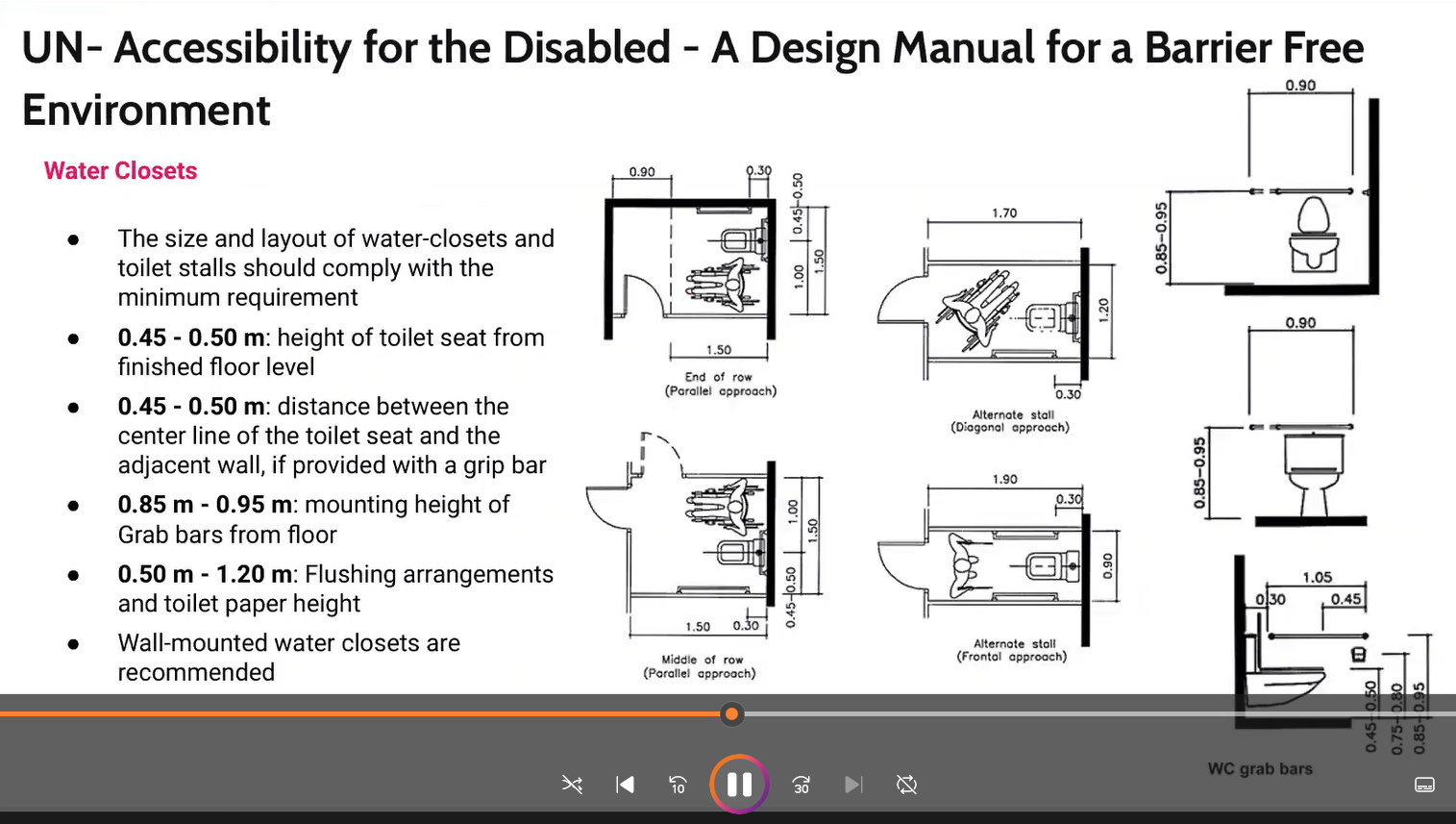
familiarize

familiarize
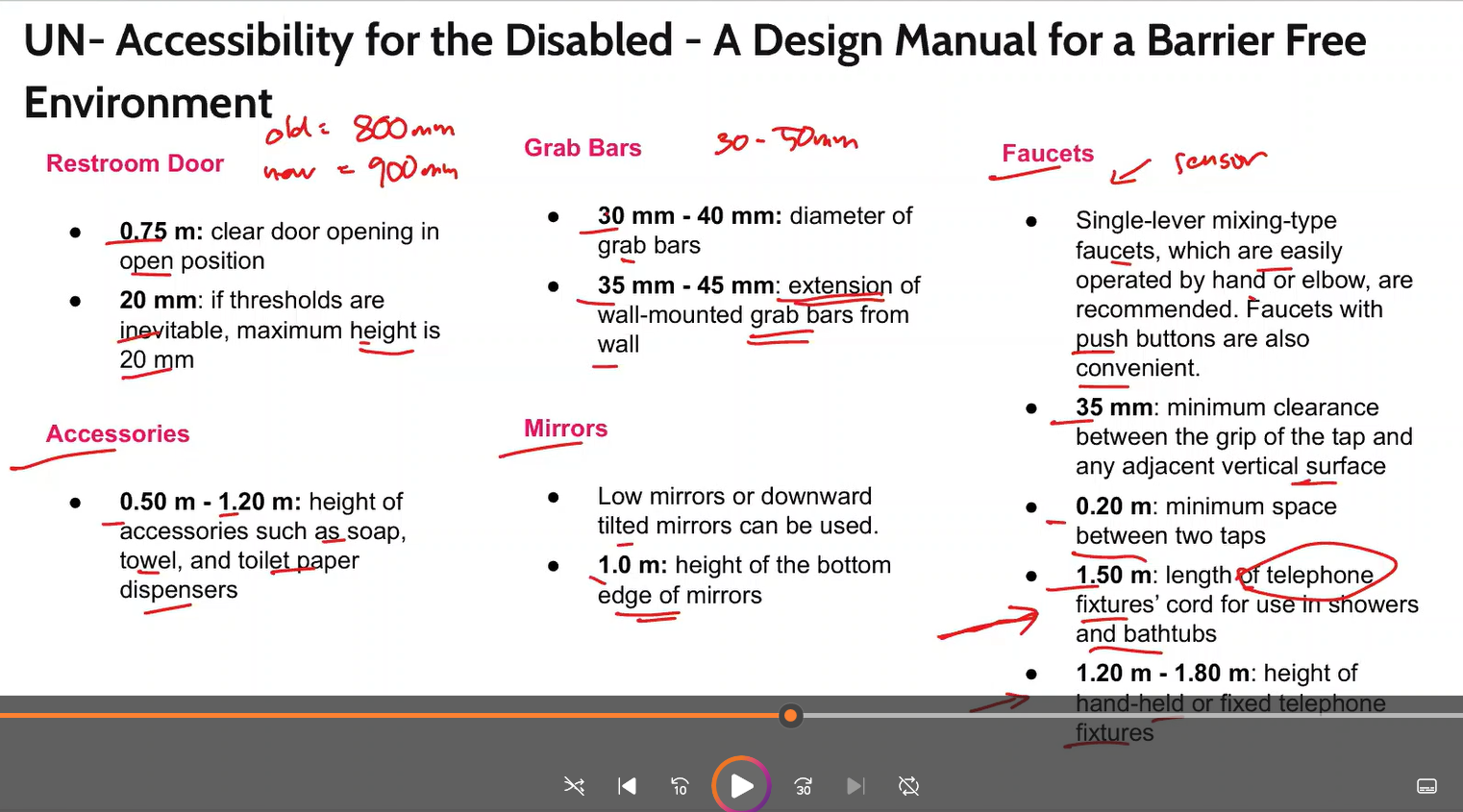
familiarize
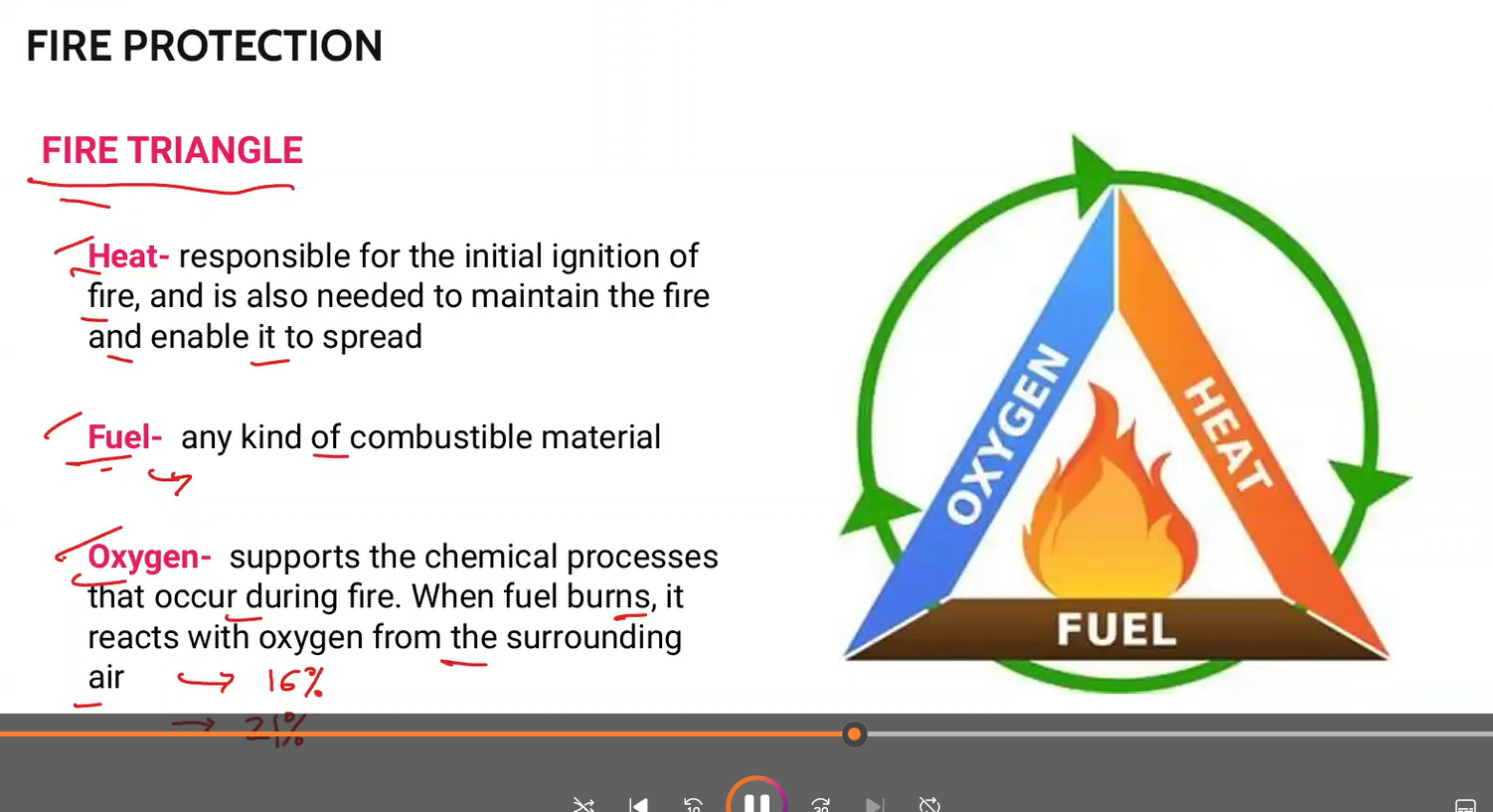
responsible for the initial ignition of fire, and is also needed to maintain the fire and enable it to spread
Heat
any kind of combustible material
Fuel
supports the chemical processes that occur during fire. When fuel burns, it reacts with oxygen from the surrounding air.
