Unit 4 (Part 3) Vocab Quizlet - 4.7 & 4.8
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
motivation
a need or desire that energizes and directs behavior

instinct
a complex behavior that is rigidly patterned throughout a species and is unlearned

physiological need
a basic bodily requirement

drive-reduction theory
the idea that a physiological need creates an aroused tension state (a drive) that motivates an organism to satisfy the need
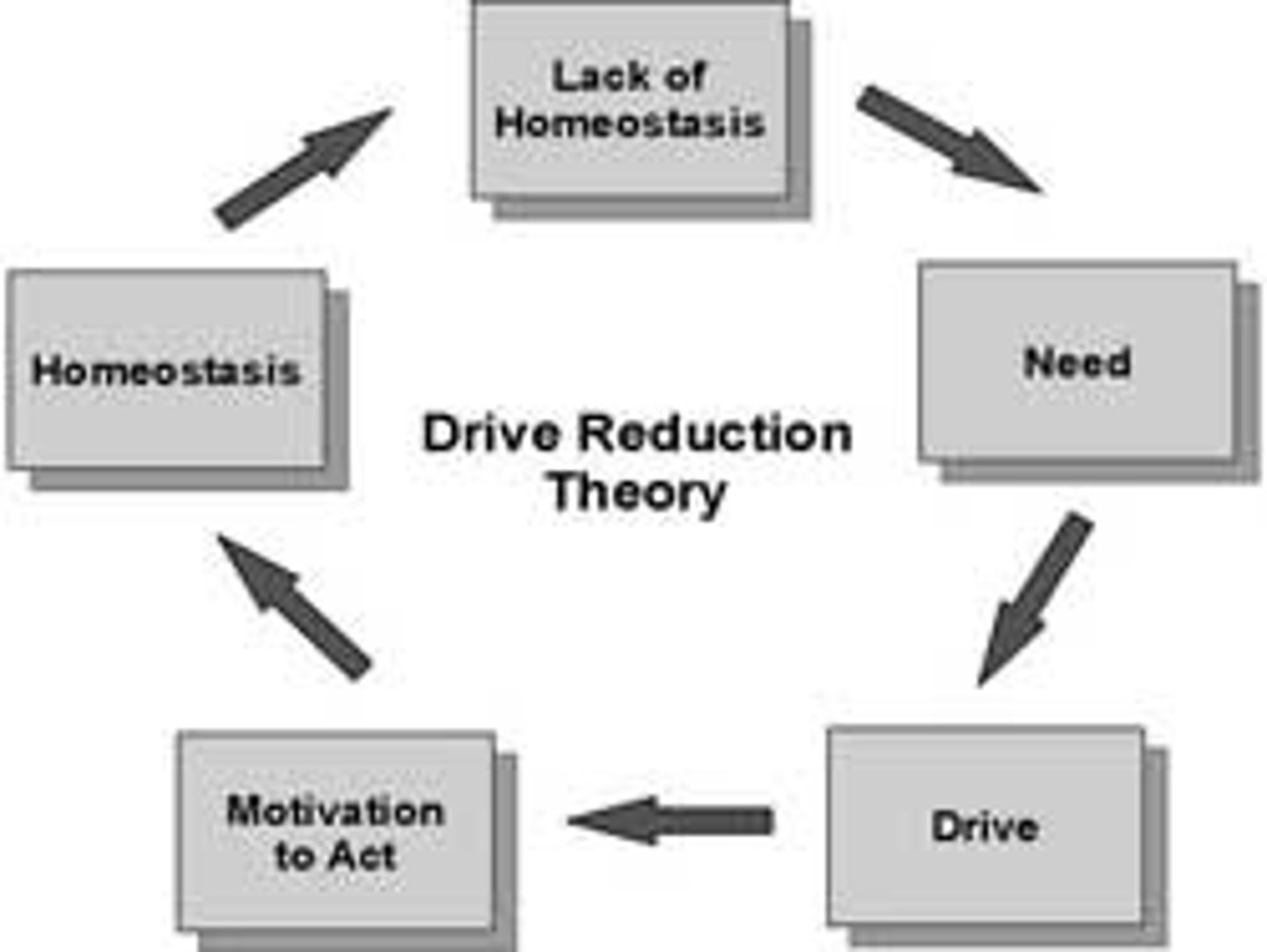
homeostasis
A tendency to maintain a balanced or constant internal state; the regulation of any aspect of body chemistry, such as blood glucose, around a particular level
incentive
a positive or negative environmental stimulus that motivates behavior

