Nursing #1 exam
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
Eudemonistic Model
Health is seen as a condition of actualization or realization of a person's potential
Health ecology
An evolving view of health recognizes the interconnection between people and their physical and social environments
EX: People are likely to go walking where there are sidewalks (within the community)
Applied research
research undertaken to solve a specific problem
implementing screening
•Community Resources: funds, workers, follow-up services, treatment referrals
•Lead agency: group which oversees program
•Stakeholders: individuals or groups witha legitimate interest (hospitals, service agencies)
•Key community individuals: leaders in community (each community has unique needs)
•Community assessment: systematic method of community data collection
•Target community: high risk population
Nursing Assessment
systematic and continuous collection and analysis of information about the client (think of yourself as a detective)
- Subjective data clients feelings and statements
- Objective are observable, perceptive and measurable
Percussion
one of both hands are used to strike a body surface to produce a sound(ex. hearing sound from stomach)
Nursing Diagnosis
describes an actual risk or wellness human response to a health problem that nurses are responsible for treating independently. Describes the clients response to the disease process, developmental stage, or life process and provide a convenient way to communicate nursing therapies or interventions.
Nursing Implementation
- Control of infections already in the body (UTI or pressure ulcers)
- Monitoring and intermediately report of S&S
- Provided patient comfort through pan control
- Dressing (wet-to-dry)
- Prevent cross-contamination
- Good body alignments
- Frequent body reposition
- Prevent foot drop
- teach patient about toxic reactions
- Continuous psychologic and emotional support
Holism
acknowledges and respects the interaction of a person's mind, body, and spirit within the environment; thus, it cannot be fully understood if examined solely in pieces apart from their environment.
Before 1940 nursing
Health=absence of disease
- Infectious diseases prominent
- Physician: independent primary practitioner
- Government: start public health/welfare
1940s to 1950s nursing
health=ability to fulfill roles
- physicals for fitness
- physicians linked to hospital services
