Maternal Care and Attachment
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
attachment (Bowlby)
strong disposition to seek proximity to and contact with a specific figure and to do so in certain situations
2
New cards
attachment in infants
- relatively enduring emotional bond of the infant to the caregiver
- enables the infant to deal with stressors and negative emotions
- evolutionary need: dependent on adults for caregiving and protection
- virtually all children develop attachment bonds
- fully developed ~12 months of age
- enables the infant to deal with stressors and negative emotions
- evolutionary need: dependent on adults for caregiving and protection
- virtually all children develop attachment bonds
- fully developed ~12 months of age
3
New cards
Normative development of attachment phases
Phase 1: (0-8 weeks) initial preattachment phase
Phase 2: (2-12 months) attachment in the making
Phase 3: (\>12 months) clear-cut attachment
Phase 2: (2-12 months) attachment in the making
Phase 3: (\>12 months) clear-cut attachment
4
New cards
Phase 1: (0-8 weeks) initial pre-attachment phase
- caregivers maintain proximity
- newborn is equipped to be responsive to others, and to elicit caregiving and affection
- some ability to discriminate between caregivers, not yet relevant for their needs to be met
- newborn is equipped to be responsive to others, and to elicit caregiving and affection
- some ability to discriminate between caregivers, not yet relevant for their needs to be met
5
New cards
Phase 2: (2-12 months) attachment in the making
* more clearly discriminates between caregivers
* build up expectations of how needs will be met
* directing their attachment behaviors, actively seeking attention, not only passively responding
* more complex behaviors, less crying
* build up expectations of how needs will be met
* directing their attachment behaviors, actively seeking attention, not only passively responding
* more complex behaviors, less crying
6
New cards
Phase 3: (\>12 months) clear-cut attachment
- attachment fully developed
- strange situation can be performed
- strange situation can be performed
7
New cards
Circle of Security
parent attending to the toddlers needs; secure base in non-stressful situations and safe haven during stress
\
uncomplicated contact seeking and free exploration
\
uncomplicated contact seeking and free exploration
8
New cards
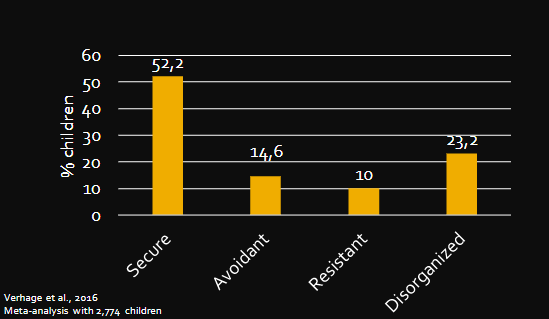
Attachment classifications
A) Avoidant attachment
B) Secure attachment
C) Resistant attachment
D) Disorganized attachment
B) Secure attachment
C) Resistant attachment
D) Disorganized attachment
9
New cards
A) Avoidant attachment
- strategy: minimize attachment
- interaction history: caregiver rejecting, unavailable, less holding, less responding to infant's cries, controlling
- interaction history: caregiver rejecting, unavailable, less holding, less responding to infant's cries, controlling
10
New cards
C) Resistant attachment
- strategy: maximize attachment behavior
- interaction history: caregiver inconsistent, angry, anxious
- interaction history: caregiver inconsistent, angry, anxious
11
New cards
D) Disorganized attachment
* strategy: no strategy (fear of caregiver, contradictory behaviors)
* interaction history: caregiver unpredictable, abusive, frightening, contradictory cues, role confusion
* --> fear in the attachment relationship serves as the driving force behind disorganization
* interaction history: caregiver unpredictable, abusive, frightening, contradictory cues, role confusion
* --> fear in the attachment relationship serves as the driving force behind disorganization
12
New cards
reactive attachment disorder (RAD)
children who are very withdrawn from their caregivers and who don't show proximity seeking or contact maintenance to the caregivers, even when highly distressed
13
New cards
disinhibited social engagement disorder
failure to show a preference for familiar caregivers even when the child is frightened or distressed
14
New cards
later outcomes through parent-infant regulatory processes
secure and insecure infants use different regulating behaviors when psychologically stressed:
\
external dyadic regulation of emotions and behavior --> internalizers --> self regulation
\
insecure attachment (ACD) ---> regulatory problems
\
external dyadic regulation of emotions and behavior --> internalizers --> self regulation
\
insecure attachment (ACD) ---> regulatory problems
15
New cards
later outcomes through internal working models
parent-infant attachment as prototype --\> internal working models --\> foundation for later relationships
16
New cards
experimental evidence for internal working models (Kirsh & Cassidy)
- secure children recalled stories about sensitive mother-child interactions better
- insecure children recall rejecting stories better
- insecure children recall rejecting stories better
17
New cards
later outcomes through biological processes
parent-infant attachment as cue of stress environment --\> adaptations related to reproductive success
18
New cards
life history theory
all about trade-offs, allocating resources and energy; optimal trade-offs depend on the environment
* safe /predictable environment → slow life history strategy
* harsh/unpredictable environment → fast life history strategy
* safe /predictable environment → slow life history strategy
* harsh/unpredictable environment → fast life history strategy
19
New cards
Jay Belsky et al., 2010
individuals who had been insecure infants initiated and completed pubertal development earlier compared with individuals who had been secure infants
20
New cards
precurses of attachment: central to attachment theory
a sensitive, responsive caregiver is of fundamental importance to the development of a secure attachment bond
21
New cards
Ainsworth rating scales of maternal sensitivity
1. Awareness of the signals
2. An accurate interpretation of them
3. An appropriate response
4. A prompt response
2. An accurate interpretation of them
3. An appropriate response
4. A prompt response
22
New cards
child characteristics: temperament, esp. negative affectivity
not proven to be a (major) contributor to attachment security
23
New cards
technological gap of sensitivity
quality, intensity, or context of measurement is suboptimal
24
New cards
domain gap of sensitivity
predictive elements of parenting not yet defined
25
New cards
intergenerational transmission of attachment (→ cycle of abuse)
this link across generations is partially explained by
- aspects of caregiving behaviors
- the caregiver's representation of their child
- aspects of caregiving behaviors
- the caregiver's representation of their child
26
New cards
cycle of abuse
connection between a parent's own history of abuse and an increased probability that the parent will mistreat their own child (~30-40%)
27
New cards
Verhage et al., 2016 attachment styles in children