Biology I Lesson 1: Nervous System
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
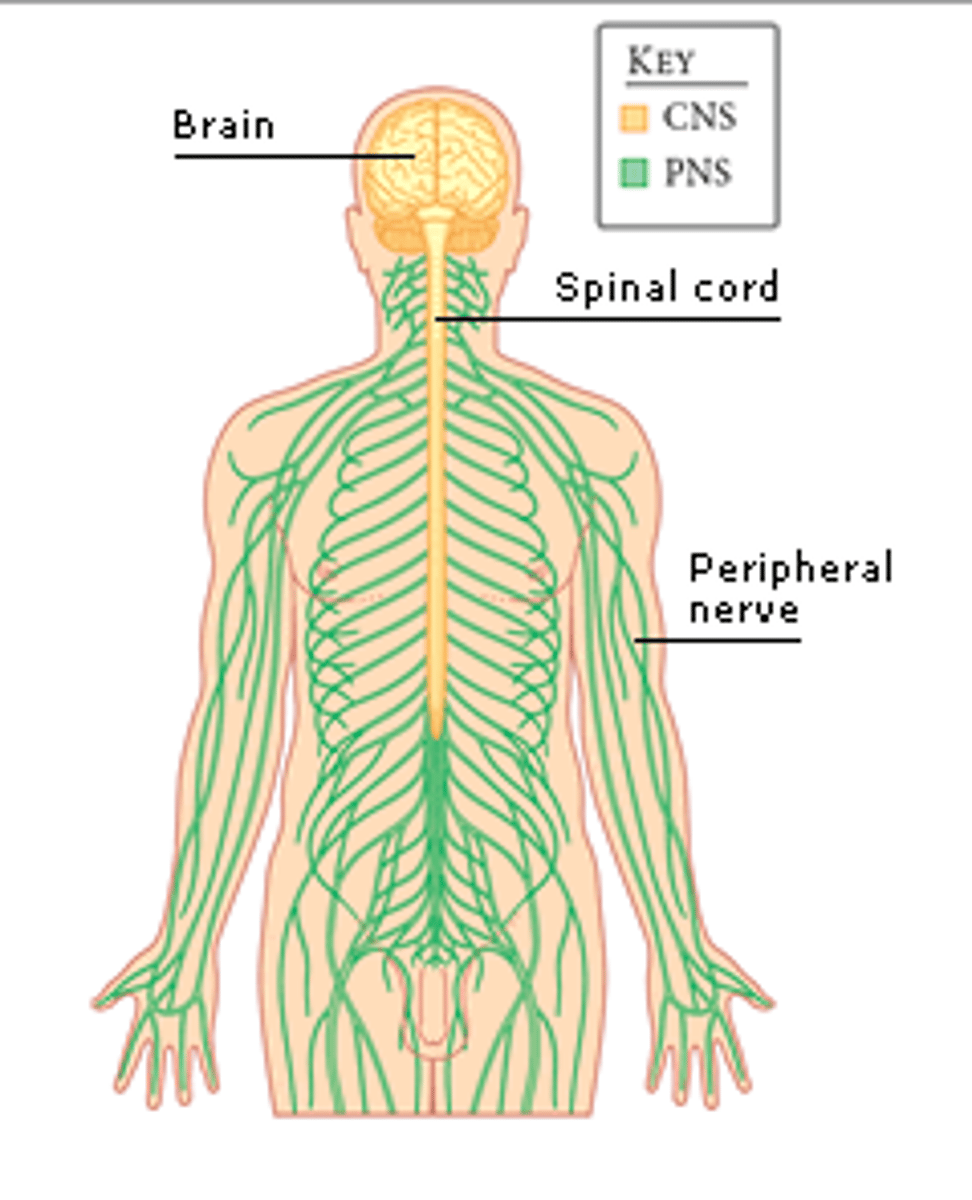
The nervous system is broken into two parts. What are they?
(A) Brain & Peripheral
(B) Central & Spinal Cord
(C) Central & Peripheral
(D) Brain & Spinal Cord
(C) Central & Peripheral
The nervous system is broken into the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. CNS is made of mostly interneurons.
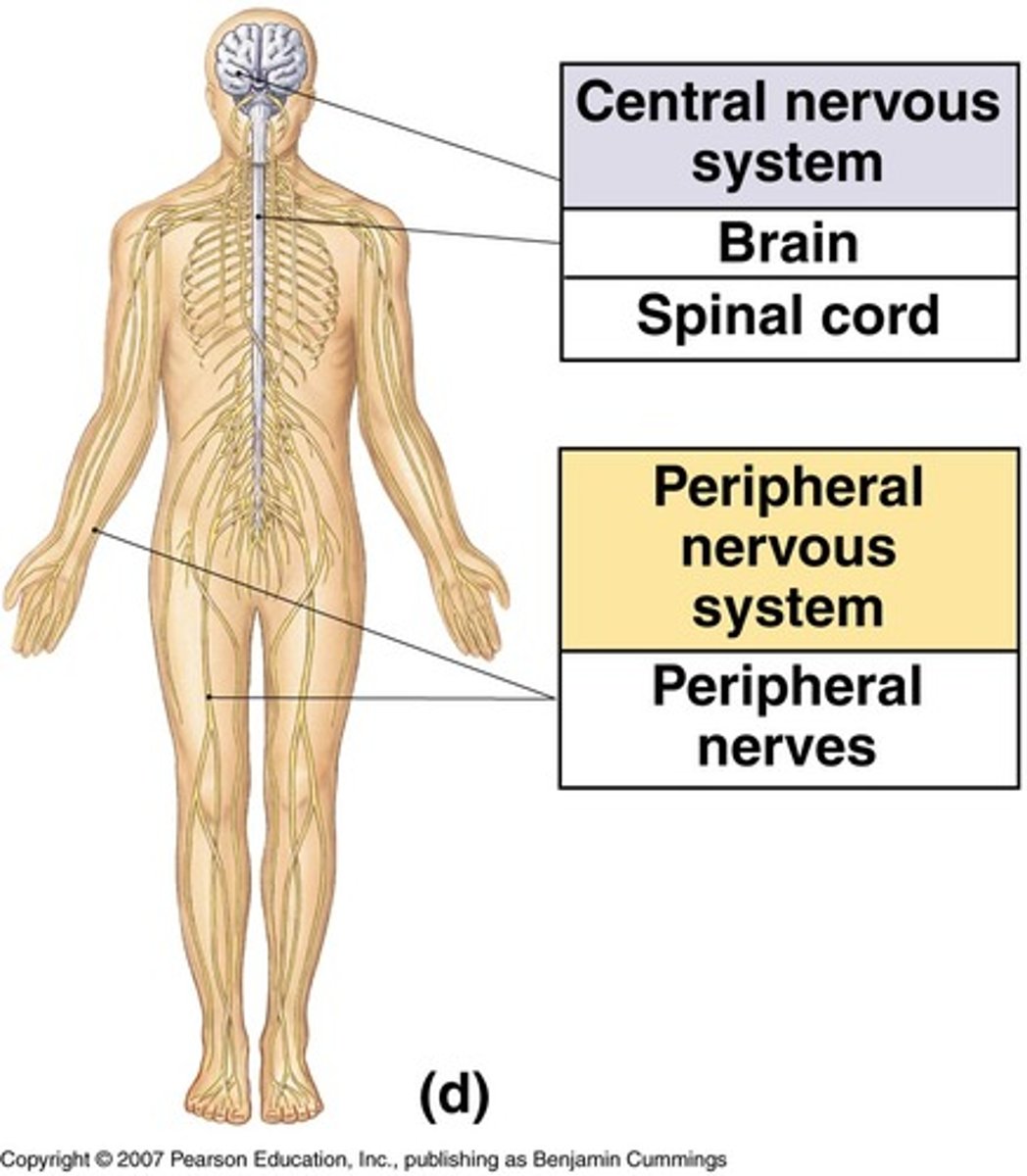
The central nervous system is also broken down into two parts. What are they?
(A) Brain & Peripheral
(B) Central & Spinal Cord
(C) Central & Peripheral
(D) Brain & Spinal Cord
(D) Brain & Spinal Cord
The central nervous system is also broken down into two parts: The Brain and Spinal Cord.
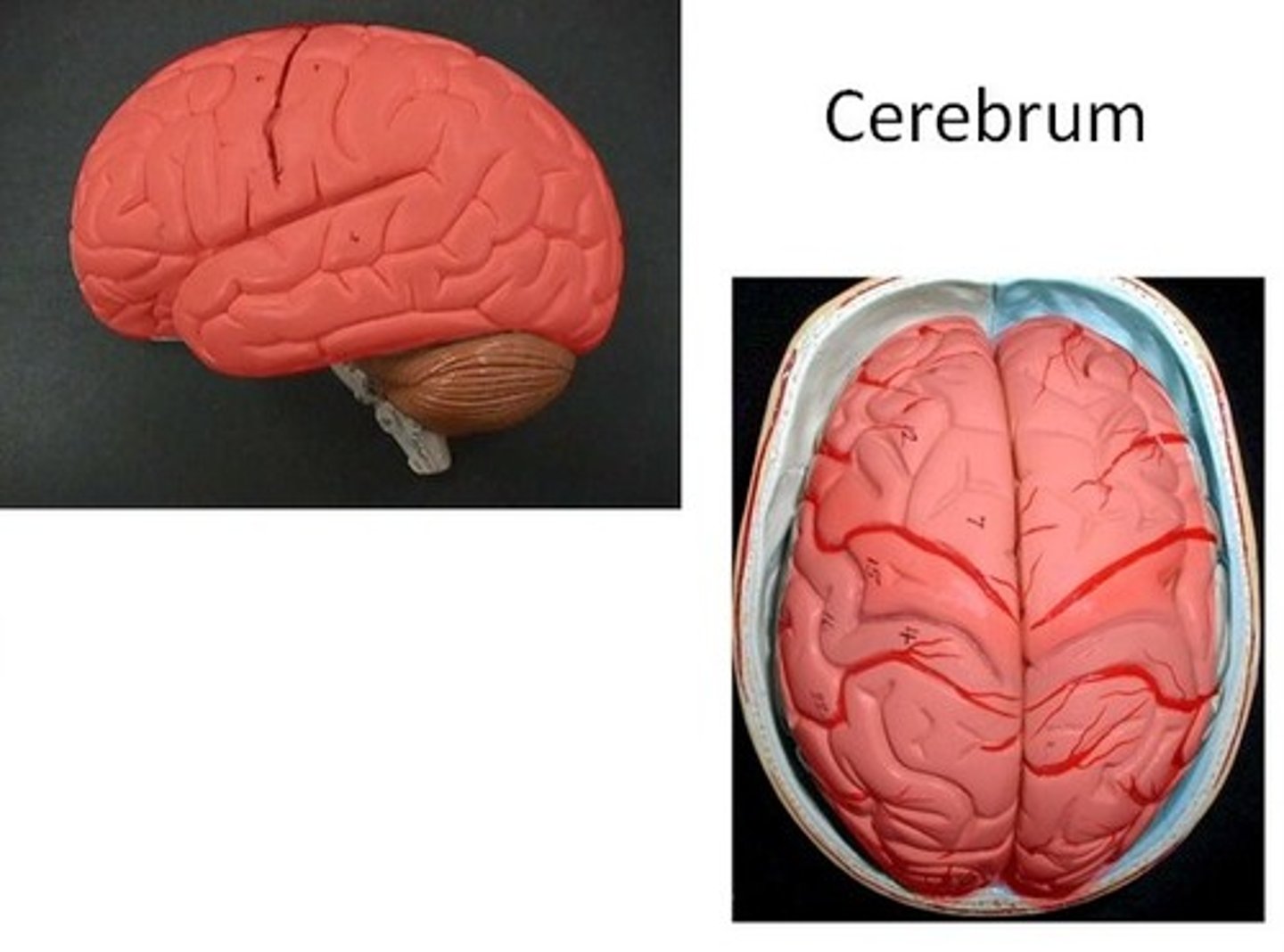
If we're looking at the brain from the top, what major part will we see (the most superficial part)?
(A) Cerebrum
(B) Midbrain
(C) Medulla
(D) Brain Stem
(A) Cerebrum
The Cerebrum is the most superficial part of the brain at the top. It is divided into left and right hemispheres.
The Cerebrum can be divided into left and right:
(A) halves.
(B) orbitals.
(C) hemispheres.
(D) lobes.
(C) hemispheres.
The Cerebrum can be divided into left and right hemispheres.
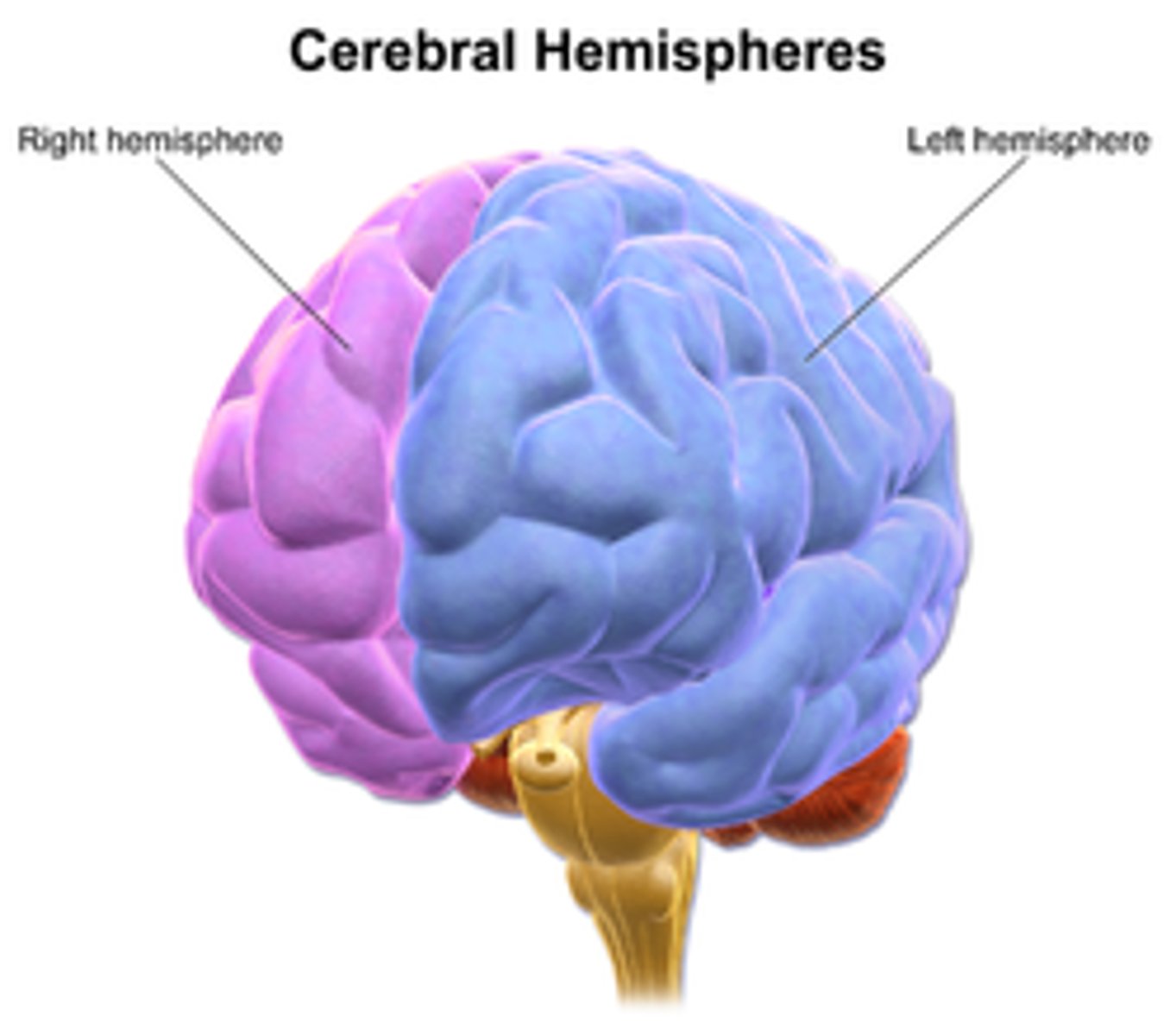
What part of the brain connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord?
(A) Cerebrum
(B) Midbrain
(C) Medulla
(D) Brain Stem
(D) Brain Stem
The Brain Stem connects the cerebrum to the spinal cord.
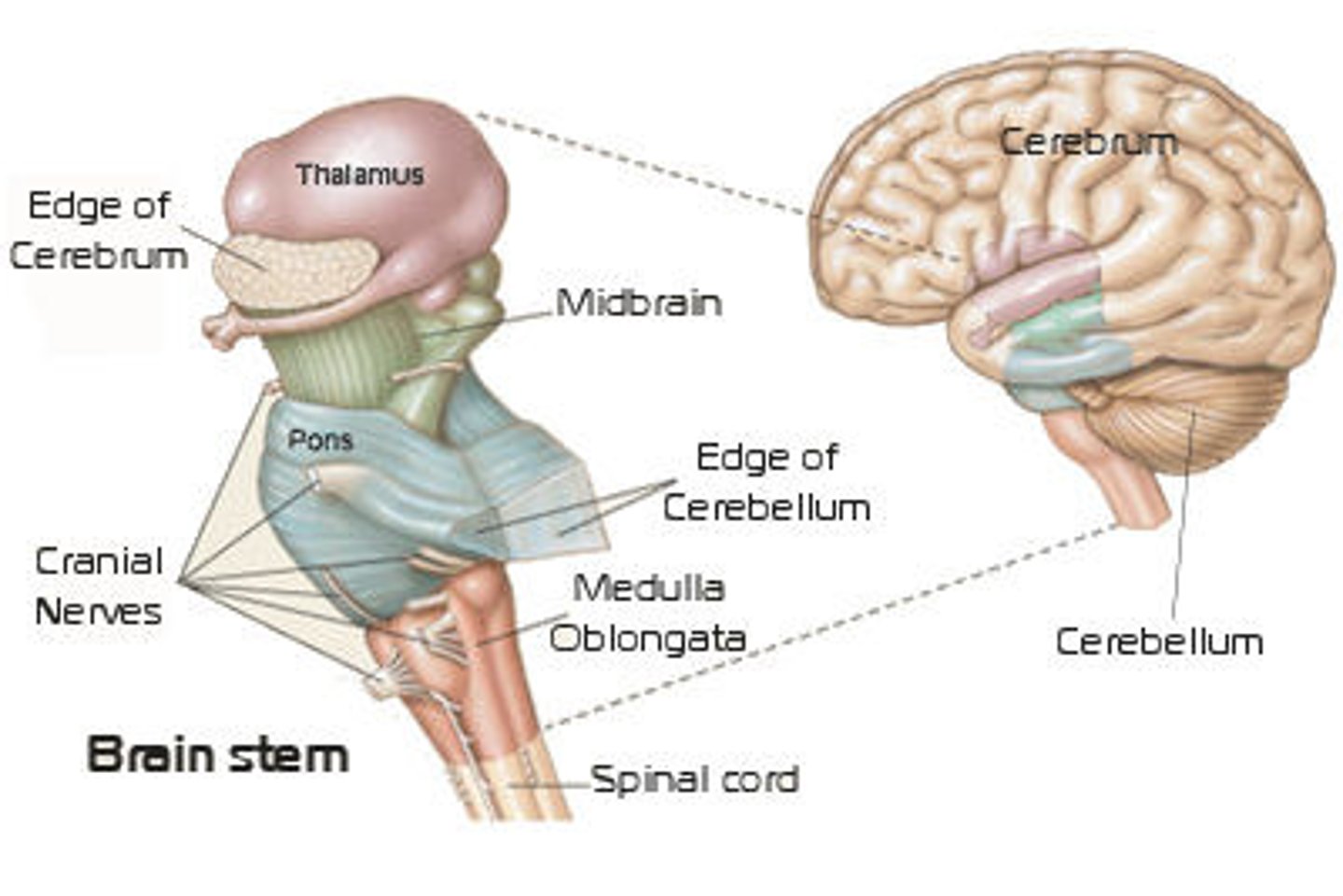
Which of the following is not one of the three main parts of the brain stem?
(A) Midbrain
(B) Hindbrain
(C) Pons
(D) Medulla
(B) Hindbrain
The brain stem is composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla.
The Hindbrain is not a part of the brainstem, but rather an umbrella term that encompasses the medulla and pons (both parts of the brain stem) and the cerebellum.
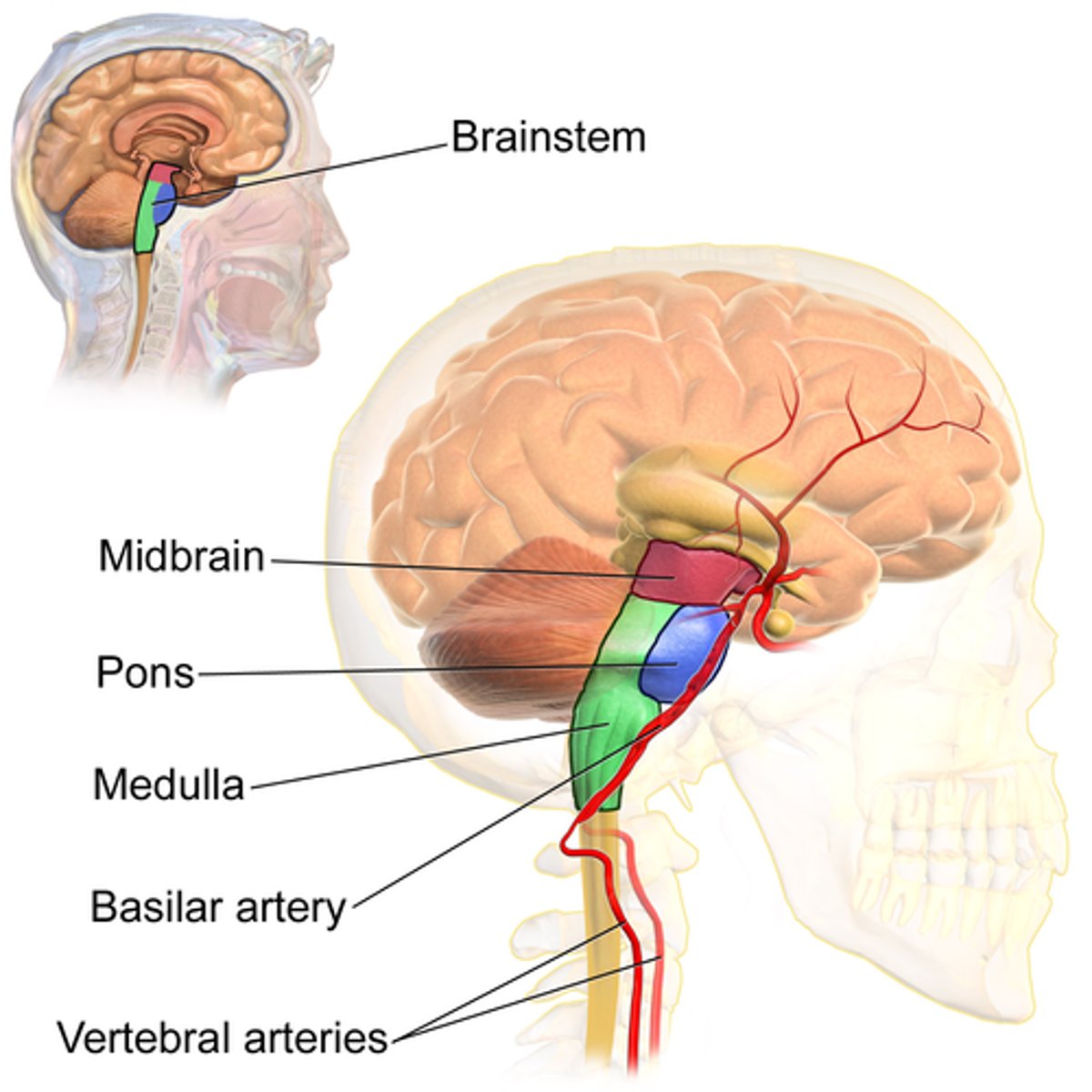
Which part of the brain stem connects to the cerebrum?
(A) Cerebellum
(B) Midbrain
(C) Medulla
(D) Pons
(B) Midbrain
The Midbrain is the part of the brain stem that connects to the cerebrum.
Note that the cerebellum does connect to the cerebrum, but is not part of the brain stem!
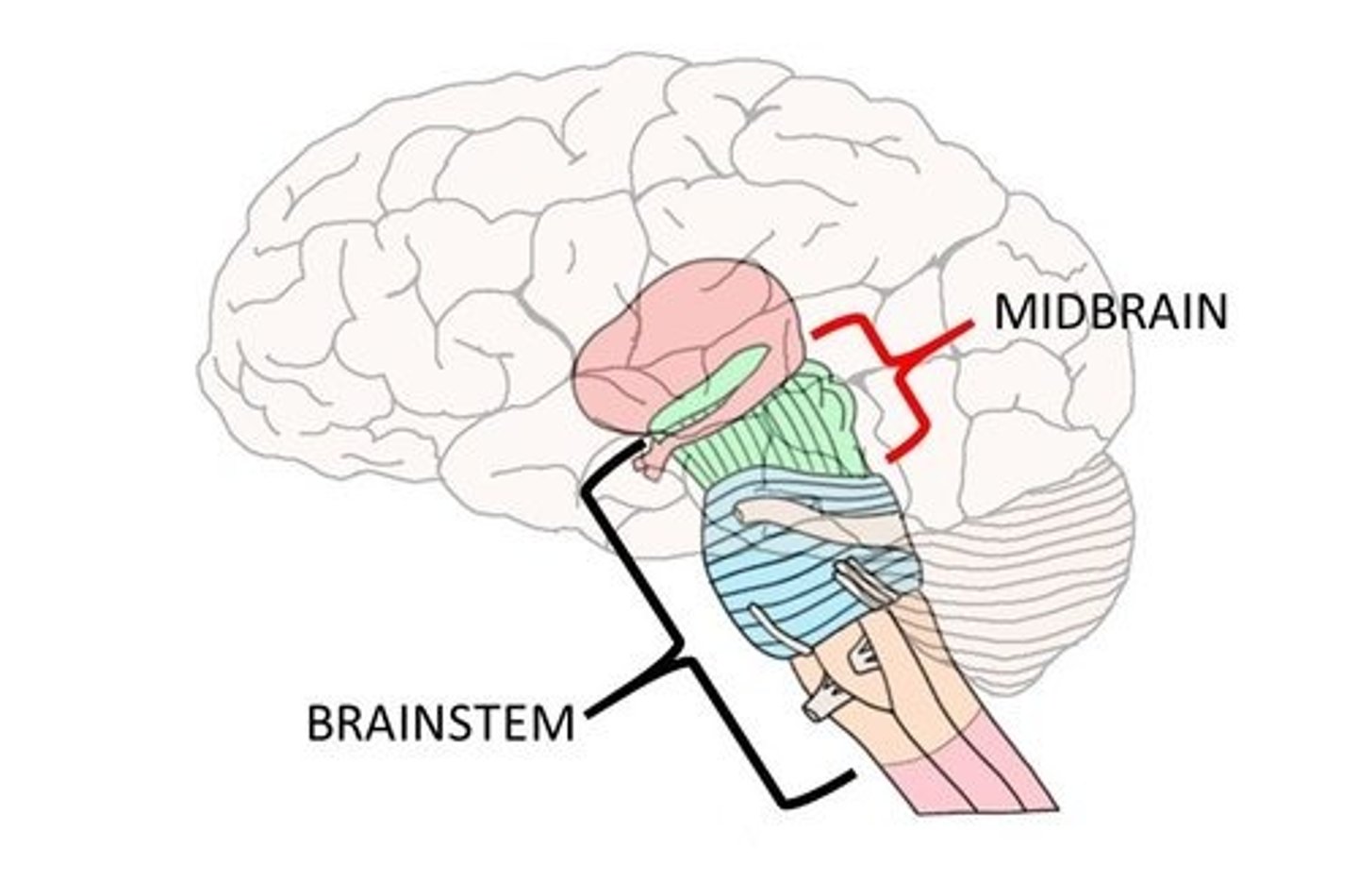
Which part of the brain stem connects to the spinal cord?
(A) Cerebellum
(B) Midbrain
(C) Medulla
(D) Pons
(C) Medulla
The Medulla is the part of the brain stem that connects to the spinal cord.
