3 - ANATOMY OF THE THORAX (BRS) 2025
1/135
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
136 Terms
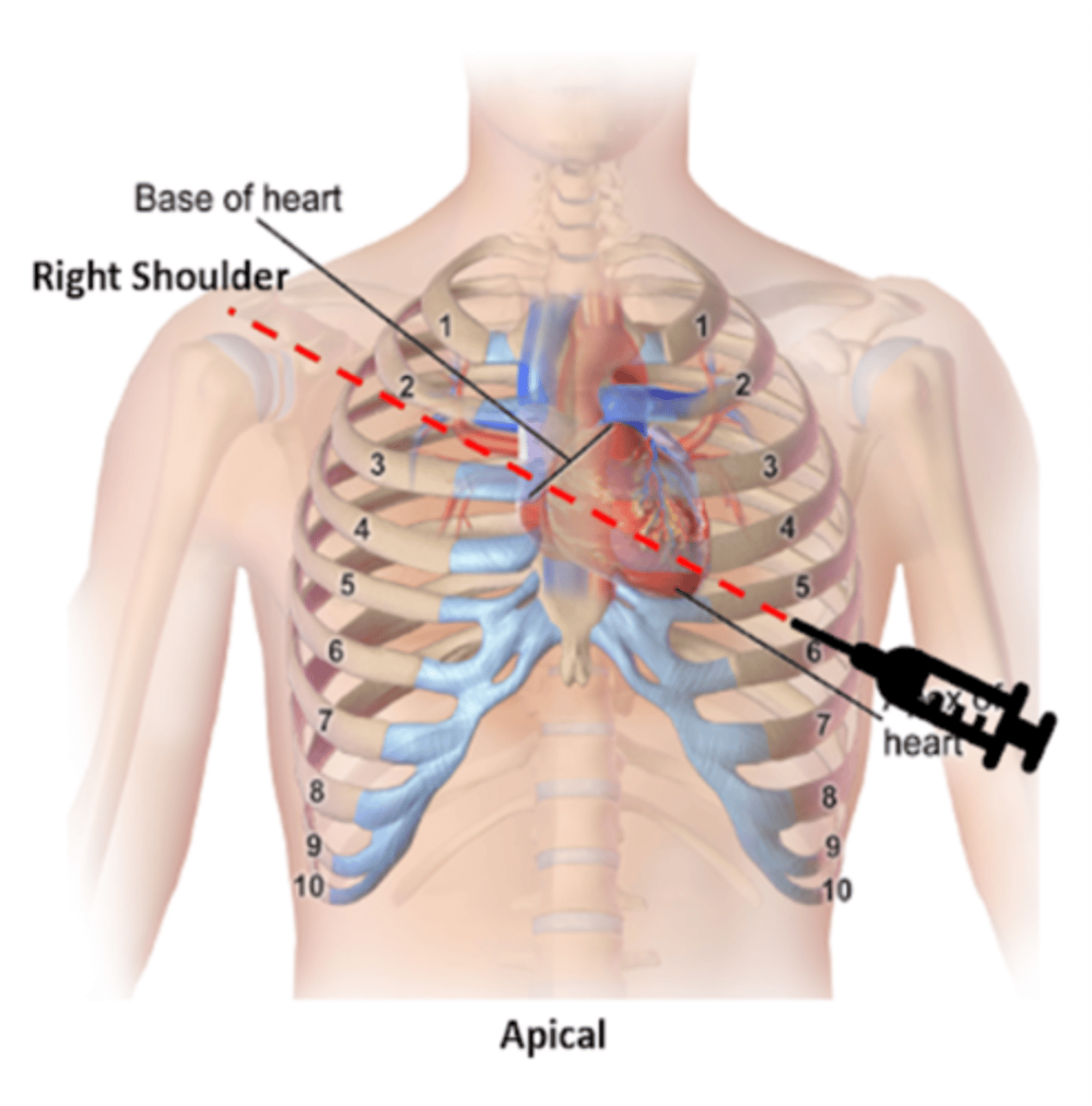
Location of the apex of the heart
5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line
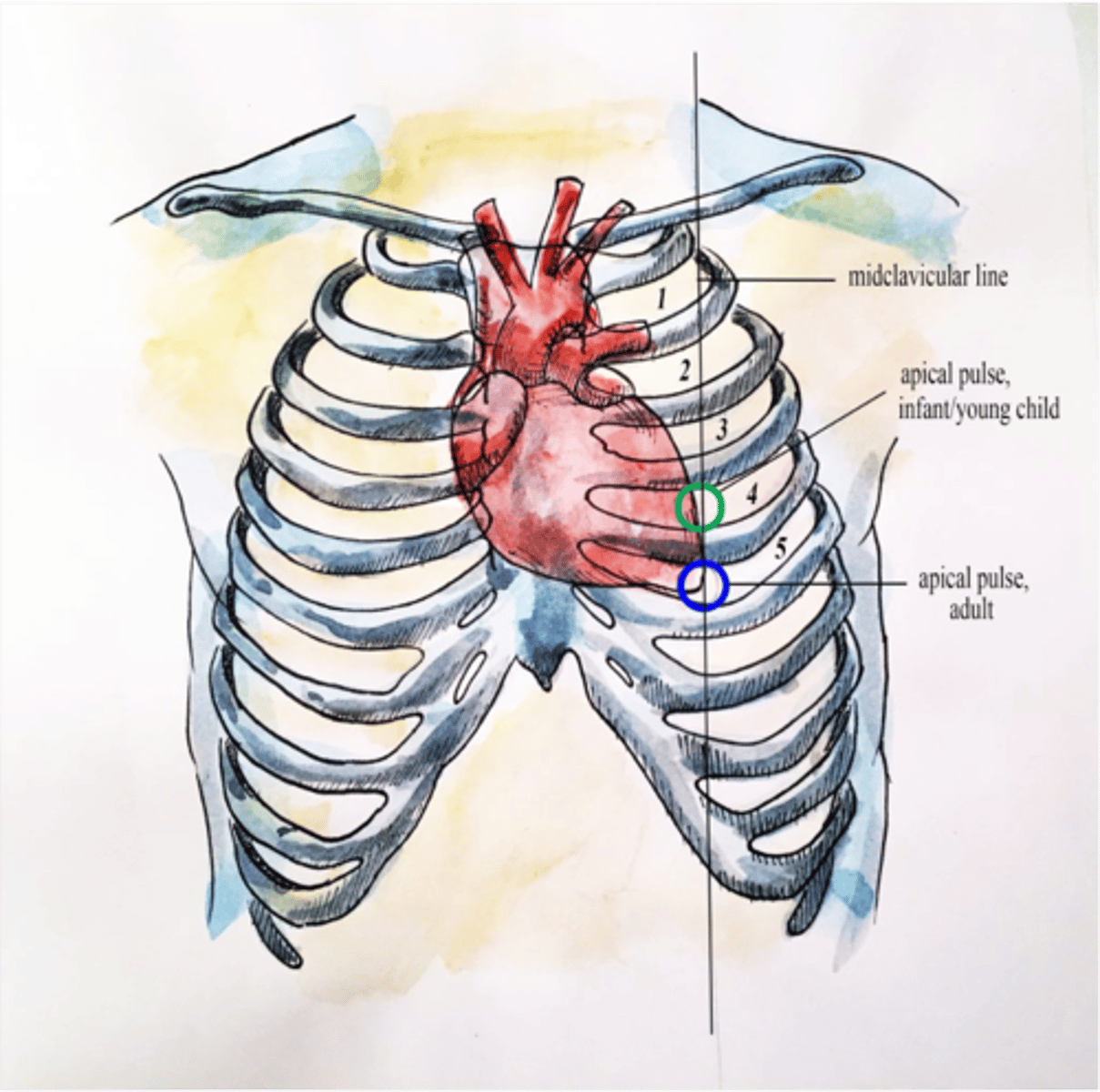
5th intercostal space, left midclavicular line
Quiet expiration - none, only the elastic recoil of lungs and thoracic wall
Forced expiration - Internal intercostal muscles
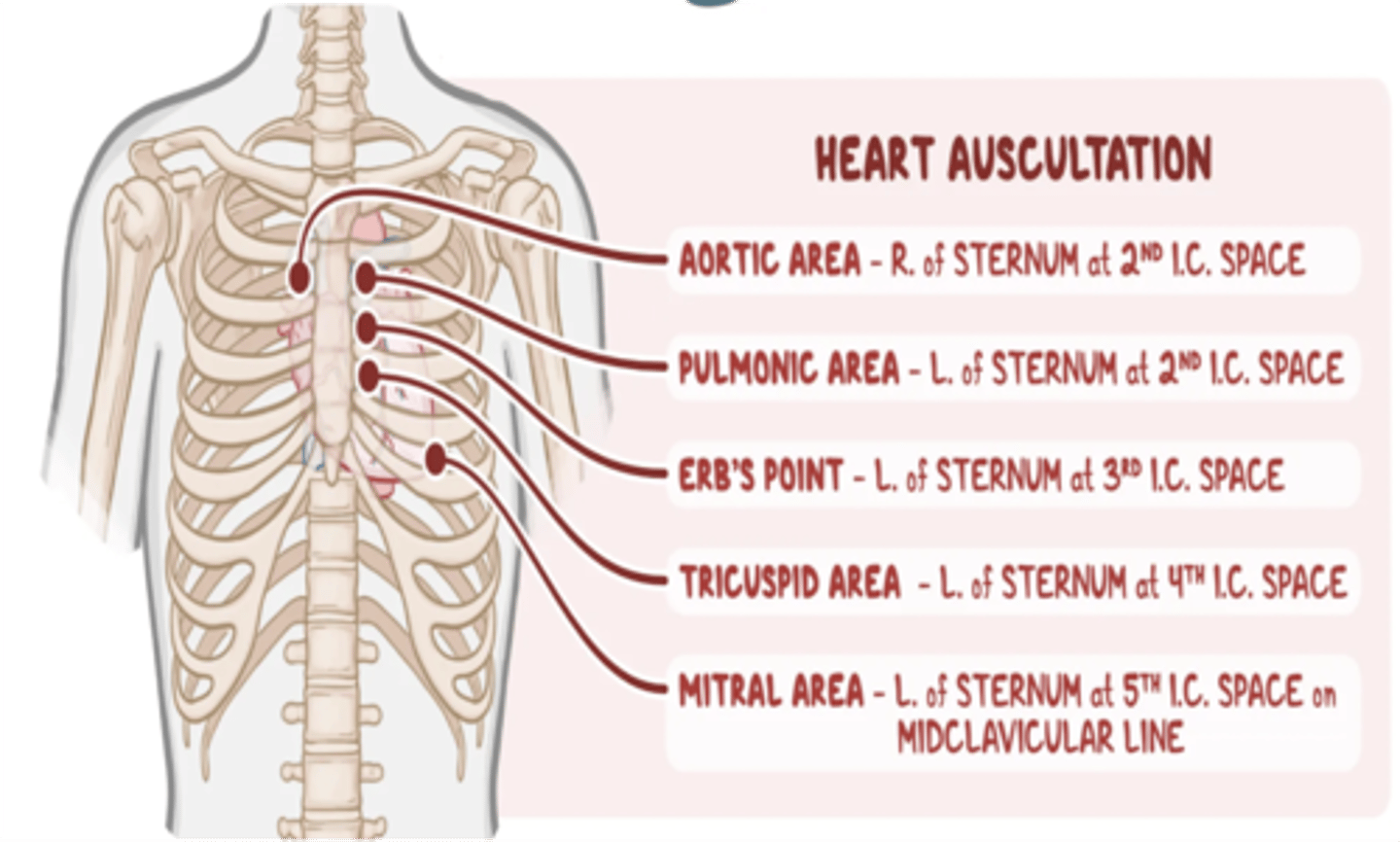
On what area should one place his/her stethoscope to listen to the aortic valve of the heart?
2nd ICS, right parasternal border
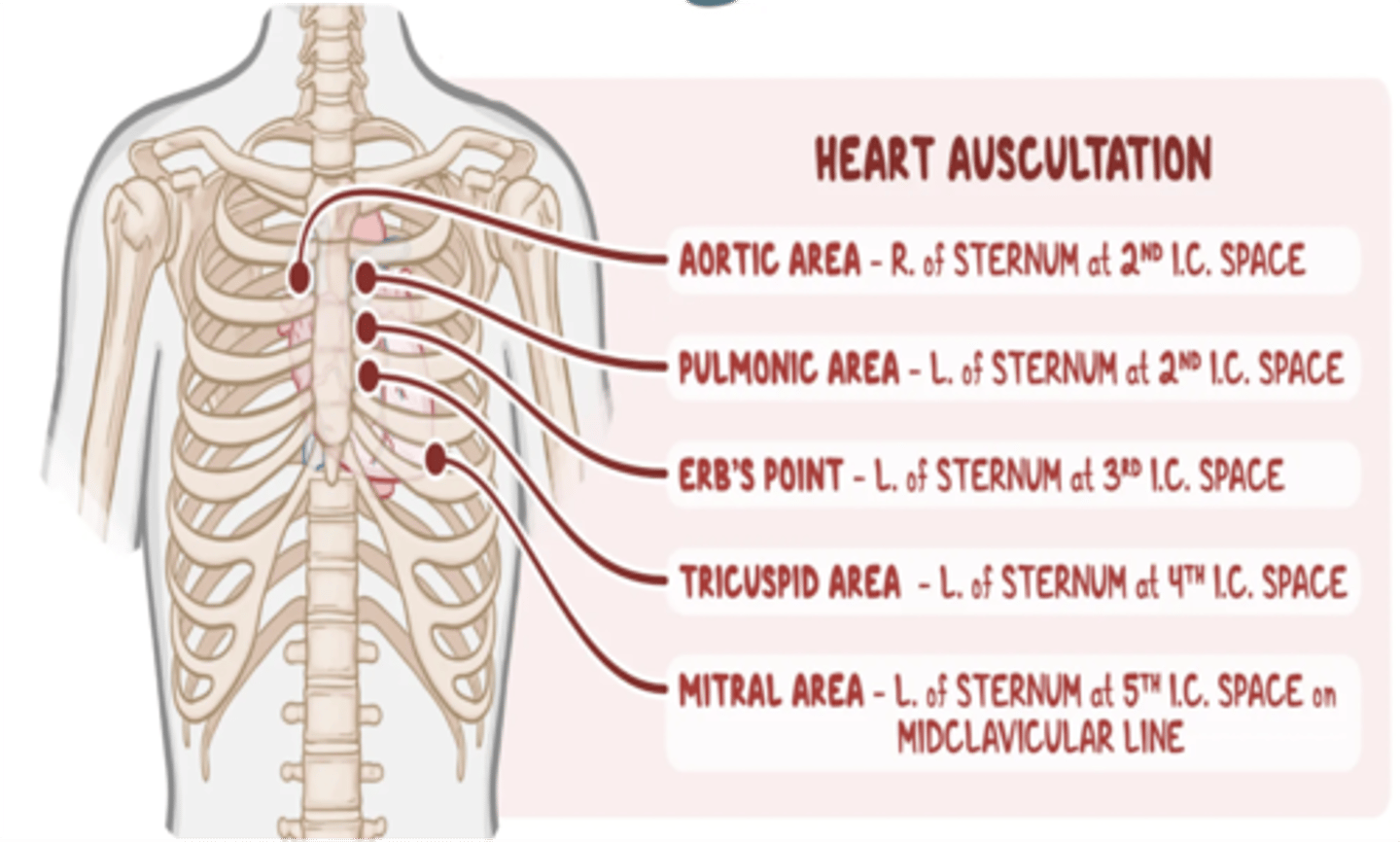
On what area should one place his/her stethoscope to listen to the pulmonic valve of the heart?
2nd ICS, left parasternal border
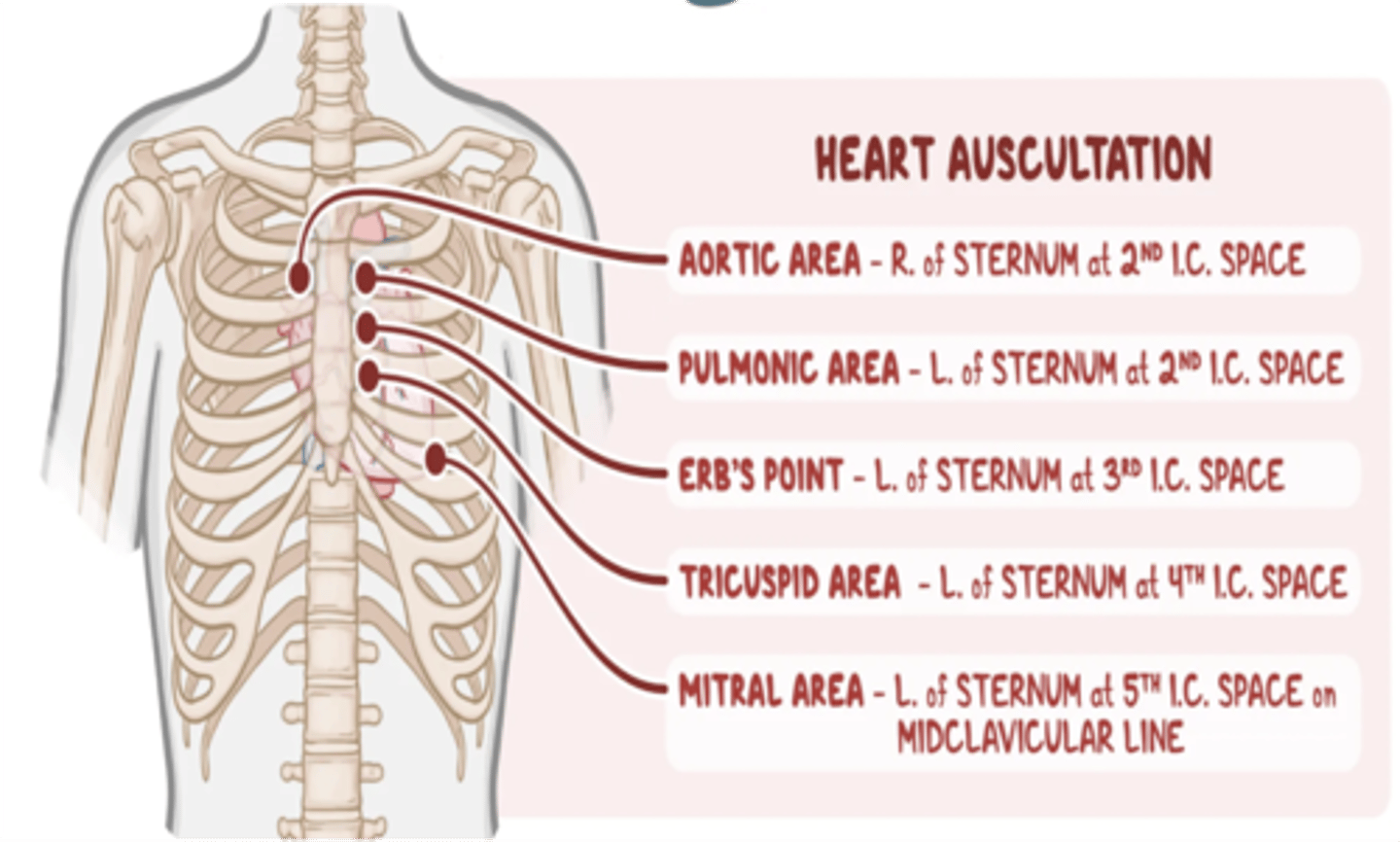
On what area should one place his/her stethoscope to listen to the tricuspid valve of the heart?
4th ICS, left parasternal border
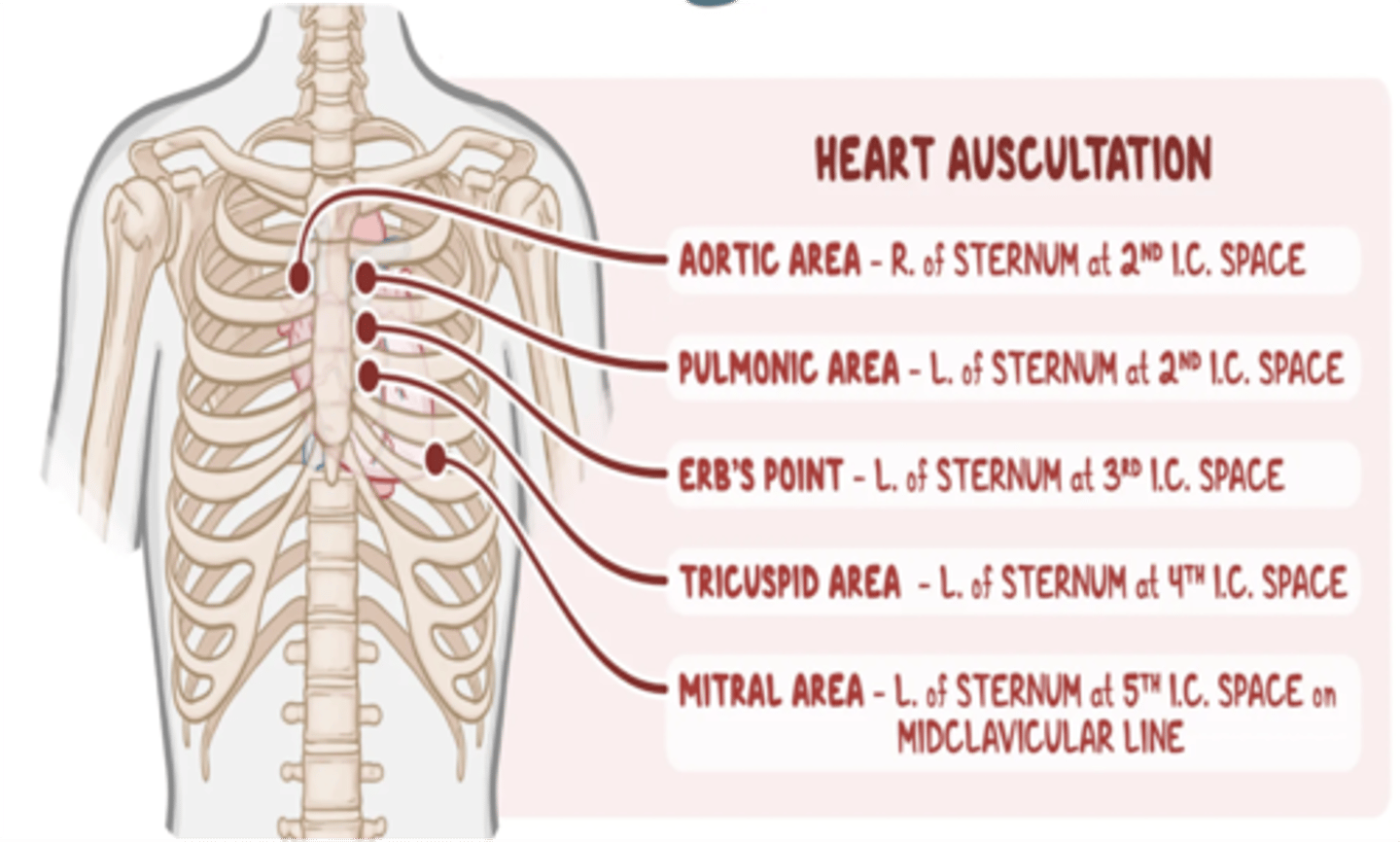
On what area should one place his/her stethoscope to listen to the mitral valve of the heart?
5th ICS, midclavicular line
What coronary vein accompanies the anterior interventricular artery?
Great cardiac vein
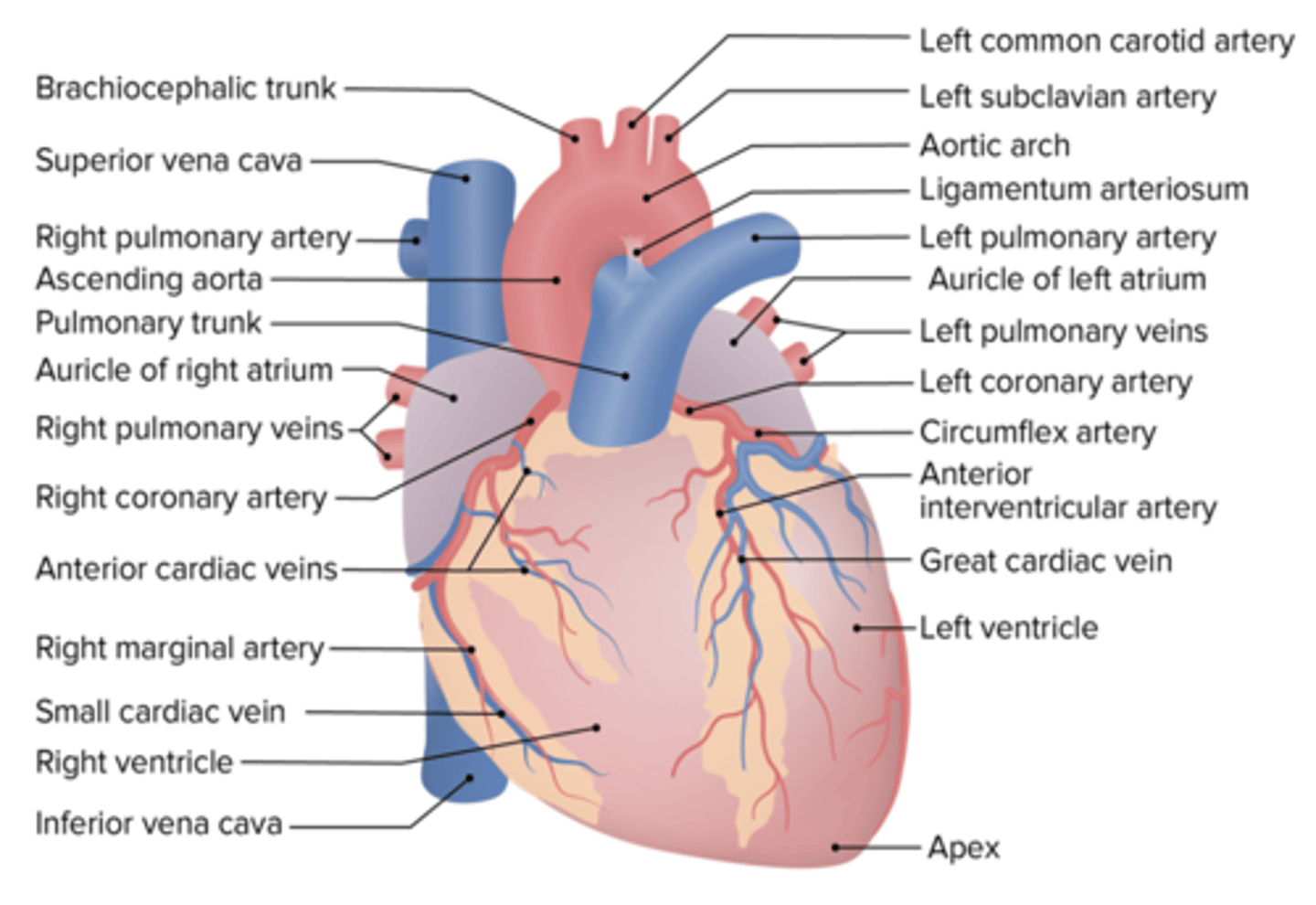
What coronary vein accompanies the right marginal artery?
Small cardiac vein
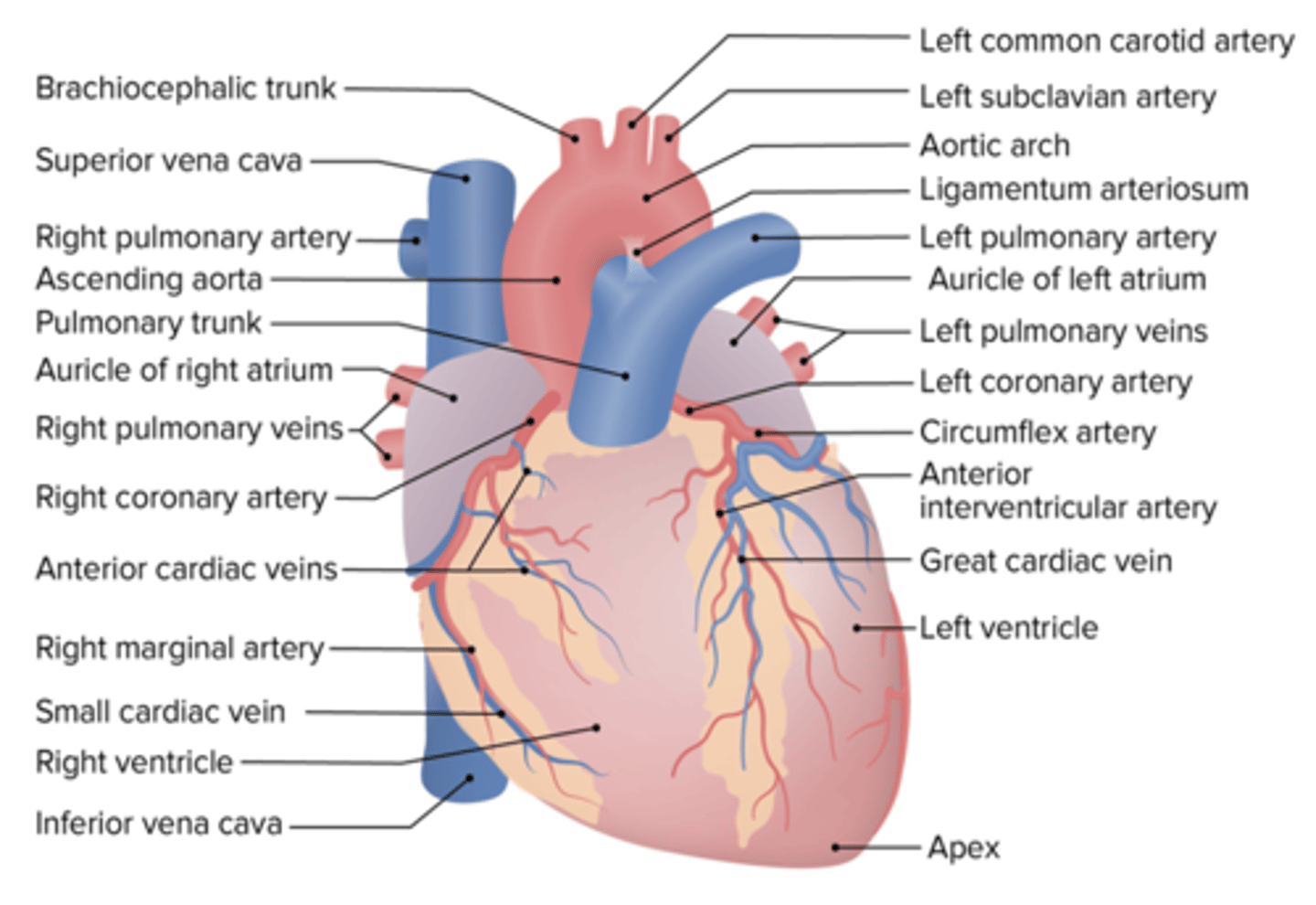
What coronary artery accompanies the great cardiac vein?
Anterior Interventricular Artery
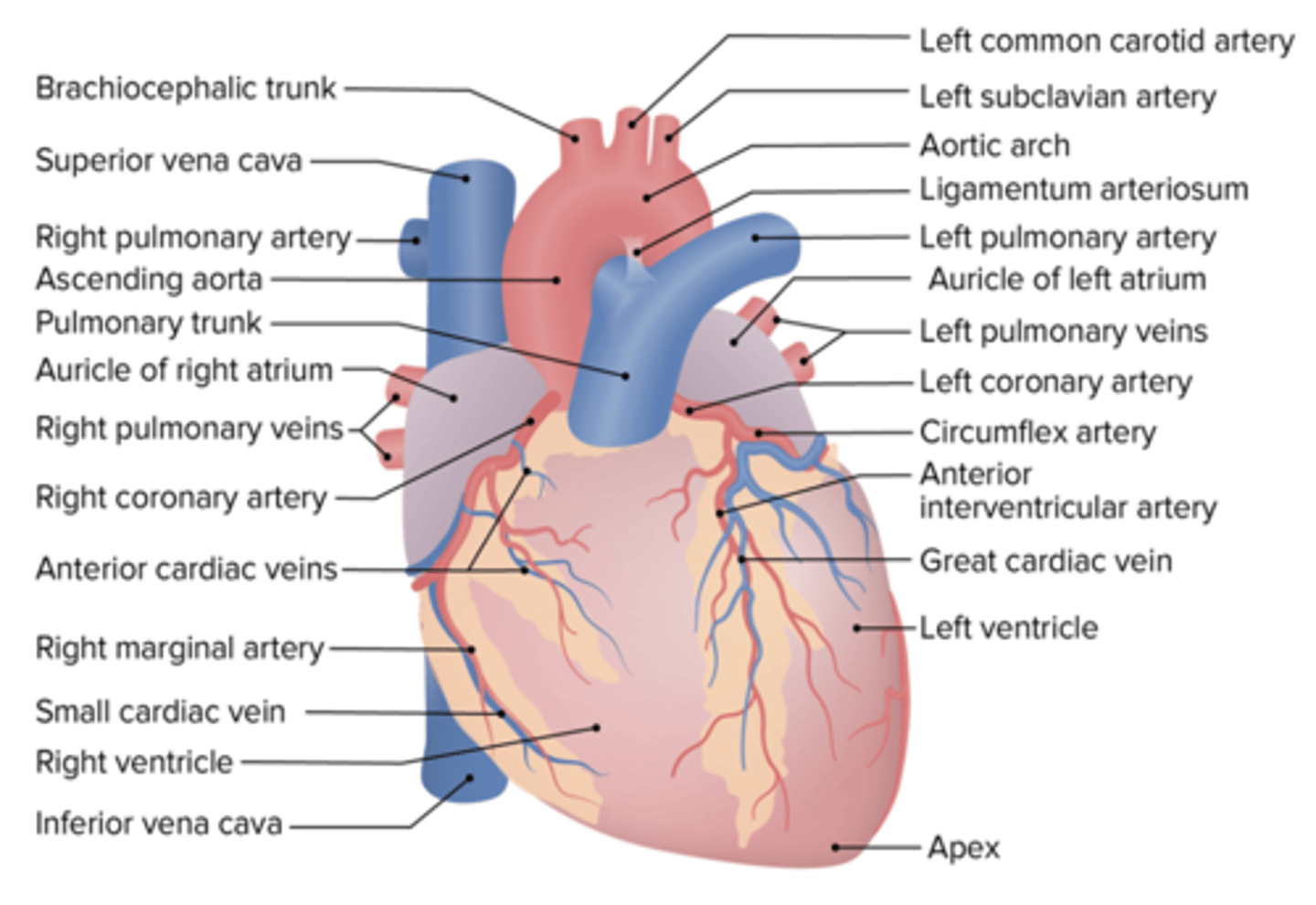
What coronary artery accompanies the small cardiac vein?
Right Marginal Artery
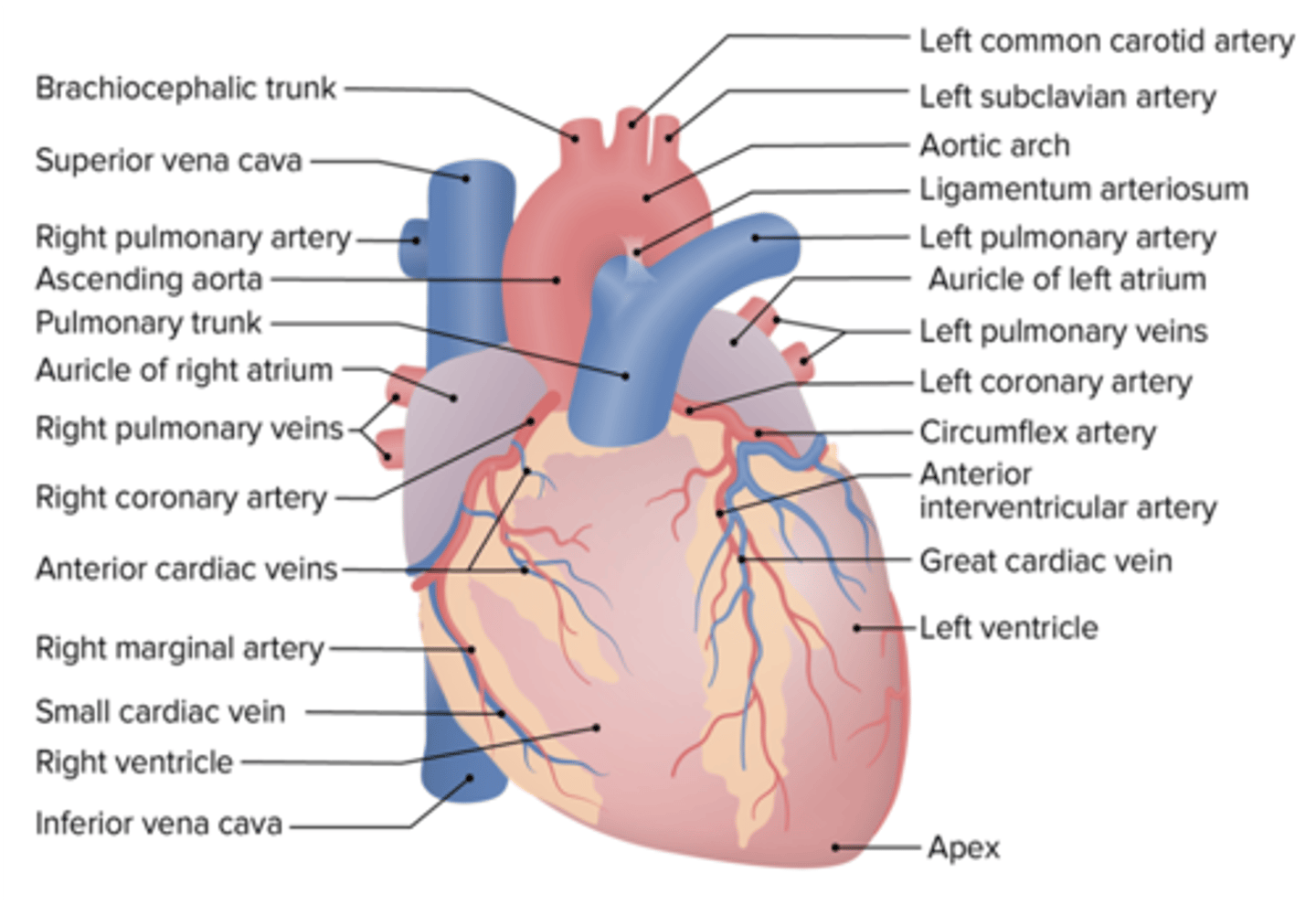
What coronary vein accompanies the posterior interventricular artery?
