Antibodies & Antigen Receptors
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
IgM
What is the most primitive antibody?
IgM
What antibody is short lived and does not have memory?
IgG
What antibody is long lived and has a memory function?
Humoral immune response
Secretion of antibodies
1. Isotype switch
2. High affinity and specificity
3. Memory B cells
What 3 things only occur via T cell dependent activation?
Efferent lymph
Mature B cells travel to the lymph node via the bloodstream and leave via the ___________________
High endothelial venules
Specialized capillary that helps activated lymphocytes get into the peripheral blood from lymph node (also does the opposite)
A
T or F: Both B and T cells after being activated will move to the edge of the follicle for T-B activation
Immunoglobulins
Glycoprotein molecules which are produced by plasma cells in response to an immunogen and which function as antibodies
Antigenic determinant
Each immunoglobulin binds to a specific ___________________
Antigen binding
What is the primary function of antibodies that can result in protection of the host?
Antitoxin
Antibodies against a specific toxin
Normal serum
Describe the serum electrophoresis
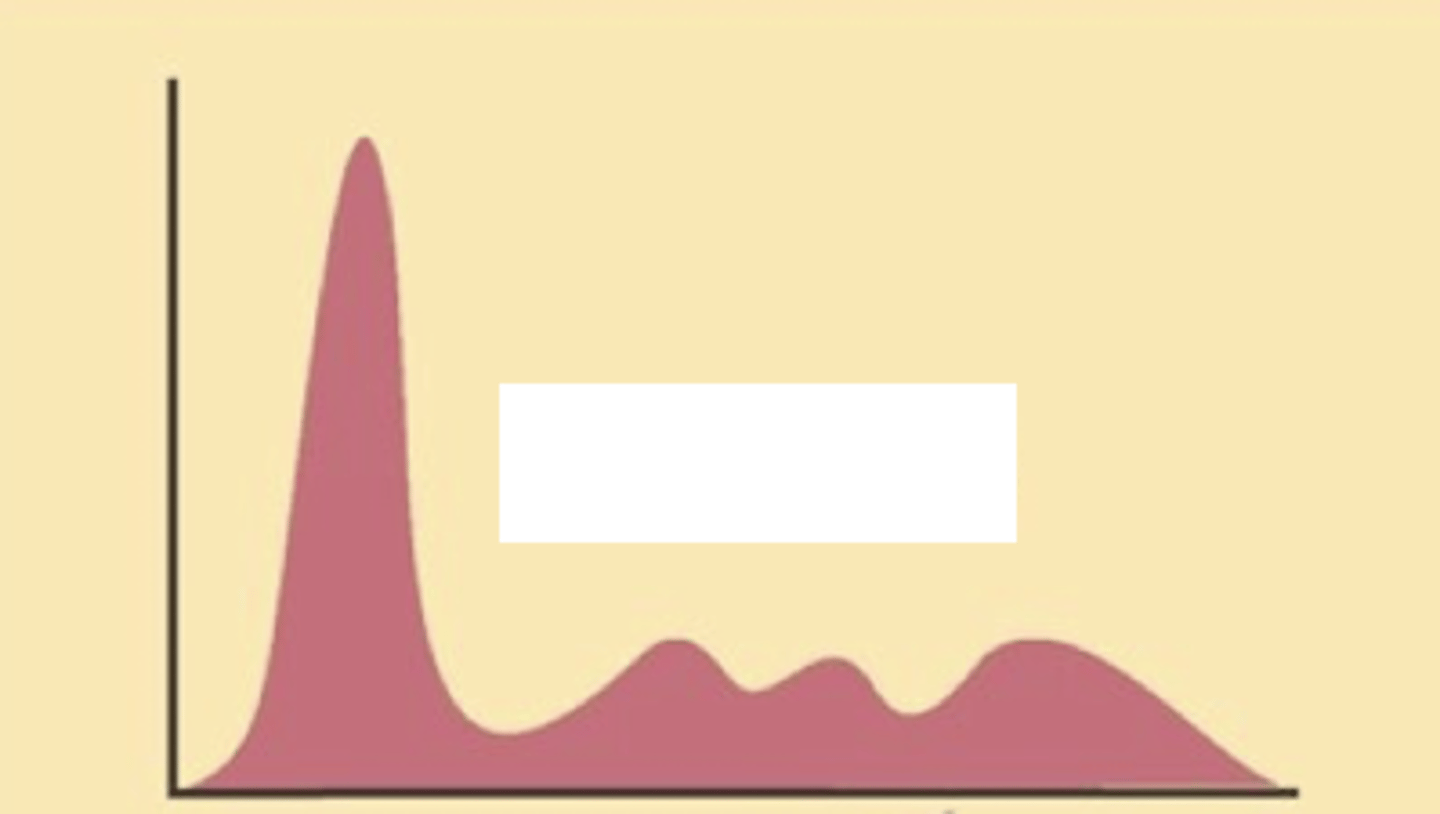
Polyclonal gammopathy
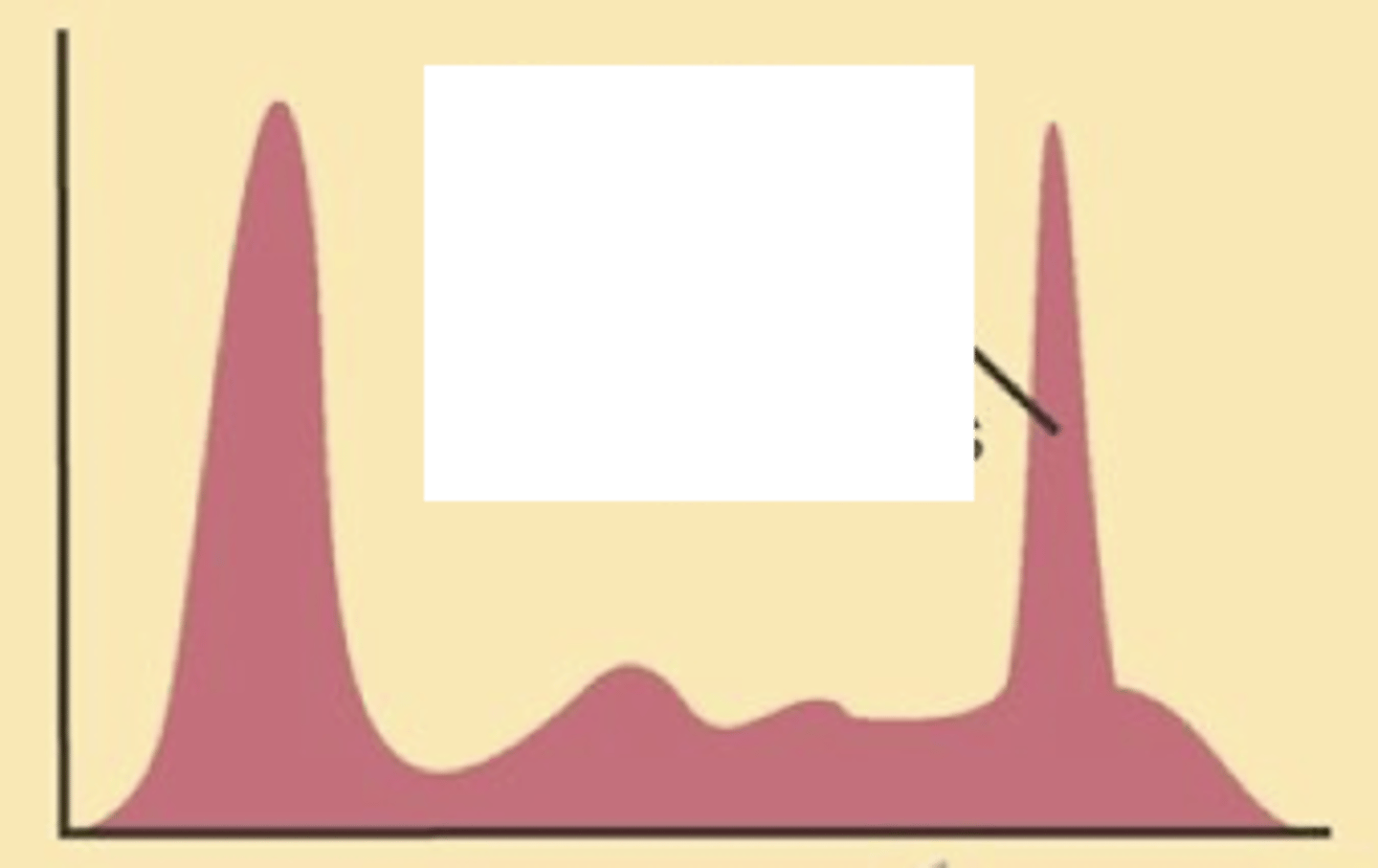
Describe the serum electrophoresis
Monoclonal gammopathy
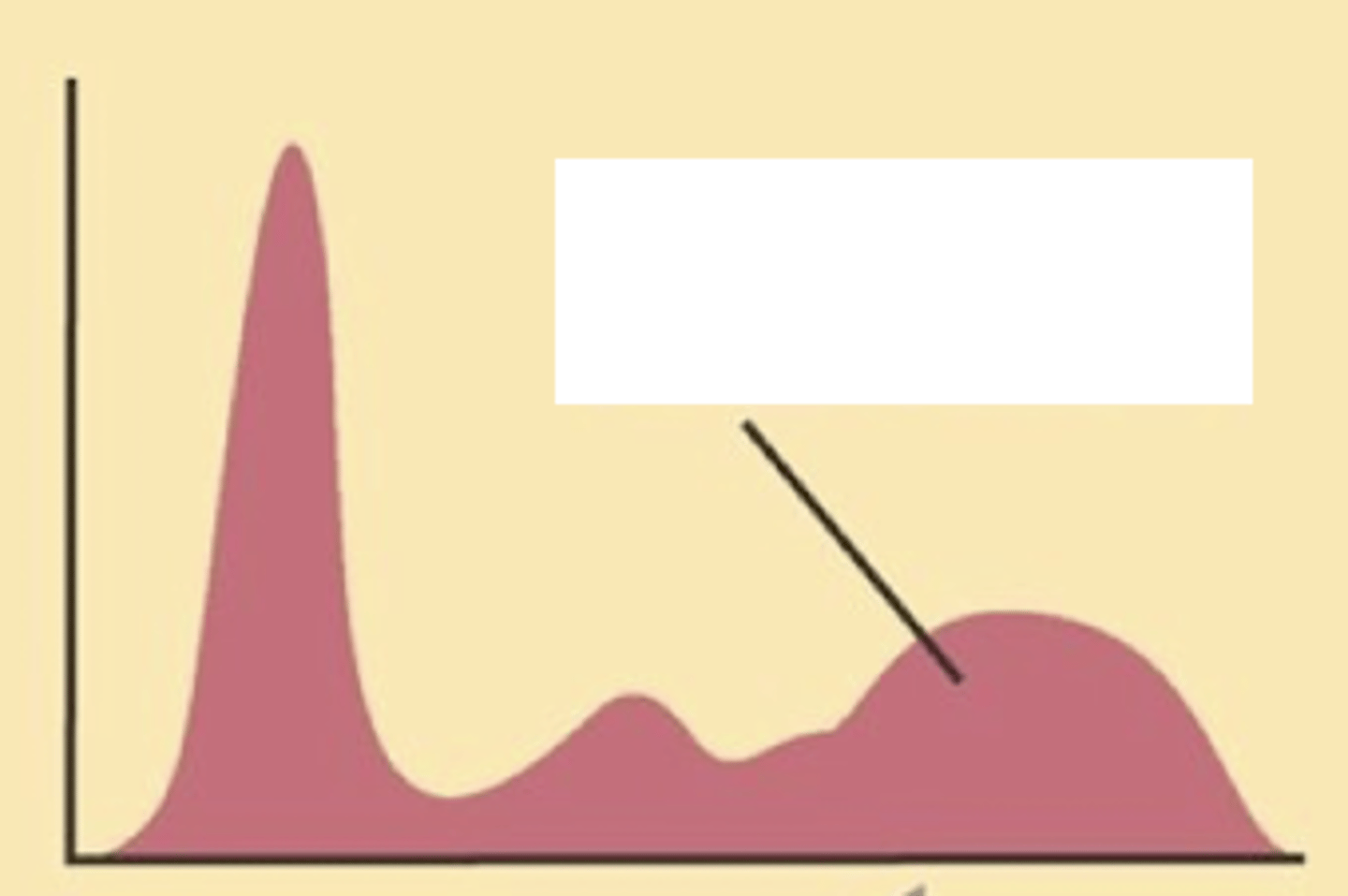
Describe the serum electrophoresis
Polyclonal gammopathies
Characterized by an increased in all immunoglobulins as a result of excessive activity of many different clones of plasma cells
Infections/autoimmune disease
What should you think about for polyclonal gammopathies?
Monoclonal gammopathies
Due to a single precursor of clone plasma cell that secrete homogenous immunoglobulins
Myeloma (plasma cell tumor)
What should you think about for monoclonal gammopathies?
Valency
The number of antigenic determinants that an individual antibody molecule can bind
2
The valency of all antibodies is at least what?
Effector functions
Significant biological effects are a consequence of secondary ______________ of antibodies
1. Neutralization
2. Opsonization
3. Complement activation
4. Antibody dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity
What are the (4) antibody effector functions?