- increased federal role: hospital expansion, federal programs
1960s to present nursing
Health=adaptation and reaction to environment
- disease/prevention/ health promotion
- emphasis on individual responsibility/lifestyle choices
- advance practice nurses became health providers
- government: control costs
-person-centered care- holistic care with patient input
Resilience
one's ability to deal with stress and trauma
Models of Health
- Clinical: absence s/s disease; prevention not emphasized
- Role Performance: health based on whether person can perform societal roles
- Adaptive: ability to adapt positively to change (social, mental, physiologic)
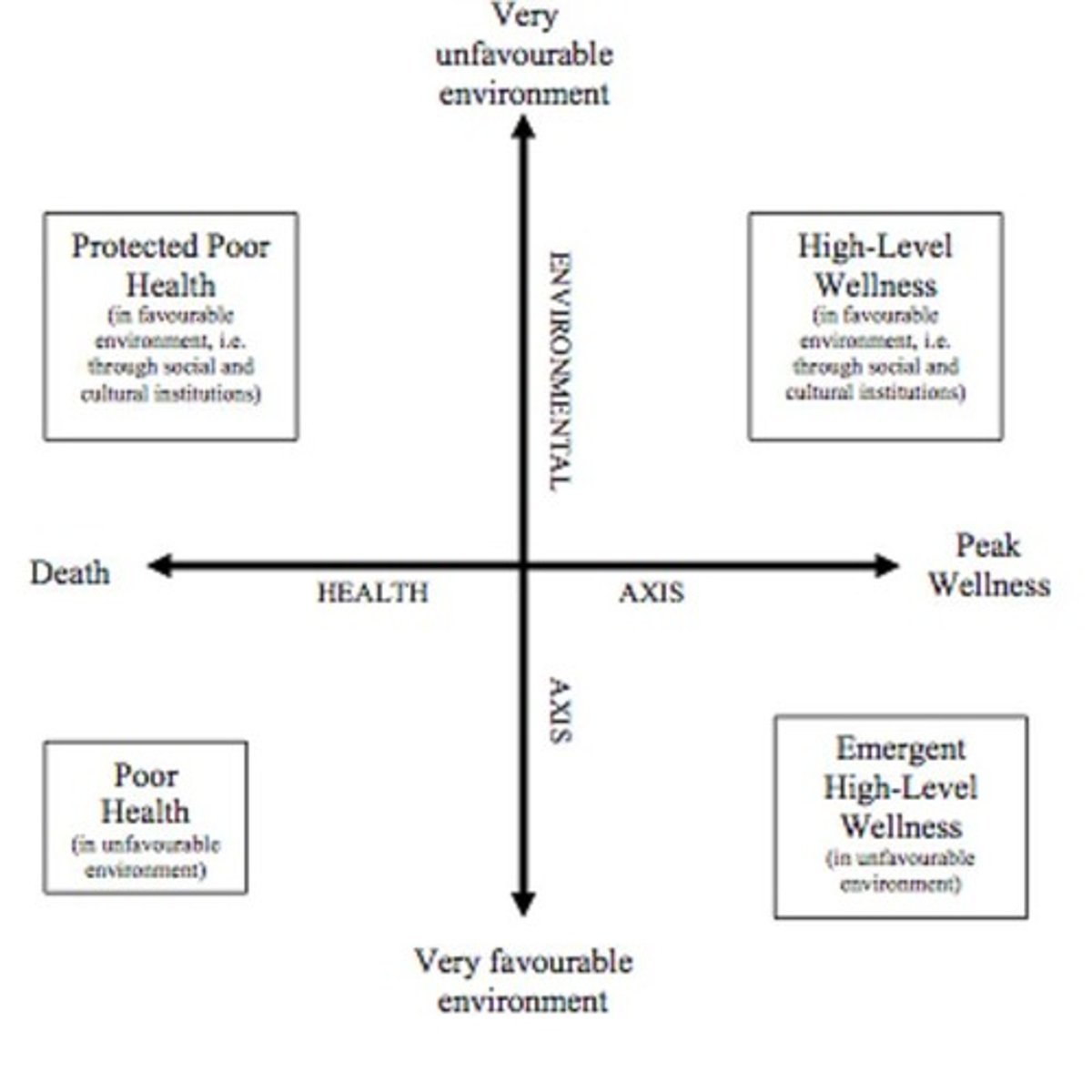
wellness-illness continuum
a dichotomized portrayal of health and illness ranging from high-level wellness at the positive end to depletion of health at the negative end
high-level wellness
A sense of well-being, life satisfaction, and quality of life.
Healthy People 2030
Attain healthy, thriving lives and well-being, free of preventable disease, disability, injury and premature death.
Eliminate health disparities, achieve health equity, and attain health literacy to improve the health and well-being of all.
Create social, physical, and economic environments that promote attaining full potential for health and well-being for all.
Promote healthy development, healthy behaviors and well-being across all life stages.
Engage leadership, key constituents, and the public across multiple sectors to take action and design policies that improve the health and well-being of all.
Levels of Prevention
- Primary: prevent/promotion
- Secondary: screen-early detection
- Tertiary: treat- to prevent further deterioration, rehab
Primordial prevention
prevention of the development of risk factors for disease
Health promotion (PCPAMR)
Precontemplative- not considering change
Contemplative- aware but not considering change soon
Preparation- planning to change
Action- has begun to make behavioral change (recent)
Maintenance- continued commitment to behavior (long term)
Relapse- reverted to old behavior
Evidence-based practice
searching for best evidence to answer clinical research questions
Quantitative studies
measure, test, and quantify variable's related to care
Qualitative studies
Research studies that describe phenomena or define the historical nature, cultural relevance, or philosophical basis of aspects of nursing care.
