APES Unit 3 (3.5-3.9) Human Population
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
mortality
death rate
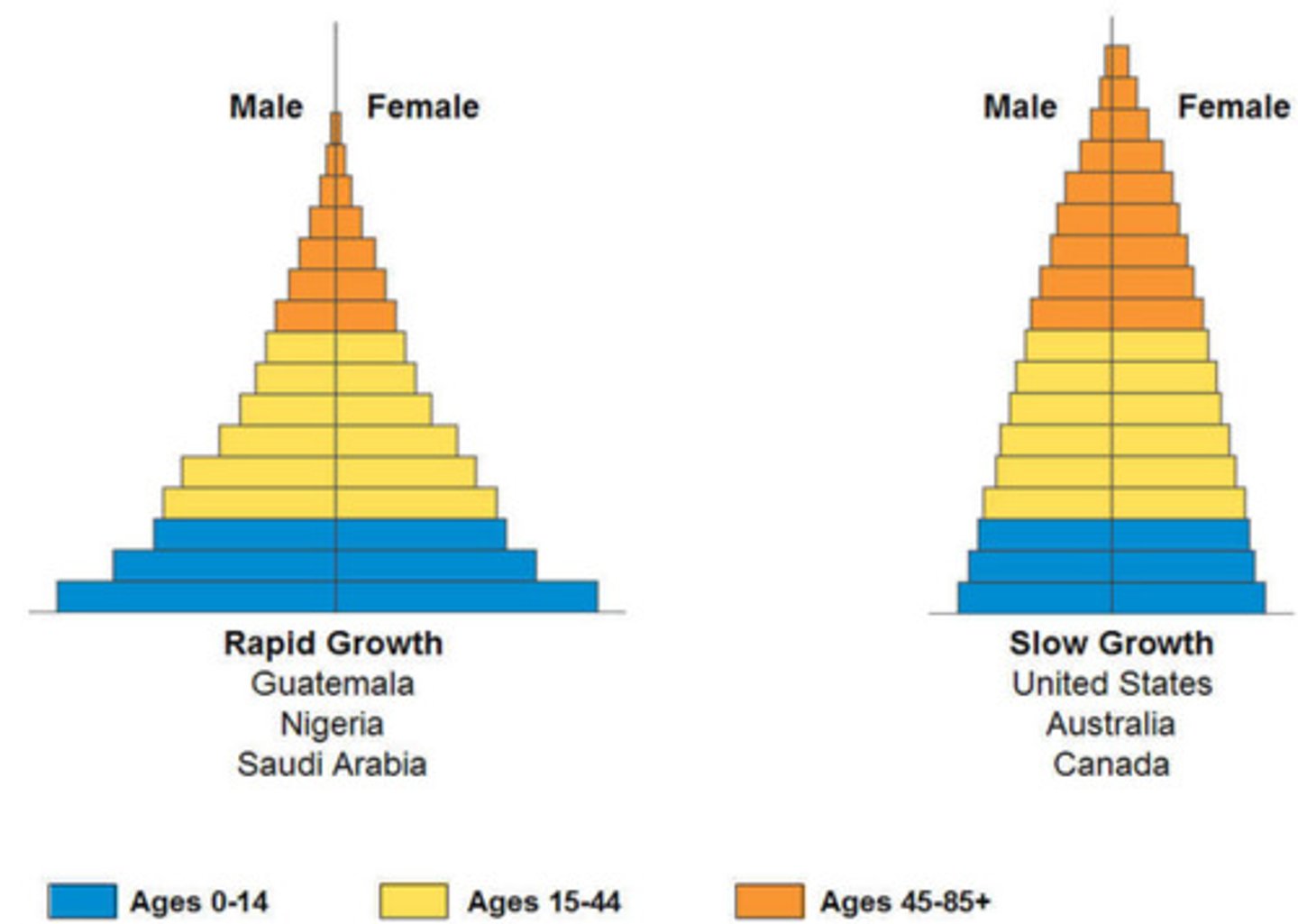
age structure diagram
graph of the numbers of males and females within different age groups of a population
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
the number of births per 1,000 individuals in a population per year
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
the number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a population per year
Human population growth rate (percentage)
(CBR-CDR)/10
doubling time
the time required for a population to double in size. calculated by 70/growth rate (70/2% growth rate = 35 years to double)
TFR (total fertility rate)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years.
Replacement level fertility
The number of children that a woman/couple must have in order to replace the number of people in the population who die. roughly 2.1 for developed nations, higher for undeveloped nations
infant mortality rate
The number of deaths in a year of infants under age 1 for every 1,000 live births. higher in developing countries with less access to health care and clean water
child mortality
the number of deaths per year of children under age 5 per 1000 live births
per capita
per person
population momentum
continued population growth after growth reduction measures have been implemented (basically the lag time between enacting birth control policies and them actually having an effect on population growth)
affluence
wealth. as a country develops further, its citizens become more affluent, and they consume more resources. this increases their environmental impact.
standard of living
Quality of life based on ownership of necessities and luxuries that make life easier.
The theory of demographic transition
the theory that as a country moves from a subsistence economy to industrialization and increased affluence it undergoes a predictable shift in population growth with 4 distinct stages
Phase 1: Preindustrial Country
High birth rate and high death rate = little population growth. Low GDP, low standard of living, high TFR, agriculture-based economy with little development. (Virtually no country on earth is still in stage 1)
Phase 2: Industrializing Country
Death rate drops, birth rate stays high, leading to rapid population growth. Improving access to healthcare, clean drinking water, and per capita GDP cause standard of living to rise and infant mortality to drop. (India, Congo, Haiti)
Phase 3: Stable Pop. Growth
Economic and educational improvements lead to slow, gradual population growth. Per capita GDP increases, causing families to have fewer children as they go to school longer and work more. Availability and knowledge of birth control also decrease TFR. (US, Canada)
Phase 4: Declining Pop. Growth
Affluence and economic development are so high that TFR & CBR decline even further. Increased access to health care and higher standard of living lead to increased life expectancy. With people living longer, and having fewer children, CDR can actually pass CBR, leading to slight population decline. (Japan, UK, Germany, Italy)
GDP
Gross Domestic Product- the total market value of all final goods and services produced annually in an economy. The higher, the more wealthy or affluent a country is.
per capita GDP
GDP divided by the total population. The higher, the more affluent or wealthy the citizens of a country.
family planning
The practice of regulating the number or spacing of offspring through the use of birth control (pills, condoms, information about sex ed)
developing country
A country that has low industrial production and little modern technology. Typically has low GDP, low standard of living.
developed country
a modern, industrialized country in which people are generally better educated and healthier and live longer than people in developing countries do