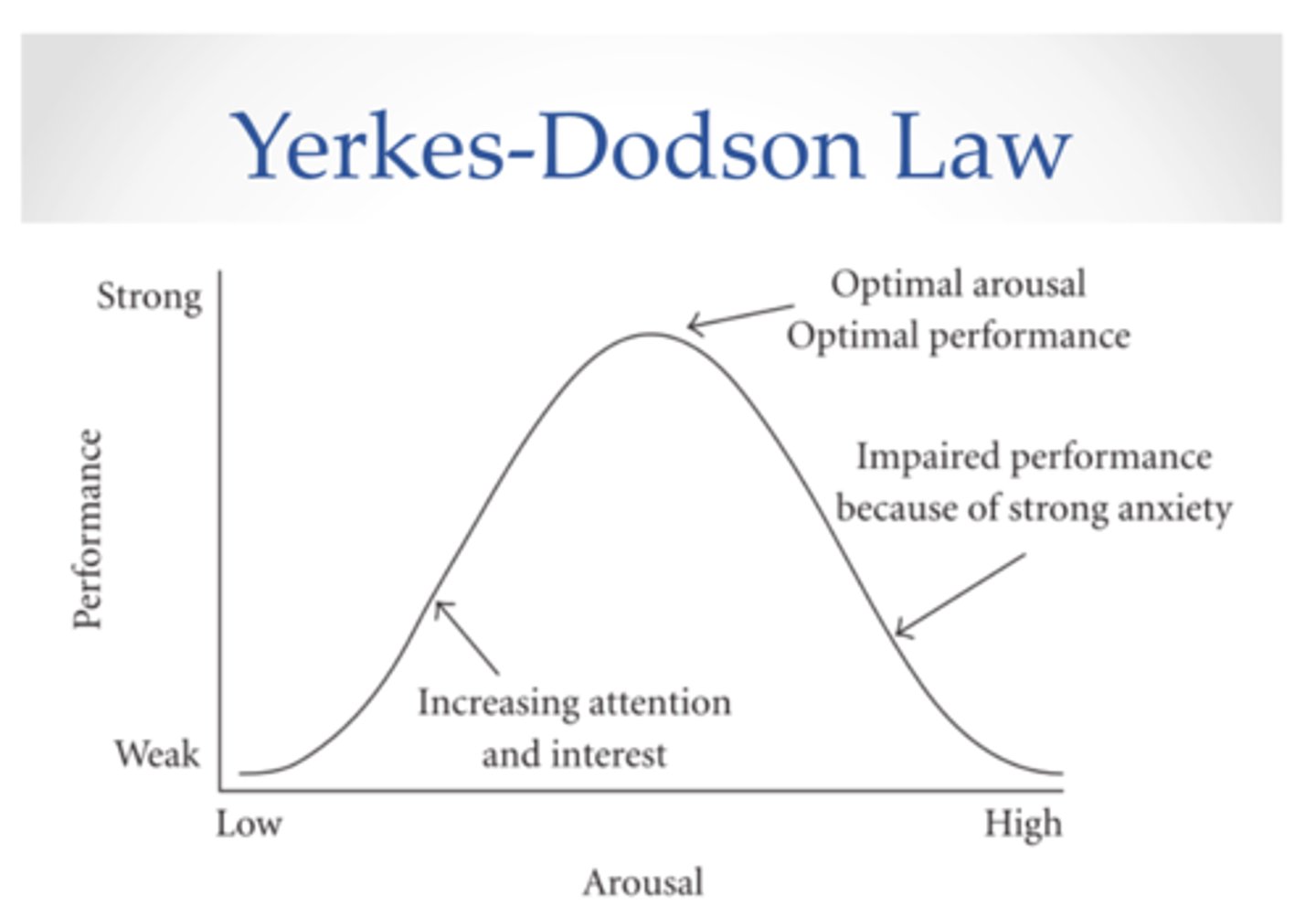
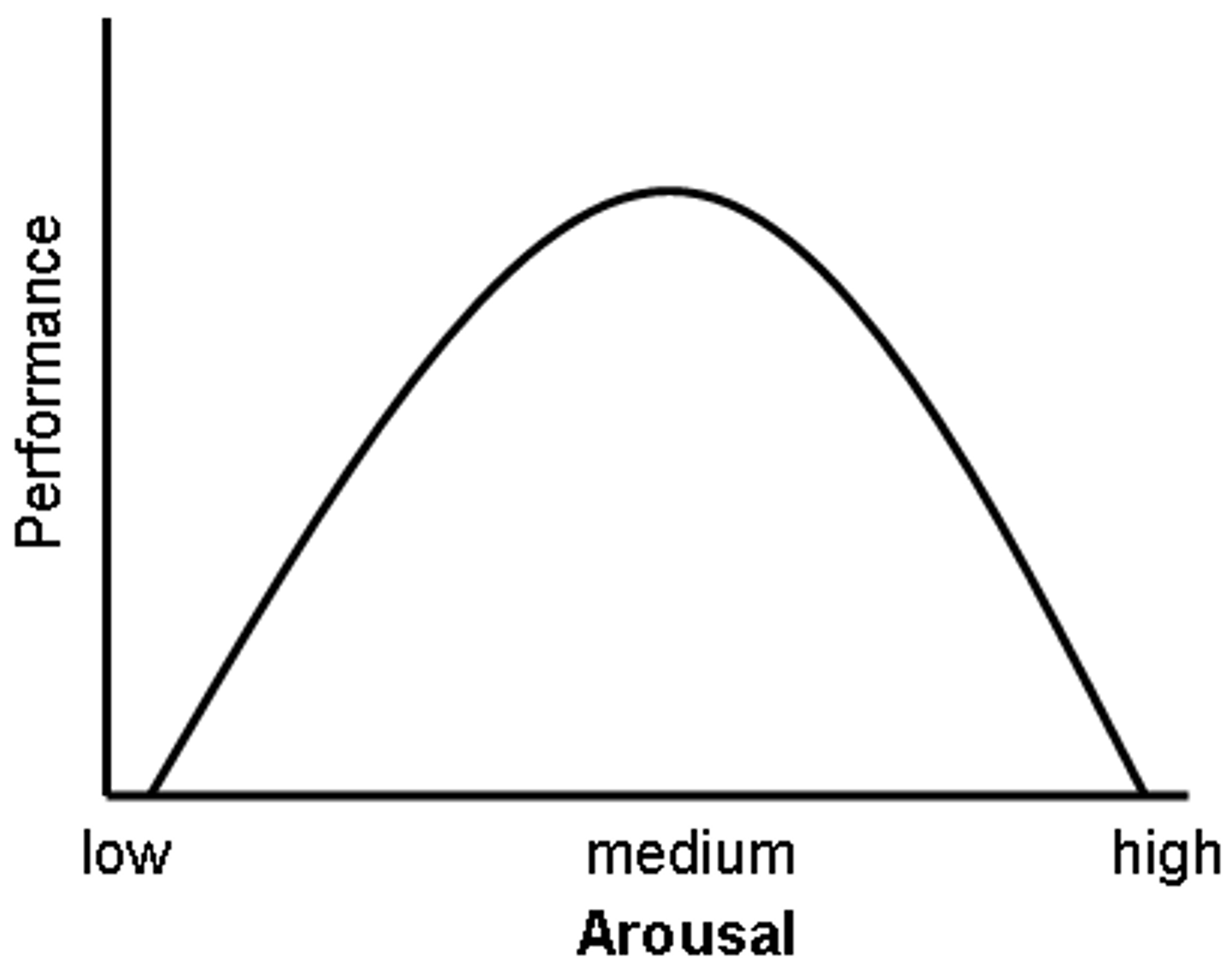
Yerkes-Dodson Law
the principle that performance increases with arousal only up to a point, beyond which performance decreases
cultural awareness
An in-depth self-examination of one's own background, recognizing biases, prejudices, and assumptions about other people