-fire needs 16% to ignite
Oxygen
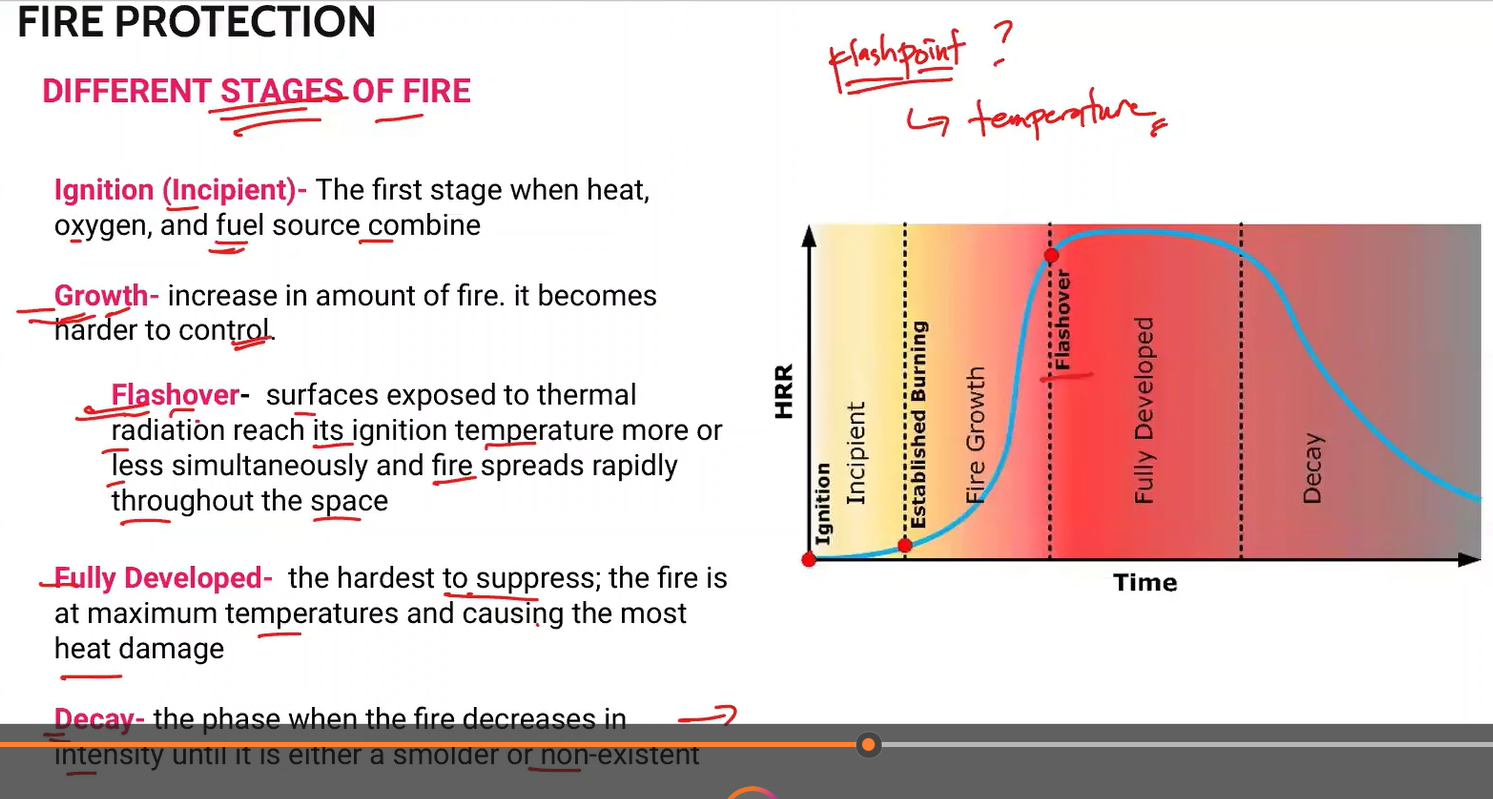
Different Stages of Fire
Ignition
Growth
Flashover
Fully Developed
Decay
The first stage when heat, oxygen, and fuel source combine.