Middle cardiac vein
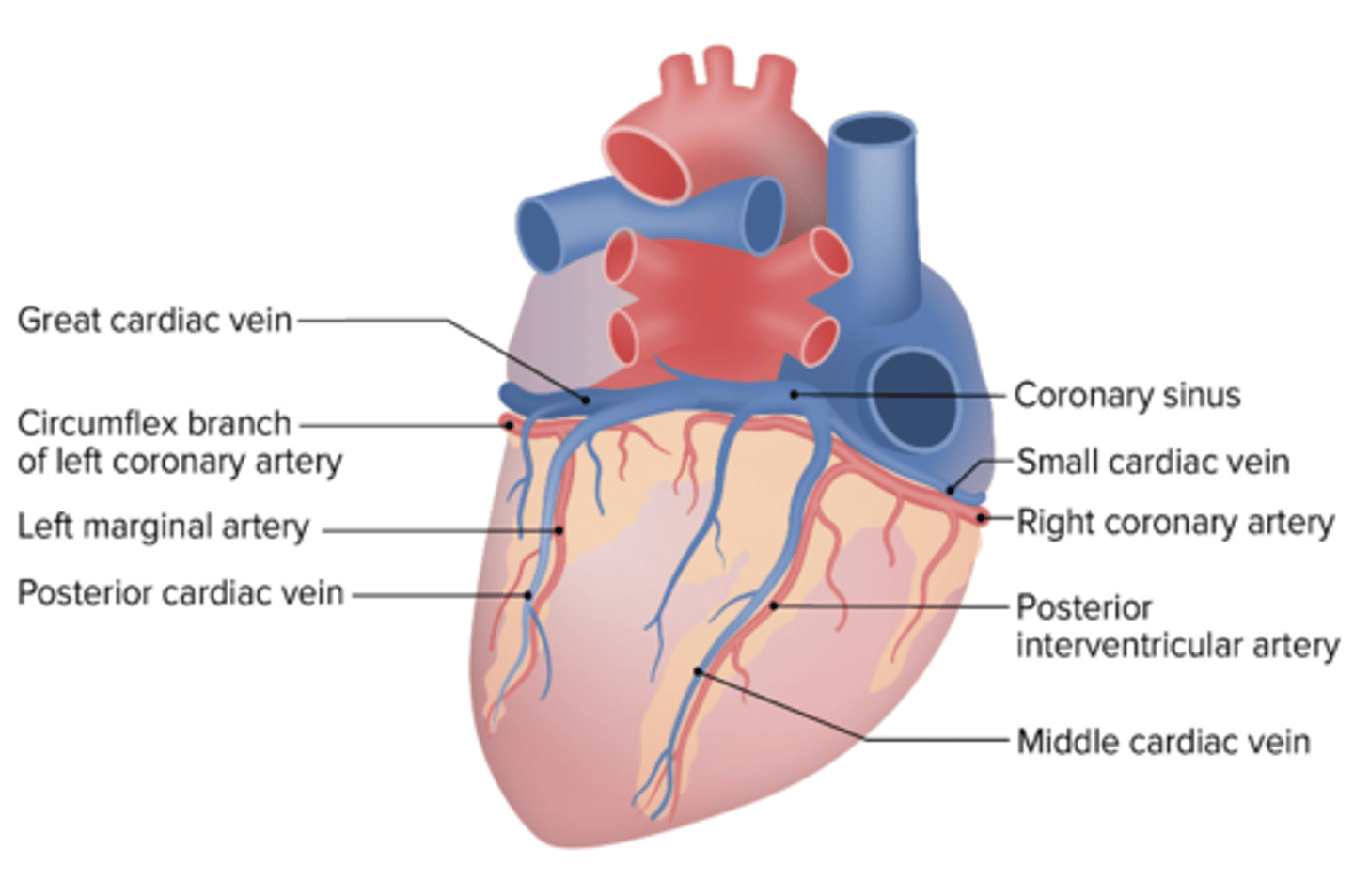
What coronary vein accompanies the left marginal artery?
Posterior Cardiac Vein
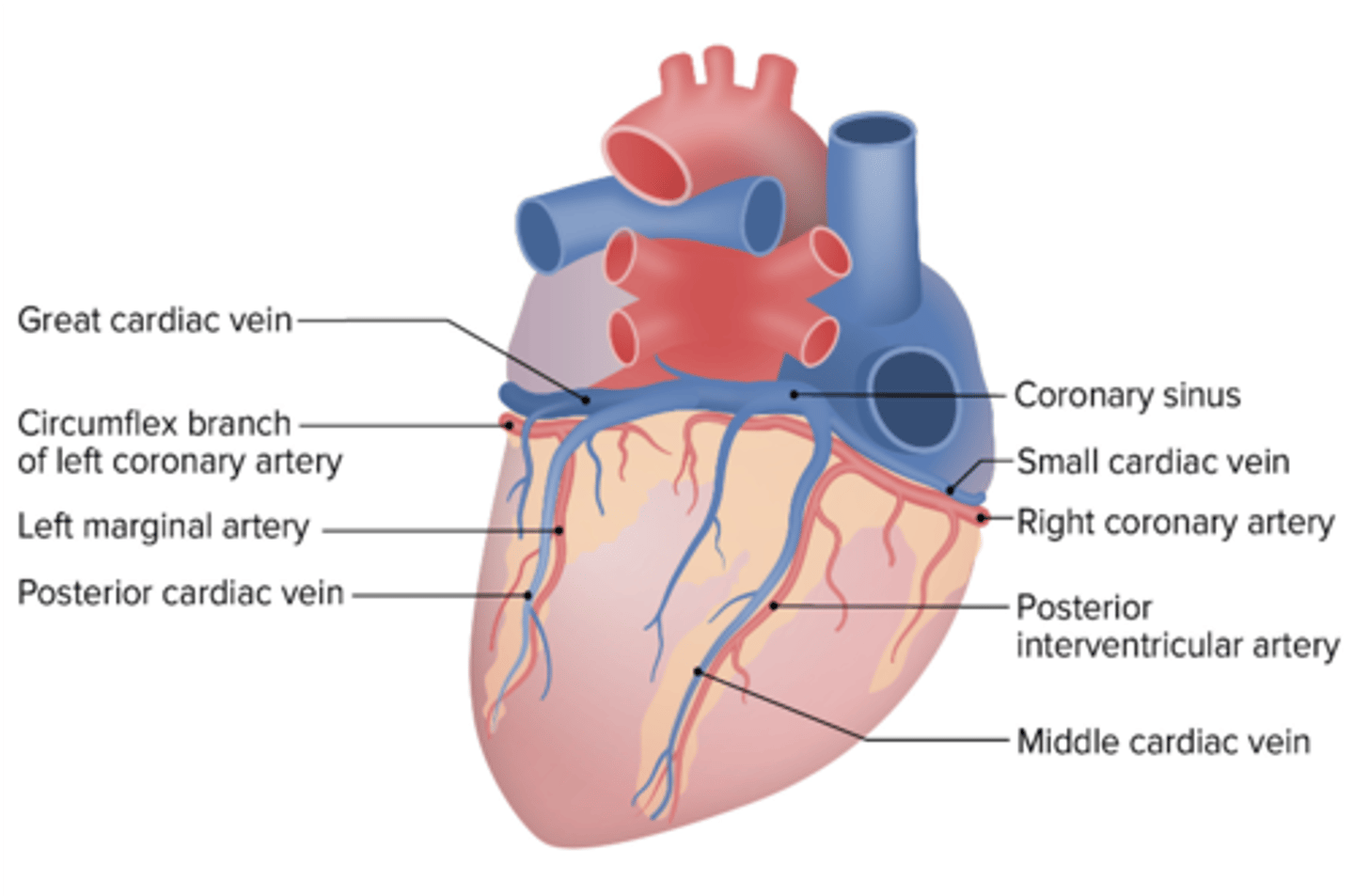
What coronary artery accompanies the middle cardiac vein?
Posterior Interventricular Artery
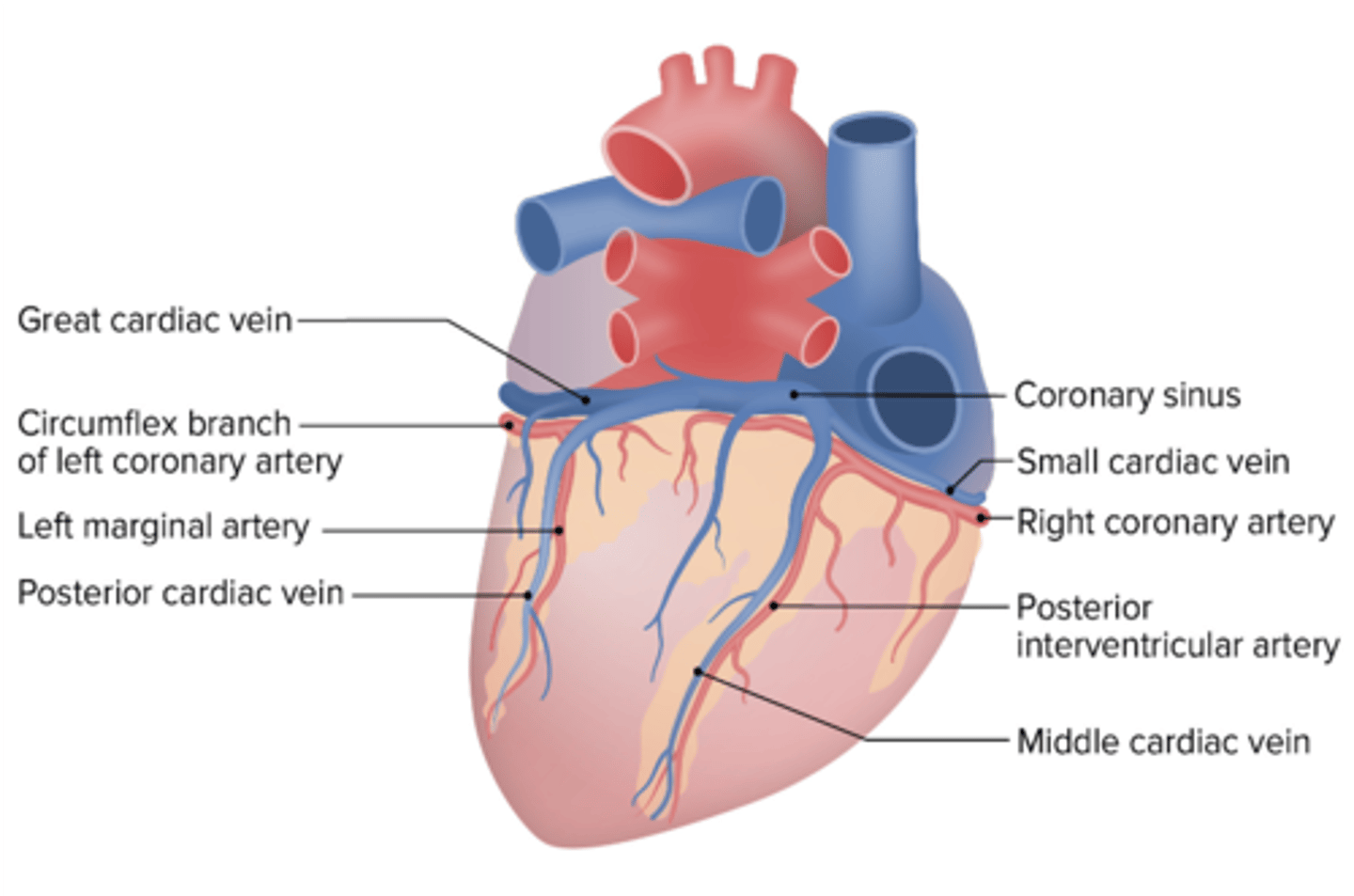
What coronary artery accompanies the posterior cardiac vein?
Left marginal artery
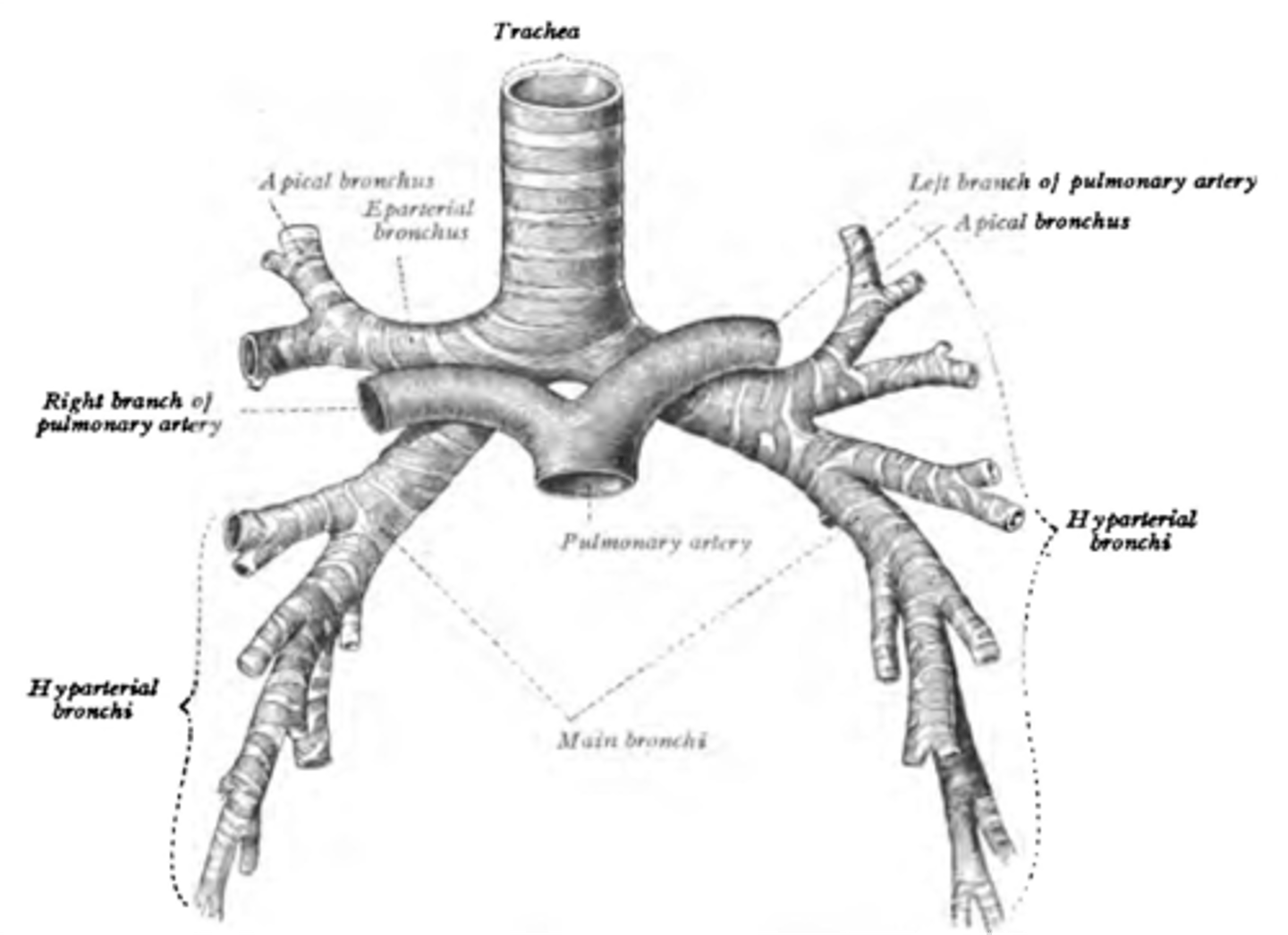
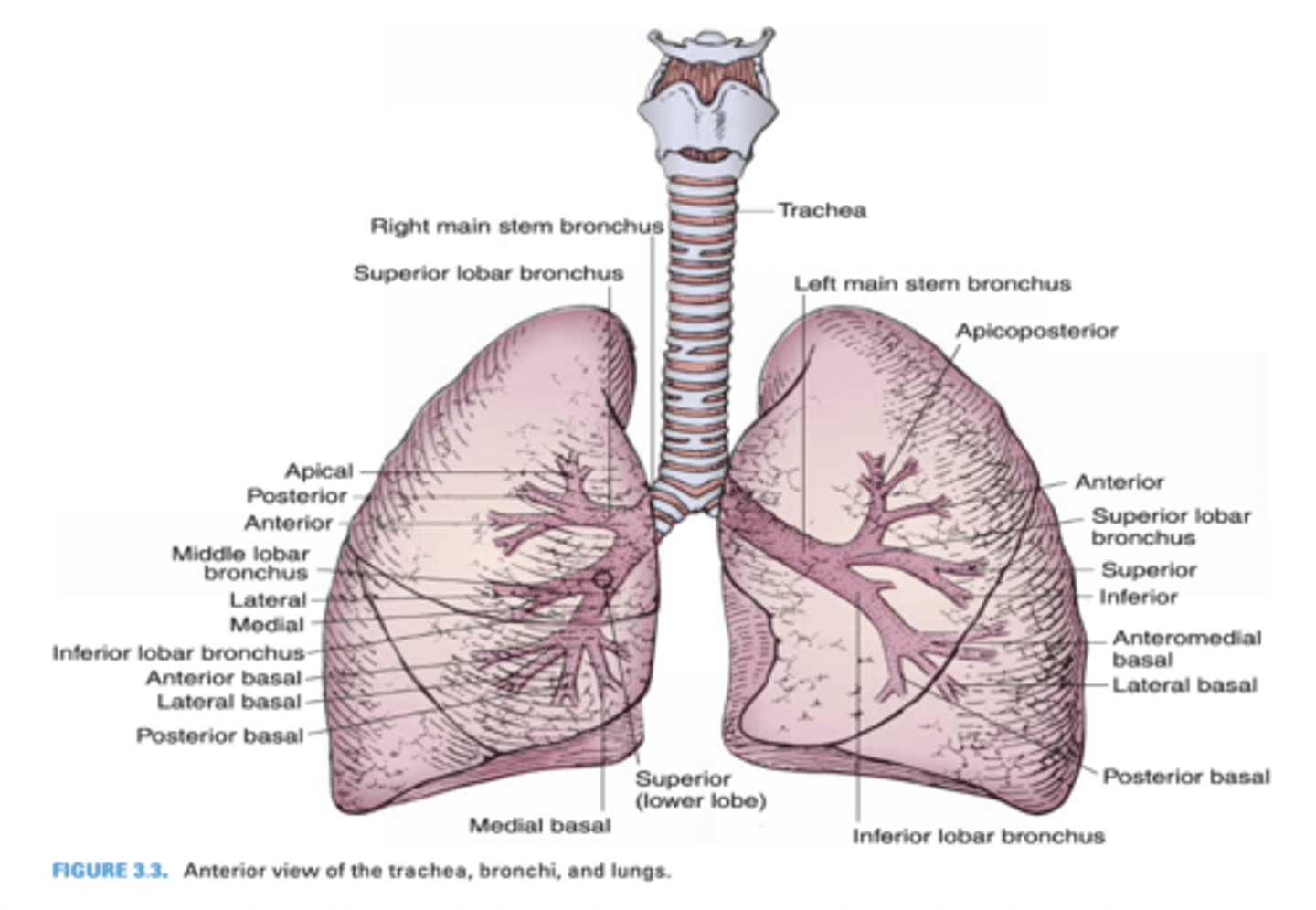
Another term for eparterial bronchus
Right superior lobar (secondary) bronchus
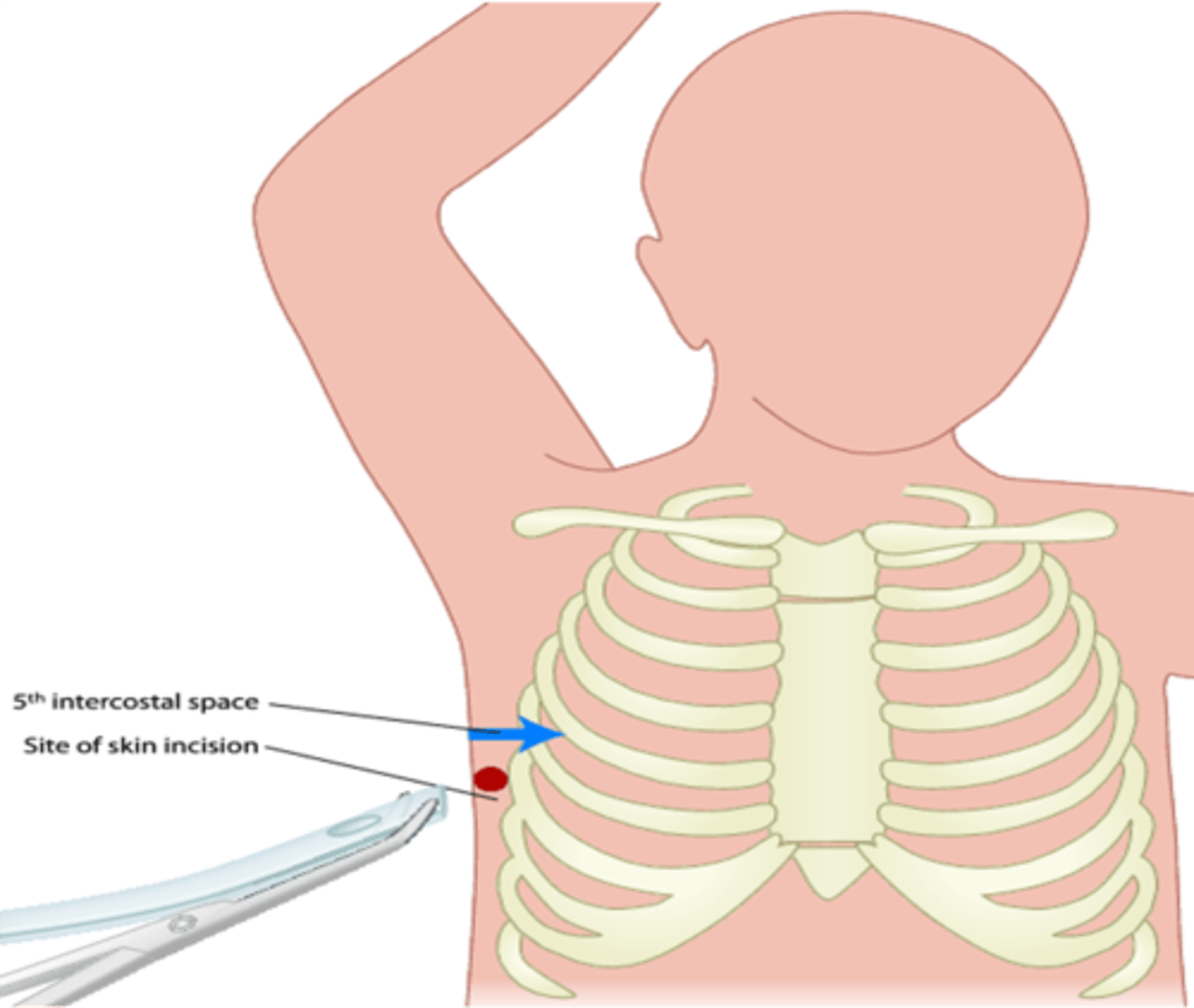
Intercostal space at the mid-axillary line through which needle for thoracentesis can be safely inserted
5th ICS
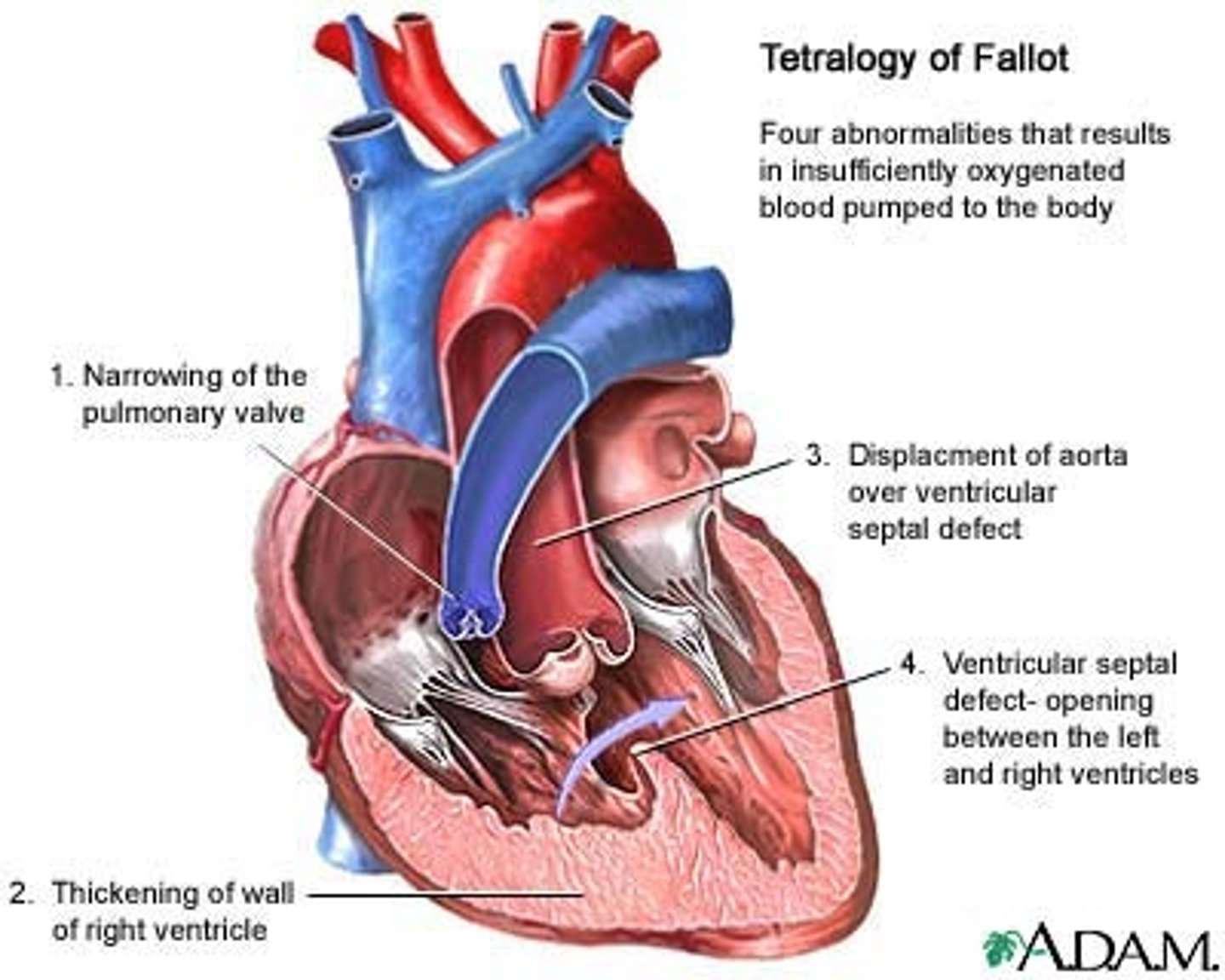
Components of Tetralogy of Fallot
-Pulmonary stenosis
-Dextroposition of aorta
-Interventricular septal defect
-Hypertrophy of right ventricle
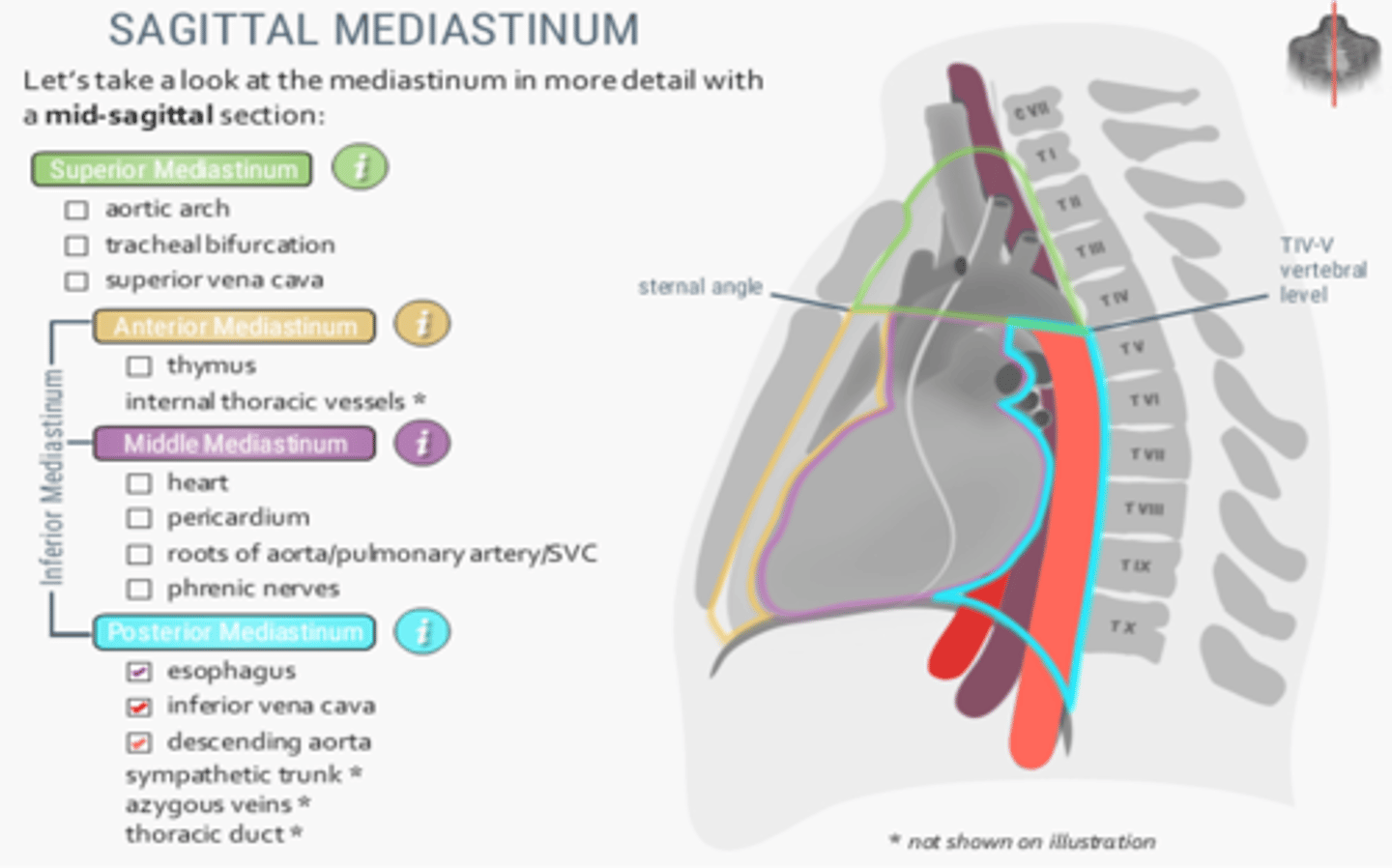
Structures located at the posterior mediastinum
-Esophagus
-Inferior vena cava
-Descending aorta
-Sympathetic trunk
-Azygous veins
-Thoracic duct
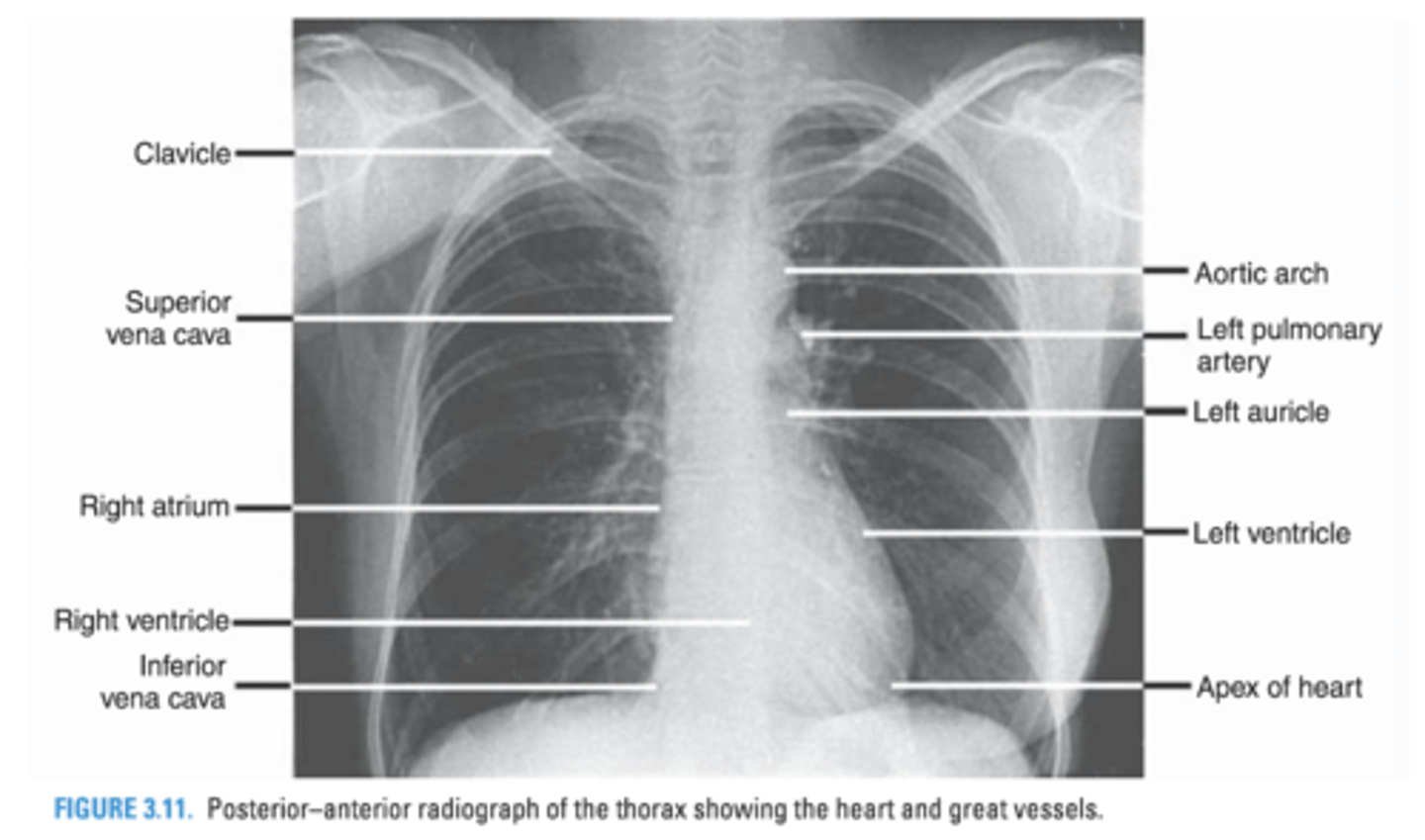
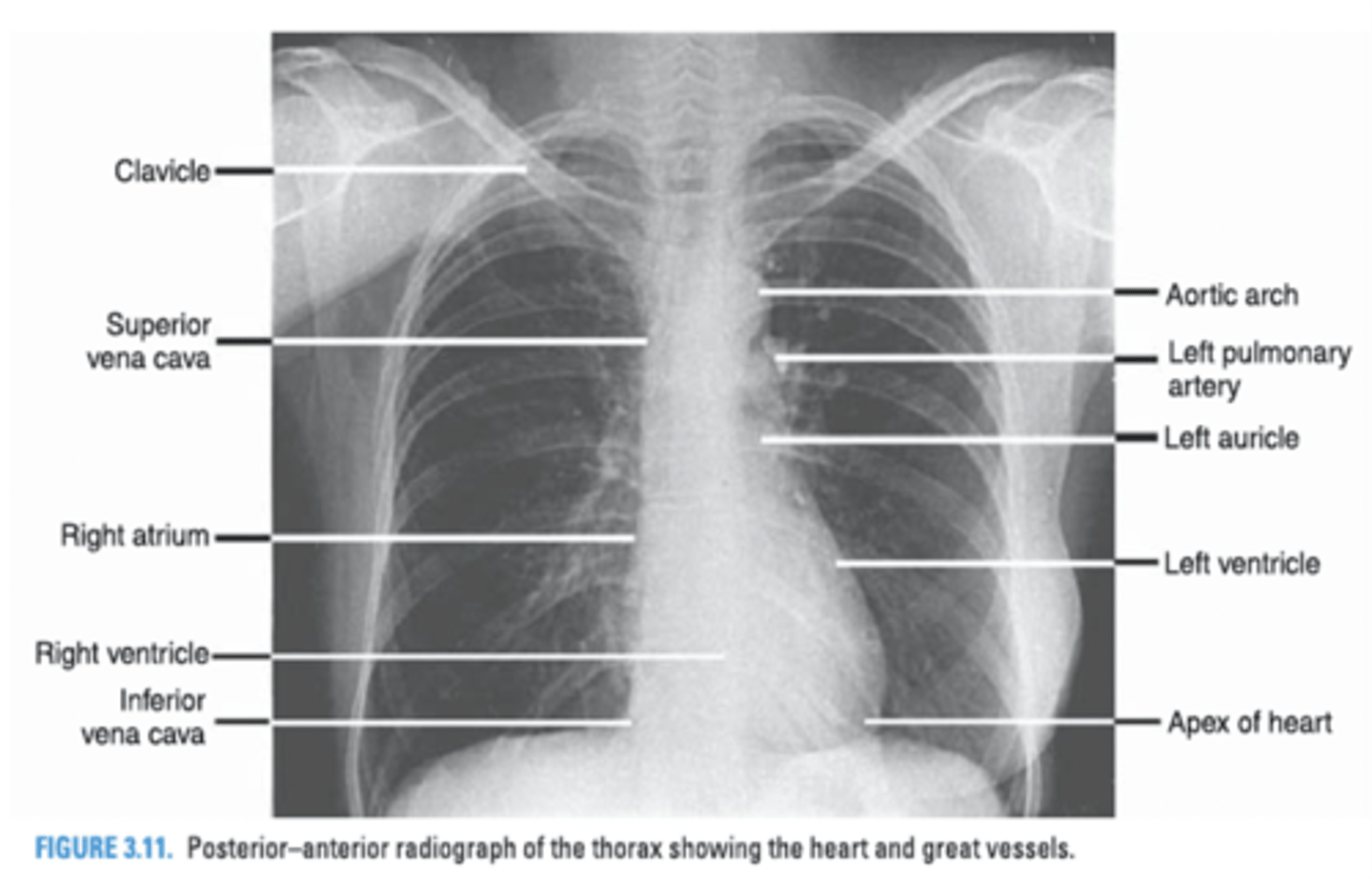
Structures that form the right border of the cardiovascular silhouette.