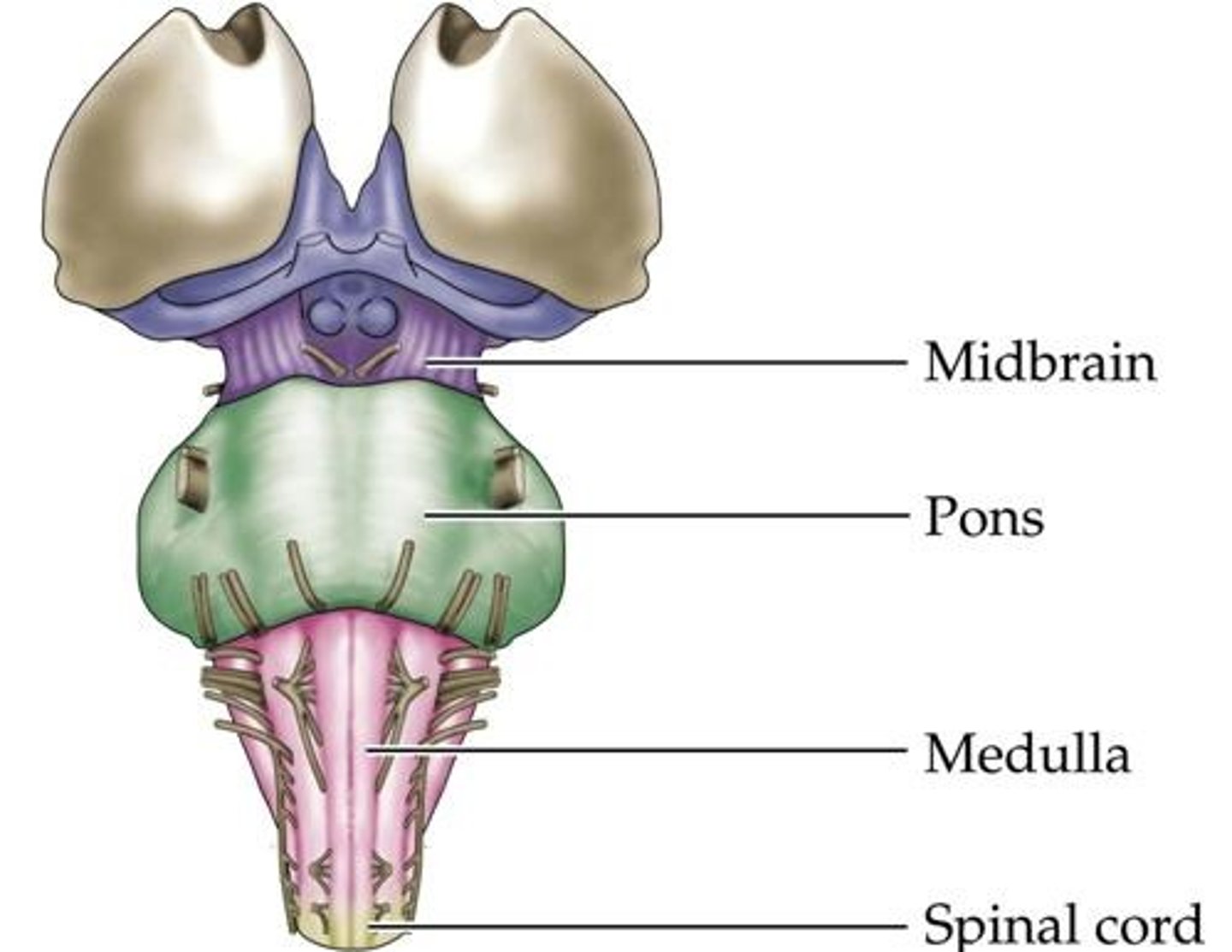
What is posterior to the brain stem, connected to the brain stem, and can't be seen if you're looking at the brain from the top?
(A) Cerebrum
(B) Cerebellum
(C) Medulla
(D) Brain Stem
(B) Cerebellum
The Cerebellum is posterior to the brain stem, connected to the brain stem, and can't be seen if you're looking at the brain from the top.
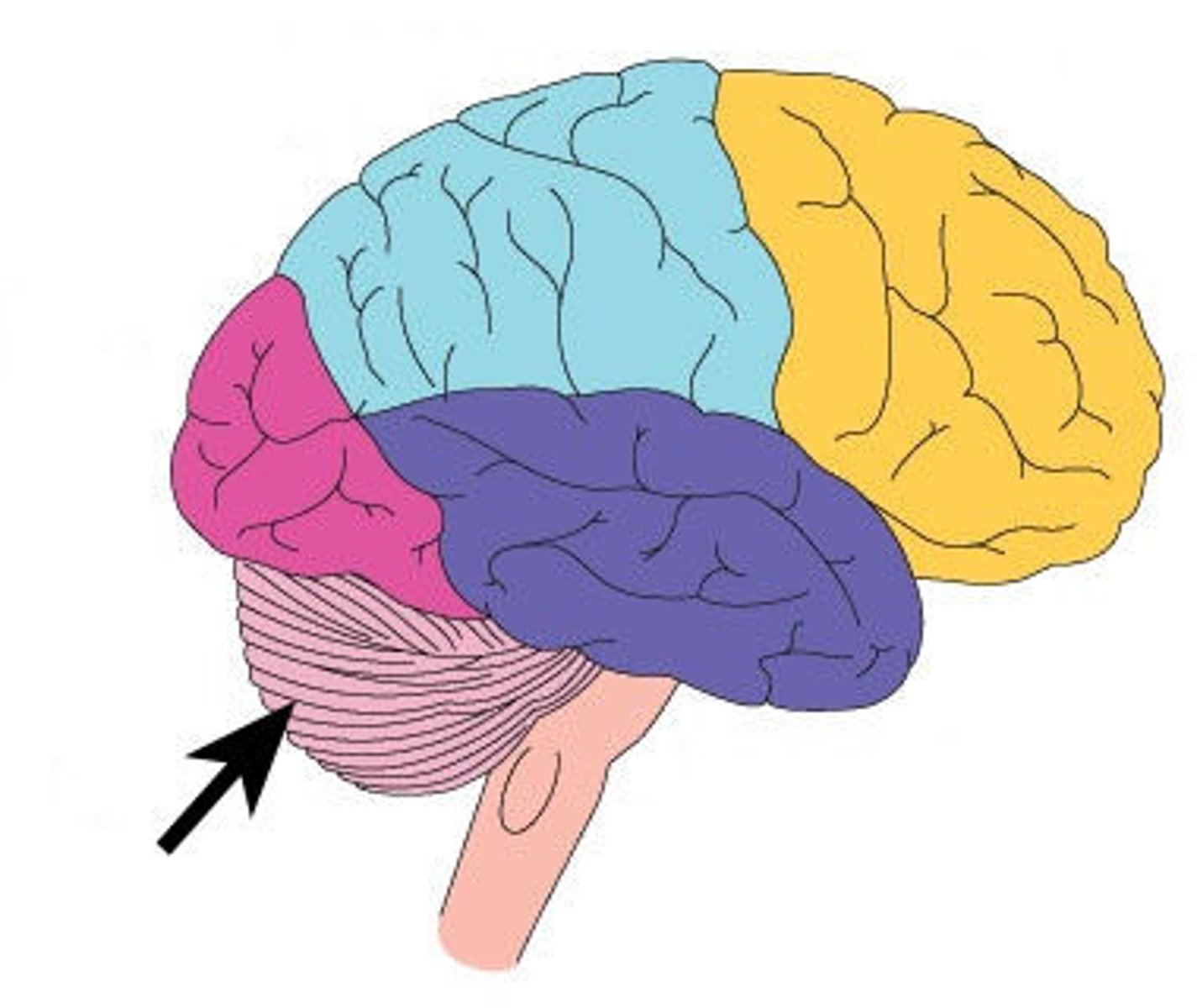
Match each of the following to the structure they are derived from:
(A) Forebrain
(B) Midbrain
(C) Hindbrain
(1) Mesencephalon
(2) Prosencephalon
(3) Rhombencephalon
(A) Forebrain --> (2) Prosencephalon
(B) Midbrain --> (1) Mesencephalon
(C) Hindbrain --> (3) Rhombencephalon
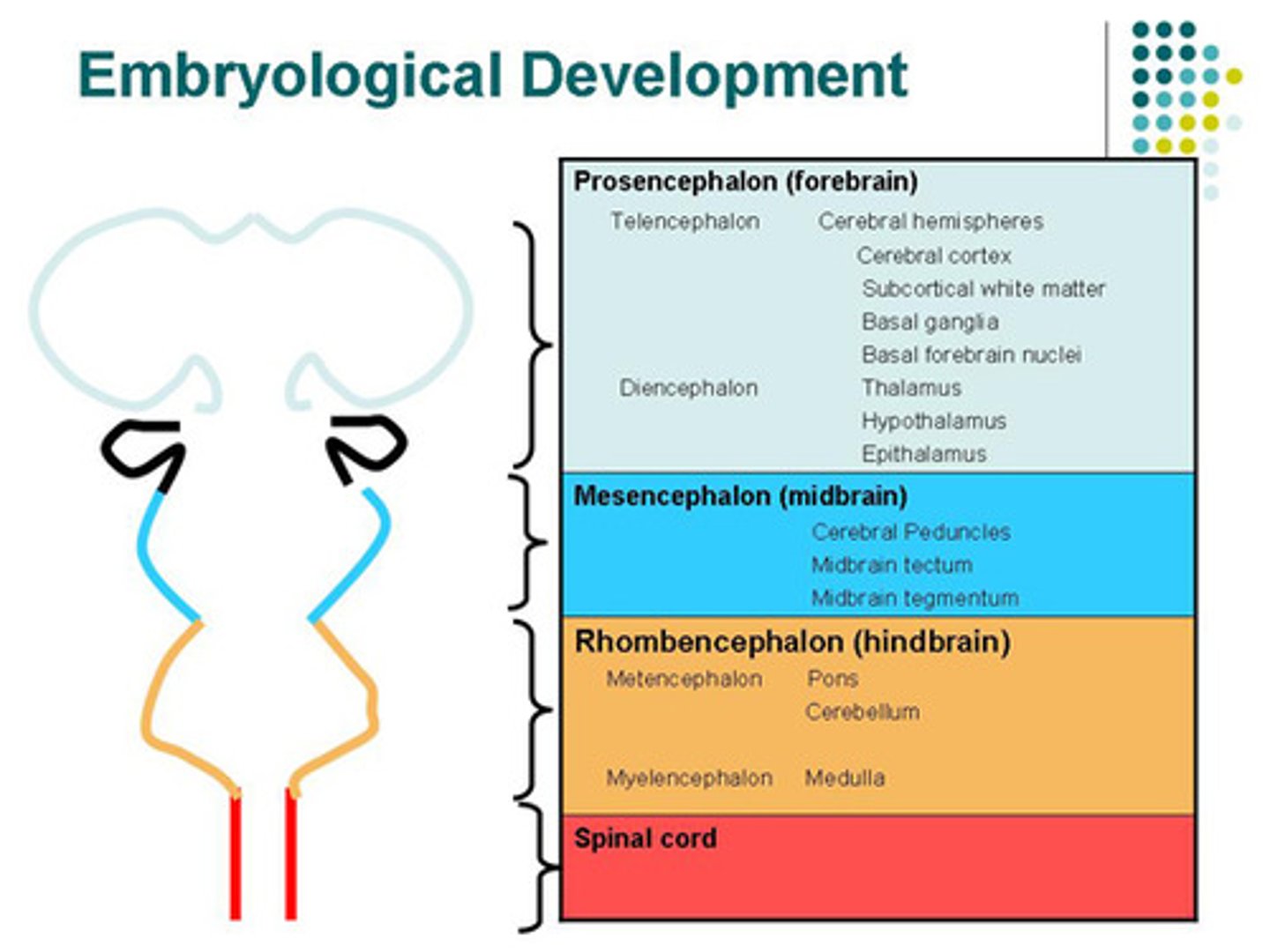
Match the three brain areas with the following structures:
(A) Forebrain
(B) Midbrain
(C) Hindbrain
(1) Cerebrum
(2) Medulla
(3) Midbrain
(4) Cerebellum
(5) Pons
(A) Forebrain --> (1) Cerebrum
(B) Midbrain --> (3) Midbrain
(C) Hindbrain --> (2) Medulla, (4) Cerebellum, (5) Pons
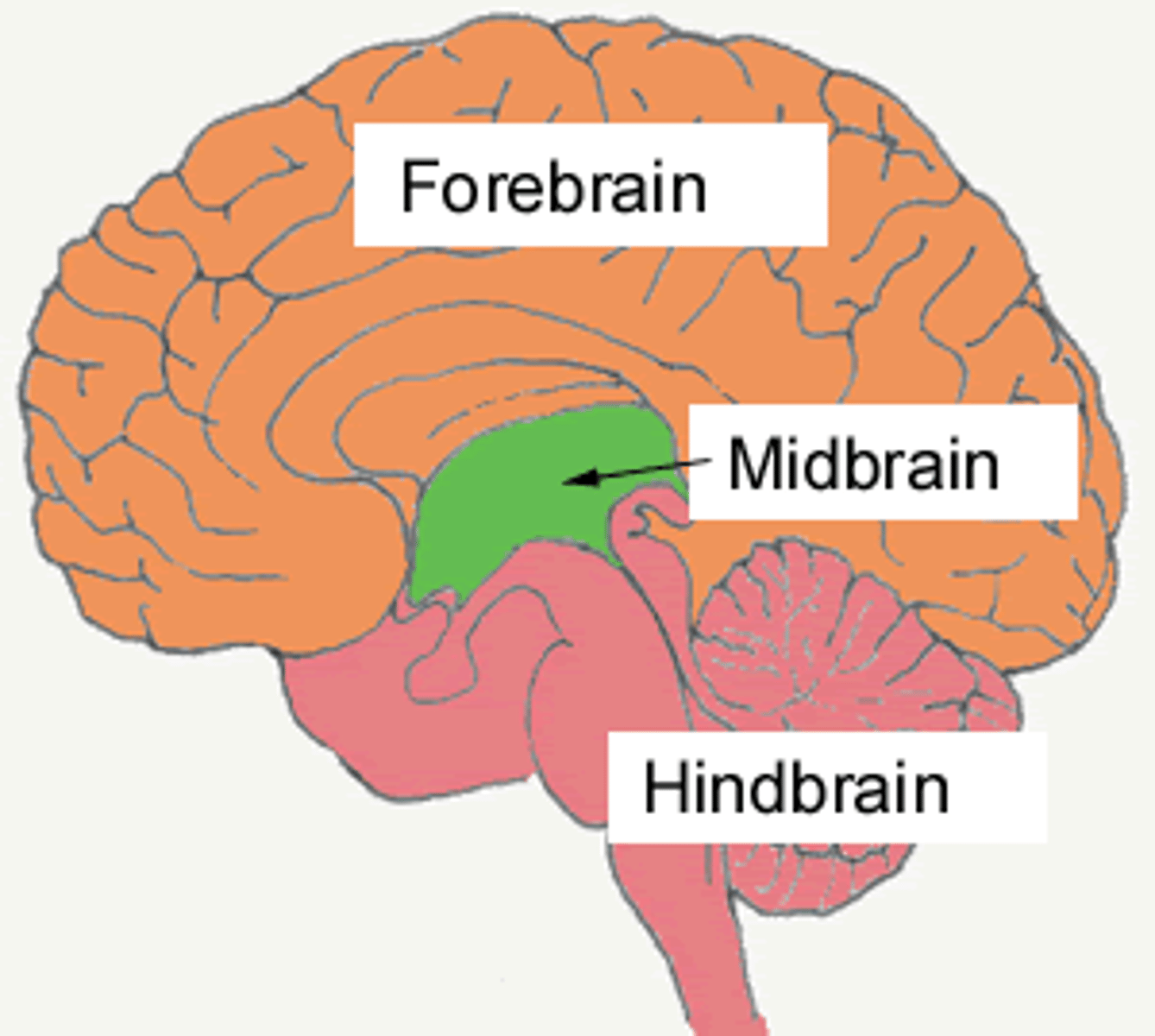
What does the peripheral nervous system contain?
I. Nerves
II. Ganglia
III. Sulci
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) II and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and II Only
The peripheral nervous system contains Nerves & Ganglia
Sulci are the grooves of the brain
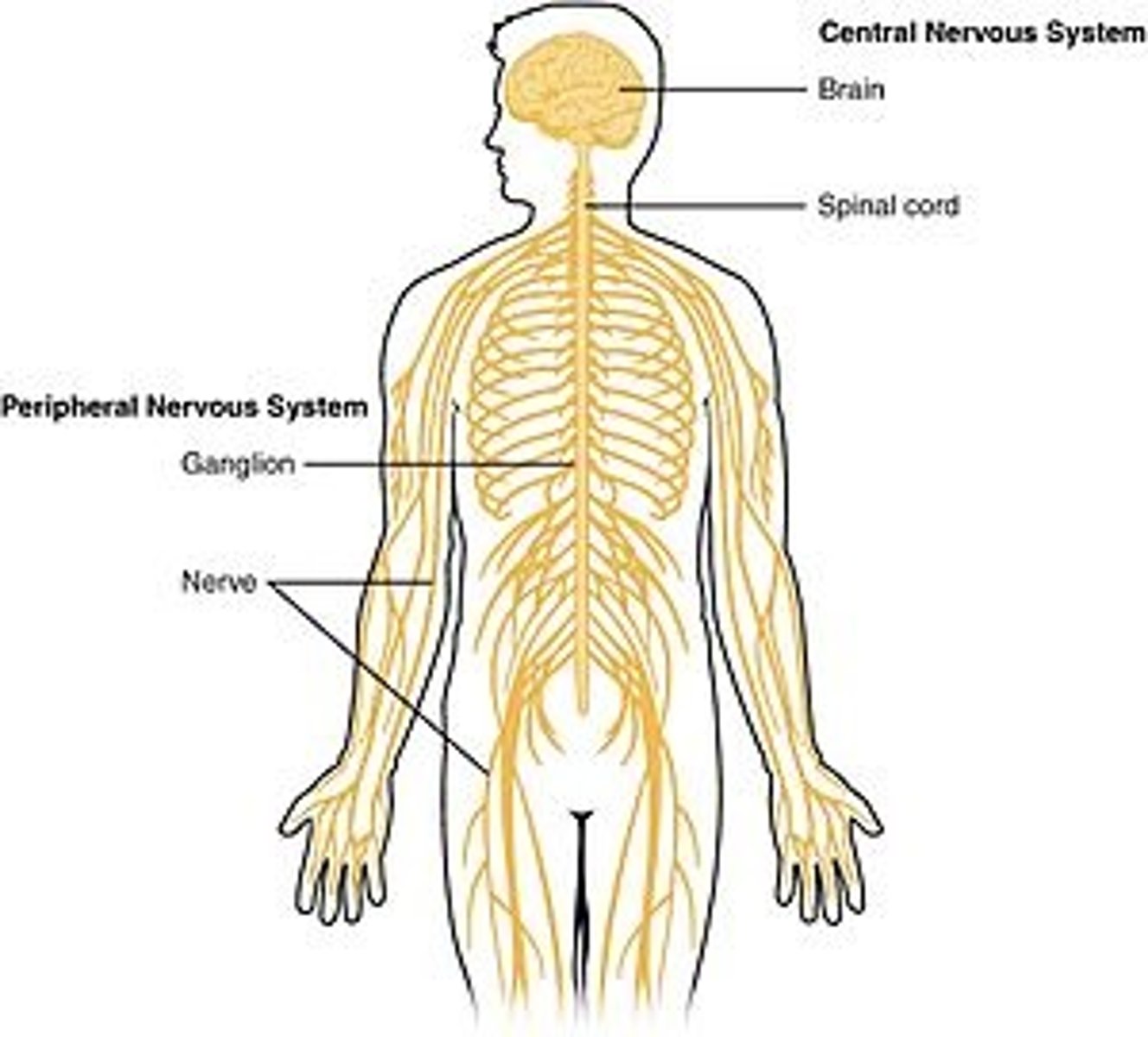
CRB Which of the following statements about the Nervous system after leaving the spinal cord is NOT true?
(A) There are two types of neurons that pass the message from the spinal cord: Pre- and Post-Ganglionic Neurons.
(B) The soma of the Pre- and Post-Ganglionic Neurons are both in the CNS
(C) The Preganglionic Neuron synapses onto the Postganglionic Neuron.
(D) The Postganglionic Neuron innervates the target tissue.
(B) The soma of the Pre- and Post-Ganglionic Neurons are both in the CNS
Only the Soma of the Preganglionic Cells are in the CNS. Their axons exit the CNS, and the Postganglionic Neurons are entirely part of the PNS.
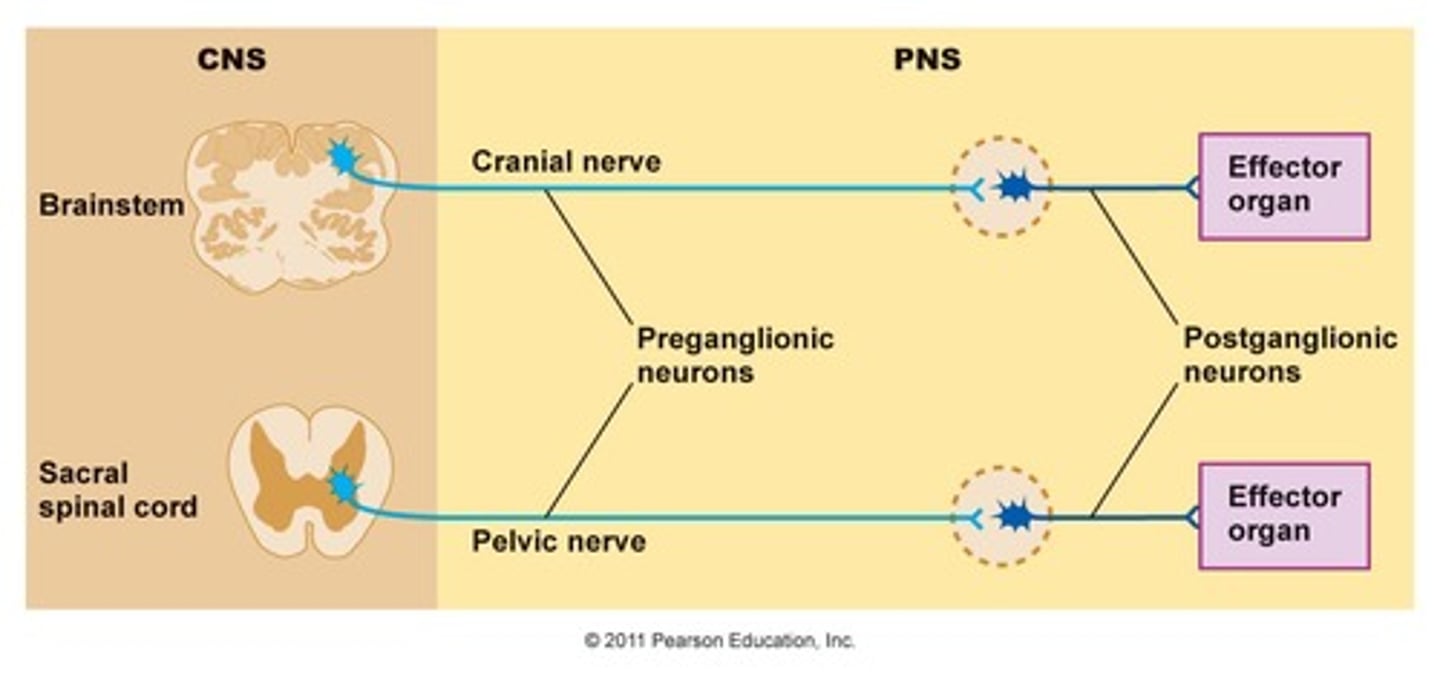
Compare Nerves and Ganglia.
Nerves contain the axons of neurons in a bundle.
Ganglia contain the soma (cell bodies) of neurons.
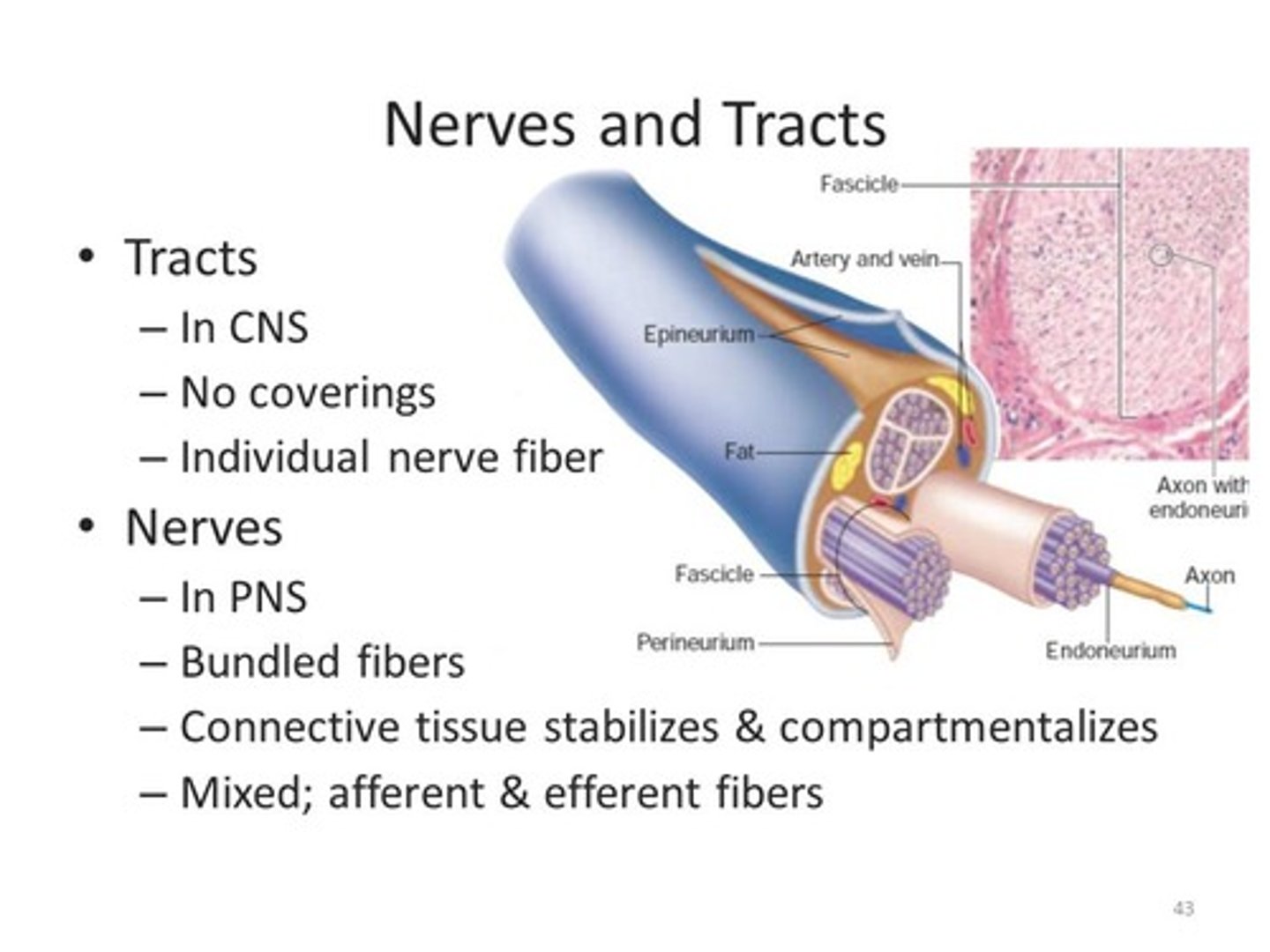
CRB Compare Nerves and Tracts.
Both Nerves and Tracts are multiple neurons' axons bundled together.
Nerves can contain sensory neurons, motor neurons, or a mix of the two.
Tracts can only carry one type of information.
CRB Draw out the structure of a neuron, from the Soma to the Nerve Terminals. Assume it is a neuron from the peripheral nervous system. Label all major structures.
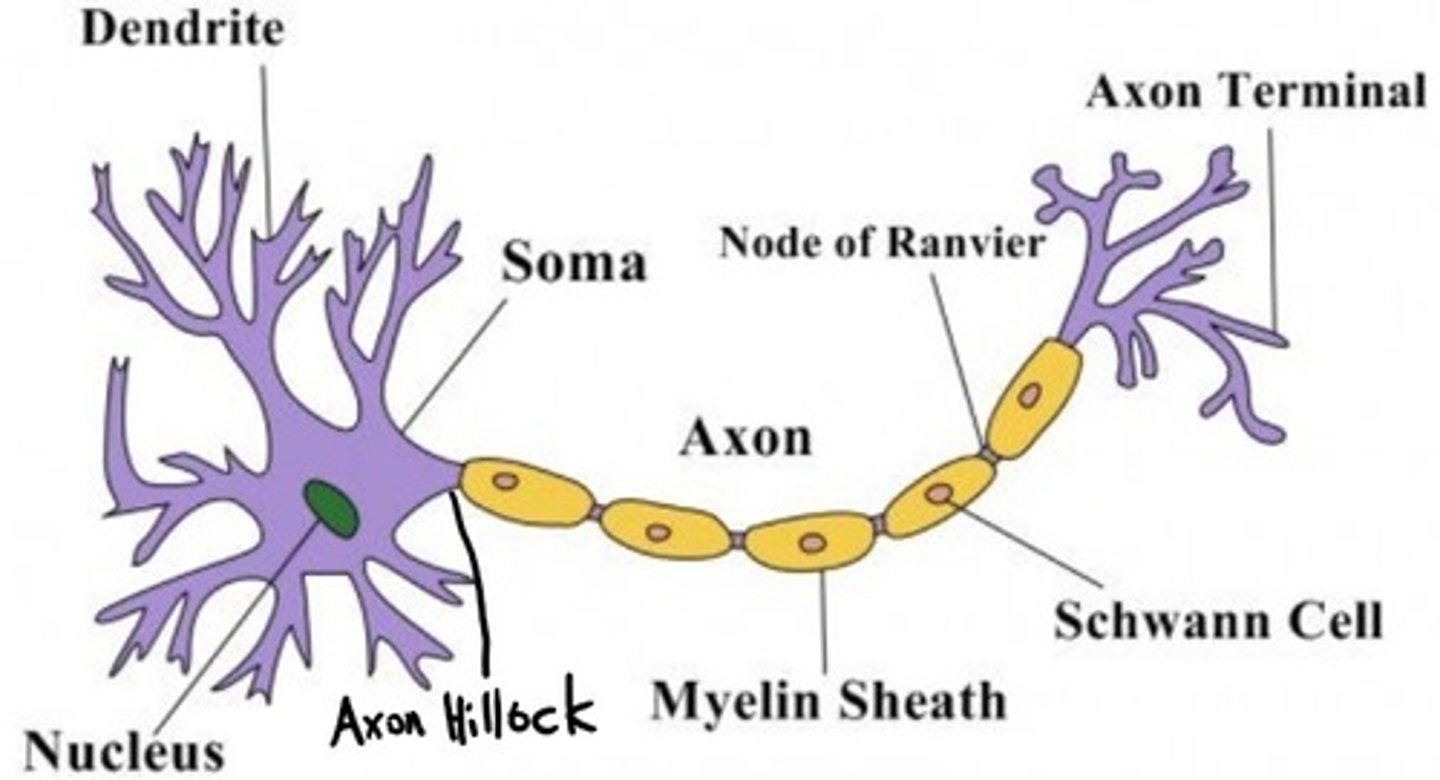
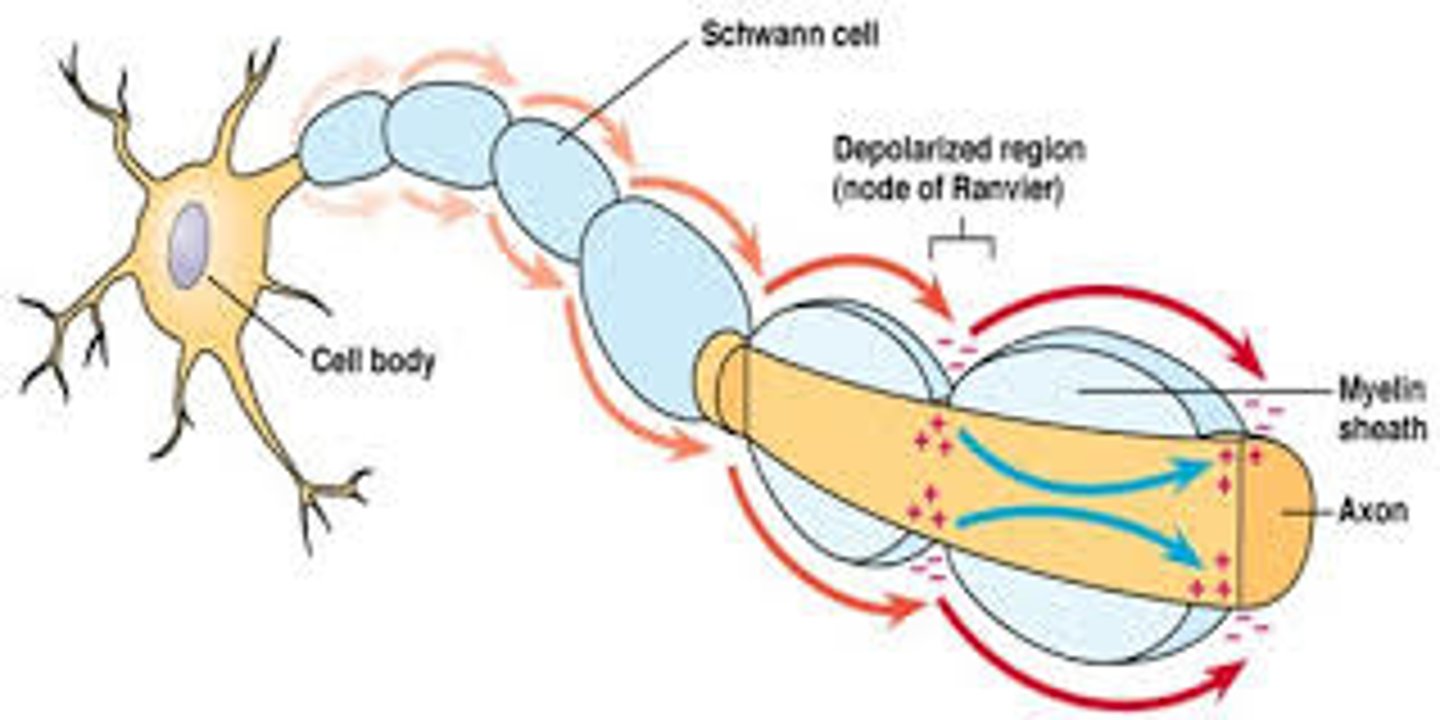
CRB Which of the following are true statements about the Nodes of Ranvier on myelinated axons?
