Cardiovascular System Notes
1/197
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Yellow: arrhythmias + hypertension Red: heart failure + intro to CV Purple: arteriosclerosis Blue: valvular diseases Green: vascular diseases
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
198 Terms
What characterizes Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) in terms of heart rate, rhythm, and intervals?
60-100 bpm
Normal rate, rhythm & intervals
How is Sinus Tachycardia defined?
100-160 bpm
No other ECG abnormalities
Regular distance between RR
All p waves present
What are some common causes of sinus tach?
Exercise
Anxiety
Caffeine & nicotine
Fever & shock
CHF & HTN
Pain
Define Sinus Bradycardia, and under what circumstances is it typically not concerning?
< 60 bpm
No other ECG abnormalities
Not typically concerning if you can pinpoint a cause & also asymptomatic
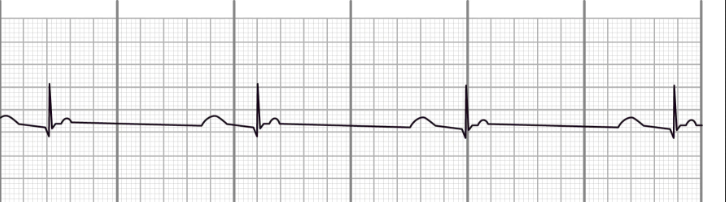
What are some causes of sinus brady?
SA node dysfunction
Athletes
Vasovagal response
Hypothermia
Inferior MI
Meds (digoxin, BBs)
What is the general heart rate range for Supraventricular Tachycardias (SVTs), and where do these beats originate?
160-250 bpm
Beats originate from above the ventricles
Most SVTs have a p wave
What are some treatments for SVT?
vasovagal maneuvers
rate-lowerings meds
cardioversion
ablations
What are the types of SVTs?
Paroxysmal
Wolff-parkinson-white
AV nodal reentrant
Atrial tachycardia
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial flutter
What is Atrial Flutter, and how does it affect atrial and ventricular rates?
Atrial rate: 250-400 bpm
Ventricular rate: 70-150 bpm
P waves have saw tooth pattern
Can lead to a-fib or alternate between the 2
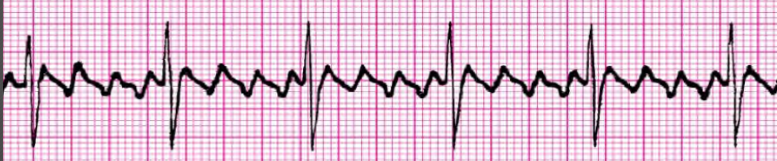
What are some causes of atrial flutter?
Ischemic ♥ disease/MI
Meds (digoxin)
Valvular disease
Stress & hyperthyroidism
Pulmonary embolism
Describe atrial fibrillation
Atrial rate: 350-600 bpm
Ventricular rate: variable but can be “rate controlled”
If < 100 = controlled a-fib
If > 100 = uncontrolled a-fib
Wavy & fibrillating p waves
What are some causes of a-fib?
Ischemic ♥ disease/MI
CHF
Valvular disease
Meds (digoxin)
What defines a 1st-degree heart block?
PR interval > 0.20s & p waves can get buried in preceding T wave
Not typically serious but can progress to more dangerous ♥ blocks
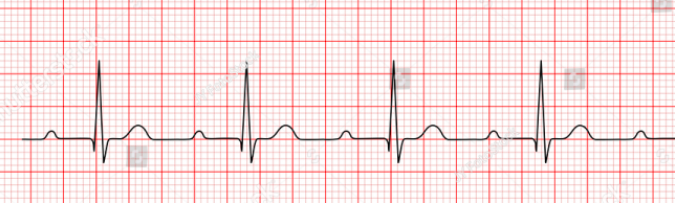
What are the causes of 1st degree heart block?
Increasing age
Hyperthyroidism
Electrolyte abnormalities
Damage to ♥ tissue
Extreme athletes
Genetics
Explain the characteristics of 2nd-degree heart block Type I (Mobitz I or Wenckebach).
Irregular rhythm
PR interval gets longer & longer, eventually QRS complex is dropped
QRS gets bigger & bigger, then is gone
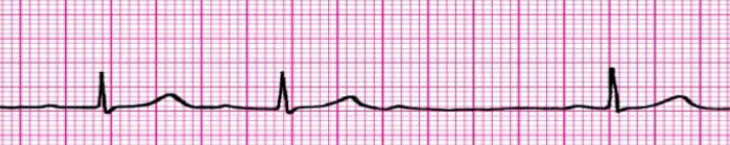
What are some causes of 2nd degree heart block?
