Respiratory Procedures| Unit 3a and 3b
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Monitoring gas exchange
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
what are the levels of hypoxemia
normal
mild
moderate
severe
refractory
hypoxemia
abnormal deficiency of O2 in the arterial blood
what is the range of normal hypoxemia
80-100 mmHg
what is the range of mild hypoxemia
60-79 mmHg
what is the range of moderate hypoxemia
40-59 mmHg
what is the range of severe hypoxemia
below 40 mmHg
refractory hypoxemia
severe hypoxemia that is unresponsive to increased levels of O2
Hazards associated with Oxygen Therapy
retinopathy of prematurity
oxygen toxicity
retinopathy of prematurity
PaO2 greater than 80mmhg may lead to disorganized growth in retinal blood vessles.
what can retinopathy of prematurity result to
scarring and retinal detachment which can lead to blindness
oxygen toxicity
high PaO2 that damages capillary endothelium, damages the cells that create new tissue and causes an inflammatory response
What does an Oxygen Blender do
has precise control over both FiO2 and total flow output, and mixes gas manually
what is the Polarographic Fuel Cell Analyzer also known as
Clark electrode
galvanic fuel cell analyzer
relies on a self-generated electrical potential to measure oxygen concentration. _________is "self-powered" and are generally considered less accurate but longer-lasting
polarographic fuel cell analyzer
requires an applied voltage to the electrodes to measure oxygen. ________sensor needs an external power source to operate effectively and offer faster response times and higher accuracy
What does an Oxygen Analyzer 2-point calibration consist of
21% FiO2 and 100%FiO2
What does an Oxygen Analyzer do
measures the amount of oxygen in a given environment
What is a Pulse Oximeter