Health disparities
systematic (avoidable) health differences that adversely affect socially disadvantaged groups
Empowerment
belief one can make a difference in one's health
Health education
any combination of planned learning experiences using evidence based practices and/or sound theories that provide the opportunity to acquire knowledge, attitudes, and skills needed to adopt and maintain healthy behaviors
ANA
Health teaching and health promotion is primary nursing responsibility
Health Literacy
the degree to which individuals have the capacity to obtain, process, and understand basic health information and services needed to make appropriate health decisions
Ecological Model
health behavior viewed as complex interaction of individuals with environment-multiple influences
Health Belief model
A theory of health behaviors; the model predicts that whether a person practices a particular health habit can be understood by knowing the degree to which the person perceives a personal health threat and the perception that a particular health practice will be effective in reducing that threat.
Self-efficacy
individual's belief in ability to influence his own health
Individual screening
one person tested; often chosen based on risk factors
Group or mass screening
target population selected on basis of increased risk
One-test disease specific screening
single test. Detects characteristic indicating high risk
multiple test screening
2 or more tests to detect one disease
Morbidity
diseased state or disability from any cause
Mortality
deaths in a given population as end outcome indices
Incidence
rate of a new population problem and estimates risk of individual developing disease(acute)
Prevalence
proportion of the population with disease at any one point in time(chronic)
Nursing Process (ADPIE)
Assessment
Diagnosis
Planning
Implementation
Evaluation
Test Question on assessment
Primary source is the client, the only one person: the patient)
