Redo and Reflect Assignment
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Bacteria are typically 10 to 20 times smaller than eukaryotic cells. Therefore,
bacteria....
A. ...contain smaller organelles and a less complex cytoplasm than eukaryotes
B. ...have a lower surface area : volume ratios than eukaryotes
C. ...have a higher surface area : volume ratios than eukaryotes
D. ...exhibit a slower diffusion of waste products out of the cell than eukaryotes
E. None of the statements above are correct
C. ...have a higher surface area : volume ratios than eukaryotes
Which of the following TWO elements of the mitotic spindle are INCORRECTLY paired
with their description?
A. Centromere – DNA region in the middle of the chromosome where the
kinetochore is assembled.
B. Microfilaments – attach to the kinetochores of each sister chromatid.
C. Centriole – positioned at opposite poles of the cell during cell division.
D. Kinetochore – binds to the motor protein Dynein that moves the chromosomes towards each pole of the spindle.
E. All of these elements are correctly paired with their functions.
B. Microfilaments – attach to the kinetochores of each sister chromatid.
In the experiment conducted by Gorbsky using fluorescently-labeled tubulin to determine the dynamics of microtubules during mitosis, which of the following was NOT observed?
A. It was demonstrated that kinesin and dynein move the chromosomes towards the poles of the spindle.
B. The photo bleached stayed stationary
C. It was demonstrated that treadmilling occurs at both ends of the microtubule.
D. It was demonstrated that microtubules disassemble near what was the metaphase plate
E. None of the statements was not observed.
C. It was demonstrated that treadmilling occurs at both ends of the microtubule.
True or False: Egg cells are always larger than sperm cells, and sperm cells are more mobile than egg cells.
A. True
B. False
B. False
A new drug is developed that disrupts mitochondrial function. Why would this be an
ineffective antibiotic against bacterial infections?
A. Bacterial mitochondria are structurally different from those in eukaryotic cells,
making the antibiotic ineffective.
B. Bacterial mitochondria are gram positive, making them very resistant to
antibiotics because of their robust cell walls.
C. This antibiotic would actually be effective because bacteria rely on
mitochondria for ATP production.
D. When mitochondria within bacteria are impaired, they can rely on other
metabolic pathways to produce ATP.
E. Bacteria do not have mitochondria.
E. Bacteria do not have mitochondria.
Which function or characteristic is mismatched with its corresponding element of
the cytoskeleton?
A. Microtubule – requires Actin for polymerization to regulate cellular migration
B. Intermediate filament - It not dynamic or bound by motor proteins
C. Microfilament - requires ATP for polymerization
D. Microfilament - is bound by the motor protein myosin in muscle cells
E. Microtubule - responsible for chromosomal movement during mitosis
A. Microtubule – requires Actin for polymerization to regulate cellular migration
7 Which of the options listed below is FALSE regarding prokaryotic cells?
A. In Gram-positive bacteria, peptidoglycans compose the most exterior
surface of the cell walls
B. Peptidoglycans are present in Gram-positive bacteria but are absent in
Gram-negative bacteria
C. Pili enable a bacterium to transmit genetic information to other bacteria
D. Adhesins allow bacteria to adhere to one another and to surfaces
E. All of the listed options are true for prokaryotes
B. Peptidoglycans are present in Gram-positive bacteria but are absent in
Gram-negative bacteria
Which of the bacterial processes below are disrupted by penicillin?
A. The synthesis and function of bacterial flagella.
B. DNA replication in the bacterial nucleus.
C. The cross-linking of peptidoglycan layers in the bacterial cell wall.
D. Protein synthesis on bacterial ribosomes.
E. The assembly and maintenance of the bacterial plasma membrane.
C. The cross-linking of peptidoglycan layers in the bacterial cell wall.
The yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) has 6 pairs of chromosomes. How many
chromosome rearrangements can occur during metaphase I?
A. 16
B. 32
C. 36
D. 64
E. 128
D. 64
Which of the following organelles is mismatched with its function?
A. Smooth ER – lipid synthesis and detoxification of certain poisons.
B. Lysosome – store hydrolases to digest macromolecules.
C. Golgi apparatus – site of modification to proteins destined for cell secretion.
D. Rough ER – site of synthesis for proteins destined for cell secretion.
E. All of these organelles are correctly matched to their function.
E. All of these organelles are correctly matched to their function.
There are limits to cellular size because...
A. As the cell radius increases, the surface area increases at a slower rate than
that of the volume
B. The cell cytoskeleton is unable to span large distances or support large cells
C. The rate of movement for nutrients into cells and waste products out of cells
is limited by diffusion
D. A and C
E. None of the above
D. A and C
Which of the following components is NOT present in the nucleus of a human cell?
A. A nuclear envelope consisting of a double lipid bilayer.
B. Pores that regulate nuclear import and export.
C. Intermediate filaments.
D. Circular chromosomes.
E. Nucleolus.
D. Circular chromosomes.
Which statement correctly describes the functions or characteristics of specific
structures within the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell?
