AP Human Geography Unit 7 MCQ Practice Set
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
79 Terms
Each image (Image A: train, Image B: boat) shows a different way that products of the Industrial Revolution were transported. Which of the following statements best compares the impacts of the two forms of transportation?
A) The form of transportation in image A allowed for more global transportation of goods, while the form of transportation in image B allowed for more local transportation of goods.
B) Both forms of transportation required use of sustainable energy resources.
C) Both forms of transportation accelerated production and distribution of goods.
D) The form of transportation in image A generally transported goods, while the form of transportation in image B generally transported people.
E) Both forms of transportation discouraged the growth of cities.
C) Both forms of transportation accelerated production and distribution of goods.
Which of the following changes in global economic patterns occurred because of the innovations depicted in the two images (Image A: train, Image B: boat)?
A) Most regions developed the two innovations shown in the images independently, with a rapid increase in output and worldwide distribution capabilities.
B) The two innovations led to the development of many new cities and expansion of the leisure travel industry for people living near major transportation hubs.
C) Early adopters of the two innovations began to increase colonization in search of new sources of raw materials for manufacturing goods.
D) Development of the two innovations significantly increased economic equality in the world as goods could be spread much more evenly between countries.
E) Development of the two innovations allowed most people to stop working in agriculture and train for jobs in the travel industry.
C) Early adopters of the two innovations began to increase colonization in search of new sources of raw materials for manufacturing goods.
Which of the following best explains how the diffusion of industrialization relates to the two images shown (Image A: stone bridge, Image B: steel bridge)?
A) The stone bridge predates the Industrial Revolution. The technology for steel bridgework became available through the diffusion of steel manufacturing processes.
B) Both bridges were built after the diffusion of technologies from the Industrial Revolution because the technology for constructing permanent bridges was not available until the late 1700s.
C) The steel bridge was not built until the very end of the Industrial Revolution because stone bridges were stronger in their design and the strength of steel was not realized until much later.
D) Bridge construction types are specific to local culture and do not indicate a diffusion of technology because there is little evidence of a specific pattern of diffusion between cities.
E) The stone bridge is a safer de
A) The stone bridge predates the Industrial Revolution. The technology for steel bridgework became available through the diffusion of steel manufacturing processes.
Which of the following explains the development patterns for a country that has a large proportion of its economy engaged in the secondary economic sector?
A) The country exhibits extremely high land values as vast acreage is needed for manufacturing plants and luxury housing developments for manufacturing executives.
B) The country has an aging urban population and is importing day laborers from rural areas to keep up with the demands of production.
C) The country has a large population of well-educated labor, but it is widely dispersed around the country, distant from manufacturing facilities and employment opportunities.
D) The country has access to shipping lanes and inexpensive transport options that lead to establishment of factories close to raw materials or to markets, depending on the manufacturing process.
E) The country has available resources important to manufacturing, such as water and fossil fuels, but
D) The country has access to shipping lanes and inexpensive transport options that lead to establishment of factories close to raw materials or to markets, depending on the manufacturing process.
Which of the following best explains the relationship of a country's economic sector employment to its development level?
A) Semiperiphery countries and periphery countries have the highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector because of the emphasis on technology development.
B) Semiperiphery countries and core countries have the highest percentage of workers in the secondary sector because of the economic dominance of manufacturing.
C) Periphery countries have the highest percentage of workers in the secondary sector because of the availability of natural resources.
D) Core countries have the highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector and the lowest percentage of workers in the primary sector because of the economic emphasis on services.
E) Periphery countries have highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector and the lowest percentage of workers in the primary sector because of their impor
D) Core countries have the highest percentage of workers in the tertiary sector and the lowest percentage of workers in the primary sector because of the economic emphasis on services.
The higher gross domestic product per capita in some less developed countries such as Brazil, South Africa, and Malaysia is best explained by increases in the value of the country's
A) manufacturing output and service industry employment
B) textile and clothing manufacturing
C) agricultural land development and the number of farmers
D) foreign aid payments and food aid from other countries
E) women-owned business and microloan programs
A) manufacturing output and service industry employment
Which of the following factors best explains a limitation of GDP by country in comparing the level of productivity among countries?
A) Different agricultural outputs, such as Malaysia, Russia, and Greece
B) Similar-sized land areas, such as Germany, Italy, and the United Kingdom
C) Significant petroleum exports, such Iran, Iraq, and Mexico
D) Similar workforces, such as South Korea, Spain, and France
E) Different population sizes, such as China, Japan, and the United States
E) Different population sizes, such as China, Japan, and the United States
Explain how a map showing India's GDP per capita by state represents an incomplete picture of the economy in India.
A) The data do not measure the informal economy, which in regions with high employment in agriculture could be significant.
B) The data are measured per capita, so the total economy for each state in India cannot be compared.
C) The data do not show the different sectors of the economy, so states in India with low employment in agriculture appear to be wealthier.
D) The data do not include population figures, and without that information an accurate comparison cannot be made.
E) The data are measured in rupees and cannot be compared to data from countries that use a different currency.
A) The data do not measure the informal economy, which in regions with high employment in agriculture could be significant.
A table ranks countries by their HDI scores; however, each of their GDPs vary significantly. Which of the following statements explains a limitation of using gross national income per capita compared to the Human Development Index as a measure of development?
A) Using gross national income per capita in a composite measure of development does not allow for cross-national comparisons of purchasing power, a key indicator of development.
B) Using gross national income per capita as a measure of development puts too much importance on economic production as the sole measure of development.
C) The importance of gross national income per capita as a measure of development is reduced because it factors in life expectancy and education with the value of economic production.
D) Gross national income per capita does not factor in population and therefore reduces the overall accuracy as a measure of development.
E) The differen
B) Using gross national income per capita as a measure of development puts too much importance on economic production as the sole measure of development.
By tradition it is uncommon for women to hold personal bank accounts in Pakistan, and until the 1990s this was much the same in Bangladesh. Which of the following best explains the significant increase in the percent of women with bank accounts in Bangladesh?
A) The increased access to microlending institutions for women, such as the Grameen Bank
B) The increased number of women leaders in national politics, such as Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina Wazed
C) The increased number of coeducational universities, such as the University of Dhaka
D) The decrease in access to landownership for many women, such as those working in agriculture
E) The decrease in the total fertility rate due to health initiatives, such as government-sponsored family-planning programs
A) The increased access to microlending institutions for women, such as the Grameen Bank
A table ranks countries by their GII scores; however, each of their GDPs vary significantly. Which of the following statements explains the data relationship between the statistics shown in the table?
A) A high level of economic development does not guarantee that women will have an equitable position in society.
B) A high level of economic development guarantees that women will have an equitable position in society.
C) A high GII score indicates high levels of gender equality and a high level of economic development.
D) A high GII ranking, in the top 6, indicates a low level of gender equality and a high level of economic development.
E) A high GII ranking, in the top 6, indicates a high level of gender equality and a low level of economic development.
A) A high level of economic development does not guarantee that women will have an equitable position in society.
Rostow's stages of development can easily be applied to countries such as the United States and Japan, but not so easily to countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Bolivia, because the theory
A) is predicated on less developed countries receiving financial assistance from more developed countries
B) places emphasis on developed nations having less developed nations to exploit for resources
C) ignores unevenness in development across the globe
D) does not take into account the interdependence of places and regions
E) highlights the semiperiphery as the most successful in development
B) places emphasis on developed nations having less developed nations to exploit for resources
Which of the following explains the most significant weakness of Wallerstein's world system theory?
A) The levels of development described in world system theory have little in common with the levels described in Rostow's stages of growth.
B) World system theory relies on a global system of trade, without which industrializing states like Brazil could not develop economically.
C) World system theory does not explain that historical core countries, like China, could decline and be reclassified as semiperiphery.