I. The Nodes of Ranvier are breaks in the Myelin Sheath
II. The electrical impulses jump from sheath to sheath, known as Saltatory Conduction.
III. That Myelin is produced by Schwann Cells in the PNS and Oligodendrocytes in the CNS.
(A) I only
(B) I and III only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and III only
Each of the following statements are true:
I. The Nodes of Ranvier are breaks in the Myelin Sheath
II. The electrical impulses jump from node to node, known as Saltatory Conduction.
III. That Myelin is produced by Schwann Cells in the PNS and Oligodendrocytes in the CNS.
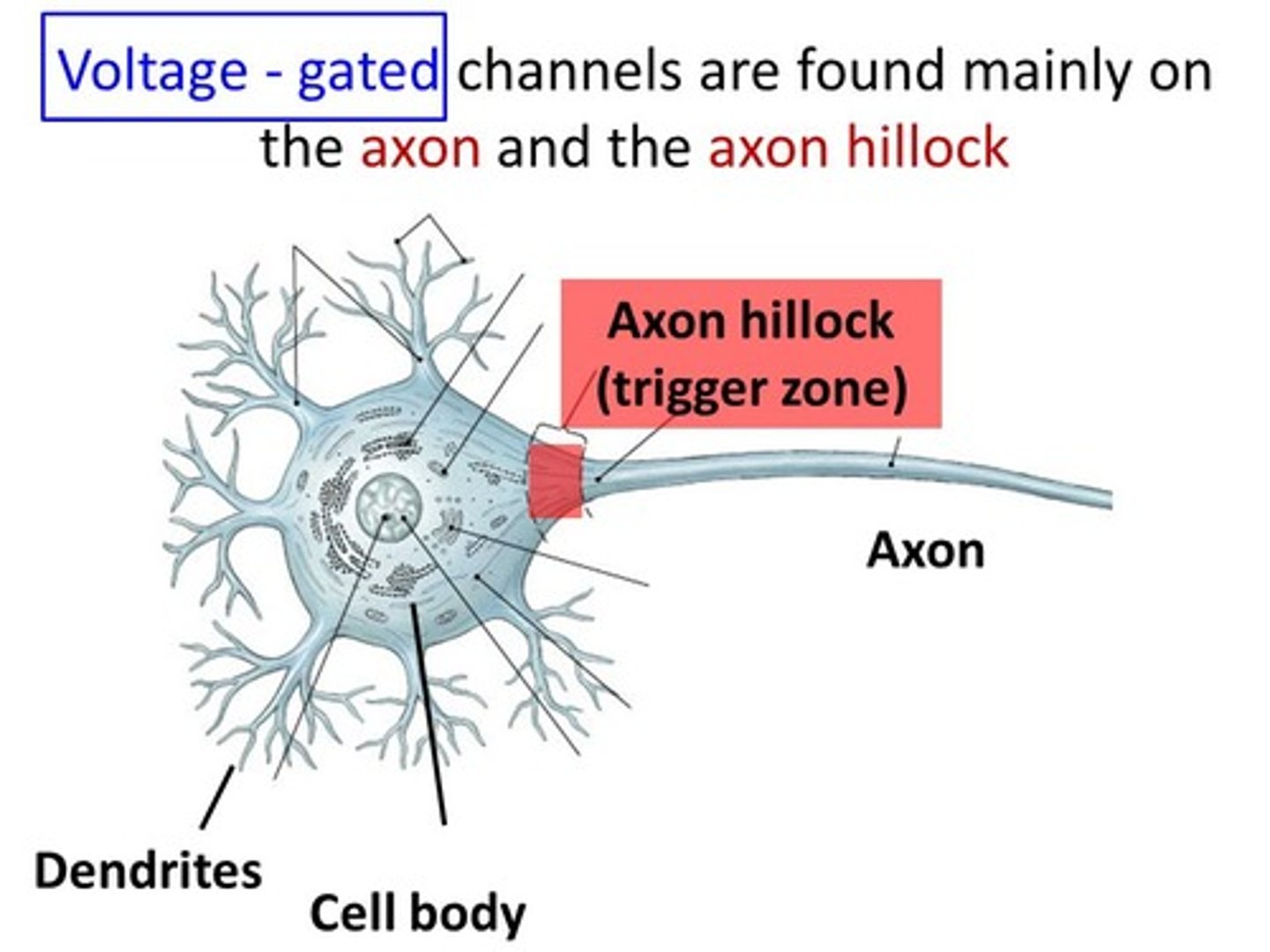
CRB Fill in the blanks: The ____________ integrates the incoming signals from dendrites and can trigger a(n) _____________________.
(A) Soma, Analog Response
(B) Soma, Action Potential
(C) Axon Hillock, Analog Response
(D) Axon Hillock, Action Potential
(D) Axon Hillock, Action Potential
The Axon Hillock integrates the incoming signals from dendrites and can trigger an Action Potential.
Do Afferent Neurons carry information from the PNS to the CNS or vice versa? What about Efferent Neurons?
Afferent Neurons carry information in from the PNS to the CNS (Afferent = info ARRIVES at CNS)
Efferent Neurons carry information from the CNS to the PNS (Efferent = info EXITS CNS)
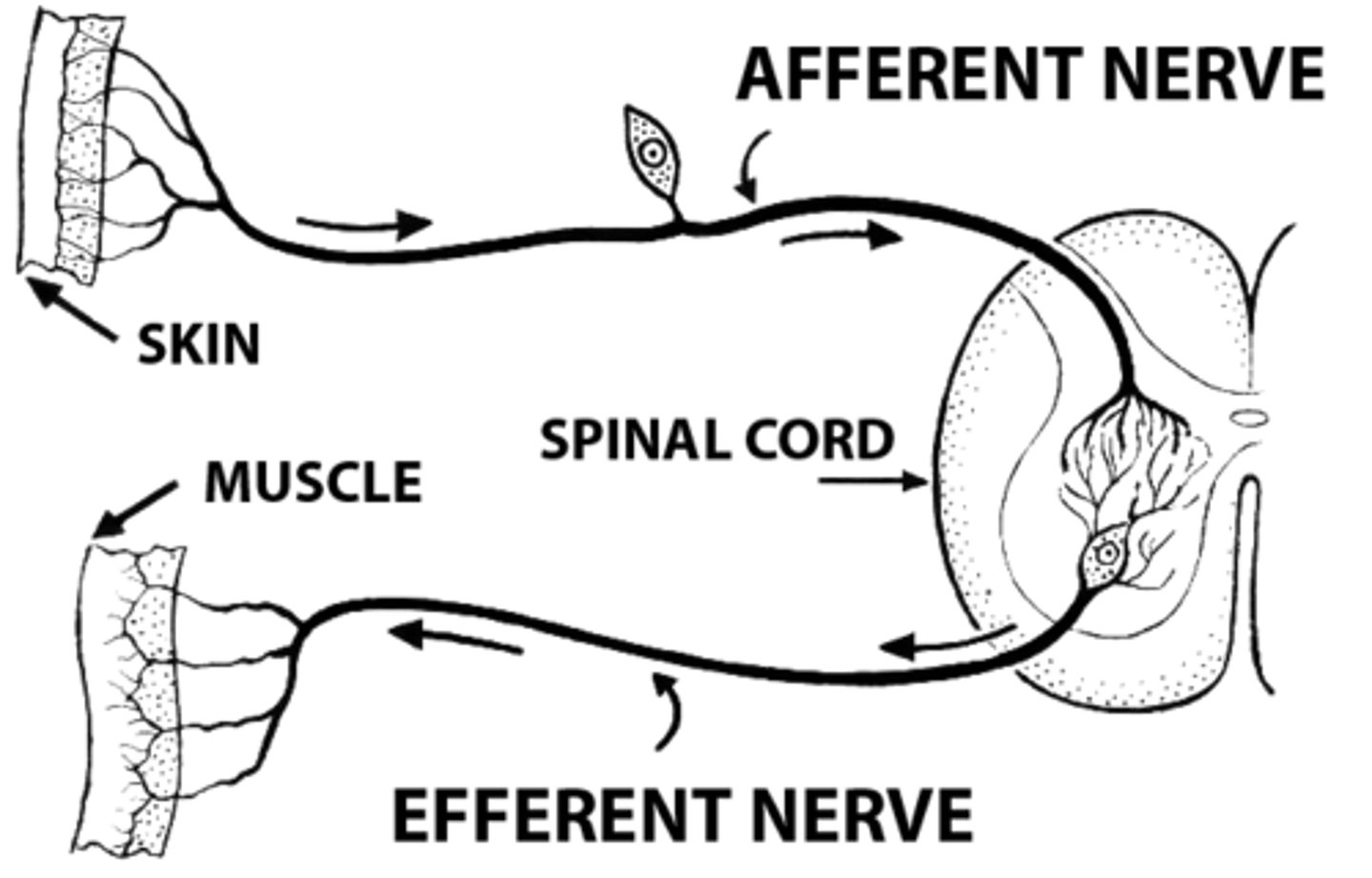
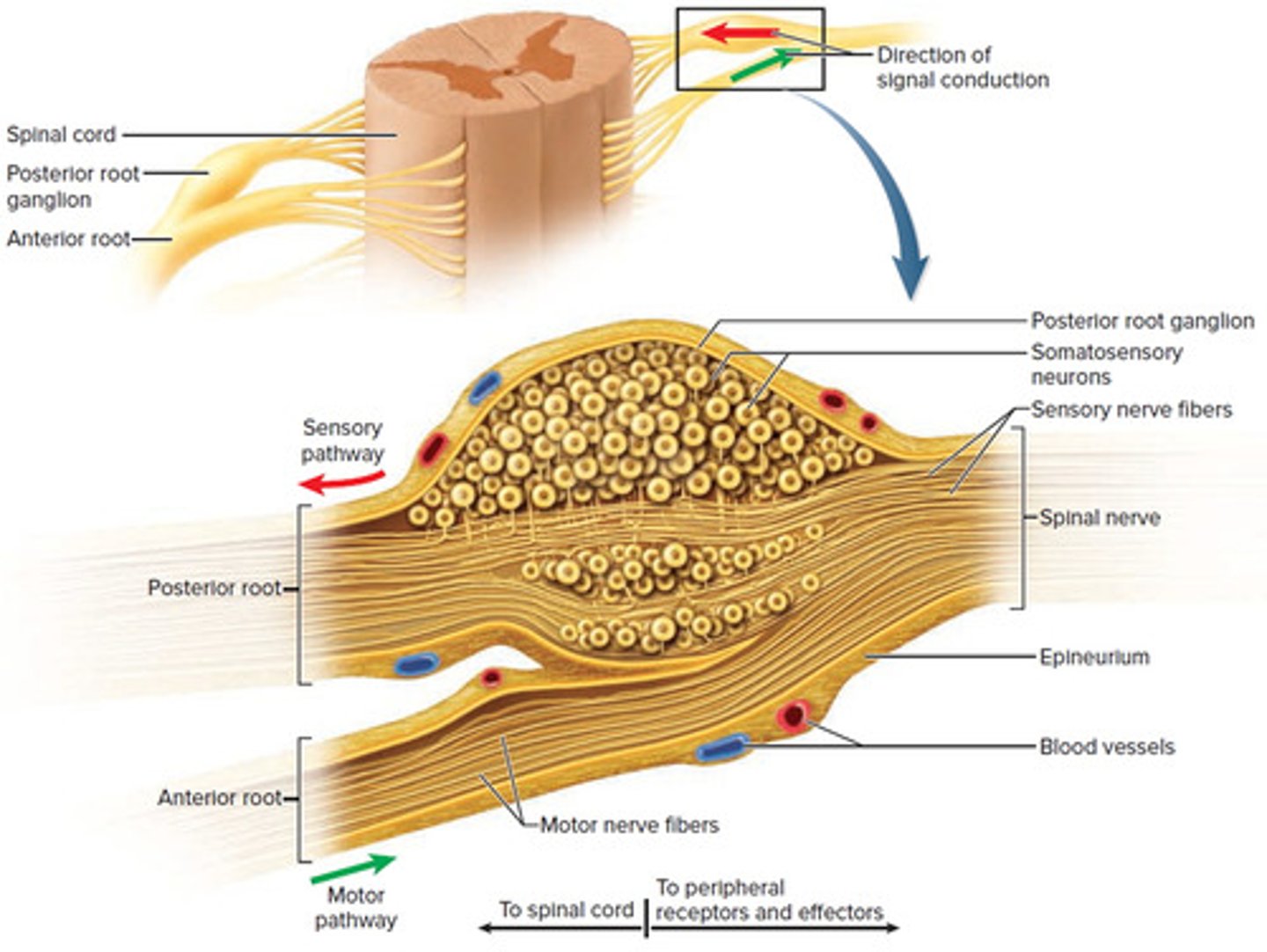
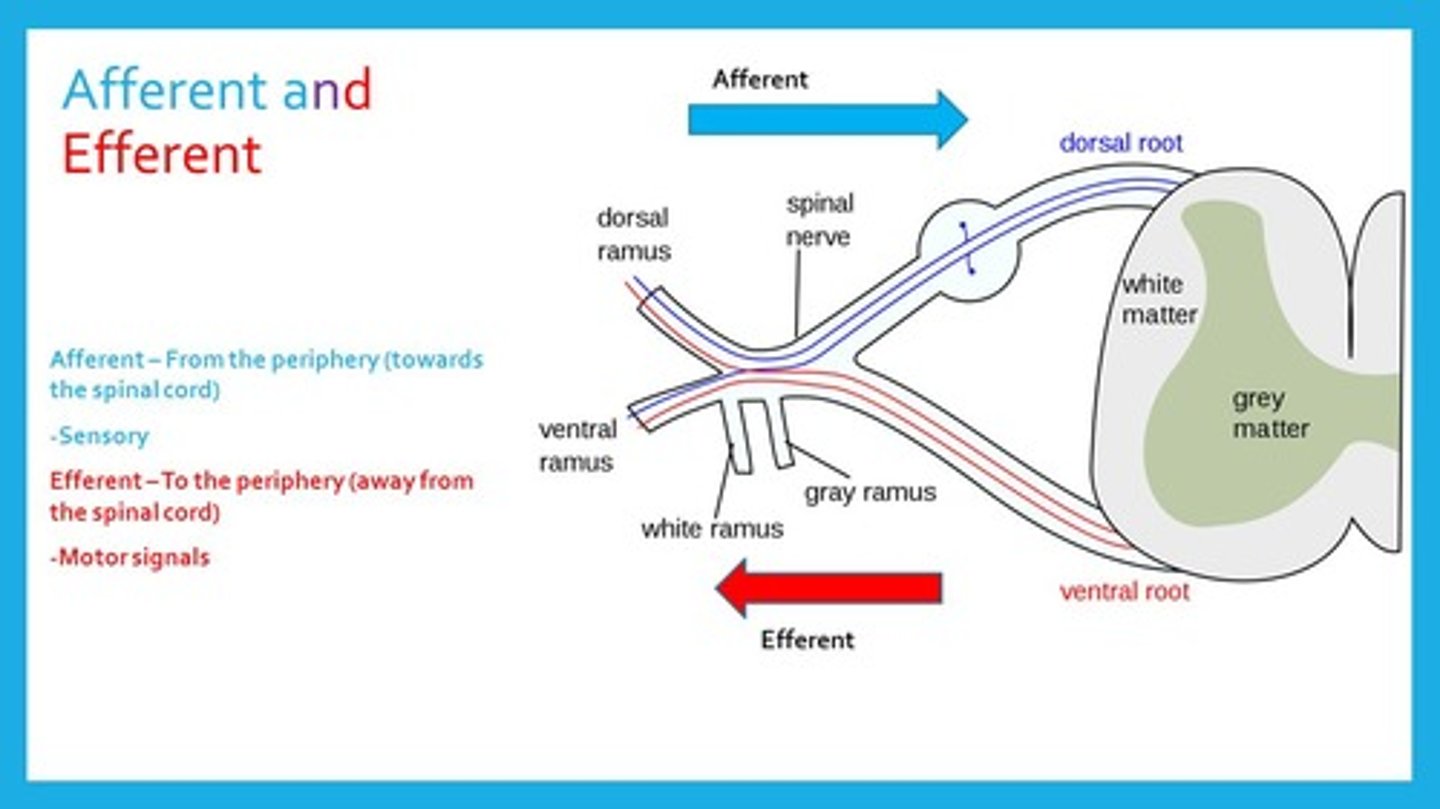
True or false? For the spinal nerve roots, the afferent neurons travel through the posterior spinal nerve roots and the efferent neurons travel through the anterior spinal nerve roots.
True. For the spinal nerve roots, the afferent neurons travel through the posterior (dorsal) spinal nerve roots and the efferent neurons travel through the anterior (ventral) spinal nerve roots.
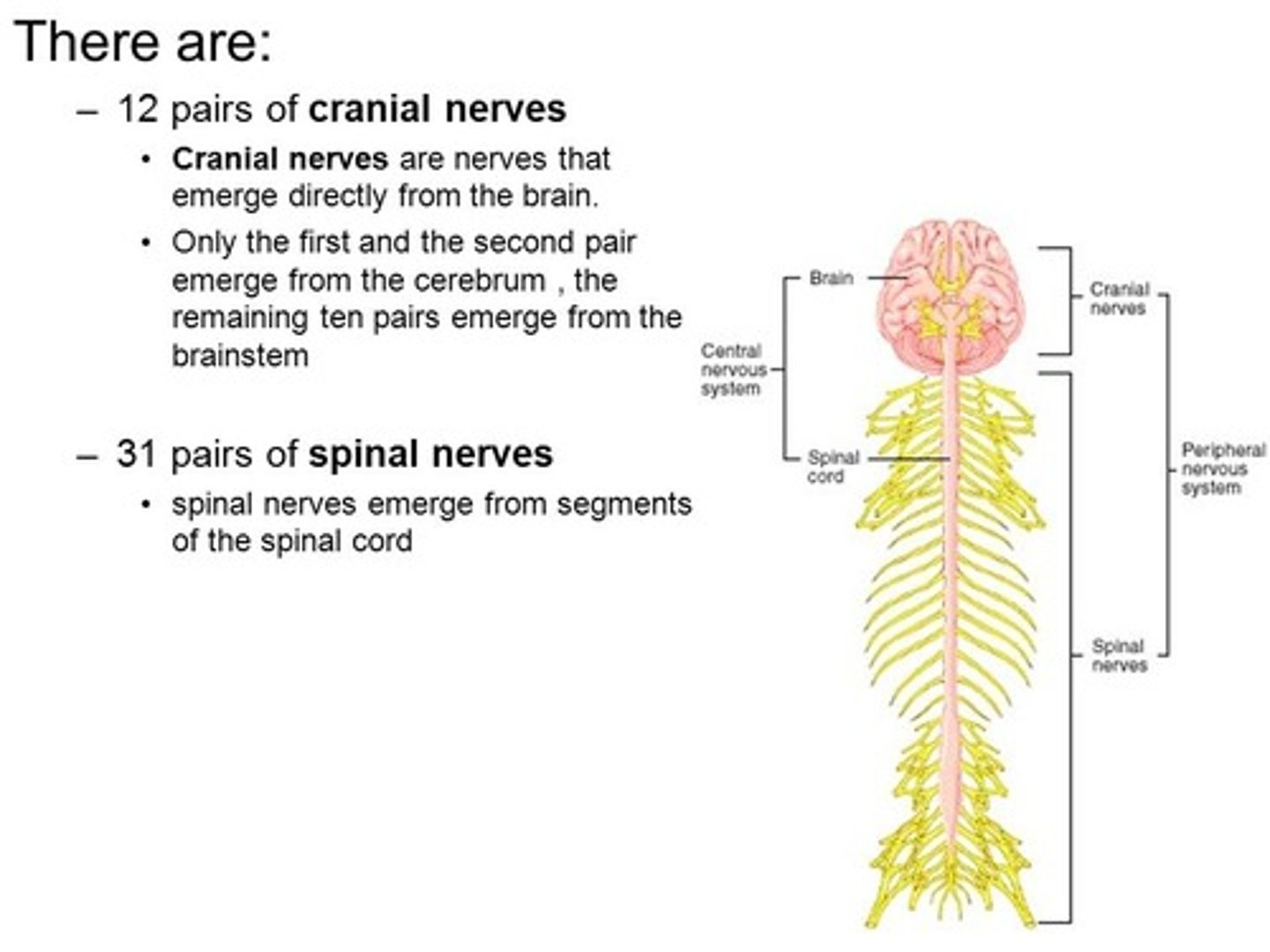
Nerves that exit the skull are called _________ nerves while nerves that exit the spinal cord are called ___________ nerves.
(A) Cerebral, Vertebral
(B) Cerebral, Spinal
(C) Cranial, Vertebral
(D) Cranial, Spinal
(D) Cranial, Spinal
Nerves that exit the skull are called cranial nerves while nerves that exit the spinal cord are called spinal nerves.
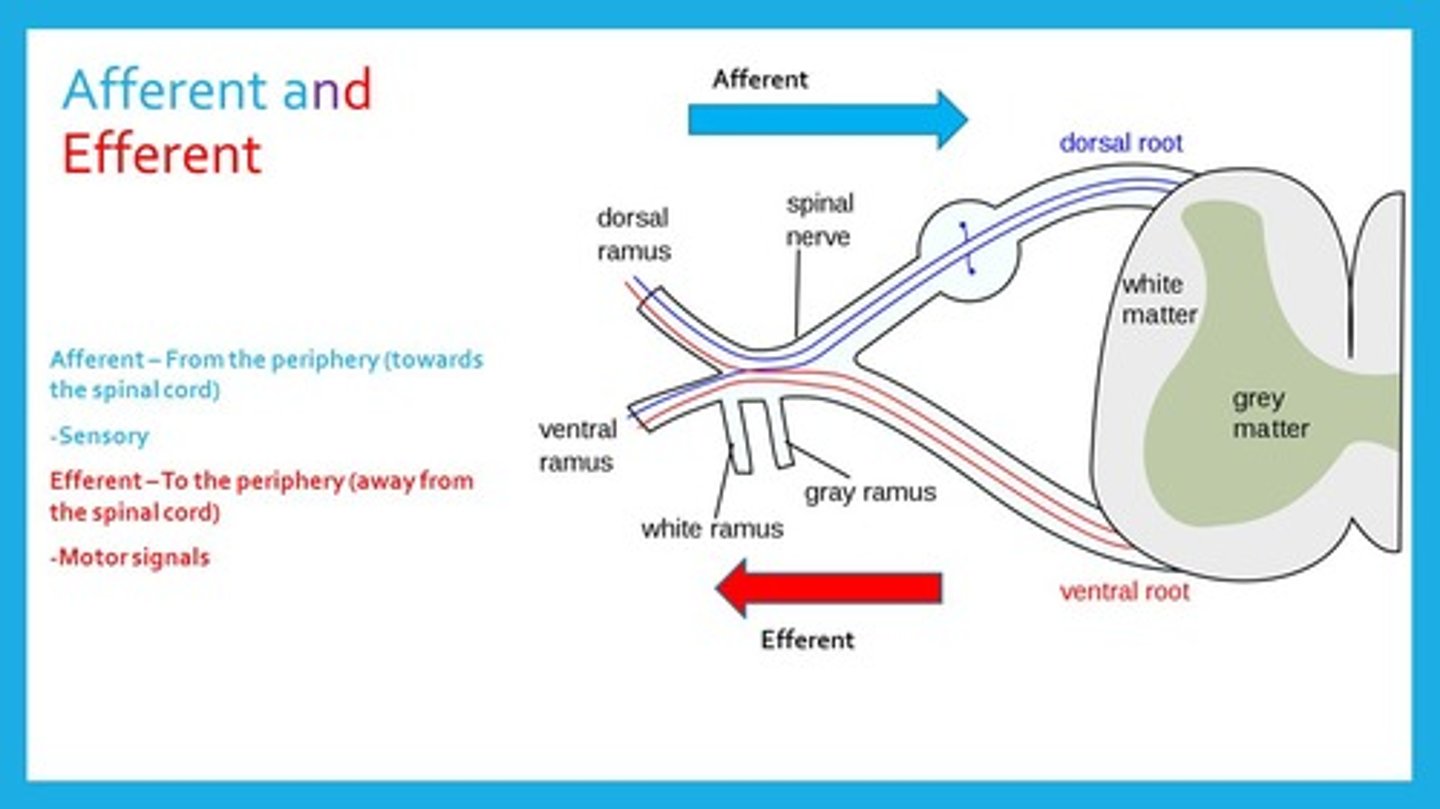
Afferent Neurons carry information via the _______________ root while Efferent Neurons carry information via the ___________ root.
(A) Dorsal, Dorsal
(B) Dorsal, Ventral
(C) Ventral, Ventral
(D) Ventral, Dorsal
(B) Dorsal, Ventral
Afferent Neurons carry information via the Dorsal root (the one in the back) while Efferent Neurons carry information via the Ventral root (the one in the front).
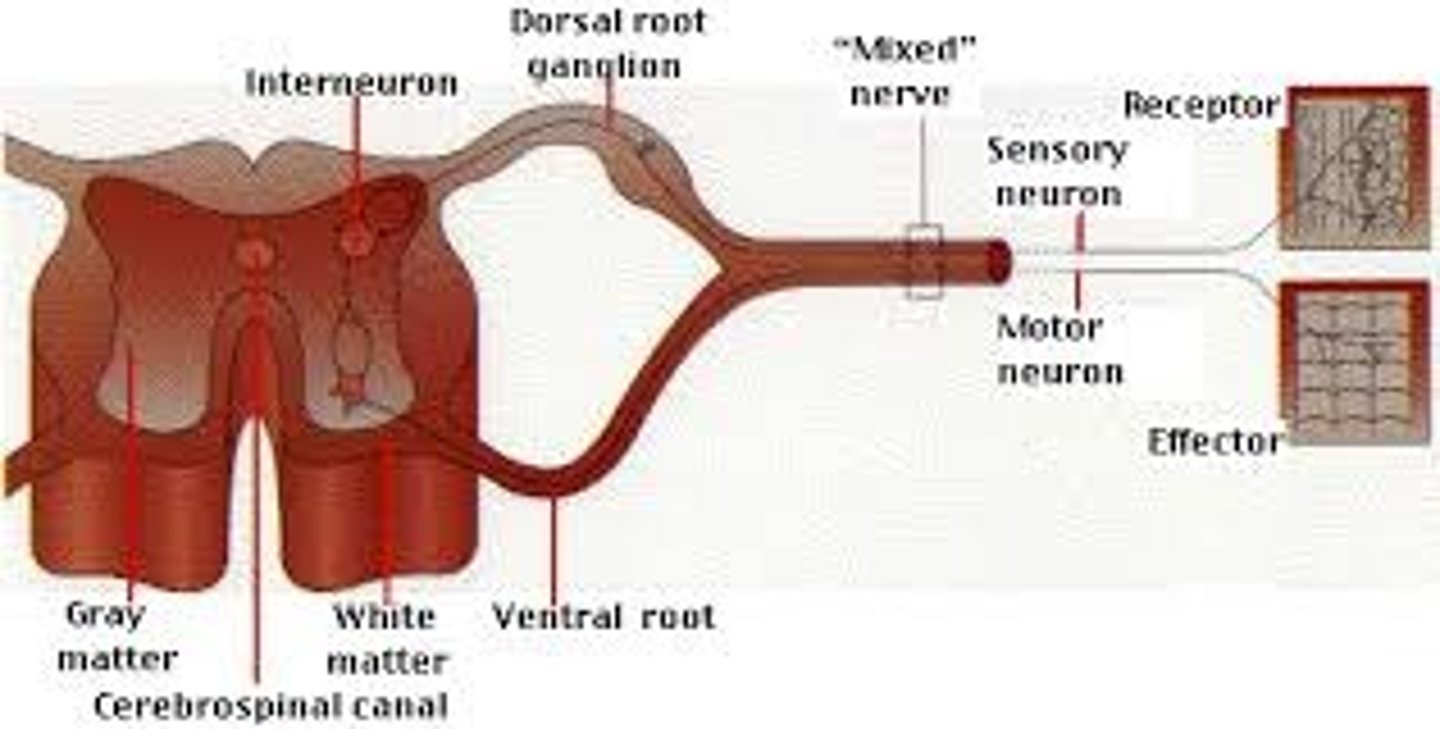
Mahmoud falls and lands right on his funny bone, which damages a mixed nerve. Which of the following may be affected?