affiliation need
the need to build relationships and to feel part of a group

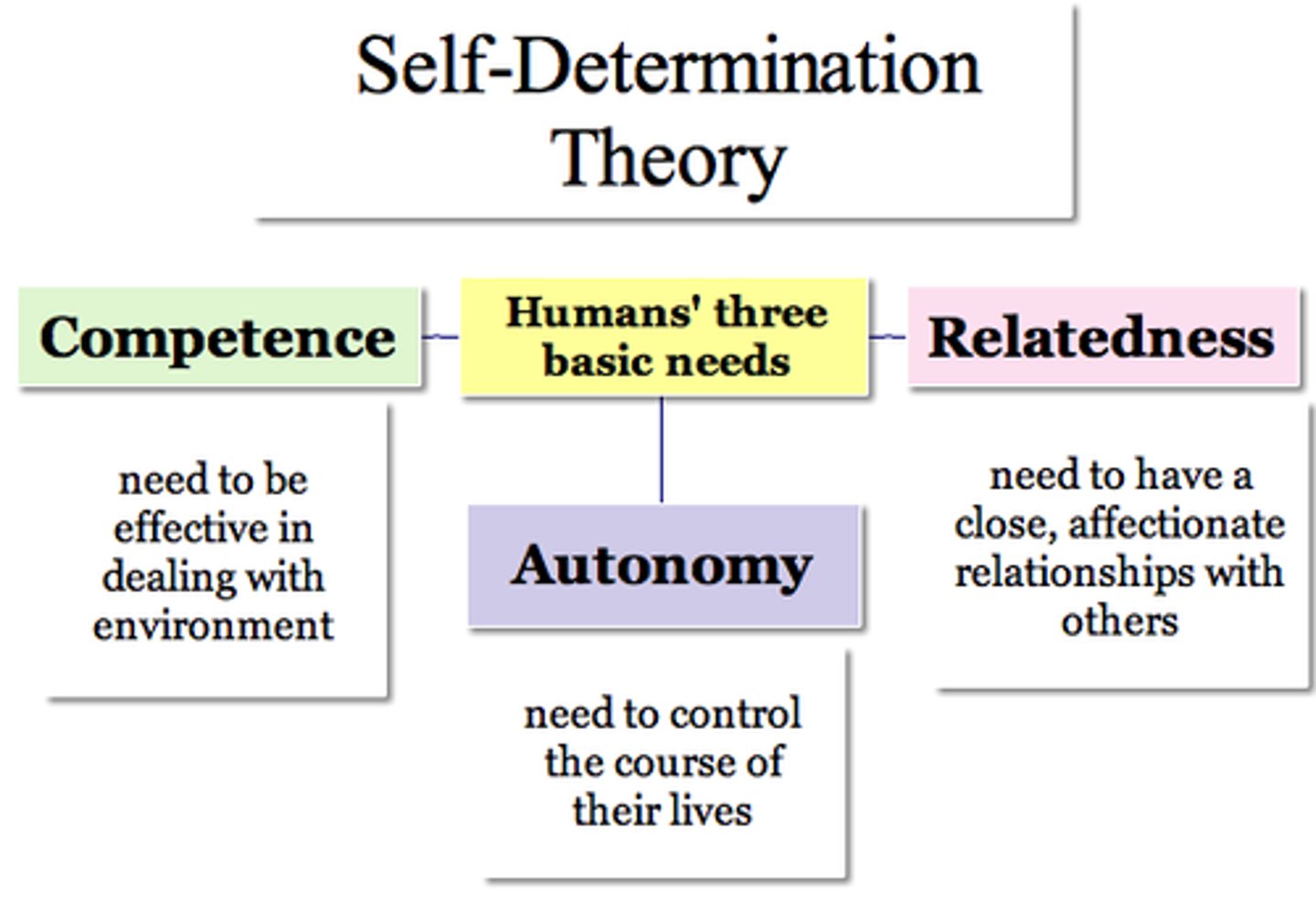
self-determination theory
a theory of motivation that is concerned with the beneficial effects of intrinsic motivation and the harmful effects of extrinsic motivation
intrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior effectively for its own sake

extrinsic motivation
a desire to perform a behavior to receive promised rewards or avoid threatened punishment

ostracism
deliberate social exclusion of individuals or groups
achievement motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment: for mastery of things, people, or ideas; for attaining a high standard

grit
in psychology, grit is passion and perseverance in the pursuit of long-term goals

glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues. When its level is low, we feel hunger.

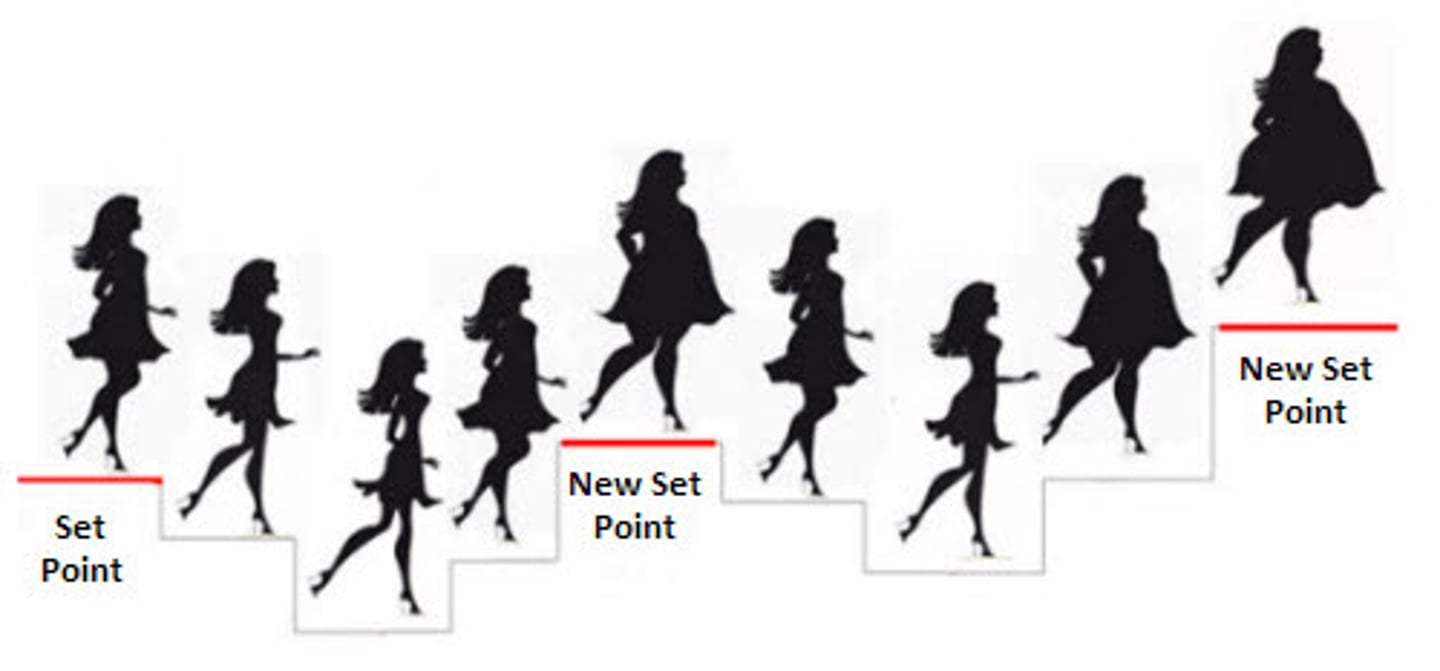
set point
the point at which an individual's "weight thermostat" is supposedly set. When the body falls below this weight, an increase in hunger and a lowered metabolic rate may act to restore the lost weight.
basal metabolic rate
the body's resting rate of energy expenditure