(secondary source are family, significant others, other healthcare professionals, health records)
Inspection
visual examination in a systemic way (ex. looking at skin, cellulitis, etc.)
Palpation
use of touch for data collection augments inspection(ex. touching, feeling for something, appendix)
Auscultation
listening to body sounds with a stethoscope (ex. sounds from heart rate (listening), bowel sounds)
Intuition
use of insight, instinct, and clinical experience to make clinical judgments (ex. feeling like something isn't right do something)
Medical diagnoses
describes a disease or pathology of specific organs or body systems
Nursing Planning
- the establishment of client goals/outcomes
- working with the client to prevent, reduce, or resolve problems
-to determine related nursing interventions that are most likely to assist client in achieving goals
-this about improving the quality of life for your patient
- this is about what the patient needs to do to improve their health status or better cope with illness.
Nursing Evaluation
Involves measuring if goals in planning step were met: progress is evaluated; changes in nursing diagnoses, goals & care plan may result; NA has keep role as NA's observations are used for this step
Critical thinking in nursing
-Purposeful, outcome-directed
-Essential to safe, competent, skillful nursing practice
-Based on principles of nursing process and the scientific method
-Requires specific knowledge, skills, and experience
-New nurses must question
-Guided by professional standards and ethic codes
-Requires strategies that maximize potential and compensate for problems
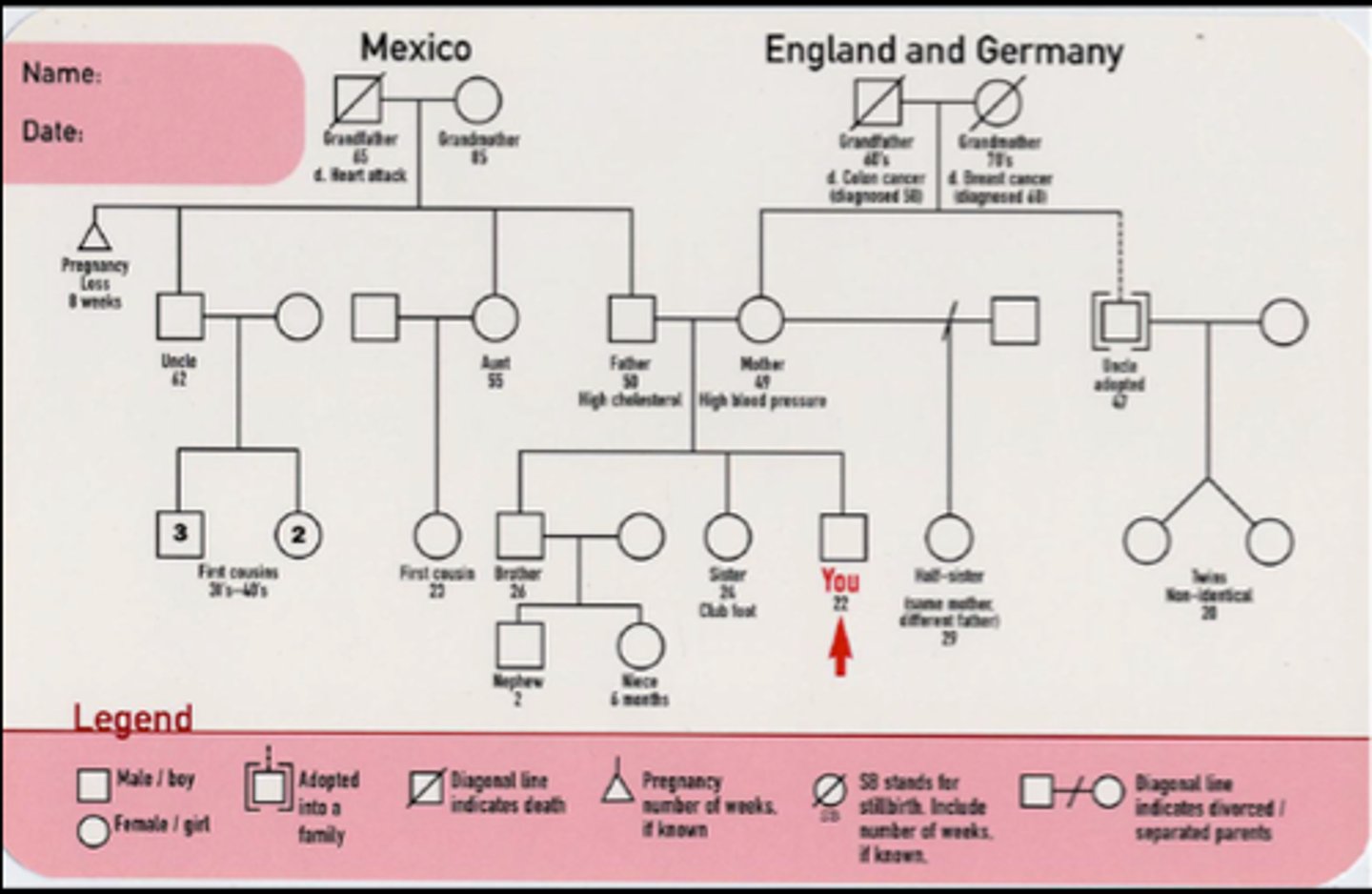
Genogram
A family diagram that depicts each member of the family and shows connections between the generations.
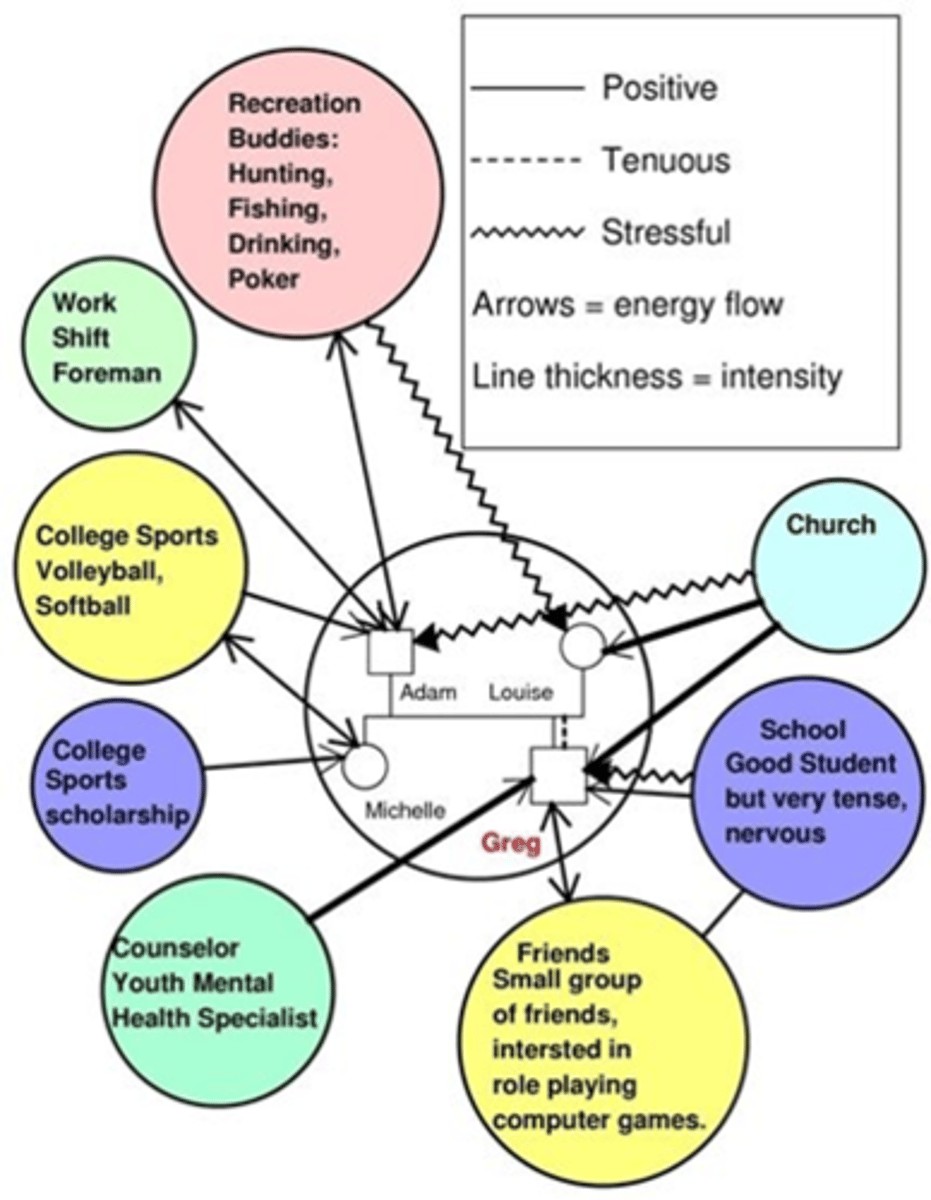
Ecomap
diagram used to identify the direction and intensity of family relationships between members and/or community institutions of importance to the family