D) World system theory provides little explanation about how a country like South Korea could rise from a peripheral country to a core economy.
E) World system theory does not factor labor as a resource that all countries are dependent on for economic development.
D) World system theory provides little explanation about how a country like South Korea could rise from a peripheral country to a core economy.
Which of the following best explains a political-economic weakness or limitation of Rostow's stages of economic growth?
A) The model does not hold up to modern times because essentially all countries around the world have moved through Rostow's stages of economic growth as expected.
B) Rostow made the inaccurate assumption that all countries want modernization as defined in the model and would pass through the outlined stages in order.
C) According to Rostow, countries will become less dependent on the sales of their commodities as they advance.
D) Some critics claim commodities were exchanged between core and periphery areas well before modern times.
E) The stages as defined by Rostow are not useful because sustainability is not addressed.
B) Rostow made the inaccurate assumption that all countries want modernization as defined in the model and would pass through the outlined stages in order.
Chile is able to grow and harvest grapes and strawberries in the months of October through April, while in the United States such fruit is harvested from April through October. The United States has a much larger manufacturing capacity and ships durable goods such as cars and trucks to Chile. These examples can best be explained by
A) divergent patterns of spatial diffusion
B) the economic concept of transferability
C) the industrial processes of a commodity chain
D) the economic principle of comparative advantage
E) the uneven development resulting from colonialism
D) the economic principle of comparative advantage
Which of the following explains how microlending policies can lead to interdependence in the world economy?
A) Microlending policies increase debt in less developed countries because banks in more developed countries make the loans.
B) Microlending policies result in decreased infrastructure expenditures in less developed countries because the loans are specifically for improvements in more developed countries.
C) Increased restrictions for the lending of microloans by banks and international lending agencies make it difficult for less developed countries to succeed in their goals.
D) Decreased funding opportunities for governments in less developed countries through microlending policies have led to isolationism and decreased trade.
E) Increased funding opportunities for individuals in less developed countries have led to increased economic stability on a local level and trade opportunities with other countries.
E) Increased funding opportunities for individuals in less developed countries have led to increased economic stability on a local level and trade opportunities with other countries.
In 2008, a debt crisis within the United States housing market triggered a global economic crisis. Which of the following best explains how this process occurred?
A) Because the United States is a member of the World Trade Organization (WTO), all members of the WTO were equally affected by the crisis within the United States.
B) Properties owned by American businesses and individuals experienced a sharp decrease in value throughout the world.
C) Because the global financial system is interconnected, banks in other countries were negatively affected by the crisis in the United States.
D) Following the debt crisis in the United States, other countries disengaged from supranational free trade agreements with the United States.
E) The debt crisis prompted many Americans to move abroad, causing housing shortages in countries with a lower cost of living.
C) Because the global financial system is interconnected, banks in other countries were negatively affected by the crisis in the United States.
An image simply shows an open-pit coal mine in the United States. Which of the following best explains a limitation of the image in analyzing economic patterns of coal mining?
A) It does not indicate the pattern of environmental impacts associated with open-pit coal mining.
B) It does not convey the availability of alternative sources of energy within the area shown.
C) It does not indicate potential health risks associated with working at a coal mine.
D) It does not indicate patterns of restructuring that have resulted in a decrease in coal mining jobs.
E) It does not convey the distance of the coal mine to the closest urban area.
D) It does not indicate patterns of restructuring that have resulted in a decrease in coal mining jobs.
A map shows the 2017 GDP per capita by country, with darker shading indicating higher GDP per capita. Which of the following best explains a limitation of the map in answering questions about the world's changing economic landscape?
A) The map shows all the countries of the world and their level of development according to GDP per capita without regard to the size of the country's population.
B) The map suggests that the most productive economies are located mostly in the global north and that the least productive are located mostly in the global south, revealing a global pattern of development.
C) The map shows GDP at the country scale, which is not appropriate for the analysis of change in the contemporary economic landscape at the global scale.
D) The map shows economic productivity as GDP per capita in each country for a single year, but does not show change over time that would indicate a level of economic growt
D) The map shows economic productivity as GDP per capita in each country for a single year, but does not show change over time that would indicate a level of economic growth or decline.
In less developed countries, ecotourism blends environmental sustainability with the travel and hospitality service industry. This combination attracts global tourists to locations such as Mount Kilimanjaro, the Serengeti Plain, and Victoria Falls in Africa. Which of the following best explains the relationship between global ecotourism and economic sustainability at the local scale?
A) As ecotourism increases in popularity, it is predicted to become the only viable path to local economic sustainability in less developed countries.
B) The largest ecotourism resorts lead to economic sustainability at the local scale, whereas smaller resorts have little effect on local economies.
C) Global ecotourism does not necessarily lead to local economic sustainability, as workers might not be paid a living wage at ecotourism resorts.
D) Global ecotourism always leads to economic sustainability at the local scale, but it also lea
C) Global ecotourism does not necessarily lead to local economic sustainability, as workers might not be paid a living wage at ecotourism resorts.
Microfinance is a form of banking whereby financial institutions issue small loans to people with low incomes, generally in less developed countries. Which of the following best explains how microfinance loans are intended to contribute to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals?
A) Microfinance loans are used for environmental remediation, which contributes to the goal of reversing land degradation.
B) Microfinance loans are available exclusively to women, which contributes to the goal of gender equality.
C) Microfinance loans are used to pay for college tuition, which contributes to the goal of providing quality education.
D) Microfinance loans fund research on renewable fuels, which contributes to the goal of providing clean and affordable energy.
E) Microfinance loans enable people to start small businesses, which contributes to the goal of ending poverty.
E) Microfinance loans enable people to start small businesses, which contributes to the goal of ending poverty.
Which of the following scenarios is best explained by the increasing global popularity of ecotourism?
A) The expansion of luxury resorts owned by multinational hotel companies along Thai and Indonesian beaches that is based on tourists' attraction to tropical locations
B) The high traffic and congestion at sites like Yellowstone National Park due to tourists' increased desire to experience the outdoors
C) The expansion of cruise experiences that take passengers to multiple Caribbean and Central American countries because of tourists' desire to experience a variety of global cultures
D) The increased use of snowmobiles, aircraft, and off-road vehicles by tour companies in Alaska as people seek to experience more remote locations to view wildlife
E) The development of small, locally owned lodges near ecological preserves in the Brazilian Amazon due to tourists' desire to benefit the local economy and minimize their env
E) The development of small, locally owned lodges near ecological preserves in the Brazilian Amazon due to tourists' desire to benefit the local economy and minimize their environmental impact
Outsourced industrial production in less-developed countries often relies on female labor because
A) men are engaged mainly in agriculture
B) wage rates for women are much lower than for men
C) women are more skilled at operating machinery than men are
D) social taboos prevent women from working in the service sector
E) women are not protected by international labor laws
B) wage rates for women are much lower than for men
Which of the following arguments help explain why seventy-five percent of those employed in Export Processing Zones, such as maquiladoras, are women?
I. Women have better educational qualifications than men.
II. Women are paid less than men.
III. Many employers consider women to be more dexterous than men.
IV. Many employers consider women more likely to organize unions than men
A) I and III only
B) II and III only
C) II and IV only
D) I, II, and III only
E) I, II, III, and IV
B) II and III only
Free-trade zones such as the countries of the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) are established to increase the ease and volume of international trade by
A) increasing diplomatic relations between member states
B) opening borders to migrant guest workers from member states
C) establishing a common monetary unit among member states
D) offering large economic-development loans to poorer member states
E) eliminating tariffs on goods that cross borders between member states
E) eliminating tariffs on goods that cross borders between member states
Which of the following has fostered the most significant economic growth by eliminating import tariffs between member states?