Superior vena cava
Right atrium
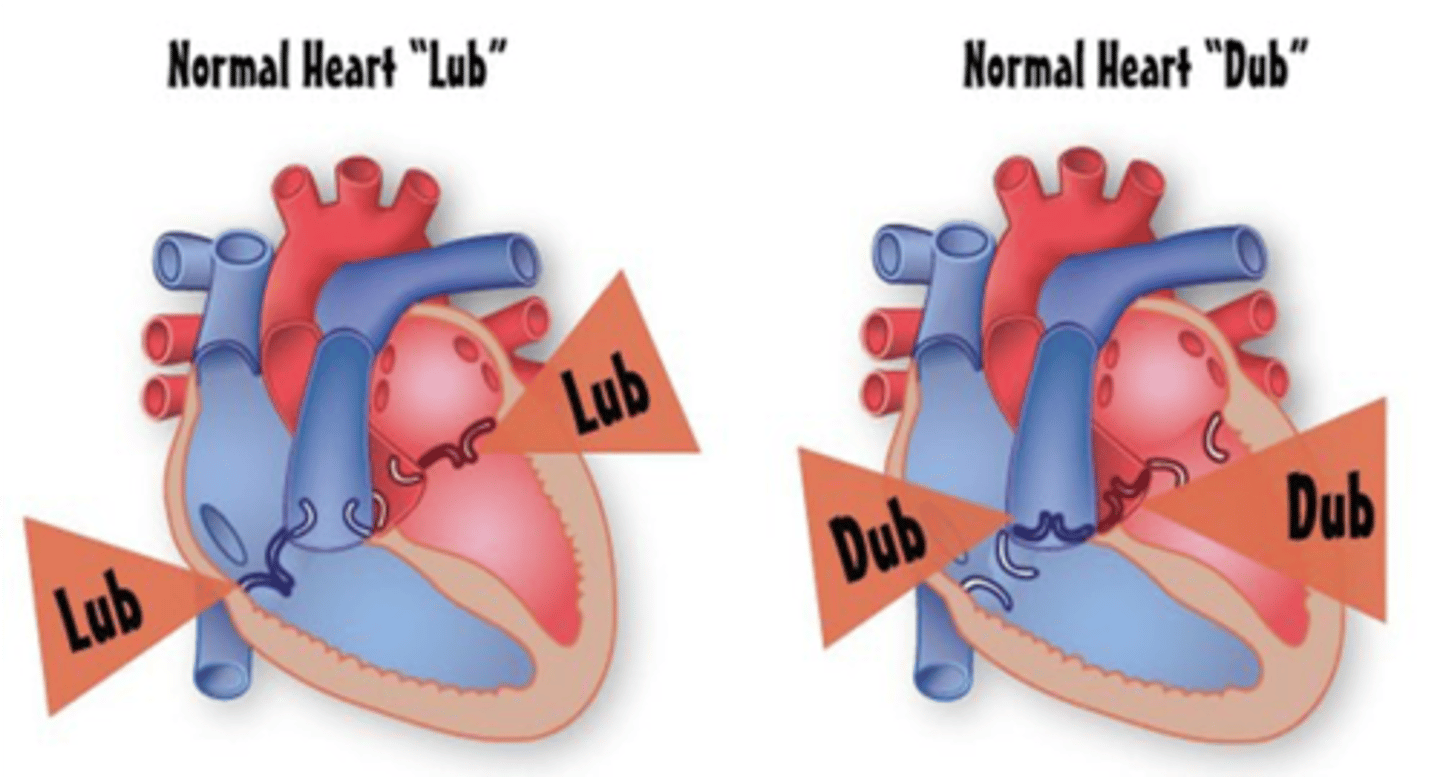
Which valves close during the first heart sound?
Tricuspid and Mitral Valves
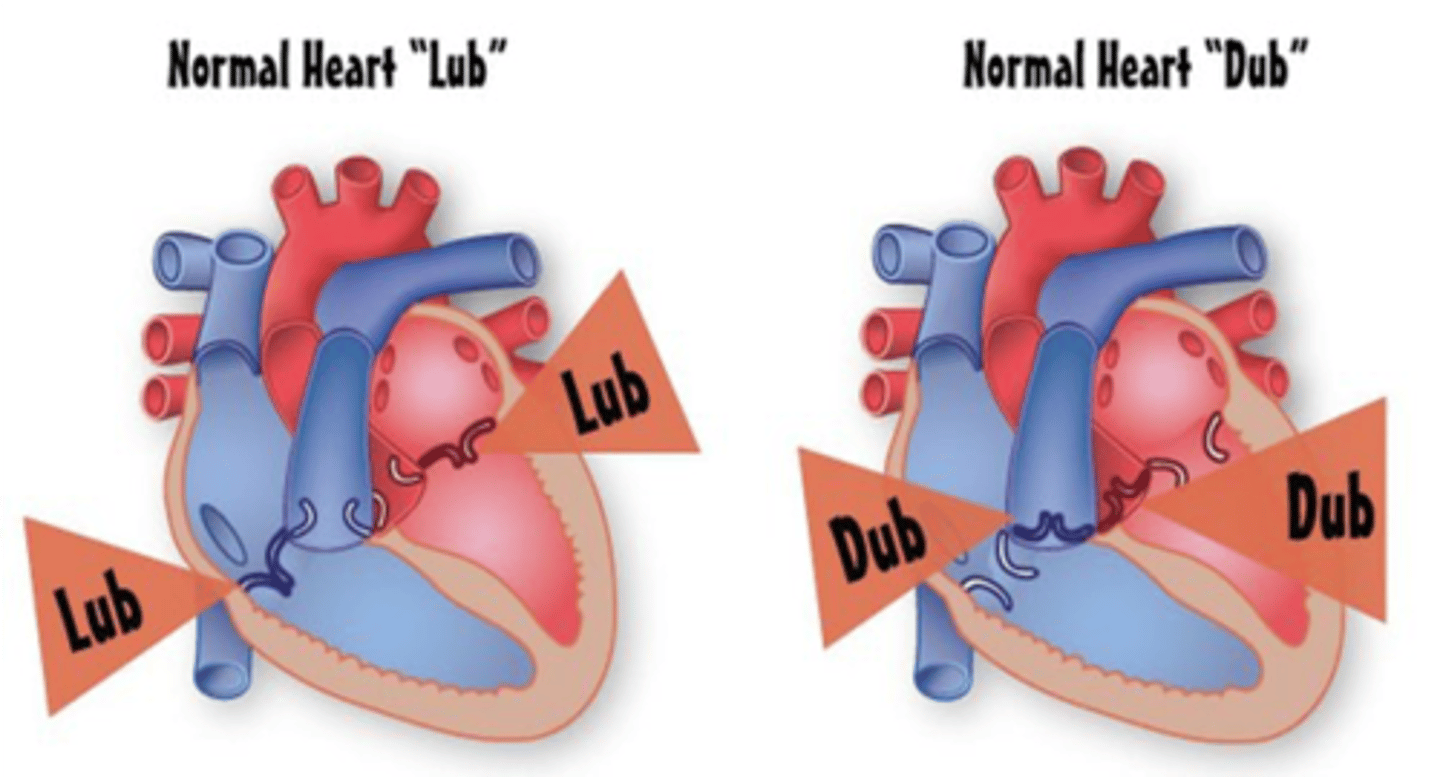
Which valves close during the second heart sound?
Pulmonic and Aortic Valves
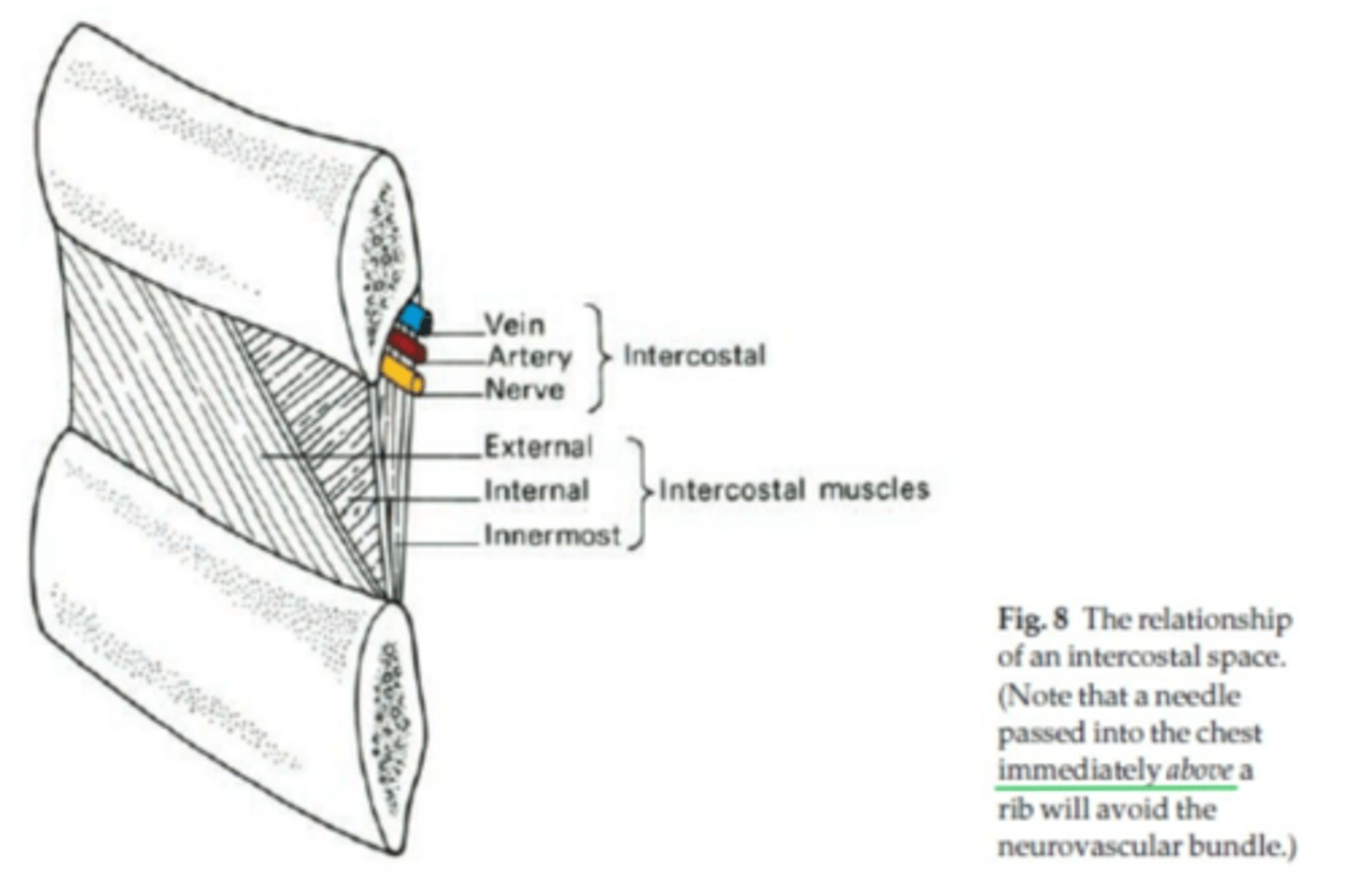
To avoid the intercostal neurovascular bundle, the needle during needle aspiration of tension pneumothorax must be inserted where?
Above the upper border of the ribs
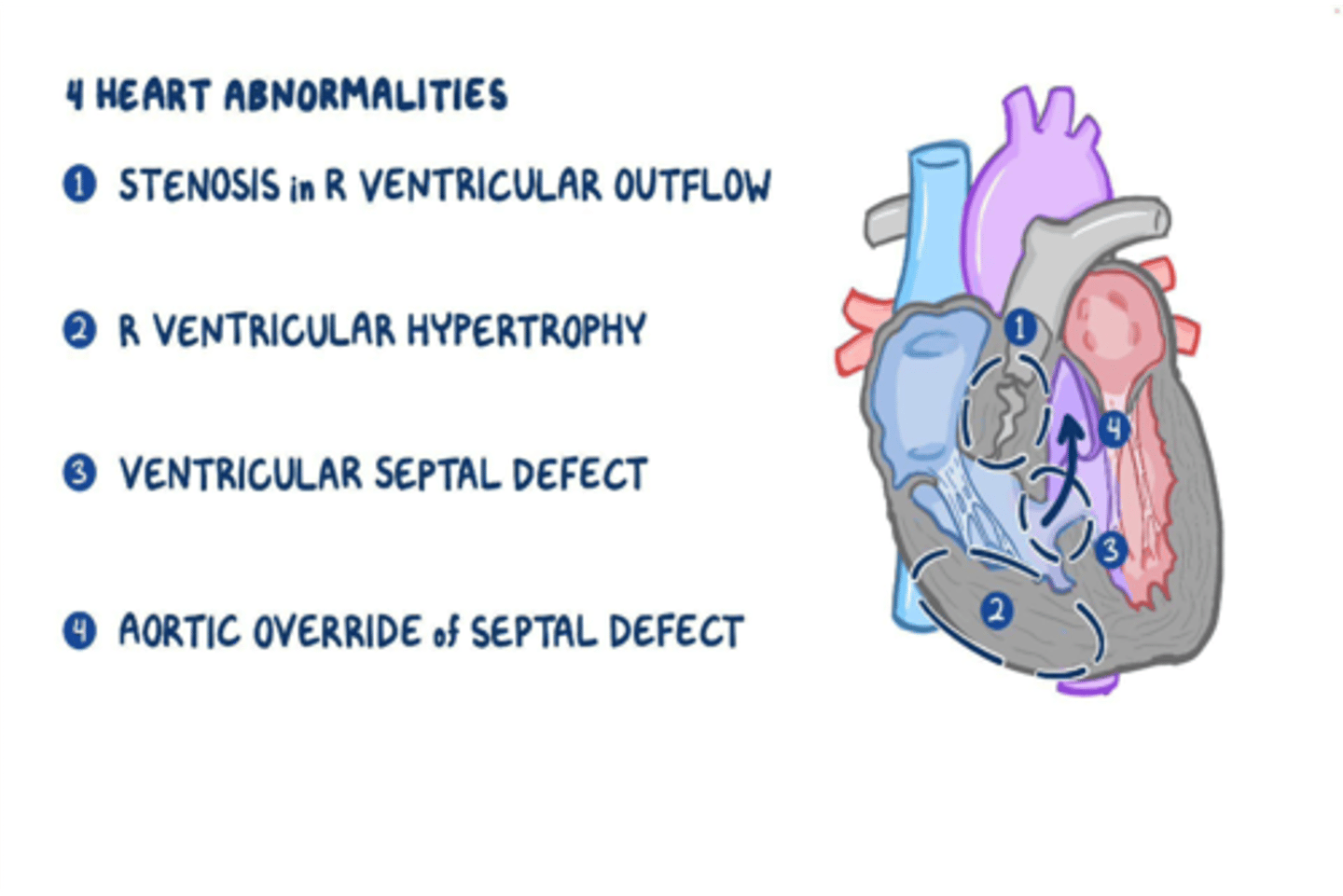
What are the four congenital cardiac defects in the Tetralogy of Fallot?
-Pulmonary stenosis
-Dextroposition of the aorta
-Ventricular septal defect
-Right ventricular hypertrophy
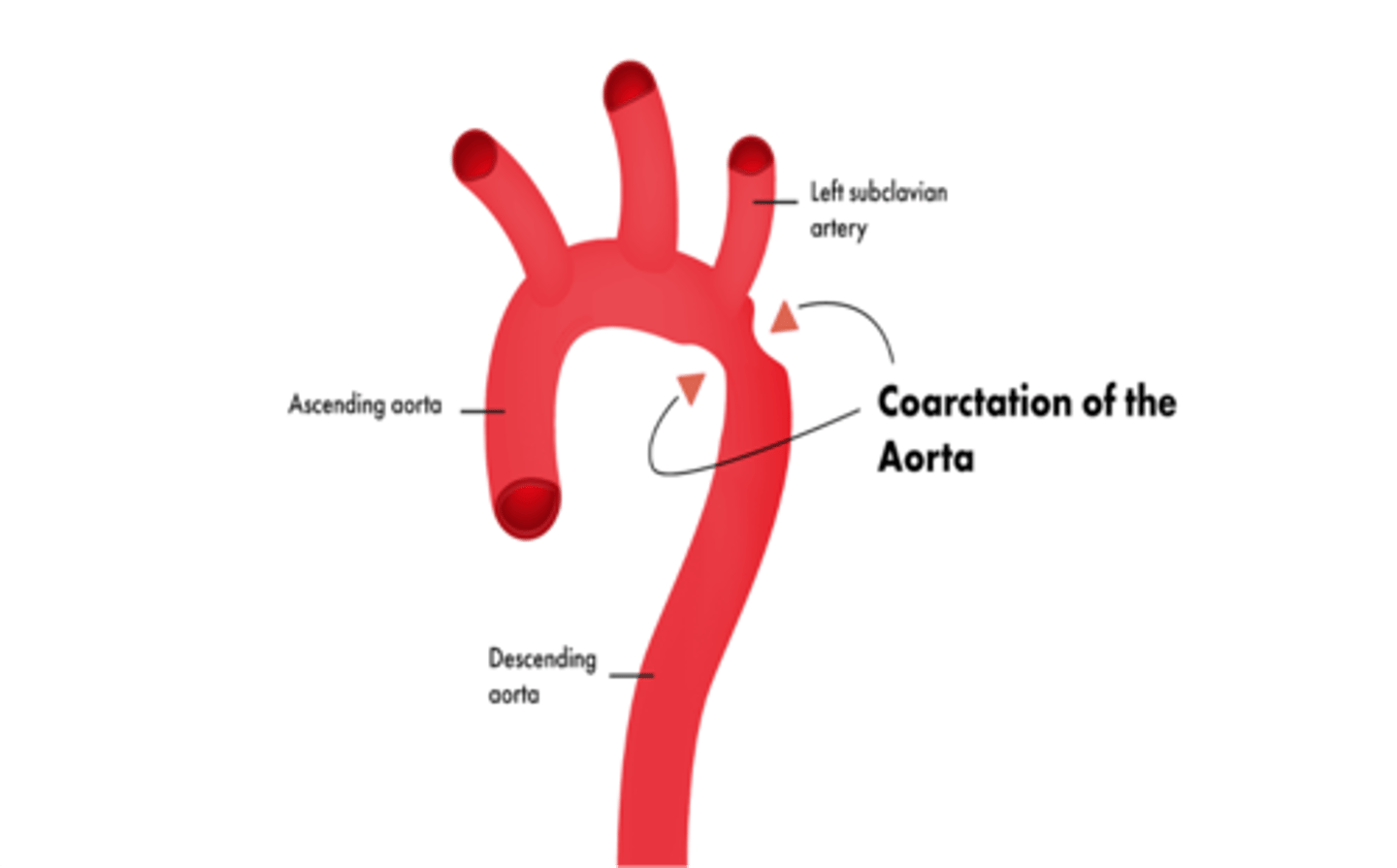
Coarctation of the aorta usually occurs just distal to what artery?
Left subclavian artery
The first two posterior intercostal arteries are branches of which artery of the costocervical trunk?
Highest (Superior) Intercostal Artery
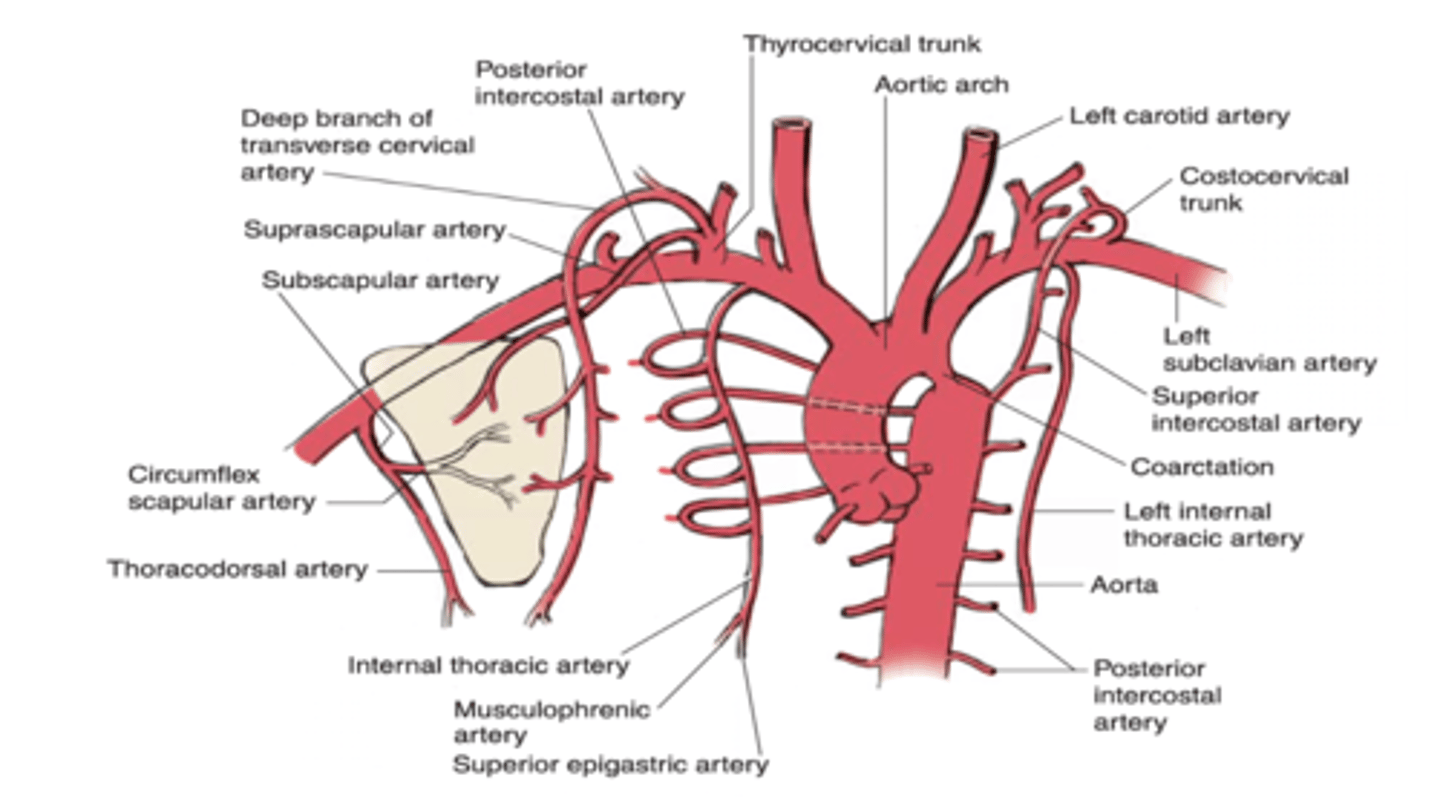
The highest (superior) intercostal artery is a branch of what artery?
Costocervical trunk
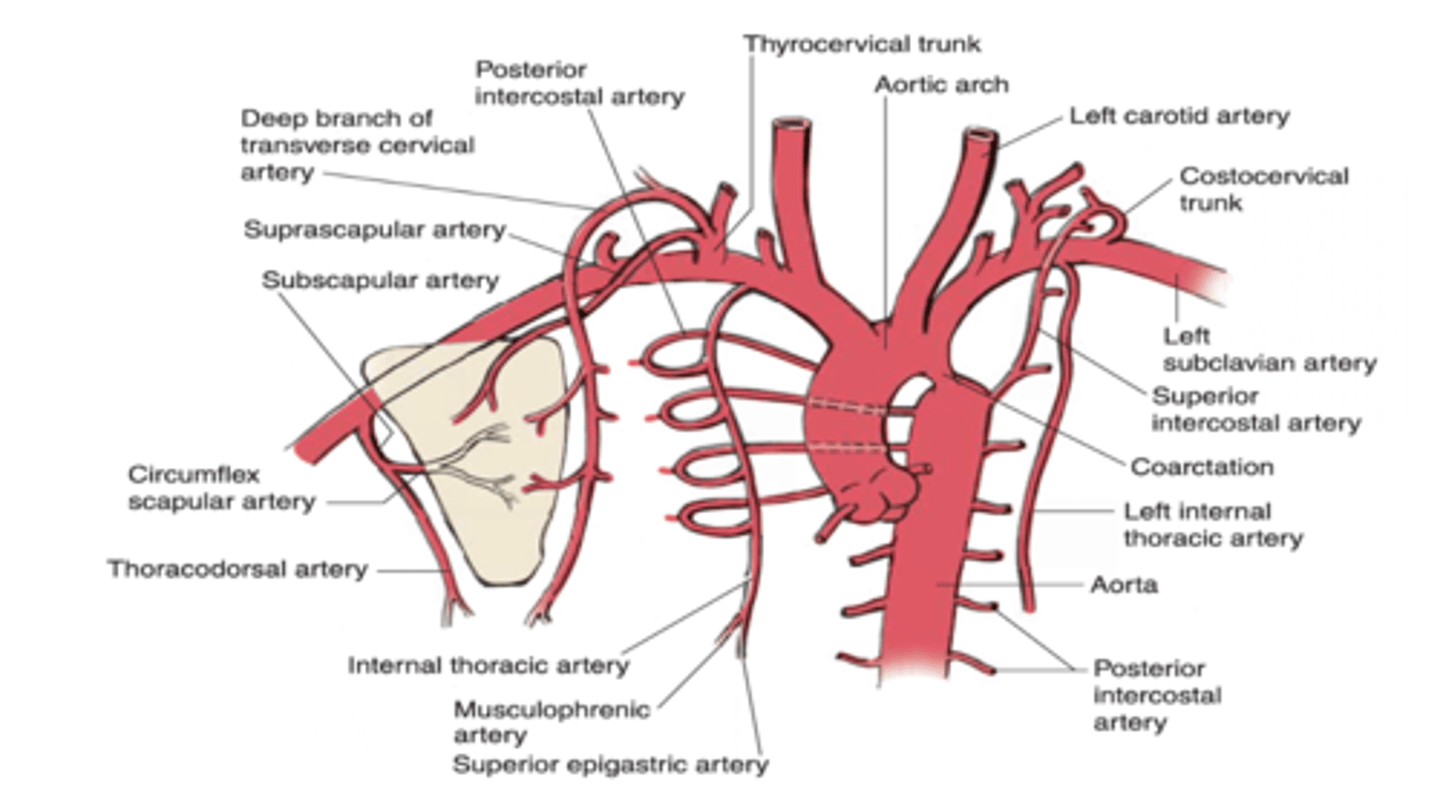
The lower nine posterior intercostal arteries are branches of what artery?
Thoracic aorta
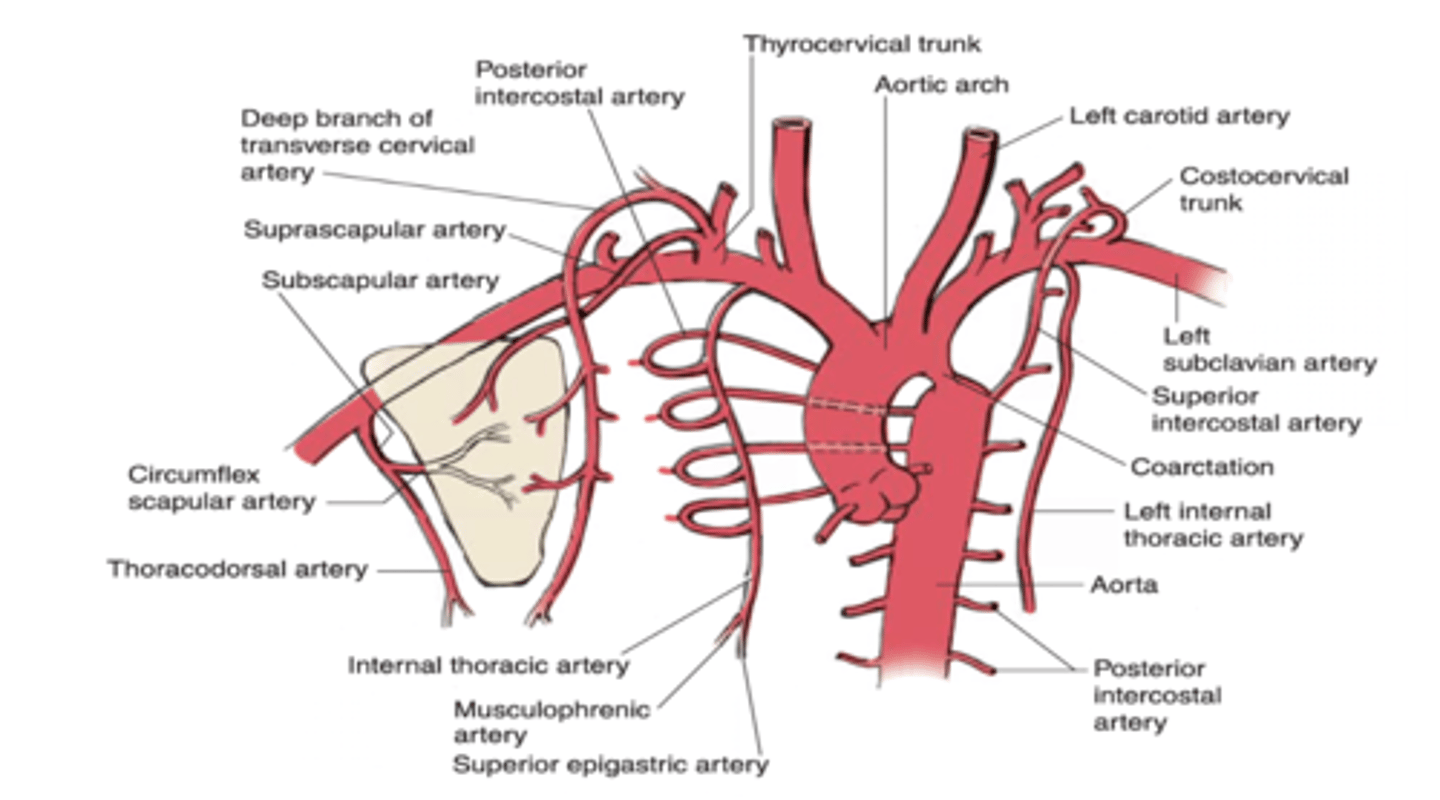
The internal thoracic artery gives off which intercostal arteries?
Upper six anterior intercostal arteries
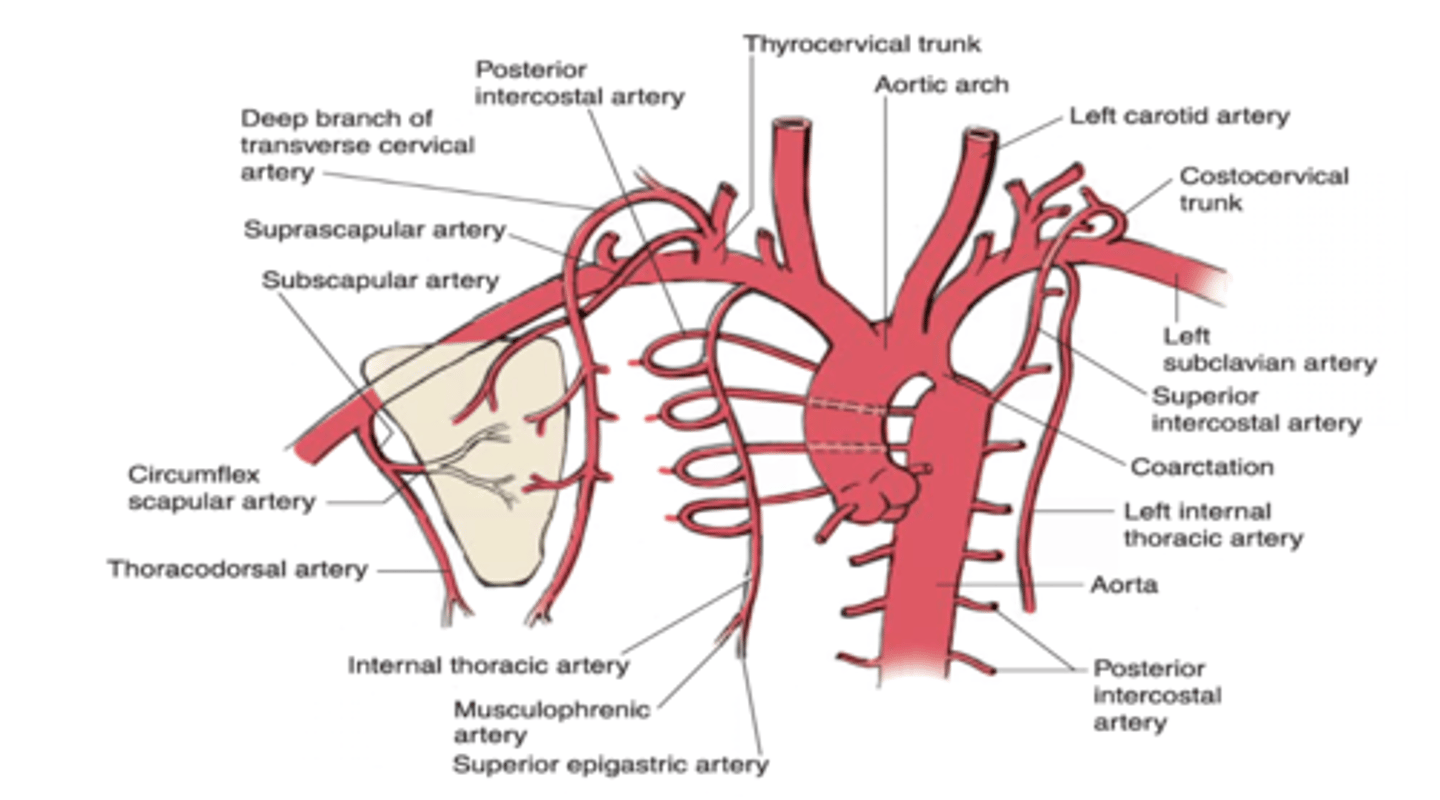
The internal thoracic artery divides into two branches at its distal portion.