a noninvasive monitoring technique performed at bedside
how does a Pulse Oximeter work
It uses light absorption patterns to indicate saturation levels of “pulsed” blood
Things that can provide an erroneous reading with Pulse Oximetry
motion artifact
abnormal hemoglobins
intravascular dyes
low perfusion states
thick nails
nail polish/artificial nails
skin pigmentation
Contraindications of Pulse Oximetry
ongoing need for actual measurements of pH, PaCO2, total hemoglobin, and abnormal hemoglobins
Accuracy of a pulse oximeter
within + 2%-4%
Tissue Oximetry
noninvasive or invasive method of measuring saturation of hemoglobin at tissue level
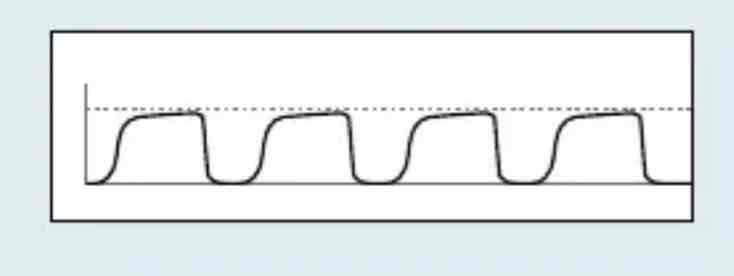
which Capnography waveform is this
Normal
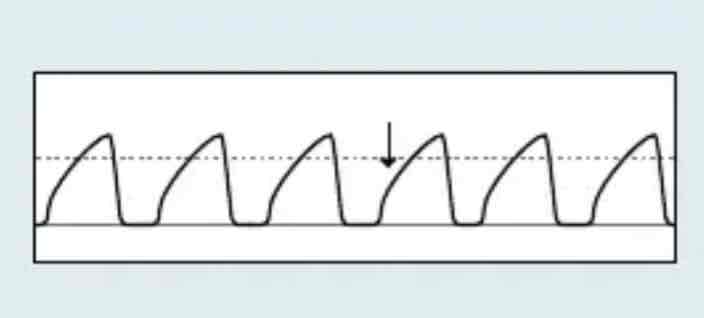
which Capnography waveform is this
Shark fin
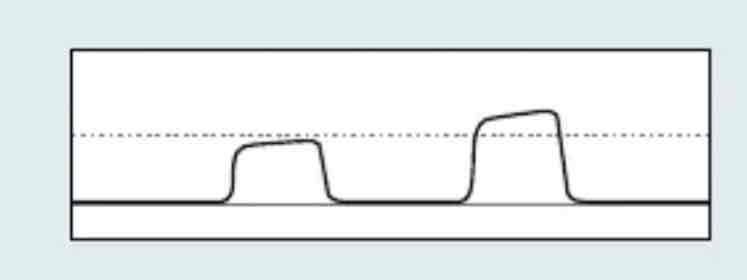
which Capnography waveform is this
Hypoventilation