I. Ability to feel temperature
II. Ability to think
III. Ability to move
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I and III Only
(D) I and III Only
Mixed nerves contain both afferent neurons (carrying sensory information such as temperature) and efferent neurons (carrying motor information).
Compare Proximal and Distal nerves.
Proximal nerves are close to the center of the body (spinal cord) and are larger than distal nerves, which are located in the extremities, far from the spinal cord.
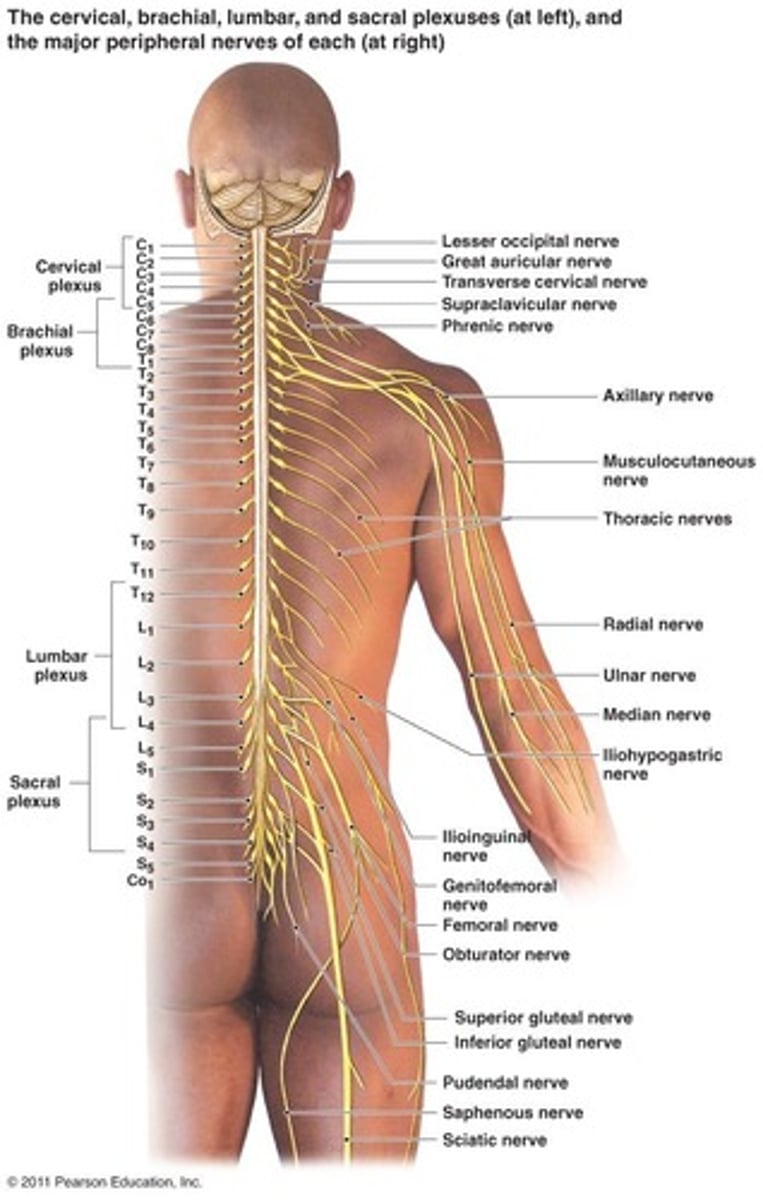
Patterns of abnormalities within the nervous system are known as:
(A) Conditions
(B) Diseases
(C) Syndromes
(D) Symptoms
(C) Syndromes
Patterns of abnormalities within the nervous system are known as syndromes.
Which of the following is not a function of the nervous system?
(A) Sensory
(B) Motor Control
(C) Autonomic
(D) Protection
(D) Protection
The following are functions of the nervous system:
Sensory
Motor Control --Skeletal Muscle
Autonomic -- Reflexes
Cognition
Emotions
Consciousness
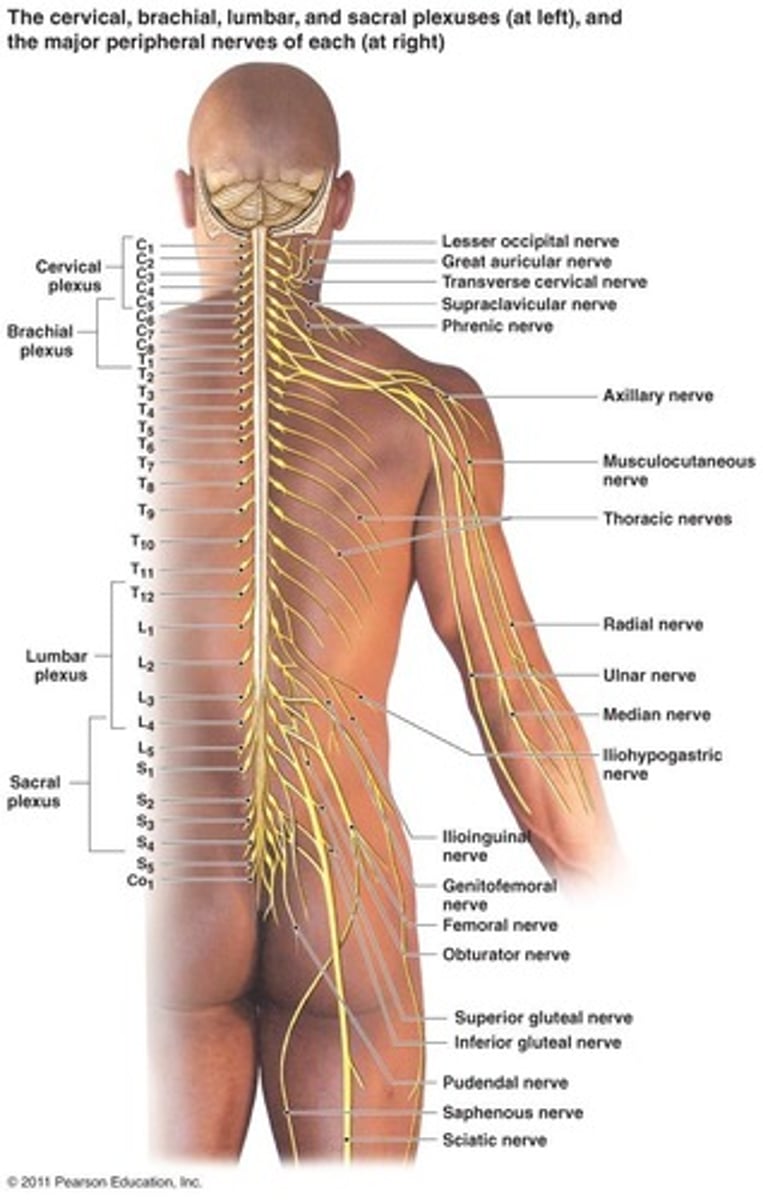
Describe how the following terms relate to a Motor Unit?
- Lower Motor Neurons
- Skeletal Muscle Cells
- Neuromuscular Junction
Lower Motor Neurons make contact with Skeletal Muscle Cells, synapsing at the Neuromuscular Junction. This is what then controls a Motor Unit (a group of skeletal muscle cells innervated by one lower motor neuron).
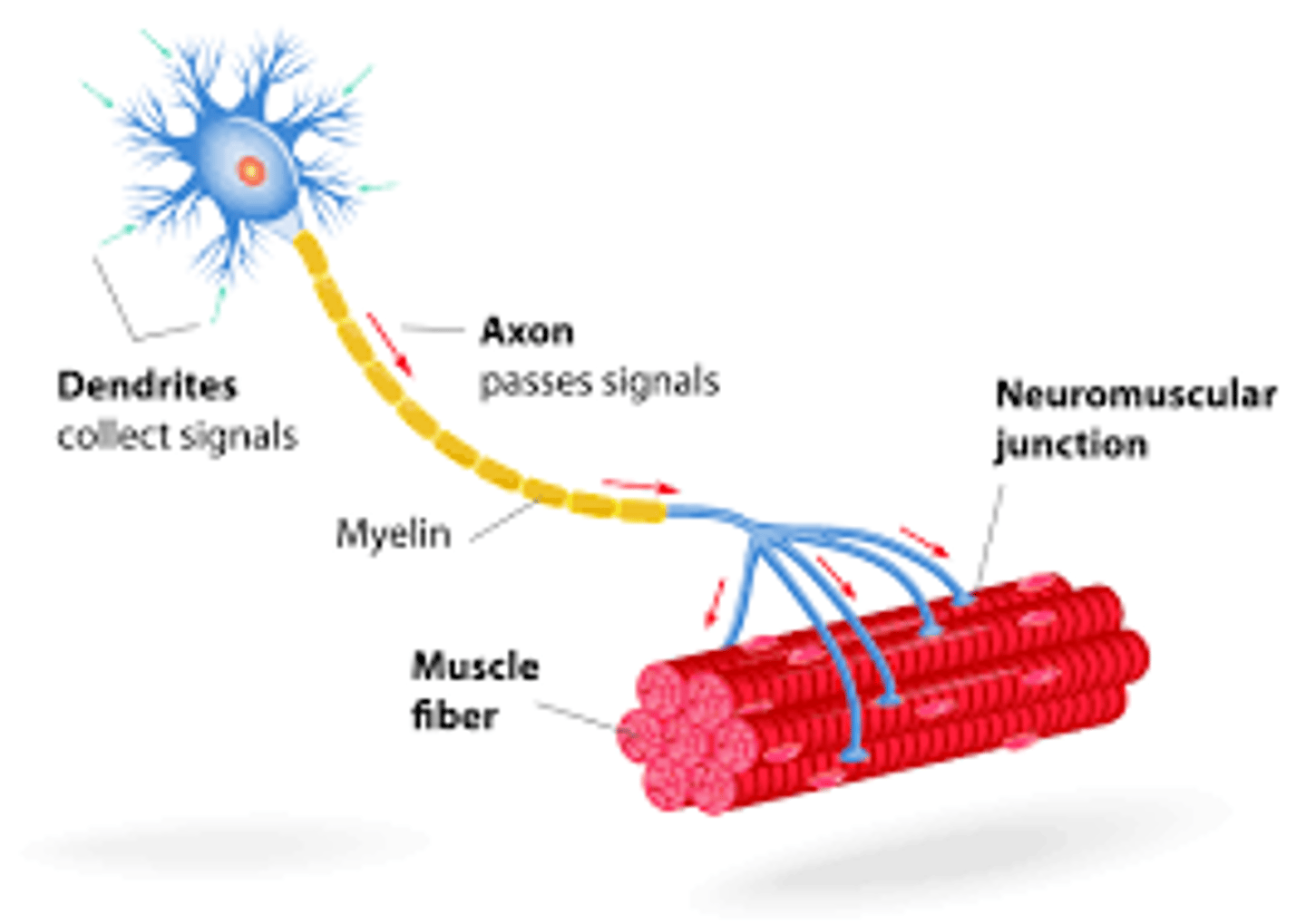
When a lower motor neuron fires an action potential how many skeletal muscle cells in that motor unit contract?
(A) One
(B) Some
(C) All
(D) It depends
(C) All
All the skeletal muscle cells in it's unit contract.
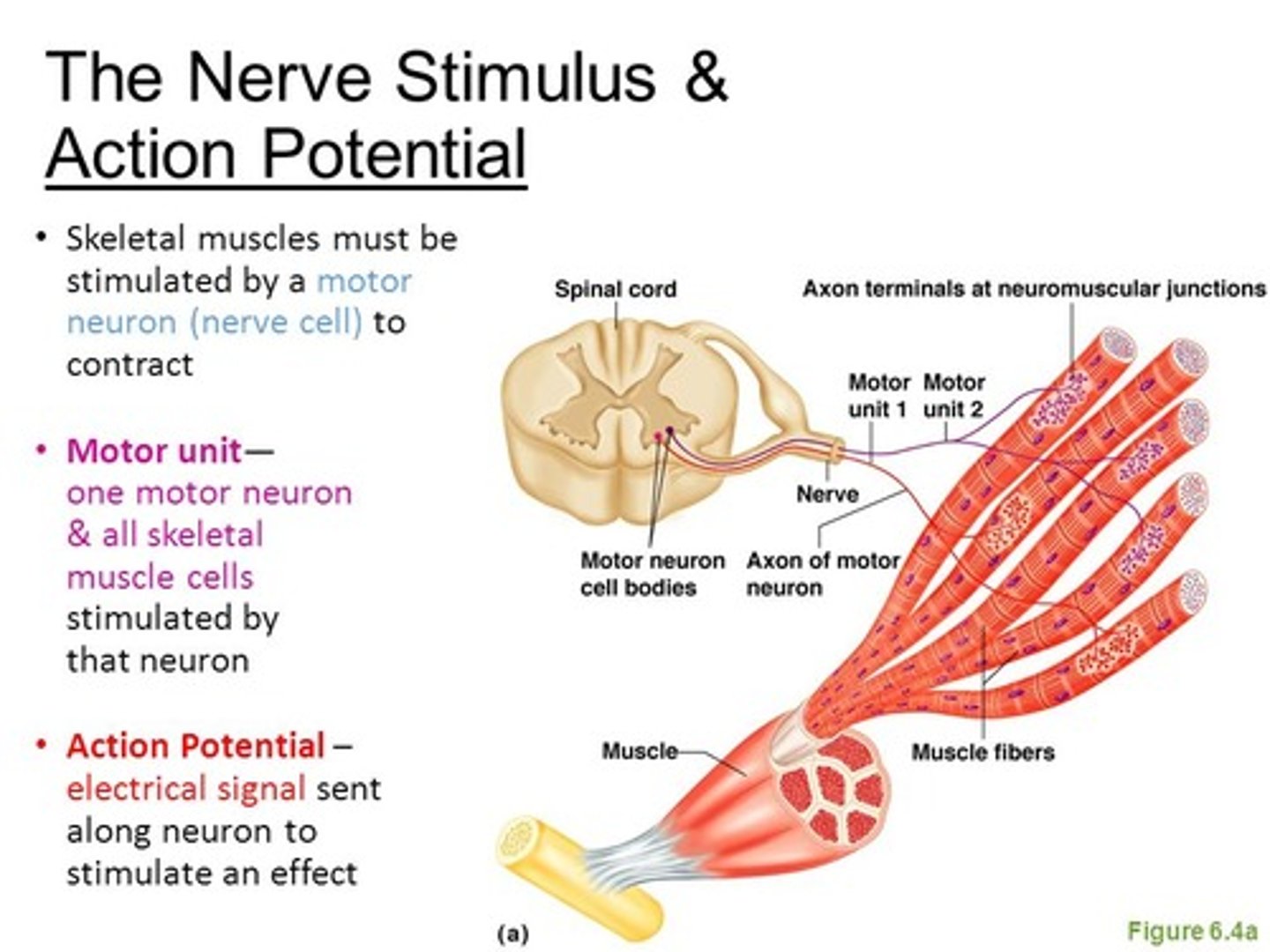
Cranial nerves control the ___ and pass out from the ___. Spinal nerves control the ___ and pass out from the ___.
Fill in the blank using the following terms:
- Skull
- Spinal Cord
- Limbs & Trunk
- Head & Neck
Cranial nerves control the Head & Neck and pass out from the Skull. Spinal nerves control the Limbs & Trunk and pass out from the Spinal Cord.
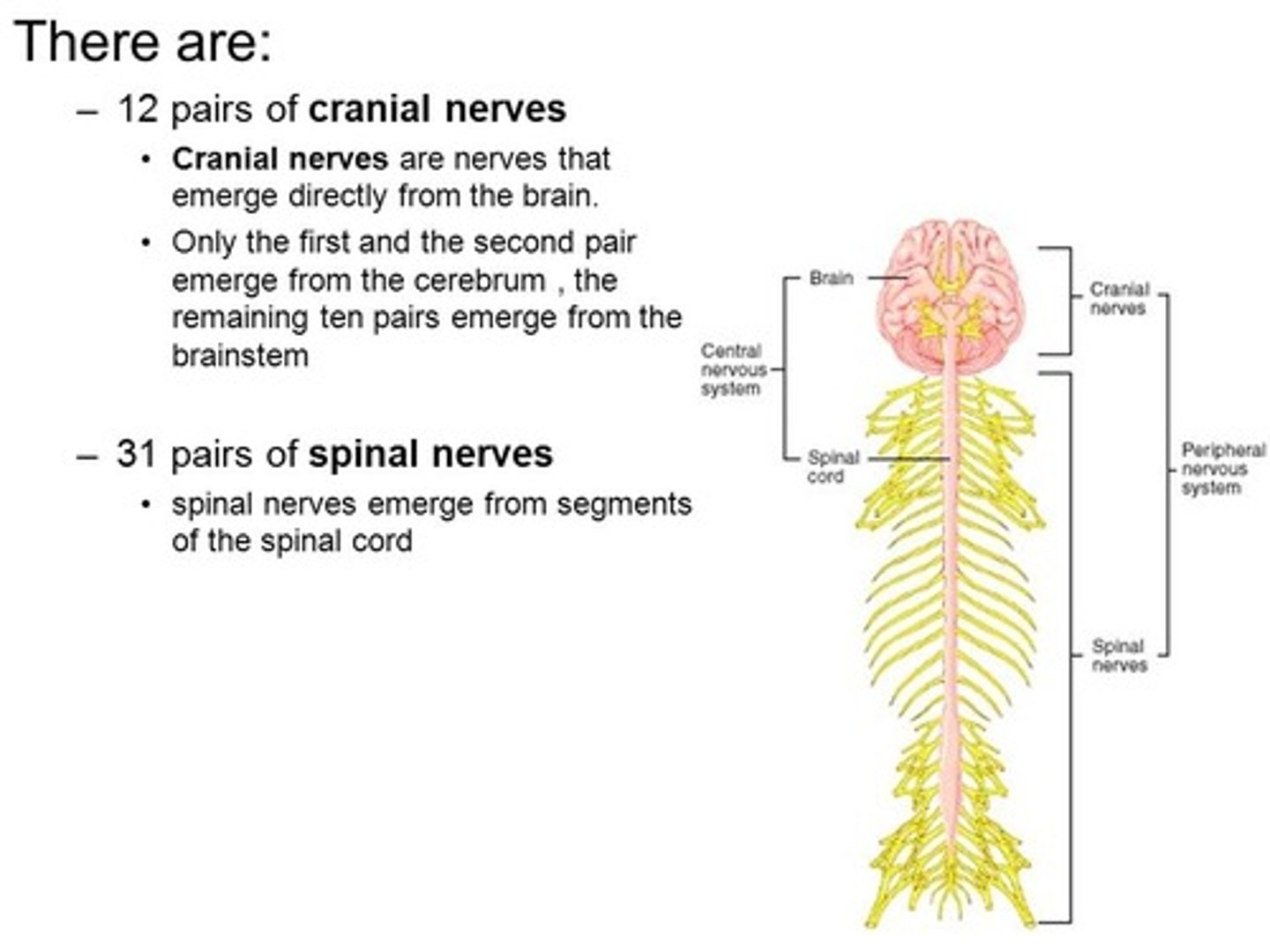
The soma of lower motor neurons are located in which of the following locations?
I. Spinal Cord
II. Brain Stem
III. Peripheral Nervous System
(A) I Only
(B) I and II Only
(C) I and III Only
(D) I, II, and III
(B) I and II Only
The soma of lower motor neurons are located in the following locations:
(1) Spinal Cord
(2) Brain Stem (particularly for the cranial nerves)
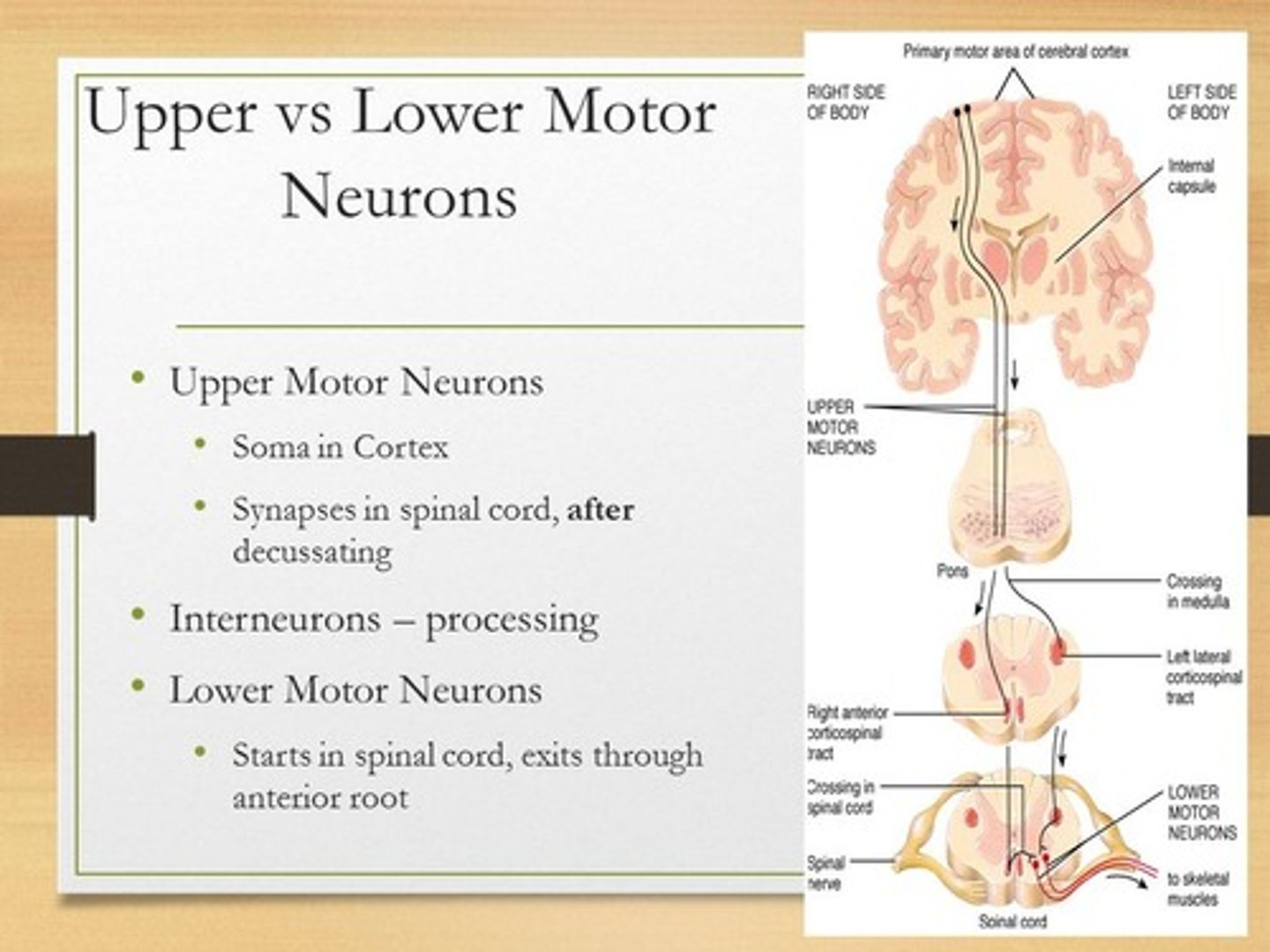
True or false? An area that needs very fine movements, like the fingers or eyes, will have larger motor units.
False. An area that needs very fine movements, like the fingers or eyes, will have smaller motor units.
Smaller motor units allow for more precise control.
True or False? Xavier is noticing that his muscles are getting smaller and smaller. He is most likely experiencing atrophy.
True. Atrophy is a loss in muscle mass. Hypertrophy is the opposite of Atrophy and is a gain of muscle mass.
Dylan visits his grandfather and notices that his hands are continually twitching. Which of the following is his grandfather likely dealing with?
(A) Atrophy
(B) Fasciculations
(C) Hypertonia
(D) Hyporeflexia
(B) Fasciculations
Fasciculations are involuntary twitches of skeletal muscle.

Which of the following is not a lower motor neuron lesion sign (abnormality of a lower motor neuron)?
(A) Atrophy
(B) Fasciculations
(C) Hypertonia
(D) Hyporeflexia
(C) Hypertonia
All of the following are lower motor neuron lesion signs:
(1) Atrophy - a loss in muscle mass
(2) Fasciculations - involuntary twitches
(3) HYPOtonia - a decrease in tone of skeletal muscle (how much remains contracted at rest)
(4) Hyporeflexia - decreased muscle stretch reflexes
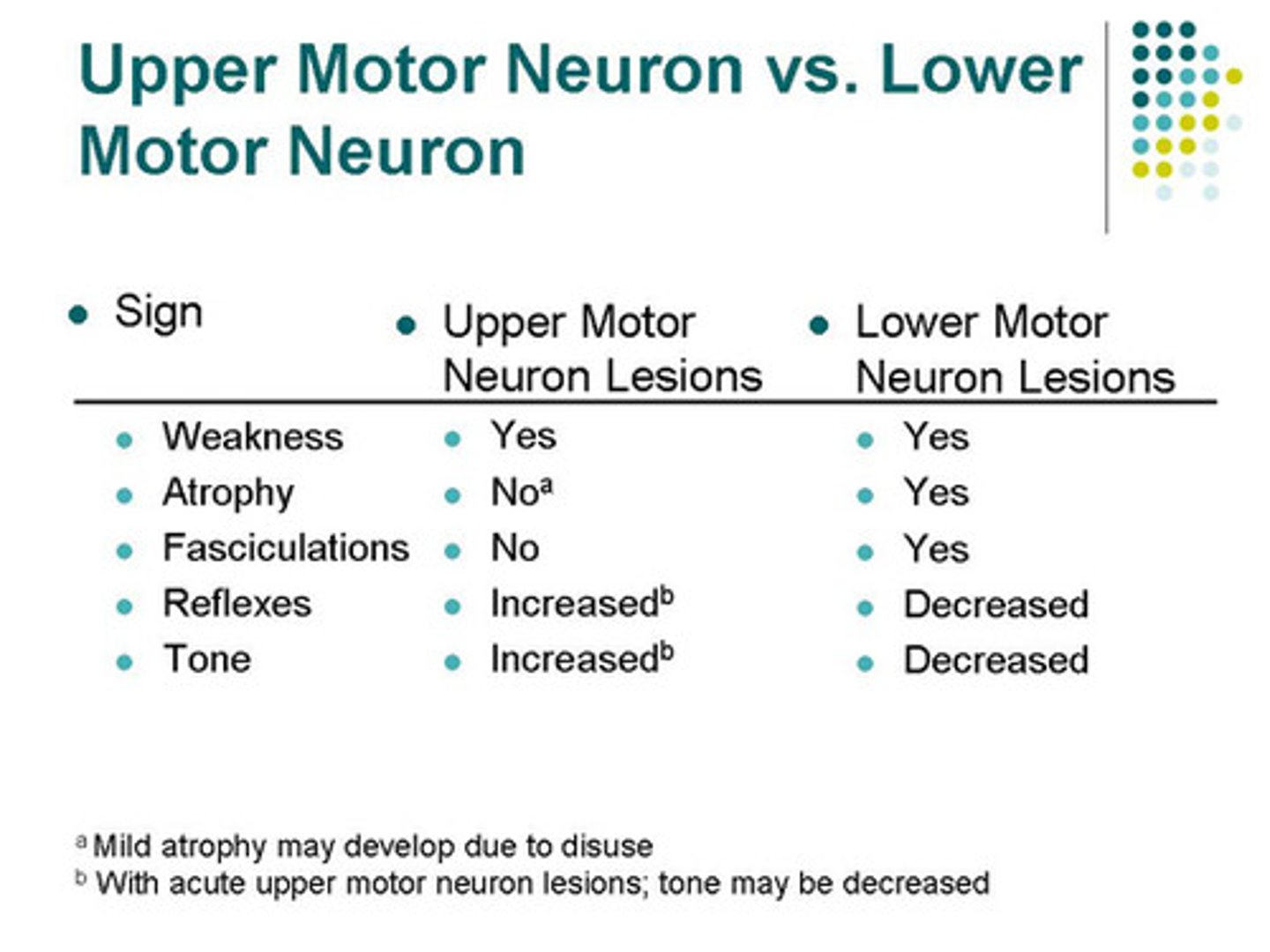
Compare the terms Atrophy and Hypotonia.
Atrophy is when skeletal muscles actually decrease in size.