-Superior epigastric artery
-Musculophrenic artery
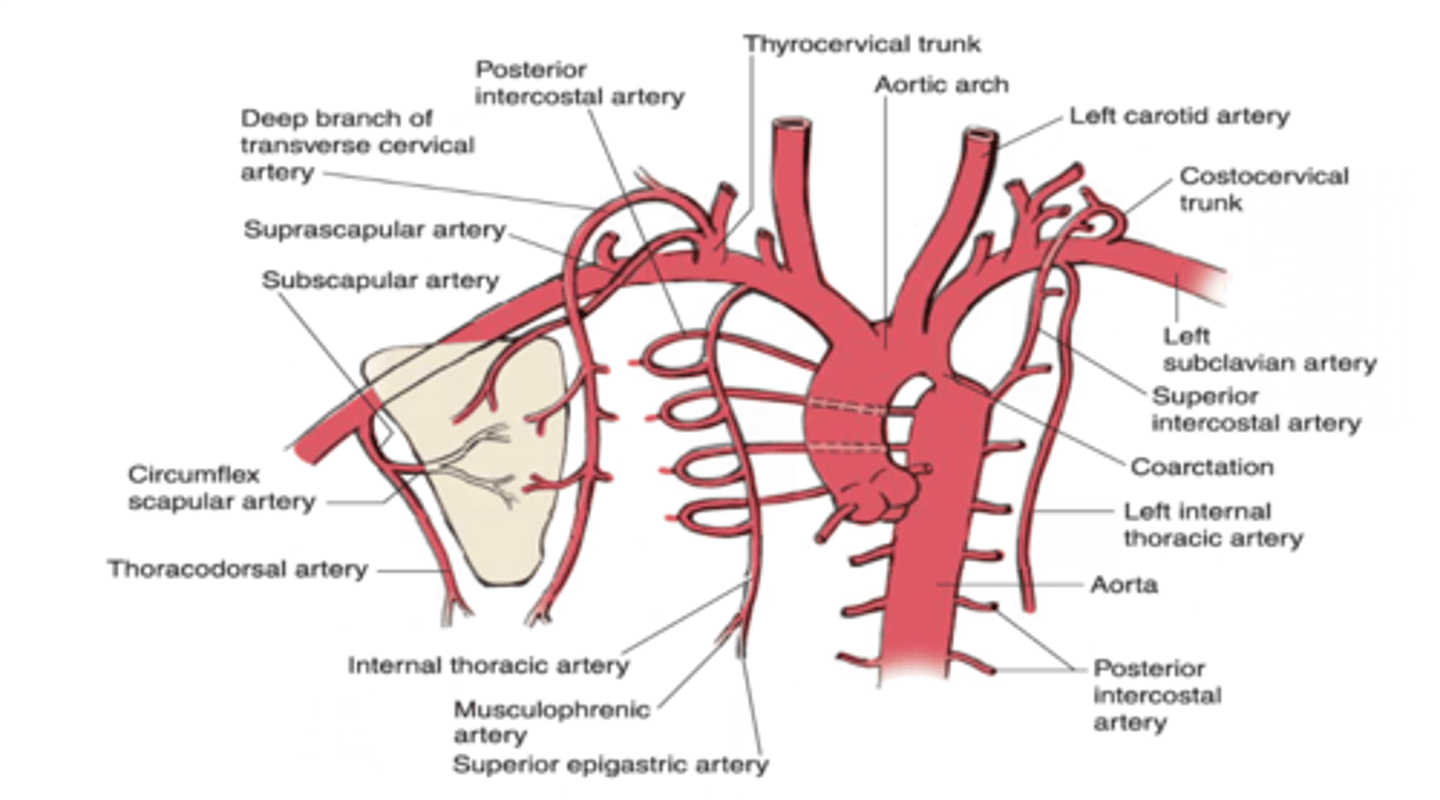
Which branch of the internal thoracic artery provides anterior intercostal arteries in the 7th - 9th intercostal spaces and ends in the 10th intercostal space
Musculophrenic artery
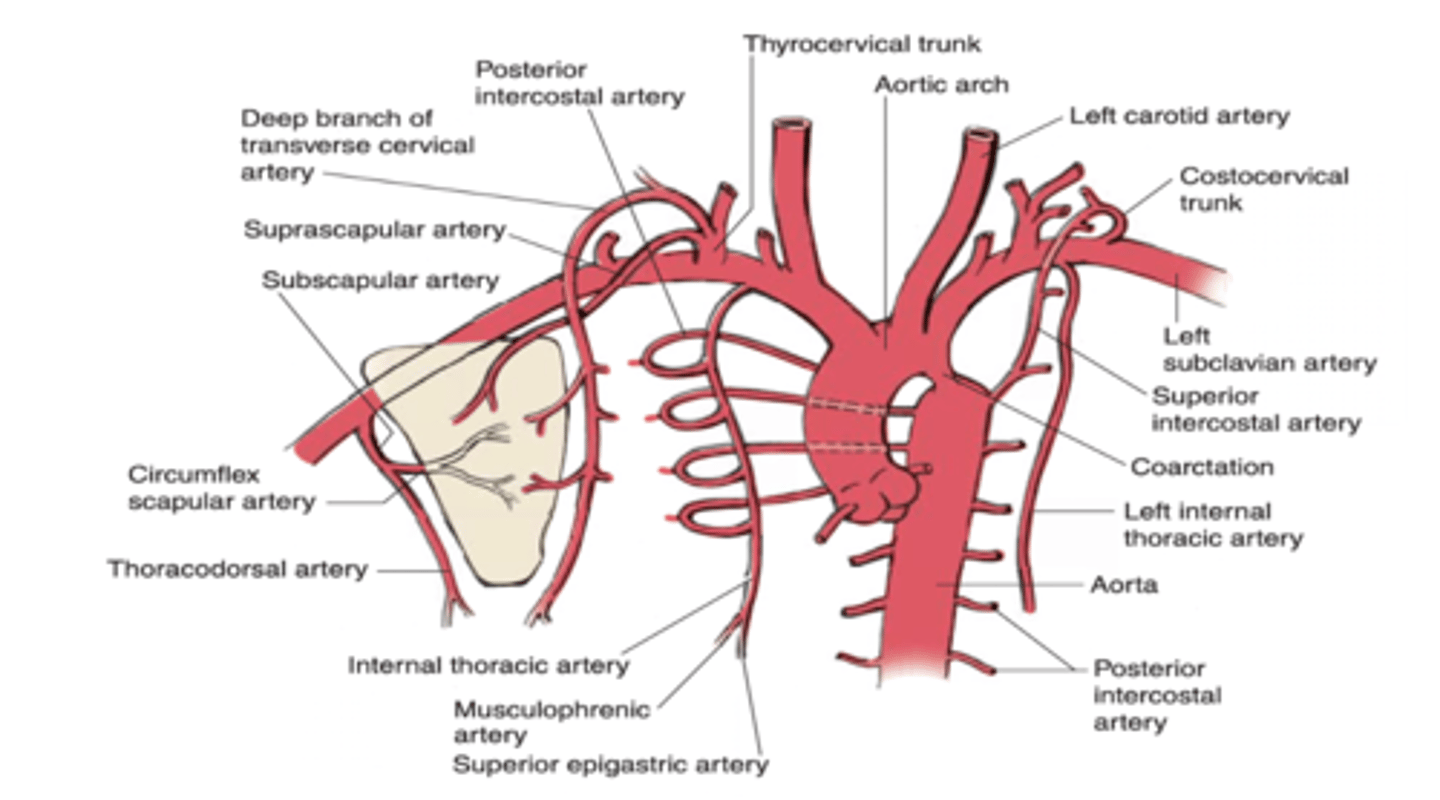
The musculophrenic artery anastomoses with what artery at the 10th intercostal space?
Deep circumflex iliac artery
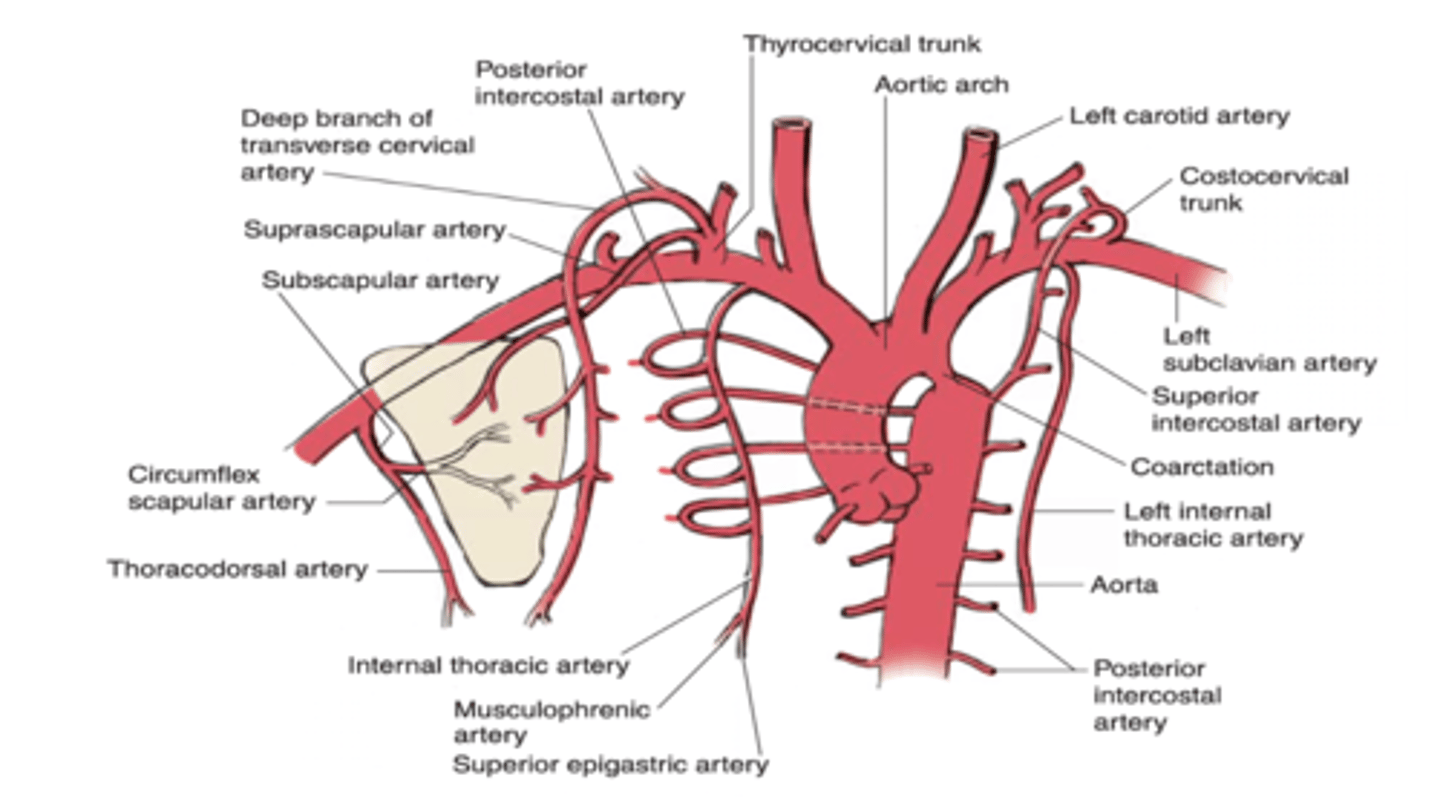
The apex of the heart receives blood from what branch of the left coronary artery?
Anterior interventricular branch
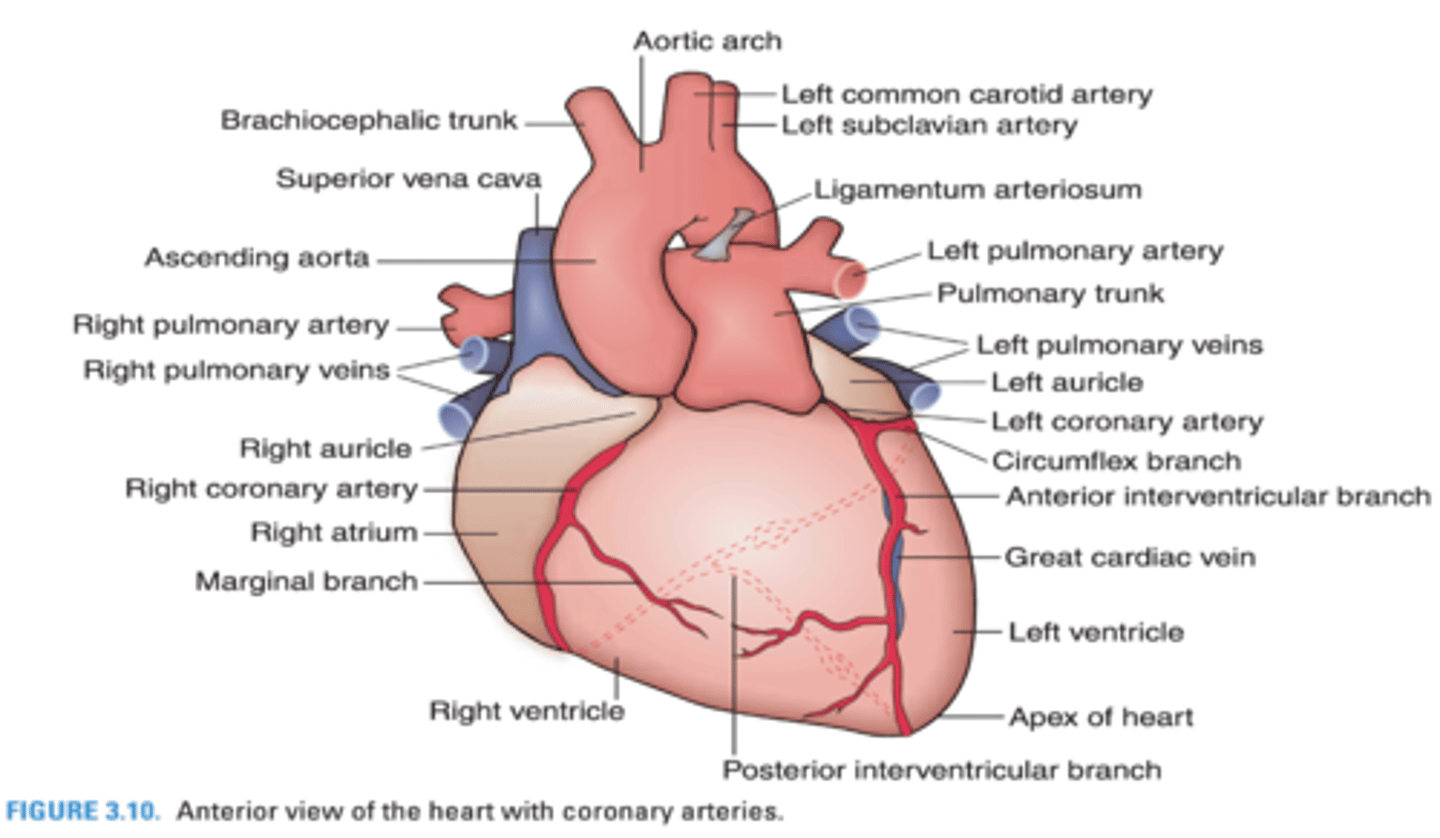
What coronary artery supplies the right inferior margin of the right ventricle?
Right marginal artery
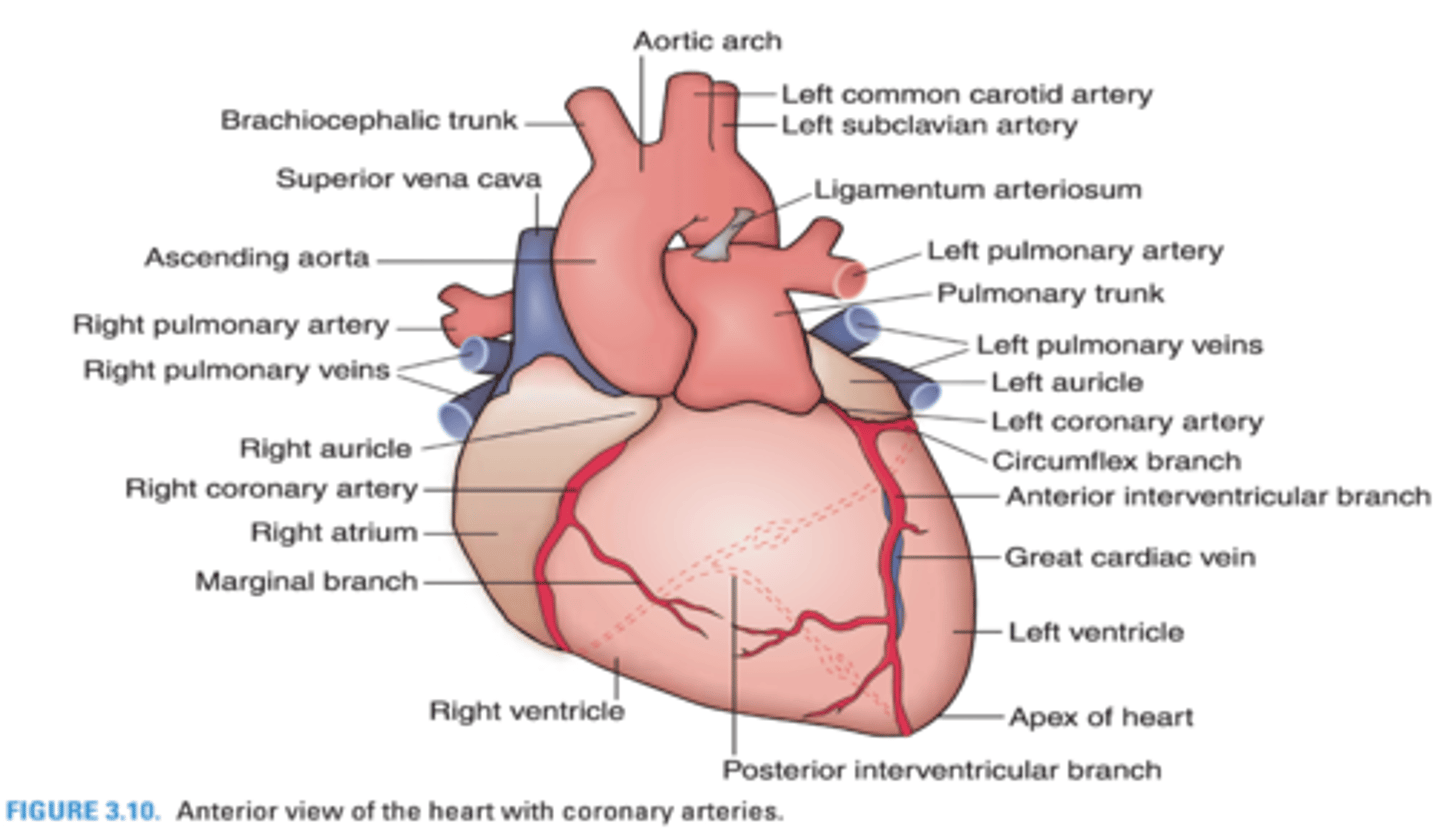
What 2 coronary arteries supply the left ventricle?
Posterior interventricular arteryCircumflex branch of left coronary artery
What is the tongue-shaped portion of the left lung?
Lingula
In what lobe of the left lung can one find the lingula?
Upper lobe of the left lung
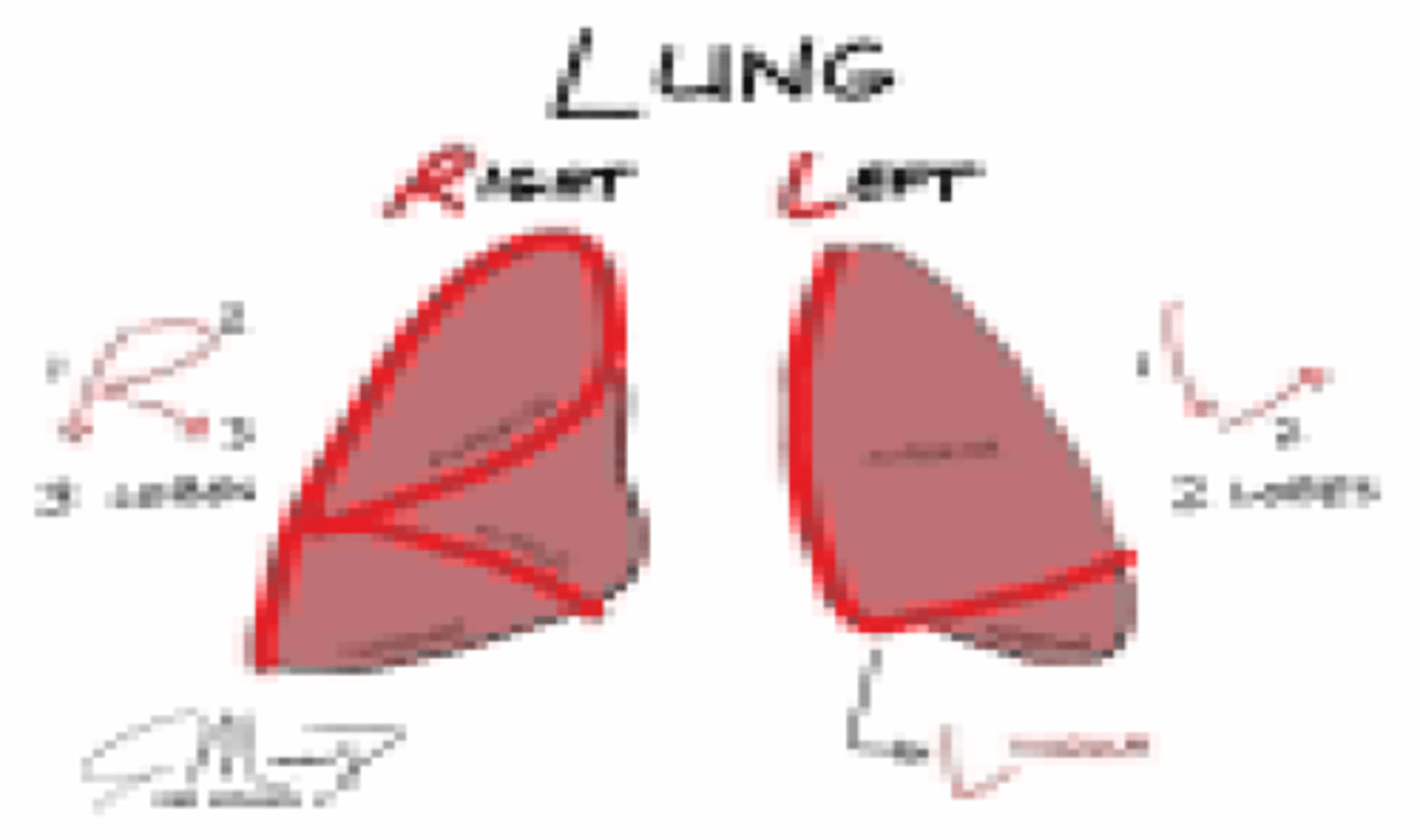
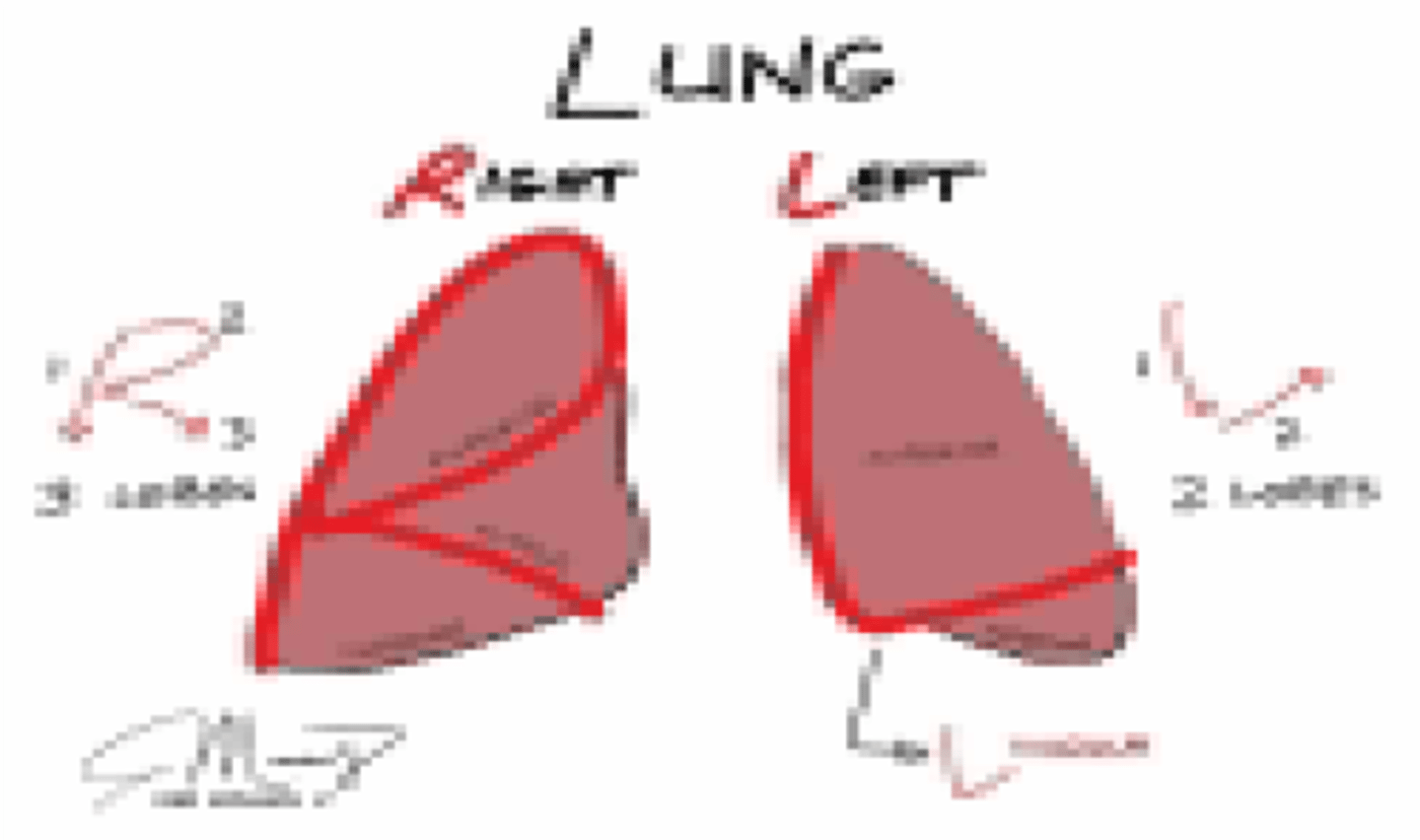
Which lung has a larger capacity?
Right lung
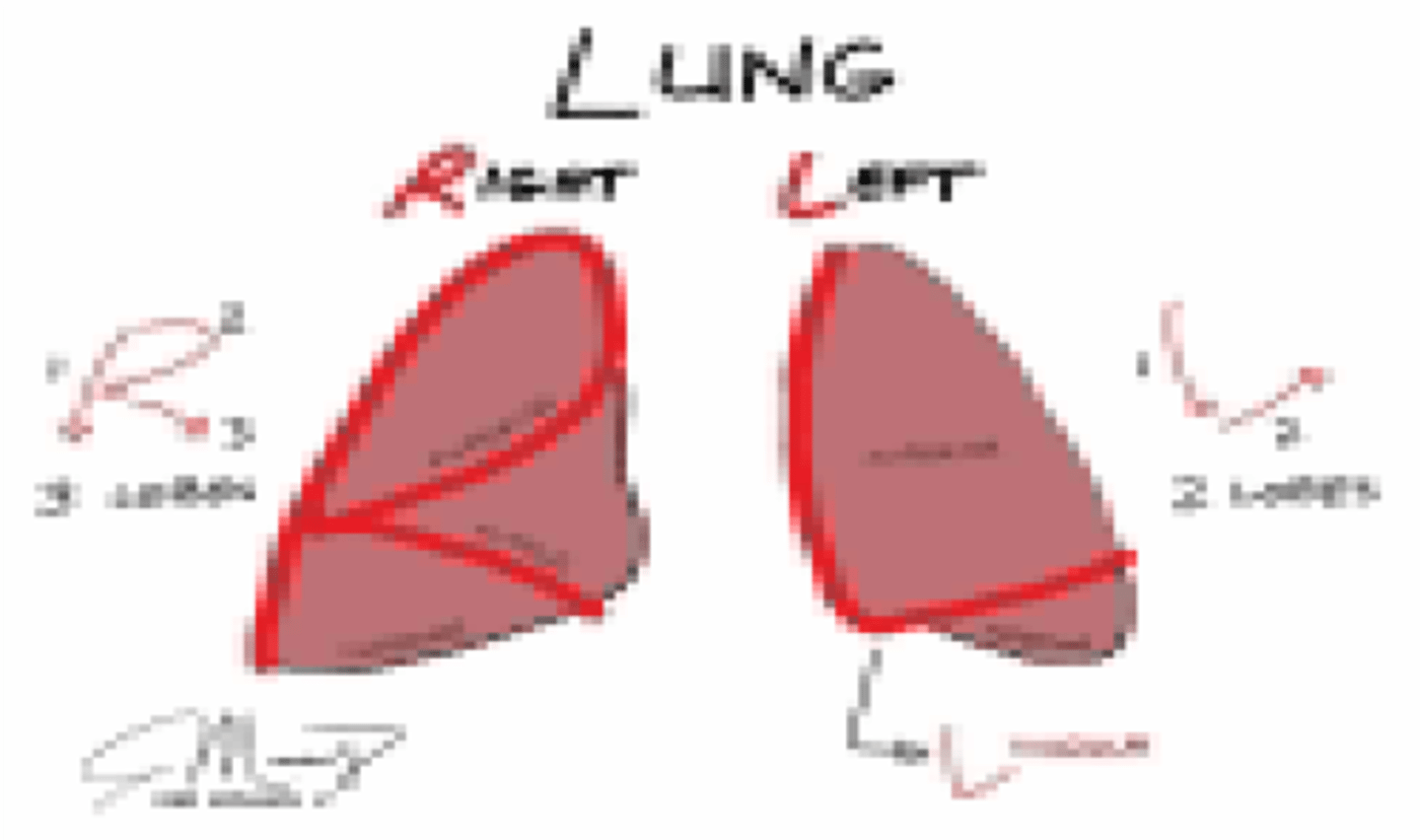
Which lung has a middle lobe?
Right lung
Abdominal muscles are used for which phase of respiration?
Expiration (forced)
The hemiazygos vein is located in which division of the mediastinum?
Posterior mediastinum
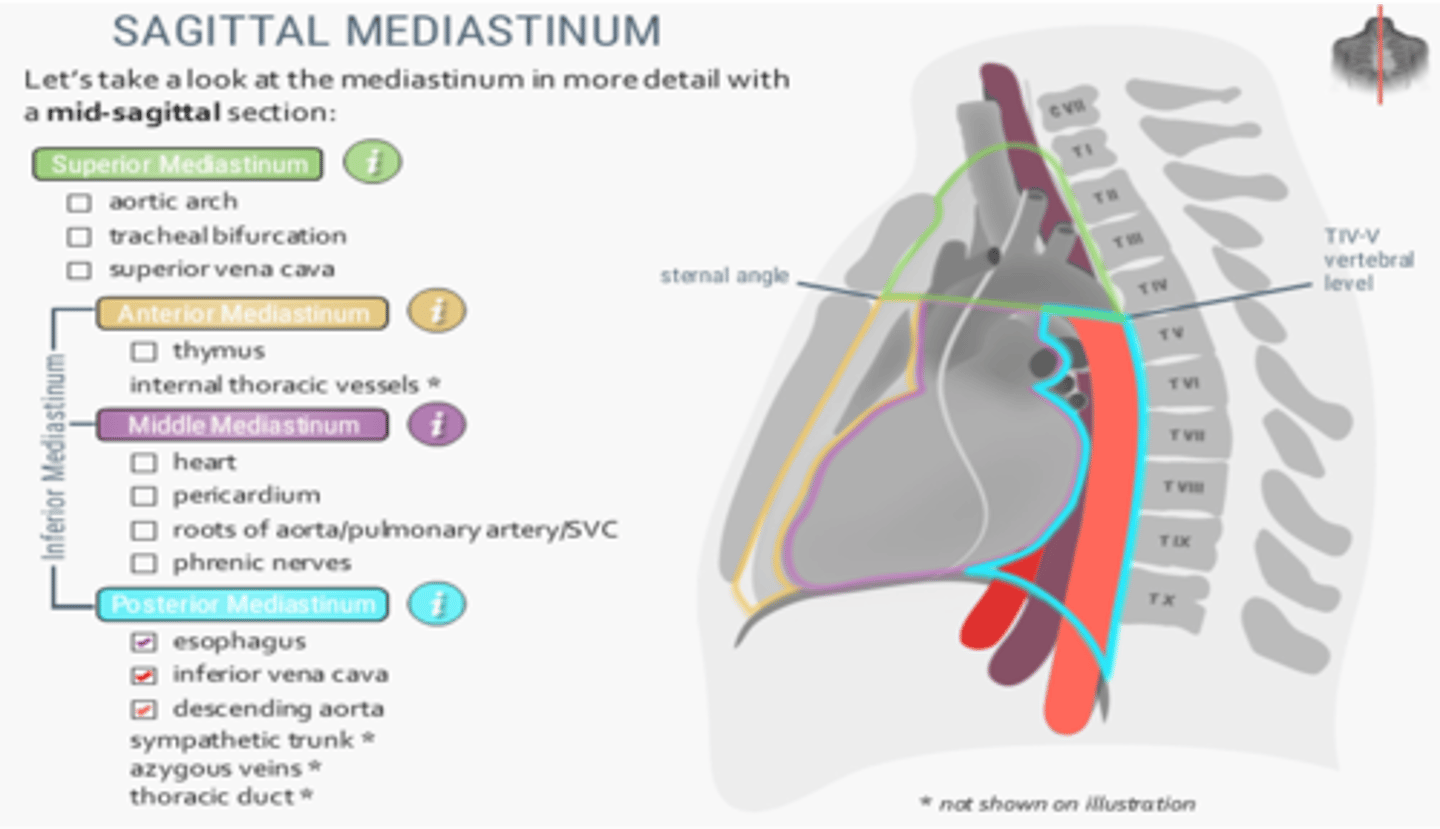
The brachiocephalic veins, trachea and arch of the aorta are located in which division of the mediastinum?
Superior mediastinum
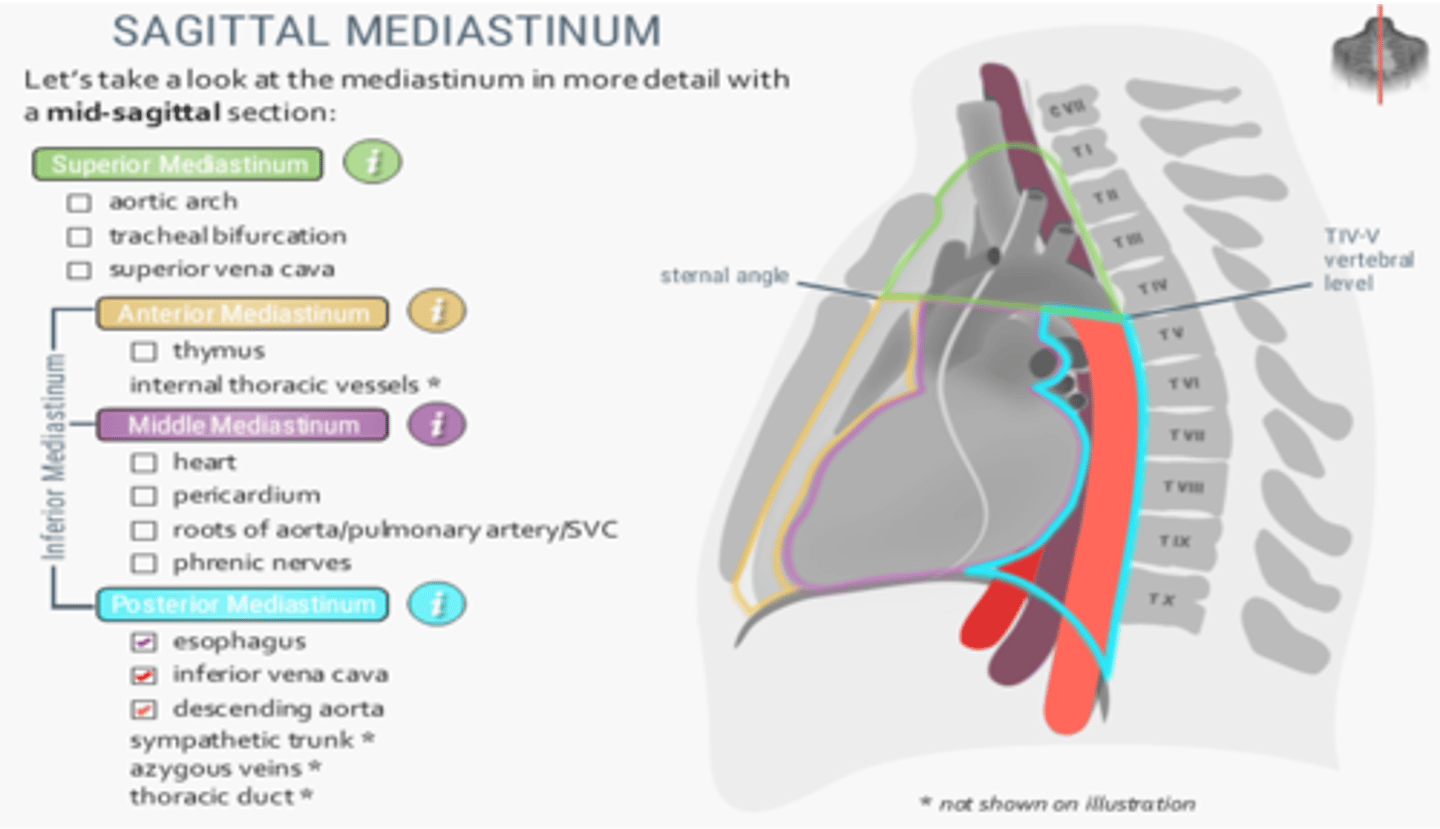
The arch of the azygos vein is found in which division of the mediastinum?
Middle mediastinum
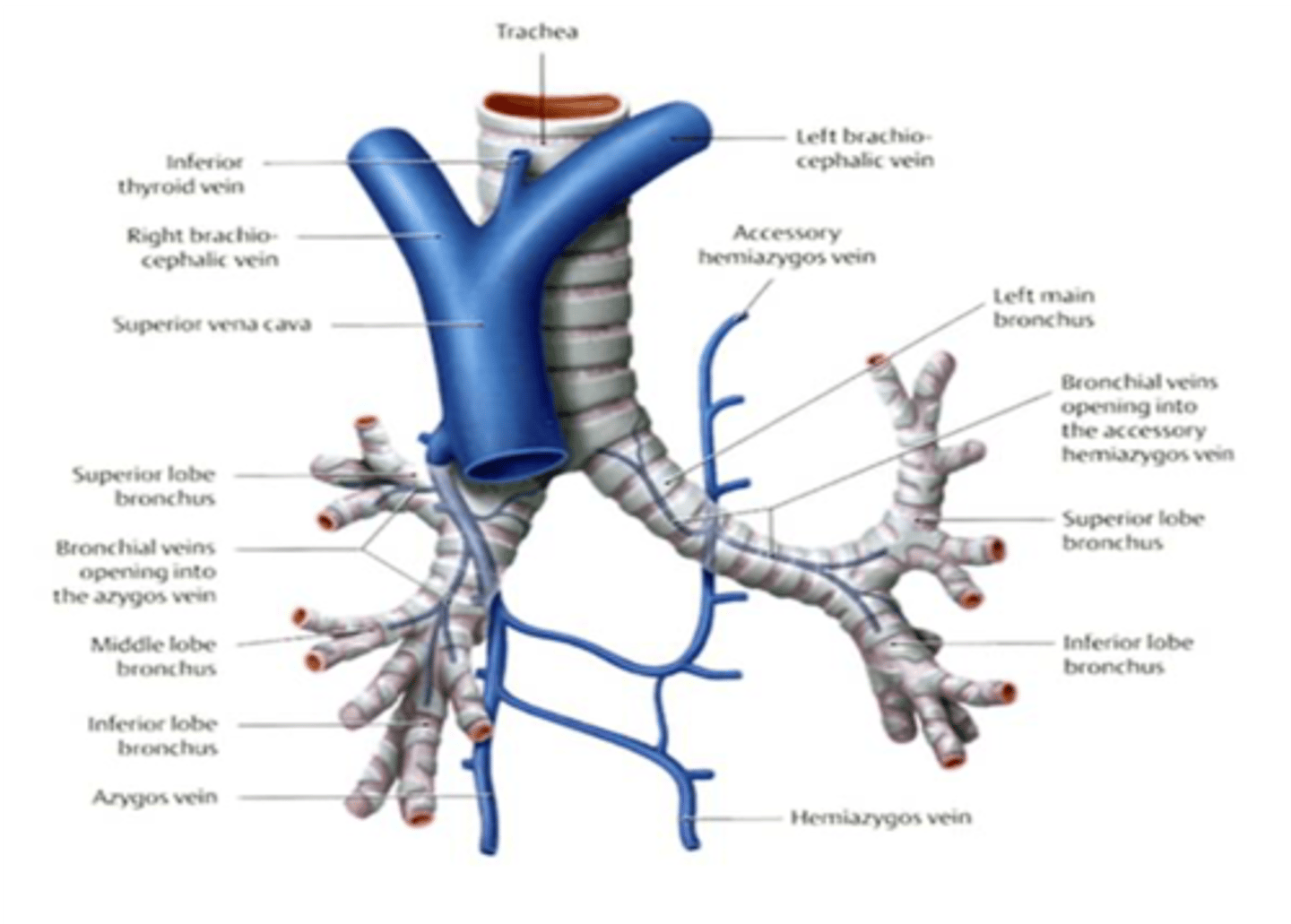
What vein arches over the root of the right lung and empties into the superior vena cava?