A) European Union (EU)
B) Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)
C) North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
D) Association of Caribbean States (ACS)
E) United Nations (UN)
A) European Union (EU)
It is generally agreed that the current trend in climate change is caused by
A) sea-level rise
B) increased use of fossil fuels
C) reduction in biodiversity
D) tilt of Earth's axis
E) changes in the velocity of ocean currents
B) increased use of fossil fuels
The popularity of which of the following is an example of the trend toward ecotourism?
A) Time-share condominiums on the coast of Spain
B) Ski resorts in Chile
C) National parks in Costa Rica
D) Recreational canals in Florida
E) Artificial lakes in Texas
C) National parks in Costa Rica
Which of the following has contributed most to the deindustrialization of regions like the English Midlands and the North American Manufacturing Belt?
A) The increased percentage of women in the labor force
B) Competition from foreign imports
C) Environmental legislation
D) The formation of free trade associations
E) The decline of labor unions
B) Competition from foreign imports
Political geographers consider which of the following as the core area of the United States?
A) The Los Angeles-San Francisco area
B) The New York-Washington, D.C., area
C) The Chicago-Detroit area
D) The Atlanta-Birmingham, Alabama, area
E) The Buffalo-Cleveland area
B) The New York-Washington, D.C., area
Which of the following concepts explains the decision to relocate market-oriented factories in the United States from the Midwest and Northeast to locations in the southern United States or Mexico?
A) Comparative advantage, because products can be made more efficiently in the southern United States and Mexico. Operating costs and wages are lower, and the manufactured products are easily transported to major United States markets.
B) Growth poles, because governments in southern United States cities and Mexico strive to stimulate economic development by providing a guaranteed market for all products manufactured at these locations.
C) Just-in-time delivery, because the United States population is shifting to the south and west, and the Mexican population is growing. It is critical to produce goods closer to the consumer base to reduce shipping times.
D) Complementarity, because the regional economy of the midwestern a
A) Comparative advantage, because products can be made more efficiently in the southern United States and Mexico. Operating costs and wages are lower, and the manufactured products are easily transported to major United States markets.
A table shows shows statistics for Spain and Kuwait. Spain has a GDP per capita of $28,157, and a GII score of 0.080. On the other hand, Kuwait has a GDP per capita of $29,040, and a GII score of 0.270. Which of the following statements is most consistent with the data shown in the table?
A) There are a large number of women in the Spanish legislature, but few women have been elected in Kuwait.
B) Spain and Kuwait are countries that have very similar levels of economic and social development.
C) An increase in per capita wealth will almost always result in an improvement in gender equity in a country.
D) Spain and Kuwait are countries that have very different levels of economic development.
E) There is a close correlation between the two statistics displayed on the chart above.
A) There are a large number of women in the Spanish legislature, but few women have been elected in Kuwait.
A map shows the locations of world financial, banking, and investment centers. Which of the following best explains a limitation of the map's representation of global economic patterns?
A) The map does not show major population centers located in the Southern Hemisphere.
B) The map does not show the locations of export processing zones in more developed countries.
C) The map does not show the growth of investment in businesses in less developed countries.
D) The map does not show growth poles that stimulate regional economic activity.
E) The map does not show the environmental pollution associated with industrial cities.
C) The map does not show the growth of investment in businesses in less developed countries.
A table ranks countries by their HDI scores, however each of their GII scores vary significantly. Which of the following statements accurately compares a difference between the Human Development Index (HDI) and Gender Inequality Index (GII) as shown in the table?
A) Although women workers are often paid less than their male counterparts, GII scores can remain high.
B) High numbers of women working in education and health care directly result in a higher GII score.
C) Although there are more women in the wage labor force, females do not necessarily have the same level of empowerment as men.
D) In most countries women's life expectancy is higher than men's, which improves gender equality.
E) Although HDI and GII indicators are measured on a scale of 0 to 1, a high HDI score should indicate a high GII score.
C) Although there are more women in the wage labor force, females do not necessarily have the same level of empowerment as men.
The Internet is reshaping traditional economic arrangements by
A) reinforcing the dominance of the central business district for retail sales
B) expanding the importance of express package delivery systems
C) increasing the importance of rail transportation as compared to truck transportation
D) bringing consumers and producers into face-to-face contact
E) creating more enclosed shopping malls
B) expanding the importance of express package delivery systems
The maquiladoras of northern Mexico are
A) manufacturing outsourcing plants
B) illegal migrant-labor camps
C) border squatter settlements
D) organic agricultural cooperatives
E) commercial produce farms
A) manufacturing outsourcing plants
A map shows medical technology growth poles in the United States. Which of the following statements best explains a limitation of the map in showing the geographic context of these growth poles?
A) Each growth pole location is a small special economic zone occupying a few city blocks.
B) Each growth pole location has an international division of labor where low-technology jobs are handled in less developed countries.
C) The pattern of medical technology growth poles across the country indicates the transformation of post-Fordist production systems.
D) Each growth pole location is supported by an international network of researchers and multinational corporate partners.
E) The pattern of medical technology growth poles across the country indicates a dependence on just-in-time production systems.
D) Each growth pole location is supported by an international network of researchers and multinational corporate partners.
Which of the following explains a significant obstacle to sustainable development in more developed countries?
A) The reliance on fossil energy sources for electric generation and vehicle fuel has depleted resources globally and contributed to atmospheric pollution in cities.
B) The reliance on renewable energy for local electric generation and home heating creates significant risks, as alternative energy storage is more expensive than using fossil fuels.
C) High energy prices and low energy consumption have reduced the need for the development of additional sources of renewable energy for individual vehicles and homes.
D) Low population growth in more developed countries has reduced the need for the development of additional sources of renewable energy for individual vehicles and homes.
E) Increased economic productivity in less developed countries has moved investment funding away from the development of new source
A) The reliance on fossil energy sources for electric generation and vehicle fuel has depleted resources globally and contributed to atmospheric pollution in cities.
The country of Costa Rica has protected 25 percent of its land in the form of national parks or other protected areas. Which of the following best explains the desired effect of Costa Rica's process of land preservation?
A) Costa Rica's national parks and preserved areas are intended to promote international ecotourism and support the country's sustainable local economic development.
B) Costa Rica's national parks and preserved areas are designed to attract multinational corporations, providing Costa Rica with economic sustainability.
C) Costa Rica preserved these areas to meet the requirements to join the Central American Common Market, which funds environmental sustainability initiatives in member countries.
D) Costa Rica preserved these areas to establish special economic zones for the exportation of manufactured products to the United States.
E) Costa Rica is predominately an agricultural nation and preserved the
A) Costa Rica's national parks and preserved areas are intended to promote international ecotourism and support the country's sustainable local economic development.
Which of the following explains a negative effect that can occur in countries that depend on ecotourism as a pathway to sustainable economic development?
A) A well-developed ecotourism industry can limit the amount of foreign currency entering a country's economy, reducing funds available for local infrastructure projects.
B) The development of an ecotourism industry can result in a decrease in the number of tourist visits to a country because of limitations on tourist visas.
C) Fees generated by ecotourists can contribute to income inequality in less developed countries.
D) The development of an ecotourism industry can reduce income opportunities for local workers by converting farms to parks.
E) The development of ecotourism can attract multinational tourism corporations that take their earnings out of the country while attracting tourists who impact the local environment.
E) The development of ecotourism can attract multinational tourism corporations that take their earnings out of the country while attracting tourists who impact the local environment.
Which of the following statements explains a weakness in Rostow's stages of economic growth model?
A) The model is based on the principle of initial advantage that highlights the importance of an early start in economic development for all countries in the world.
B) The model is based on successive stages that countries must pass through independently until they reach high mass consumption without taking into account that countries are interdependent.
C) The model is based on the permanent classification of countries into the core, semiperiphery, and periphery, and countries are unable to move up or down from one category to another.
D) The classification for a country pertains to the entire country with no condition for variation in the level of development within a country.
E) The model is based on the premise that development in one place requires underdevelopment in another place.