Ignition (Incipient)
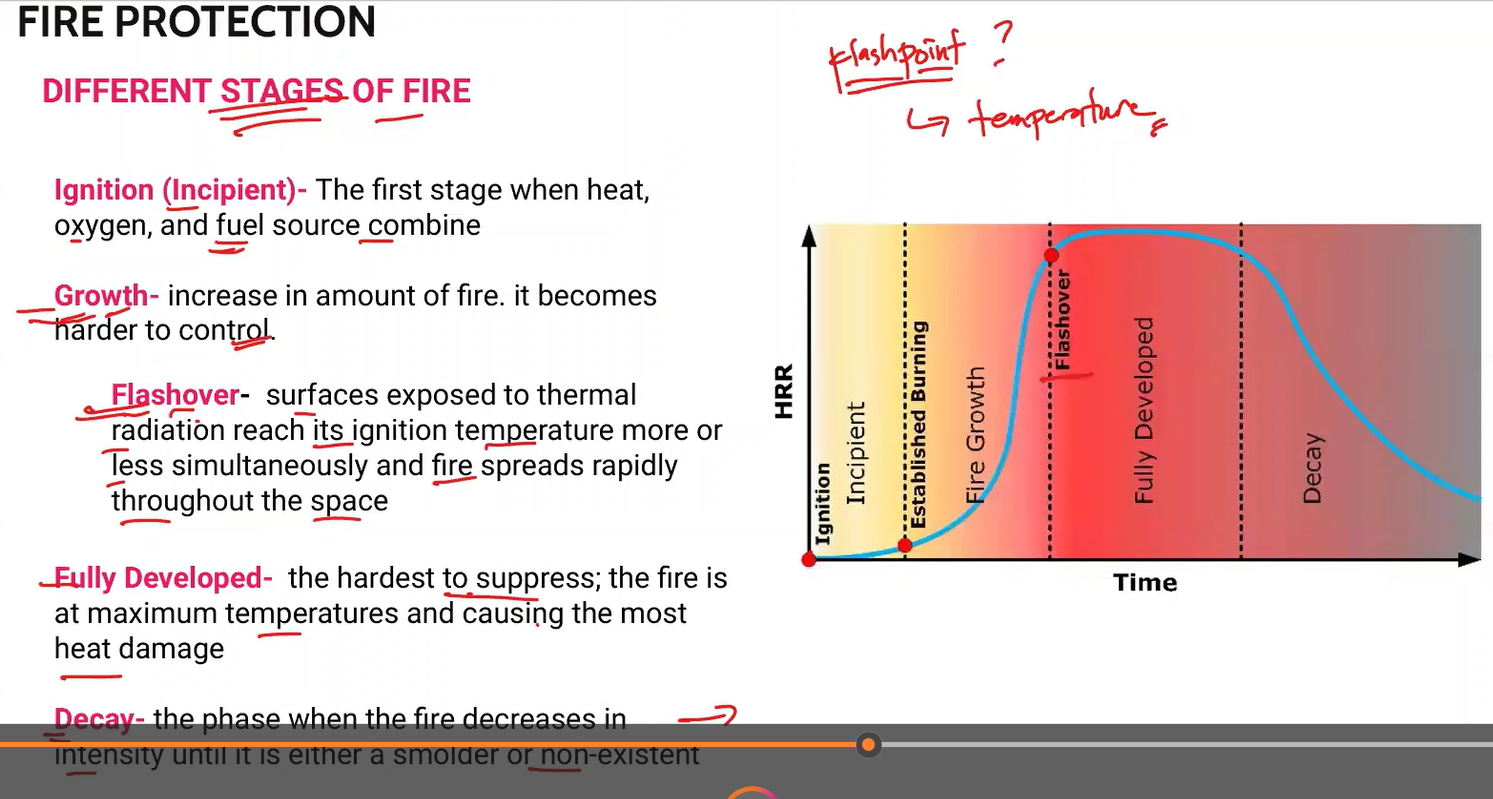
Increase in amount of fire. It becomes harder to control
Growth
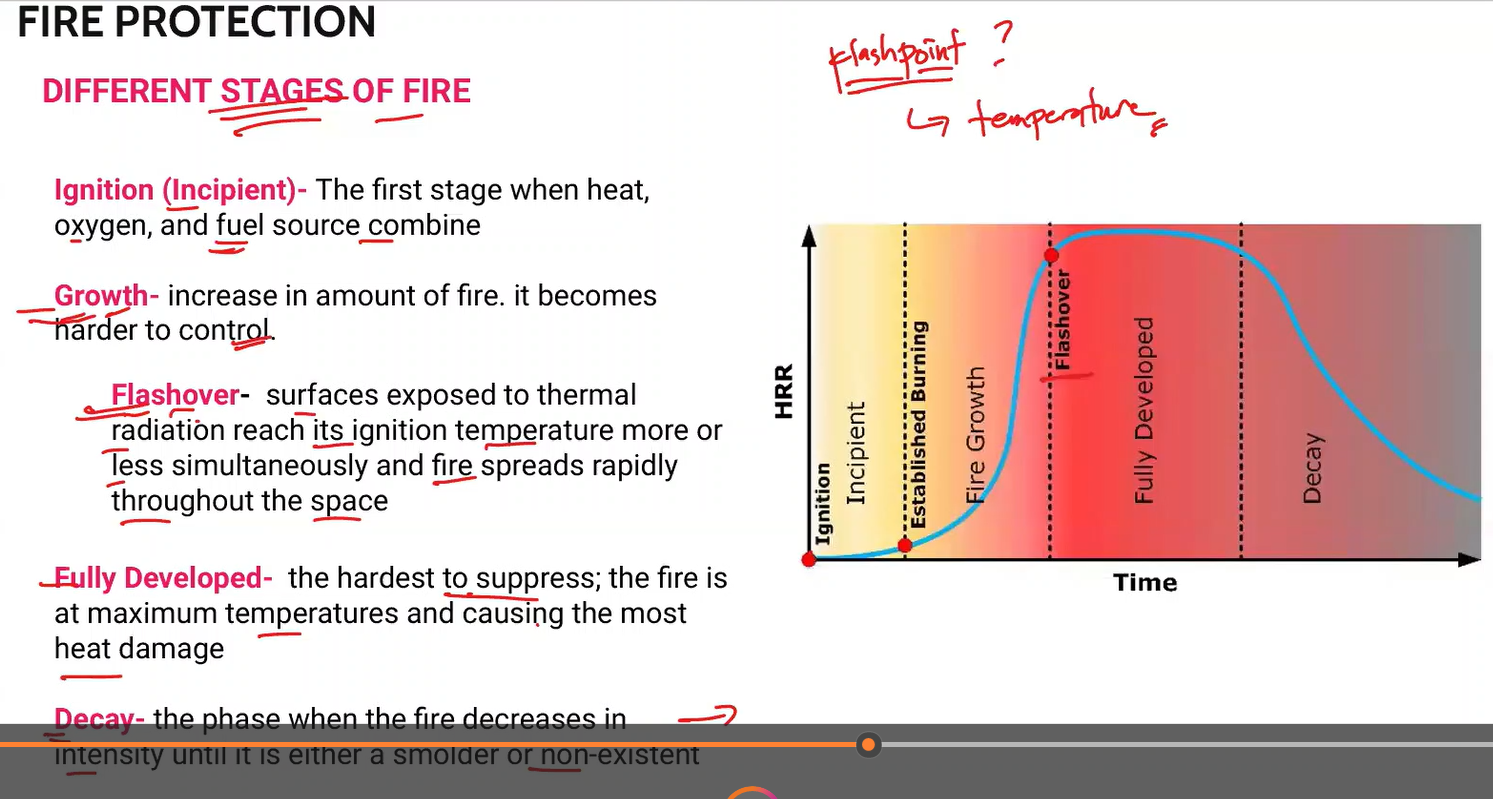