Azygos vein
What cranial nerve supplies parasympathetic fibers to the lungs and heart?
Vagus nerve
What cranial nerve carries afferent fibers of pain, cough reflex, and stretch of the lung?
Vagus nerve
What is the effect of the parasympathetic stimulus to the bronchial lumen?
Constricts the bronchial lumen
What is the effect of the parasympathetic stimulus to the bronchial smooth muscles?
Contracts bronchial smooth muscle
What is the effect of the parasympathetic stimulus to the bronchial glands?
Stimulates/increases gland secretion
What is the effect of the parasympathetic stimulus to the heart rate?
Decreases
What is the effect of the parasympathetic stimulus to the coronary artery?
Constricts the coronary artery
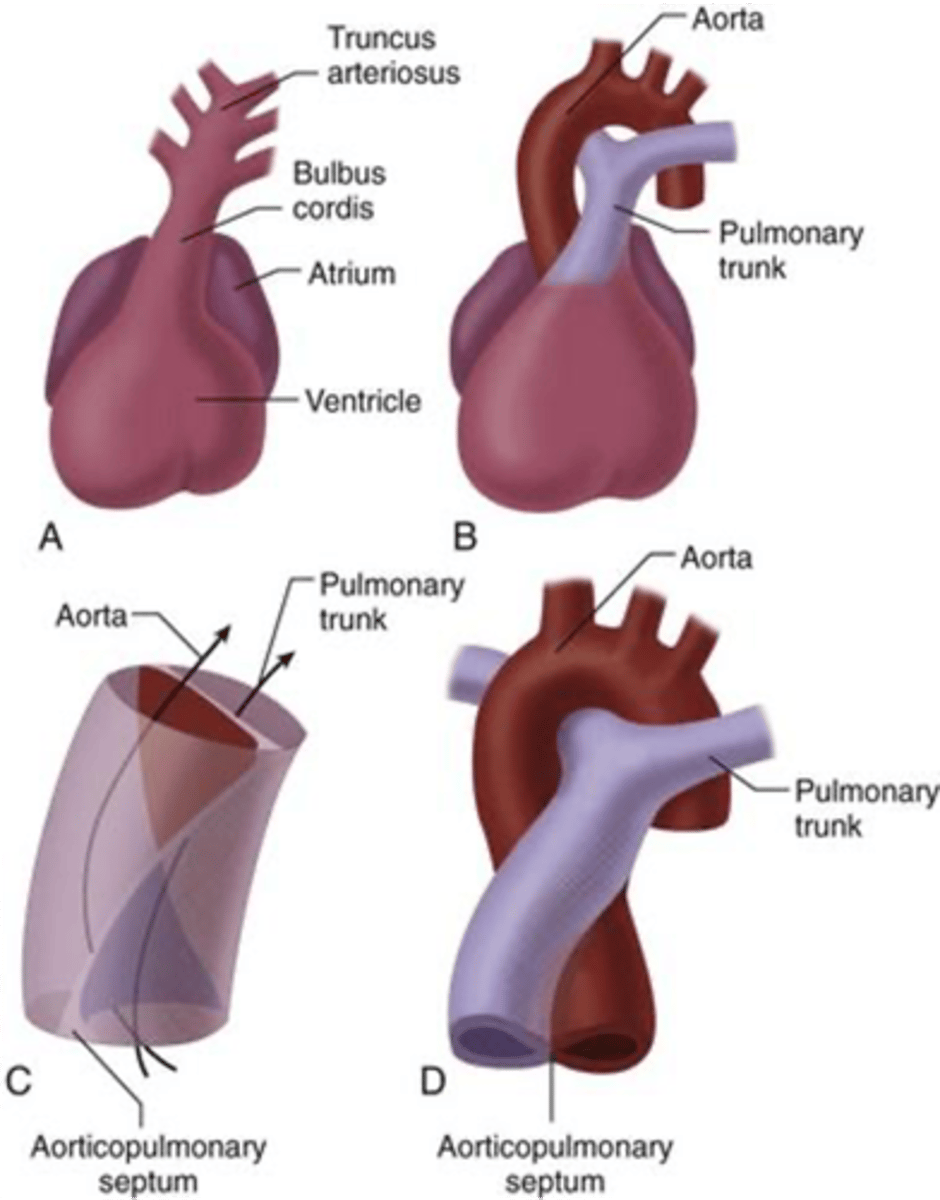
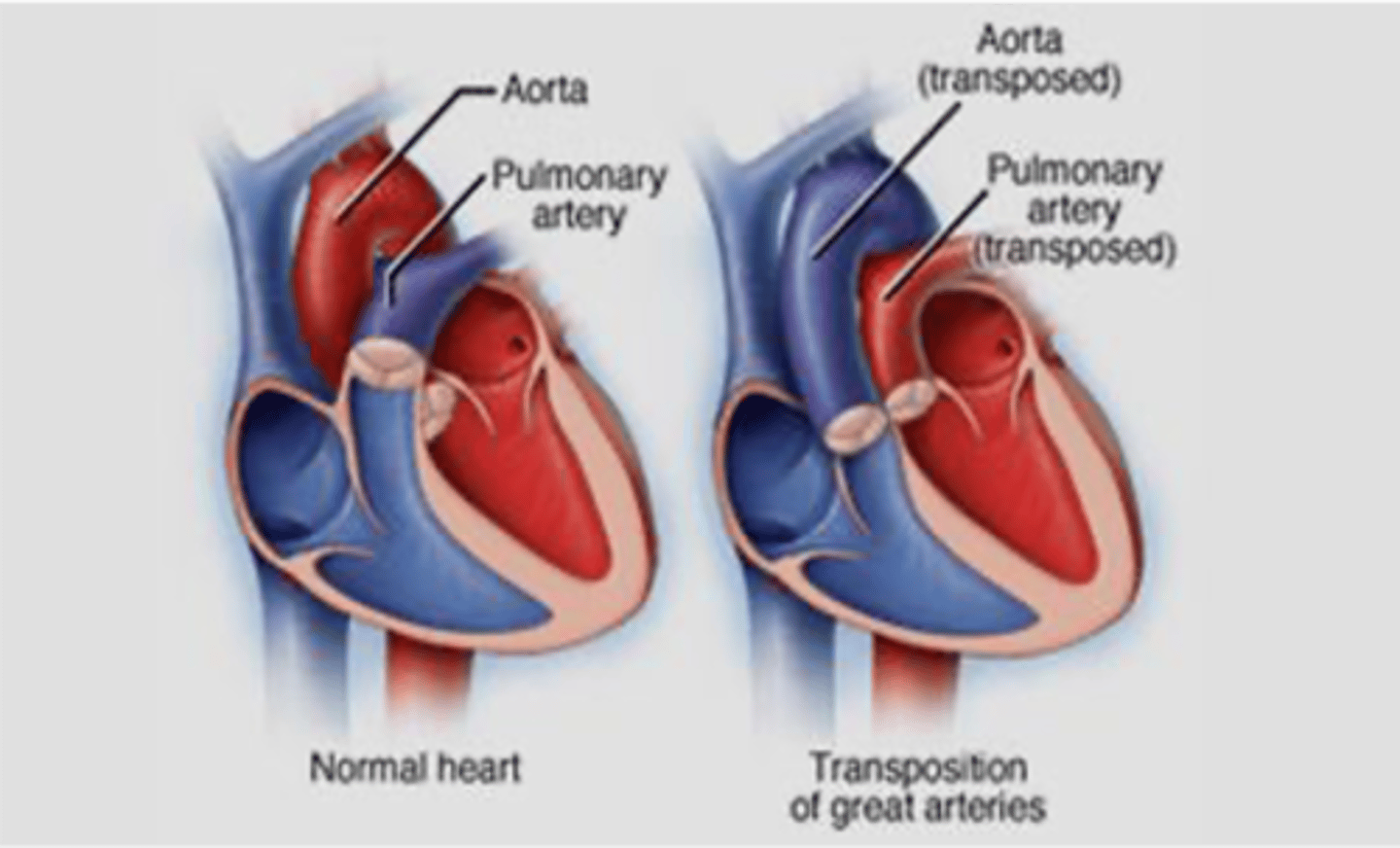
Failure of what embryologic structure results in transposition of great vessels?
Aorticopulmonary (AP) septum
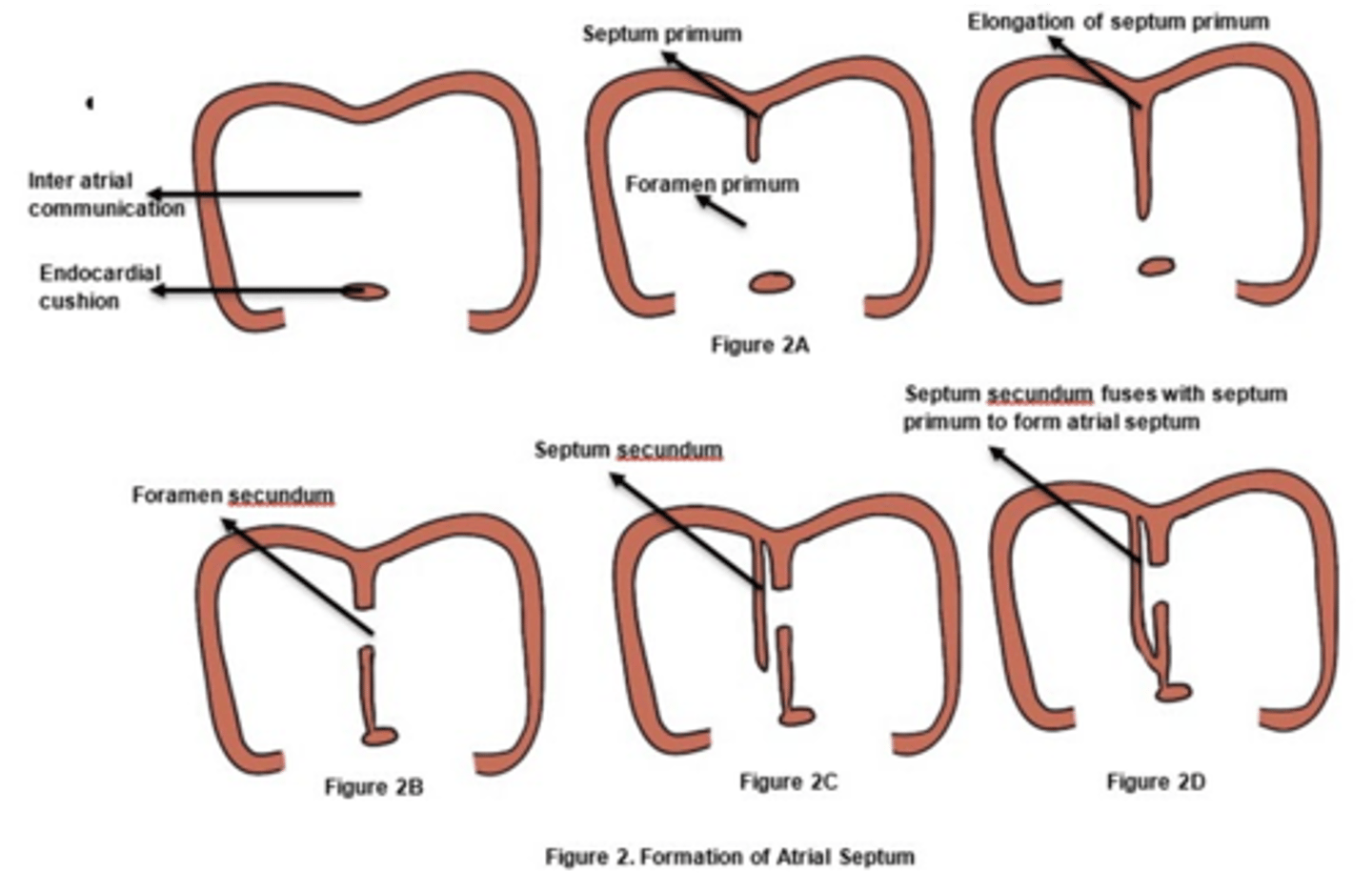
Excessive resorption of what embryologic structure results in secundum type of atrial septal defect?
Septum primum
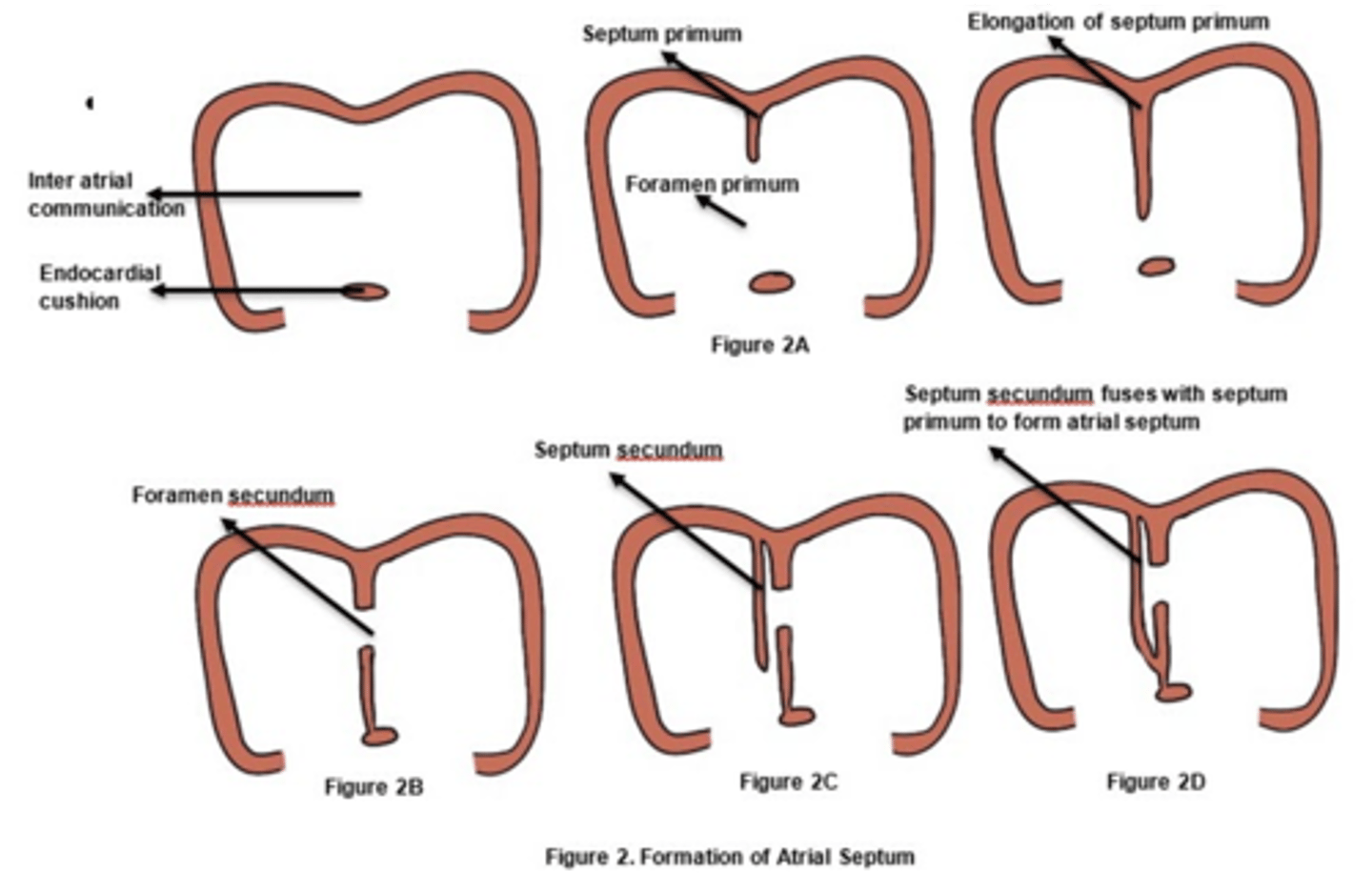
Excessive resorption of septum primum results in what defect?
Secundum type of atrial septal defect
What congenital condition is characterized by the aorta being located to the right of the pulmonary trunk?
Transposition of Great Vessels
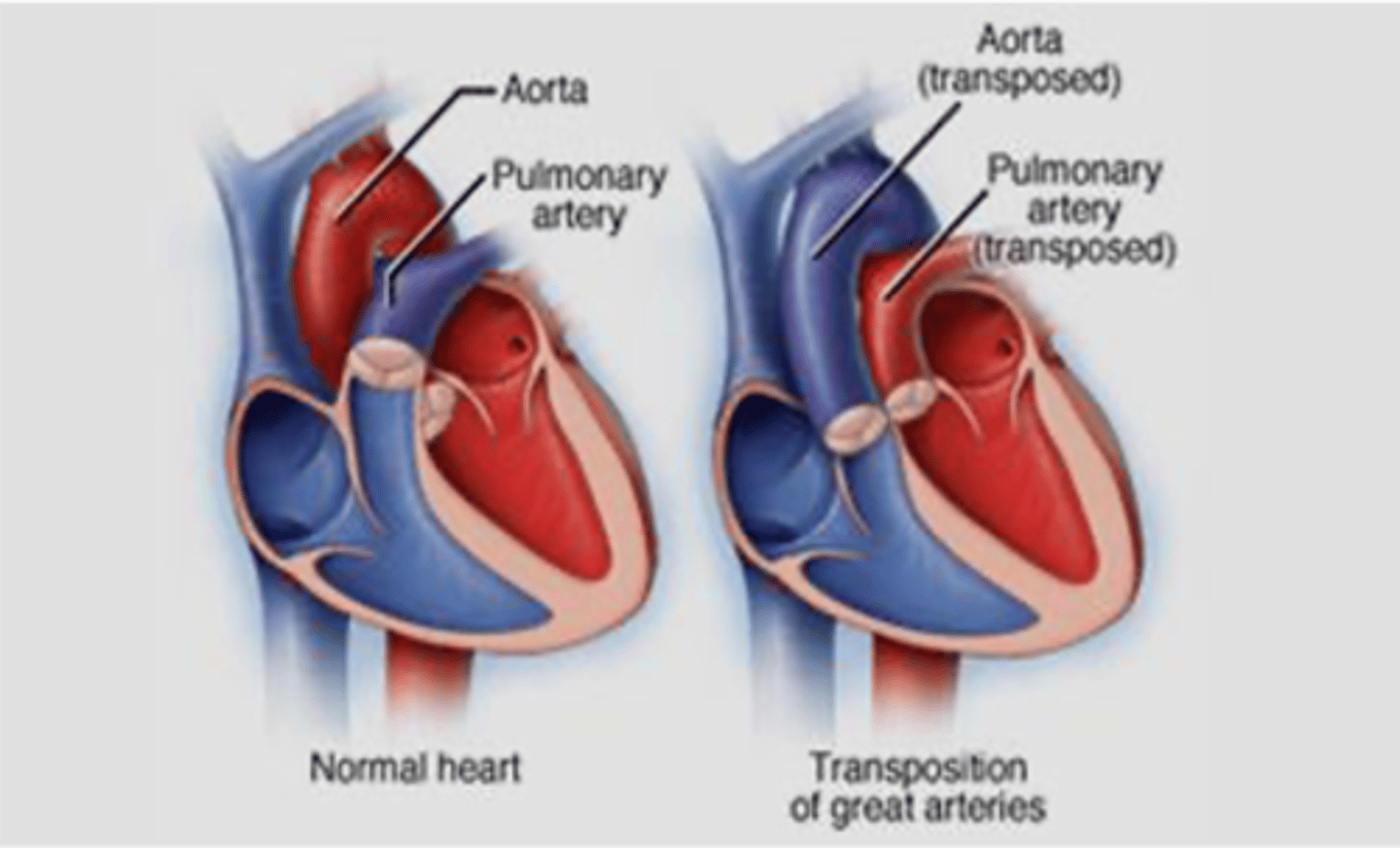
Failure of the aorticopulmonary septum leads to what congenital condition?
Transposition of Great Vessels
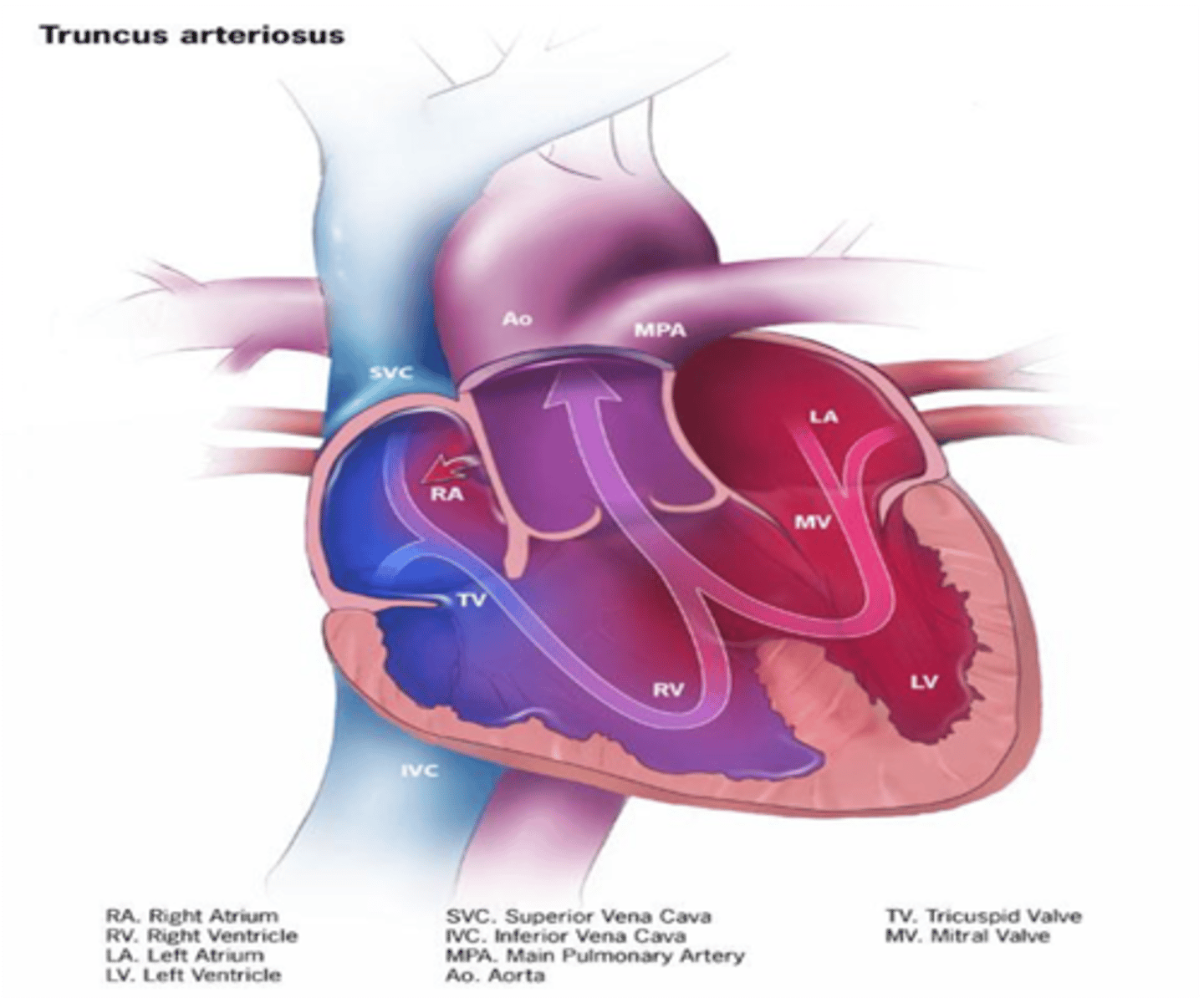
Lack of development of the aorticopulmonary septum leads to what congenital condition?
Persistent truncus arteriosus (Single outflow track)
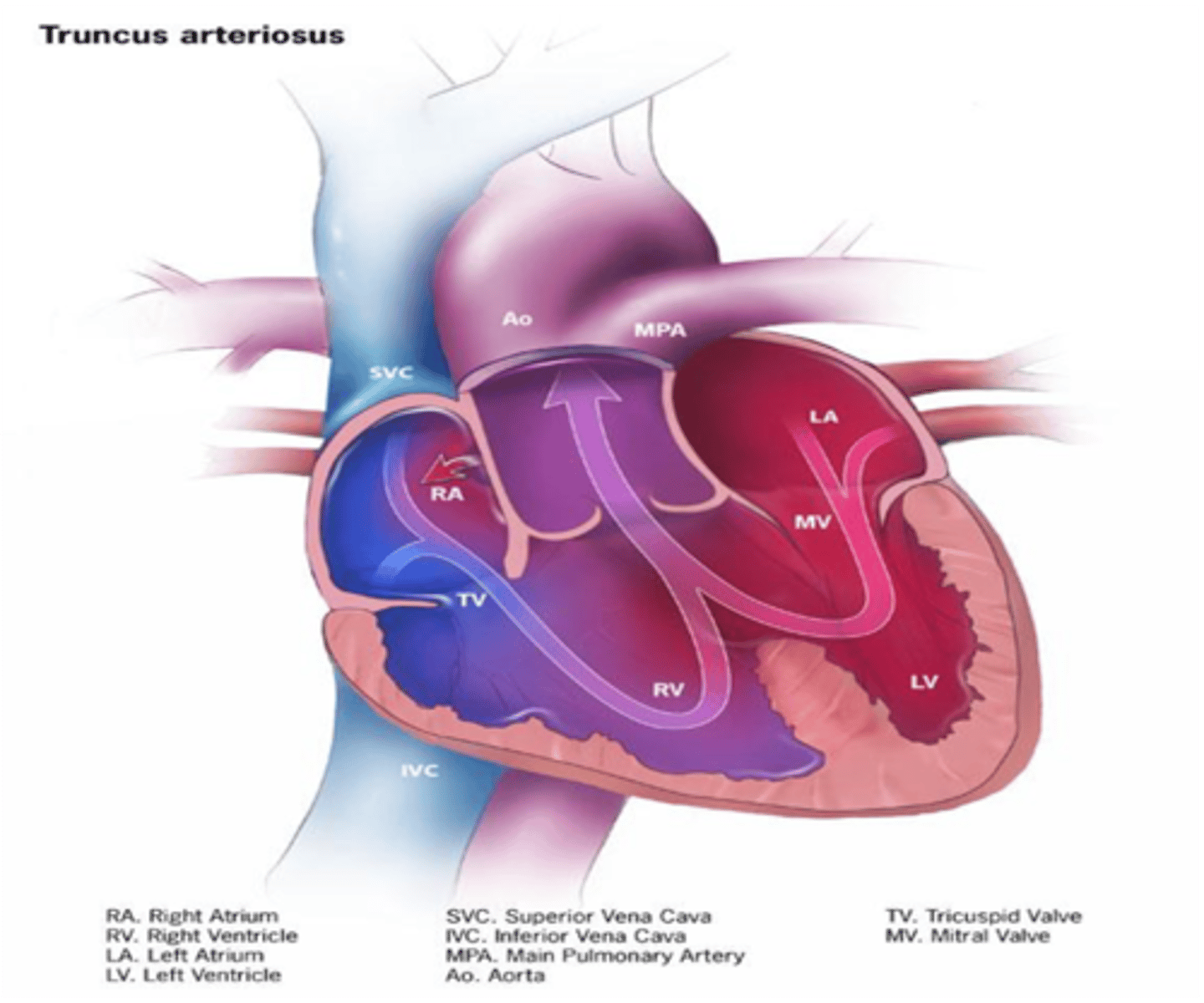
Lack of development of the aorticopulmonary septum leads to persistence of what embryologic structure?
Truncus arteriosus
What congenital disorder is characterized by severe narrowing of the aorta?
Coarctation of the aorta
Which primary bronchus is shorter?
Right Primary Bronchus
Which primary bronchus has a larger diameter?
Right Primary Bronchus
Which primary bronchus is more vertical in orientation?
Right Primary Bronchus
Which primary bronchus is longer?
Left Primary Bronchus
Which primary bronchus has a smaller diameter?
Left Primary Bronchus
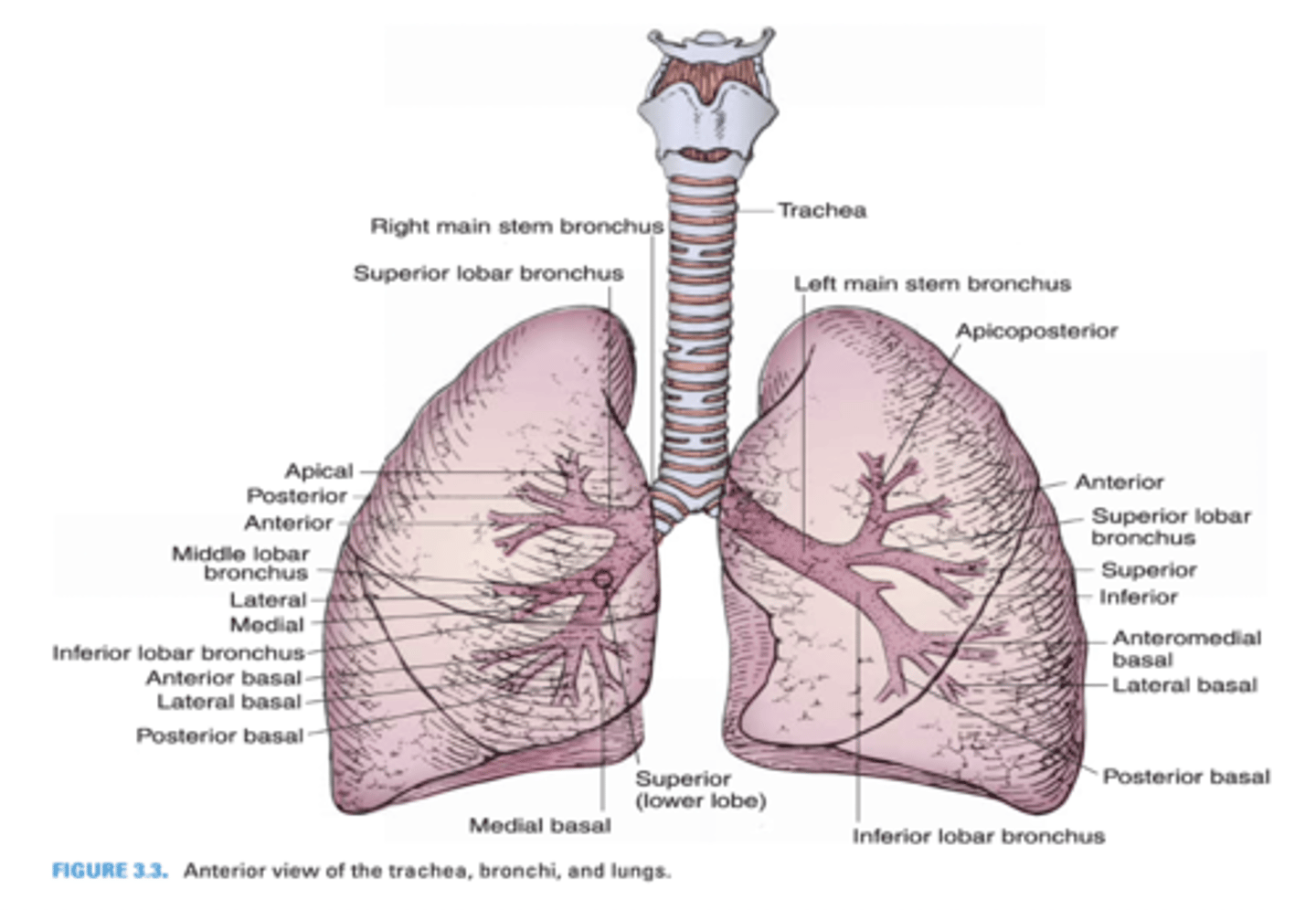
Which primary bronchus runs in a less vertical direction?
Left Primary Bronchus
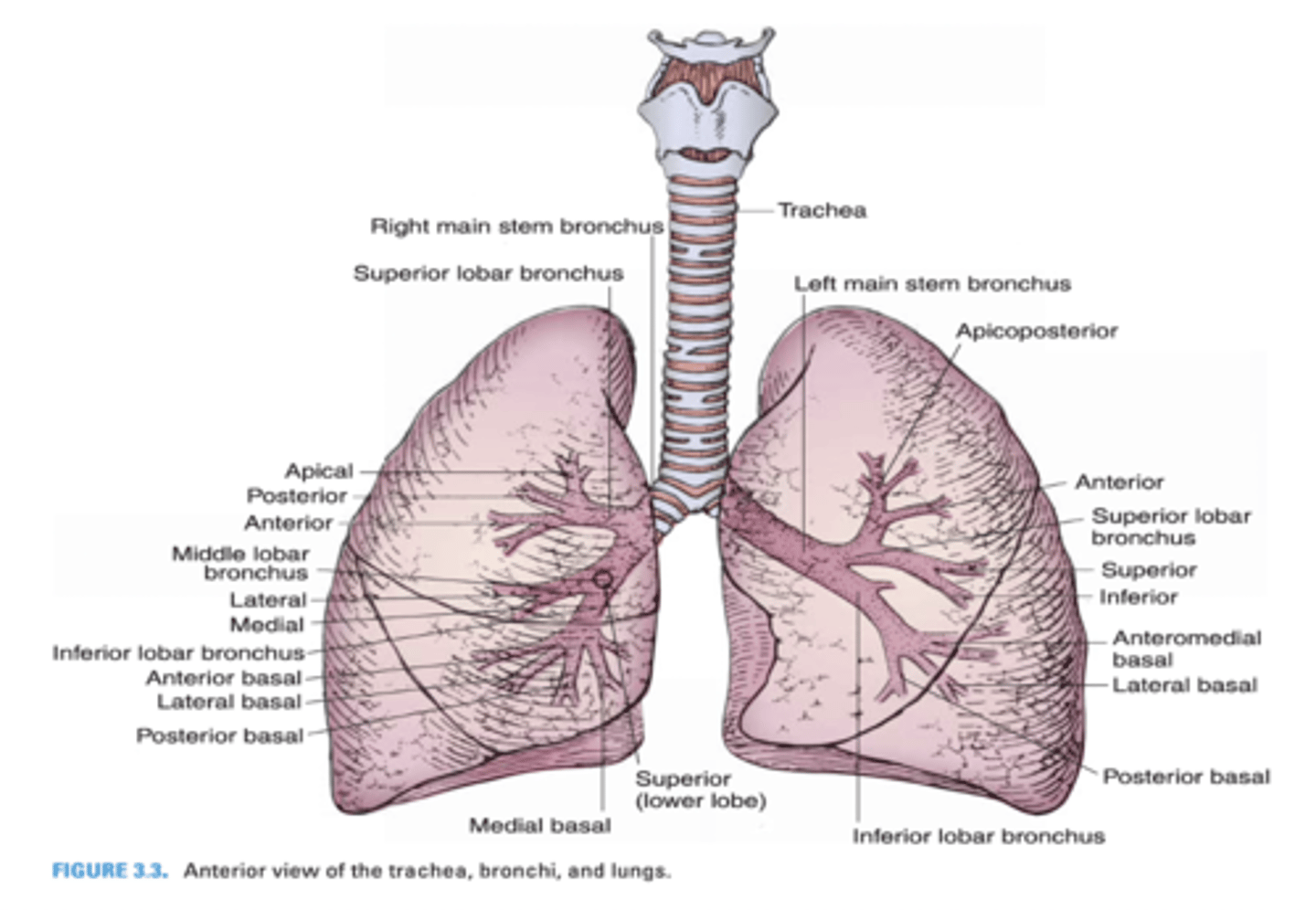
In which primary bronchus do foreign objects usually enter?