B) The model is based on successive stages that countries must pass through independently until they reach high mass consumption without taking into account that countries are interdependent.
Which of the following best explains a trading relationship between two countries based on comparative advantage?
A) One country exports raw materials and the other country exports manufactured goods, resulting in a global economic balance.
B) One country implements tariffs on goods that are imported from another country because the importing country will benefit from profits on the sale of the goods.
C) Each country specializes in the type of good for which it has the lowest opportunity cost, resulting in a higher global output of both types of goods.
D) Two countries trade in luxury items, but the volume of trade is limited by the highest cost of long-distance trade.
E) Each country exports the same type of good because the countries are similar in terms of natural resources and labor costs.
C) Each country specializes in the type of good for which it has the lowest opportunity cost, resulting in a higher global output of both types of goods.
Which of the following explains a limitation of the three-tiered structure of Wallerstein's world systems theory?
A) The model does not provide for countries outside of the core to accomplish any of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
B) The scale of the model does not pertain to individual countries but rather to regions in the global contexts of core, semiperiphery, and periphery.
C) Individual countries can score higher on certain indicators of development and lower on other indicators as they shift from the periphery to the core.
D) The model locks most countries into the development model of core, semiperiphery, and periphery with little opportunity for peripheral economies to advance into the wealthy core.
E) The three-tiered system of the model cannot be mapped; therefore, the model has no spatial application.
D) The model locks most countries into the development model of core, semiperiphery, and periphery with little opportunity for peripheral economies to advance into the wealthy core.
Which statement explains one way in which the transformation of India's economy contradicts Wallerstein's world system theory?
A) As a British colony, India functioned as a peripheral region supplying resources to benefit the core.
B) Using a development strategy to avoid economic dependency, India has been able to develop its own industries and participate fully in the global economy.
C) The outsourcing of high-tech jobs with high wages to India by U.S. companies is not economic exploitation because the jobs are high paying.
D) India's ethnically, linguistically, and religiously diverse populations serve as centrifugal forces, preventing India from participating in the global economy.
E) India's emphasis on nonalignment with and isolation from the Heartland has limited the country's role in supranational organizations and international decision-making.
B) Using a development strategy to avoid economic dependency, India has been able to develop its own industries and participate fully in the global economy.
In the context of industrialization, how does the use of stone in bridges compare to the use of metal in bridges?
A) The change from stone to iron bridges had no impact on industrialization because stone was readily available and stronger than iron.
B) The change from stone to iron bridges created a great demand by Europeans for bridges because iron bridges were less expensive to build.
C) The scarcity in stone for building bridges facilitated the need to import new materials such as iron, leading to globalization and the rise of industrialization in Europe.
D) The development of the metals industry led to the construction of higher and longer bridges, a reduced need for stone as a building material, and rapid industrialization.
E) Bridges of stone were not constructed in Europe until modern times because the use of iron as a building material developed in the United States and did not diffuse to Europe until the ear
D) The development of the metals industry led to the construction of higher and longer bridges, a reduced need for stone as a building material, and rapid industrialization.
The two images (first one = 1 train, second one = numerous trains) illustrate advancements in technology resulting from the Industrial Revolution. Comparing the images, which of the following statements best illustrates an impact of the Industrial Revolution on society?
A) Industrialization technologies were applied to agriculture and to the transportation of agricultural products to widespread markets that led to greater food supplies and a surge in the population.
B) One major unintended change that came with industrialization was the standardization of time in order to provide nationwide schedules that were an aid to improving the efficiency of train travel in the United States.
C) The invention of the steam engine and the construction of steel bridges to carry trains across various physical features led to ever-increasing demand for the materials and labor to build more trains and tracks.
D) The Industrial Revolu
C) The invention of the steam engine and the construction of steel bridges to carry trains across various physical features led to ever-increasing demand for the materials and labor to build more trains and tracks.
Compare the two images (first = train, second = ship). What do the technologies shown demonstrate about the Industrial Revolution?
A) The dependence on large quantities of steel has limited industrial growth to areas with high concentration of coal and iron.
B) The increased transportation technology has enabled the diffusion and expansion of industrial activities.
C) Industrial centers must be built along rivers or waterways to facilitate the transportation of raw materials and finished goods.
D) The initial take-off stages of the Industrial Revolution focused solely on heavy, material-oriented industries.
E) Due to the cost of such large-scale industrial projects, industrialization has been unable to diffuse to developing countries.
B) The increased transportation technology has enabled the diffusion and expansion of industrial activities.
Economic activities that involve the extraction of natural resources, such as lumbering, fishing, mining, and agriculture, are called
A) subsistence activities
B) organic activities
C) secondary economic activities
D) primary economic activities
E) tertiary economic activities
D) primary economic activities
Quaternary economic activities are those that
A) extract natural resources from the environment
B) transform raw materials into finished products
C) involve the collection, processing, and manipulation of information
D) involve the exchange of goods and the provision of services
E) involve the production of fresh produce for urban markets
C) involve the collection, processing, and manipulation of information
Compared with more-developed countries, which of the following statements is true of less developed countries?
A) A higher percent of the labor force is engaged in food production.
B) The population pyramids exhibit narrower bases.
C) The per capita consumption of energy is higher.
D) The natural increase of the population is lower.
E) Fertility rates are lower.
A) A higher percent of the labor force is engaged in food production.
Which of the following explains the spatial patterns of economic development for most countries in Southeast Asia, including Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam?
A) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the semiperiphery because of the extensive growth of the secondary economic sector.
B) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the semiperiphery because of the dominance of the primary economic sector.
C) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the periphery because of the dominance of the tertiary economic sector.
D) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the periphery because of the dominance of the secondary economic sector.
E) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the core because of the dominance of the tertiary economic sector.
A) Most Southeast Asian countries are considered to be part of the semiperiphery because of the extensive growth of the secondary economic sector.
Which of the following best explains the relationship between GDP per capita and world system theory?
A) There is an uneven distribution of economic development and geographical division of labor in the world.
B) There is an even distribution of economic development and geographical division of labor in the world.
C) The countries with the highest GDP are also those with primary economic activities.
D) The countries with the lowest GDP are those with tertiary economic activities.
E) The peripheral countries have higher levels of both GDP and primary economic activities.
A) There is an uneven distribution of economic development and geographical division of labor in the world.
What would be the most profitable location for an ethanol manufacturing plant that converts corn into alcohol for use as an additive for gasoline?