A. Nuclear pores are small gaps in the nuclear membrane that only allow
molecules through if they contain a nuclear localization signal (NLS)
B. Lamins form a dense fibrous network inside the core of the nucleus that
prevent DNA molecules from interacting with each other
C. The nucleolus is a distinct region within the nucleus primarily involved in the
synthesis of tRNAs
D. The nuclear envelope consists of a double lipid bilayer that separates the
contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
E. Chromatin consists exclusively of DNA; it does not include any protein
components and serves solely to compress DNA to fit within the nucleus
D. The nuclear envelope consists of a double lipid bilayer that separates the
contents of the nucleus from the cytoplasm
True or False: All cytoskeletal filaments exhibit dynamic polymerization /
depolymerization, which is often referred to as “treadmilling” and imparts a high
degree of versatility for various cellular functions.
A. True
B. False
B. False
Which of the following statements accurately describes the role and function of
lysosomes in cellular processes?
A. When a lysosome fuses with a phagosome, it forms a phagolysosome where
hydrolases break down engulfed material such as bacteria or worn-out
organelles.
B. Lysosomes are primarily involved in the breakdown of fatty acids and the
detoxification of hydrogen peroxide, protecting the cell from oxidative
damage.
C. Lysosomes are primarily involved in the synthesis and storage of cellular
waste before expulsion through the cell membrane.
D. The enzymes within lysosomes are highly active at the normal pH found in the
cytoplasm, which is why the rupture of a lysosome often leads to rapid
degradation of cellular components and cell death.
E. Lysosomes are derived from the Golgi apparatus and function to export
undigested substances out of the cell through exocytosis.
A. When a lysosome fuses with a phagosome, it forms a phagolysosome where
hydrolases break down engulfed material such as bacteria or worn-out
organelles.
Which cell division stage is being represented by the cell below?
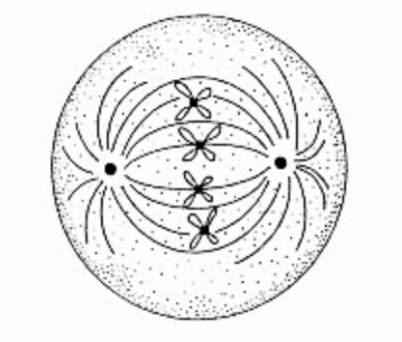
Which cell division stage is being represented by the cell below?
A. Prophase
B. Prometaphase
C. Metaphase
D. Anaphase
E. Telophase / Cytokinesis
C. Metaphase
Various molecules of cyclin and CDK can form complexes that regulate the
progression of the cell cycle. Which of the statements below is FALSE about these
complexes?
A. A mutation that prevents a CDK from binding to its corresponding cyclin
would result in cells dividing uncontrollably
B. Cyclin is only produced at the appropriate time of the cell cycle
C. Cyclin-CDK complexes are required for cells to divide and activate other cell
division factors through phosphorylation
D. A mutation that prevents cyclin from being produced would result in cell
quiescence or senescence
E. More than one of the above statements is false
A. A mutation that prevents a CDK from binding to its corresponding cyclin
would result in cells dividing uncontrollably
Refer to the following net equation for cellular respiration:
CxHyOz + 6O2 > 6CO2 + 6H2O + ENERGY (ATP & heat)
In that equation, what do the variables x, y, and z stand for?
A. X = 12, Y = 6, Z = 6
B. X = 6, Y = 12, Z = 6
C. X = 6, Y = 6, Z = 12
D. X = n, Y = 2n, Z = n
E. X = n, Y = 2n, Z = 2n
B. X = 6, Y = 12, Z = 6
If we consider DNA replication and chromosomes during the eukaryotic cell cycle...
A. The total amount of DNA in the cell doubles such that each daughter cell will
receive the same genome as the parent cell.
B. Sister chromatids are identical in terms of the nucleotides that comprise the
chromatids.
C. Homologous chromosomes have the same genes, but slightly different DNA
sequences/versions for those genes, called alleles.
D. Cohesin is a protein that holds sister chromatids together along the
chromosome arms.
E. All of the above statements are true.
E. All of the above statements are true.
Which of the following events accurately characterizes anaphase I of meiosis?
A. Homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled toward opposite poles
of the cell.
B. Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell along the metaphase plate.
C. Sister chromatids separate and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell.
D. Nuclear envelopes reform around the separated chromosomal sets.
E. The cell membrane begins to furrow, preparing for cytokinesis.
A. Homologous chromosomes separate and are pulled toward opposite poles
of the cell.
In diploid organisms like humans and tomatoes, a replicated chromosome is
composed of ______.
A. A homologous pair of chromosomes held together at the centromere.
B. Two homologous chromosomes held together at the centromere.
C. Four homologous chromosomes held together at the centromere.
D. Two chromatids bound together at the centromere.
E. Four chromatids bound together at the centromere.
D. Two chromatids bound together at the centromere.
Fill in the blanks: in humans, ______ is the fusion of ______ sperm and egg cells
leading to fusion of their nuclei to produce a ______ zygote.