Right Primary Bronchus
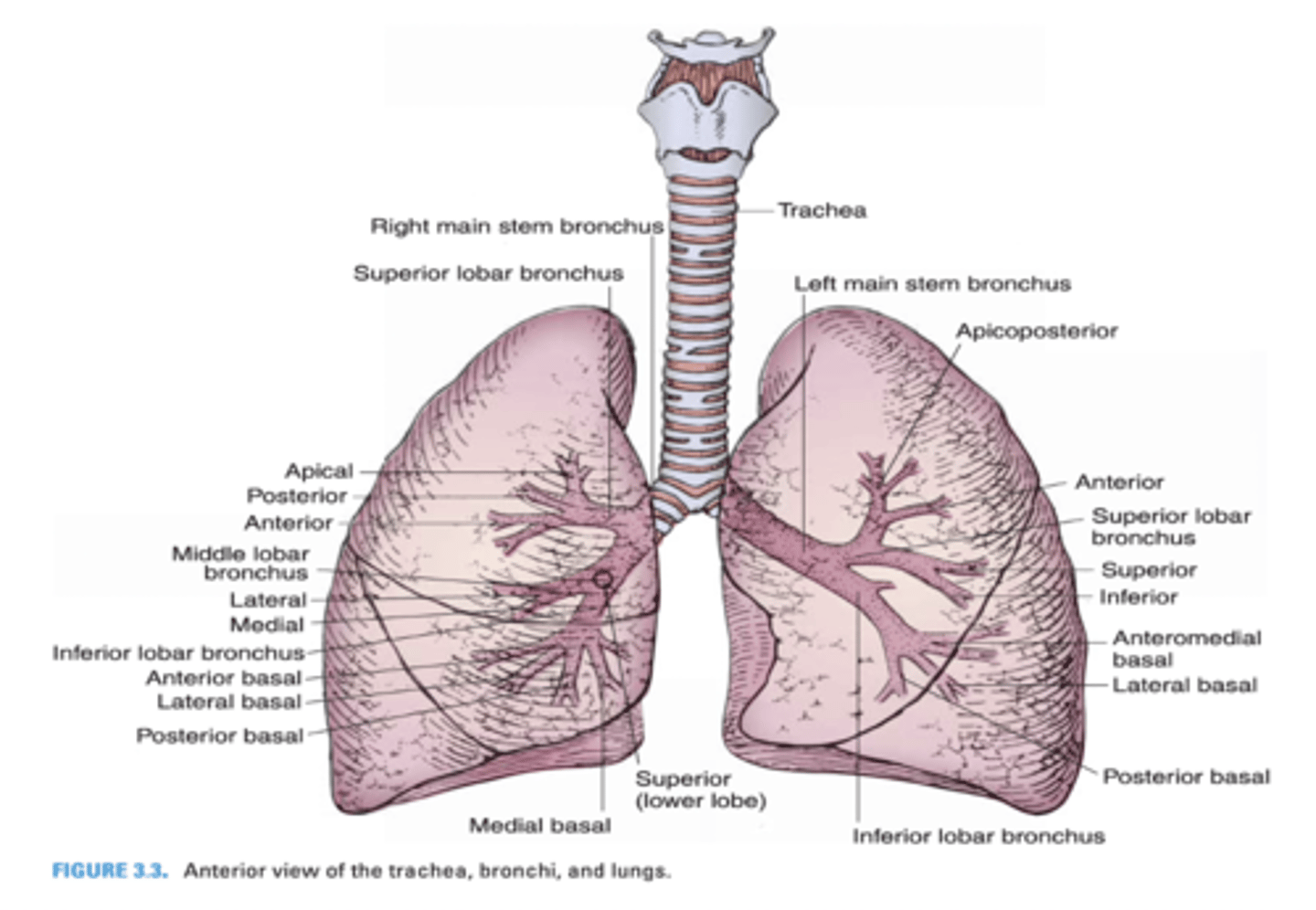
Which primary bronchus gives rise to the eparterial bronchus?
Right Primary Bronchus
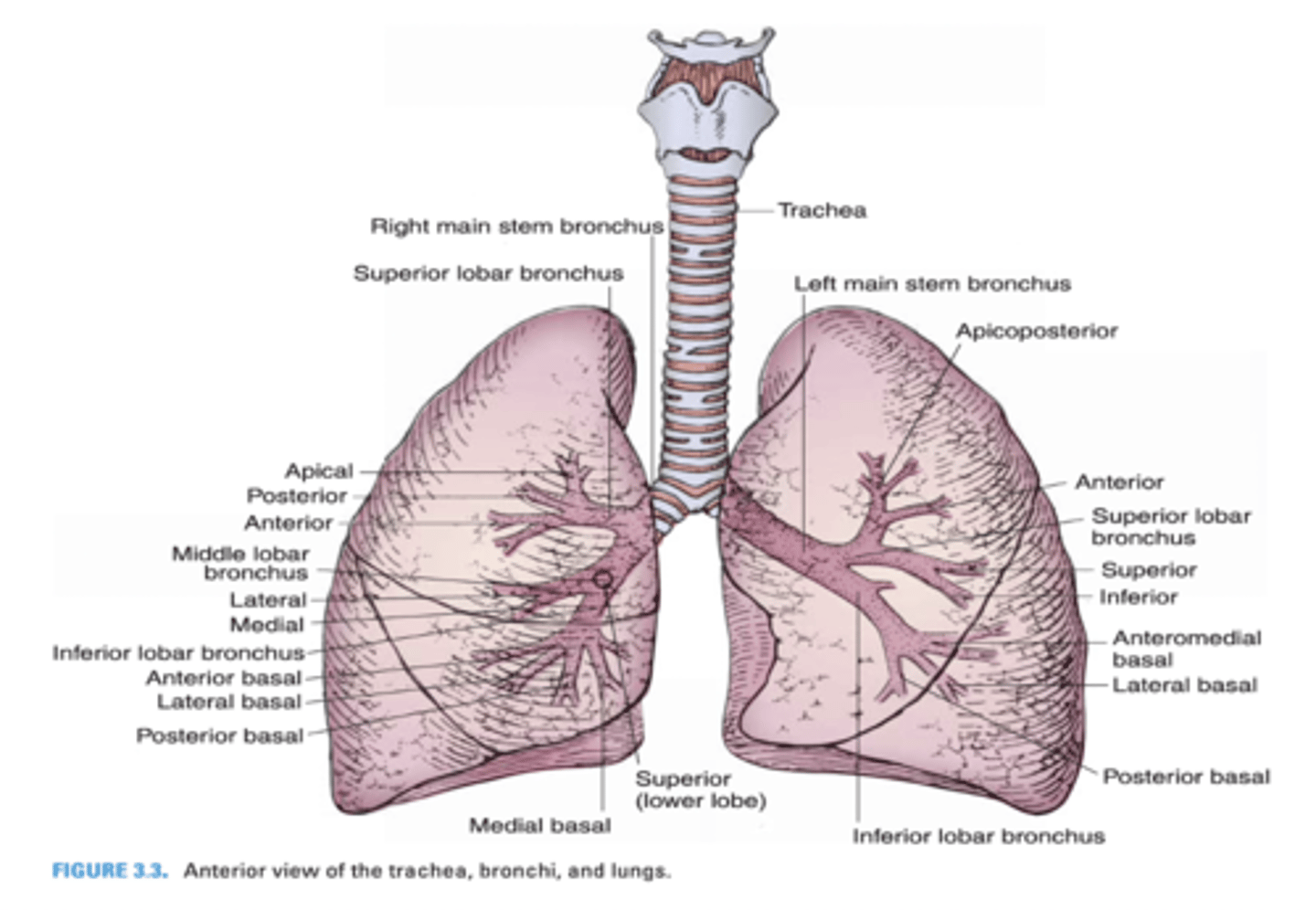
The right primary bronchus runs below what vein?
Azygos vein
In a Chest PA radiograph, what 3 structures form the right border of the cardiac silhouette?
-Superior Vena Cava
-Right atrium
-Inferior Vena Cava
The right primary bronchus runs below what vein?
Azygos vein
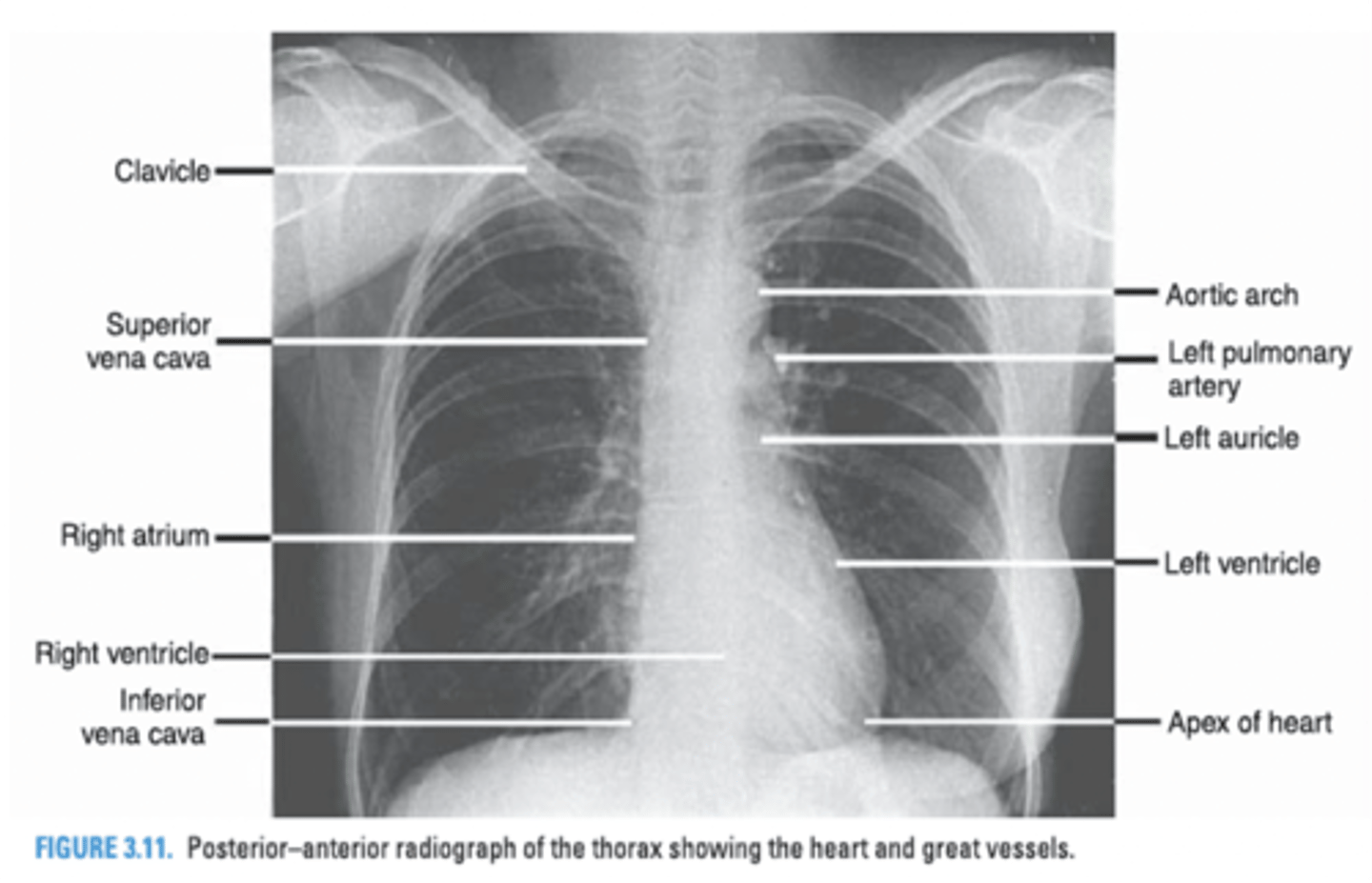
In a Chest PA radiograph, what 3 structures form the right border of the cardiac silhouette?
-Superior Vena Cava
-Right atrium
-Inferior Vena Cava
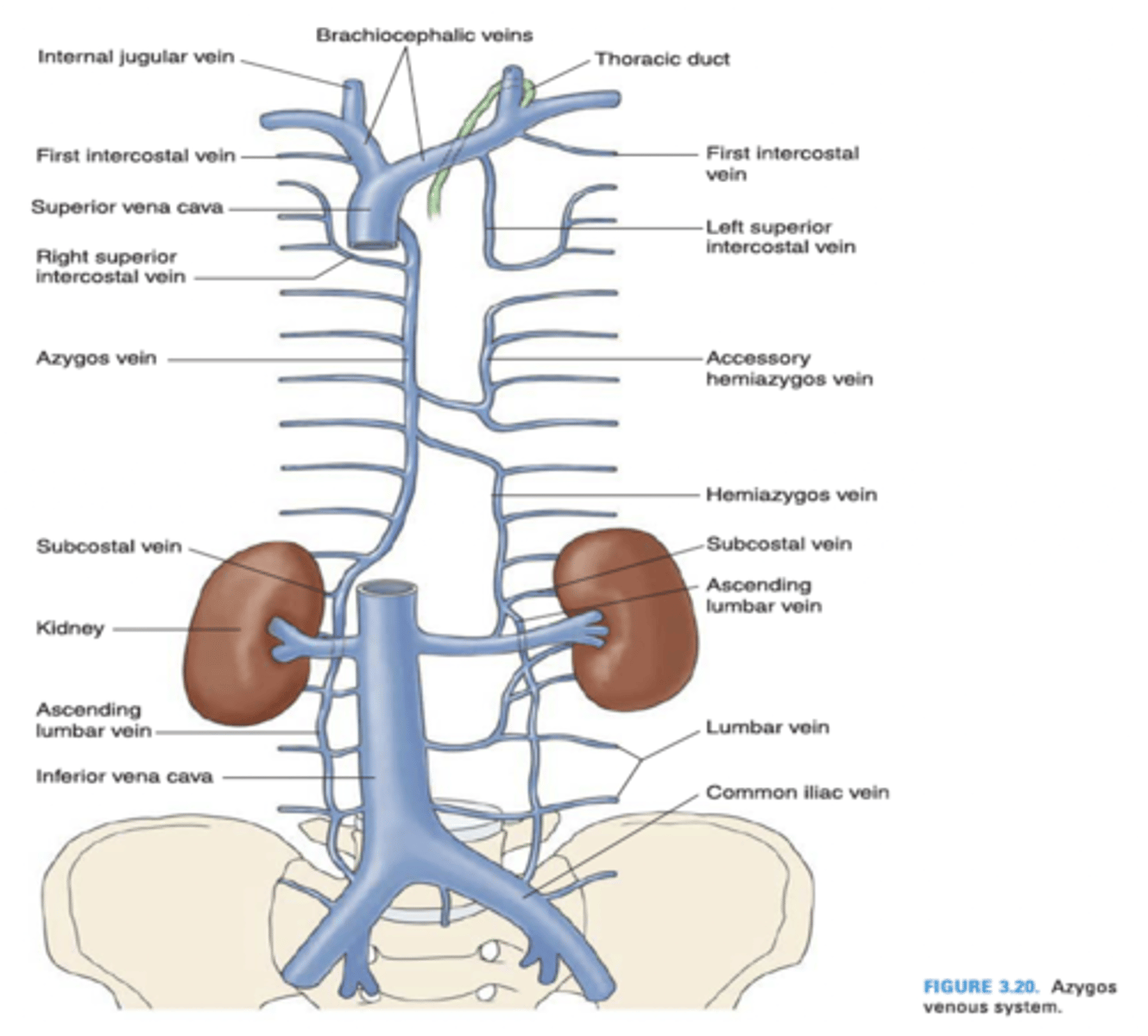
The left superior intercosal vein drains into what vein?
Left brachiocephalic vein
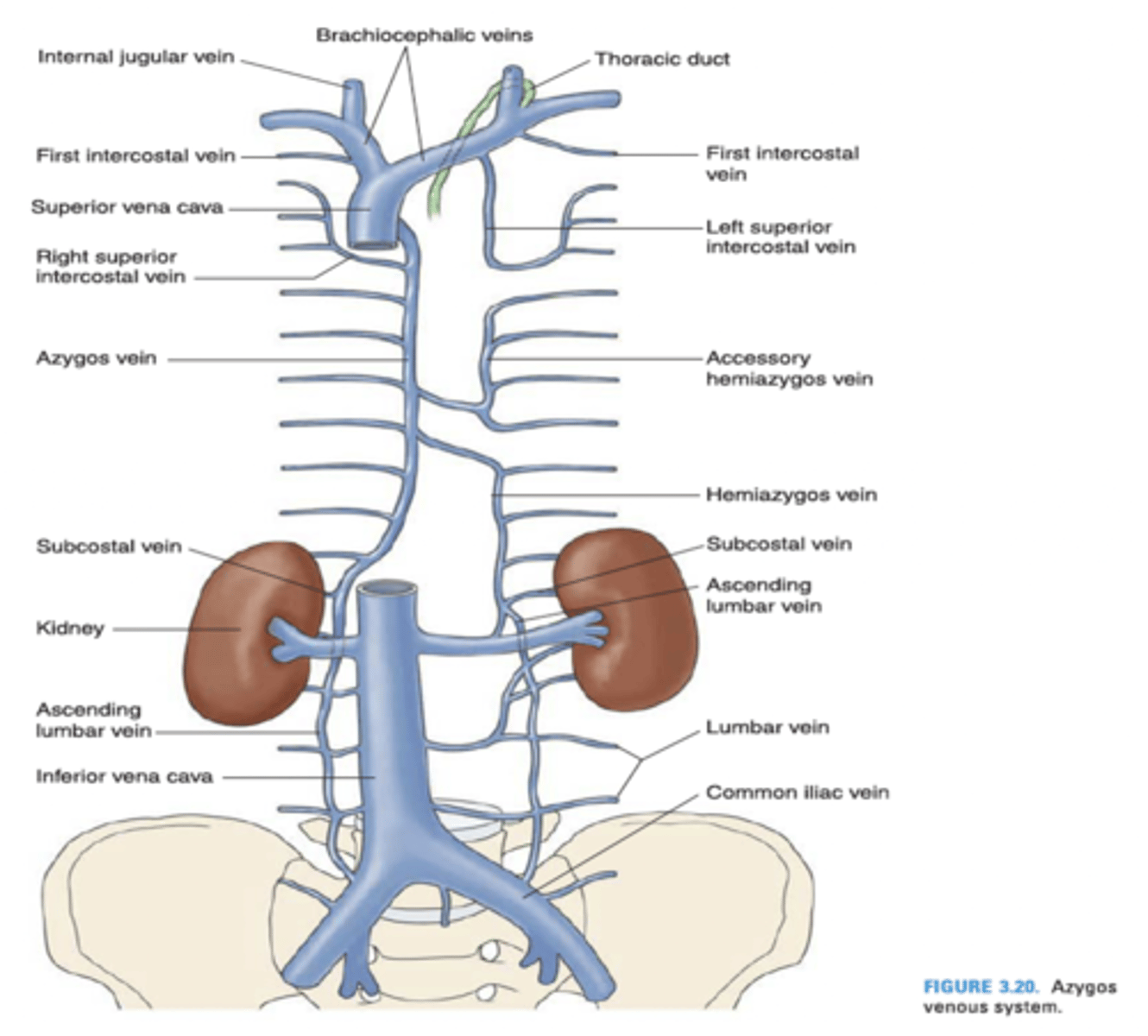
Left brachiocephalic vein
Azygos vein
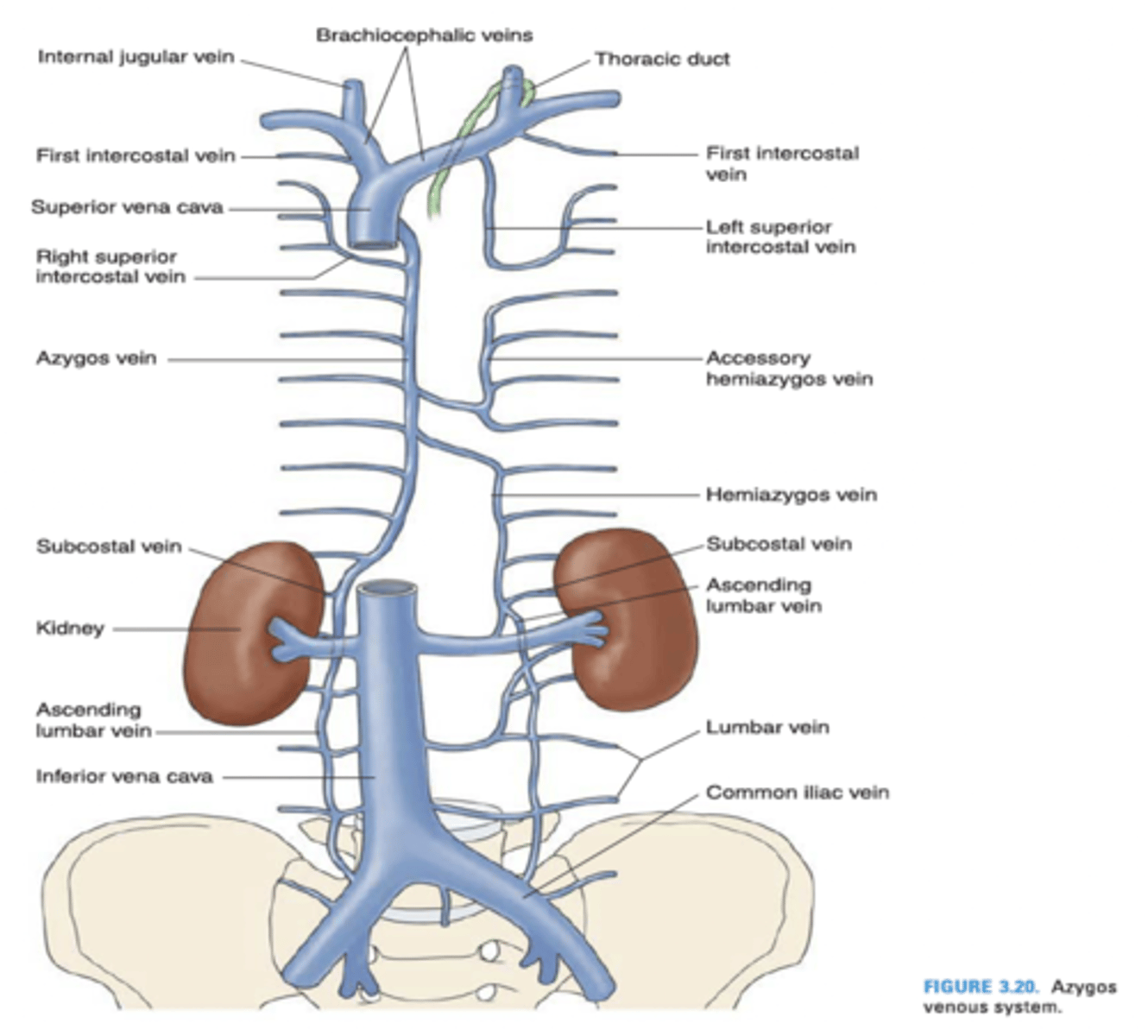
The left superior intercostal vein is composed of what intercostal veins?
2nd, 3rd and 4th posterior intercostal veins
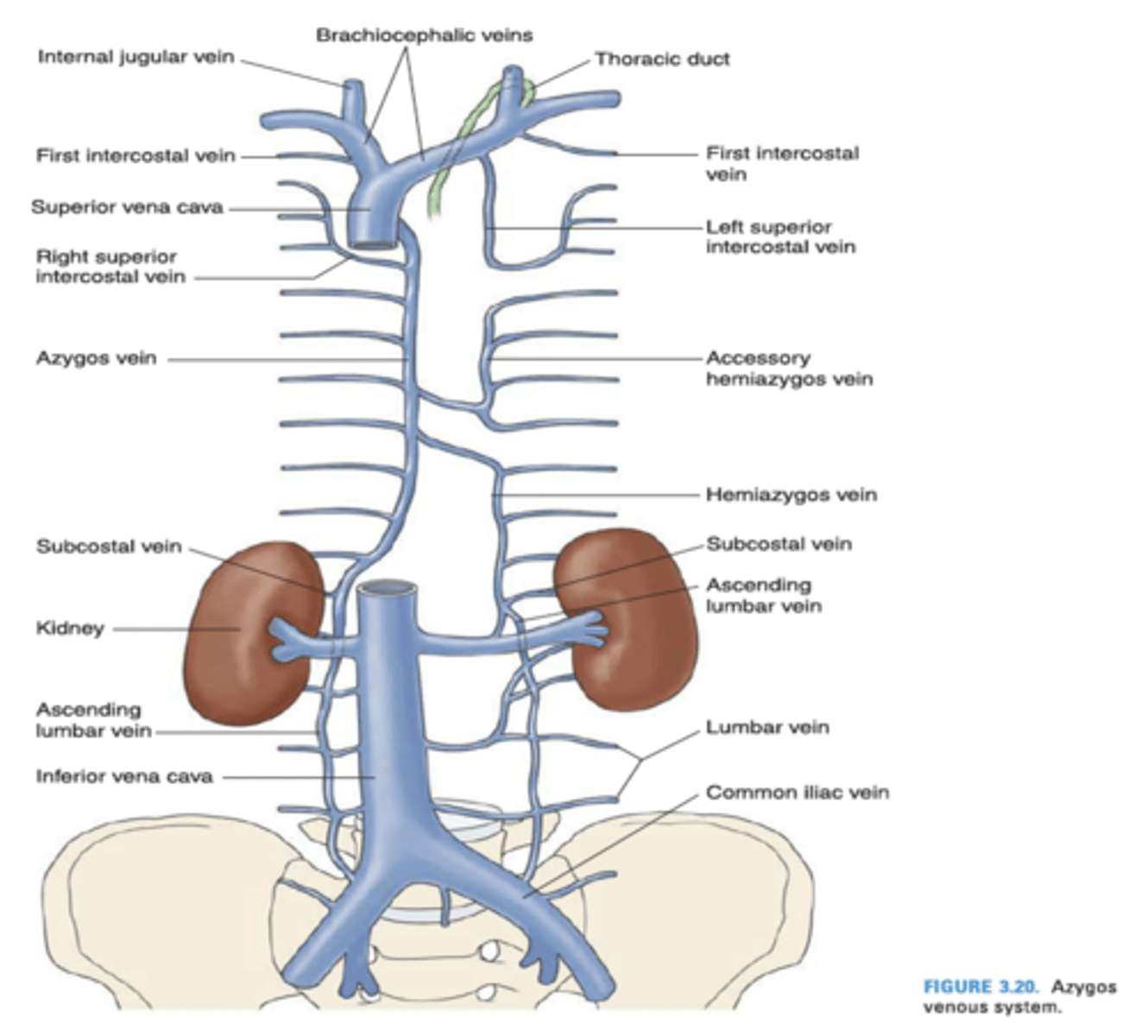
The azygos vein drains into what vein?
Superior vena cava
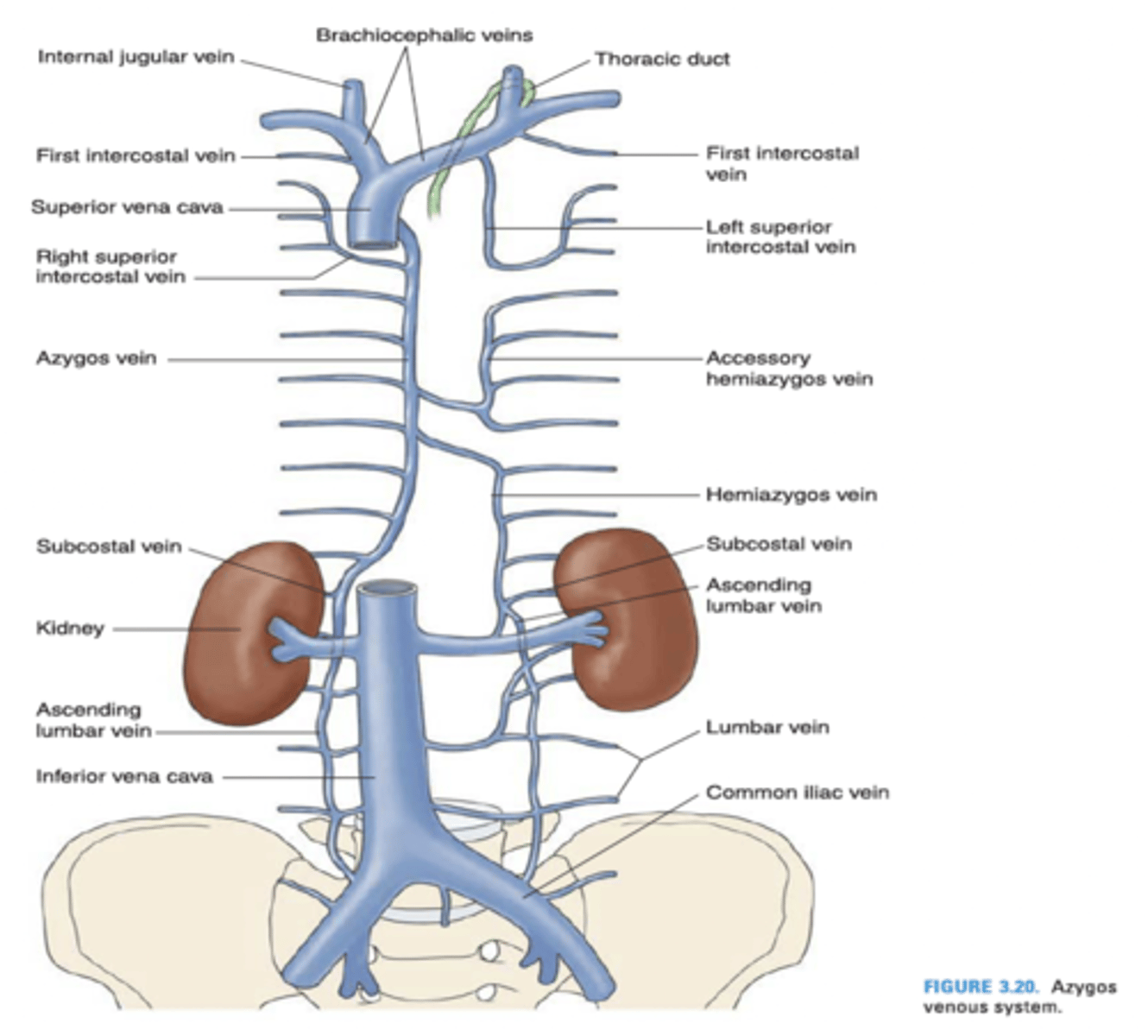
The hemiazygos vein drains into what vein?
Azygos vein
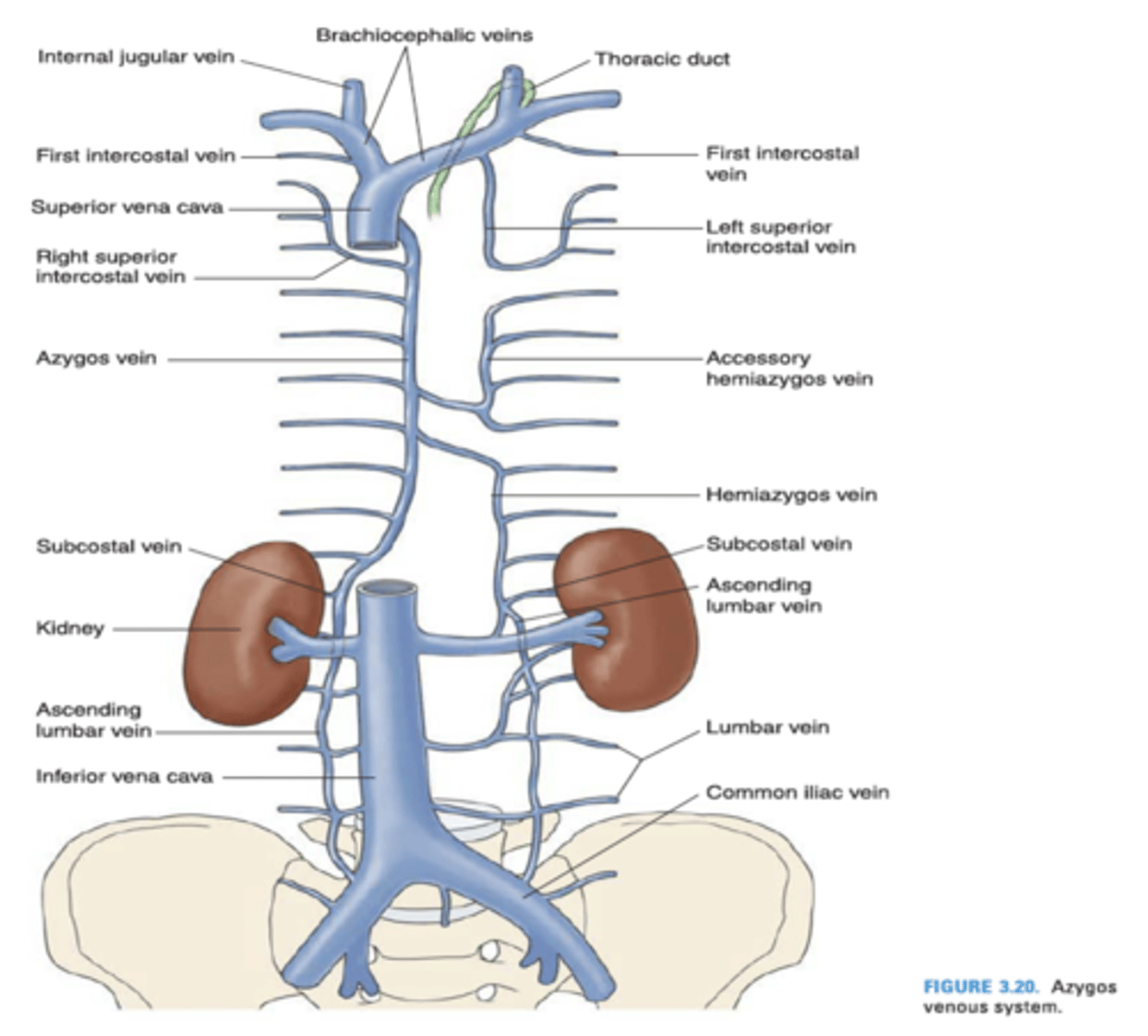
The internal thoracic vein empties into what vein?
Brachiocephalic vein
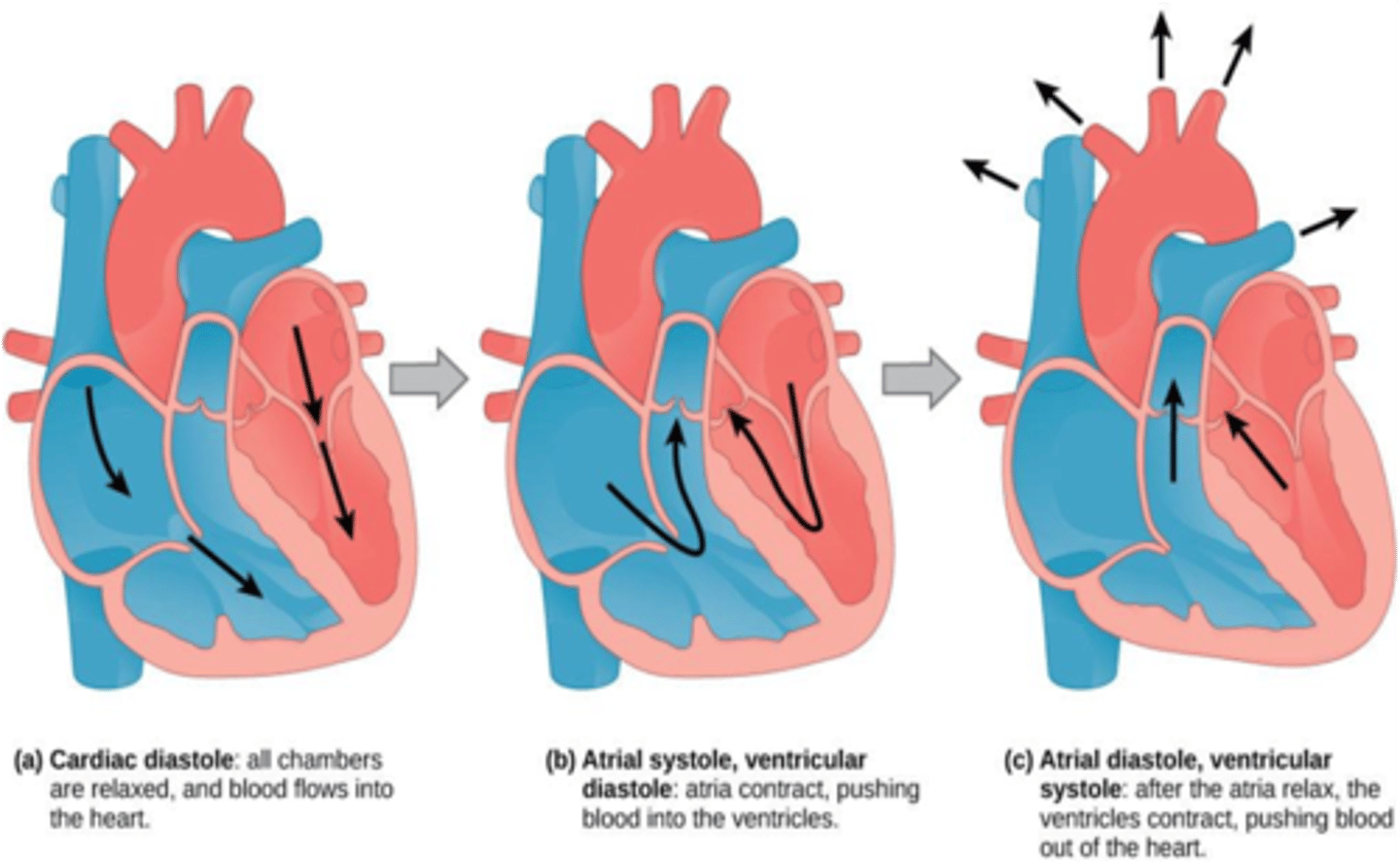
During ventricular diastole, what valves are open?