Hypotonia is when skeletal muscles have less tone, meaning that the muscles are not as contracted at rest
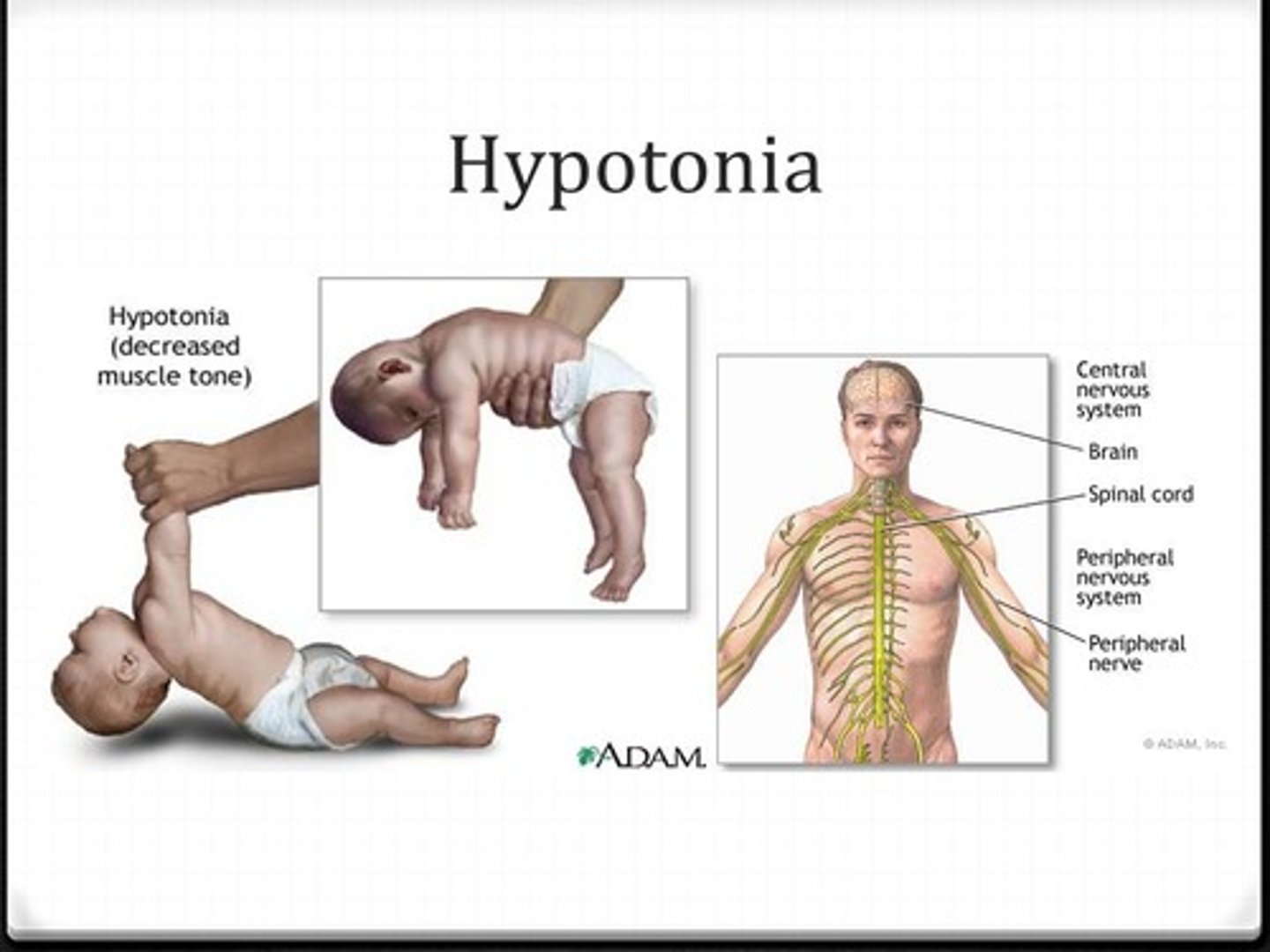
Jack visits his physician who is concerned that Jack may be suffering from Hypotonia. He tells Jack to relax his leg, and then proceeds to move Jack's leg around. What would the doctor expect to feel if Jack has Hypotonia?
His doctor would feel a lack of resistance. His leg would feel "floppy".
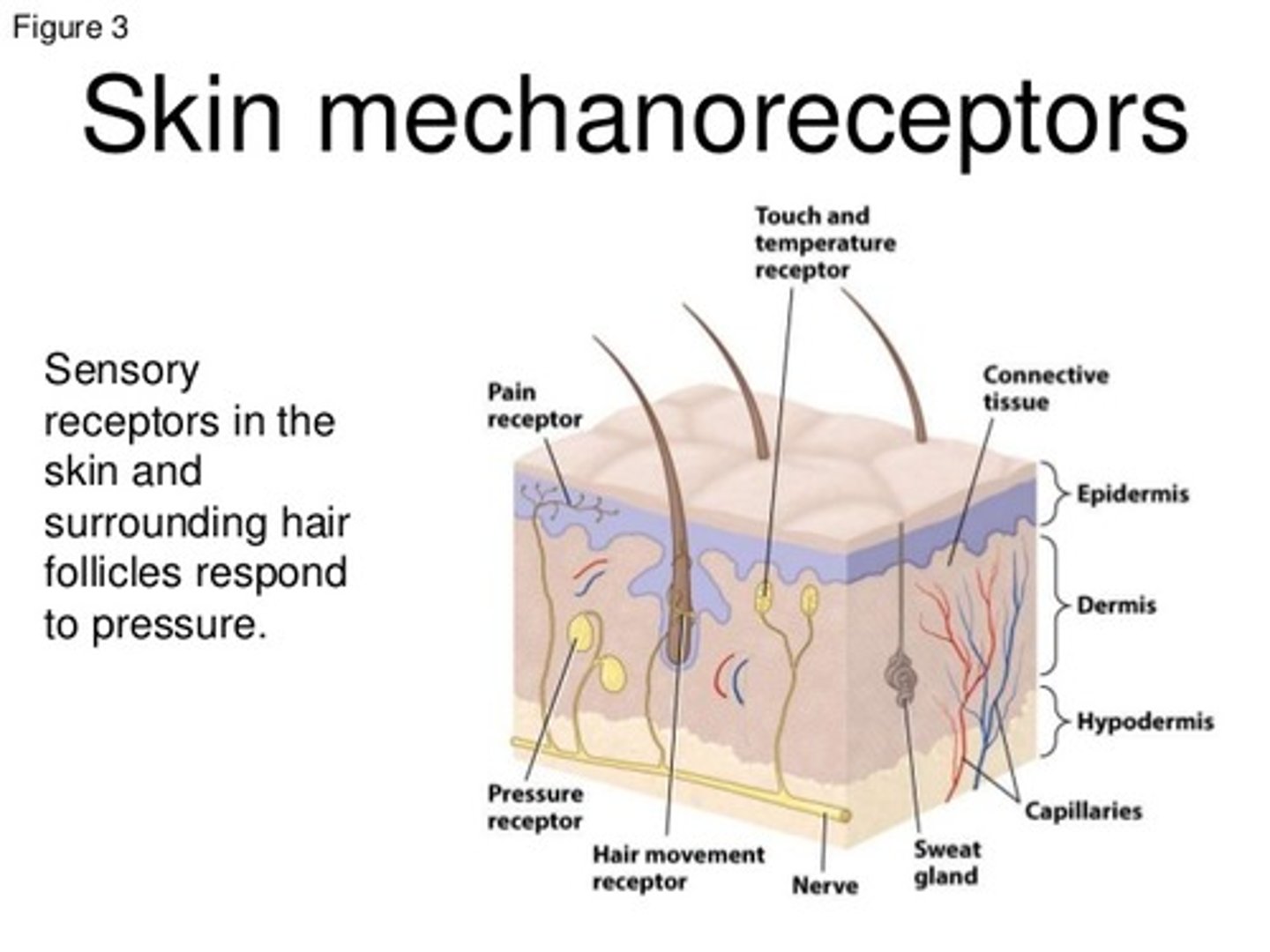
Mechanoreceptors detect which of the following?
I. Position
II. Vibration
III. Pain
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) II and III Only
(C) I and II Only
Mechanoreceptors detect Position, Vibration, Touch (mechanical stimuli).
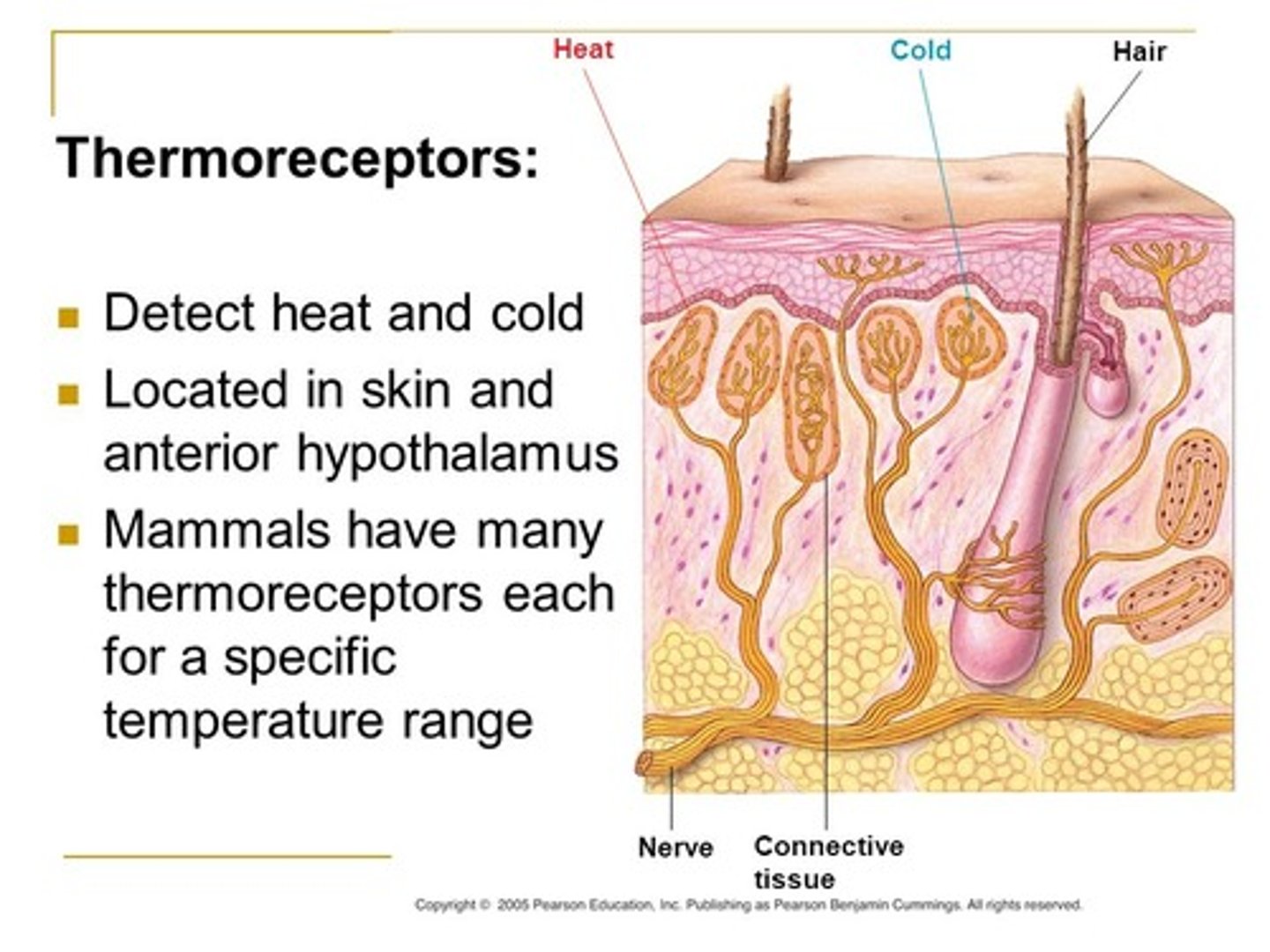
Thermoreceptors detect which of the following?
(A) Position
(B) Temperature
(C) Touch
(D) Pain
(B) Temperature
Thermoreceptors detect temperature.
Nociceptors detect which of the following?
(A) Position
(B) Temperature
(C) Touch
(D) Pain
(D) Pain
Nociceptors detect pain
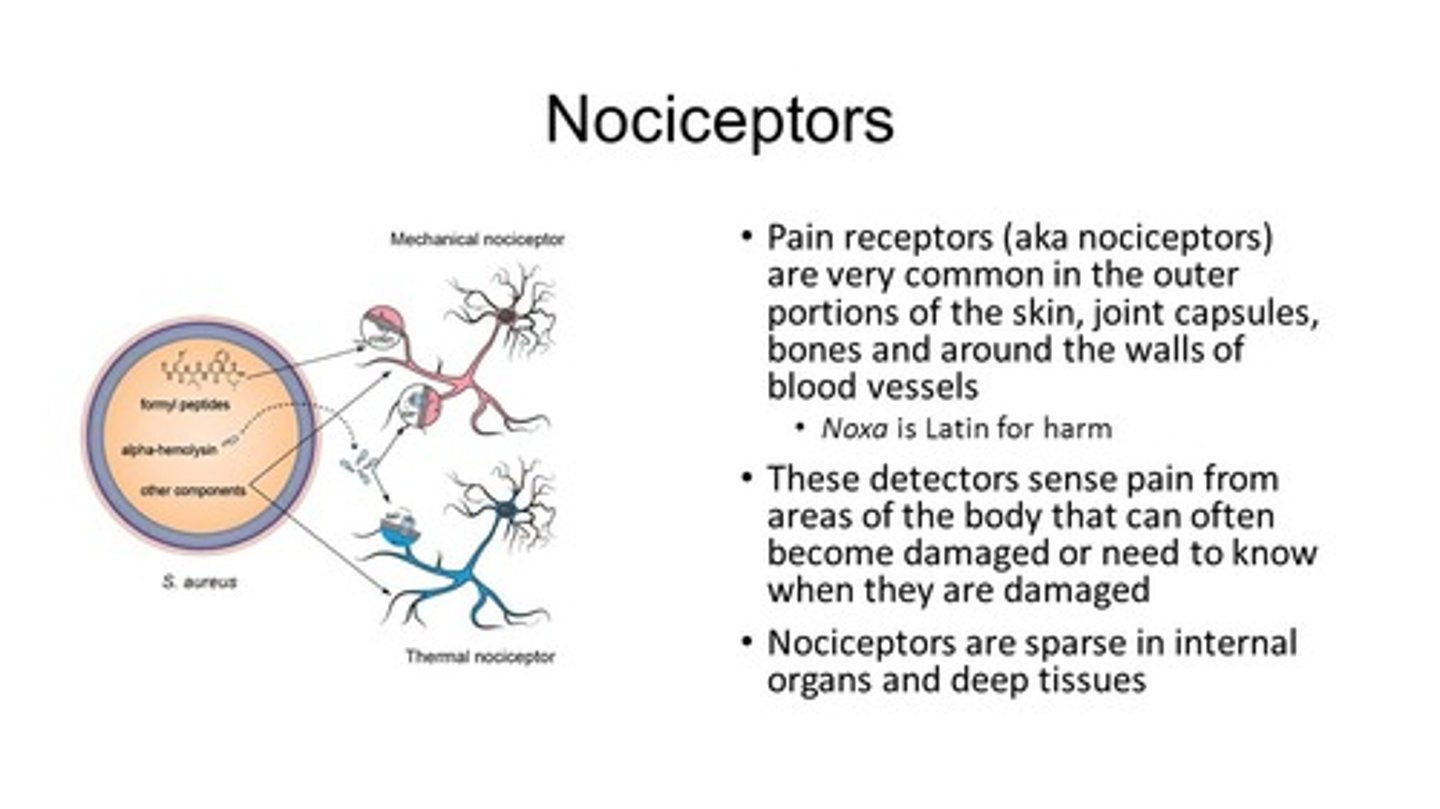
Which receptors can have bare nerve endings?
I. Nociceptors
II. Thermoreceptors
III. Mechanoreceptors
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II, and III
(D) I, II, and III
Nociceptors, Thermoreceptors, and Mechanoreceptors can all have have bare nerve endings (it’s more common in nociceptors/thermoreceptors than mechanoreceptors)
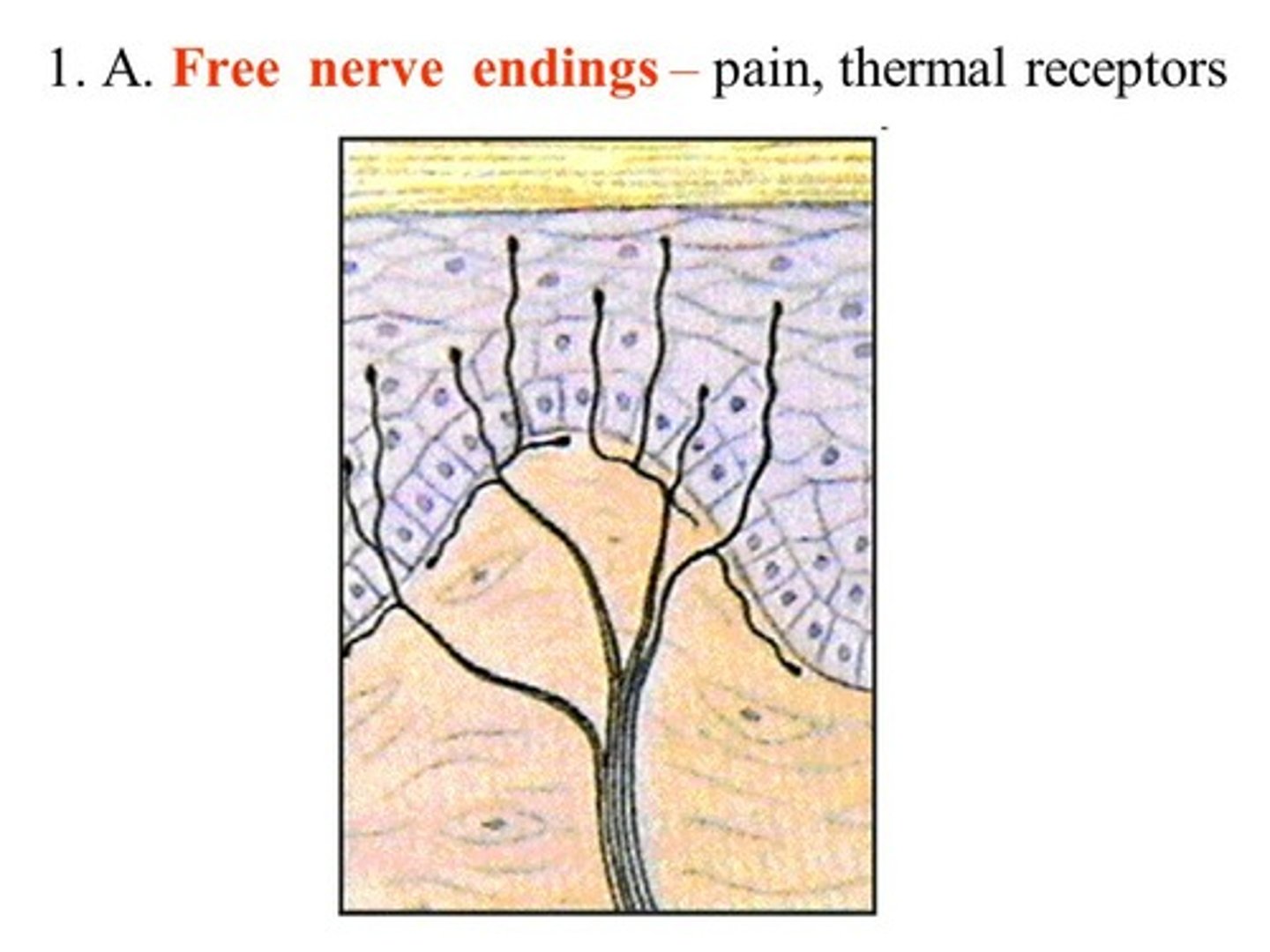
You expect to find receptors that detect which of the following the farthest from the surface of the skin?
(A) Position
(B) Vibration
(C) Touch
(D) Pain
(A) Position
Mechanoreceptors for position (stretch receptors) are located within muscles.
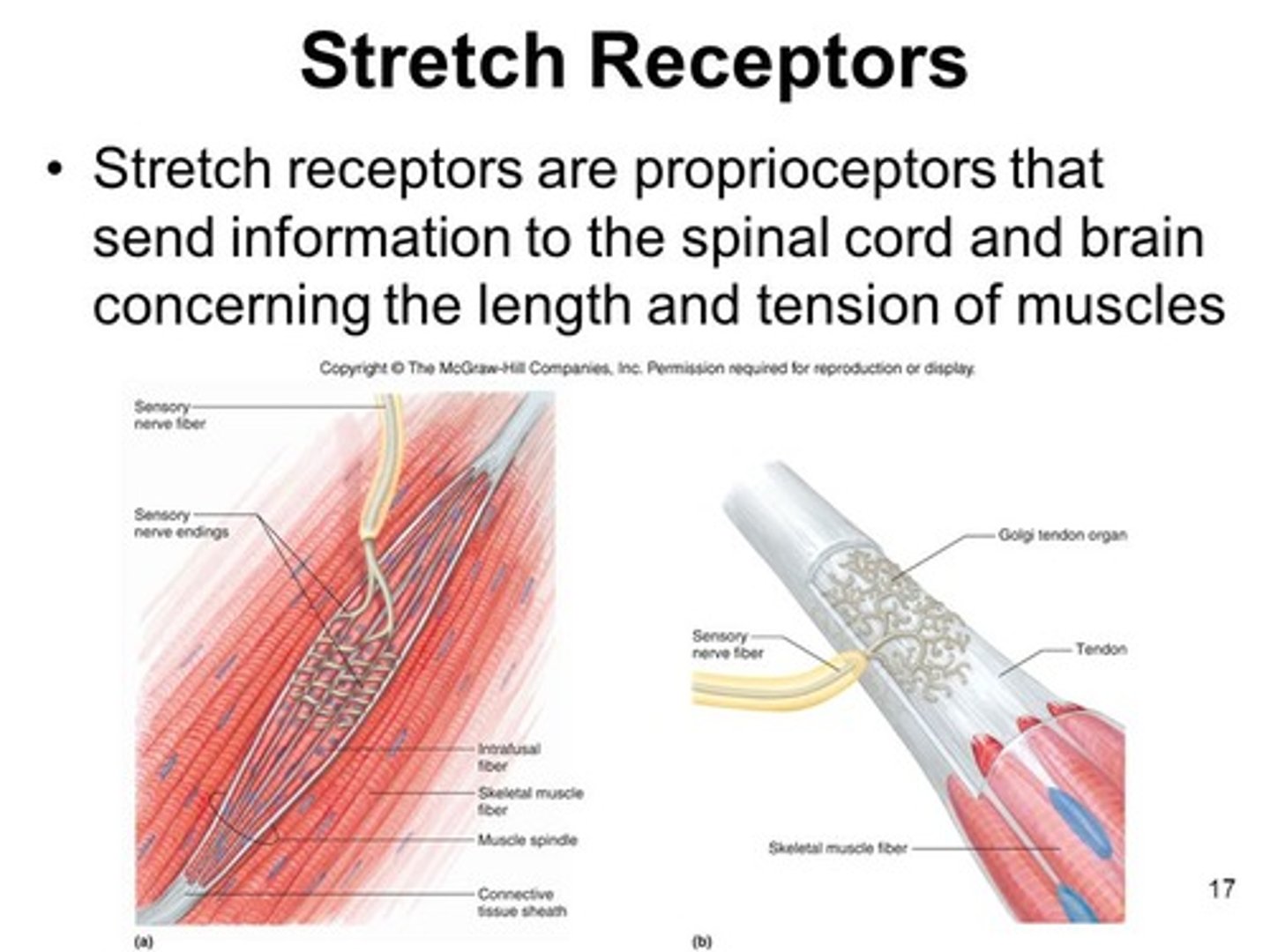
Which receptors carry information back to the central nervous system through somatosensory neurons?
I. Nociceptors
II. Thermoreceptors
III. Mechanoreceptors
(A) I Only
(B) III Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I, II and III
(D) I, II and III
Mechanoreceptors, nociceptors and thermoceptors carry information back to the central nervous system through somatosensory neurons
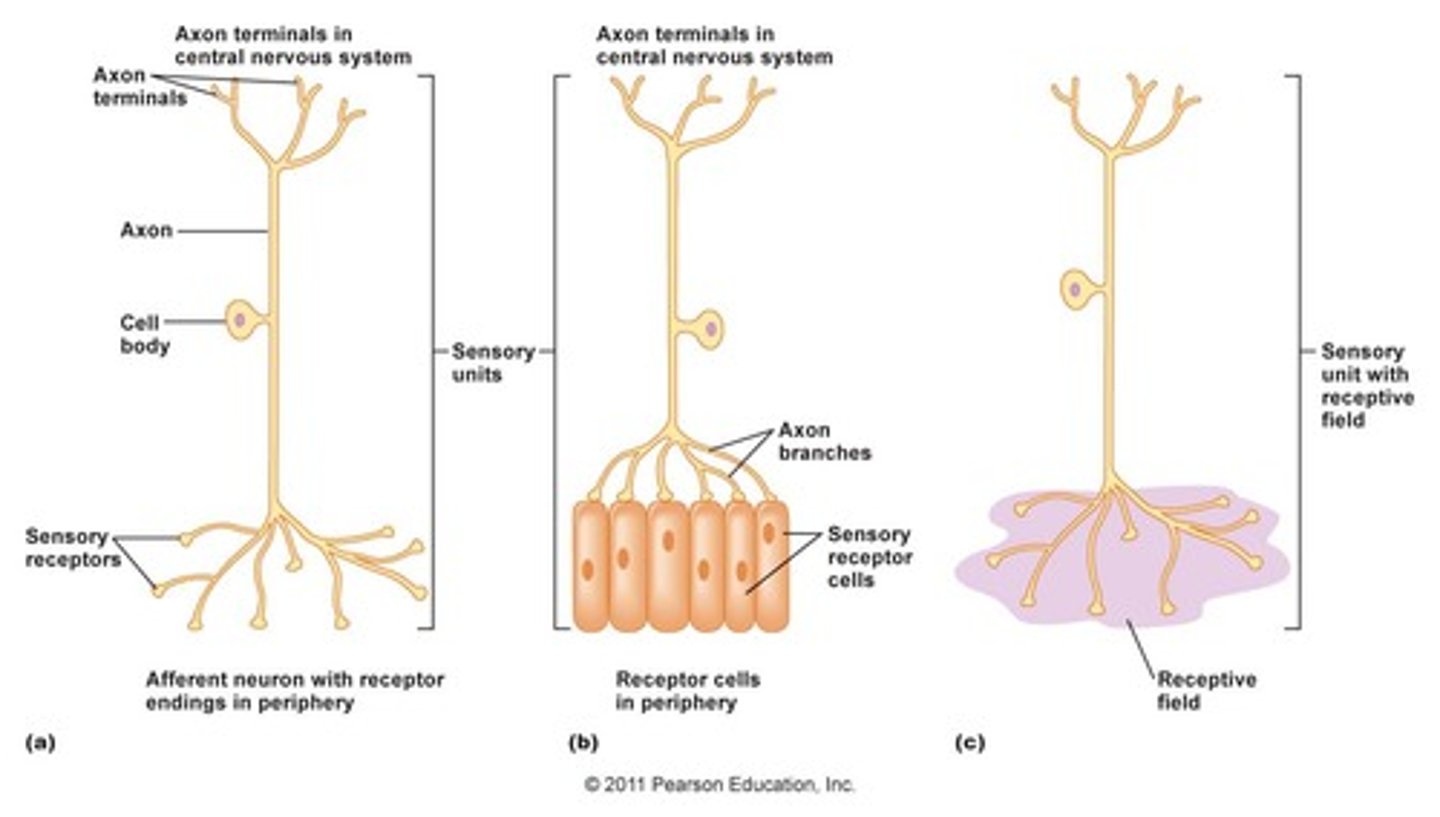
CRB Which of the following are functions of neurons?
(A) Transmit electrical impulses long distances.
(B) Translate electrical signals to chemical signals
(C) Both A and B
(D) Neither A nor B
(C) Both A and B
Neurons:
(A) Transmit electrical impulses long distances.
(B) Translate electrical signals to chemical signals
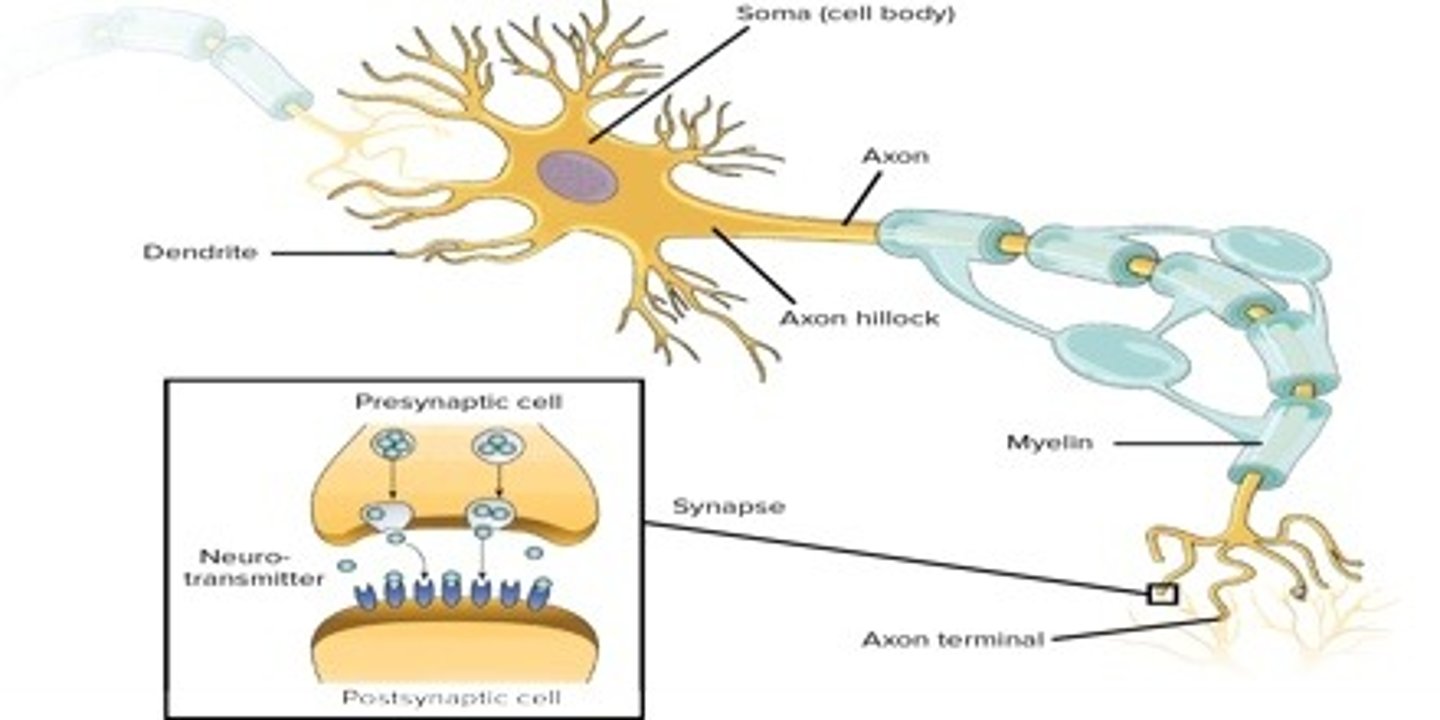
Somatosensory neurons for position, vibration, and some touch have ______ diameter axons with ______ layers of myelin sheath.