A. Fertilization, haploid, diploid
B. Mitosis, haploid, diploid
C. Meiosis, diploid, haploid
D. Meiosis, haploid, diploid
E. Fertilization, diploid, haploid
A. Fertilization, haploid, diploid
Maritza is studying the production of sperm cells and is observing the stages of
Meiosis. If Martiza is looking at a cell that is in the stage of Meiosis II, then which of
the following is NOT something that she would observe in a cell going through one
of its phases?
A. Chromosomes lining up down the center of the cell.
B. Sister chromatids being pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
C. Tetrads visible in the cell that are most likely performing the action of
crossing over.
D. Cleavage furrows followed by cytokinesis
E. More than one of these choices are correct
C. Tetrads visible in the cell that are most likely performing the action of
crossing over.
Which phase of Meiosis is the moment of separation, where each progeny
(daughter) cell receives only one chromatid per cell instead of two paired
chromatids?
A. Anaphase I
B. Anaphase II
C. Prophase II
D. Prophase I
E. Metaphase I
B. Anaphase II
An individual with the genotype AaBbCcDd is crossed with another individual
whose genotype is aaBbCCDd. What is the probability of having two offspring with
the genotypes AabbCCDd AND aaBBCcDD (one of each)?
A. 1/64
B. 3/256
C. 1/1,024
D. 1/2,048
E. That genotype would be impossible
D. 1/2,048
How does meiosis generate genetic variation that contributes to evolution?
A. Crossing over leads to exchange between homologous chromosomes and
generates new combinations of alleles during prophase I
B. Homologous chromosome pairs are assorted randomly along the
metaphase plate during metaphase II
C. It produces new combinations of alleles on each chromosome during
prophase I
D. It produces mutations during the second round of S phase via DNA
replication.
E. Both A and C are correct
E. Both A and C are correct

Which cell division stage is being represented by the cell below? Assume recombination due to crossing over is not shown.
A. Metaphase of mitosis
B. Metaphase I of meiosis
C. Anaphase I of meiosis
D. Metaphase II of meiosis
E. Telophase II of meiosis
C. Anaphase I of meiosis
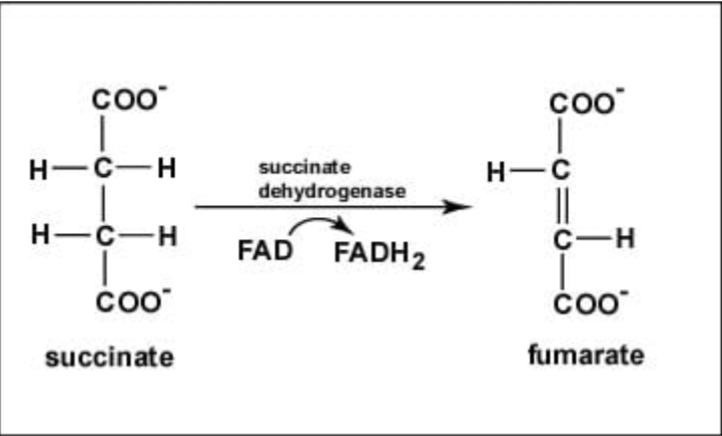
The conversion of succinate to fumarate, a step in the citric acid cycle, is shown below. Referencing this reaction, which of the following is FALSE?
A. Succinate is oxidized to fumarate
B. FAD is oxidized to FADH2
C. FADH2 is carrying high energy e-
D. Succinate is in a more reduced state than fumarate
E. All of the above are TRUE
B. FAD is oxidized to FADH2
Which of the following comparisons between prokaryotes and eukaryotes is FALSE?
A. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes undergo DNA replication before cell division.
B. Prokaryotes can have transcription and translation occur simultaneously, but
eukaryotes cannot.
C. Prokaryotes, but not eukaryotes, are capable of forming a protective cell
wall.
D. Eukaryotes and prokaryotes contain flagella they use for cell movement.
E. None of the above.
C. Prokaryotes, but not eukaryotes, are capable of forming a protective cell
wall.
Why is genetic diversity beneficial to a population of a given species?
A. Genetic diversity increases the rate at which the species approaches the
ideal, most fit version of that species
B. Genetic diversity helps weed out bad alleles because organisms carrying the
bad versions of an allele cannot reproduce successfully
C. Genetic diversity increases the likelihood that at least one offspring will be
able to survive any given environment, even if the circumstances change
D. Genetic diversity is good because it involves mutations that arise during
meiosis, which are well-regulated and controlled, so they are less likely to be
bad
E. Genetic diversity is not actually advantageous– that’s why natural selection
favors the good alleles, and the bad alleles disappear over time
C. Genetic diversity increases the likelihood that at least one offspring will be
able to survive any given environment, even if the circumstances change
Which of the following peptides could be found inside a phospholipid bilayer
membrane due to its hydrophobic properties?
A. Arg-Lys-Glu
B. His-Gly-Asp
C. Gly-Thr-Cys
D. Leu-Met-Val
E. Ser-Thr-Ala
D. Leu-Met-Val
Which statement correctly compares triglycerides and phospholipids?
A. Both are amphipathic molecules each containing a glycerol backbone
bonded to 2 or 3 fatty acids.
B. Both are hydrocarbons, but while triglycerides consist of three fatty acids
attached to a glycerol backbone, phospholipids consist of two fatty acids
and one phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone.