Mitral and Tricuspid valves
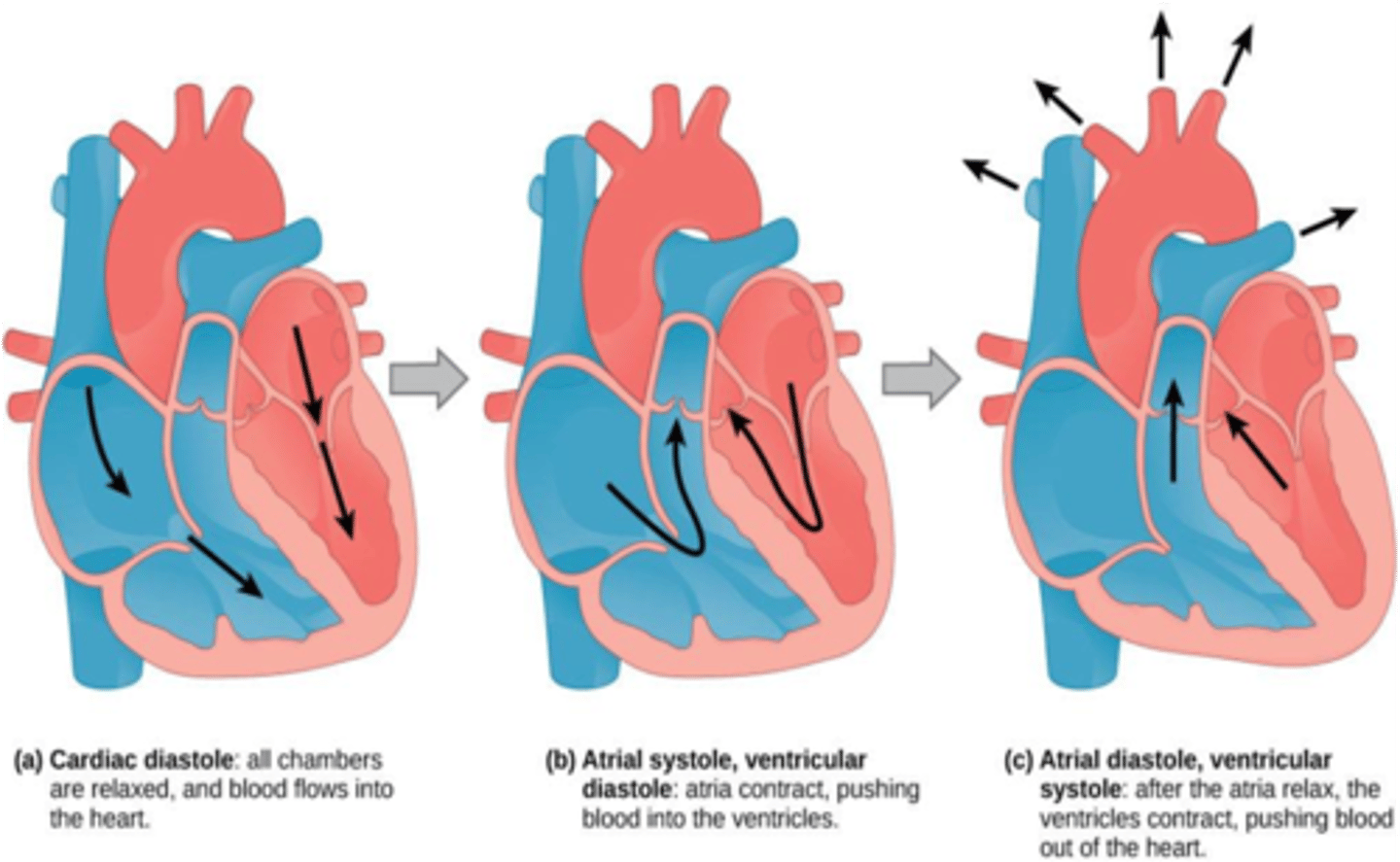
During ventricular systole, what valves are open?
Aortic and pulmonary valves
The aortic and pulmonary valves are closed during which phase of the cardiac cycle?
Ventricular diastole
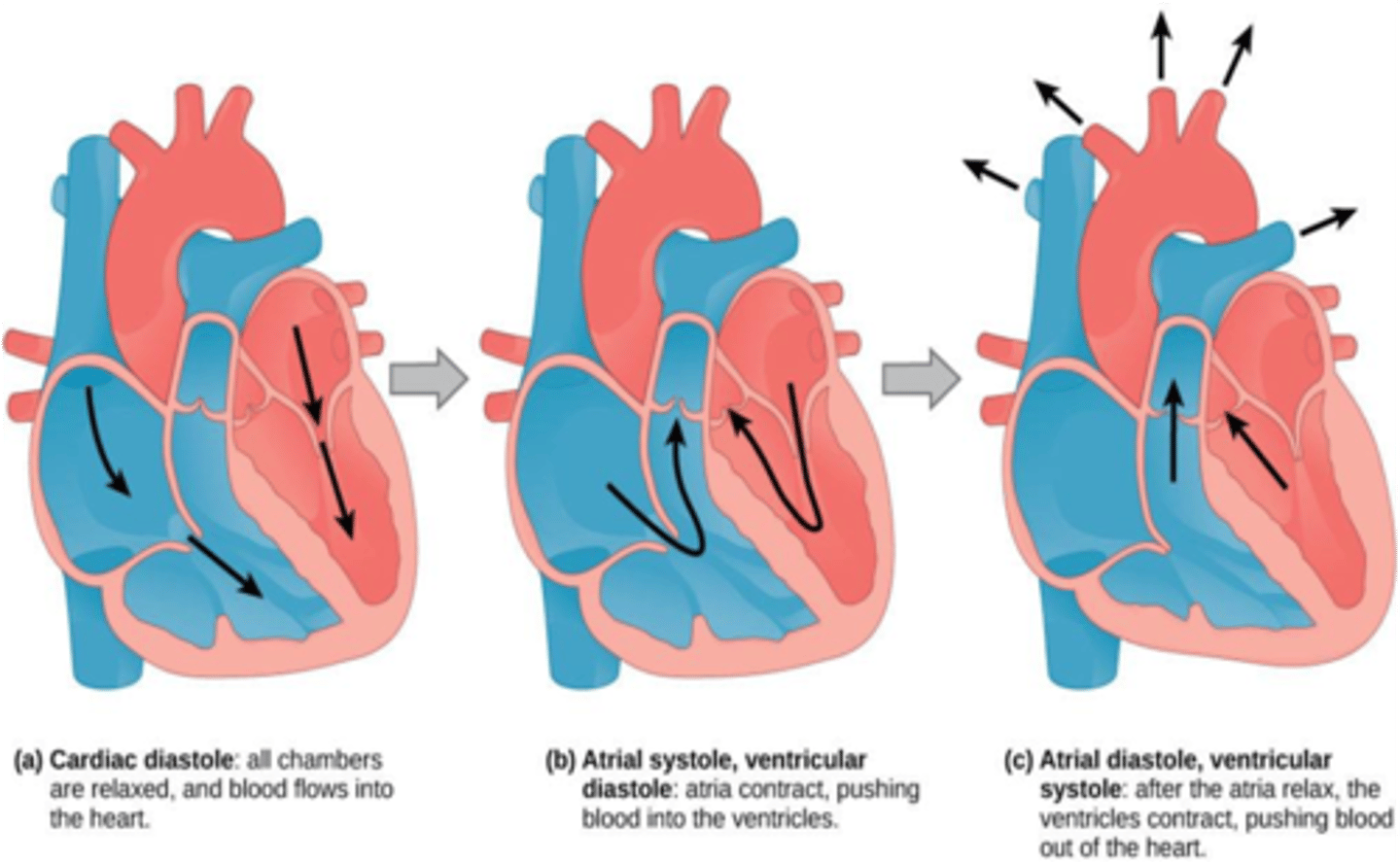
The mitral and tricuspid valaves are closed during which phase of the cardiac cycle?
Ventricular systole
The left atrium and ventricle receive blood from which coronary artery?
Circumflex branch of the left coronary artery
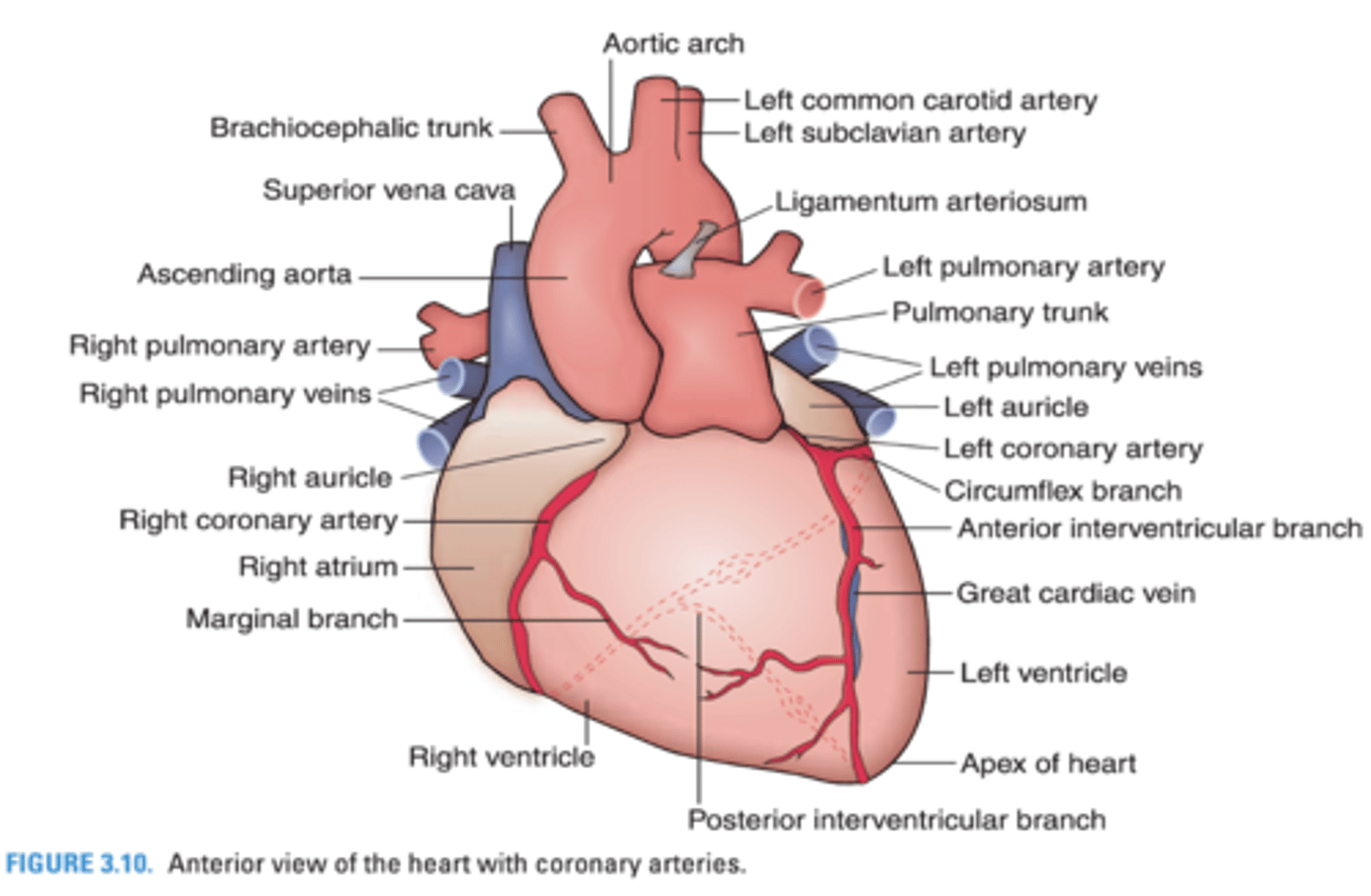
What heart structures are supplied by the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery?
Left atrium and ventricle
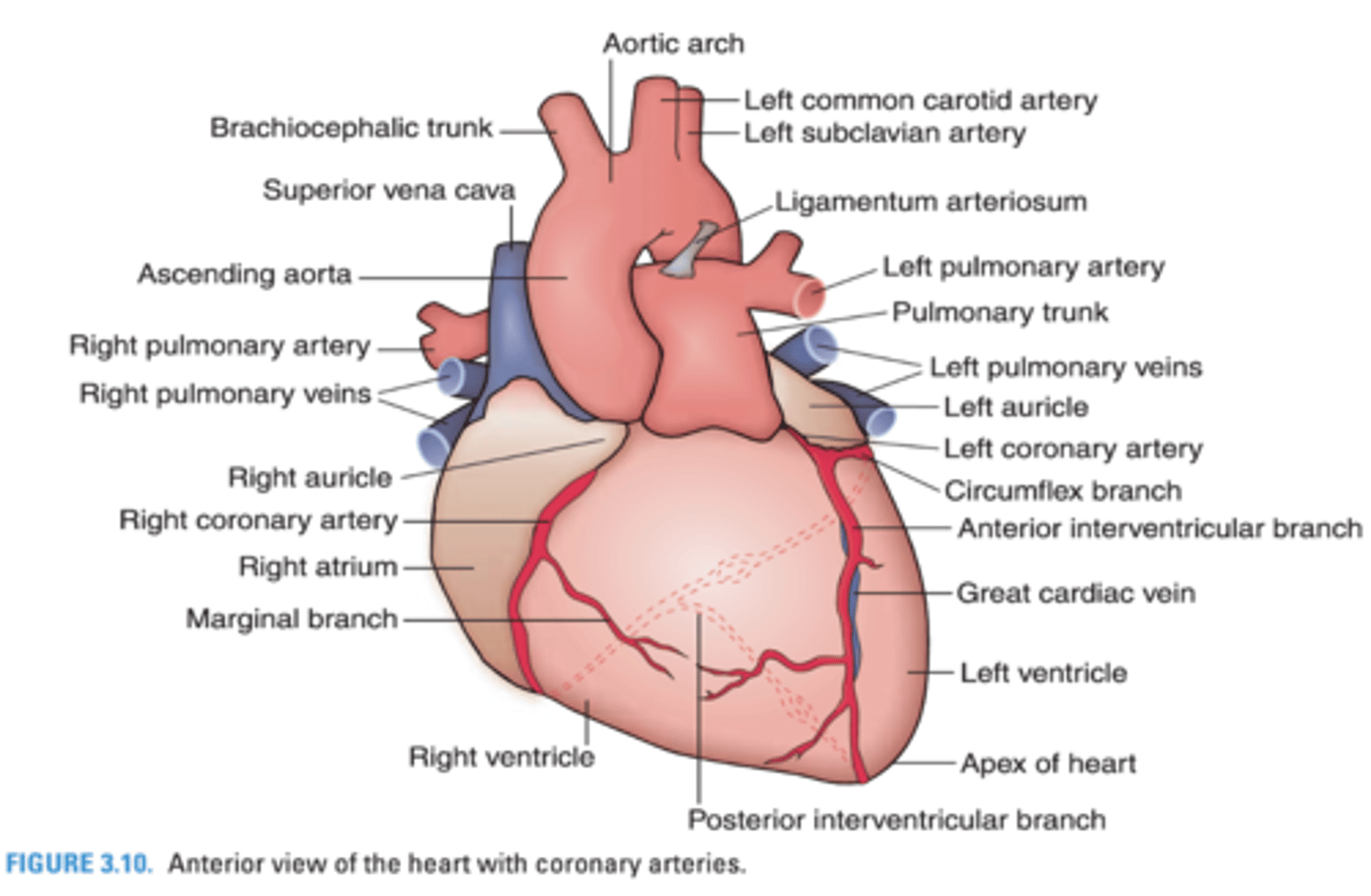
The interventricular septum and apex of the heart are supplied by what branch of the left coronary artery?
Anterior interventricular branch
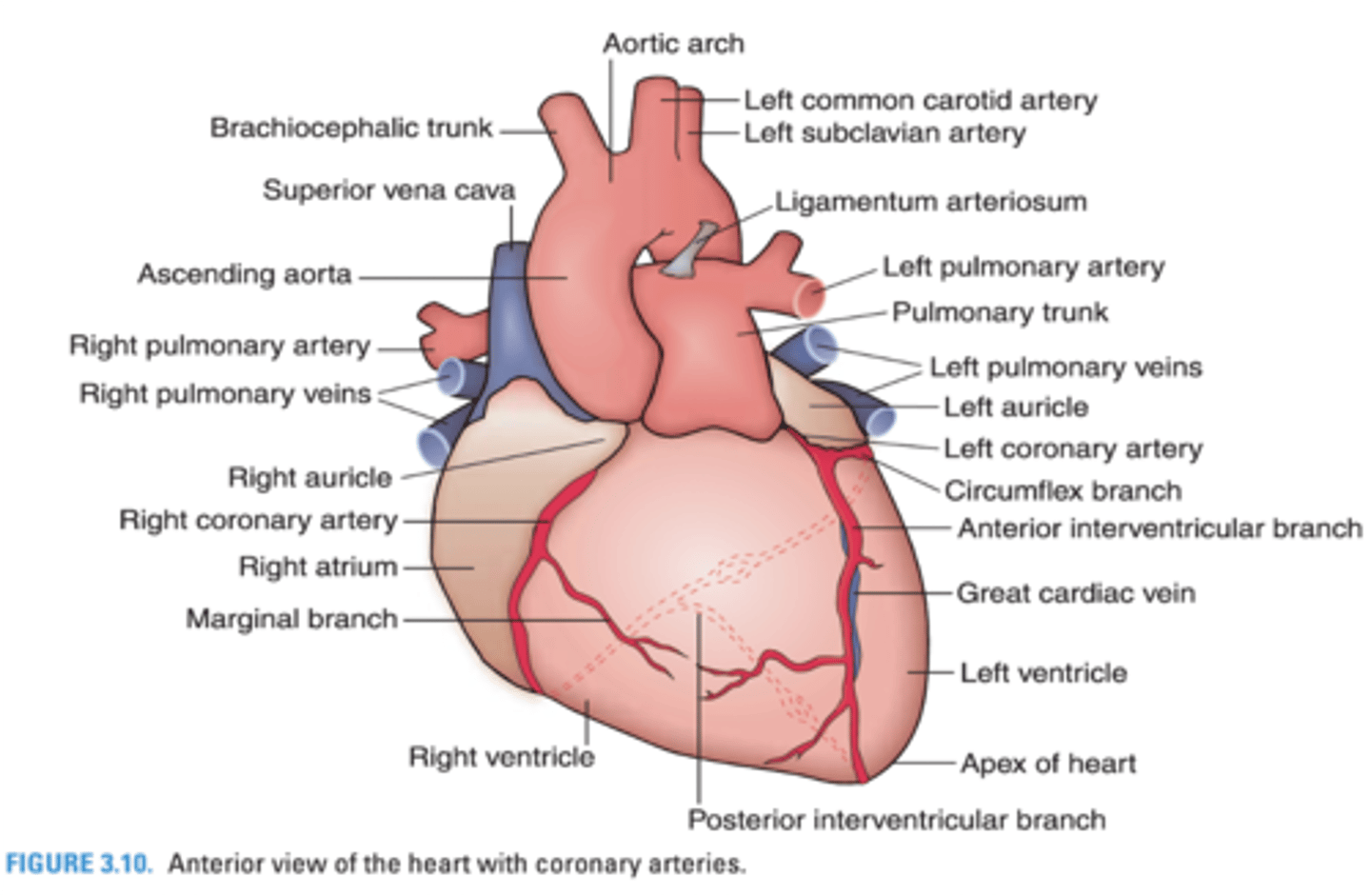
The right ventricle receives blood from what 2 coronary arteries?
-Anterior interventricular branch of the left coronary artery
-Marginal branch of the right coronary artery
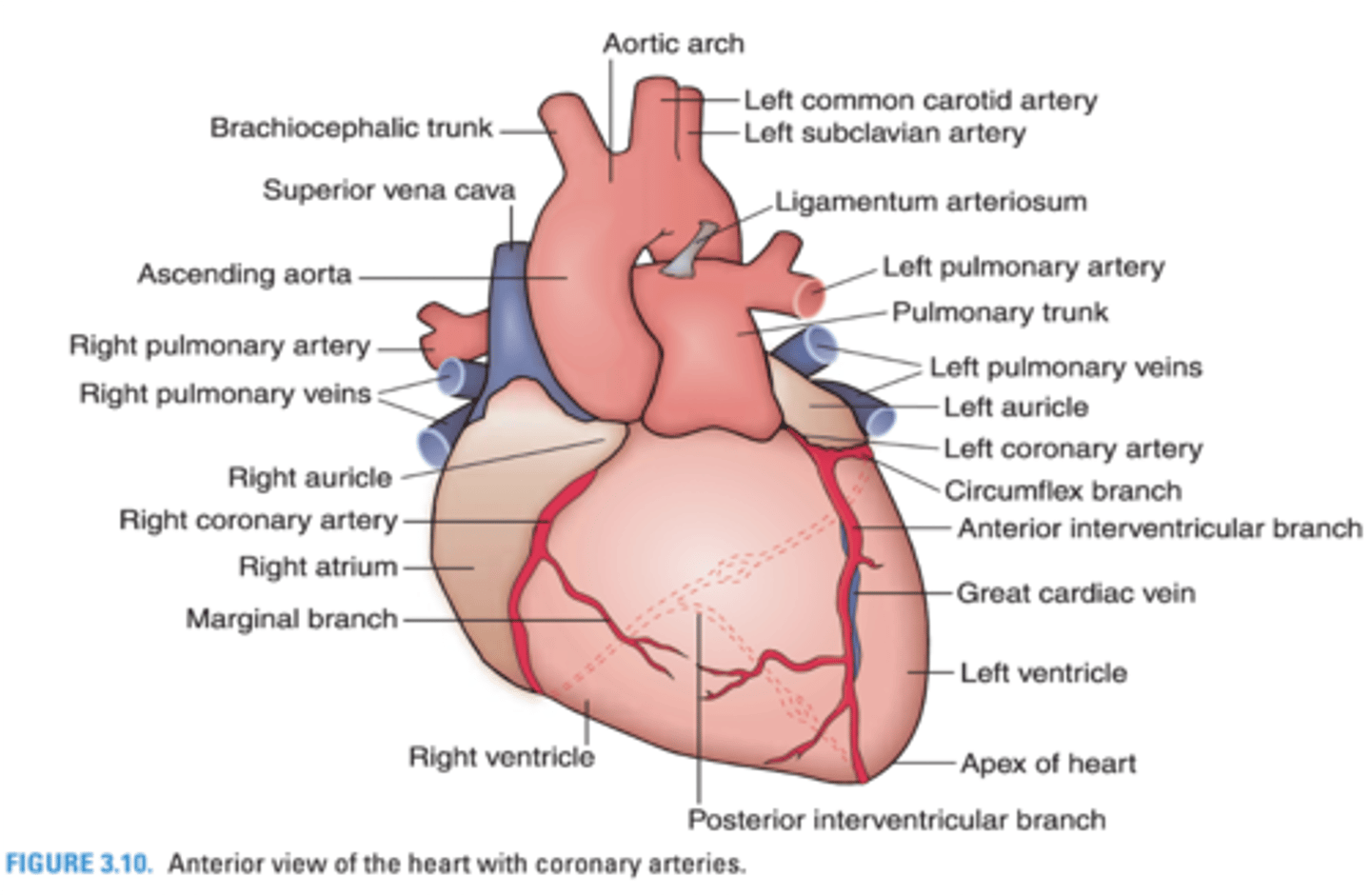
The right atrium is supplied by what coronary artery?
Right coronary artery
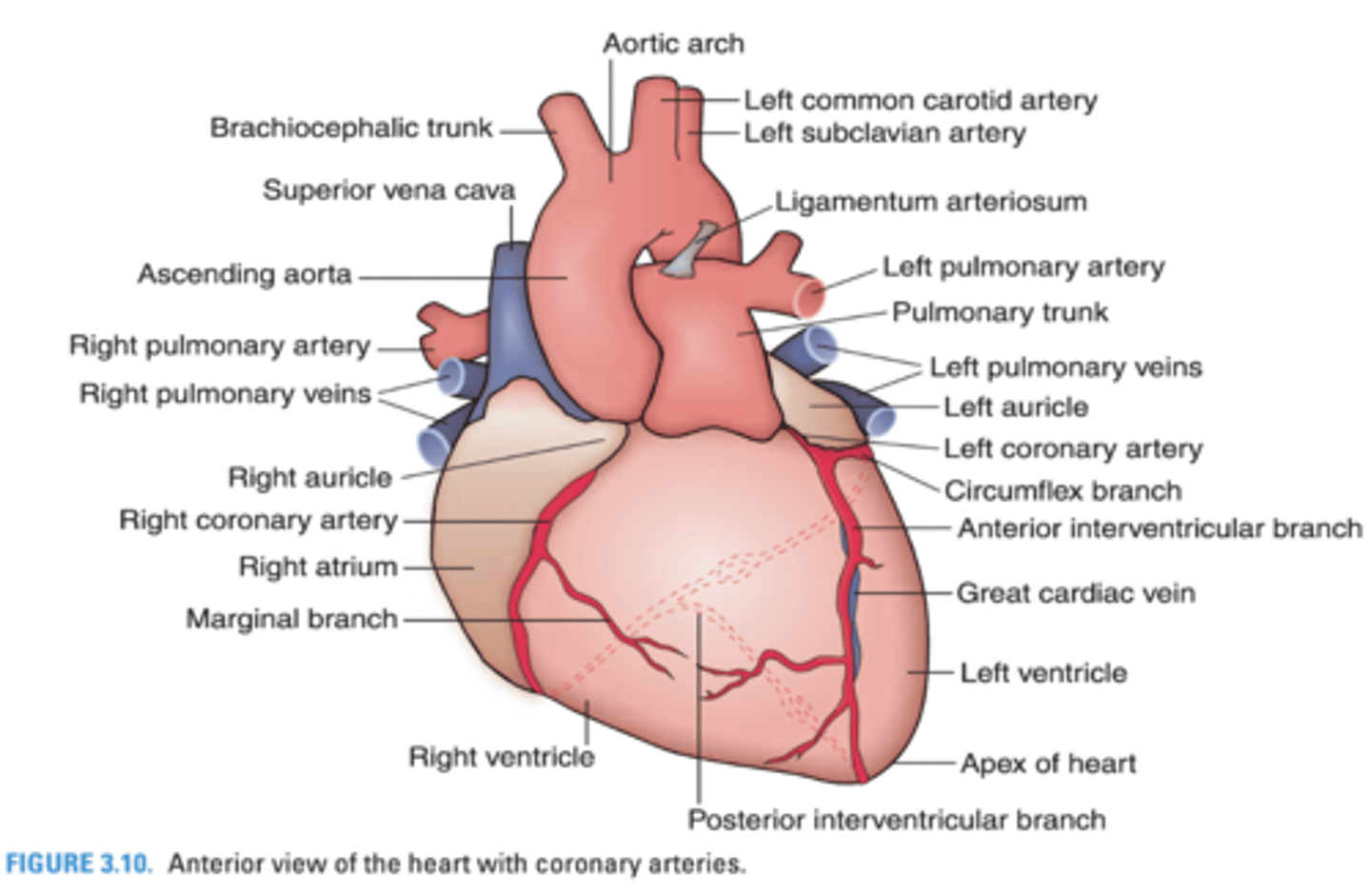
The _______________ is the junction between the manubrium and the body of the sternum
Sternal Angle (of Louis)
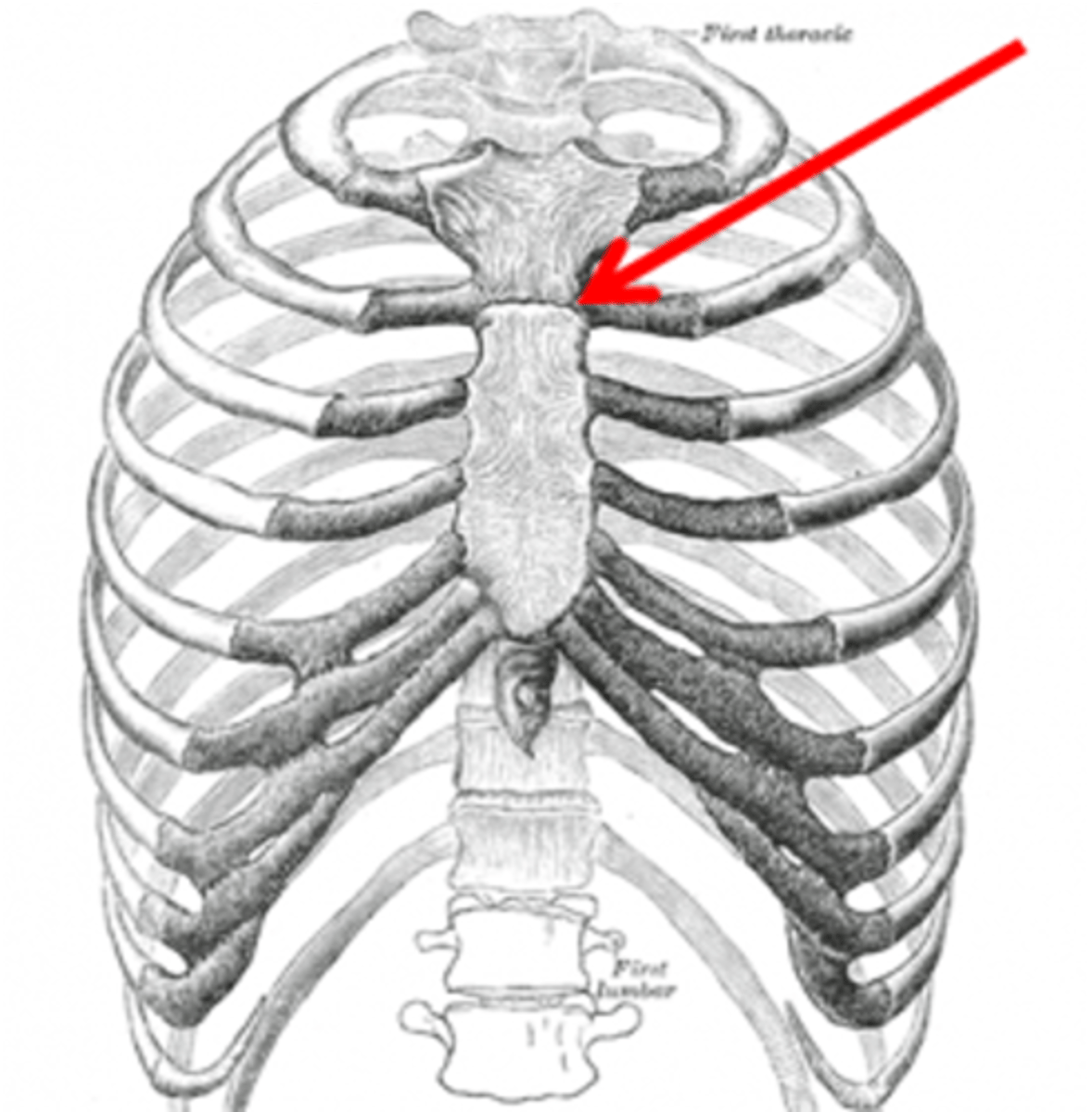
What rib articulates with the sternal angle of Louis?
Second rib
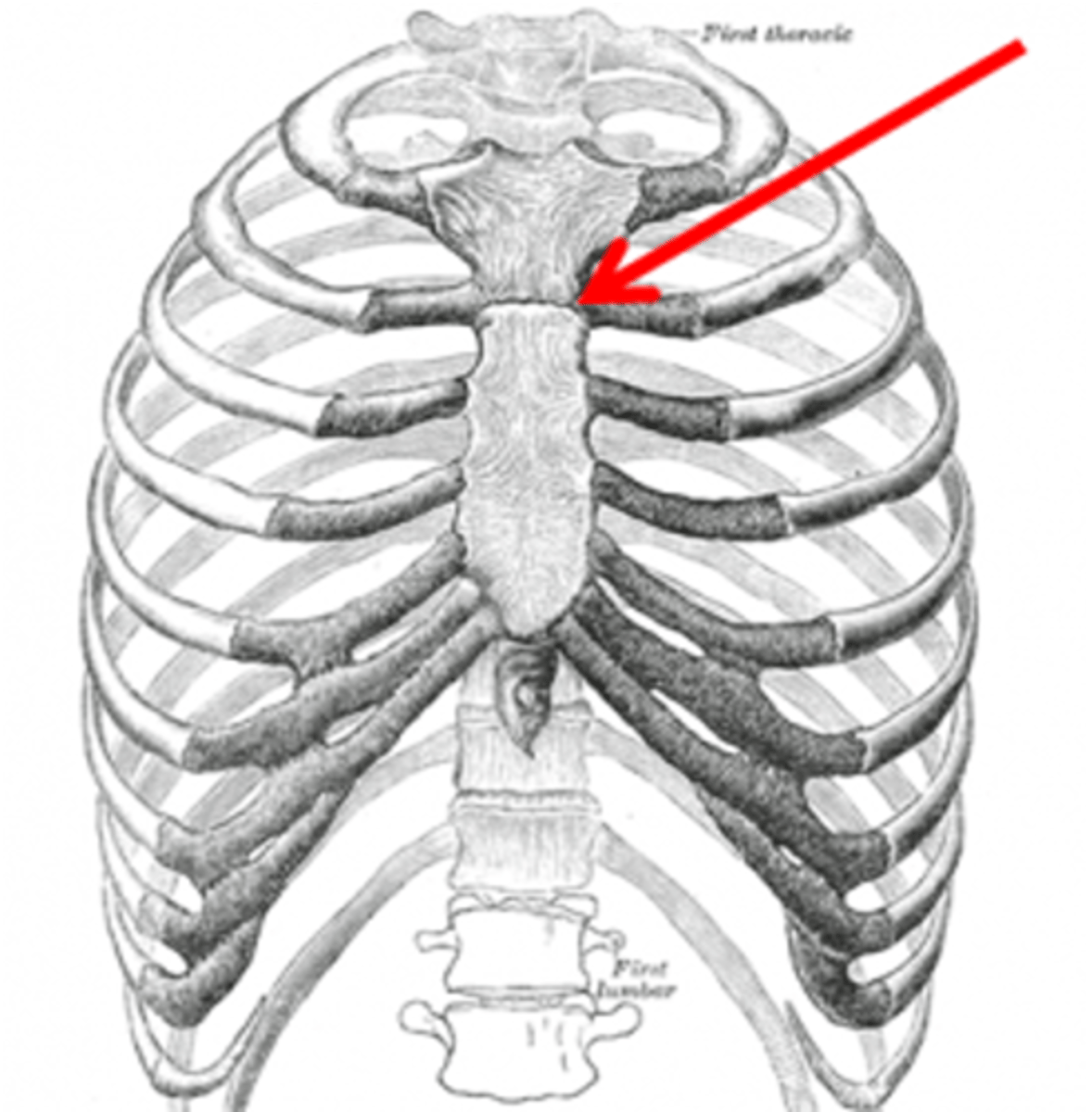
The trachea bifurcates into the right and left bronchi at which sternal structure?