(A) thin, thin
(B) thin, thick
(C) thick, thick
(D) thick, thin
(C) thick, thick
Somatosensory neurons for position, vibration, and some touch have thick diameter axons with thick layers of myelin sheath
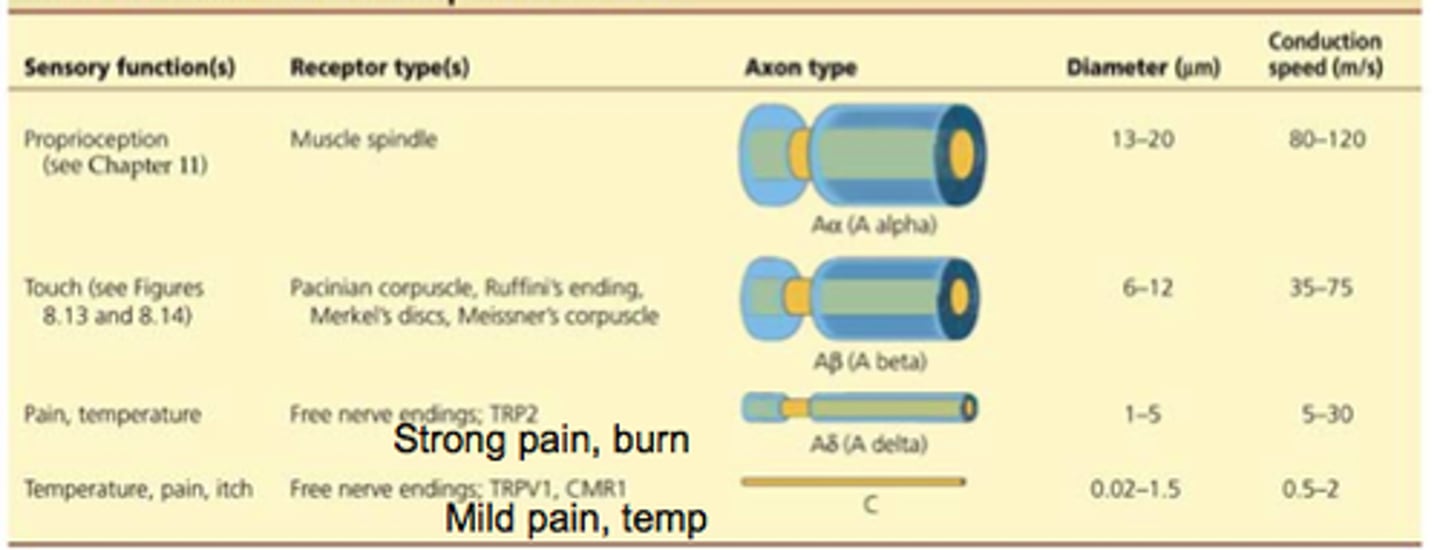
Somatosensory neurons for temperature, pain, and some touch have _______ diameter axons with _______ layers of myelin sheath.
(A) thin, thin
(B) thin, thick
(C) thick, thick
(D) think, thin
(A) thin, thin
Somatosensory neurons for temperature, pain, and some touch have thin diameter axons with thin layers of myelin sheath.
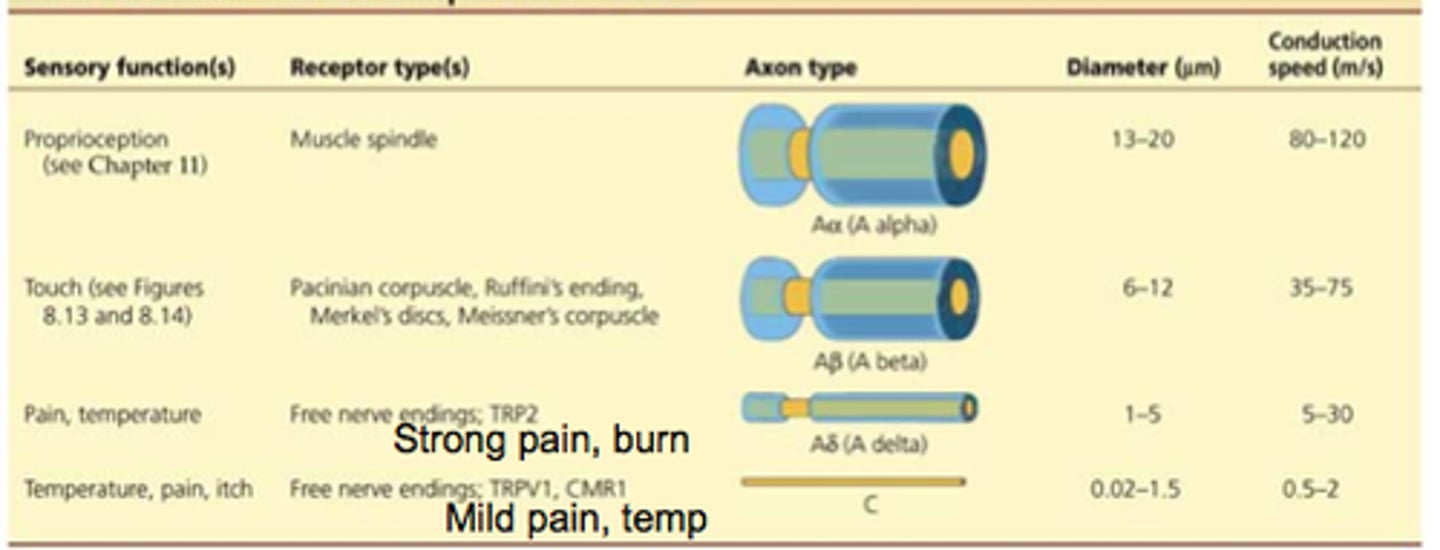
What about the structure of mechanoreceptors makes it so their action potentials travel faster than nociceptors and thermoreceptors?
Mechanoreceptors have a thicker myelin sheath and a larger axon diameter than nociceptors and thermoreceptors.
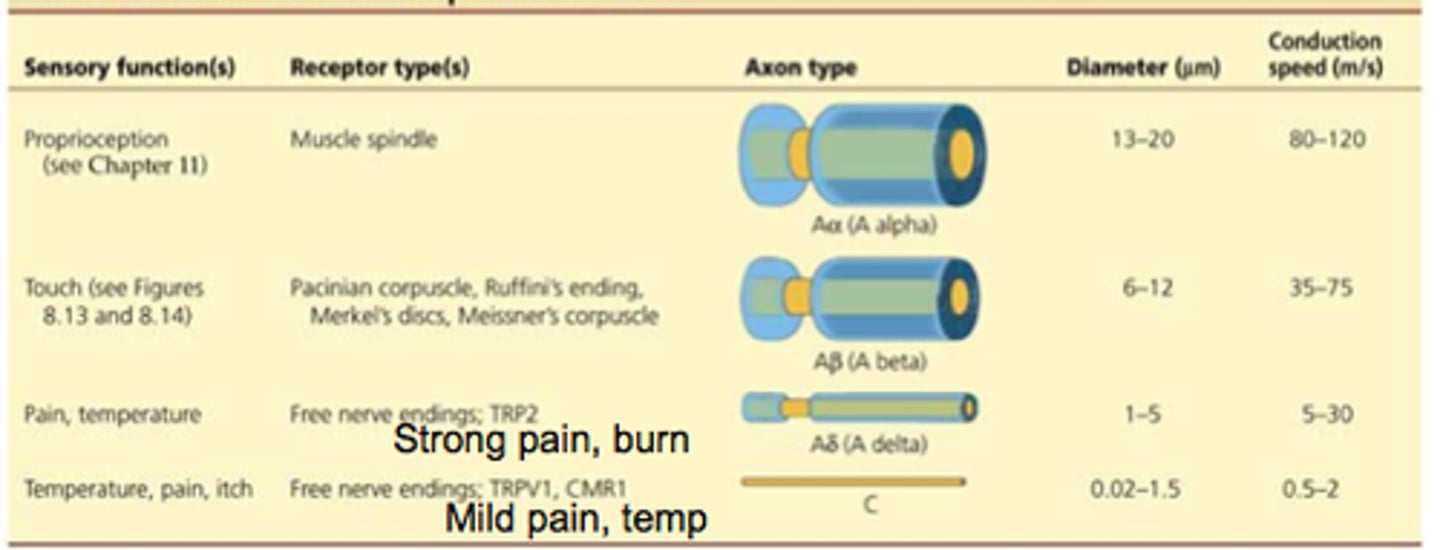
Match the following touch sense to the speed of its somatosensory neuron.
(1) Fine Touch Sense
(2) Gross Touch Sense
(A) Slower somatosensory Neuron
(B) Faster somatosensory Neuron
(1) Fine Touch Sense -> (B) Faster somatosensory Neuron
(2) Gross Touch Sense -> (A) Slower somatosensory Neuron
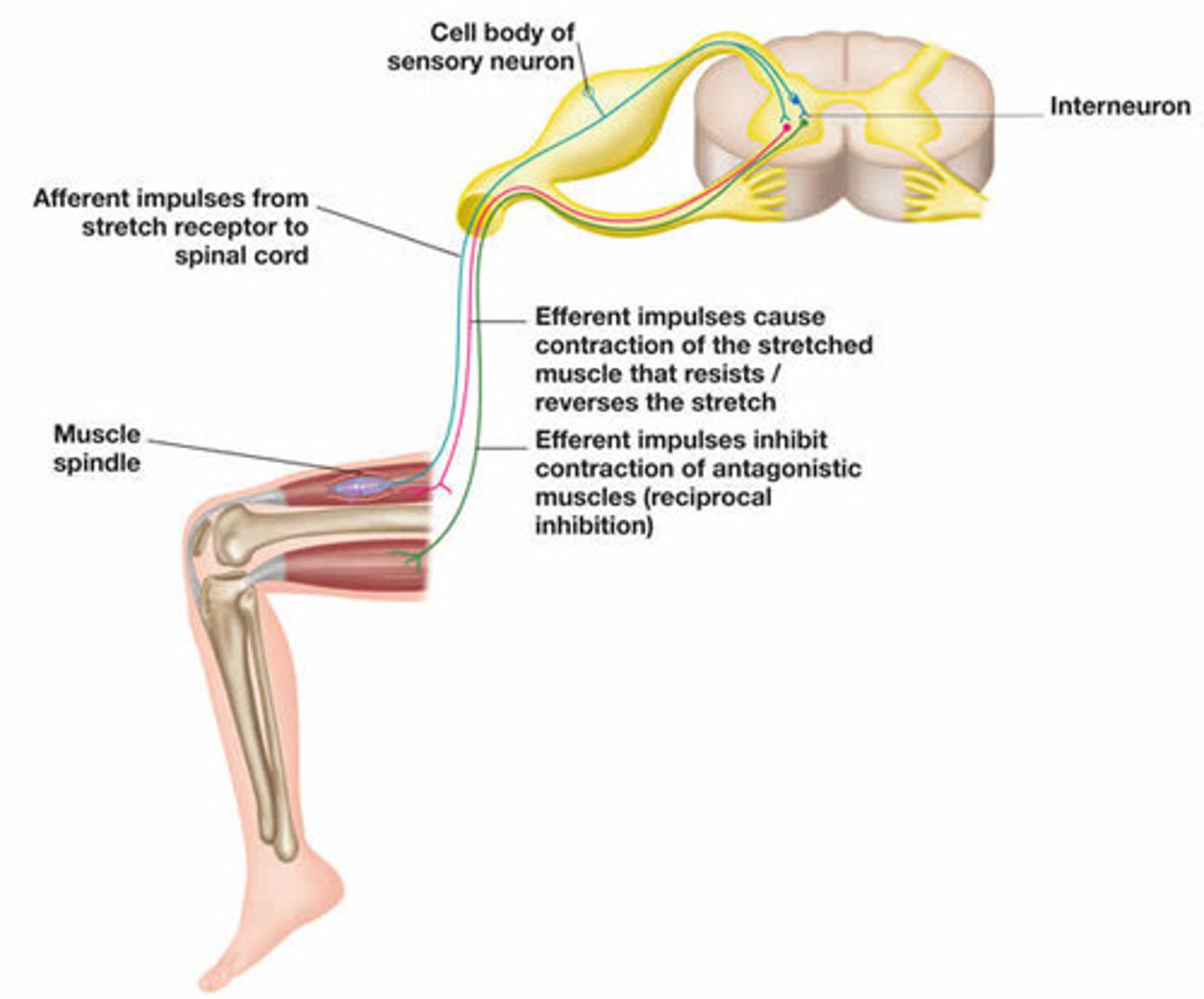
During the knee-jerk muscle reflex, what does the afferent part of the reflex do?
Carries information from stretch receptors back to the central nervous system, telling it that the muscle was stretched. These are the somatosensory neurons.
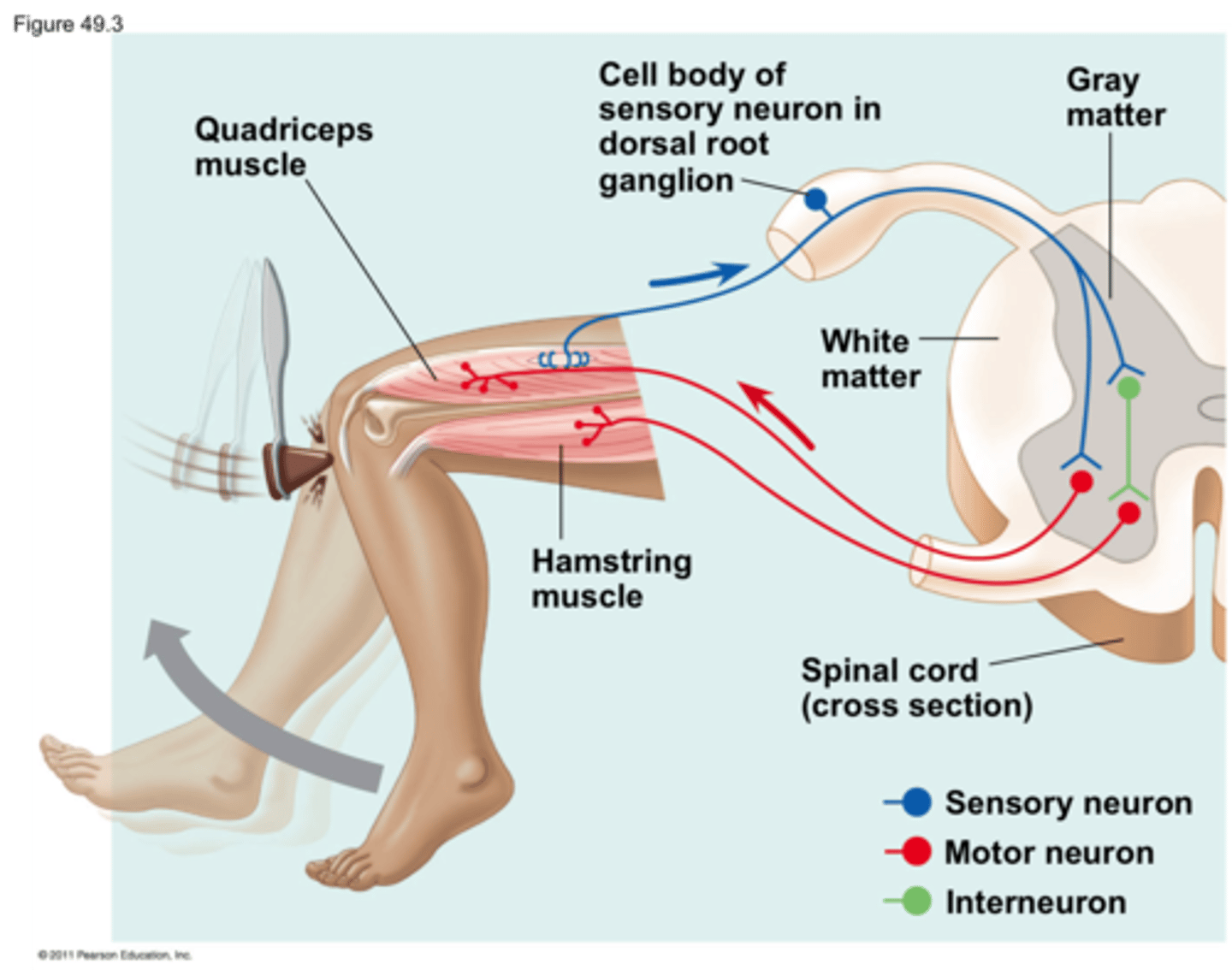
During the knee-jerk muscle reflex, what does the efferent part of the reflex do?
The efferent neuron (lower motor neuron) is excited by the somatosensory neuron. Then, the efferent neuron's axon will synapse and excite the muscle that was stretched, causing a contraction.
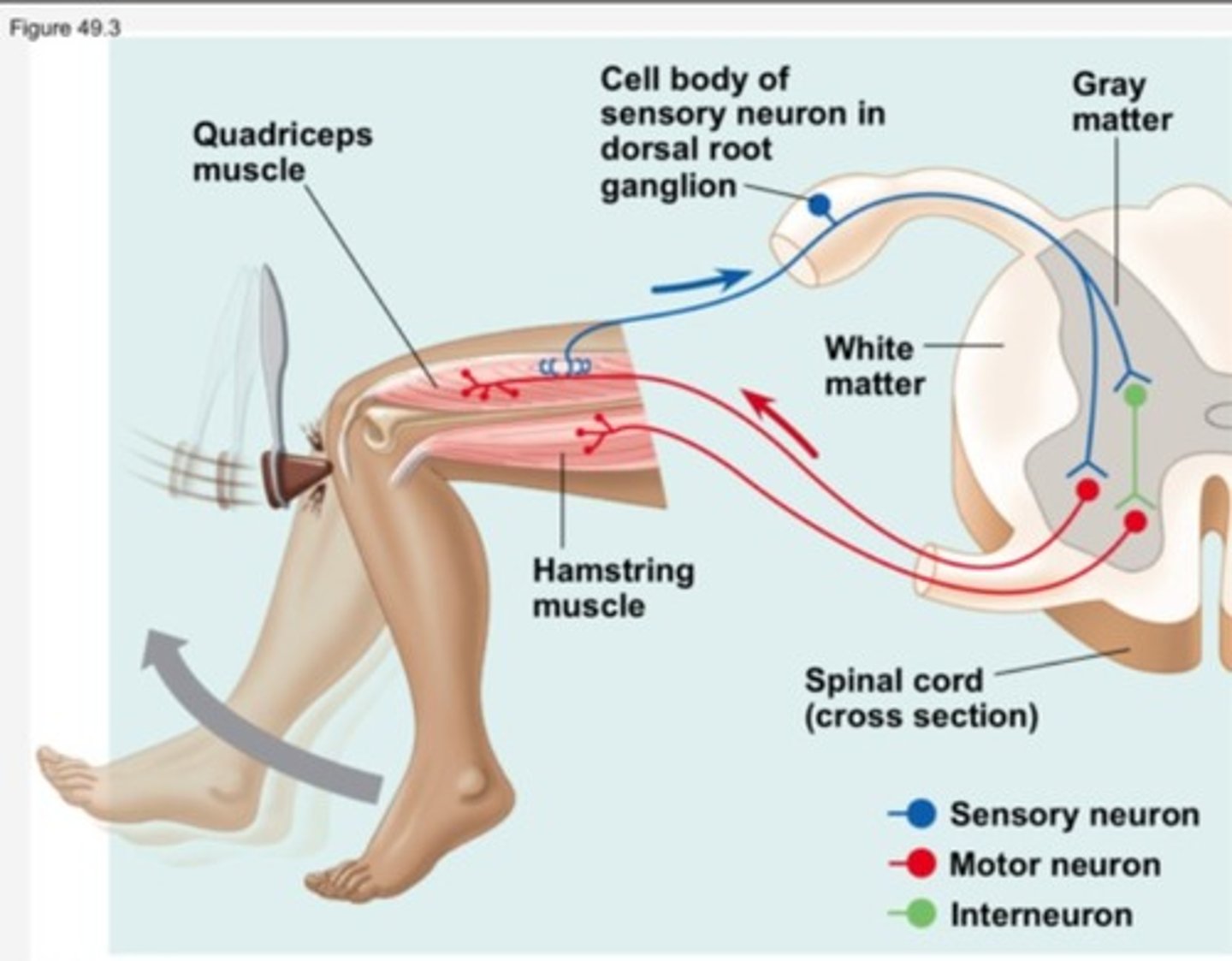
During the knee-jerk muscle reflex, what role might an inhibitor neuron play?
An inhibitory neuron may synapse onto a lower motor neuron for the opposing muscle group, causing that muscle group to relax. This allows the muscle that was stretched to more easily contract, maximizing the reflex.
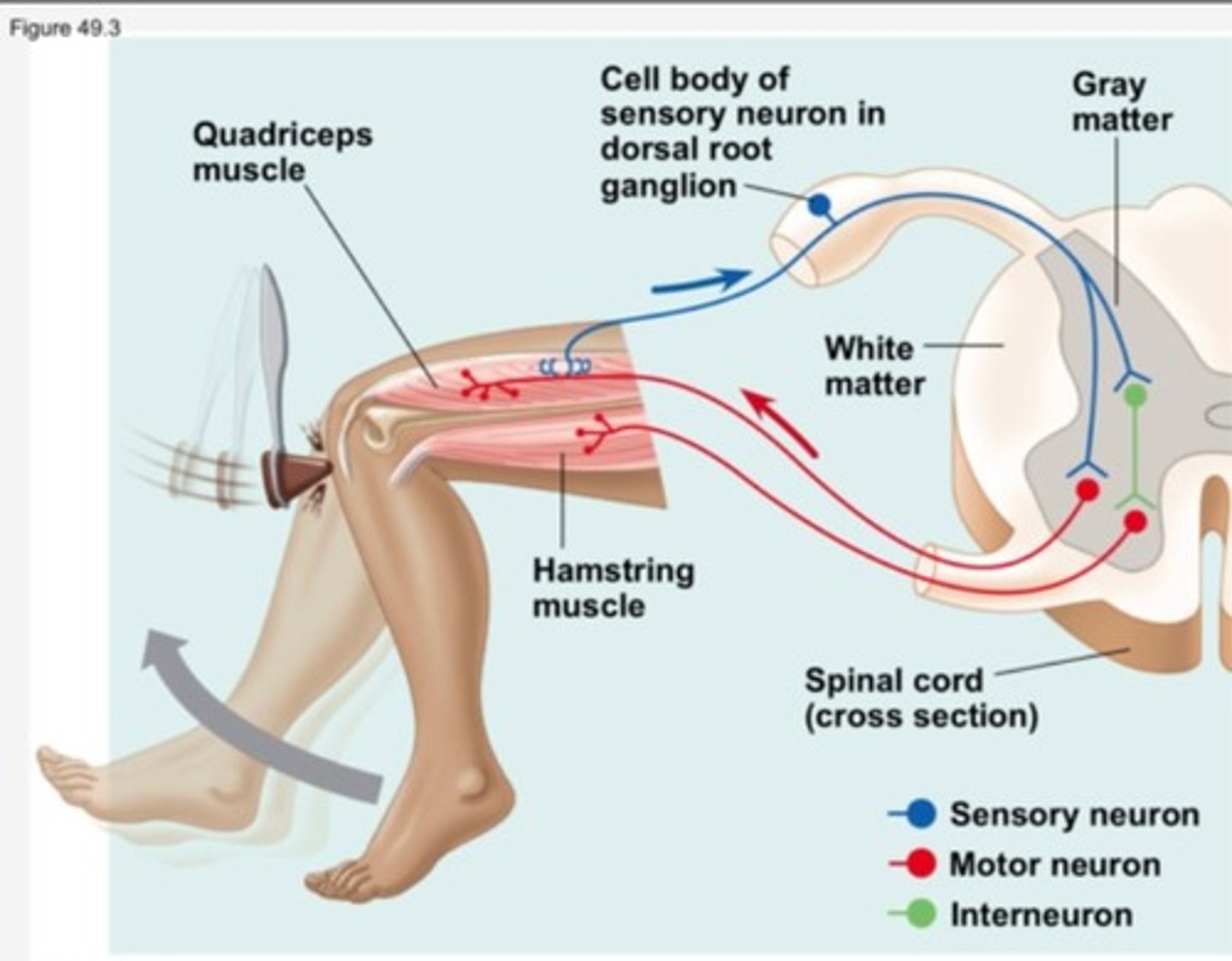
CRB True or false? The Combination of that excitatory Lower Motor Neuron and Inhibitory Neuron produce an effect of Reciprocal Inhibition, to ensure that the desired motion occurs.
True. The Combination of that excitatory Lower Motor Neuron and Inhibitory Neuron produce an effect of Reciprocal Inhibition, to ensure that the desired motion occurs.
If there is a problem with lower motor neurons, what can be seen during the knee-jerk reflex?
(A) Diminished Reflex
(B) Heightened Reflex
(C) Variable Reflex
(D) Opposite Reflex
(A) Diminished Reflex
If there is a problem with lower motor neurons, a diminished or lost reflex will be observed.
A similar effect would be seen if the somatosensory neurons (afferent neurons) were affected too.
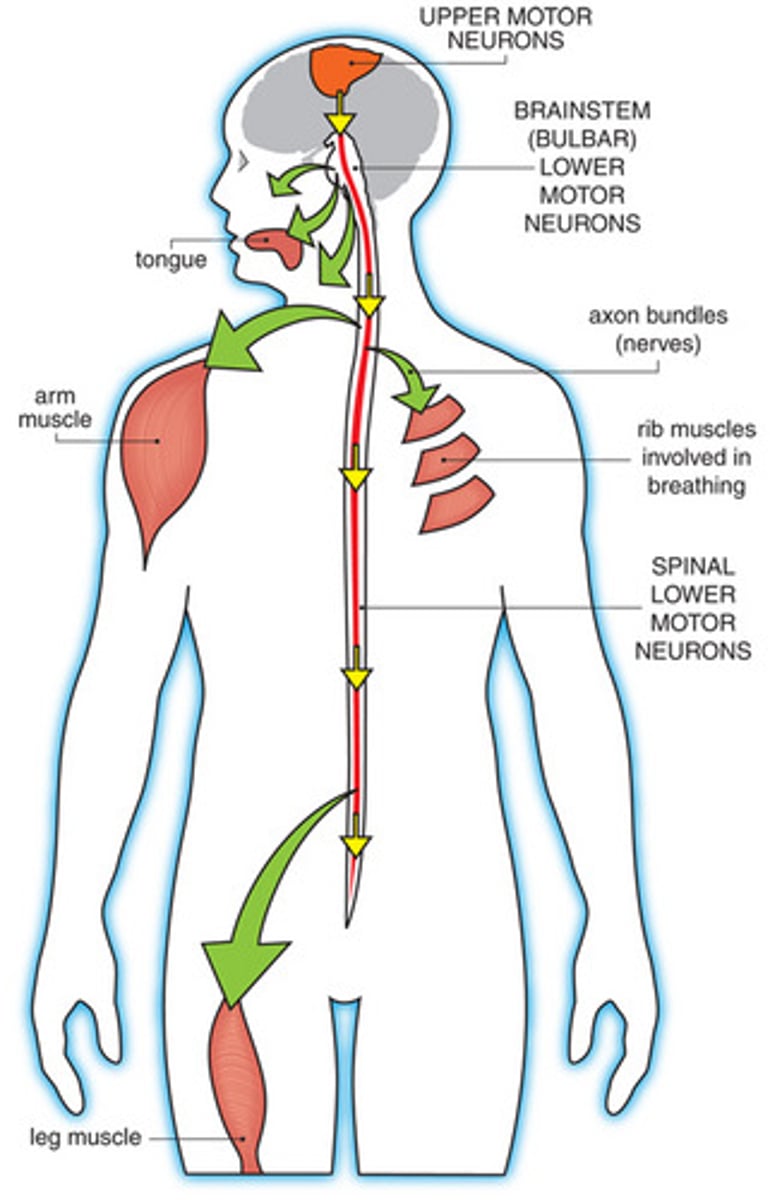
CRB True or false? There are also Polysynaptic Reflex arcs, which unlike the knee-jerk reflex, incorporate at least 2 synapses between neurons.
True. There are also Polysynaptic Reflex arcs, which unlike the knee-jerk reflex, incorporate at least 2 synapses between neurons.
