PP 11: Water Pollution
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
History- water contamination
1880s: water caused disease
1920s-30s: BPA, PCBs, and DDT released
1940s: Sewage control, fluorination
1960s: Silent spring, book about silent periods where you wouldn’t hear birds. birds were dying from DDT. Used it on bugs, and birds ate bugs
1980s: Endocrine disruptors
1990s: pharmaceuticals
2000s: microplastics
Health effects: Great Lakes Chronology
Theo’s work, wrote Our stolen future
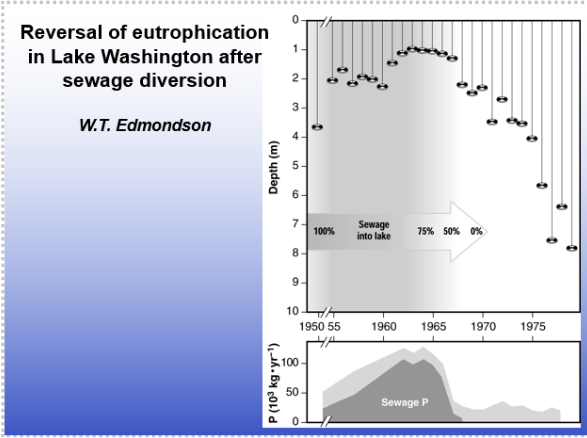
1950s Erie: Major eutrophication; algal blooms; hypoxia
1960s Michigan: mink industry crashes
1963 Michigan: herring gulls- reproductive failures
1968 Ontario and Huron: High Hg (mercury) in sediments
1970 Eria, Ontario: some commercial fisheries close- Hg
1971 Ontario: Herring gulls- chicks die/crossed bills
1978 Love canal: health emergency 1030 homes evacuated
1988 Ontario: intersex fish (white perch)
Exposure chronology
1920s-30s: BPA, PCBs, and DDT released. Chlorine industry expanding
WWII-1940s: first wide-scale exposure to antrophogenic chemicals
1940s-50s: first generation exposed postnatally
1950s-70s: first generation born that was exposed in the womb
1970s-90s: first generation that was exposed in the womb reached reproductive age
1980s-present: second generation born that was exposed in the womb. production volume and exposure still increasing
a lot of endocrine disruptors making things skip generations, etc. breast cancer
toxins and other health hazards
Intensive agriculture, cities, industry: all of these produce wastewater faster than nature can process it
out of site- out of mind