obesity
having an excess amount of body fat

emotion
a response of the whole organism, involving (1) physiological arousal, (2) expressive behaviors, and (3) conscious experience

the spillover effect
when one emotion continues from one situation to another; more happy about getting job after running as opposed to just waking up

emotional arousal
the arousal of strong emotions and emotional behavior
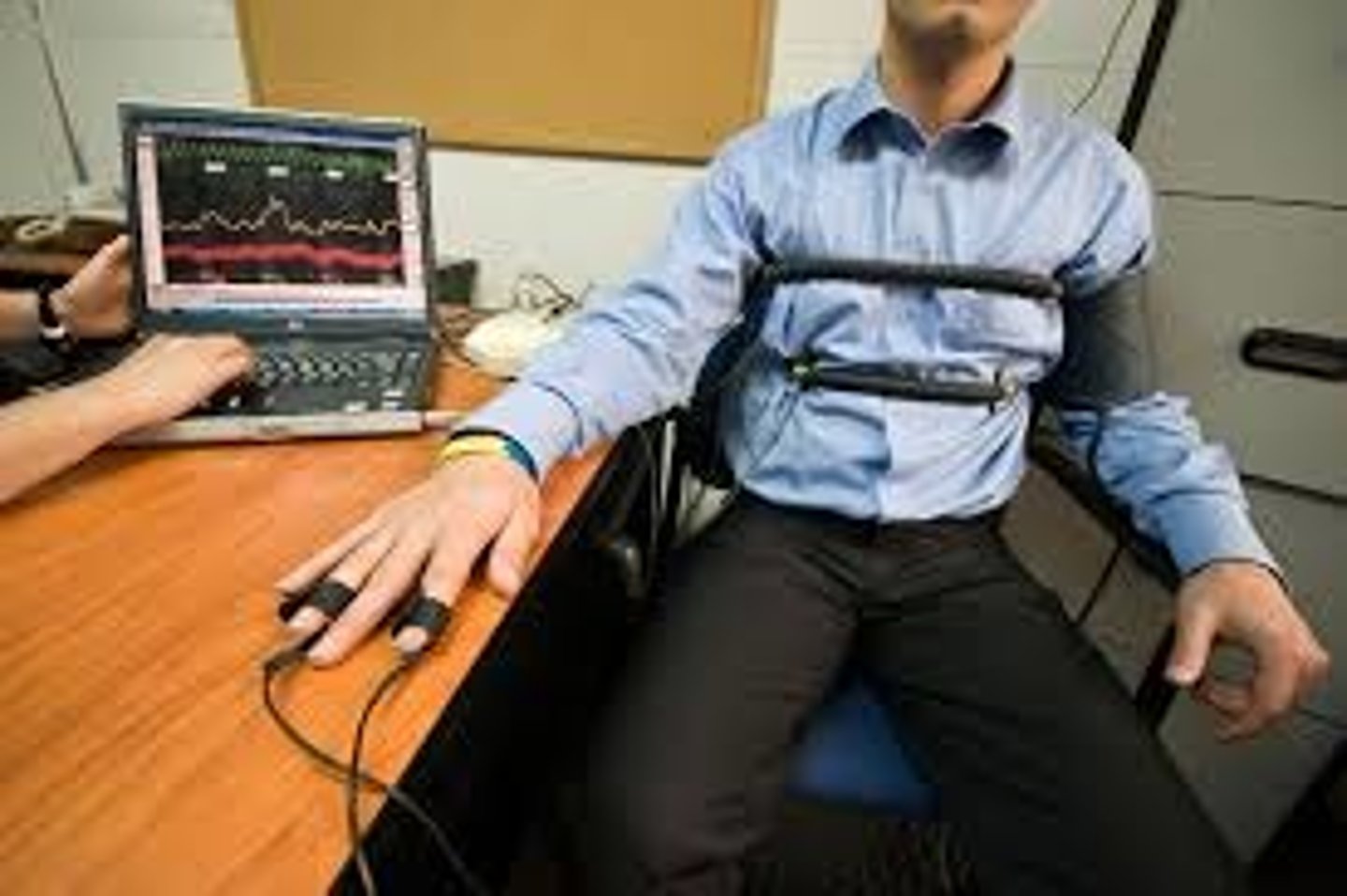
polygraph
a machine, commonly used in attempts to detect lies, that measures several of the physiological responses accompanying emotion (such as perspiration and cardiovascular and breathing changes).