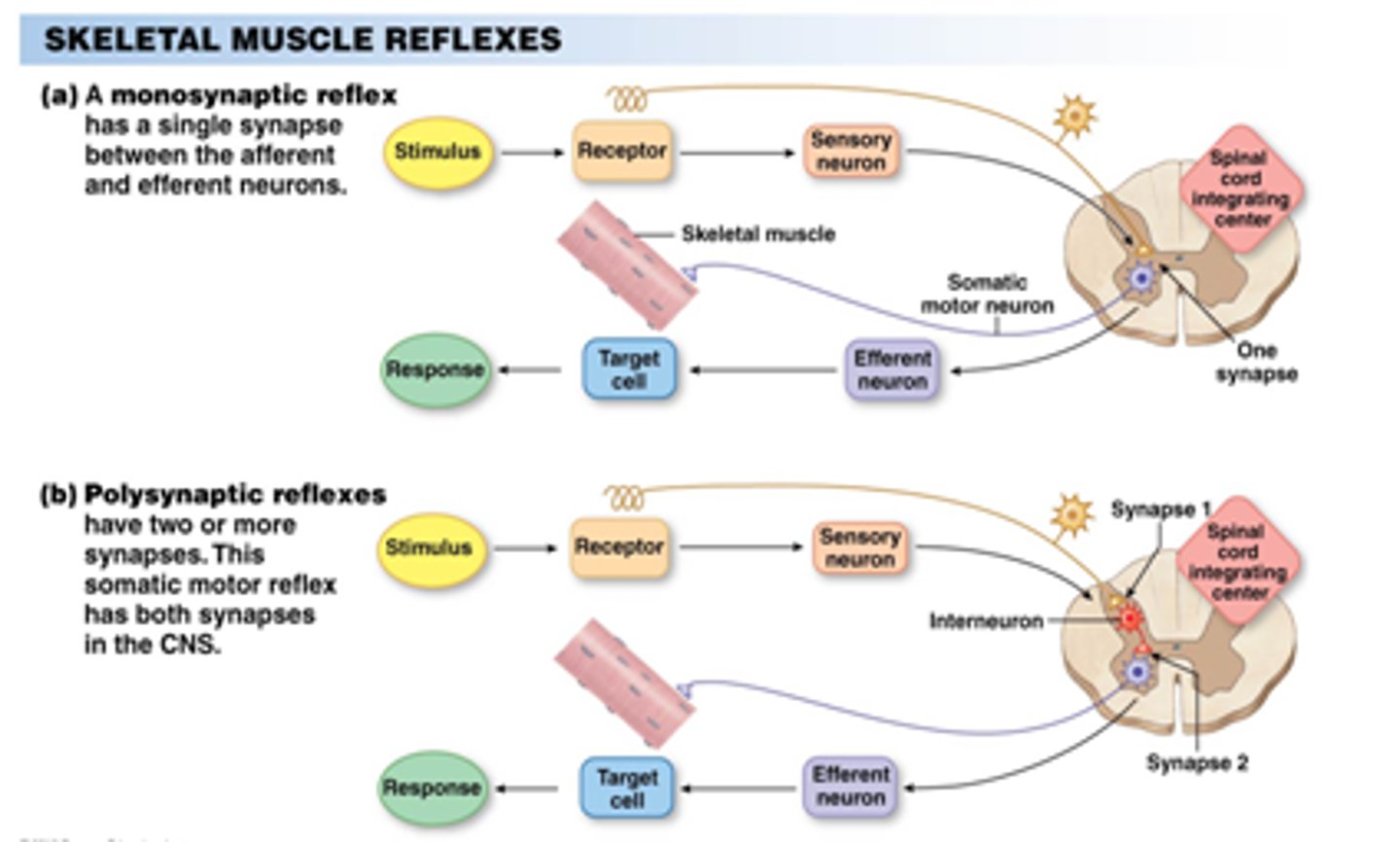
For a reflex, like the knee-jerk reflex, how is the cerebrum involved?
It is not involved. Reflexes are responses to stimuli that don't require consciousness.
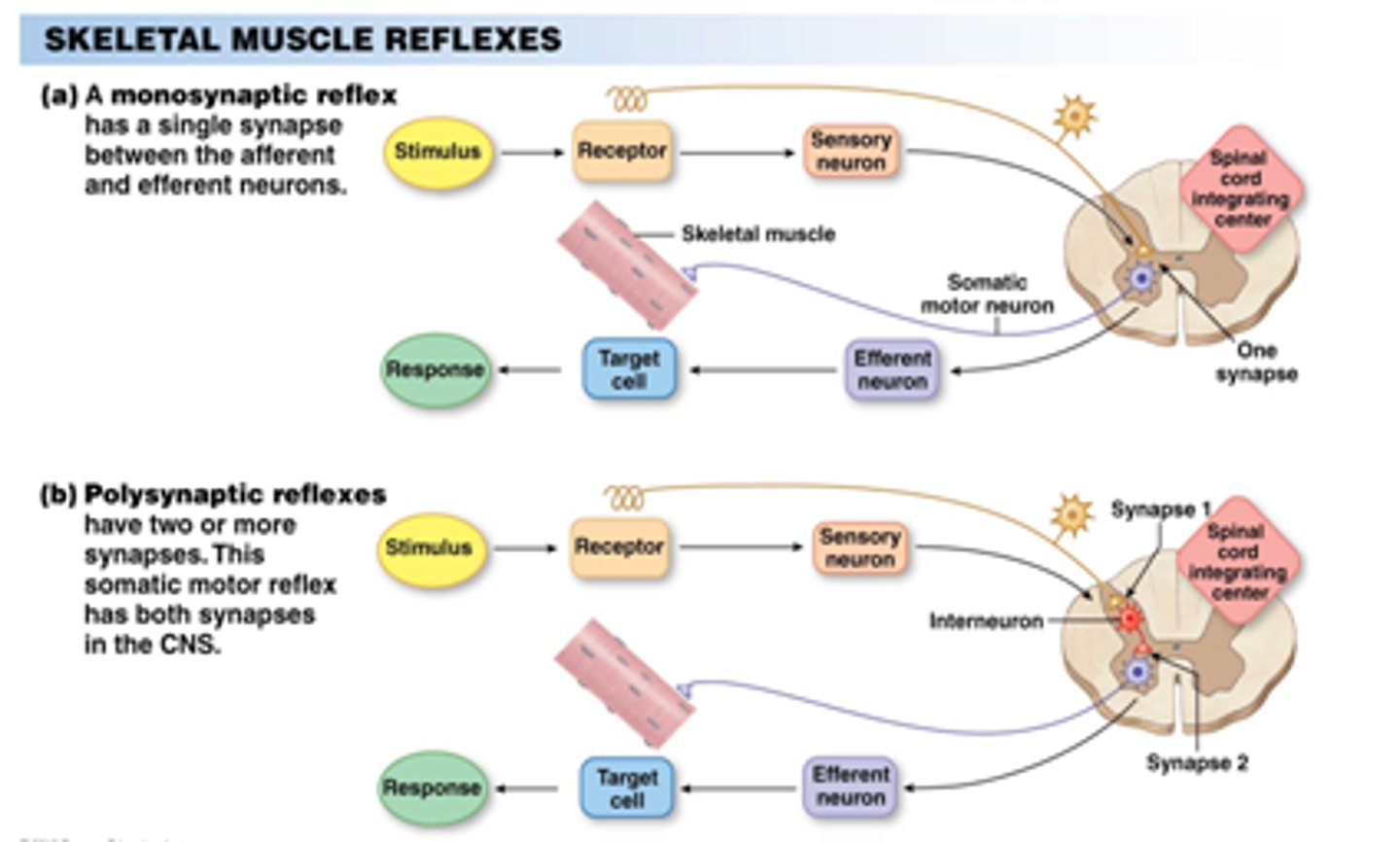
CRB If reflexes don't involve the cerebrum, then how are we aware of our reflexes?
I. There is an innate sense of knowing outside of the nervous system.
II. The sensory neuron in the reflex also branches to go to the CNS; it just doesn't need the CNS input for the action to occur.
III. There is other sensory information received once the reflex is occurring.
(A) II only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(C) II and III only
There are two ways that we are aware of our reflexes:
II. The sensory neuron in the reflex also branches to go to the CNS; it just doesn't need the CNS input for the action to occur.
III. There is other sensory information received once the reflex is occurring.
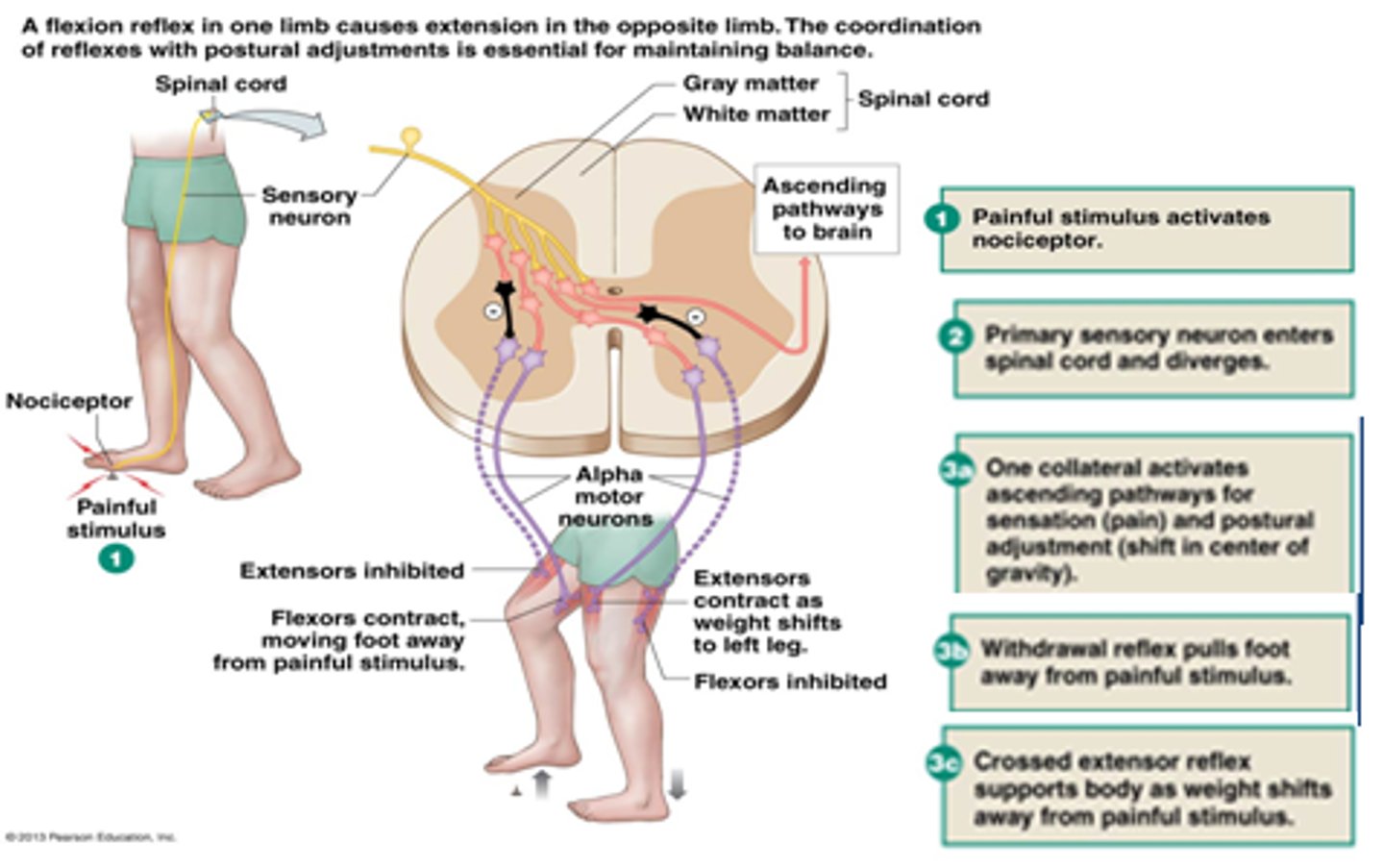
CRB Which of the following terms best describes the opposite of a reflex circuit, a circuit where input from the brain or brainstem is needed?
(A) Superior Circuits
(B) Integrated Circuits
(C) CNS
(D) Supraspinal Circuits
(D) Supraspinal Circuits
Supraspinal Circuits incorporate the brain and brainstem.
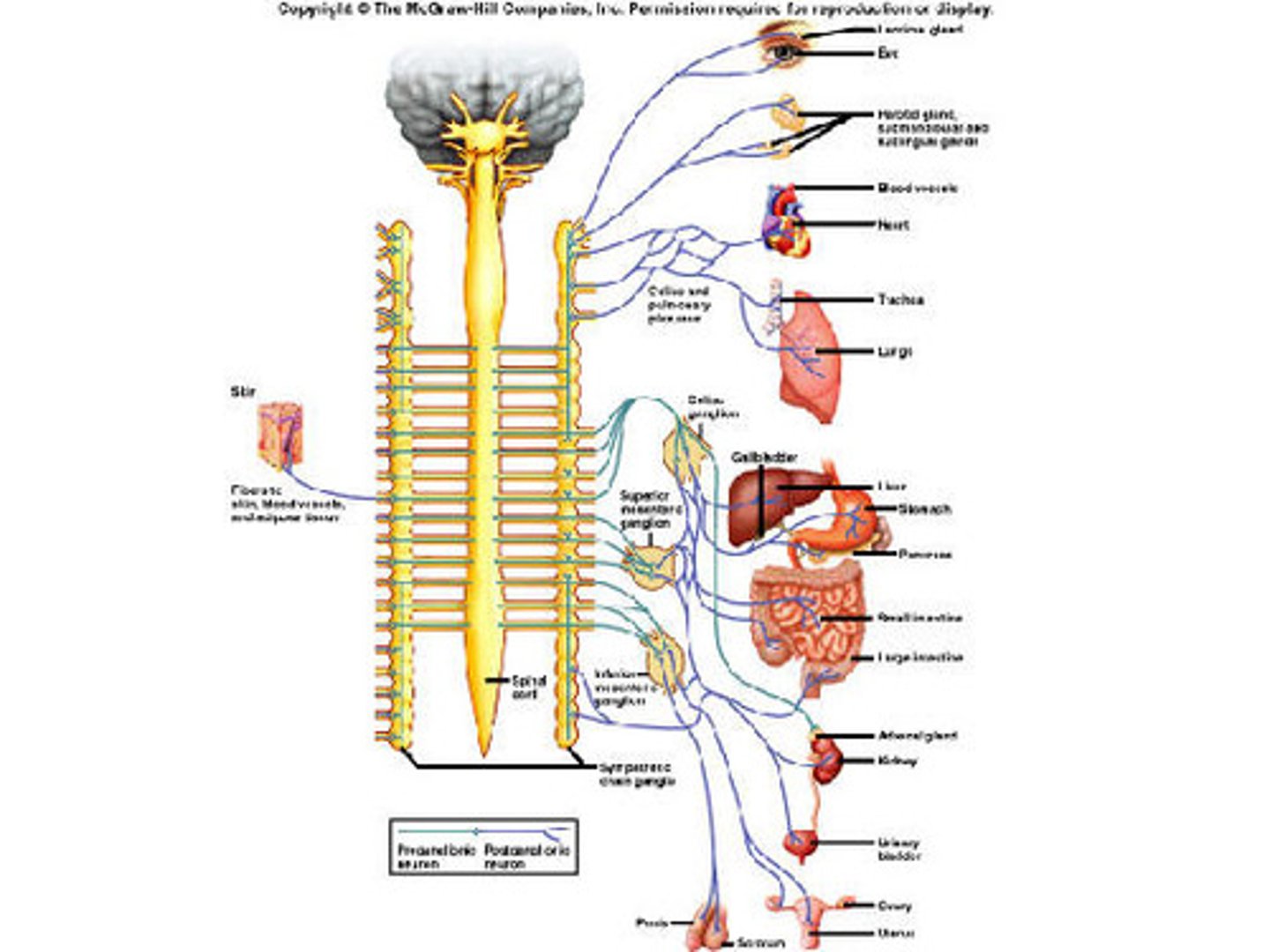
The efferent neurons of the autonomic nervous system control which of the following types of cells?
I. Smooth muscle cells
II. Skeletal muscle cells
III. Cardiac muscle cells
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) I and III Only
(D) I and III Only
The efferent neurons of the autonomic nervous system control the following types of cells:
- Smooth muscle cells
- Cardiac muscle cells
- Gland Cells
Skeletal muscle cells are controlled by the somatic nervous system.
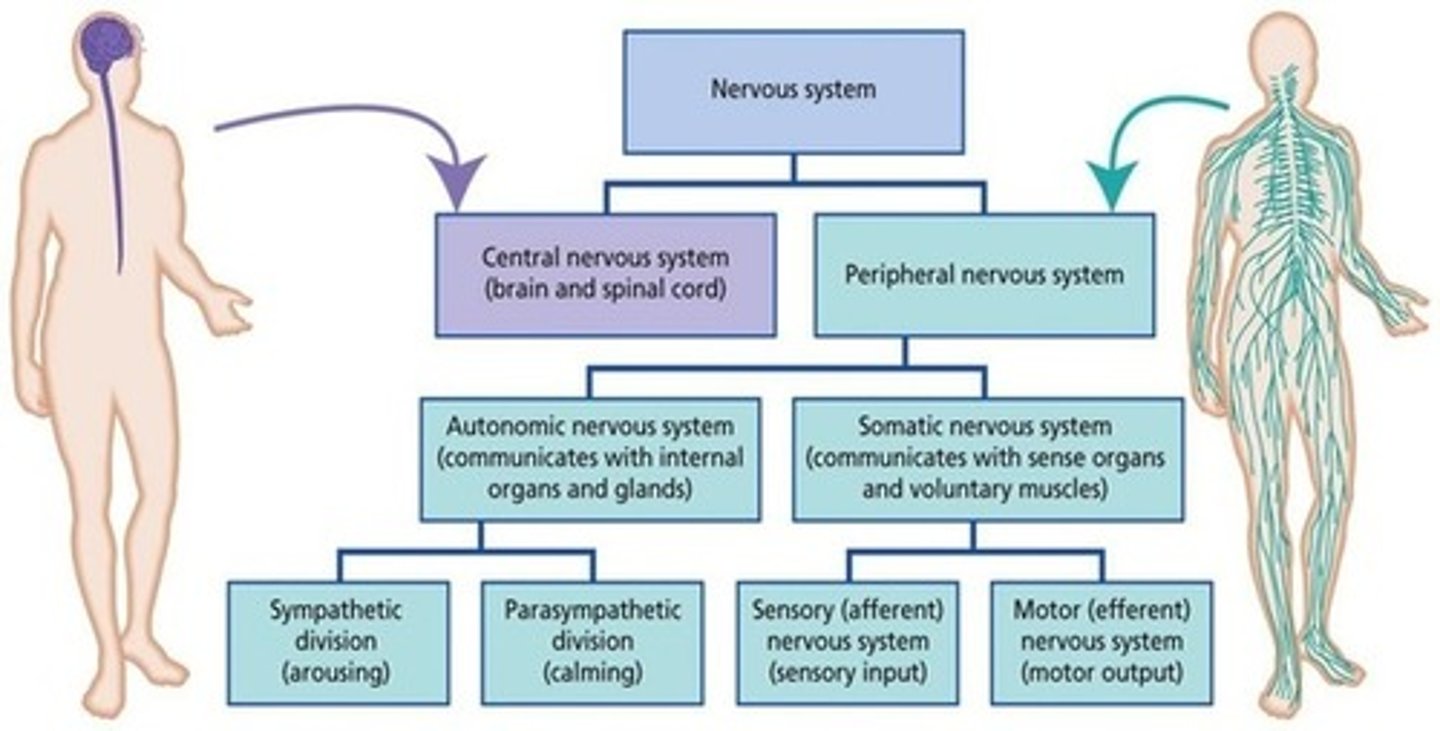
For the most part, how much consciousness is involved in the autonomic nervous system?
Very little to none. All these jobs are done without us "telling" the body to do it.
The Parasympathetic nervous system's first neuron starts in the ______. The Sympathetic nervous system's first neuron starts in the ______.
(A) Middle of the spinal cord, Middle of the spinal cord
(B) Middle of the spinal cord, Brain stem & lower spinal cord
(C) Brain stem & lower spinal cord, Brain stem & lower spinal cord
(D) Brain stem & lower spinal cord, Middle of the spinal cord
(D) Brain stem & lower spinal cord, Middle of the spinal cord
The Parasympathetic nervous system's first neuron starts in the Brain stem & lower spinal cord. The Sympathetic nervous system's first neuron starts in the Middle of the spinal cord.
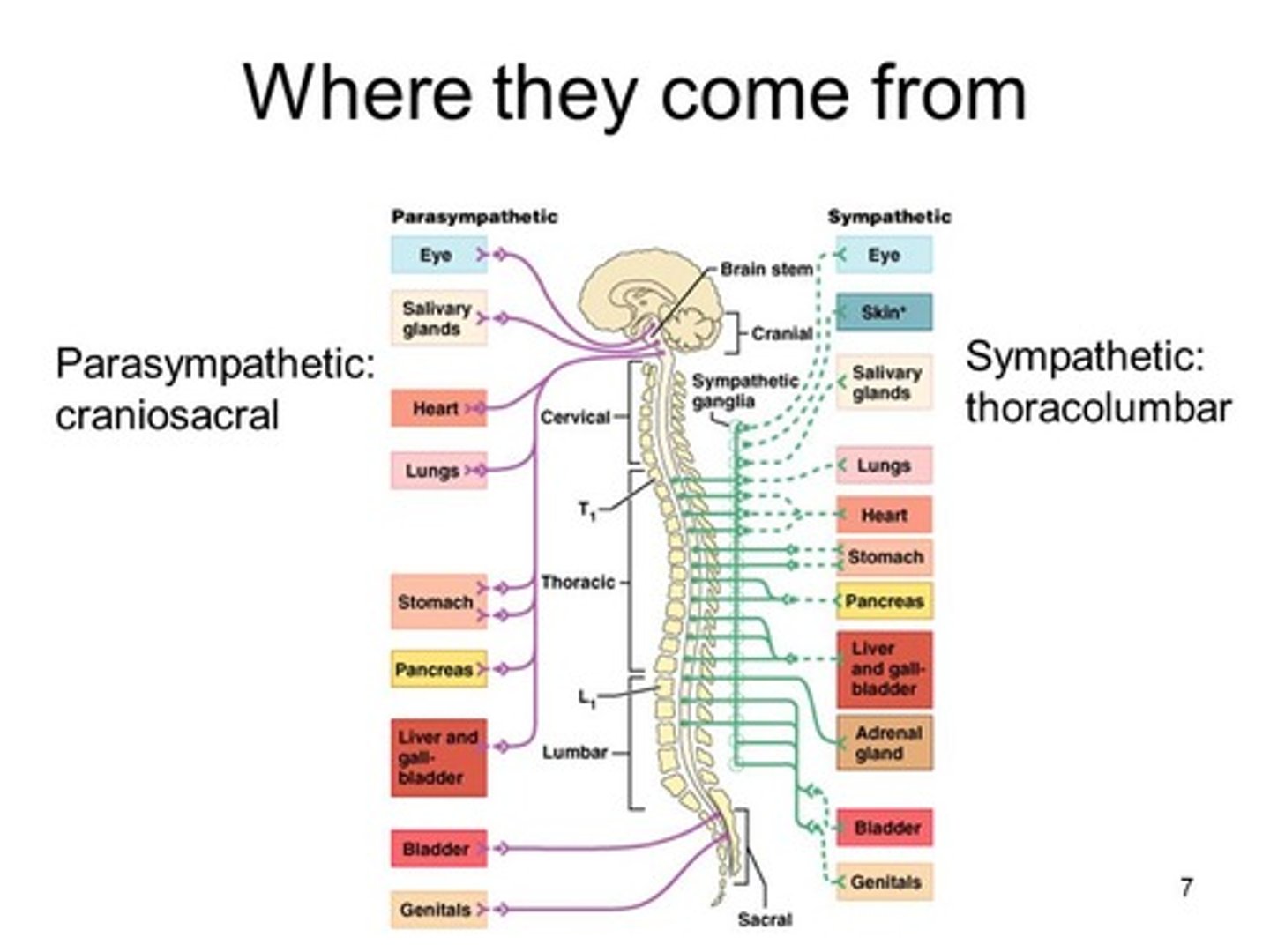
The Parasympathetic nervous system has a _____ first axon, and _____ second axon.
(A) long, long
(B) long, short
(C) short, short
(D) short, long
(B) long, short
The Parasympathetic nervous system's first neuron has a long first axon, and short second axon.
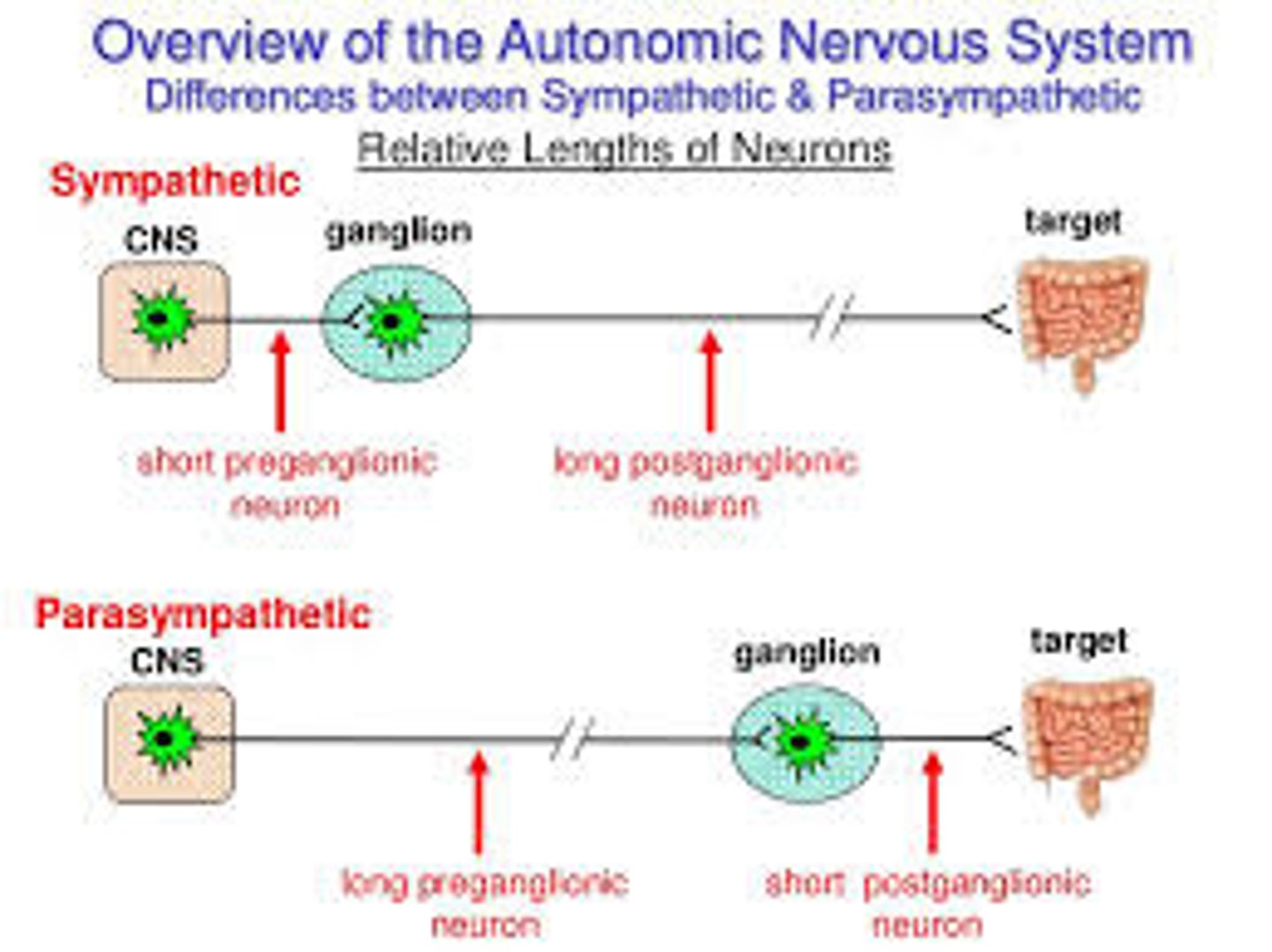
Why might a signal from the sympathetic nervous system result in a body-wide response faster than a signal from the parasympathetic nervous system? (hint: think about the sympathetic trunk)
The sympathetic nervous system's ganglia are all connected. This connected system of ganglia is called the sympathetic trunk, which would allow signals to spread between all the sympathetic neurons very quickly.
The Sympathetic nervous system has a _____ first axon, and _____ second axon.
(A) long, long
(B) long, short
(C) short, short
(D) short, long
(D) short, long
The Sympathetic nervous system has a short first axon, and a long second axon.
Threatening situations usually activate the Parasympathetic or Sympathetic Nervous System?