C. Both contain phosphate groups; however, triglycerides are used for energy
storage while phospholipids are amphipathic and participate in forming cell
membranes.
D. Both triglycerides and phospholipids are primarily used for energy storage,
with triglycerides containing a phosphate group making them amphipathic,
unlike phospholipids which are not.
E. None of the above.
B. Both are hydrocarbons, but while triglycerides consist of three fatty acids
attached to a glycerol backbone, phospholipids consist of two fatty acids
and one phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone.
Which of the following characteristics do you expect to observe in an amoeba
living adjacent to a hot geyser?
A. A high concentration of unsaturated phospholipids on its membrane.
B. A low concentration of amphipathic lipids on its membrane.
C. A high concentration of short-tail phospholipids on its membrane.
D. A high concentration of saturated phospholipids on its membrane.
E. A high concentration of triglycerides on its membrane.
D. A high concentration of saturated phospholipids on its membrane.
Which aspect of the 1928 Griffith experiment contributed most significantly to the
understanding of bacterial genetics?
A. The distinction between the S and R strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae
B. The use of heat to kill bacteria
C. The observation that uptake of extracellular genetic material can occur in
bacteria, a process called transformation
D. The identification of the polysaccharide capsule in the virulent bacteria that
relates to pathogenicity
C. The observation that uptake of extracellular genetic material can occur in
bacteria, a process called transformation
Which of the following atoms is not found in major macromolecules?
A. Sulfur (S)
B. Nitrogen (N)
C. Chlorine (Cl)
D. Phosphorous (P)
C. Chlorine (Cl)
Analysis of an mRNA molecule shows that it is composed of 26% Adenine. What
percentage of this same molecule is expected to be composed of Guanine?
A. 24%
B. 26%
C. 48%
D. 52%
E. It is impossible to determine with the given information.
E. It is impossible to determine with the given information.
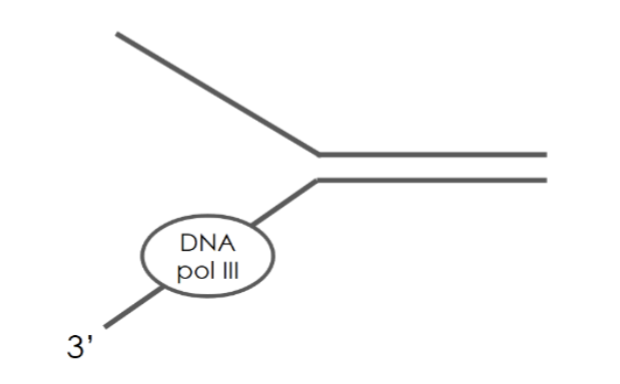
The following diagram represents a replication bubble. Which new strand will be
synthesized by the DNA polymerase shown in the diagram? Is it moving to the right
or to the left?
A. Lagging strand, to the left
B. Leading strand, to the left
C. Lagging strand, to the right
D. Leading strand, to the right
E. It is impossible to determine with the given information
D. Leading strand, to the right
In an experiment similar to Griffith's, two strains of bacteria are grown in
antibiotic-containing media. Strain A can grow in this media while strain B cannot.
Strain A was then heat-killed and mixed with live strain B before plating again on
antibiotic-containing media. Unexpectedly, bacterial growth was observed.
Conversely, when only strain B was plated on the same media, no growth occurred.
What explains this outcome?
A. The heat-killed strain A released a toxin that inhibited the antibiotic's
effectiveness on strain B.
B. The progeny of strain A were able to mate with strain B and the resulting
bacteria was able to grow.
C. Strain B underwent genetic transformation by taking up plasmid DNA from
the heat-killed strain A, conferring resistance to the antibiotic.
D. Strain A produced enzymes that degraded the antibiotic, allowing strain B to
grow.
E. None of the above.
C. Strain B underwent genetic transformation by taking up plasmid DNA from
the heat-killed strain A, conferring resistance to the antibiotic
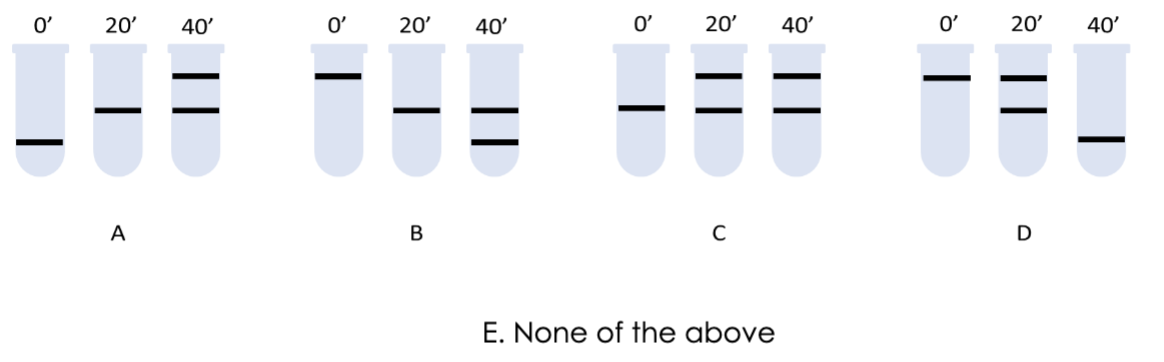
Imagine that the Meselson-Stahl experiment was redone but the order of the
Nitrogen isotopes was changed so that the bacteria was grown in 14N first, then
switched to 15N, with DNA samples from these cells centrifuged before switching
them to 15N (at 0’ min), and again after one and then two rounds of replication (at
20’ and 40’ min). Which of the following tube sets would best represent the
expected results?