Ischemia
Myocarditis
Medications
Explain the characteristics of 2nd-degree heart block Type II (Mobitz II).
Irregular rhythm
Intermittent losses of the QRS complex
Single, double, triple dropping of QRS
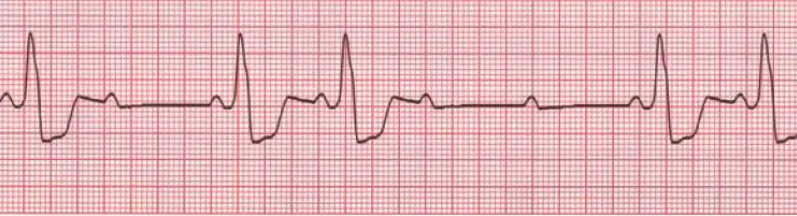
What distinguishes 2nd-degree heart block Type II (Mobitz II) from Type I?
In type I QRS eventually gets dropped
In type II QRS is intermittently lost
Describe 3rd-degree heart block (complete heart block).
Atria & ventricles are completely dissociated from each other
Independent p wave & QRS complex activity
Regular PP & RR intervals
What are some causes of 3rd degree heart block?
Ischemia
Meds
Nodal ablation
Electrolyte imbalance
Post op
Lyme disease
What are Premature Ventricular Contractions (PVCs), and why is the number of consecutive PVCs important?
Ventricular muscle is stimulated w/o signal from the atria
This causes the ventricular contraction
Contraction shows up on ECG as a wide & bizarre ectopic beat
The # of PVCs in a row
Considered a “run of vtach”
2 = couples, 3 = triplets
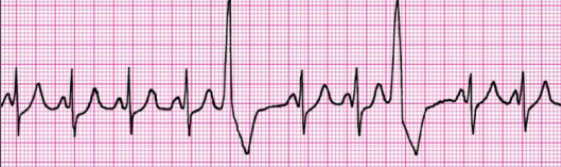
What can PVCs lead to?
vtach, which may then lead to vfib, etc.
What are the causes of PVCs?
Stress
Caffeine
Meds
Underlying disease
Define Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) in terms of heart rate, presence of P waves, and QRS characteristics.
> 100 bpm
P waves are absent
QRS complexes are wide & abnormal
All beats are ventricular in nature
What are some causes of vtach?
MI/ischemia
Myocarditis/endocarditis
Cardiac scarring (Sx)
Conduction disorder
Explain what Torsades de Pointes is.
Specific form of polymorphic vtach
Twisting or helical tracings
Defibrillate
What are some causes of torsades de pointes?
Myocardial ischemia/MI (most common)
Long QT syndrome (genetics)
Electrolyte imbalances
Meds
What is the purpose of cardioversion?
delivers low-energy shocks to the ♥ to restore an arrhythmia
What types of rhythms can be cardioverted?
A-fib
Atrial flutter
SVTs
Vtach
Vfib
Describe the difference between synchronized and unsynchronized cardioversion.
Synchronized: Shocks are delivered in a very precise point & time + synchronizes with pt’s rhythm
Unsynchronized: Delivers a not-so precise & not synchronized shock + must be correct amount of electricity & given at the right time
What must be present in order to defibrilate?
a true rhythm
What are 2 nonshockable rhythms?
asystole & pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
What do you do for nonshockable rhythms?
ACLS, CPR, or admin epinephrine
What does PEA look like?
can look like a normal rhythm, would never know the pt has no pulse
How does an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) work, and what are the basic steps for its use?
Step 1: turn on AED
Step 2: place pads on pt in correct locations
Shave any hair & pat site with towel if sweaty
Step 3: follow AED instructions
Explain the functions of an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD) and the settings it can have.
it can cardiovert (administers precise low-energy shocks) & defibrilate (shocks a dangerous [or potentially] rhythm)
has settings to control at what HR to start cardioverting (shock zones)
What is the role of an Implantable Pacemaker, and how does it function when a patient's heart rate falls below certain parameters?
it paces the ♥ following provided parameters & starts functioning when the HR goes below parameters
What is an ablation procedure and how does it treat arrhythmias?
Problem areas of electrical misfiring are shocked/ablated until the tissue no longer creates impulses
Can be used to help treat majority of SVT-based conditions
What is heart failure, and what does it involve in terms of the heart's ability to function?
The inability of the ♥ to pump sufficient blood to meet needs of the tissues (CO is not high enough)
Explain what ejection fraction (EF) measures.
fraction of blood ejected out of the left ventricle during systole vs. how much is left in the ventricle after systole; the higher the more efficient
What is the normal ejection fraction range?