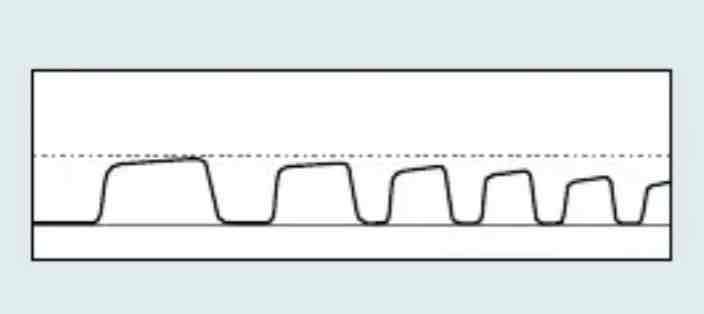
which Capnography waveform is this
Hyperventilation
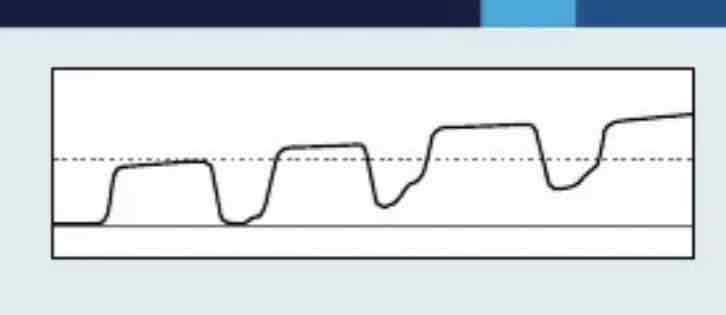
which Capnography waveform is this
Rebreathing
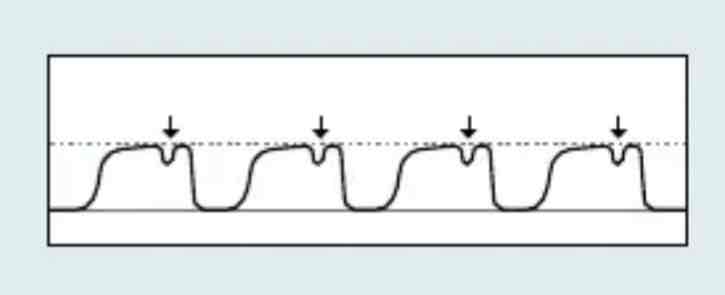
which Capnography waveform is this
Mechanically ventilated
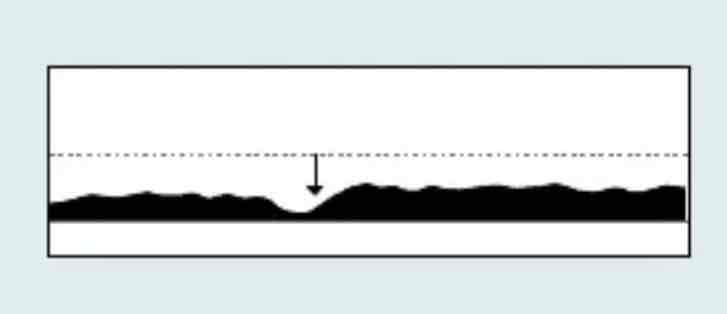
which Capnography waveform is this
Cardiac arrest
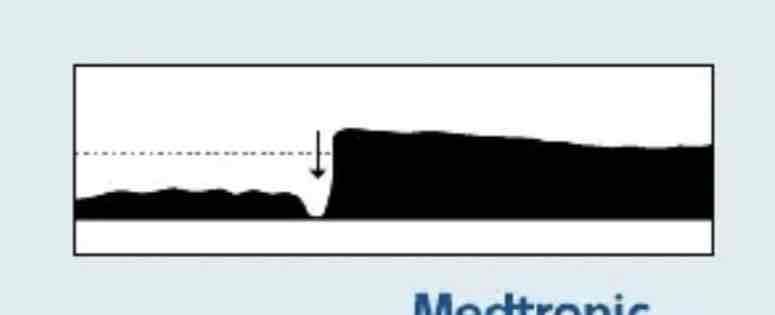
which Capnography waveform is this
Return of spontaneous circulation
Capnometry
Co2 levels measures provided in a numeric display
capnography
graphic display of CO2 levels as they change during breathing(shown in a waveform)
Mainstream capnometry
placed directly in the breathing circuit directly at the airway
sidestream capnometry
uses small bore tubing to aspirate gas from or adjacent to the airway, which is then delivered to a remote measuring chamber for analysis
