IMED1002 - Nucleotides
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Monomer of Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
nucleotide
Heredity
Passing of traits from parents to offspring
Nucleotides
nitrogenous base + pentose monosaccharide + phosphate
- are negatively charged
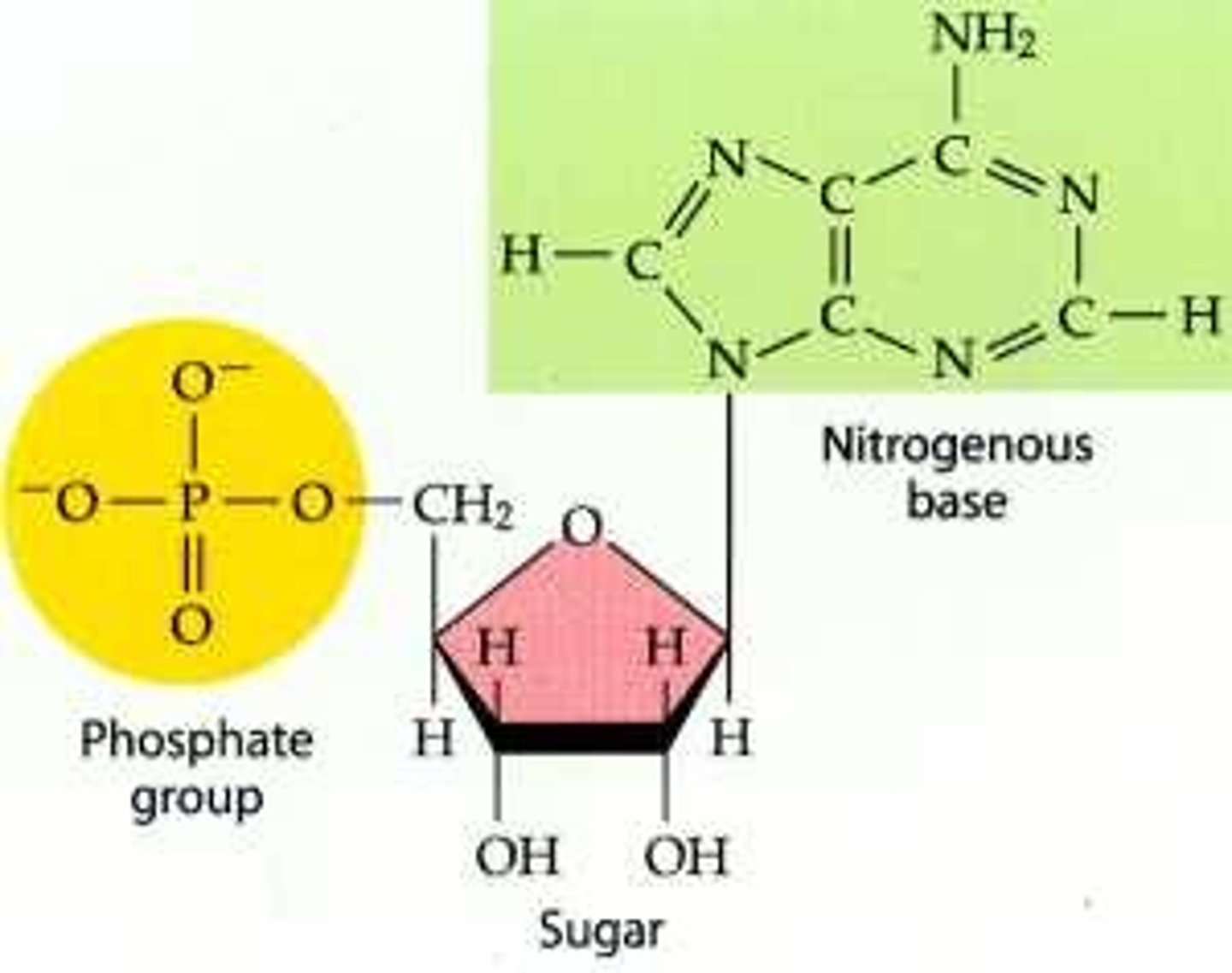
Phosphate
- simple molecule - phosphorus and oxygen atoms only
- at physiological pH (7-7.5), the hydroxyl groups are completely dissociated... H+ readily dissociate
- Hence phosphate has a net charge of -2
Pentose Monosaccharides
- Pentose sugars have 5 carbon atoms. In nucleotides there is either ribose or deoxyribose
- when free in solution, ribose exists as a straight chain aldehyde in equilibrium with a ring furan form
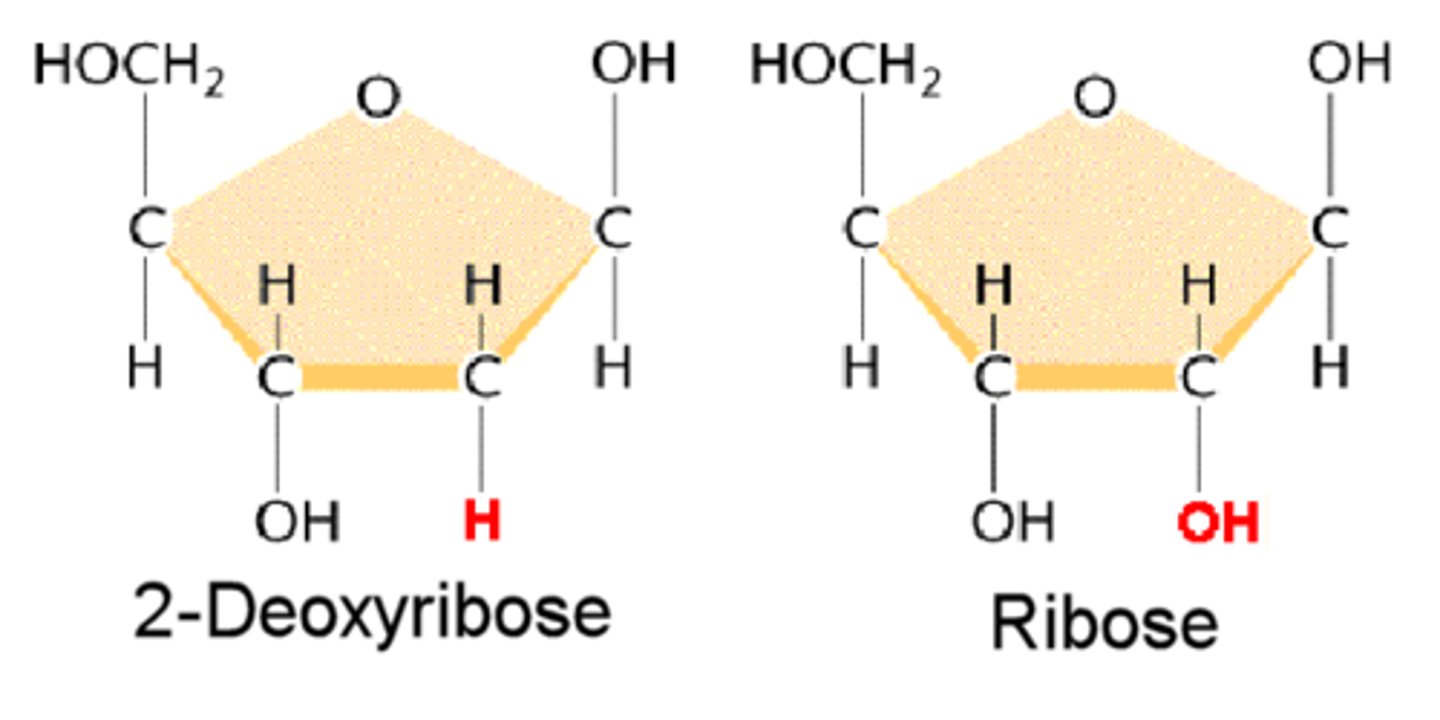
Deoxy/ribose in a nucleotide form
- it exists as a ring form
- C atoms are numbered 1 to 5. They are also designated 1', 2' etc. to distinguish them from C in the nitrogenous bases
Nitrogenous Bases
- Bases are heterocyclic aromatic amines and fundamental to coding information of nucleic acids
- Two categories of bases (Purines and Pyrimidines):
PURINES: Purine, Adenine (A), Guanine (G)
PYRIMIDINES: Pyrimidine, Cytosine (C), Uracil (U, RNA only), Thymine (T, DNA only)
Properties of Nitrogenous Bases
- hydrophobic and relatively insoluble in water at cellular pH
- Double bonded: significant because it results in bases being highly cojugated molecules. The electrons are no longer localised over only 2 atoms but spread over several - 'delocalisation'
Resonance
many atoms of the ring gives most bonds a partial double bond character
Difference between Purine and Pyrimidine
purine: 2 rings
pyrimidine: 1 ring
significance of double bonds in bases
- results in bases being highly conjugated molecules.