50-70%
What is the formula for ejection fraction?
stroke volume / end diastolic volume
What is the formula for stroke volume?
end diastolic - end systolic
Define heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)
the ♥ muscle contracts normally, but the ventricles don’t relax as they should during ventricular filling; aka diastolic HF
Define heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)
the ♥ muscle doesn’t contract effectively, therefore less oxygenated blood is pumped out to the body; aka systolic HF
What are some of the common causes or etiologies of heart failure?
Ischemic ♥ disease
MI
Myocarditis
Peripartum cardiomyopathy
Stress cardiomyopathy
Genetic ♥ disease
Infiltrative ♥ disease
Chemotherapy/cardiotoxic meds
HTN
List the risk factors associated with heart failure, both non-modifiable and modifiable.
CAD
Diabetes
HTN
Obesity
Valvular ♥ disease
Race (African Amer: 70% ⬆)
Hx of MI
Sleep apnea
Smoking
Alcohol
Increasing age
Familial Hx (immediate)
Gender (men: lower survival)
Describe the pathophysiology of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) as explained in the text.
it can be 1 of 2 issues, or can be both:
Stiff ventricles leads to less stretch, thus an inability to accommodate adequate volumes of blood
Ventricle hypertrophy & reduced chamber size lead to reduced space/volume for blood
What does less blood volume in the left ventricle lead to?
less CO, even in the presence of strong ventricular contractions
How is the EF in HFpEF (diastolic)?
normal despite reduced CO
Which gallop is specific to HFpEF (diastolic)?
S4
What is the pathophysiology of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF)?
The ♥ cannot contract with enough force to meet the systemic needs
Progression to systolic HF:
Ventricular remodeling → dilation → dysfunction → Reduced EF
Which gallop is specific to HFrEF (systolic)?
S3
What are some compensatory mechanisms of heart failure?
RAAS system activation & sympathetic nervous system
How do compensatory mechanisms, such as the RAAS system and sympathetic nervous system, come into play in heart failure, and what are their effects on the heart?
These mechanisms ⬆ BP & blood volume, therefore ⬆ ♥ strain
♥ will eventually “gas out” which is why pts with chronic HF are given an estimated time to life
How does the RAAS system activate during HF?
juxtaglomerular cells/apparatus (inside of Bowman’s Capsule within the kidneys) sense low sodium chloride concentration & low BP, releasing renin
Renin is converted into angiotensin II, causing sympathetic response, increased sodium retention, stimulates aldosterone secretion, stimulates ADH secretion
Sympathetic response — vasoconstriction, ⬆ HR
Aldosterone — leads to sodium reabsorption (water retention)
ADH — causes ⬆ water reabsorption in collecting ducts in kidneys
How does the sympathetic nervous system activate during HF?
baroreceptors in aortic arch receive less stimulation with reduction in BP, so increasing sympathetic activity & decreasing parasympathetic activity leads to ⬆ HR, contractility & vasoconstriction
What are some of the common manifestations and symptoms of heart failure?
Dyspnea
Fatigue
Edema
Coughing or wheezing
Tachycardia
Ascites
S3 (vent gallop)
Nausea, lack of appetite
Confusion
Weight gain
Anorexia
Nocturia
Angina
JVD
What are some symptoms of left sided HF?
Orthopnea & dyspnea
Low O2 sat
Crackles & wheezing
Blood-tinged sputum
Cough
Tachycardia
Decreased EF
What are some symptoms of right sided HF?
Weakness/fatigue
Ascites
Splenomegaly & hepatomegaly
Dependent edema
JVD
Weight gain
Anorexia & nausea
What are some ways to manage HF?
Best outcome involves fixing underlying pathologies (i.e. diseased ♥ valves, coronary artery bypass surgery or PCI for CAD)
O2 admin — to ⬇ oxygen demand & supply
Diuretics — loop, thiazides, potassium sparing
CCBs (HFpEF/diastolic) — blocks calcium from entering ♥, causing it to squeeze harder during systole; also blocks calcium in arteries causing vasodilation & ⬇ BP (reduced workload on ♥) not for systolic HF
ACE inhibitors & ARBs — induce vasodilation & ⬇ BP
Digoxin — ⬆ contraction, regulates rhythm
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)
Ventricular assistive devices (VADs)
♥ transplant
What is HF care centered around?
improving functional status (quality of life), extending survival & relieving client symptoms (quality of life)
What are the 2 classifications of acute heart failure?
Acute decompensation heart failure (ADHF)
De novo acute heart failure
Define acute decompensation heart failure (ADHF)
considered to be acute on chronic, a rapid ⬇ in CO in existing HF pts
Define de novo acute heart failure
occurs in those with 0 Hx of ♥ disease
What distinguishes acute heart failure from chronic heart failure?
acute HF has a sudden, rapid onset
What are some of the potential causes or etiologies of acute heart failure?