what are the advantages of mainstream capnometry
best suited for those with artificial airways
minimal deadspace added to circuit
lightweight
durable
what are the disadvantages of mainstream capnometry
accumulation of moisture/secretion
adds deadspace
what are the advantages of sidestream capnometry
can be used in patients that do not have an artificial airway
what are the disadvantages of sidestream capnometry
sensitive to moisture and secretions
delay in analyzation
What phase of capnography is the actual measurement obtained
at the peak of end-exhalation(ETCO2)
What will increase ETCO2
increased Co2 production
decreased alveolar ventilation
equipment malfunction
what are examples of CO2 production
fever
sepsis
increased metabolic rate
seizures
what are examples of decreased alveolar ventilation
COPD
respiratory center depression
muscle paralysis
hypoventilation
what are examples of equipment malfuction
rebreathing
exhausted CO2 absorber
leak in ventilation circuit
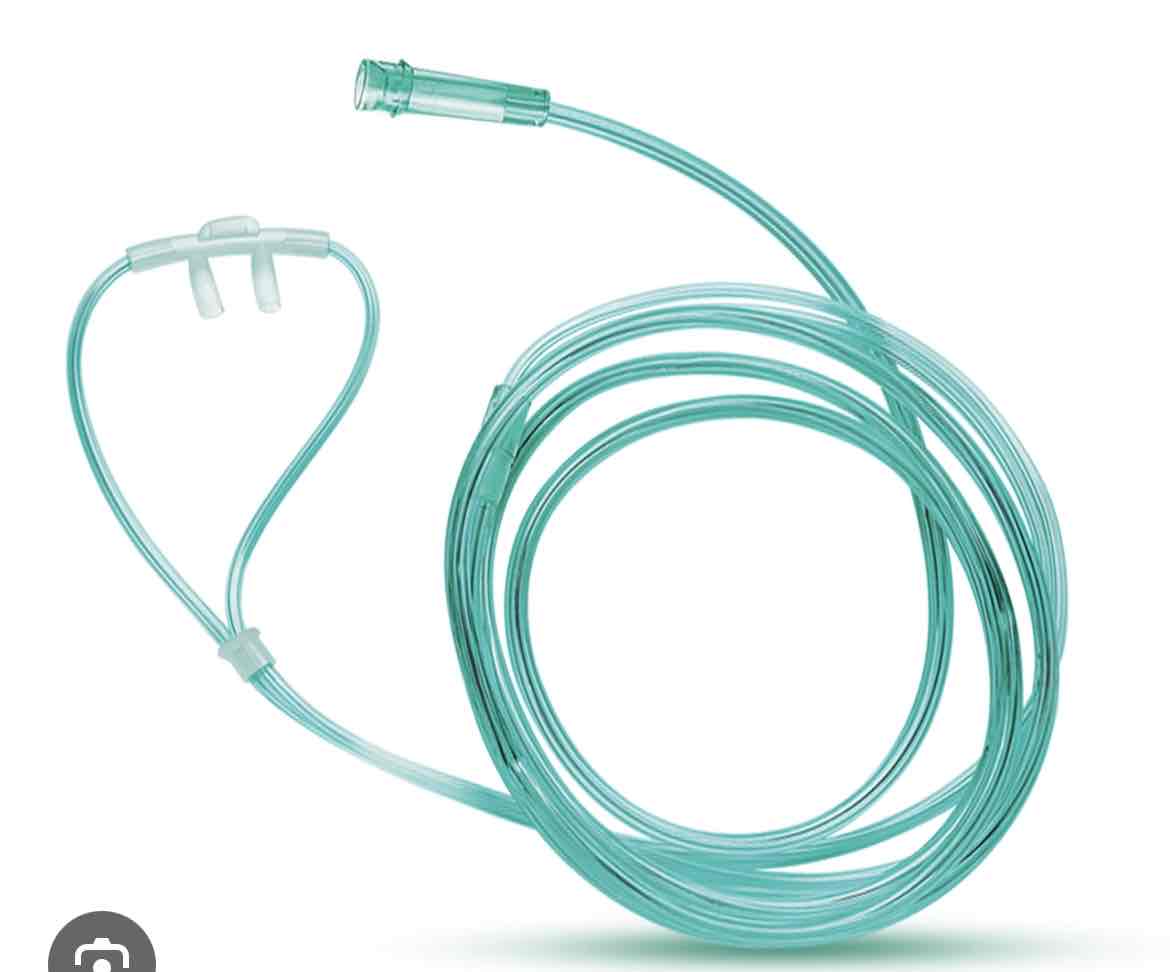
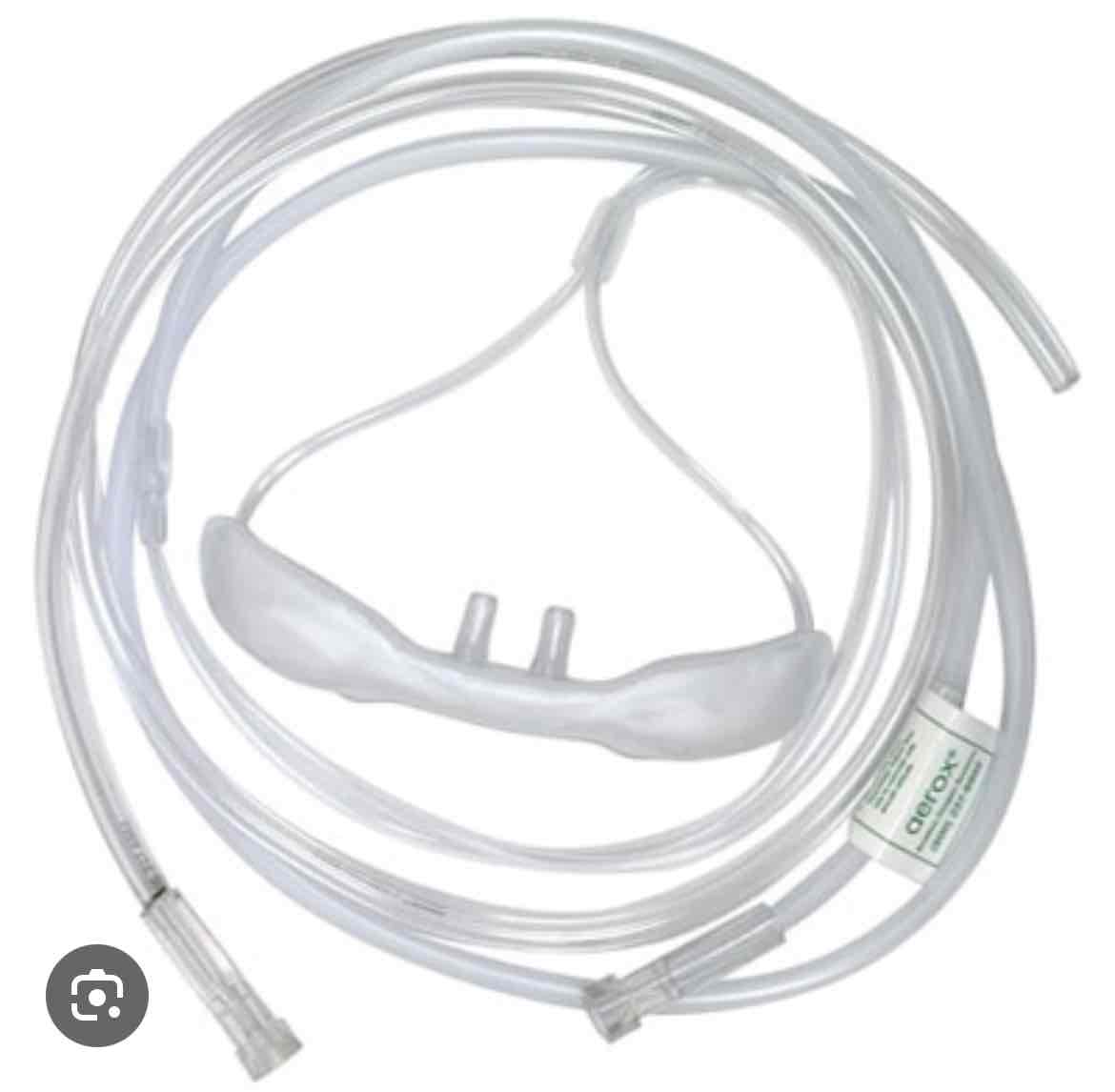
which delivery device is this
nasal cannula
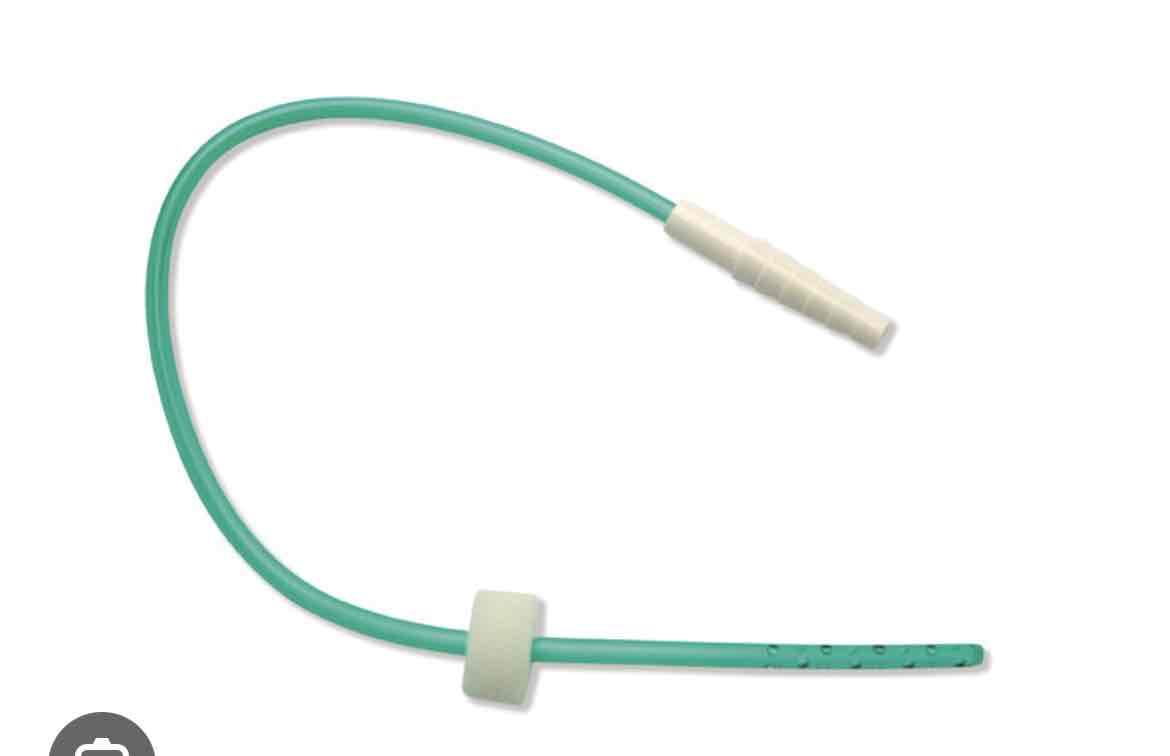
which delivery device is this
nasal catheter
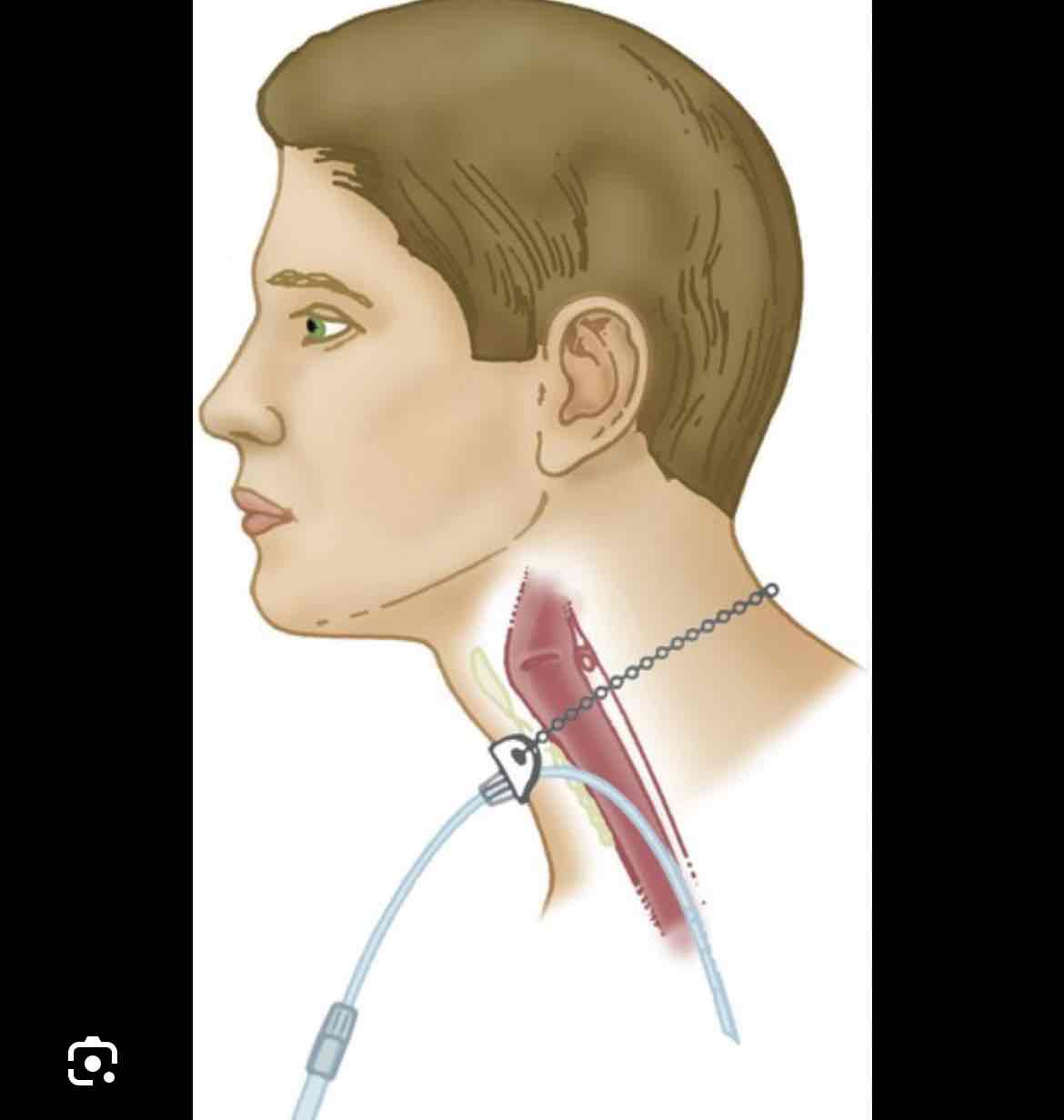
which delivery device is this
transtracheal catheter

which delivery device is this
reservoir cannula
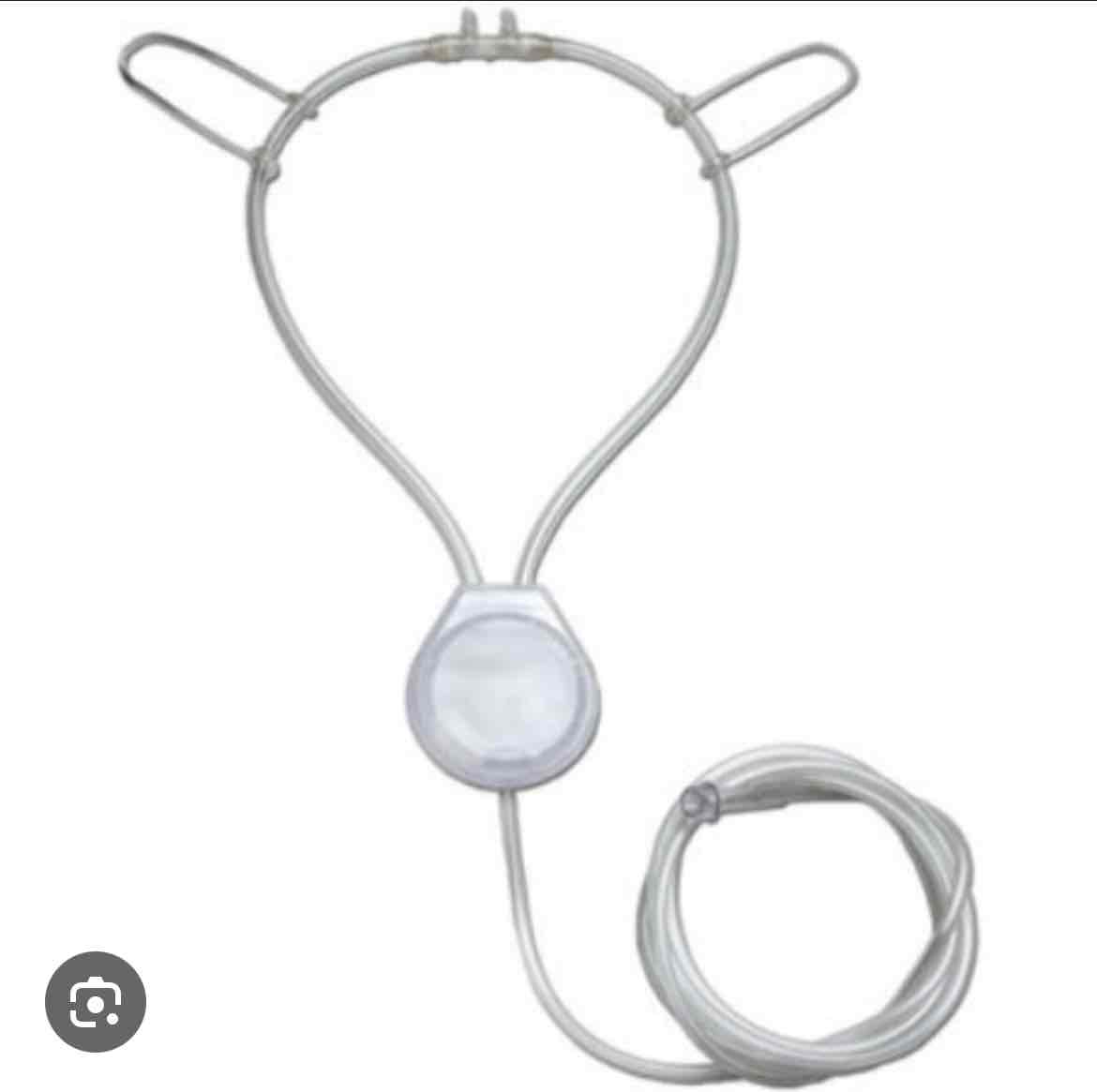
which delivery device is this
pendant reservoir cannula
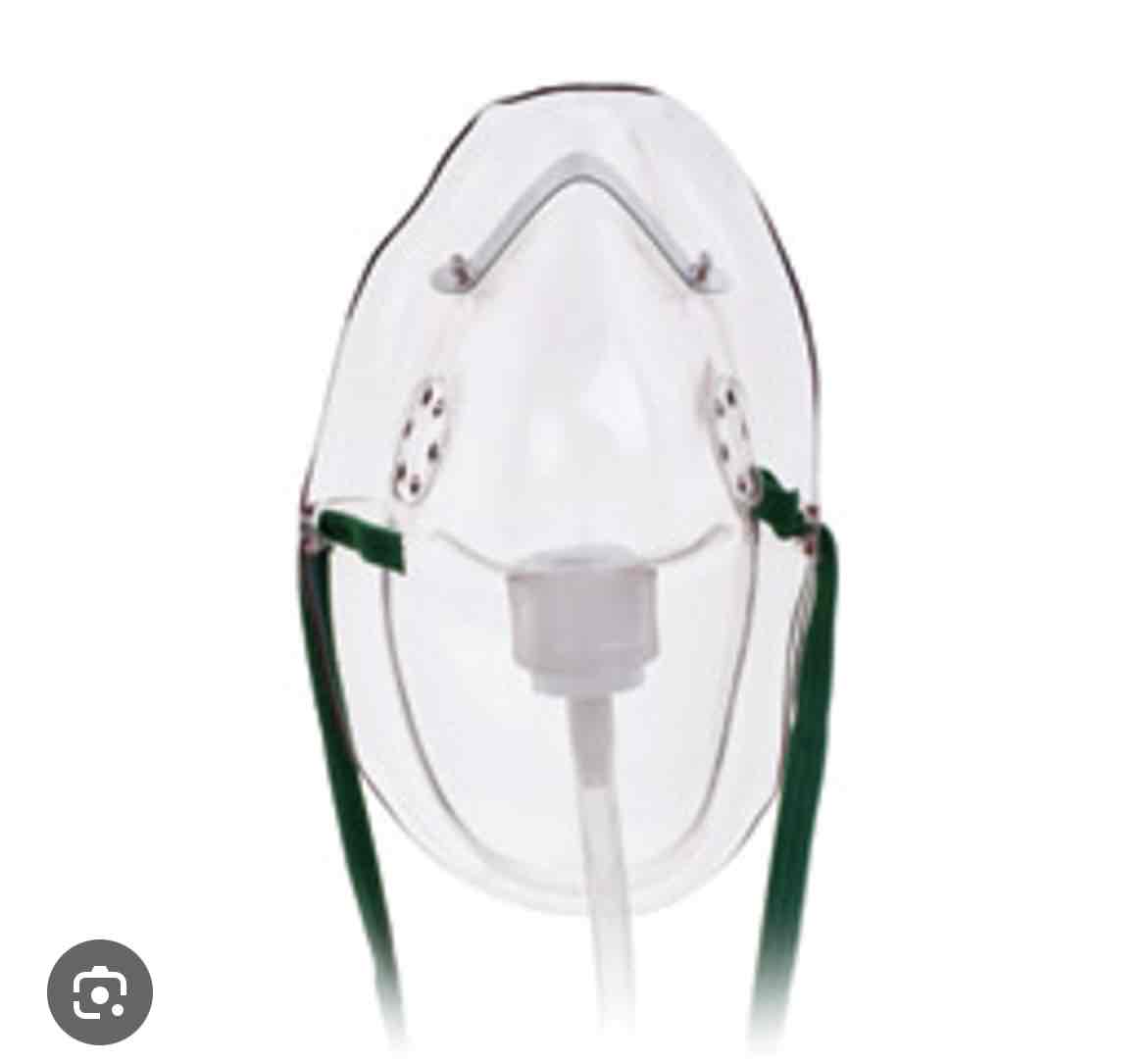
which delivery device is this
simple mask
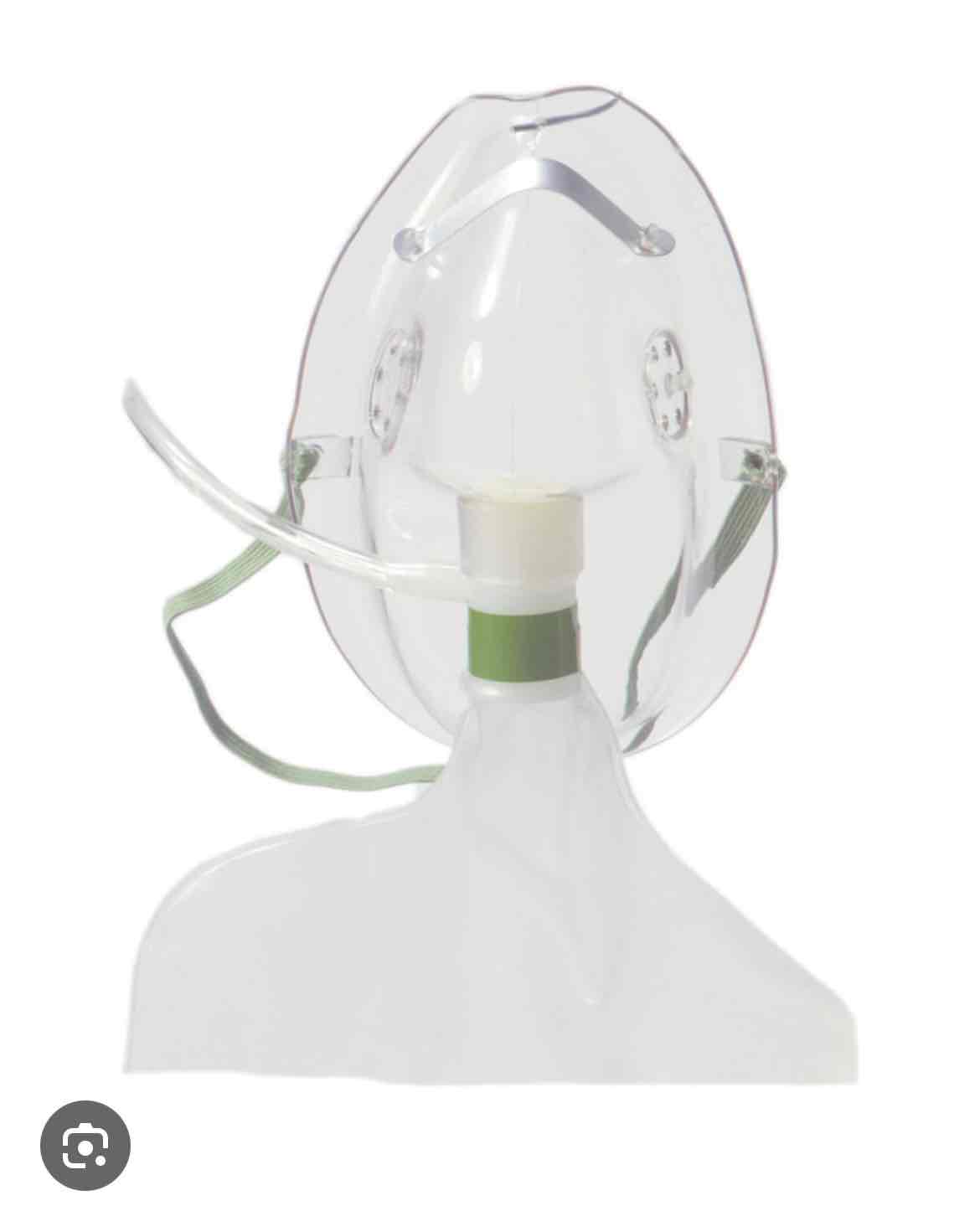
which delivery device is this
partial rebreather
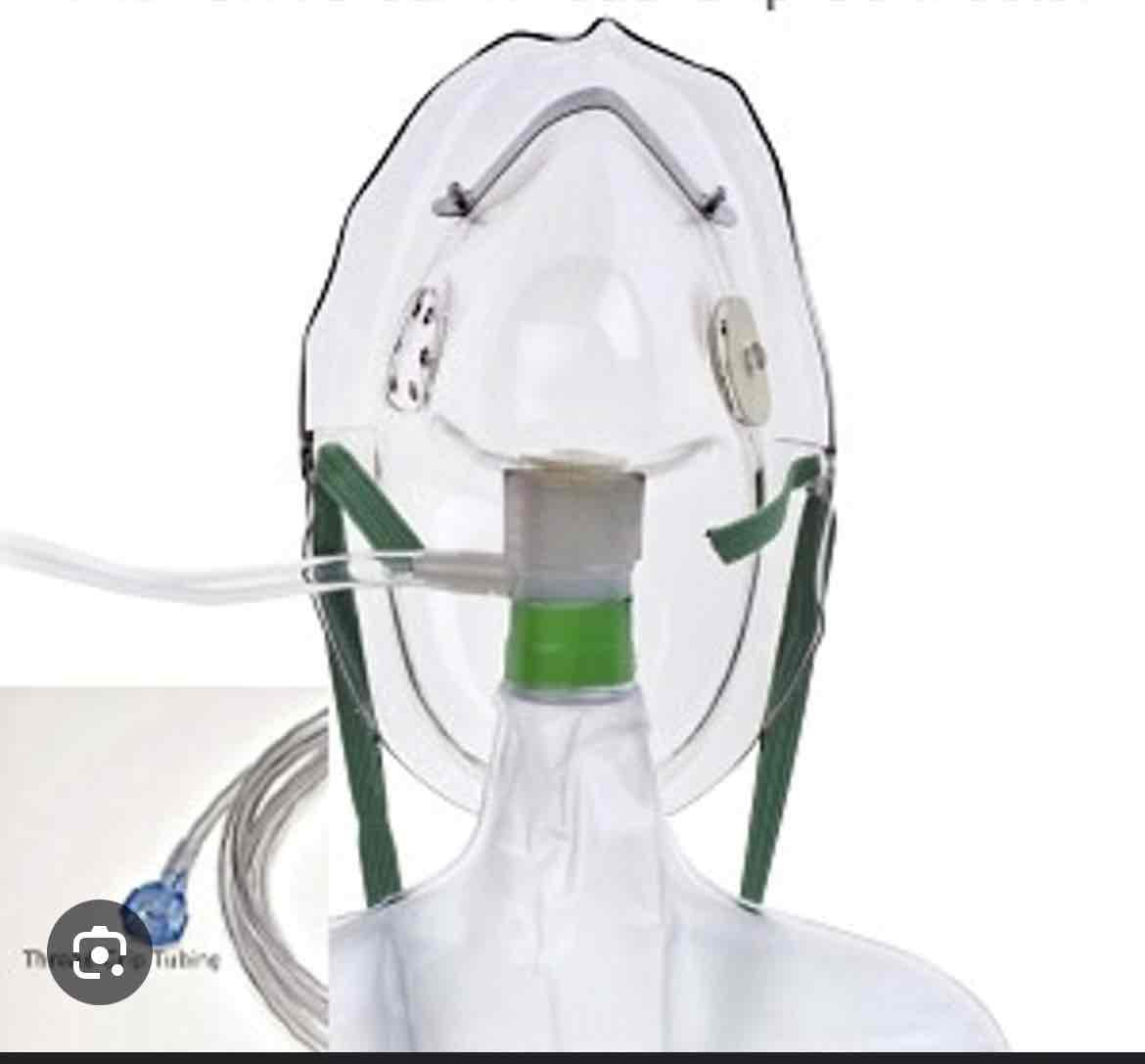
which delivery device is this
non-rebreather
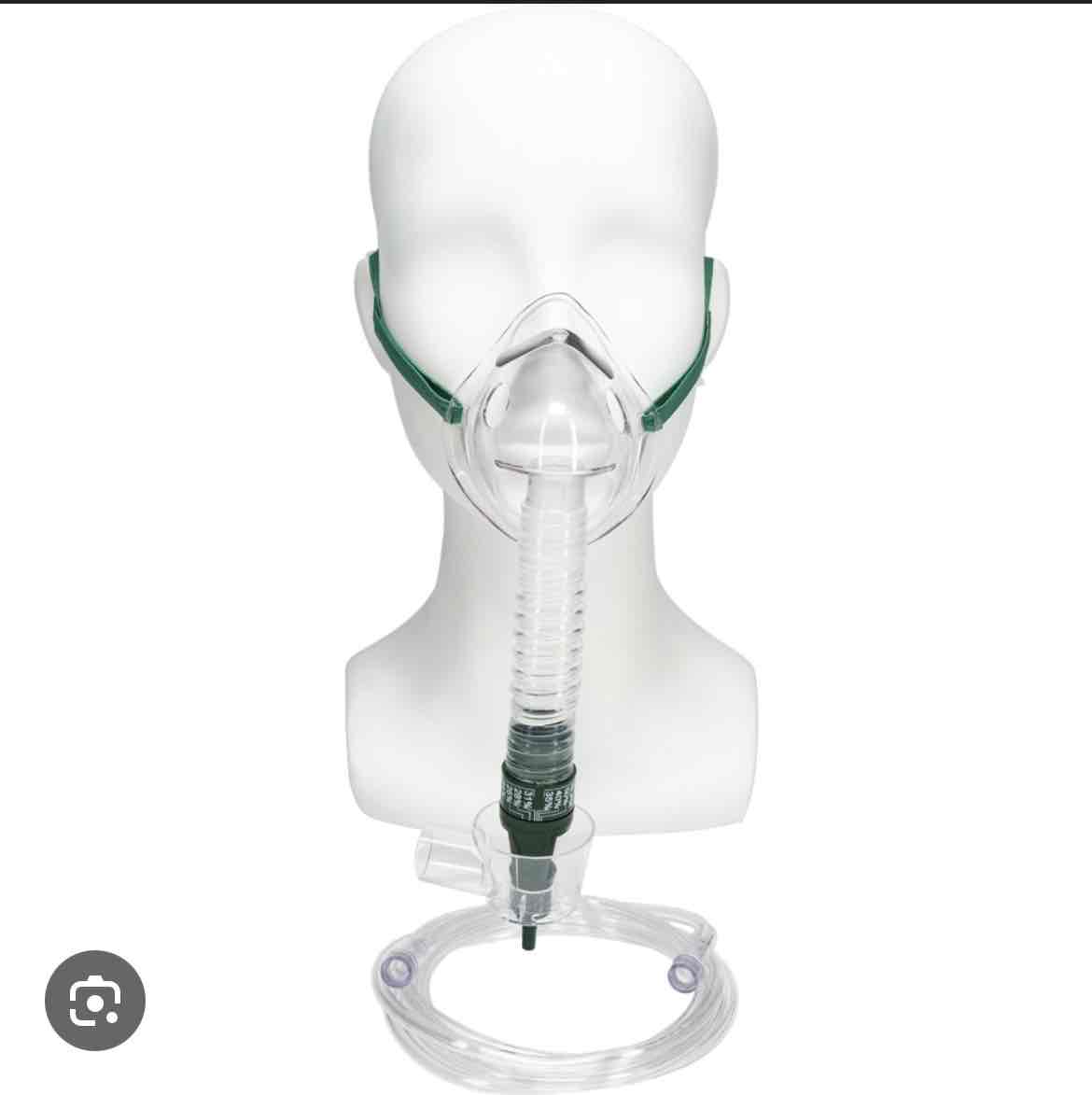
which delivery device is this
venturi(AEM) mask
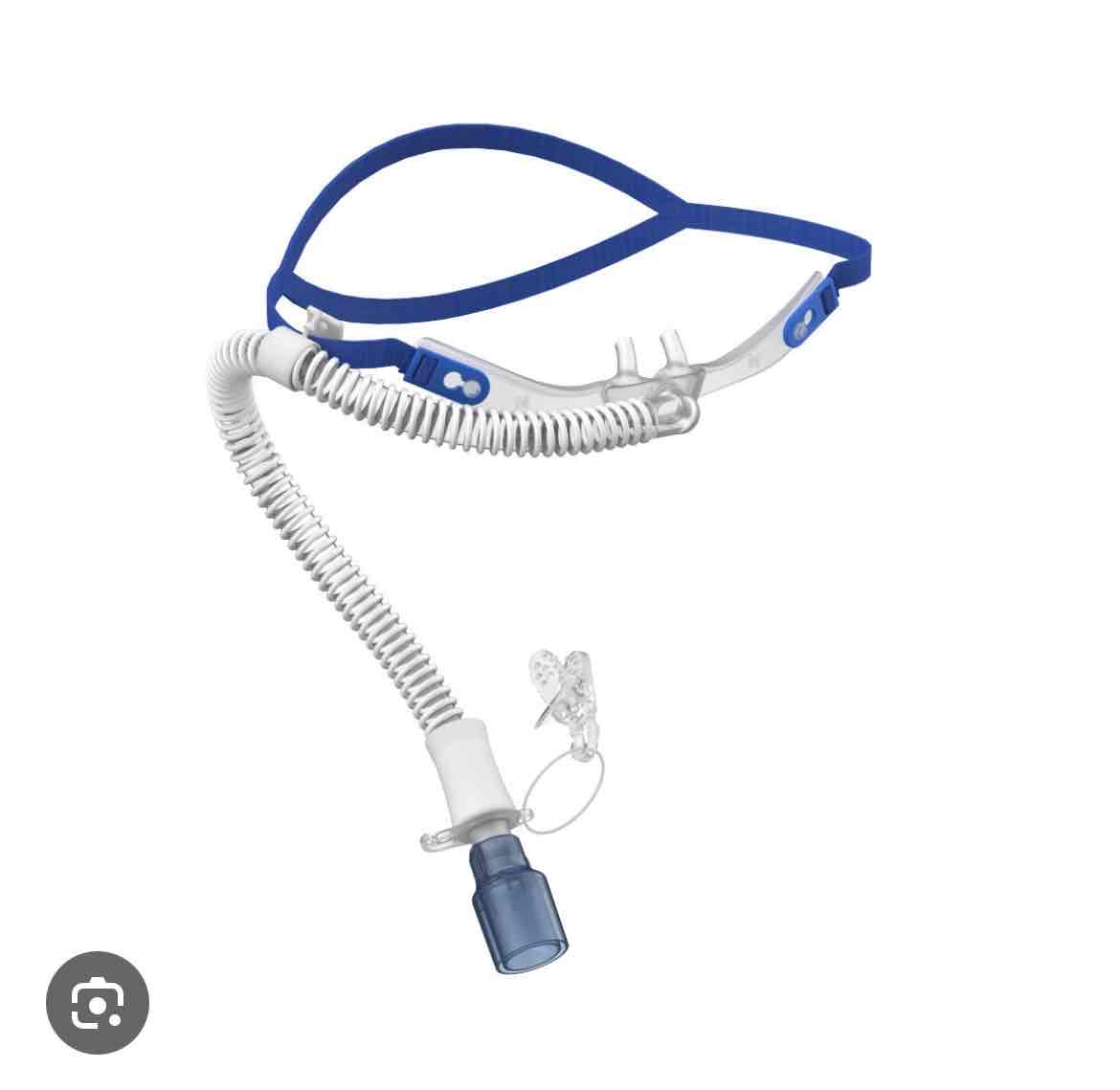