surfaces exposed to thermal radiation reach its ignition temperature more or less simultaneously and fire spreads rapidly throughout the space
Flashover
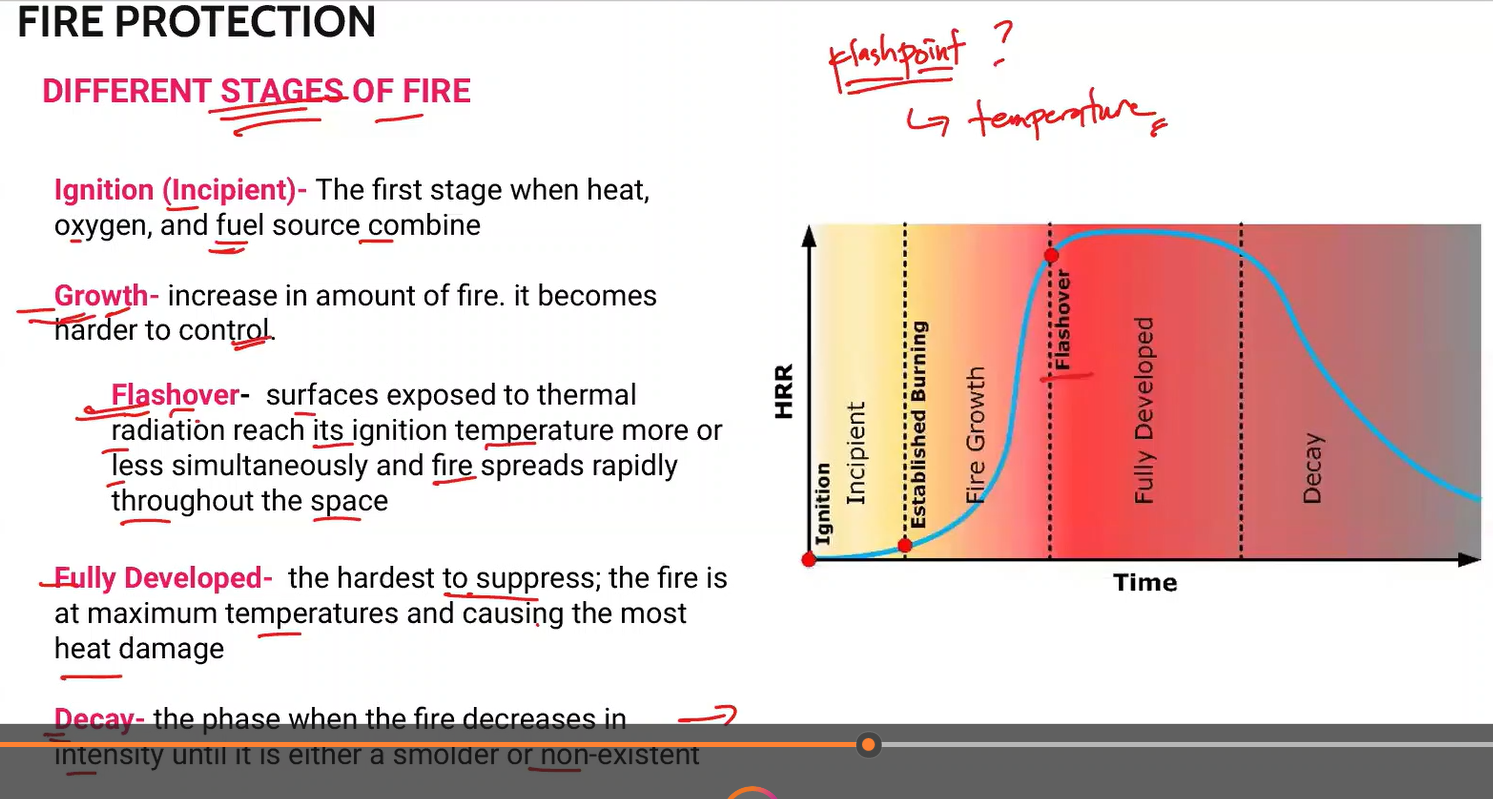
the hardest to suppress; the fire is at maximum temperatures and causing the most heat damage.