Advanced kidney disease
Alcoholism
Pulmonary embolism
Diabetes
HTN & HT crisis
Hyperthyroidism
Sleep apnea
Stroke (ischemic & hemorrhagic)
Viral ♥ infections
Exacerbations of existing ♥ disease (CAD, valvular disease)
Dysrhythmias
Mention some of the diagnostic tests or procedures that can help diagnose acute heart failure.
BNP
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
Chest x ray
Echocardiogram
Catheterization
What does BNP determine?
fluid volume status (stretch)
What does ECG determine as far as acute HF?
if cause of acute HF is anything electrophysiology-related
What does chest x-ray determine as far as HF?
cardiomegaly & pulmonary edema
What does echocardiogram determine?
EF & potential cause (valvular, muscular, etc.)
What does catheterization determine as far as HF?
if cause is from coronary artery origins
Define cardiogenic shock
lack of perfusion to the body caused by the heart
What are the medications and interventions for cardiogenic shock?
Vasopressors — dopamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine
Inotropic — dobutamine, dopamine, milrinone (PDE3 inhibitor)
Inotropic = ⬆ or ⬇ muscle contractions, in this case we would need to ⬆ in order to increase CO
Fluid resuscitation — NS, LR, albumin (be careful because you can easily overload the ♥)
What is the function of an ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation) machine?
Pumps blood throughout the body (helpful in HF)
Oxygenates the blood (helpful in acute pulmonary conditions)
What is arteriosclerosis, and what are the types?
hardening of the arteries
atherosclerosis
arteriolosclerosis
monckeberg
Define atherosclerosis
arteries develop plaque deposits, which lead to hardening & narrowing
Define arteriolosclerosis
same as atherosclerosis but it affects the smaller arteries
Define monckeberg
calcium build up in the middle layer of artery wall
What is the word for deposited plaque?
atheromas
Describe what effects atherosclerosis has on arterial walls
arterial wall hardness + ⬇ lumen size = CV complications (⬇ blood flow)
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: First step
fatty streaks of lipids deposit into arterial wall
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: What occurs after the fatty streaks are deposited into the arterial wall?
immune inflammatory response in the form of WBCs
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → _____?
WBCs ingest the lipids through phagocytosis & turn themselves into foam cells
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → WBCs ingest lipids & turn into foam cells → _____?
diseased foam cells release toxic substances contributing to endothelial damage
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → WBCs ingest lipids & turn into foam cells → diseased foam cells release toxic substances contributing to endothelial damage → _____?
platelets respond to endothelial damage by forming fibrous caps
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → WBCs ingest lipids & turn into foam cells → diseased foam cells release toxic substances contributing to endothelial damage → platelets respond by forming fibrous caps → ____?
fibrous caps take up volume within endothelium to ⬇ arterial wall lumen space
Pathophysiology of atherosclerosis: Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → WBCs ingest lipids & turn into foam cells → diseased foam cells release toxic substances contributing to endothelial damage → platelets respond by forming fibrous caps → fibrous caps decrease lumen space → _____?
fibrous caps & atheroma break off & cause an embolus
Complete pathophysiology of atherosclerosis
Fatty streaks → WBC immune inflammatory response → WBCs ingest lipids & turn into foam cells → diseased foam cells release toxic substances contributing to endothelial damage → platelets respond by forming fibrous caps → fibrous caps decrease lumen space → fibrous caps & atheroma break off & cause an embolus
What are the risk factors for atherosclerosis, both non-modifiable and modifiable?
Non modifiable
Increasing age
Gender (men)
Fam Hx/genetics
Race (African Amer, Mexican Amer, Native/Asian Amer)
Modifiable
Comorbidities (HTN, dyslipidemia, diabetes mellitus)
Smoking & tobacco use
Diet (⬆ in fat, salt)
Lack of exercise
Obesity
Stress
Metabolic syndrome (HTN, cholesterol, lipids, obesity, diabetes)
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the heart?
ACS (unstable angina, NSTEMI, STEMI), stable angina
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the extremities?
PAD, arterial wounds
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the neck (carotids)?
vision loss, carotid sinus syndrome (CSS)
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the brain?
transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), cerebral infections (stroke), vascular dementia
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the kidneys?
kidney hypoperfusion, CKD
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the intestines?
mesenteric artery ischemia (only 30%-50% survival rate)
What complications can arise with atherosclerosis in the reproductive organs?
erectile dysfunction (ED)
Define metabolic syndrome
a group of conditions that together raise your risk of CAD, diabetes, stroke, etc.
What is the criteria for metabolic syndrome?
elevated waist circumference
elevated triglycerides
reduced HDL-C
elevated BP
elevated fasting glucose