Sternal Angle (of Louis)
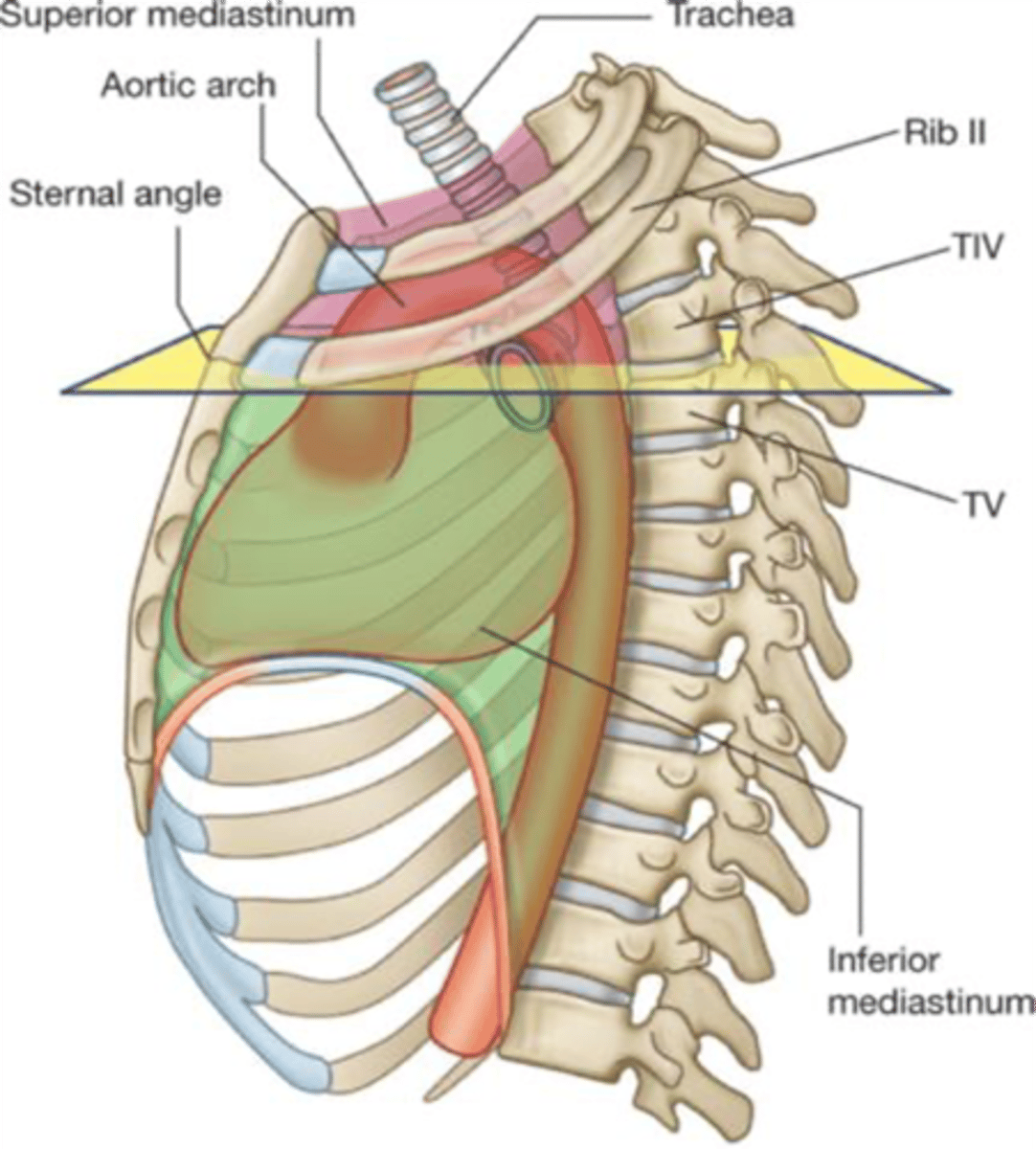
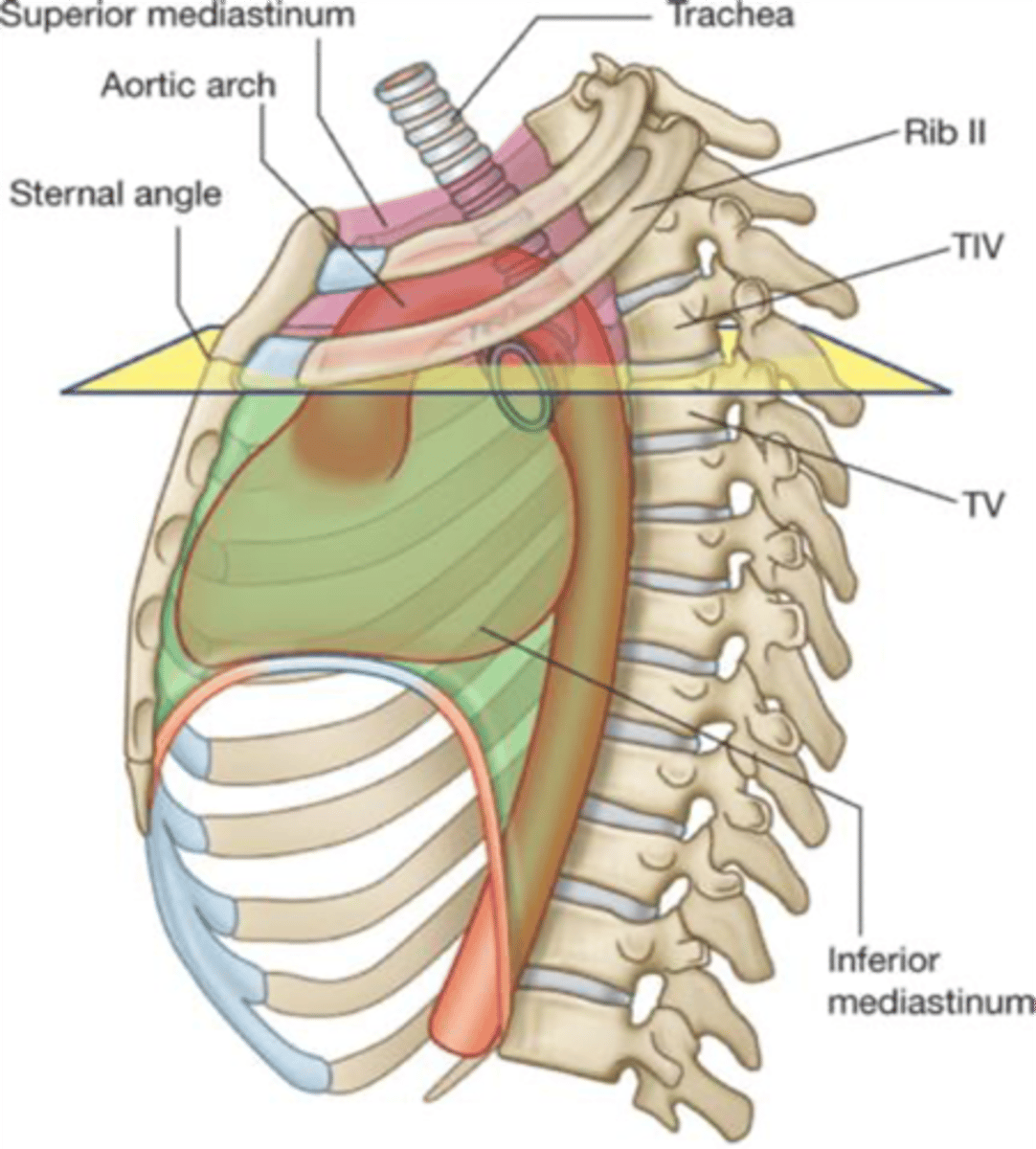
The sternal angle of Louis forms the inferior border of which division of the mediastinum?
Superior mediastinum
The 4th rib articulates with the vertebral bodies of which 2 thoracic vertebrae?
3rd and 4th thoracic vertebrae
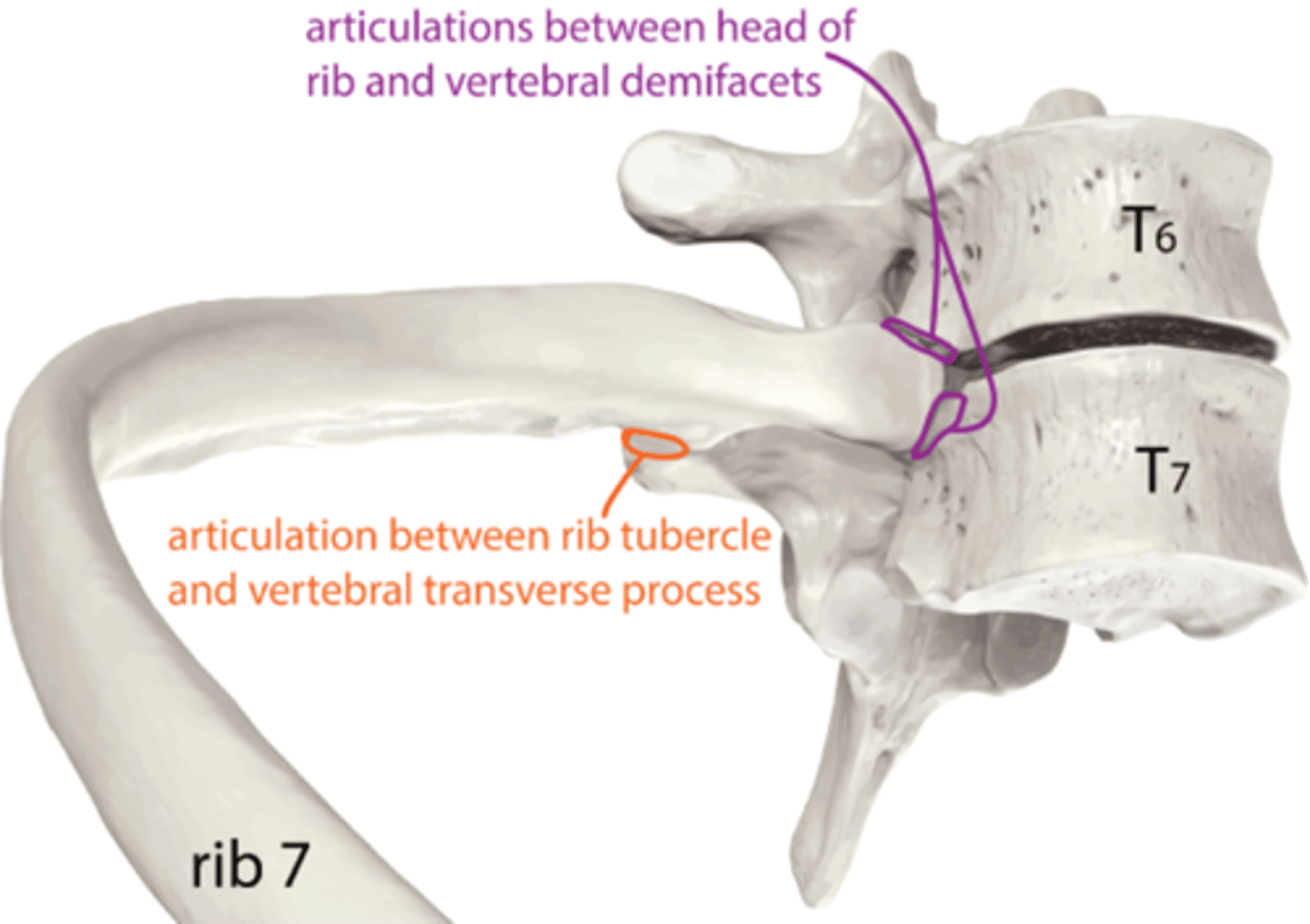
What ribs articulate with the body of the sternum?
3rd to 7th rib

The descending (thoracic) aorta is located in which division of the mediastinum?
Posterior mediastinum
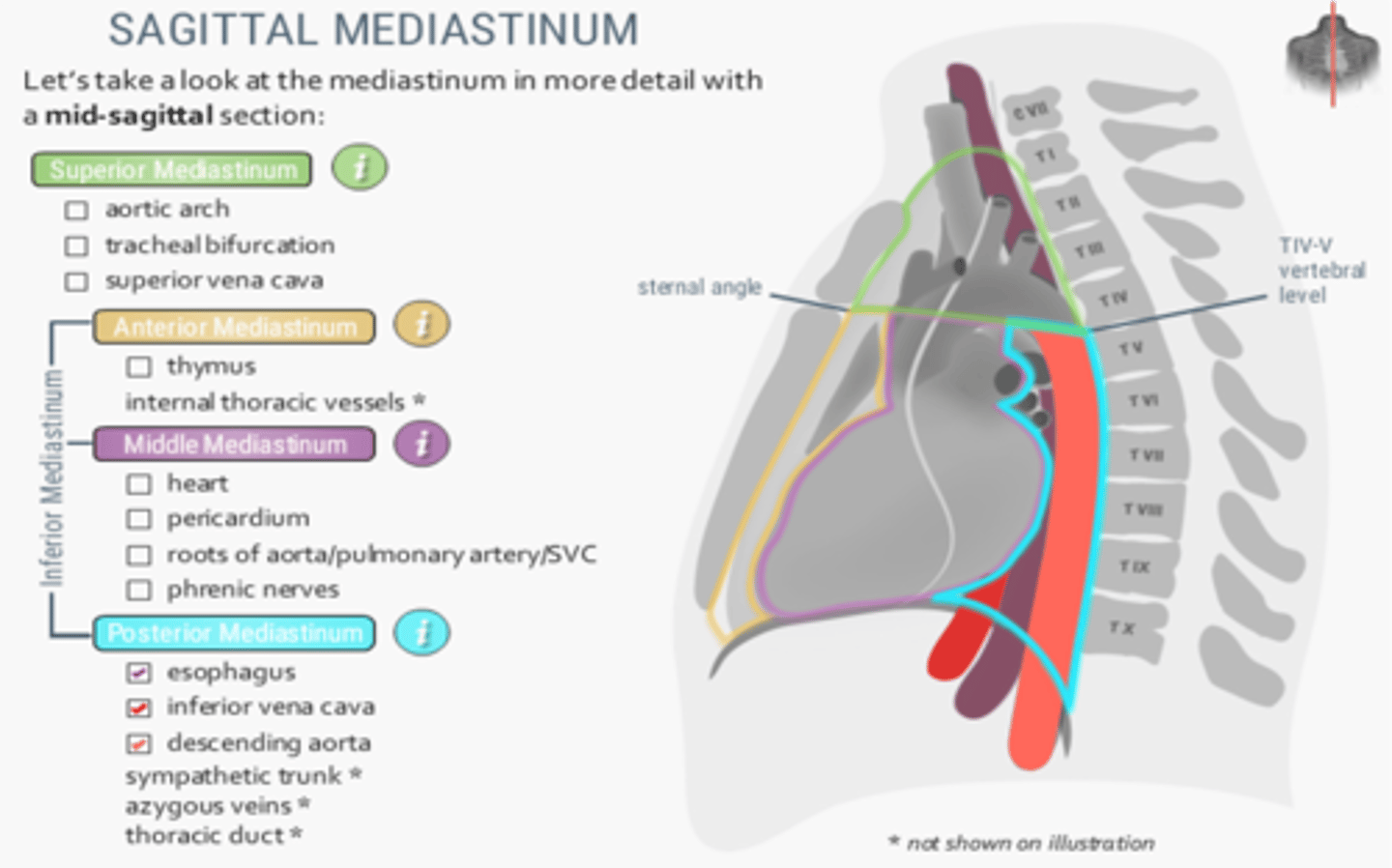
What division of the mediastinum contains the trachea and arch of the aorta
Superior mediastinum
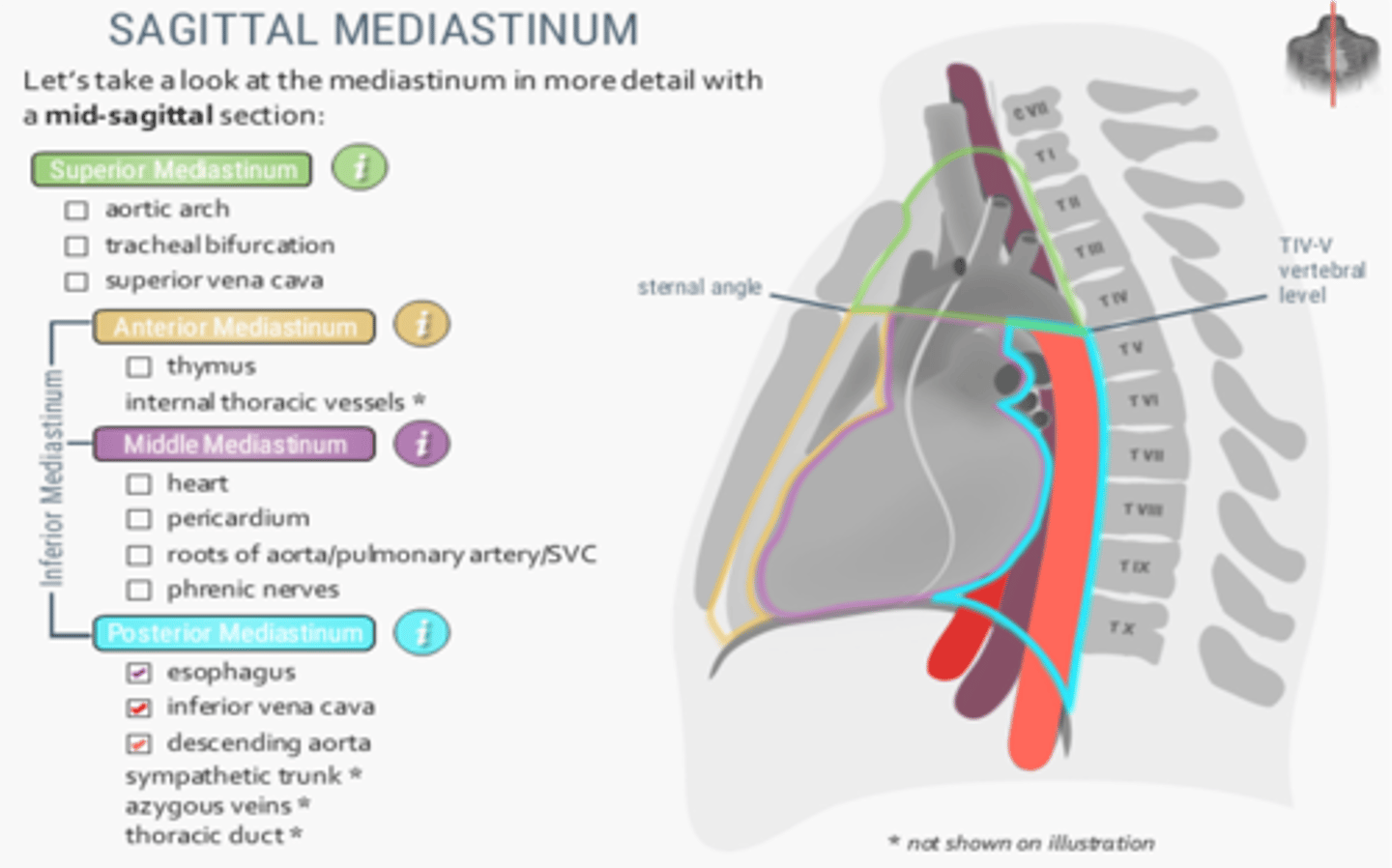
The phrenic nerve runs in which division of the mediastinum?
Middle mediastinum
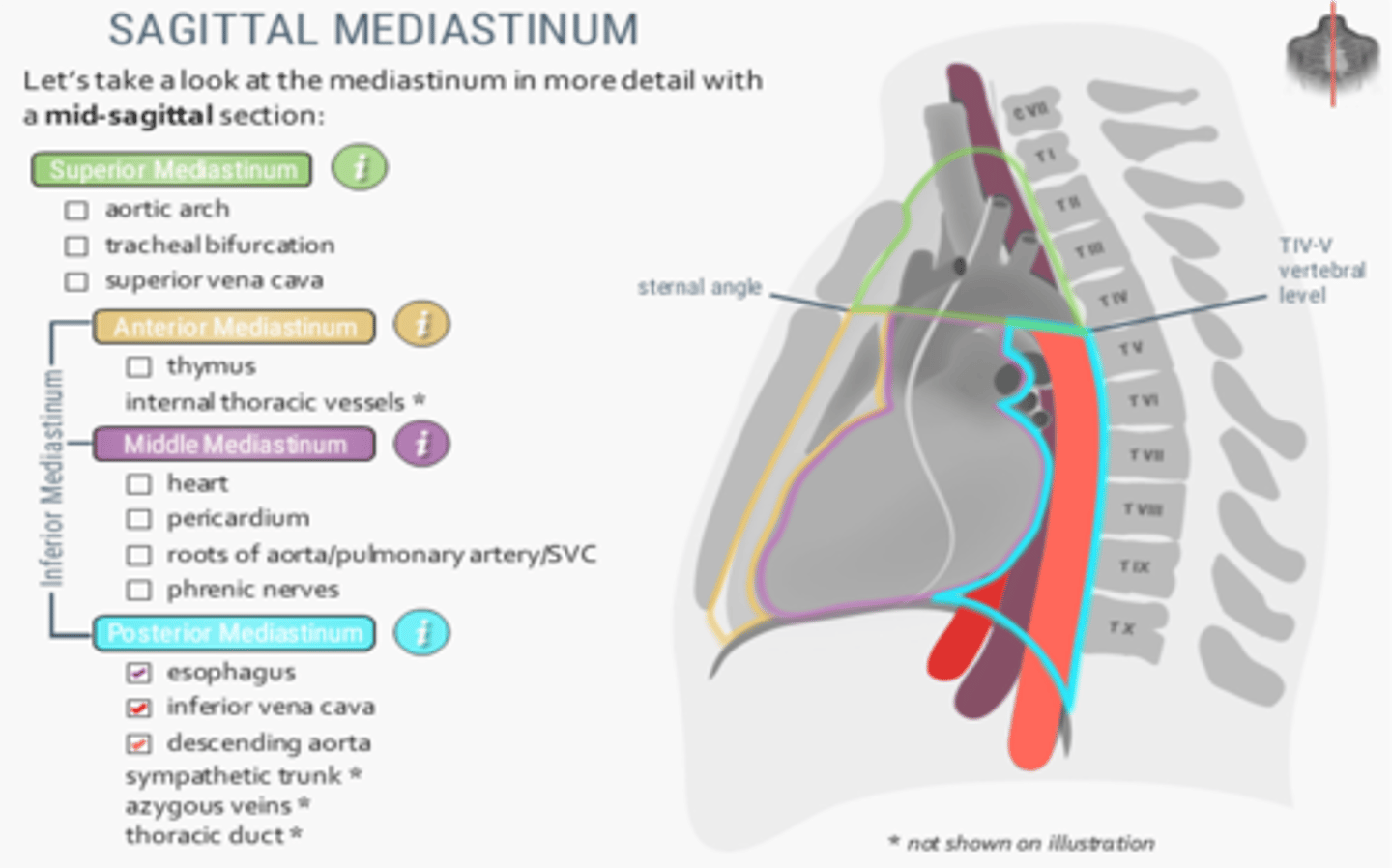
Which division of the mediastinum contains the ascending aorta, arch of the azygos vein and main bronchi?
Middle mediastinum
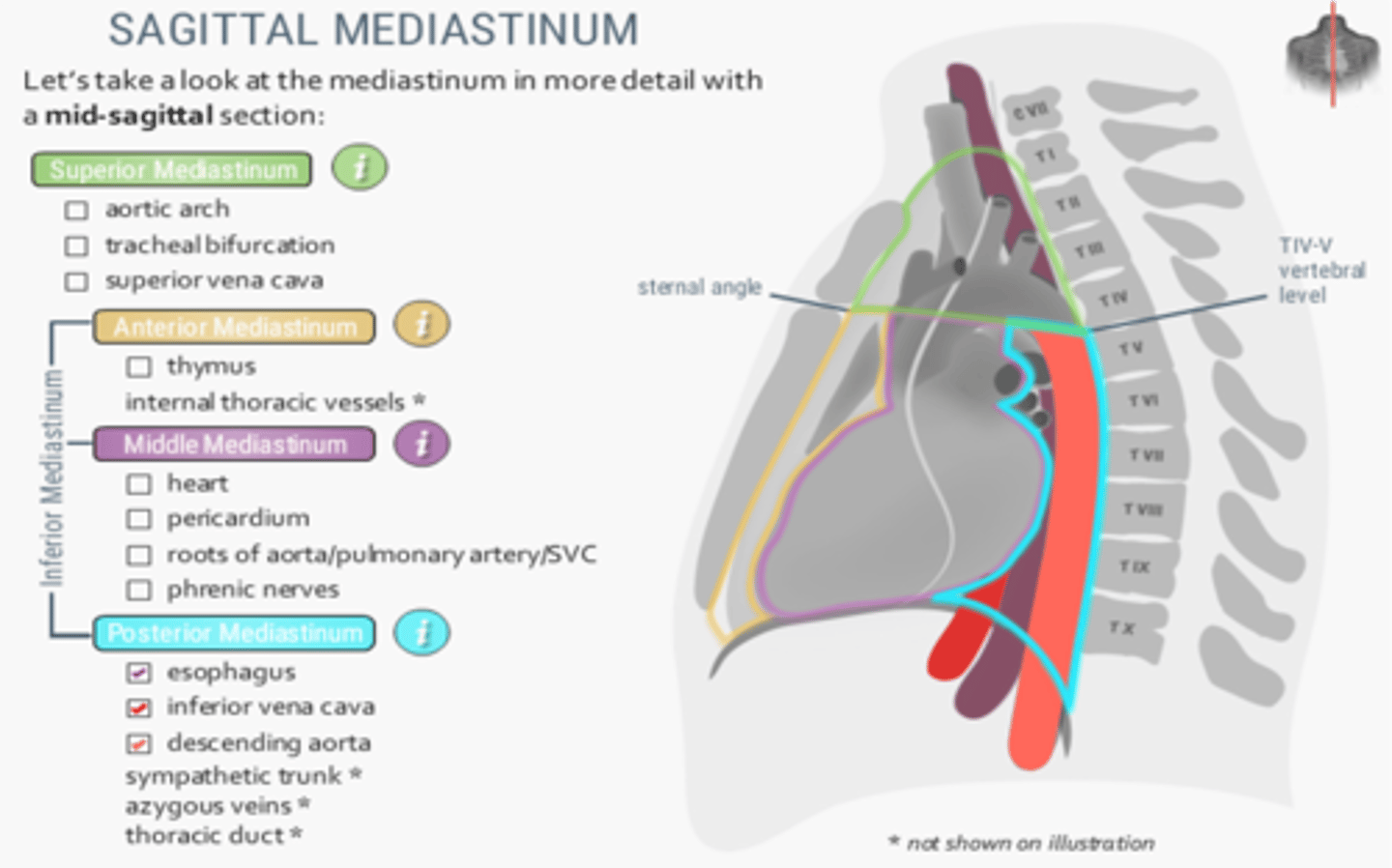
Pericardiocentesis is performed by inserting a needle into the pericardial cavity through which intercostal space, left of the sternum?
Fifth intercostal space
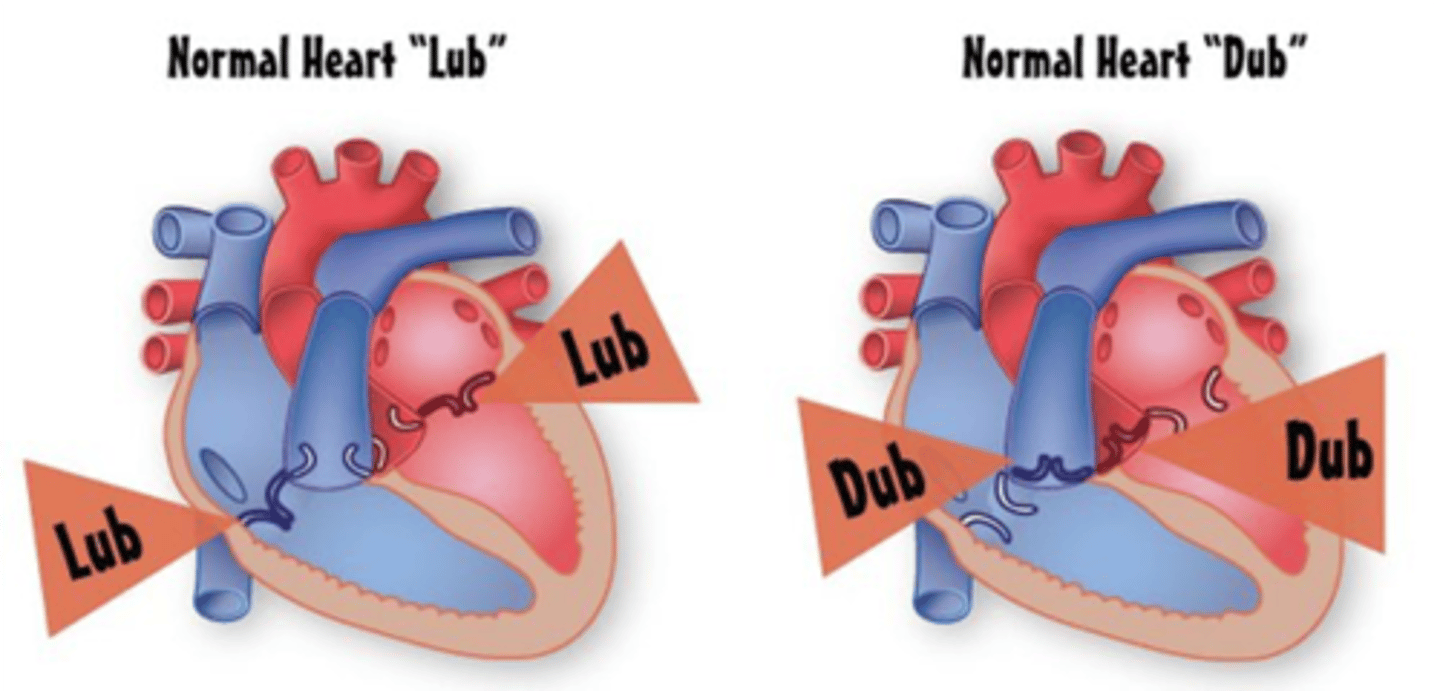
The first heart sound is produced by the closure of what 2 heart valves?
Tricuspid and mitral valves
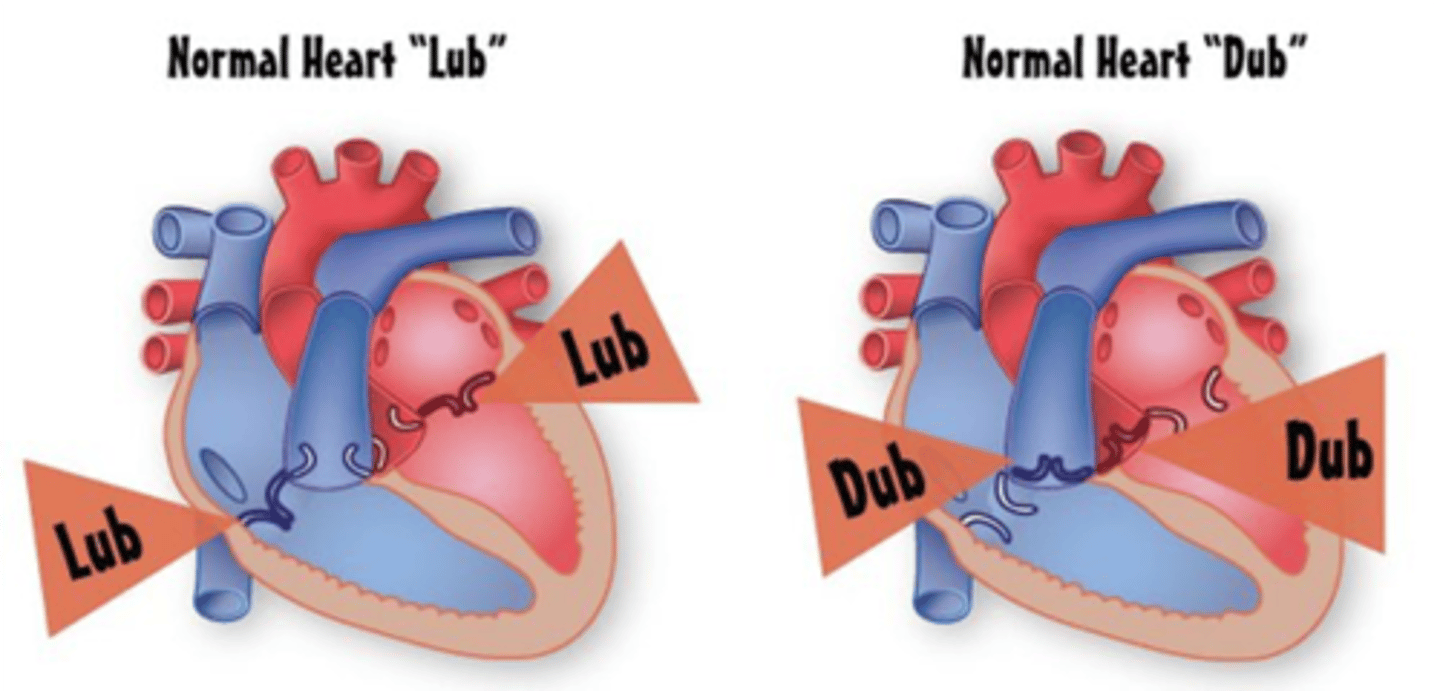
The second heart sound is produced by the closure of what 2 heart valves?
Aortic and pulmonary valves
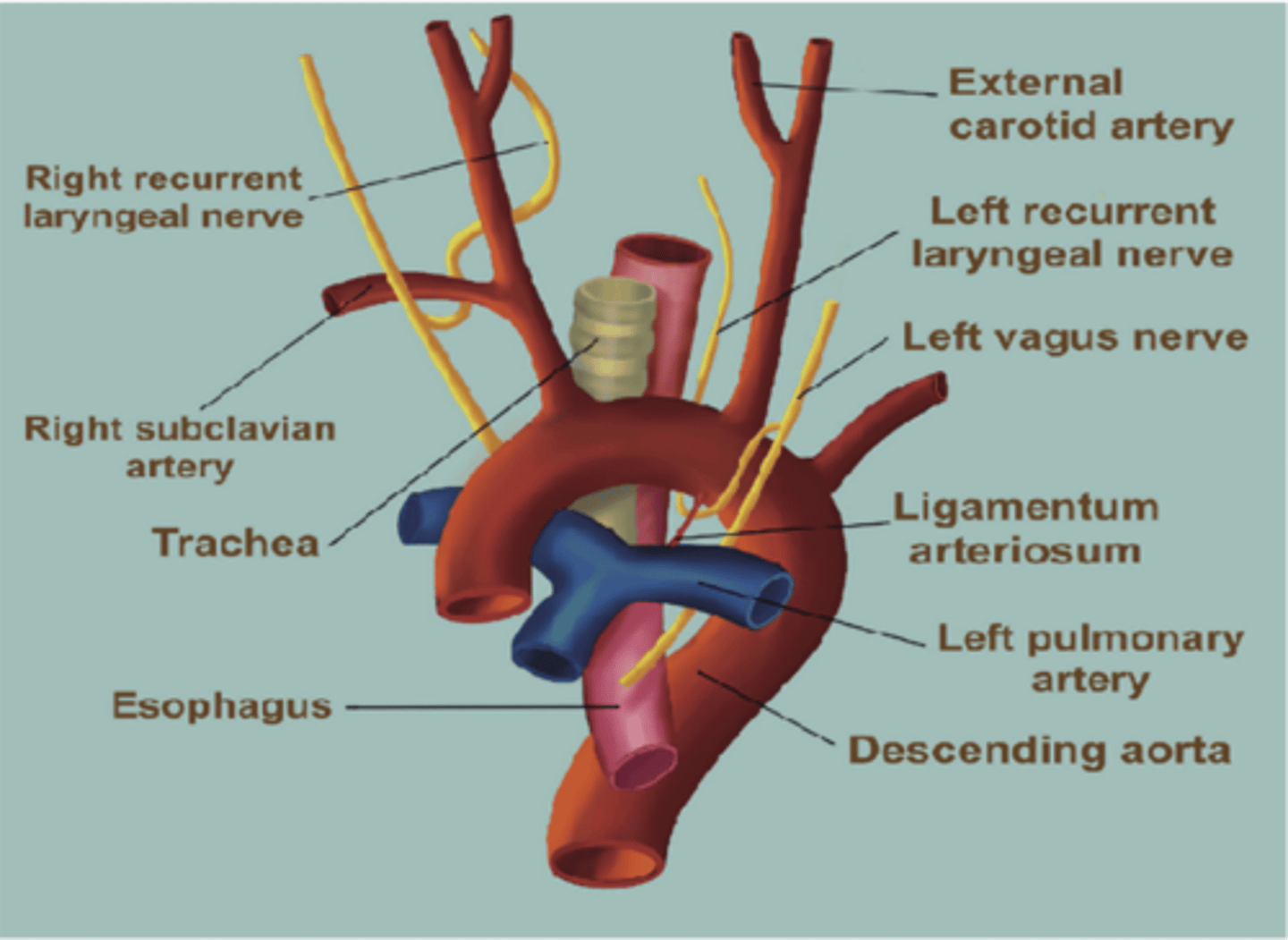
The left recurrent laryngeal nerve loops around what vessel?
Aorta (Arch of the aorta)
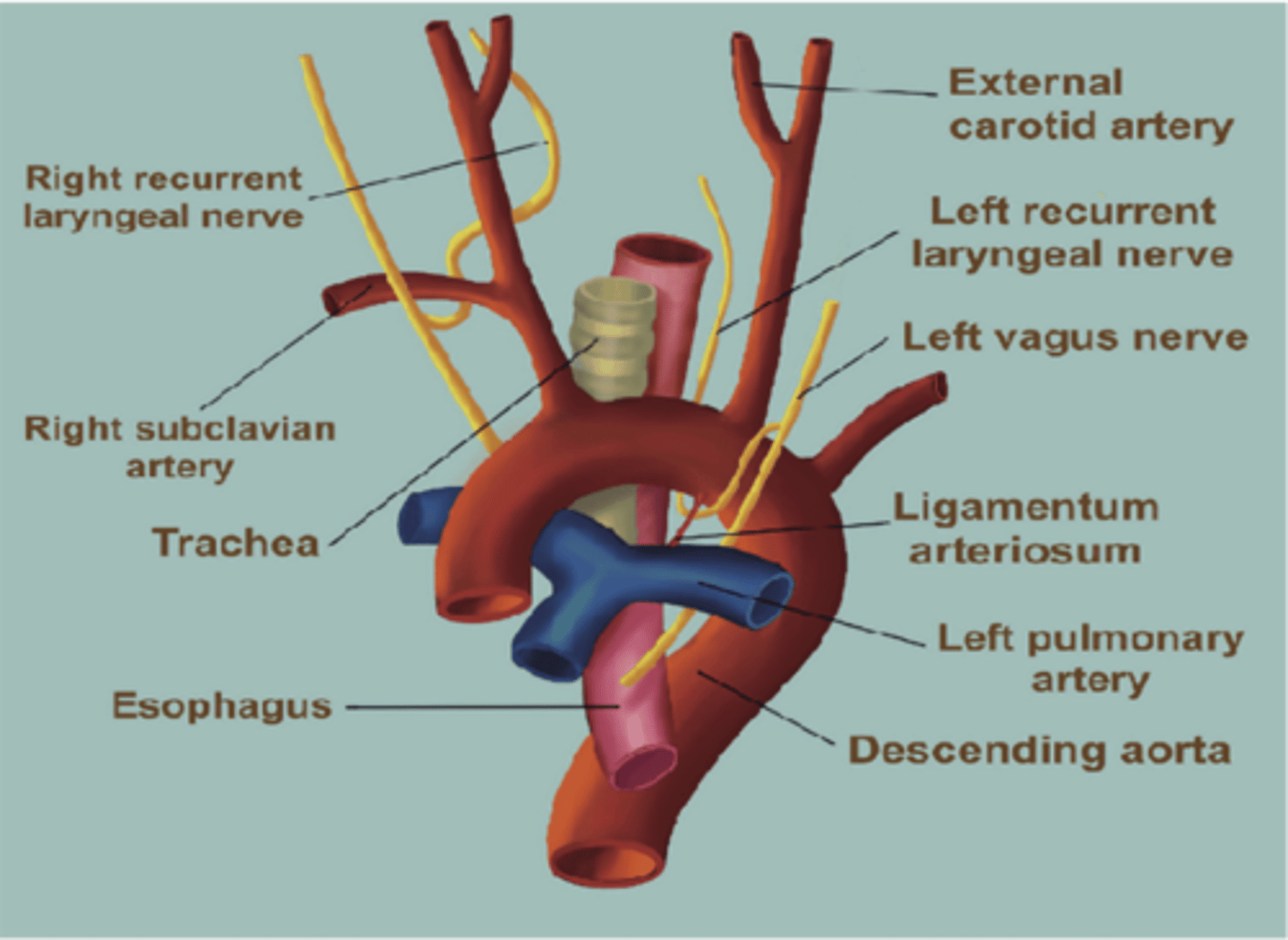
The left recurrent laryngeal nerve loops around the arch of the aorta near what ligament?
Ligamentum arteriosum