ANCIENT EGYPT TEST
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Pharaohs
Kings of ancient Egypt ruling Upper and Lower Egypt.
Old Kingdom
Period from 2686 - 2180 BCE known for pyramids.
Middle Kingdom
Period from 2055 - 1730 BCE marked by stability.
New Kingdom
Period from 1550 - 1069 BCE known for expansion.
Predynastic period
Era from 8000 to 2700 BCE before unified Egypt.
Nile River
Crucial waterway providing fertile soil and trade routes.
Mummification
Process of preserving bodies for the afterlife.
Hieroglyphics
Writing system using symbols for communication.
Gods of Egypt
Deities often depicted with human bodies and animal heads.
Horus
Sky god represented with a falcon's head.
Pyramids
Monumental tombs built for Pharaohs in Old Kingdom.
Fertile soil
Nile's silt enabling agriculture in ancient Egypt.
Transportation route
Nile facilitating trade and communication among Egyptians.
Architectural achievements
Monumental structures showcasing ancient Egyptian skills.
Intellectual prowess
Advancements in writing and knowledge in ancient Egypt.
Glorious aspects
Achievements in architecture and writing celebrated in Egypt.
Animal-headed gods
Gods symbolizing characteristics through animal representations.
Internal organs removal
Step in mummification for preserving the body.
Linen bandages
Material used to wrap mummified bodies.
Tourist attractions
Pyramids and temples drawing visitors to Egypt.
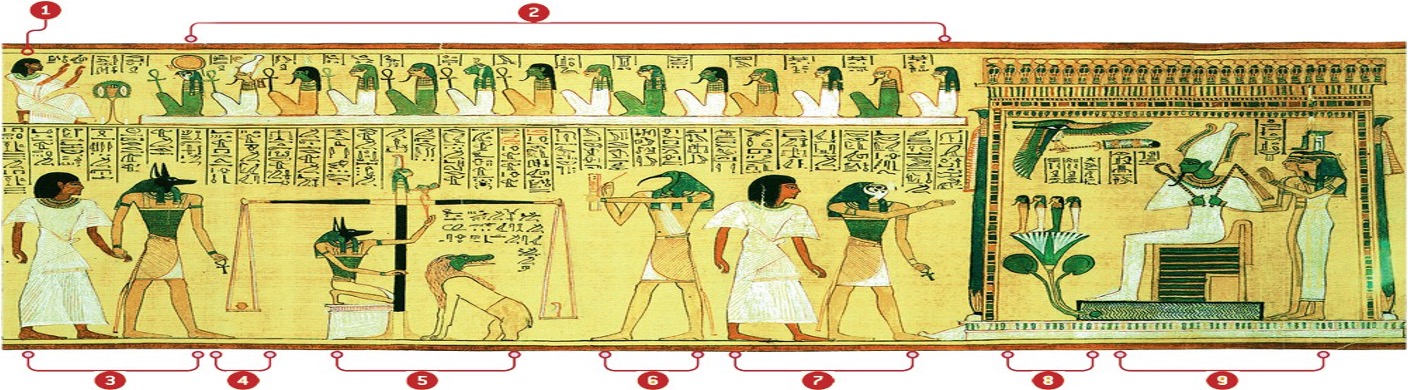
explain
The hieroglyphic illustration shows Hunefer's journey to the afterlife. Three components of this illustration are the scales of justice, the heart of the deceased being weighed, and the presence of various gods and goddesses.

explain
The artwork depicts Rameses II, an ancient Egyptian Pharaoh, and showcases his power and self-importance. Rameses II is depicted as a strong and confident ruler, emphasizing his divine status.