Culture in nursing
Respect a patient's cultural beliefs/practices—if the cultural belief or the traditional healer's advice does not cause harm to the patient, then the NP should support the practice. If
a cultural practice has an adverse effect on a patient's health, then the NP needs to explain to the patient in a sensitive manner the reason for not following the practice.
Example: A patient tells the NP that her shaman/curandero "told me not to take my medicine, but to drink herbal tea instead" or "he told me not to drink water for 2 days"—
the NP respectfully communicates/explains to the patient why the practice is harmful to her health.
Acculturation
The adoption of cultural traits, such as language, by one group under the influence of another.
Assimilation
when a cultural group loses its identity and becomes part of the dominant culture "melting pot"
Values
beliefs about the worth of something and serve as standards that influence behavior and thinking
Subculture
"way of life" customs and ideas of a particular group of people within a society beliefs held by a portion of the larger group(by gender, sexual orientation, age, hobby, profession, etc.)
Ethnocentrism
the rightness of one's culture's way of doing things "my group is the best"
cultural relativism
learning about and applying standards of another culture
Time orientation
people in cultural groups may be more orientated to the past present or future this can affect nursing care
CRASH-course in cultural competency
Culture
Show Respect
Assess/Affirm differences
Show Sensitivity and self awareness
So it all with Humility
Plan of care should be culturally sensitive
CAM
complementary and alternative medicine: consists of a cluster of medical and health approaches, methods, and items not associated with conventional medicine.
Epidemiology
Study of health and disease from a societal perspective