A) Near a large university to facilitate the recruitment highly trained chemists
B) Near a break-of-bulk point for ease of transportation
C) Near a navigable river to reduce transportation costs to distant markets
D) Near a prime corn-producing area to minimize transportation costs of raw materials
E) Near a large metropolitan area to serve a major market
D) Near a prime corn-producing area to minimize transportation costs of raw materials
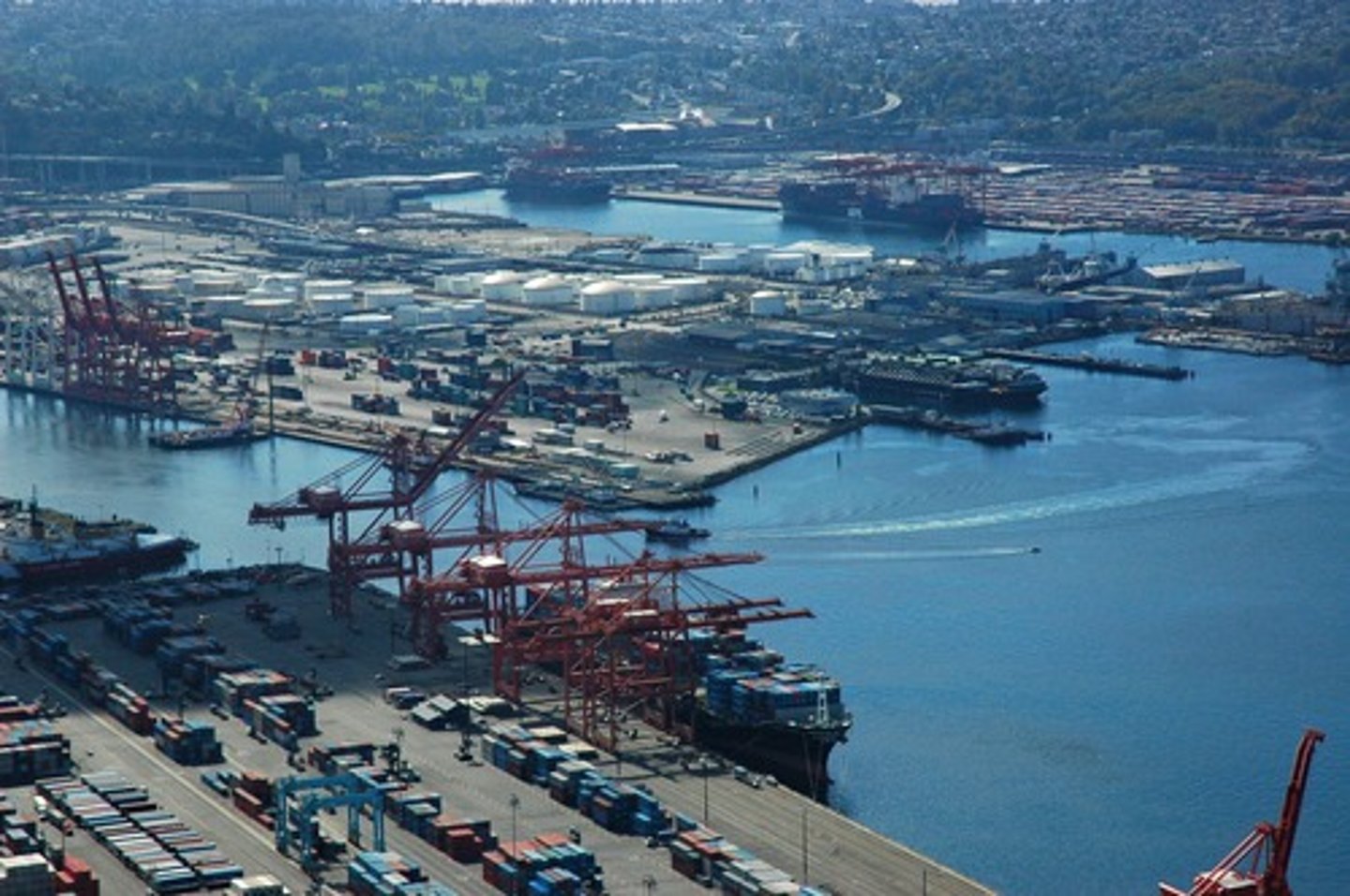
The port of Los Angeles is the busiest port in the United States and a major break-of-bulk point. Which of the following statements correctly explains why Los Angeles is a break-of-bulk point?
A) The robotic systems at the port results in fewer workers being required to unload container ships.
B) The port can accommodate large container ships that can be unloaded quickly so that containers can be transferred onto carriers that use California's highway and rail systems.
C) The massive warehouses located at the port allow goods from container ships to be stored easily for long periods of time.
D) Goods can be transferred to other container ships going to the port of San Francisco.
E) Los Angeles is on the Pacific Ocean allowing for more trade with countries in Asia.
B) The port can accommodate large container ships that can be unloaded quickly so that containers can be transferred onto carriers that use California's highway and rail systems.
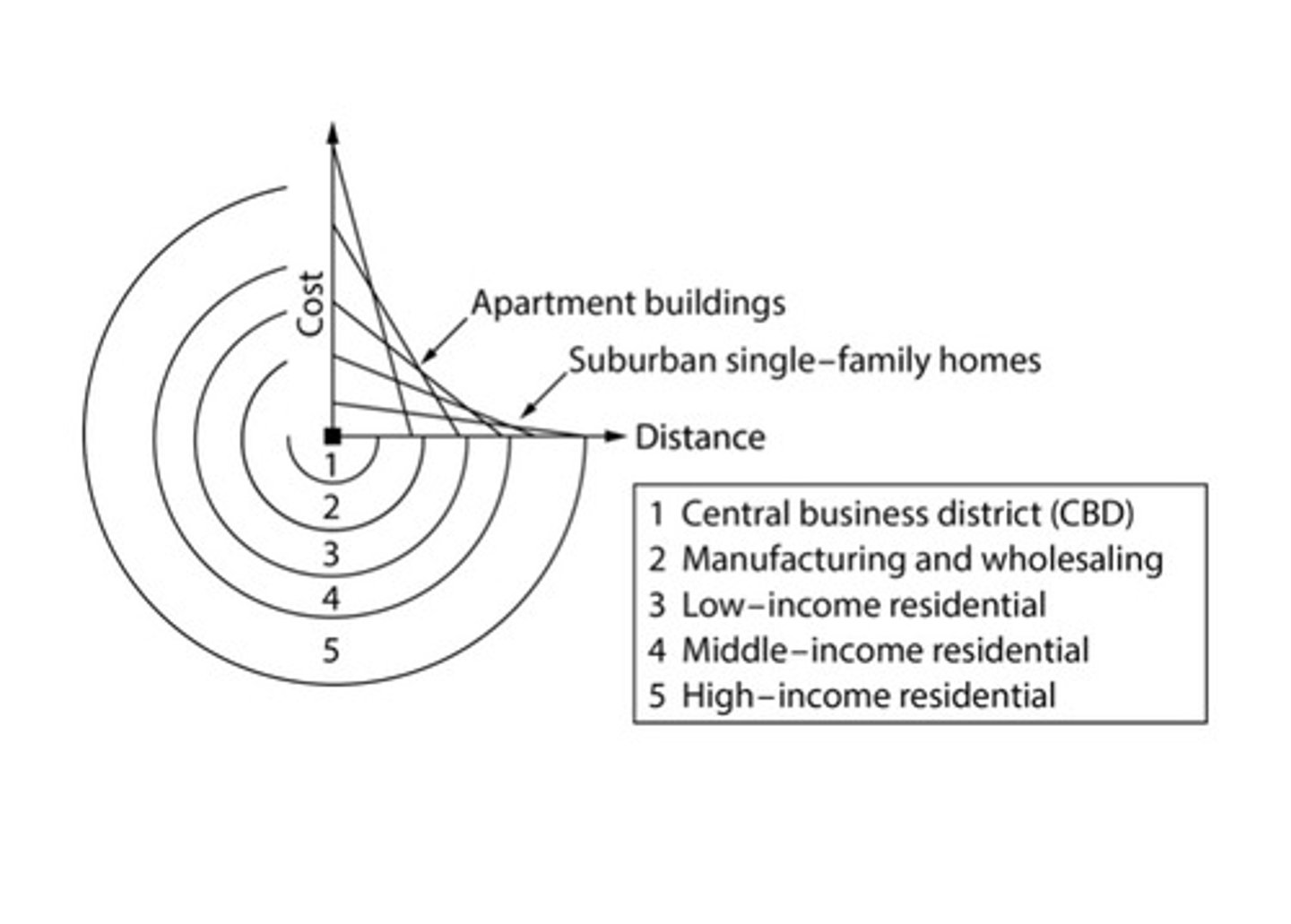
The reason for the concentration of copper smelters, refineries, and foundries close to Arizona's copper mines is that copper production is
A) a bulk-reducing industry
B) a bulk-gaining industry
C) dependent on dry climate conditions
D) attracted to low-cost migrant labor
E) oriented to the large Southern California market
A) a bulk-reducing industry
Which of the following industries will most likely locate closest to its raw material sources?