ANSWER IS B
In the Hershey-Chase experiment, the researchers used a blender to dissociate the
bacterial cells from phages in the culture samples grown in radioisotopes of sulfur or
phosphorus. How would the results of the experiment have been affected if the
blender had not been used (the phages stayed attached to the bacteria)?
A. The radioactive sulfur would have been found attached to the bacterial cells,
incorrectly suggesting that proteins carry genetic information.
B. The radioactive phosphorus would have remained outside the cells, leading
to the conclusion that DNA does not enter the bacterial cells.
C. Both the radioactive sulfur and phosphorus would have been found only
outside of the cells, causing confusion about which molecule carries genetic
information.
D. There would be no significant change in the distribution of radioactive
materials, as the viral DNA and proteins would have entered the cells without
the need for blending.
E. None of the above
A. The radioactive sulfur would have been found attached to the bacterial cells,
incorrectly suggesting that proteins carry genetic information.
Which of the sequences listed could act as an RNA primer for the DNA molecule
below?
5' - AGCTTGTCAATCCGATAGCACCCATGTAGCCAACTTGCGT - 3'
A. 5’- TCGAACAGTT-3’
B. 5’- UCGAACAGUU-3’
C. 3’- TCGAACAGTT-5’
D. 3’- UCGAACAGUU-5’
E. 5’- ACGCAATTGG-3’
D. 3’- UCGAACAGUU-5’
Suppose that the coding region of a gene contains 1,820 base pairs, with 570 in the
first exon, 440 in the second exon, and 810 in the third exon. The
post-transcriptionally-modified mRNA of the splice variant in which the second exon
was spliced out would be composed of how many base pairs?
A. 1,230
B. 1,380
C. 990
D. 1,490
E. More information is needed
B. 1,380
You have recently discovered a novel protein and are studying the effects of
various post-translational modifications on its bioactivity. You perform a series of
mutagenic screens that alter specific amino acid residues within various regions of
this protein. Interestingly, you notice that mutating one coding sequence of TCT to
ACT has no effect on the protein’s function. What kind of mutation is this, and what
amino acid has been mutated?
A. This is a frameshift mutation; Ser-Thr
B. This is a missense mutation; Ser-Thr
C. This is a frameshift mutation; Ser-Leu
D. This is a silent mutation; Ser-Leu
E. More information is required.
B. This is a missense mutation; Ser-Thr
True or False: Recessive alleles are always less common in the population than
dominant alleles
A. True
B. False
B. False
Which of the following is FALSE regarding the process of gene transcription:
A. It produces single-stranded RNA molecules, like mRNA.
B. It is comprised of initiation, elongation, and termination steps.
C. It requires the ribonucleotides ATP, CTP, UTP, and GTP.
D. It starts at the codon AUG, which codes for methionine.
E. All of the above are TRUE.
D. It starts at the codon AUG, which codes for methionine.
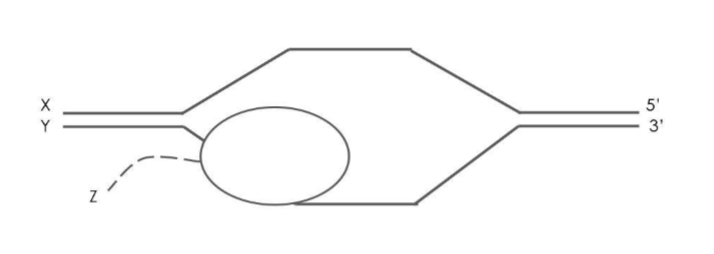
Which of the following statements is true based on the diagram below representing
transcription? (The circle represents a polymerase, which is moving to the left)
A. The letter X is marking the 3’ end of the coding strand DNA.
B. The letter Y is marking the 5’ end of the coding strand of DNA.
C. The letter Z is marking the 3’ end of the newly made RNA.
D. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is DNA polymerase III.
E. The enzyme catalyzing this reaction is DNA polymerase I.
A. The letter X is marking the 3’ end of the coding strand DNA.
Which of the following elements are required for the process of DNA replication?
A. The creation of RNA primers by DNA Primase.
B. The function of a helicase enzyme to unwind the DNA strands.
C. The function of topoisomerase to prevent supercoiling of the unzipping DNA
strands.
D. The exonuclease activity of DNA polymerase I to remove RNA primers.
E. All the above statements are correct.
E. All the above statements are correct.
During the post-transcriptional processing of pre-mRNA molecules in eukaryotic
cells, several modifications occur before the final mRNA product is exported from
the nucleus. Which of the following is NOT a modification that occurs during
pre-mRNA processing?