dilution is the solution to pollution
Ironically, historically the technology to speed up access to water and remove wastes has made water pollution worse
with endocrine disruptors, even with a small exposure, if i hits a receptor its problematic
flushed toilet is one of the highest water pollution device
General zones and sources of water pollution
-General Zones
surface water
ground water
-general sources
non-point sources
non-point is run off, when its not coming from an actual tube or pipe
-point sources
point source= landfills, septic systems, leaking spots, you can actually point to where its coming from
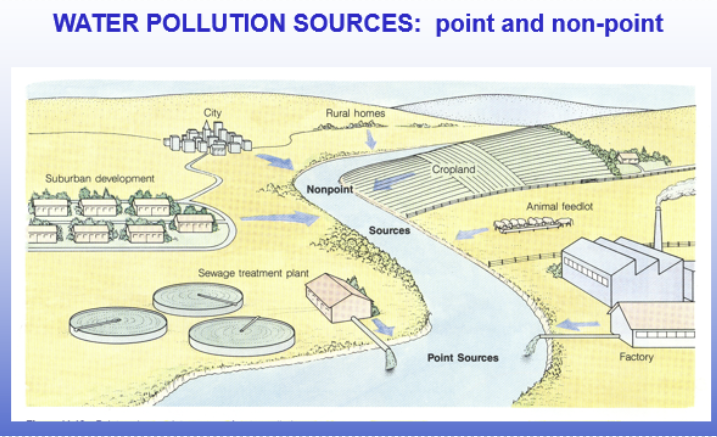
Goundwater sources
pic
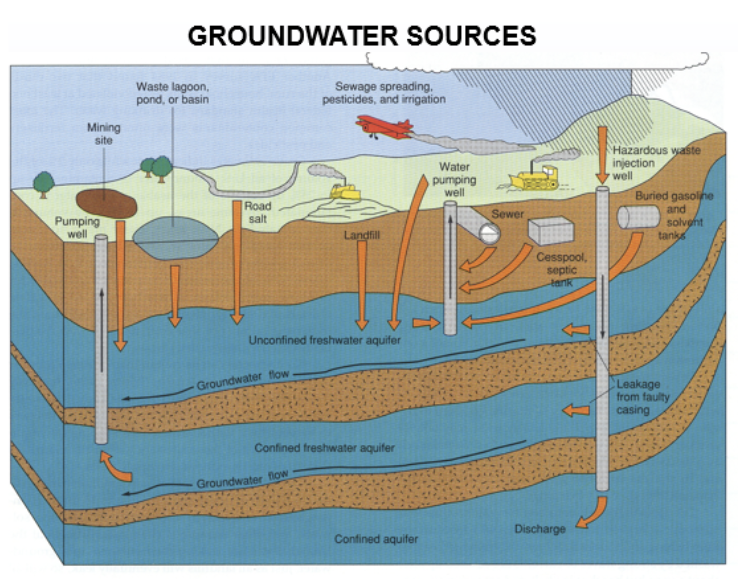
water pollution: point sources
pic

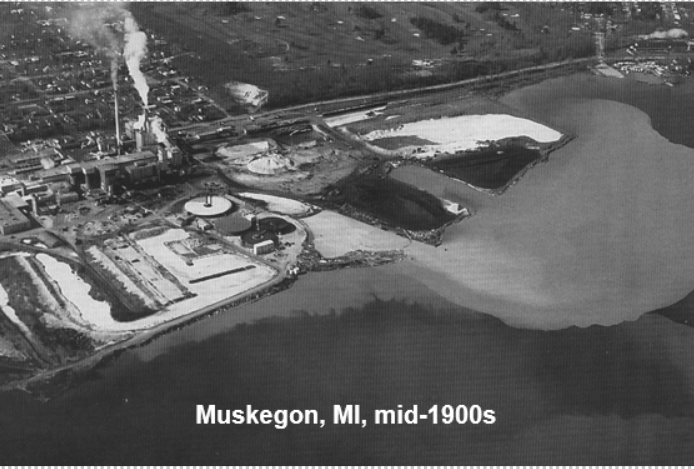
Muskegon
pic

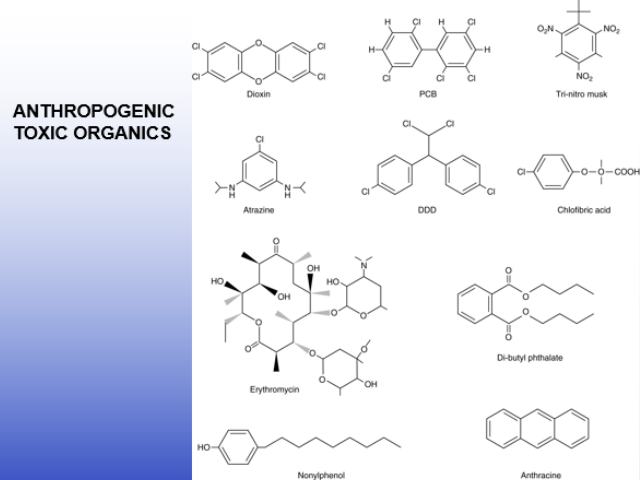
Toxins and other health hazards (directly toxin or bioconcentrated, esp in fat tissue): organic chemicals
Petroleum products and their derivates
pesticides and herbicides
Pharmaceuticals (including endocrine disrupters) other indivudal and domestic materials
when it says organic, it has a carbon
in the pic, those are all organic pollutants because of the carbon rings
Toxins and other health hazards (directly toxin or bioconcentrated, esp in fat tissue): inorganic chemicals
-Heavy metals
lead: paint, gasoline (both an organic and inorganic pollutant), plumbing, industry
mercury: coal burning, mining
Cadmium: metal industry, plumbing
Copper: pesticide, plumbing
-Strong acids and bases
-other industrial and domestic materials
-salts, esp. road salt
Radioisotopes
Esp. Uranium, cesium, iodine, thorium, radon, tritium, 14C, etc.