facial feedback effect
the tendency of facial muscle states to trigger corresponding feelings such as fear, anger, or happiness
behavior feedback effect
the tendency of behavior to influence our own and others' thoughts, feelings, and actions

human motivation
behavior involves a cycle of tension-states or need-states followed by activity and relief
approach-approach conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two attractive alternatives

approach-avoidance conflict
A conflict in which there are both appealing and negative aspects to the decision to be made.

avoidance-avoidance conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two distasteful alternatives

sensation-seeking
the pursuit of experiences that are novel or exciting

experience seeking
the tendency to seek novel experiences through the mind and the senses

thrill or adventure seeking
Desire for physical risk and adventure

disinhibition
preference for spontaneous and uninhibited activities

boredom susceptibility
aversion to routine or monotonous experiences

hormones
regulate feelings of hunger and satiety
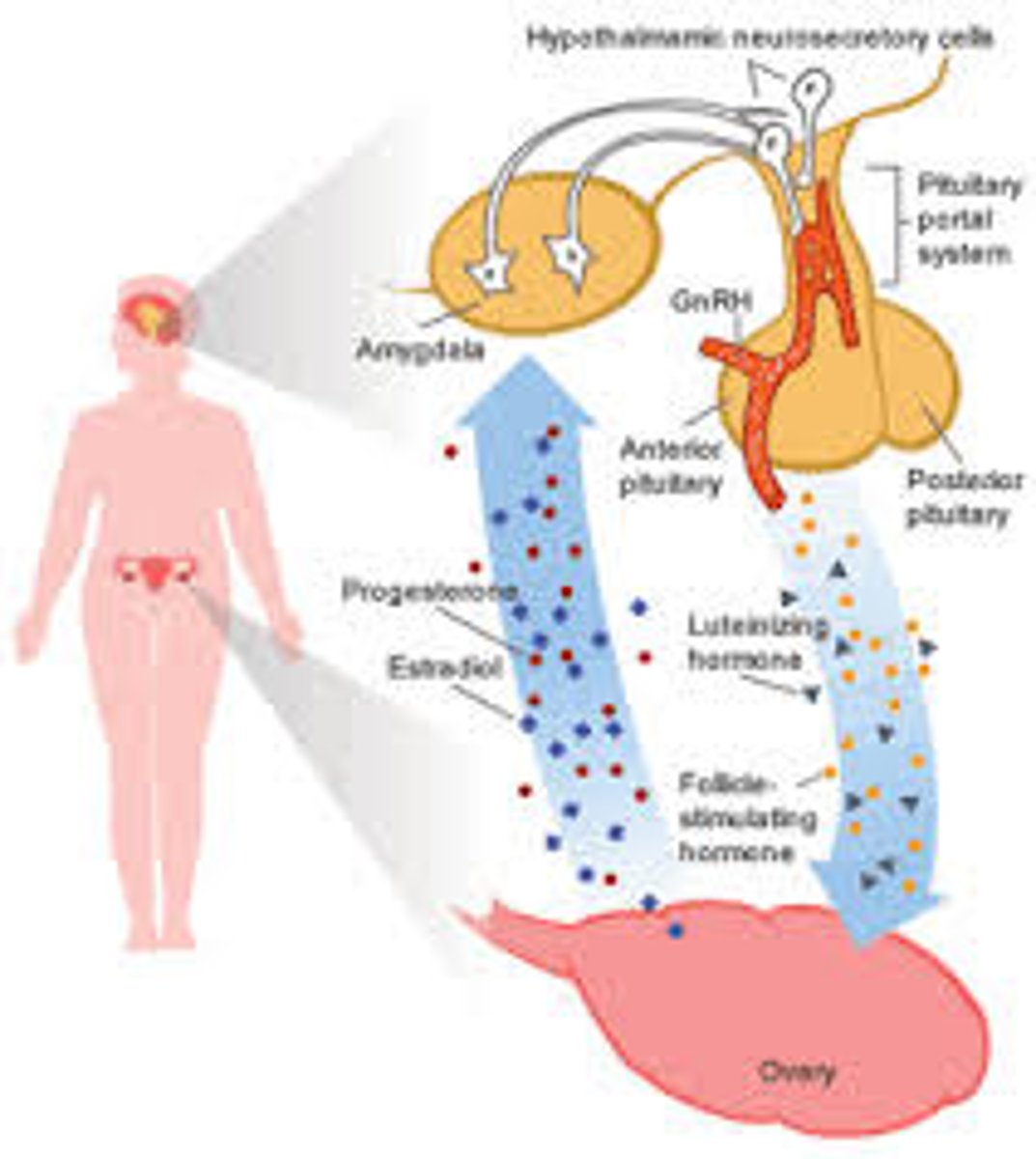
ghrelin
stimulates hunger. "If your stomach is a growling, it ghrelin"