which delivery device is this
high flow nasal cannula
what type of flow device is the nasal cannula
low flow
what is the flow range of the nasal cannula
0.25-6 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the nasal cannula
24%-44%
what type of flow device is the nasal catheter
low flow
what is the flow range of the nasal catheter
0.25-5 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the nasal catheter
22%-45%
what type of flow device is the transtracheal catheter
low flow
what is the flow range of the transtracheal catheter
0.25-4 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the transtracheal catheter
22%-35%
what type of flow device is the simple mask
reservoir
what is the flow range of the simple mask
5-10 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the simple mask
35%-50%
what type of flow device is the partial rebreather mask
reservoir
what is the flow range of the partial rebreather mask
10-15 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the partial rebreather mask
40%-70%
what type of flow device is the reservoir cannulas
reservoir
what is the flow range of the reservoir cannulas
0.25-4 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the reservoir cannulas
22%-35%
what type of flow device is the non-rebreather mask
reservoir
what is the flow range of the non-rebreather mask
10-15 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the non-rebreather mask
60%-80%
what type of flow device is the venturi(AEM) mask
high flow
what is the flow range of the venturi(AEM) mask
>60 lpm
what is the FiO2 range of the venturi(AEM) mask
24%-50%
what type of flow device is the high flow nasal cannula
high flow
what is the flow range of the high flow nasal cannula
output flow up to 60 lpm or more
what is the FiO2 range of the high flow nasal cannula
35%-100%