from mining, weapons testing, nuclear power, research, medical
Infectious organisms
Viruses, bacteria, protist, and other parasites
Algal toxins
includes neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, and dermatoxins
esp. many species of bluegreens (cyanotoxins) and some dinoflagellates
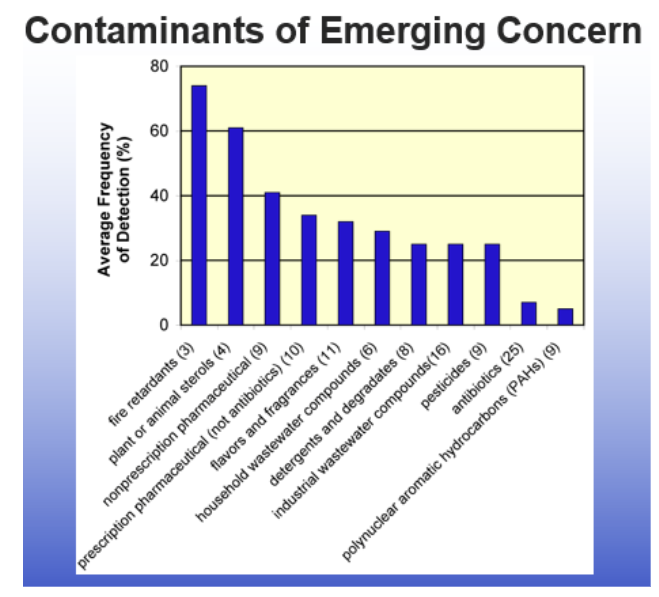
Contaminants of emerging concern
-Pharmaceuticals
antibiotics, prescription, NSAIDs, OTCs
-Personal care products (PCPs)
detergents, shampoo
-Consumer products
fire retardants, plasticizers, DEET
Nutriceuticals: vitamins, health food suplements
-Agriceuticals
Bioengineered foods (Genetically modified crops)
-Nanomaterials
things that are small enough to cross the cell membrane
supposedly inert, but no monitoring yet
-Microplastics
transfer of contaminants
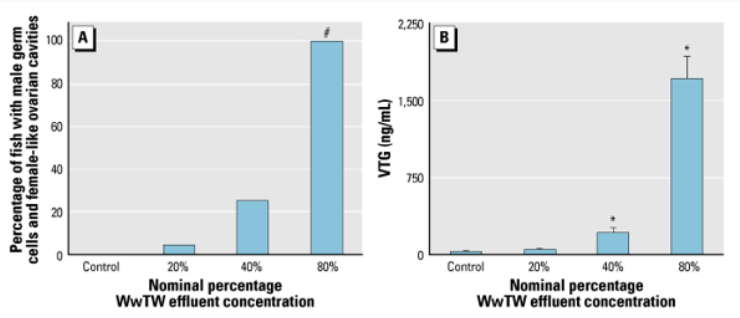
Once in the environment…
A. percentage of fish with male germ cells that had femalelike ovarian cavities (i.e., feminized males) in each treatment group
B. mean whole-body VTG concentrations (n=3-; mixed sex) for all treatment groups. Error bars are SEM. Significantly different from control: P< 0.05, #p<0.001
Mounting evidence for ecological effects
Trenblone: irreversible fish masculinization (Morthorst et al., 2010)
Sulfamethoxazole: decreased denitification rates in abcteria (Underwood et al., 2011)
Triclosan: disrupts thyroid hormine- associated gene expression in frogs (Veldoen et al., 2006; Kloas et al 2024)
Fexofenadine: behavioral changes in damselfly larvae (Jonsson et al., 2014)
less is known about envrionmental efects from exposure to complex mixtures of CECs
DONT have to know these, just examples
Ecosystem disrupters
Plant nutrients (-> eutrophication)
P
N
Oxygen-demanding wastes
organic matter- sewage, industry (esp. food, paper)
very high biological oxygen demand (BOD)
Sediment
thermal
Heated water from industrial cooling systems
Global warming
acid precipitation from air pollution
from fossil fuel combustion:
SO2 -> H2SO4 (esp. from coal) CO2 -> H2CO3
NO2 -> HNO3 (esp. from gasoline)
Acidifies soft water; kills or impairs much of biota
in calcareous watersheds, the pH is buffered to some extent
Bicarb export by Mississippi R. has risen 60% since 1950s
exotic species introduction
some ”accidental”; e.g. from ship ballast water- most current Great Lakes area exotics:
zebra mussel
Spiny water flea
round goby
Ruffe etc.