Fully Developed Fire
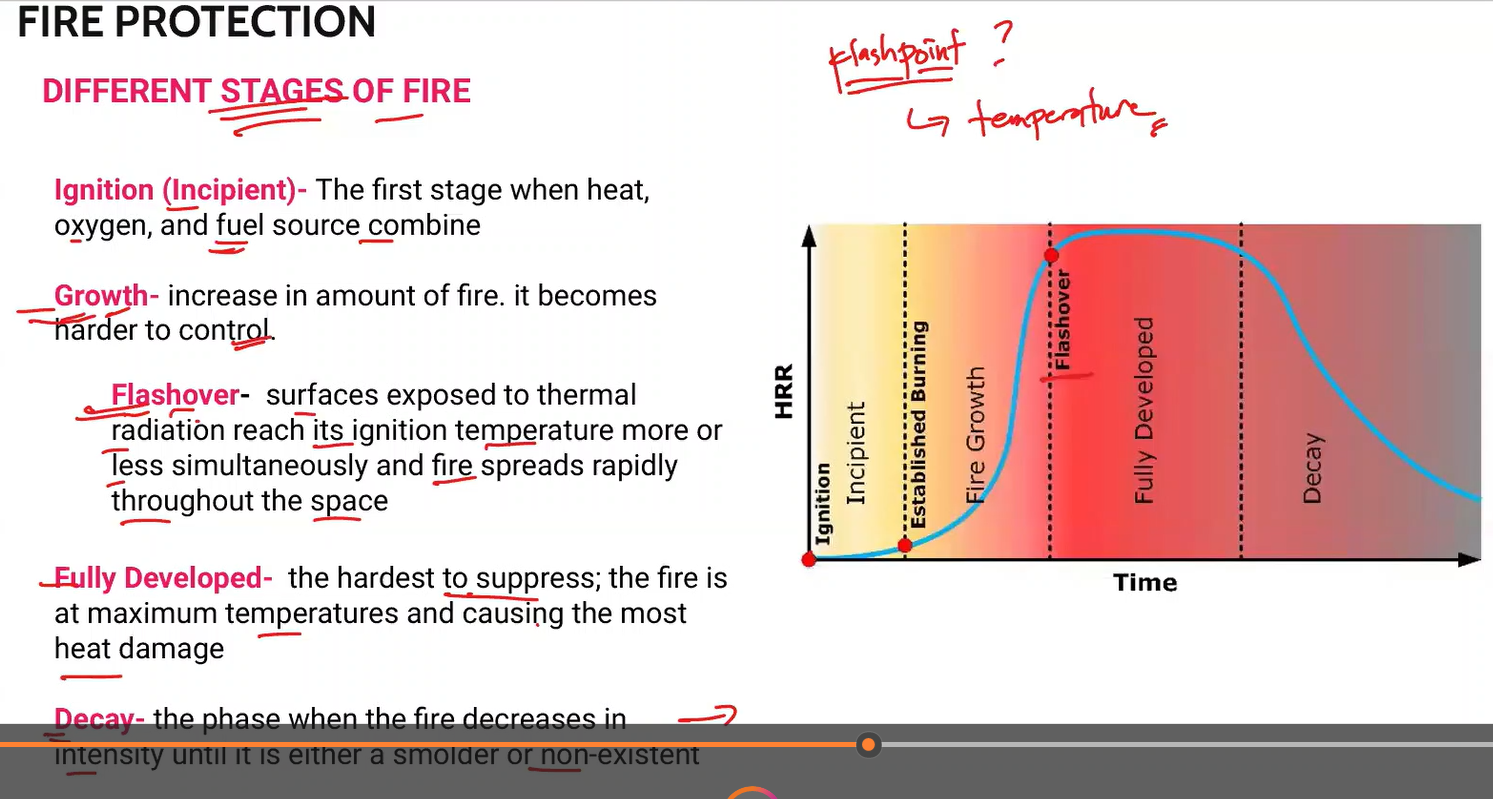
The phase when the fire decreases in intensity until it is either a smolder or non existent
Decay