leptin
promotes satiety

regulation
controlled by the hypothalamus via the pituitary gland
external factors
influence the behavior of eating
the broaden-and-build theory
positive emotions prompt people to consider novel solutions to their problems
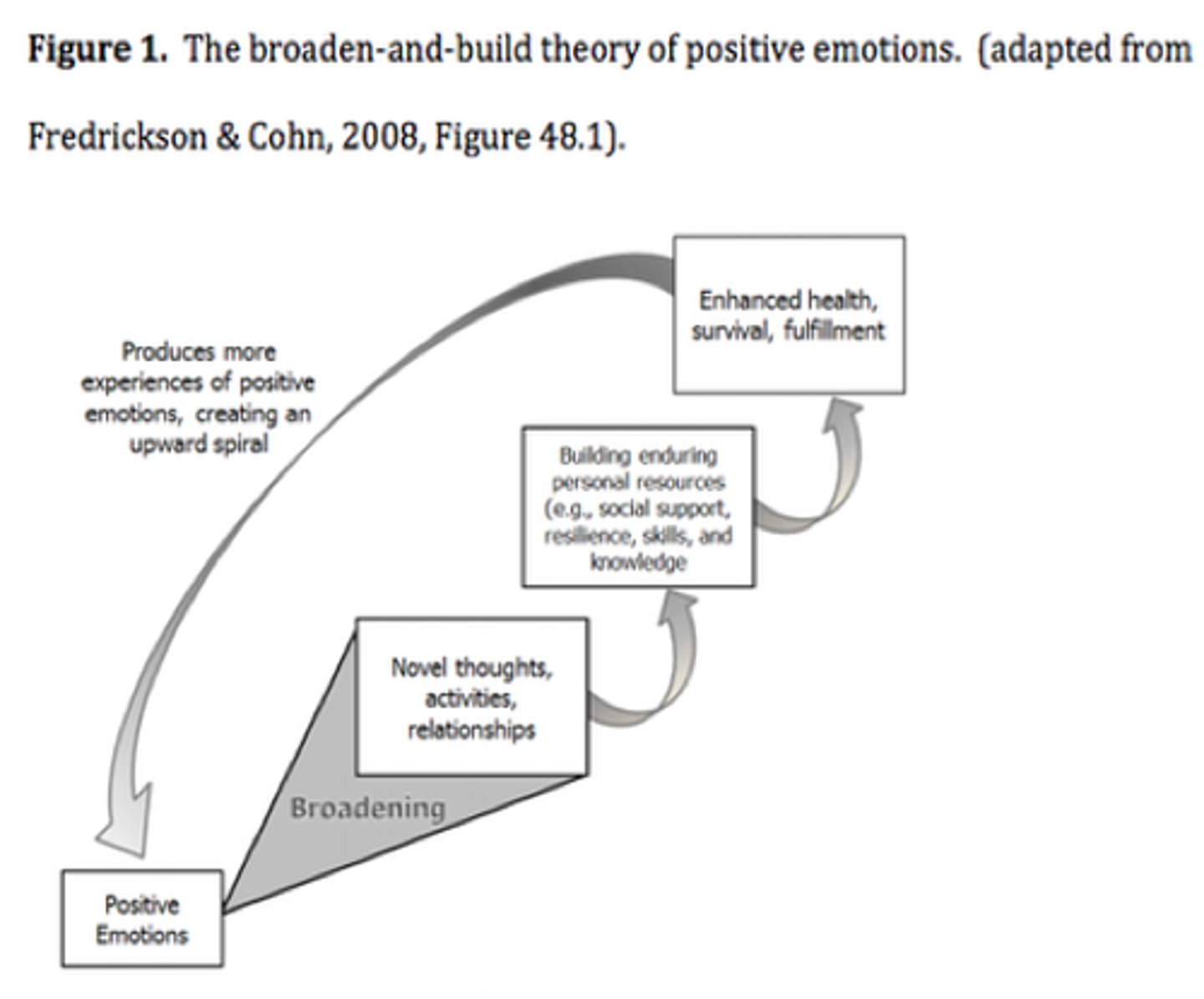
positive emotions
broaden awareness and encourage new actions and thoughts