A) Soft-drink bottling
B) Brewing
C) Nickel smelting
D) Baking
E) Automobile assembly
C) Nickel smelting
Which of the following modes of transportation is characterized by low terminal cost, high line cost, and high route flexibility?
A) Truck
B) Train
C) Ship
D) Pipeline
E) Airplane
A) Truck
It's relatively easy to load a truck, and not very expensive --> low terminal cost
You have to constantly gas up --> high line cost
You can go on a multitude of roads or highways to get to your destination --> high route flexibility
Which of the following modes of transportation is characterized by high terminal cost, low line cost, and low route flexibility?
A) Truck
B) Train
C) Ship
D) Pipeline
E) Airplane
B) Train
It's hard to load a train --> high terminal cost
You don't have to stop to get coal. The only time trains will stop is when they get to their destination --> low line cost
Trains are literally attached to a railroad can't go off it --> low route flexibility
Which of the following modes of transportation is characterized by high terminal cost, low line cost, and high route flexibility?
A) Truck
B) Train
C) Ship
D) Pipeline
E) Airplane
C) Ship
Hard to load a ship --> high terminal cost
The cost per kilometer is low --> low line cost
Ships have the entire sea to work with and operate in --> high route flexibility
Which of the following modes of transportation is characterized by high terminal cost, high line cost, and high route flexibility?
A) Truck
B) Train
C) Ship
D) Pipeline
E) Airplane
E) Airplane
Hard to load a plane --> high terminal cost
Trains have to stop to gas up and be worked on --> high line cost
Have the entire sky to work with --> high route flexibility
Environmental laws, labor availability, and access to markets are major factors affecting which of the following?
A) Political affiliation
B) Gross domestic product
C) Property tax rates
D) Manufacturing locations
E) Transportation costs
D) Manufacturing locations
The early stages of the core-periphery model describe the
A) relationship between the outward appearance of a place and its internal functioning
B) ways that suburban workers commute to urban workplaces
C) relationship between the underlying structure of a society and its outward expressions
D) social and cultural differences between urban and rural people
E) relationship of power and the transfer of resources from less developed to more developed areas.
E) relationship of power and the transfer of resources from less developed to more developed areas.
Contemporary manufacturing is characterized by
A) production facilities that are generally located as close as possible to the sites of raw material production
B) strong unions and localized involvement in all facets of the production process
C) spatial disaggregation of the production process
D) reliance on highly skilled labor at all phases of the production process
E) production facilities located close to railroads
C) spatial disaggregation of the production process
All of the following have helped create ghettos in North American cities EXCEPT
A) blockbusting and racial steering
B) redlining by financial institutions
C) concentration of public housing and social services
D) fixed school district boundaries
E) Economic Enterprise Zones