A. Addition of a 5' cap.
B. Removal of introns via splicing.
C. Addition of a poly-A tail at the 3' end.
D. Replacement of thymine bases with uracil bases.
E. All the above are part of pre-mRNA processing
D. Replacement of thymine bases with uracil bases.
Why do Chargaff’s Rules (A=T and C=G) hold true for DNA but not RNA?
A. RNA has ribose instead of deoxyribose, like DNA
B. RNA is smaller and less stable than DNA, so its complementarity is reduced
C. RNA is generally single stranded, and DNA is double stranded
D. All of the above
C. RNA is generally single stranded, and DNA is double stranded
Translate the following mRNA sequence into a polypeptide, beginning from the
start codon and ending at the stop codon.
5' CCC UGG AUG GUC CAG GAG UAC UGG CCA UAA UGA CC 3'
A. N- Met -Val -Gly-Met-Val-Gln-Glu-Tyr – C
B. N- Met -Val-Glu-Met-Val-Gln-Glu-Tyr – N
C. N- Met-Val-Gln-Glu-Tyr-Trp-Pro – C
D. C- Met-Val-Gln-Glu-Tyr-Trp-Pro – N
E. None of the above.
C. N- Met-Val-Gln-Glu-Tyr-Trp-Pro – C
While conducting a research experiment to determine the sequence of an
unknown mRNA polynucleotide, you add the unknown mRNA template to a
solution containing all the necessary components for translation. The results reveal
the synthesis of three different polypeptides: poly-serine (ser-ser-ser-...), poly-leucine
(leu-leu-leu...), and poly-phenylalanine (phe-phe-phe...). Based on this outcome,
what is the most likely sequence of the unknown mRNA? The start codon is
upstream and not illustrated.
A. 5’-...UCAUCAUCAUCA...-3’
B. 5’-...CUACUACUACUA...-3’
C. 5’-...CUCCUCCUCCUCC...-3’
D. 5’-...UUCUUCUUCUUC...-3’
E. A different sequence
D. 5’-...UUCUUCUUCUUC...-3’
The following sequence corresponds to the anticodon of a tRNA molecule. What
amino acid would you expect to find covalently bound to this tRNA?
5’-AUC-3’
A. Leu
B. Ile
C. Arg
D. Asp
E. This sequence corresponds to a stop codon.
D. Asp
During the process of translation:
A. Incoming amino acids are initially recognized at the P site and move to the A
site before exiting the ribosome.
B. The formation of peptide bonds occurs at the N-terminal end of the growing
polypeptide.
C. Ribosomes read the mRNA strand in a 3’ → 5’ direction.
D. Protein synthesis commences at the start codon AUG of the mRNA strand.
E. More than one answer is correct.
D. Protein synthesis commences at the start codon AUG of the mRNA strand.
Considering alternative splicing, what role might the spliceosome play in the
diversity of proteins?
A. It decreases protein diversity by always splicing RNA in the same way.
B. It has no impact on protein diversity as it affects RNA, not protein.
C. It increases protein diversity by allowing for multiple mRNA variants from a
single gene.
D. It restricts the expression of most genes, reducing protein diversity.
E. More than one option above is correct.
C. It increases protein diversity by allowing for multiple mRNA variants from a
single gene.
Imagine that instead of 4 nitrogenous bases, an alien organism in a distant galaxy
exhibits 6 nitrogenous bases. If they also have 20 amino acids like us, what is the
minimum number of nucleotides expected in their codons?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
B. 2
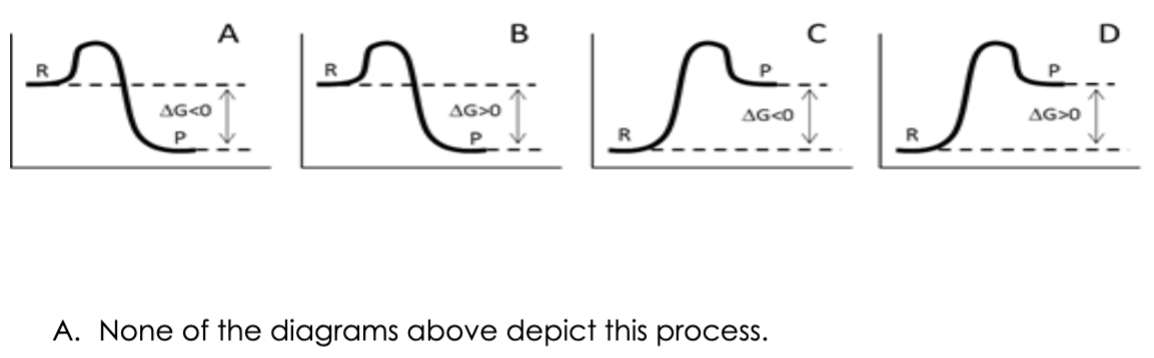
Sucrase is a digestive enzyme that facilitates the hydrolysis of sucrose into fructose
and glucose. Given your knowledge of these carbohydrates, which of the free
energy diagrams best represents this reaction?