after opening of the Welland Canal
sea lamprey
ornamentals or misguided bio pest control
water hyacinth
purple loosestrife
asian grass carp, etc
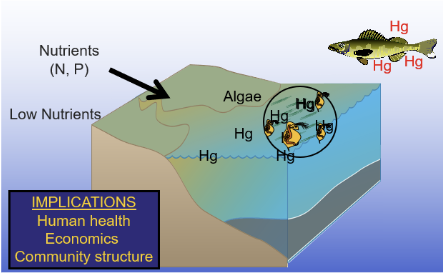
Ecosystem complexity: Lake 1
- Hg binds to anything organic, so it binds to algae
- the daphnia eat the algae
- The fish eats that algae and now has mercery
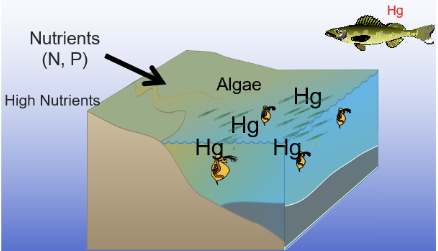
Ecosystem complexity: Lake 2
- only a little bit of algae in this lake
- because of this, a small number of daphnia
- fish comes by and eats the zooplankton, it has a much higher concentration of Hg
- the same amount of Hg was spilled into both lakes, but because there was less organic nutrients for the Hg to bind to, it was more concentrated, so this fish has much more Hg
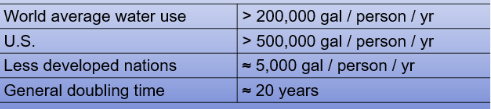
Water pollution rates are strongly correlated with water use rates
80-90% of freshwater used becomes waste water
Example: reserve mining Co., Duluth, for many decades has washed 70,000 tons per day of taconite tailings (mining waste, high in heavy metals and acid) directly into lake superior
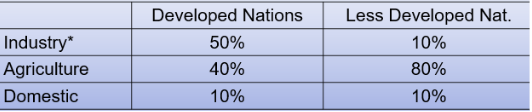
General data for US
pic

Approaches for pollution control
Input focus
output focus
Input approaches
-Industry
Enforce and strengthen restrictions
use and improve technology for recovery and recycling of waste chemiclas; other treatment procedures
upgrade storage tanks, pipes, transportation reliability
Reduce need for heavy technology, esp. Chemcially intensive ones
use cooling towers and lagoons
-Agriculture
shift to sustainable organic no-till farming techniques
return to livestock grazing rather than feed lots
-Domestic
water conserving practices
reduce or eliminate use of chemicals in home and lawn
Municipal
-Primary
30% of solids and 70% of dissolved waste remains in effluent
most toxins remain
solid sludge becomes a solid waste problem; incineration or land fill -> air or subsequent water pollution
have moved away from this in the US. If anything, primary would be in rural areas
10% of US cities have primaries
sewage sludge contains pathogens
-Secondary
bacterial decomposition of organic matter in activated sludge
removes 90% of biological oxygen demand
Remaining: 10% of BOD, 50-70% of P&N, >30% of toxins
solid sludge remains a problem
Disinfection of effluent water with chlorine
70-80% of US cities have this
-Tertiary
after secondary: specialized physical, chemical, and/or biological treatments
Precipitation by alum, FeCl3, etc.