E) Economic Enterprise Zones

According to central place theory, the threshold is defined as the
A) economic base of a central place
B) distance away from a central place
C) gross value of the product minus the costs of production
D) minimum number of people needed to support a service
E) point at which consumer movement is at a minimum
D) minimum number of people needed to support a service
La Défense is an edge city constructed in the late twentieth century and characterized by high-rise office buildings. Which of the following best explains why La Défense is located on the outskirts of Paris?
A) The land at the center of Paris is filled with numerous historic buildings that residents do not want torn down.
B) Land in the city center is not as valuable as land on the edge of the city.
C) The center of Paris is not well-served by public transportation.
D) La Défense needs access to the river in order to export manufactured goods to other countries in Europe.
E) The center of Paris is inhabited by low-income residents, and wealthy residents prefer to live in the suburbs.
A) The land at the center of Paris is filled with numerous historic buildings that residents do not want torn down.
Most Latin American cities are focused on a
A) central plaza
B) government housing project
C) zone of heavy industry
D) skyscraper office building
E) squatter settlement
A) central plaza
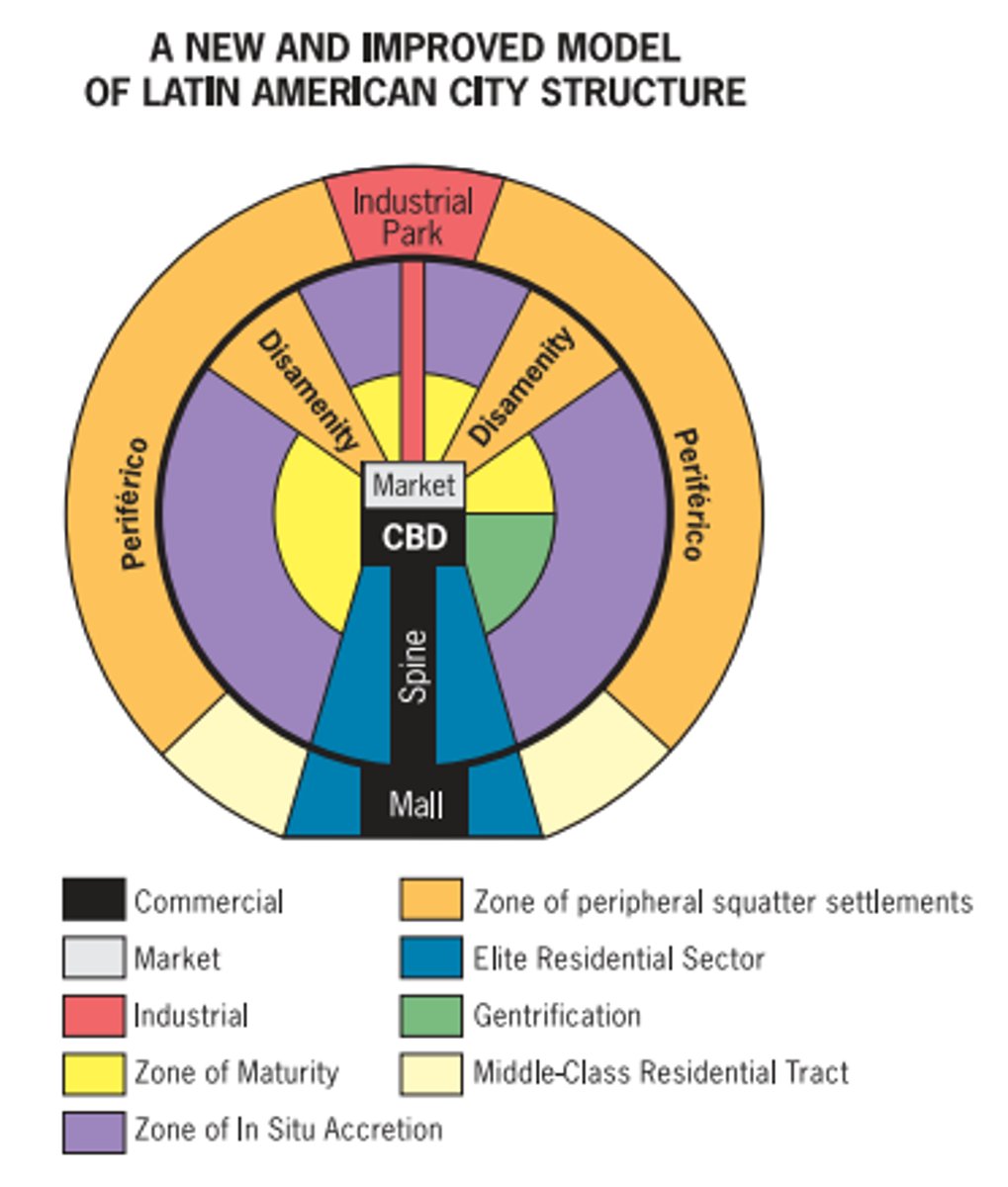
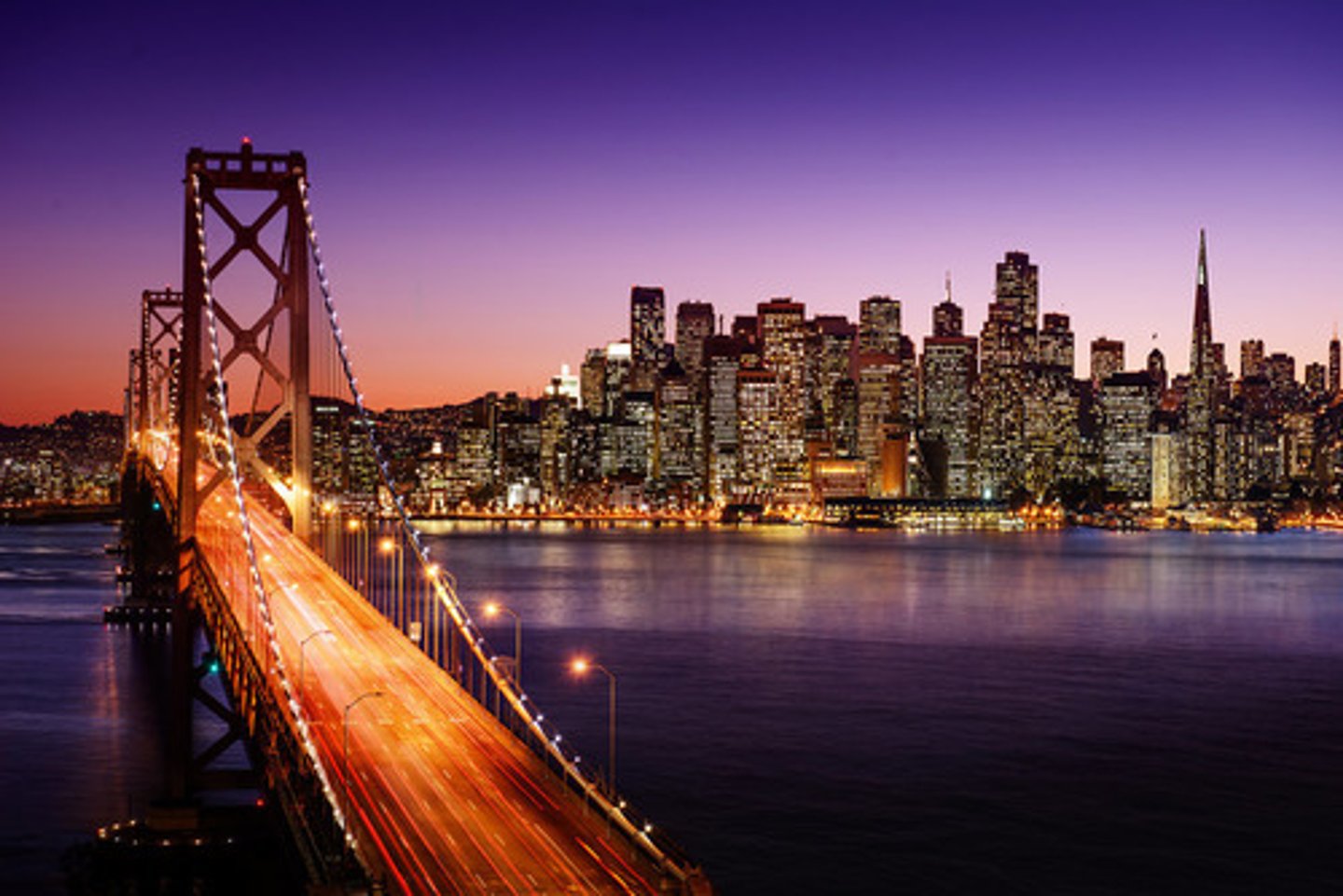
International company headquarters, significant global financial functions, and a polarized social structure are defining characteristics of
A) primate cities
B) entrepôts
C) forward capitals
D) world cities
E) edge cities
D) world cities

Which of the following factors best explains the development and expansion of squatter settlements?
A) Gentrification of megacities in more developed countries displacing large numbers of urban dwellers
B) Rapid urbanization and inability of infrastructure to keep pace with the growth of megacities in developing countries
C) Urban dwellers seeking residential housing and shopping outside the congestion of the city
D) Zoning laws in developing countries that prevent current urban dwellers from obtaining land to build residential structures
E) The growth of urban agriculture encouraging migrant farm workers to move to cities requiring more housing
B) Rapid urbanization and inability of infrastructure to keep pace with the growth of megacities in developing countries
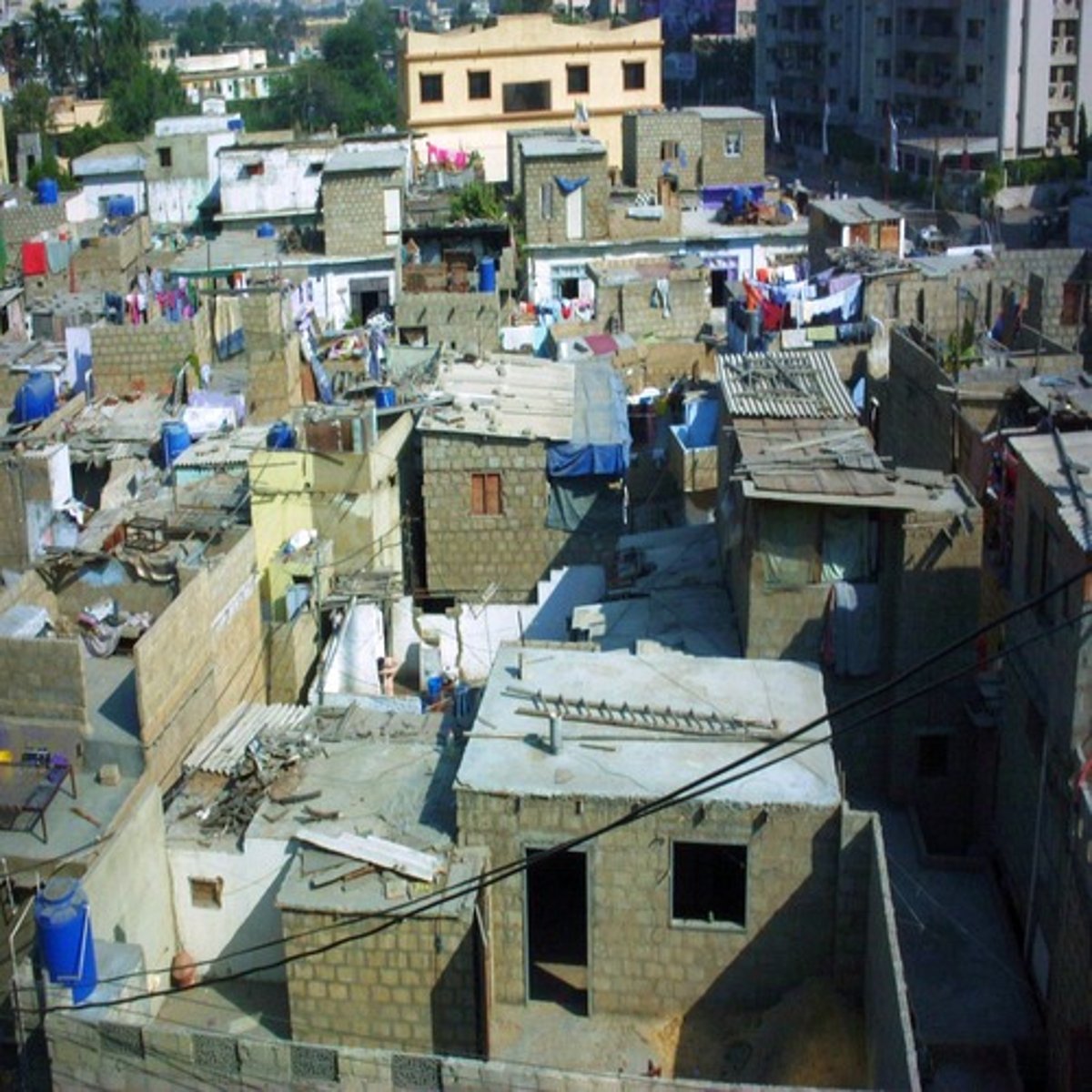

Squatter settlements exist in cities of less-developed countries because
A) city governments set aside vacant areas for new migrants
B) people want to live near the center of the city, where jobs are located
C) affordable housing is not available elsewhere for new migrants to the city
D) new migrants prefer to live in squatter settlements with other recent migrants
E) new migrants need to be isolated from other city residents until they adjust to urban life
C) affordable housing is not available elsewhere for new migrants to the city

Henderson, Nevada, a suburb of Las Vegas, has seen high population growth and lots of new housing be built. Which of the following best explains this growth in population and housing?