ANSWER IS A
When you exercise, your body builds muscle fibers by synthesizing proteins from
amino acids. This involves the formation of peptide bonds between amino acid
monomers. Which of the following statements is correct with respect to this reaction
(the creation of bonds)?
A. The overall reaction has a positive △G where the reactants have a higher
energy than the products.
B. The overall reaction has a negative △G where the products have a higher
energy than the reactants.
C. This dehydration reaction is endergonic and spontaneous.
D. This dehydration reaction is endergonic and non-spontaneous.
E. None of the above are correct.
D. This dehydration reaction is endergonic and non-spontaneous.
Which of the following most accurately describes the role of enzymes as biological
catalysts?
A. Enzymes modify the equilibrium position of the reaction to favor product
formation.
B. Enzymes reduce the activation energy required for the reaction, facilitating
the formation of the transition state more efficiently.
C. Enzymes add energy to the reaction system, making endergonic reactions
favorable.
D. Enzymes raise the overall free energy yield of a reaction, speeding up the
reaction.
E. Enzymes alter the final products of the reaction to ensure that the reaction is
more efficient.
B. Enzymes reduce the activation energy required for the reaction, facilitating
the formation of the transition state more efficiently.
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding ATP?
A. ATP is used during the synthesis of new nucleic acids (both DNA and RNA).
B. ATP hydrolysis can be used in enzyme catalyzed reactions to add phosphate
groups to other molecules (phosphorylation).
C. ATP hydrolysis can be coupled to enzymes that transport molecules out of
the cell.
D. ATP hydrolysis to form ADP + Pi is an endergonic reaction that requires energy
input.
E. ATP hydrolysis can be coupled to energetically unfavorable reactions to
drive endergonic processes.
D. ATP hydrolysis to form ADP + Pi is an endergonic reaction that requires energy
input.
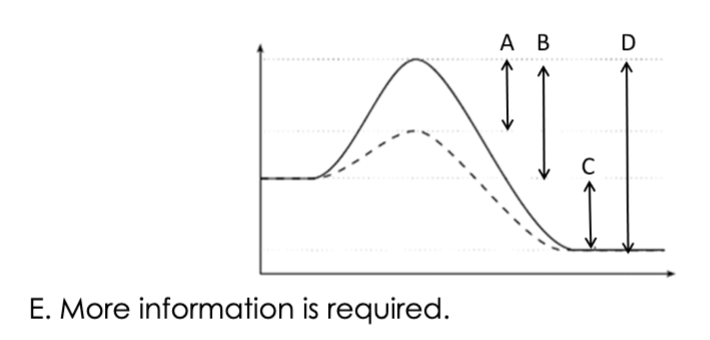
The figure below indicates the energy states of a reaction with and without an
enzyme. Which segment represents the change in free energy of this reaction?
ANSWER IS C
Considering lipids and polysaccharides, what below is UNTRUE?
A. Triglycerides are hydrophobic while carbohydrates vary in their solubility
B. The synthesis of polymers of carbohydrates and triglycerides is accomplished
via condensation reactions
C. Carbohydrates and lipids can have additional functions other than energy
storage
D. Polymers of carbohydrates are formed through covalent linkages termed
glycosidic bonds
E. All of the above are true.
E. All of the above are true.
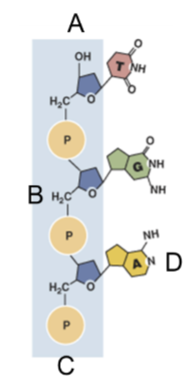
Which is the 3’ end of this partially assembled polymer/strand?
ANSWER IS C
In the DNA of certain bacterial cells, 23% of the nucleotides are Adenine. What
percentage of Guanine nucleotides would you expect to find?
A. 23%
B. 46%
C. 27%
D. 54%
E. More information is needed
C. 27%
Carbohydrates, unlike other macromolecules, can be branched. What is TRUE with
respect to the carbohydrate’s branching?
A. The branching is given by the position of the glycosidic linkage with respect
to the plane of the molecule, resulting in alpha (branched) or beta (linear)
bonds.
B. Branching is related to the solubility of the carbohydrate in water
C. In a given branched carbohydrate, the same carbons (i.e. 1 and 4) are
linked together in all the glycosidic bonds found in the molecule
D. Glycosidic bonds are a type of covalent bond formed by hydrolysis reactions
E. More than one option is TRUE
B. Branching is related to the solubility of the carbohydrate in water
Given the large amount of DNA that must be replicated in every cell division, which
of the following are strategies to aid in the speed of replication?
A. The usage of a protein clamp to allow RNA polymerase to stay attached to
the DNA longer than it would do by itself
B. Starting replication at multiple origin sites simultaneously
C. One strand of the DNA can be both the coding and the template for a gene
D. The DNA is replicated in a conservative mode to save time
E. None of the above
B. Starting replication at multiple origin sites simultaneously
What can be learned by analyzing the primary structure of a protein?
A. The three-dimensional shape of the protein.
B. The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains.
C. The sequence of amino acids in the protein.
D. The presence of disulfide bonds between amino acids.
E. None of the above
C. The sequence of amino acids in the protein.
Which of the following is NOT a true function of DNA ligase?