The Sympathetic Nervous System
Think: "Fight or Flight"
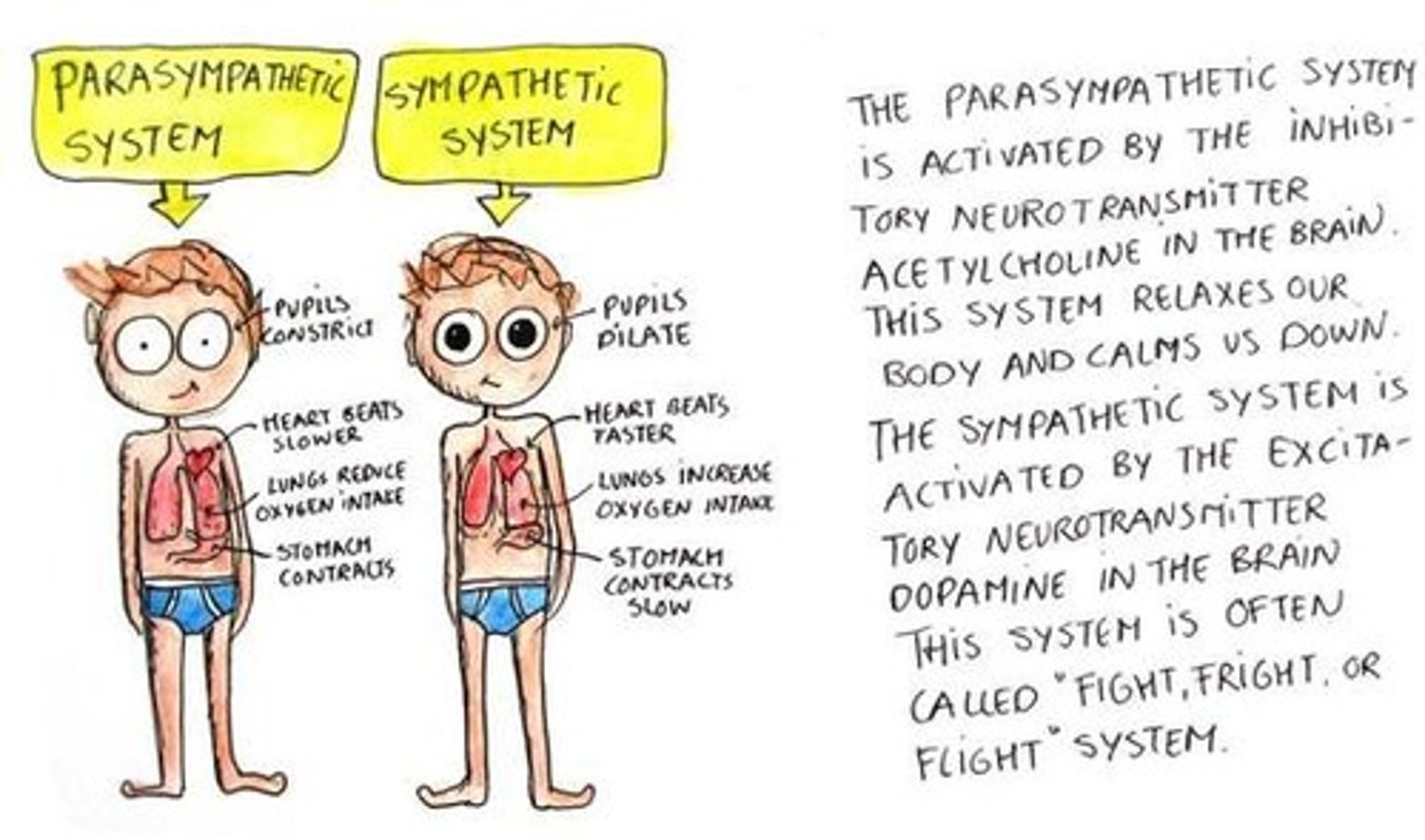
Calming and allowing the body to return back to homeostasis is usually activated by the Parasympathetic or Sympathetic Nervous System
The Parasympathetic Nervous System
Think: "Rest and Digest"
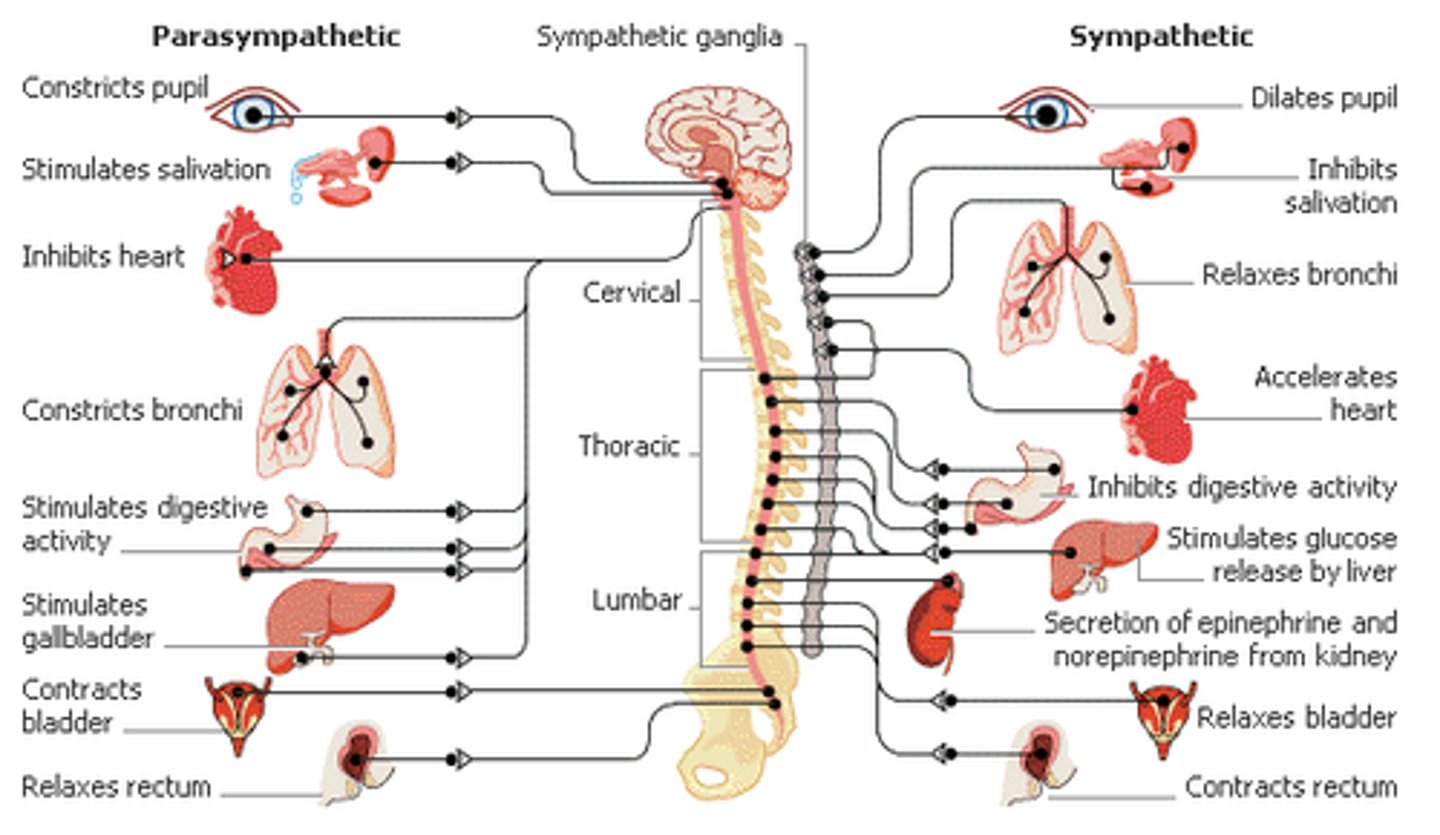
A sympathetic nervous system response would likely result in which of the following:
I. Increased blood flow to the intestines
II. Increased cardiac output
III. Increased pupil dilation
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) II and III Only
(D) II and III Only
A sympathetic nervous system response would likely result in the following:
(1) DECREASED blood flow to the intestines
(2) Increased cardiac output
(3) Increased pupil dilation
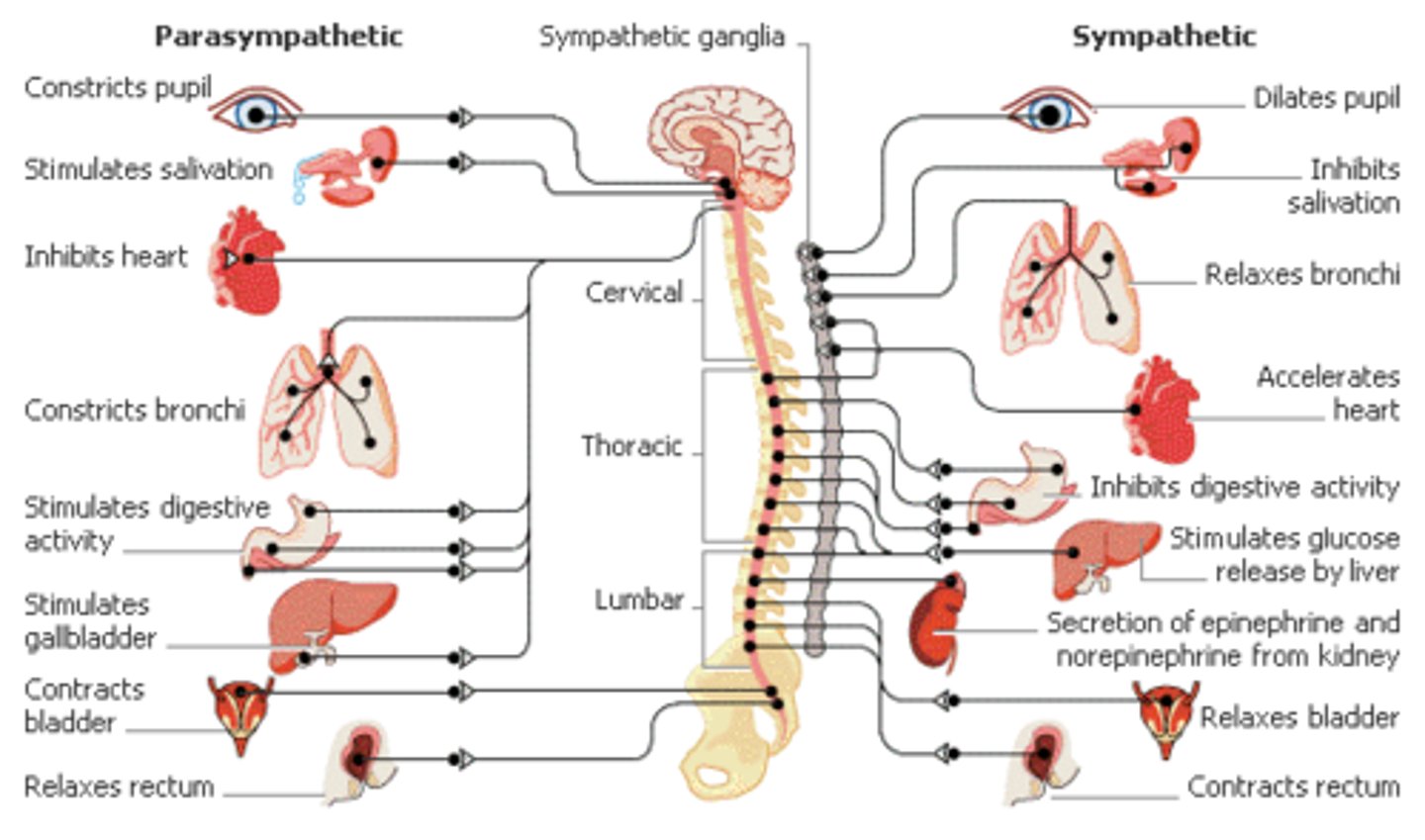
A parasympathetic nervous system response would likely result in which of the following:
I. Decreased sweating
II. Decreased salivation
III. Decreased blood flow to the kidney
(A) I Only
(B) II Only
(C) I and II Only
(D) II and III Only
(A) I Only
A parasympathetic nervous system response would likely result in:
(1) Decreased sweating
(2) INCREASED salivation
(3) INCREASED blood flow to the kidney
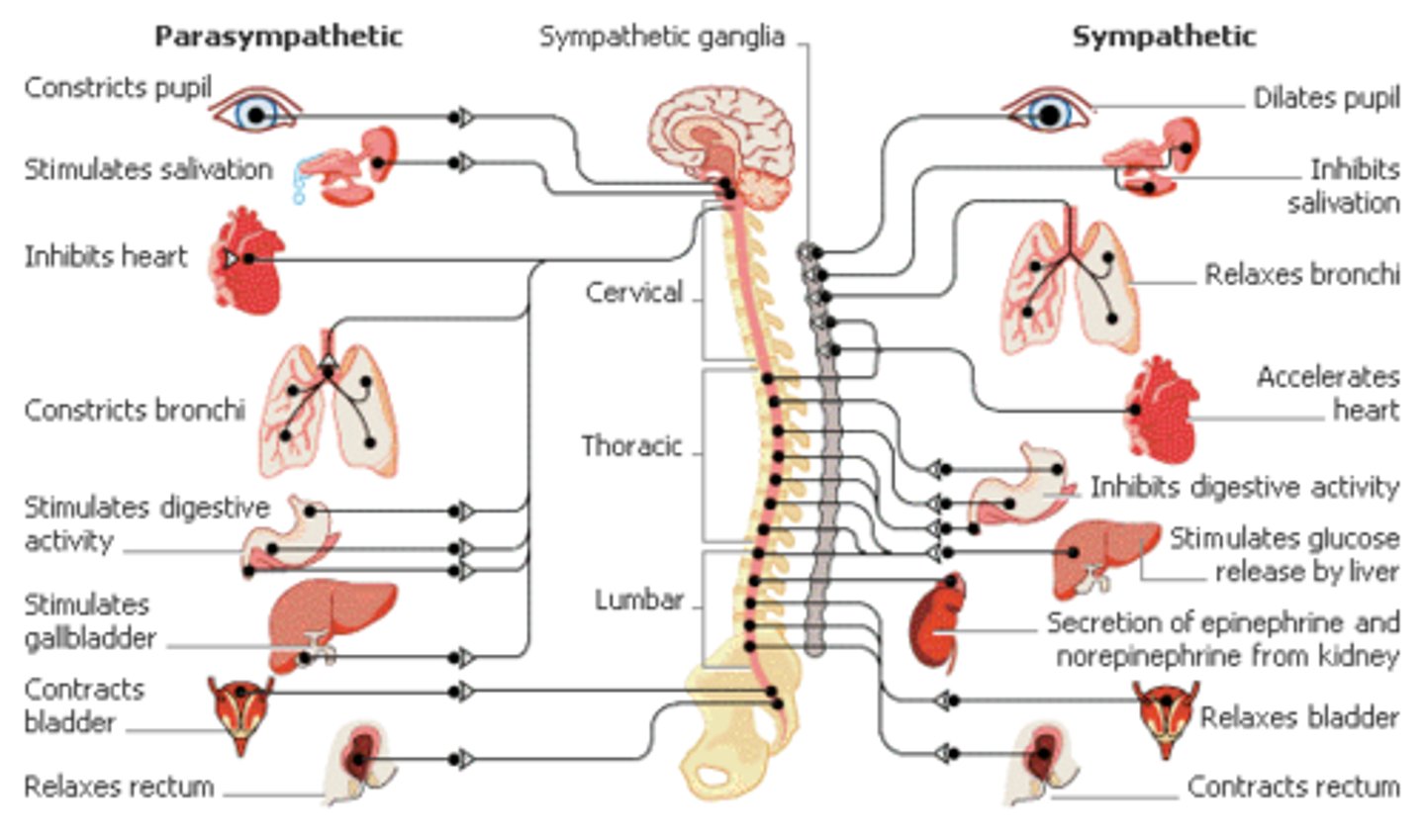
Unmyelinated neuron somas are located within _____________. Myelinated Axons are located within _____________.
(A) gray matter, gray matter
(B) gray matter, white matter
(C) white matter, white matter
(D) white matter, gray matter
(B) gray matter, white matter
Unmyelinated neuron somas are located within gray matter. Myelinated Axons are located within white matter.
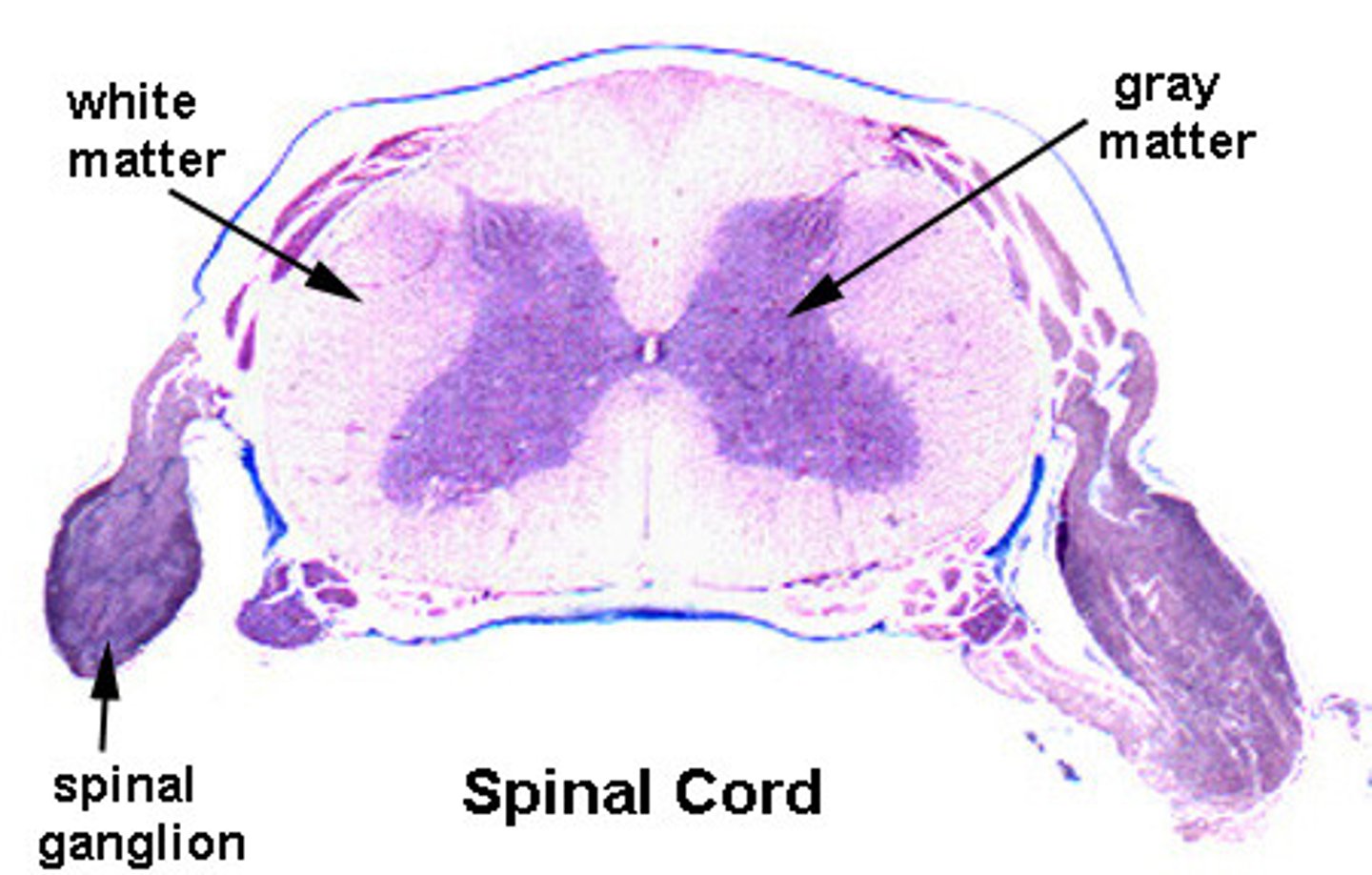
How do the locations of the gray and white matter in the spinal cord and brain differ?
Spinal cord --
Gray matter inside/white matter outside
Brain --
gray matter outside/white matter inside
They are opposite.
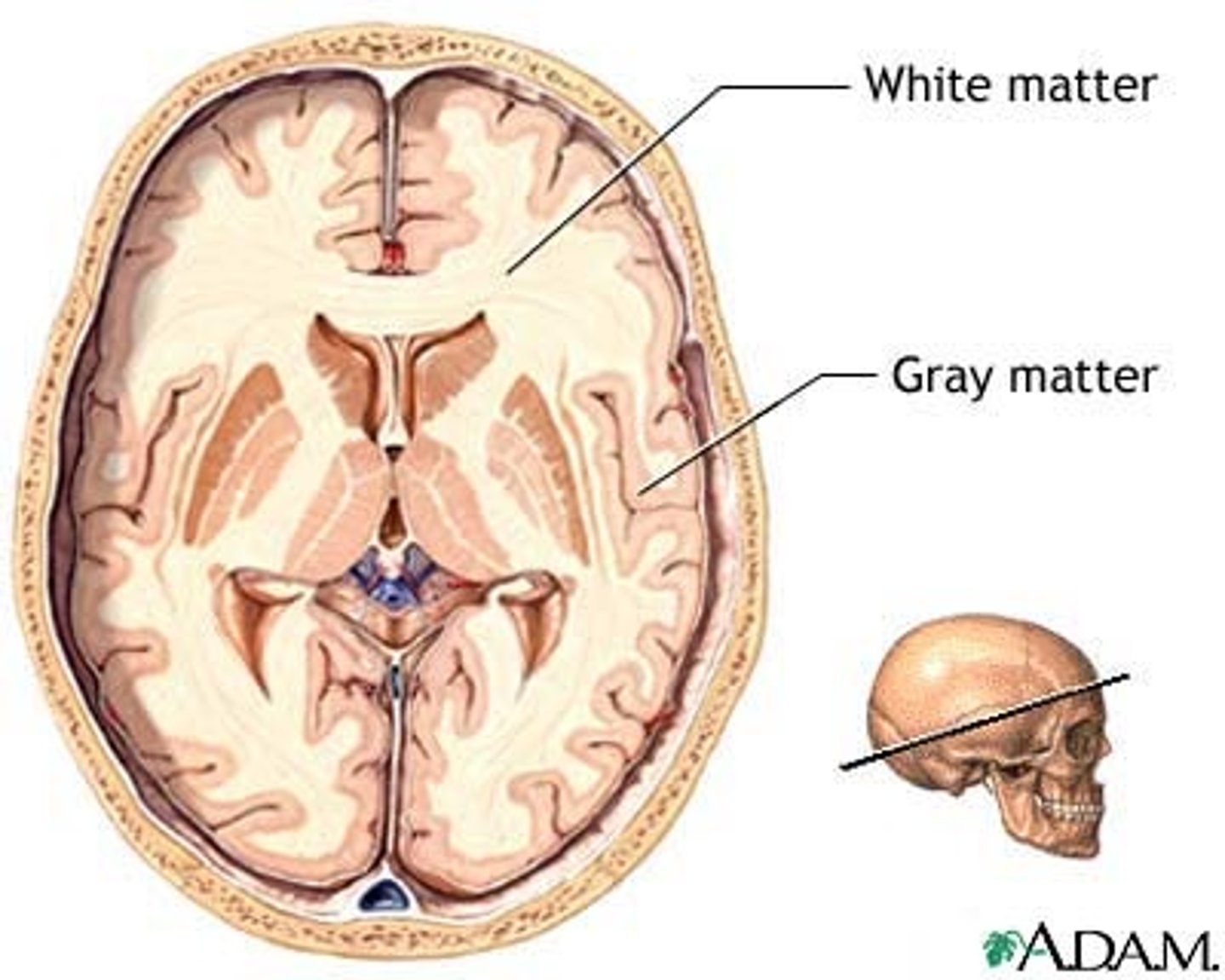
The gray matter on the outside of the brain is called _______. The little pockets of gray matter that are found deep in the brain are called ______.
(A) Cortex, Cortex
(B) Cortex, Nuclei
(C) Nuclei, Nuclei
(D) Nuclei, Cortex
(B) Cortex, Nuclei
The gray matter on the outside of the brain is called Cortex. The little pockets of gray matter that are found deep in the brain are called Nuclei.
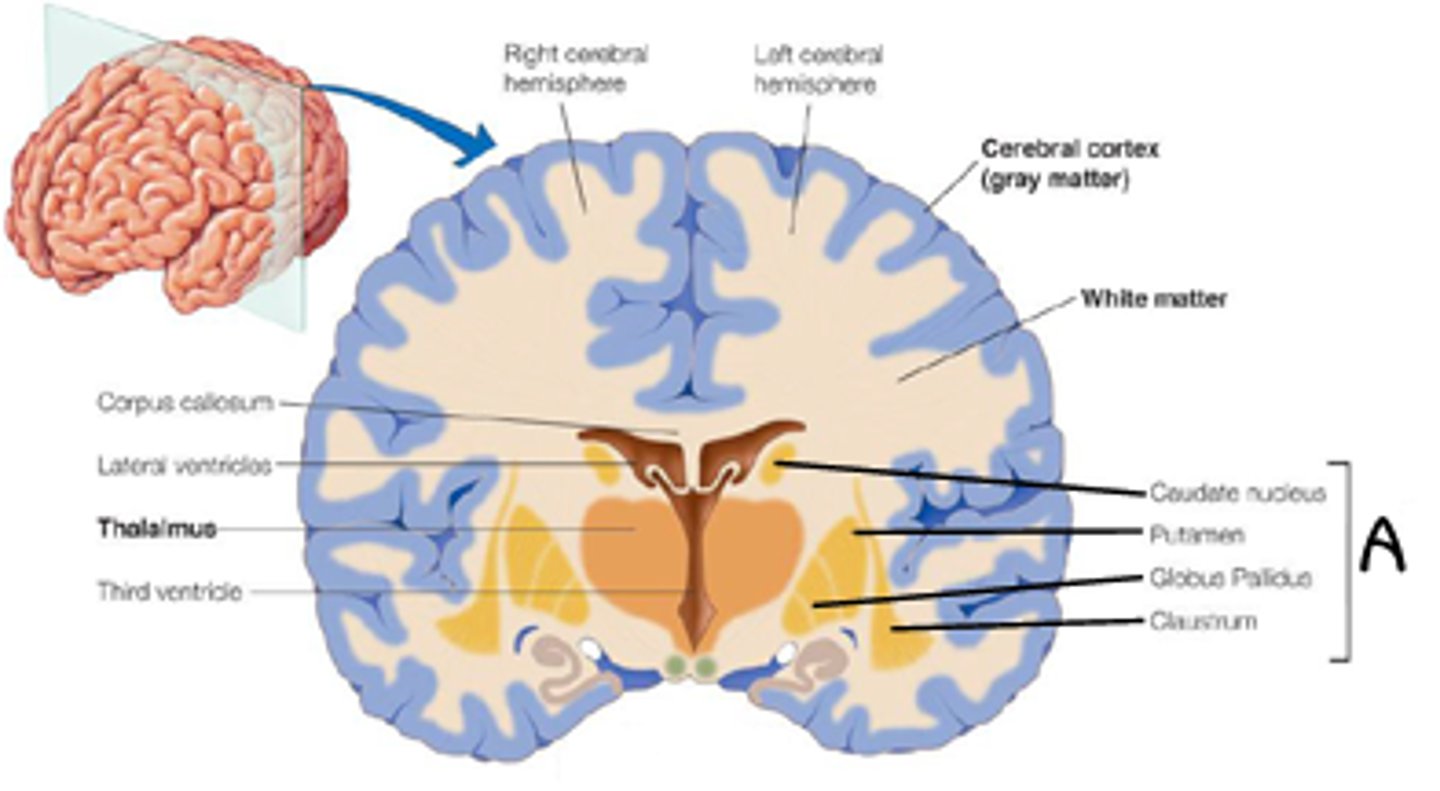
The part of the gray matter that is involved in higher cognition is called the ______. The part of the white matter involved in transmitting similar messages long distances in the central nervous system is called a ______.
(A) Nuclei, Somatosensory neuron
(B) Tract, Nuclei
(C) Somatosensory Neuron, Cortex
(D) Cortex, Tract
(D) Cortex, Tract
The part of the gray matter that is involved in higher cognition is called the Cortex. The part of the white matter involved in transmitting similar messages long distances in the central nervous system is called a Tract.
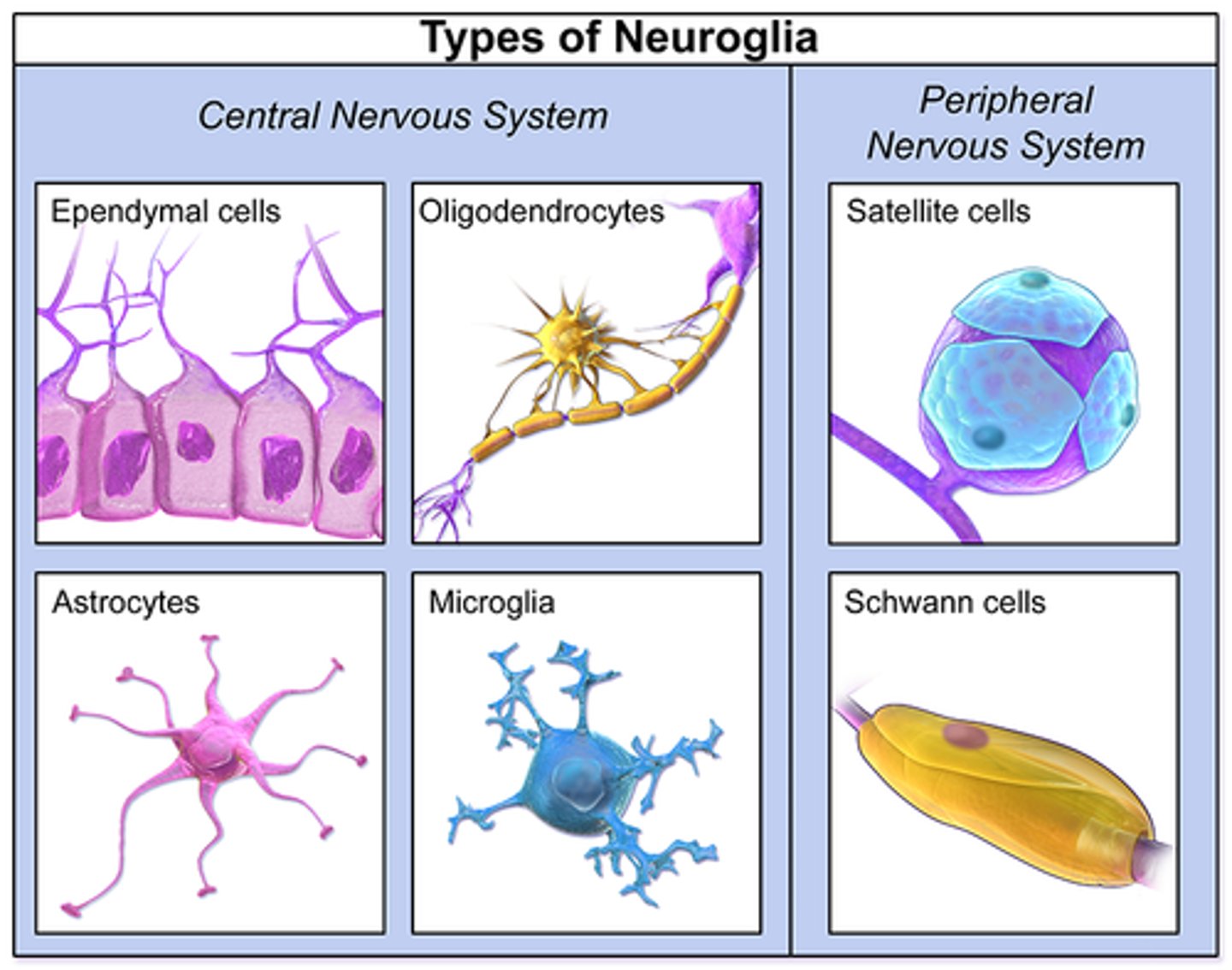
CRB The brain contains a variety of glial cell types to support the neurons. Which of the following is NOT a type of glial cell in the Central Nervous System?
(A) Astrocyte
(B) Ependymal Cell
(C) Parenchymal Cell
(D) Oligodendrocyte
(C) Parenchymal Cell (type of plant cell)
Four major types of Glial Cells are Astrocytes, Ependymal Cells, Microglia and Oligodendrocytes