1. V (variable) region
2. C (constant) region
What are the two functional parts of antibodies?
V (variable) region
H & L chains ("Fab") are the antigen binding sites
C (constant) region
Heavy chains ("Fc") determine biological role
Antigen binding site
The V (variable) region has what function?
1. Binding to Fc receptors
2. Complement binding site
3. Placental transfer
The C (constant) region has what function?
Idiotype
The specific combination of idiotopes present within an antibodies complement determining regions (CDRs)
Idiotope
Specific region within an antibodies Fv region which binds to the paratope (antigenic epitope binding site) of a different antibody
5
Mammalian B cells make how many different isotypes of heavy-chain constant regions?
2
Mammalian B cells can make _______ different types of light chain constant regions
2
What is the valency of IgG?
2
What is the valency of IgD?
4
What is the valency of IgA?
2
What is the valency of IgE?
10
What is the valency of IgM?
Cytokines
What causes isotype switching in B cells?
Isotype
The expression of a specific __________ determines the function of an antibody via the specific binding to Fc receptor molecules on different immune effector cells
A
T or F: Isotype expression reflects the maturation stage of a B cell
B (helper T cells)
T or F: Isotype switch consists of a change in the heavy-chain constant region made by B cells, which is directed by signals from other B cells
Late
Isotype switch occurs ________ in a primary immune response
Immunoglobulin allotype
The allele of the antibody chains found in the individual
IgM
What is the biggest antibody isotype?
IgD
Antigen receptor on naive B cells whose function is unknown
B
T or F: IgD binds complement
IgM
B cell receptor on naive B cells
IgM
What is the first isotype produced in the primary immune response?
Blood
IgM acts within what?
Complement
IgM efficiently activates _____________
A
T or F: IgM agglutinates more efficiently than IgG
B
T or F: IgG is more efficient at activating complement than IgM
IgG
What is the most abundant isotype in mammalian serum?
Blood and extravascular fluid (systemic)
Where is IgG located?
A
T or F: Soluble IgM and IgG will not activate complement
Late
Agglutination by IgG is greatest during what phase of the immune response?
Opsonization
IgG is very good at what?
IgA
What antibody isotype is predominant in mucosal secretions?
Microbials and toxins
IgA prevents the attachment of what?
J chain
Dimeric IgA is bound by what?
Secretory molecule
Dimeric IgA binds to what to be able to secreted into the lumen?
Parasites and allergies
IgE is associated with what?
Mast cells
IgE binds to Fc receptors on what?
Constant region (AKA Fc region)
What defines how a specific antibody will contribute to an immune response?
IgM
What is the predominant isotype for the primary antibody response?
IgG
What is the predominant isotype for the secondary antibody response?
Memory B cells
What is importantly made with the primary antibody response?
Secondary
The total immunoglobulins is higher during the (primary or secondary) antibody response?
IgG
What is the dominant immunoglobulin in animals?
T cells
(T cells or B cells) distinguish antigens through the primary amino acid sequence
1. Antigen must be processed by APC
2. Antigen must contain protein or peptide
3. Fragment must be displayed in MHC
What are the requirements for T cells to recognize an antigen?
B cells
(T cells or B cells) distinguish antigens through their 3-dimensional structure
A
T or F: Antigens are not processed for B cells to recognize antigens
B
T or F: The epitope cannot bind directly to the B cell receptor
Paired peptides
T and B cells have what in common?
T cell receptors (TCRs)
_________________ contain alpha and beta chains
B cell receptors (BCRs)
________________ contains 2 H chains and 2 L chains (H + L are paired)
2
B cell receptors have what valency?
1
T cell receptors have what valency?
A
T or F: T cell receptors ends of each peptide have different functions and composition
Heavy and light regions
B cell receptor variable regions contain variable ______________________
3
Each variable region of the antigen binding site has _____ hypervariable sites
Complementarity determining regions (CDR)
Antigenic specificity conferred by three hypervariable loops
Non-covalent
The forces that hold an antigen in the receptor are ______________
A
T or F: Antigen binding is not permanent and can be altered by minor changes in shape and charge
VDJ recombination
the process by which T cells and B cells randomly assemble different gene segments - known as variable (V), diversity (D) and joining (J) genes - in order to generate unique receptors (known as antigen receptors) that can collectively recognize many different types of molecule
In bone marrow
The earliest events of VDJ occur where?
Secondary lymphoid organs
Later steps in B cell development happen where?