A. DNA ligase generates a phosphodiester bond to link fragments of DNA
B. DNA ligase is necessary to complete DNA repair mechanisms
C. DNA ligase connects the Okazaki fragments created during synthesis of the
lagging strand of DNA replication
D. DNA ligase is necessary during transcription to rejoin the two strands of DNA
that got opened
E. All of the listed options are functions of DNA ligase
D. DNA ligase is necessary during transcription to rejoin the two strands of DNA
that got opened
Which of the following statements regarding the RNA polymerase is FALSE?
A. It ends transcription when it reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA).
B. It reads the template DNA in the 3’ to 5’ direction.
C. It binds to the promoter region of the gene to be transcribed
D. It synthesizes RNA by adding incoming nucleotides in a 5’ to 3’ direction.
E. It does not require a helicase or a topoisomerase to unwind and uncoil the
double stranded DNA.
A. It ends transcription when it reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA).
Rosalind Franklin performed the X-ray crystallography experiments that produced
the data that enabled the discovery that:
A. DNA is the molecule of genetic inheritance, not protein
B. DNA replication occurs according to the semi-conservative model
C. DNA’s structure is that of a complimentary double helix
D. The central dogma of molecular biology states that DNA is transcribed into
mRNA, which is translated into proteins
E. None of the above
C. DNA’s structure is that of a complimentary double helix
Transcription initiation requires...
A. A G-C pair rich genome area known as the origin site
B. The binding of RNA polymerase to a promoter region
C. The function of helicase to unzip the DNA
D. Single strand binding proteins to keep the DNA from closing
E. More than one of the above
B. The binding of RNA polymerase to a promoter region
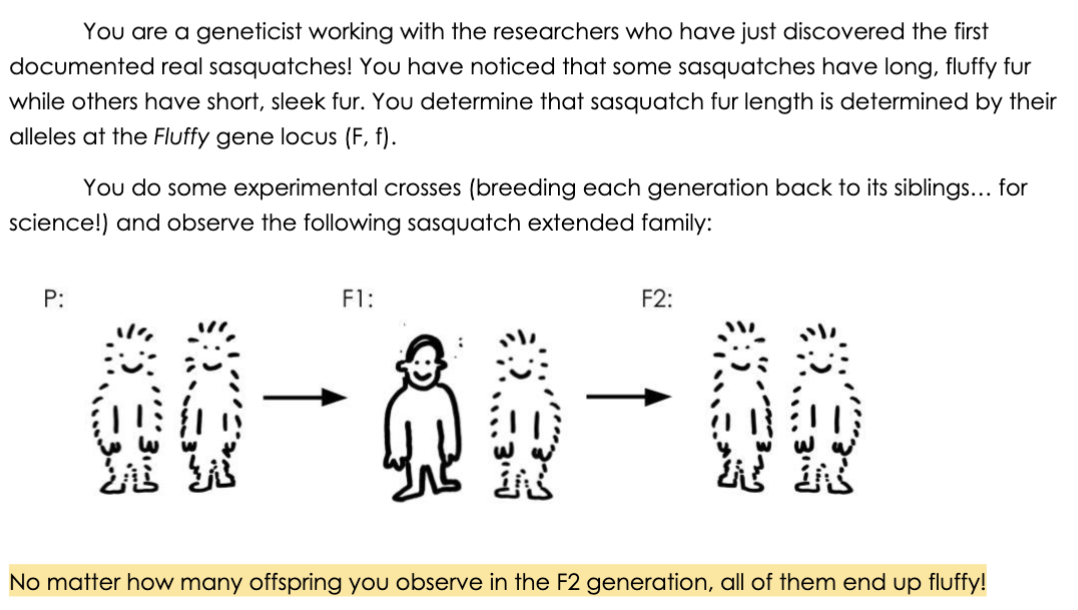
Judging from your observations of this family, is fluffy sasquatch fur dominant or recessive to
sleek sasquatch fur?
A. Dominant
B. Recessive
A. Dominant

Which of the following genotypes must represent the P generation of the sasquatches?
A. FF x Ff
B. Ff x ff
C. FF x FF
D. Ff x Ff
E. ff x ff
D. Ff x Ff

Which of the following genotypes must represent the F1 generation of the sasquatches?
A. FF x Ff
B. FF x FF
C. ff x FF
D. Ff x Ff
E. ff x ff
C. ff x FF

If you crossbred the F2 generation with itself, what would be the ratio of fluffy : sleek offspring?
A. 1 fluffy : 1 sleek
B. 3 fluffy : 1 sleek
C. 1 fluffy : 3 sleek
D. 1 fluffy : 0 sleek
E. Impossible to know
B. 3 fluffy : 1 sleek

If you bred an offspring from the F2 generation to a fluffy sasquatch whose parents are a sleek
sasquatch and a “true breeding” fluffy sasquatch, what ratio of fluffy : sleek offspring would you
expect to end up with?
A. 1 fluffy : 1 sleek
B. 3 fluffy : 1 sleek
C. 1 fluffy : 3 sleek
D. 1 fluffy : 0 sleek
E. Impossible to know
B. 3 fluffy : 1 sleek