A) The growth brought on by resource extraction and industrialization
B) The impacts of deindustrialization in other Sun Belt-region cities
C) A period of immigration from southern Europe and eastern Europe
D) A cycle of rapid economic development and real estate investment
E) A phase of water-resource and hydroelectric-power development
D) A cycle of rapid economic development and real estate investment
Using the concentric-zone model, which of the following design concepts of urban development is likely to have the most significant impact on the reduction of urban sprawl?
A) Transformation of warehouse space in zone 2 of the model into high-income rental properties
B) Construction of a large single-family housing development in zone 4 of the model
C) Gentrification of older housing in selected neighborhoods in zone 3 of the model
D) Construction of a large shopping mall in zone 1 of the model
E) Mixed-use land development in zone 5 of the model
E) Mixed-use land development in zone 5 of the model
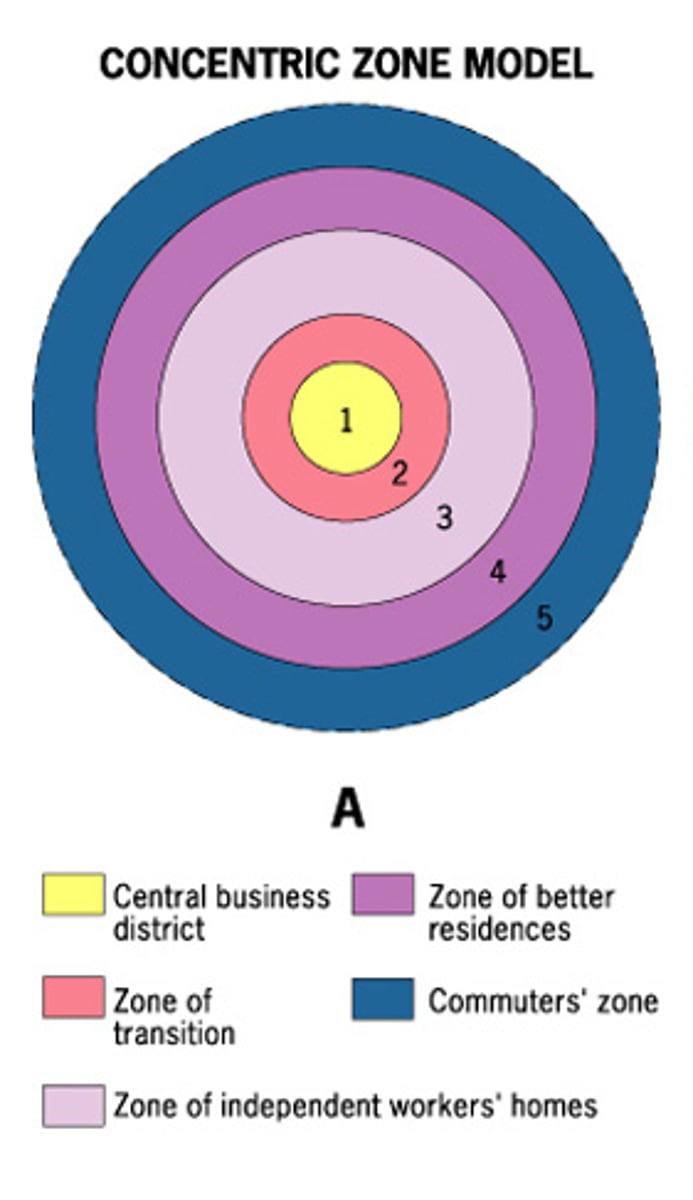
Which of the following statements explains the cost and distance relationship illustrated in the concentric-zone model in relation to the urban area's residential patterns?
A) Since land is more expensive in the suburbs, wealthier families build larger single-family homes in zone 5 in areas that provide amenities such as private schools for their children.
B) Land is cheaper near the central business district (CBD), resulting in the construction of low-income apartments and giving low-income residents access to the amenities of the CBD.
C) The lower cost of land farther from the CBD makes it affordable to build single-family homes in zones 4 and 5 for middle-income and high-income residents who desire to move into less crowded areas.
D) People do not live in the CBD because of the traffic congestion, high cost of land, and lack of amenities such as museums and restaurants.
E) Population density increases with the dis
C) The lower cost of land farther from the CBD makes it affordable to build single-family homes in zones 4 and 5 for middle-income and high-income residents who desire to move into less crowded areas.
Which of the following most closely describes the leading trend in retailing in the United States during the 1950s, 1970s, and 1990s?
A) Downtown business district --> Shopping mall --> "Big box" superstore
B) Downtown business district --> "Big box" superstore --> Shopping mall
C) Shopping mall --> Downtown business district --> "Big box" superstore
D) "Big box" superstore --> Downtown business district --> Shopping mall
E) "Big box" superstore --> Shopping mall --> Downtown business district
A) Downtown business district --> Shopping mall --> "Big box" superstore
Which of the following best illustrates how the top 10 world cities are connected globally in ways that transcend national borders?
A) Tokyo developing into one of the largest megacities
B) London building a new financial district
C) London and Tokyo being seats of national governments
D) New York City and Tokyo being located in coastal environments
E) Chinatown and the United Nations being located in New York City
E) Chinatown and the United Nations being located in New York City

Which of the following statements best explains how the top 10 world cities function within the world's urban hierarchy?
A) The top ten world cities have a significant impact on the international economy and are important drivers of globalization.
B) The cities with larger populations are the biggest drivers of global innovation.
C) The cities with smaller populations can be expected to experience the fastest rates of population growth within the next several decades.
D) The top ten world cities offer a wide array of services, but these services are restricted to local populations.
E) The top ten world cities are diminishing in financial and cultural significance due to the process of globalization.
A) The top ten world cities have a significant impact on the international economy and are important drivers of globalization.

According to the sector model of North American city structure, members of low-income groups tend to live in which of the following places?
A) The inner city only
B) Peripheral temporary settlements
C) Linear residential areas radiating from the center city outward
D) Evenly dispersed throughout the urban area
E) The suburbs and rural areas only
C) Linear residential areas radiating from the center city outward

Which of the following refers to the size and functional complexity of cities?
A) Multiplier effect
B) Urban hierarchy
C) Basic-nonbasic ratio
D) Threshold ratio
E) The Sector model
B) Urban hierarchy
California's Silicon Valley is an example of a high-technology region. Which of the following would best accompany the map shown to help explain the origins of this high-technology region?
A)A description of high-technology multinational corporations such as Google and Apple that have located their headquarters in the area
B)A description of how the area's research institutions, including Stanford University and the NASA Ames Research Center, served as growth poles for development
C)A description of the construction of interstate highways in California and how development occurred at the transportation nodes created by major highway intersections
D)A description of how residential suburbs such as Redwood City and Cupertino formed within the San Francisco-Oakland metropolitan area
E)A description of how edge cities such as Palo Alto and San Jose formed on the periphery of the San Francisco-Oakland metropolitan area
B) A description of how the area's research institutions, including Stanford University and the NASA Ames Research Center, served as growth poles for development