- The e- are no longer localised over only 2 atoms but spread over several = "delocalisation"
Result of Resonance
- resonance results in stabilisation
- double bonds of bases make pyrimidine bases planar and purines nearly planar
- electron sharing in benzene ring makes it very stable and explains why it does not undergo addition reactions like other alkenes
- ethylene undergoes addition
- benzene undergoes substitution
Absorption Spectra of Nucleotides
- due to resonance, all bases absorb UV light
- strong absorption at around 260nm wavelength
Bond between ribose and base
glycosidic bond = nucleoside, add phosphate to get nucleotide
Linkages in nucleosides and nucleotides
Condensation reaction is involved. Base + sugar + phosphate = nucleotide (great diagram in slide 21 of Lecture 7)
Nucleoside
nitrogenous base + sugar
Nucleoside and Nucleotide naming scheme (not super important to follow)
- for nucleoside: for purines, add "osine" to root. e.g if base is Adenine, nucleoside is Adenosine. For pyrimidines add "idine" to root. e.g Cytosine becomes Cytidine
- for nucleotide: for purines, add "ylate" to root. e.g if base is Adenine, nucleotide is Adenylate. For pyrimidines, add "idylate" to root. e.g Cytosine becomes Cytidylate
Deoxyribonucleotides
- deoxyribonucleoside monophosphates
- can add one or two additional phosphate groups to get diphosphate and triphosphate e.g dAMP, dADP, dATP
Ribonucleotides
- Ribonucleoside monophosphates
- can add one or two additional phosphate groups
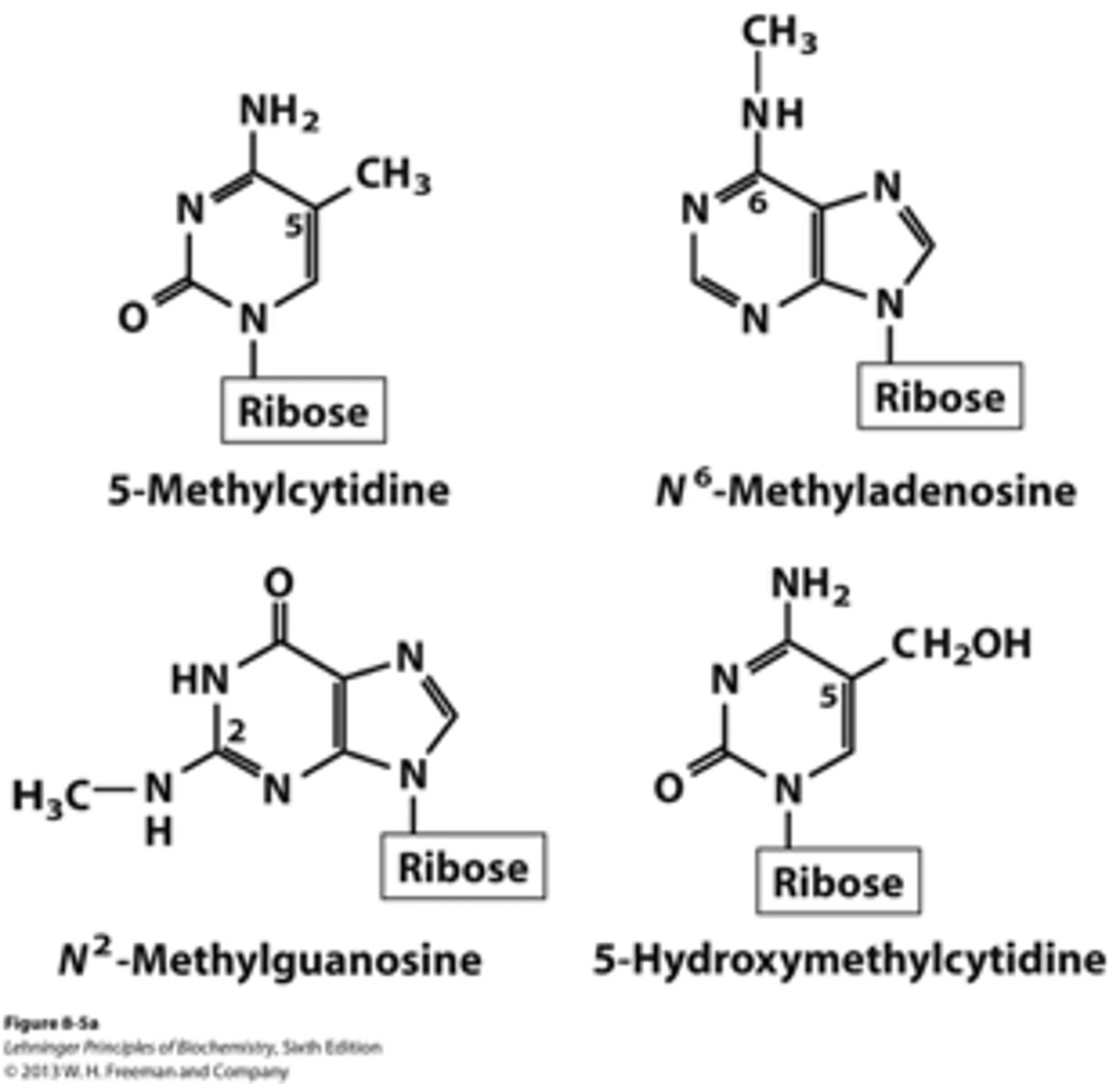
Methylation
- bases may be modified by a process called methylation
- e.g methylation of cytosine
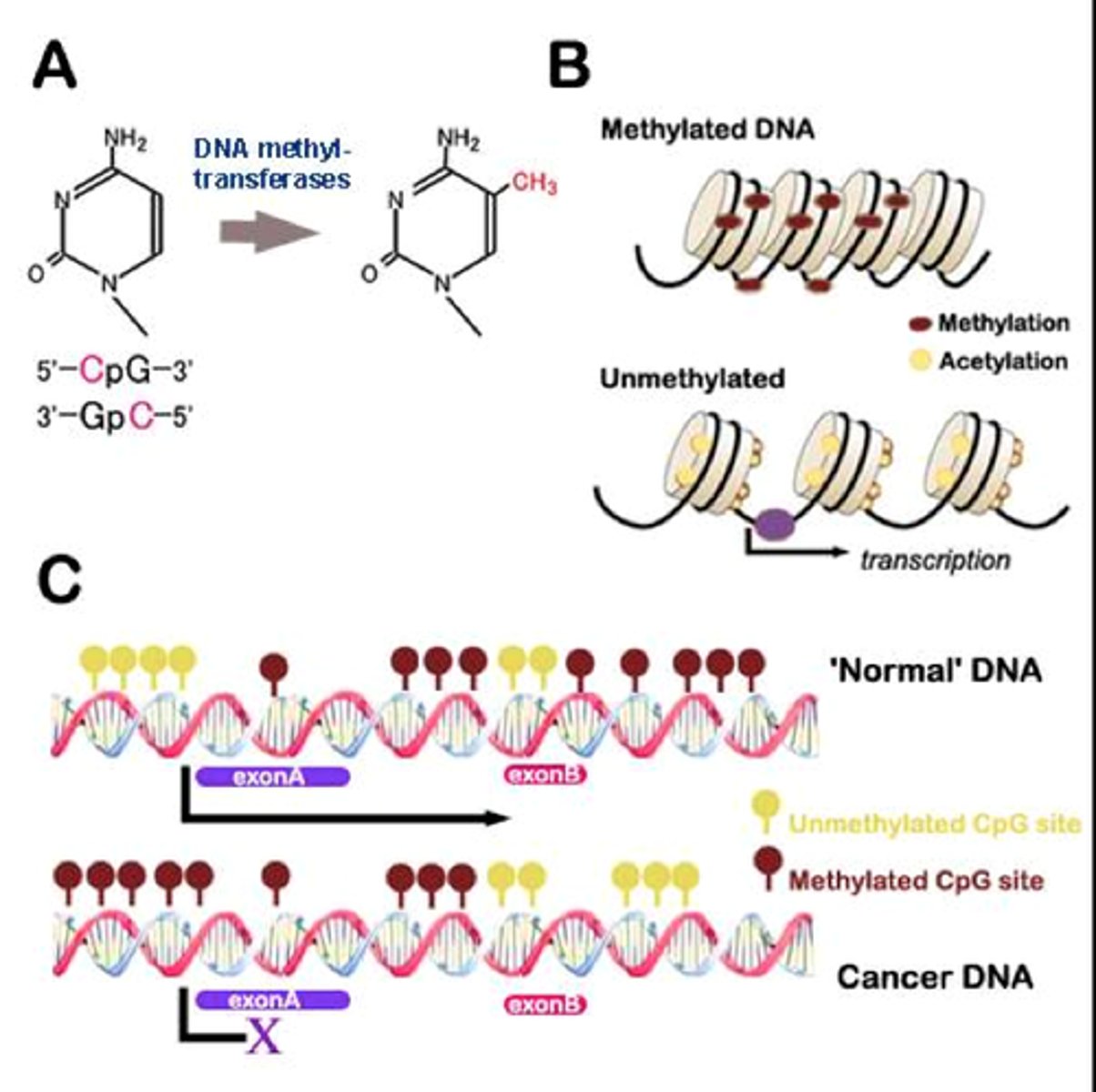
Minor Bases
- methylated forms of major bases
- e.g in tRNA
Unique cyclic structure of cells
- cells can have nucleotides where the P group is not on the 5'C and that form cyclic structures (great diagram on page 26)
Other roles in Nucleotides
- not only information storage - making RNA and proteins
- metabolic - ATP is the cellular energy "currency"
- cofactors in biochemical reactions - NAD+
- cell signalling - cAMP