Activated charcoal
Electrodialysis
Artificial wetlands
These remove most N, P, and toxins etc.; water is of very high quality
Can be expensive, require extra space, etc., but the technology is rapidly growing
15% of US cities
-Can’t have a higher level without the lower levels. If they do secondary, they also have to do primary ! test question
-! test question What is the product that they all have to deal with? Sludge
Reclamation/remediation (cleaning)
-Soil and groundwater: extremely expensive to clean groundwater
Superfund program: identified the most polluted sites in the nation
Example- IBM-Dayton site:
1970s: 100s gallons of chlorinated organics dumped
1978: groundwater had 6,100 ppb perchloroethylene
1978-84: 300Mgal/min pumped out to remove the pollutant; temporarily reduced conc. to 100 ppb
1988: concentrations had risen back to 12,500 ppm
“brownfield” sites- sites that have contamination in them
-Lakes
Toxic pollution
Assuming the effluent source has ceased, the remaining contamination is usually in the sediments; options include
Dredge and remove sediments- this can resuspend pollution
Leave alone- doesnt suspend pollution, but it may resuspend on its own
-Eutrophication
Algal and macrophyte control
Chemical
Harvesting (macrophytes)- by hand or machine
Biological control
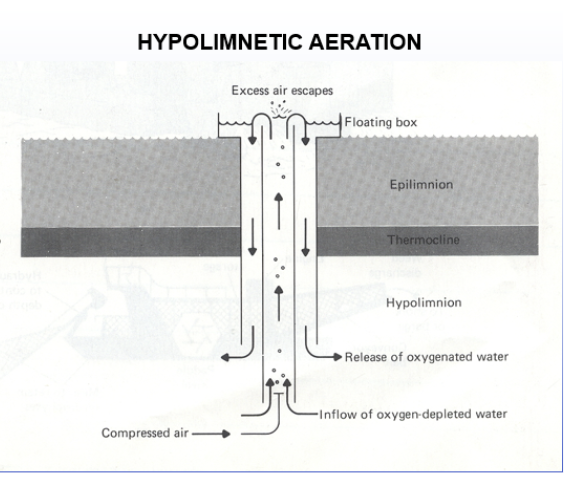
Hypolimnetic anoxia
-Water column aeration
bubbling air from the bottom of the water foutain
problem: redistrubutes nutrients. You’re constantly pulling up the nutrients. But if you dont have a bunch of nutrients in the sediment at the bottom, this is a good method
-Hypolimnetic aeration
Allows the water to remain stratified
removed the problem of preventing turnover, and you won’t get all the nutrients from the sediment
-Hypolimnetic sidestream pumping
comes in at the edge
Cuyahoga
pic

General outlook for water pollution: progress
Some significant progress in preventing or mitigating water pollution since 1972, resulting from several fairly strong federal laws including the Clean Water Act, Safe Drinking Water Act, Clean Air Act, Endangered Species Act, Forest Practices Act, etc.
Improvements greatest in sewage treatment, drinking water, and severely polluted systems such as the Cuyahoga River, and Lake Erie
GLRI has increased attention and funding to these areas
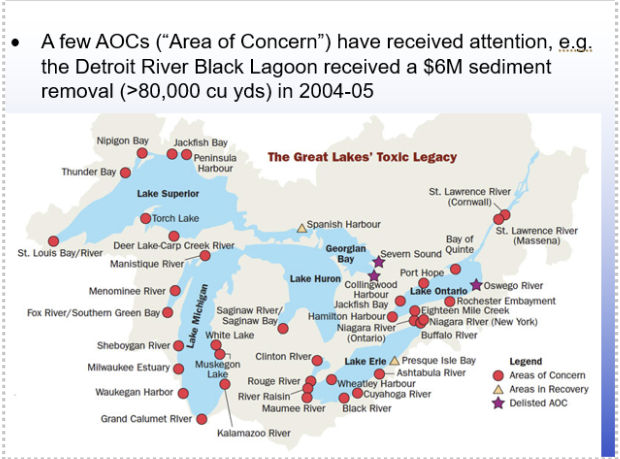
General outlook for water pollution: Limitations
The primary focus has been on the more easily controlled point sources; non-point sources have not been adequately addressed and continue or are worse than ever
The clear water act did not include research priorities, and funding for pollution research continues to decline
Limited funding and little remediation has occurred in AOCs even with “remediation action plans” written for them
The environmental protection agency has been highly political, and appointed directions in conservative administrations have been willing to relax the enforcement of existing regulations
The clean water act amendments of 1995 (H.R. 961) reversed many of the original protections by providing waivers to industries, reducing protection and treatment measures, relaxing rules, etc
Under current standards, > 1/3 of US freshwater ecosystems do not meet the standards (it would be 2/3 if more appropriately stringent standards existed)
General outlook for water pollution: Needed
Better national and global consensus on the importance of our freshwater resources
More research on causes, consequences, and correctives
Better leadership
More cooperation and political will to develop the correct mix of laws, regulations, and incentives
Reversal of eutrophication
pic