negative emotions
reduce awareness and narrow thinking and action

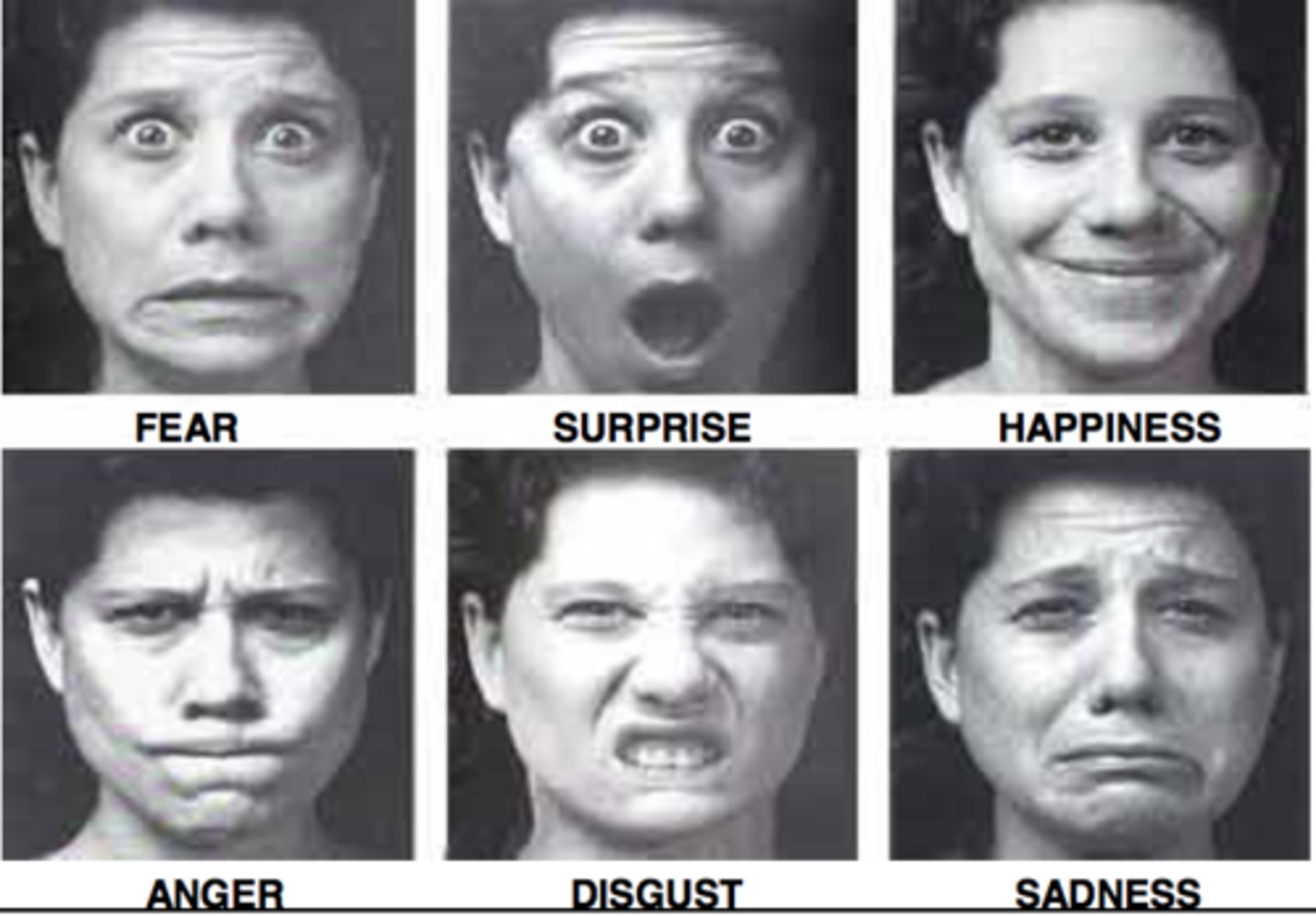
emotional expressions
outward signs that an emotion is occurring

display rules
social norms dictating how emotions should be expressed

elicitors of emotion
factors that trigger emotional responses