Pollination and double fertilization
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What problem to plants have reproduction wise?
they don’t move - because of this various independent and assisted methods have evolved to move plant male gamete (pollen) and progeny (seeds)
Which species that pollinates is the most dominant
Animals
80% of plants are animal or insect pollinated True or False?
True
Which invertebrates(no spine) are mostly involved in pollination
Wasps, Butterflies, Flies, Beetles, Moths
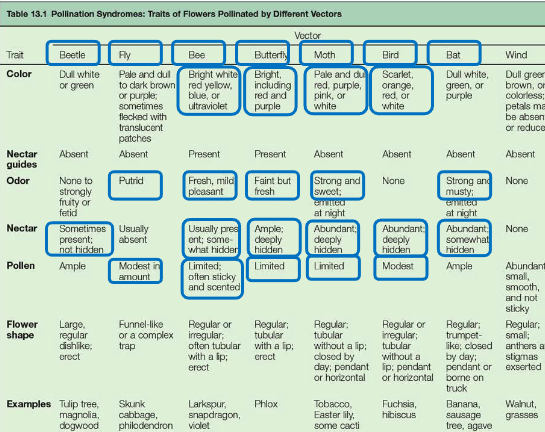
Different ways flowers attract animal pollinators
Colour, Nectar, Odor, Deception/mimicry - these methods are more metabolically efficient than relying on wind as a transfer system
Why do animals visit pollinators?
Animals visit plants for a reward (Pollen, nectar) - and only incidentally pollinate other plants in the process
Pollen is an excellent food source for animals - the cytoplasm contains proteins, sugar, fats, starch, and trace amounts of vitamins and essential elements
Nectar is a primary source of energy for many insects (ex. its rich sugar conent fuels flight and other activities)
What are some precise ways plants have evolved to attract specifically pollinators?
Most pollen is orange to yellow (highly noticeable)
Many pollen grains have a distinctive order
The timing of when pollen matures can be very precise (ex., lining up with seasonal or daily activities of pollinators - Corn anthers split open in the morning, Apple Anthers split in the afternoon, some bat-pollinated flowers release pollen only at night)
Nectar also has a limited time of availability like pollen
What is Mimicry (aka. Plant scamming)
Some flowers mimic insect shapes
The insect then attempts to copulate (have sex) or tries to fight the plant
In the end the insect ends up picking up the pollen and transfers the pollen to the next flower
Modes of Pollination
Pollen may be moved by either biotic (animal) or abiotic (wind and water) vectors
Plants have evolved unique flower and pollen traits that adapt and facilitate pollination by a particular vector
Beetles are attracted to the Tulip tree as its flowers emit musty, yeasty, and spicy fermented odours
Birds as Pollinators
Birds were not recognized as pollinators until recently
Now its known that thousands of plant species are pollinated by birds in many parts of the world (ex. Hummingbirds, Sunbirds, Honeyeaters)
Co - evolution
Plants and the animals that pollinate them have co-evolved
In some cases the flowers have shapes that are only accessible to certain pollinators
Examples: Moth visited flowers are often closed during the day
Both butterfly and moth flowers have long narrow tubes with pools of nectar at their bases - this makes it impossible for bees and beetles to enter
Some flowers specifically adapted for bird pollination
Bats as Pollinators
Most bats eat insects, but some are vegetarian - they have long snouts and tongues, small teeth, large eyes, and a good sense of smell
Bat-pollinated flowers are open at night and positioned below the foliage(leaves) of the plant
Colours are drab white, green, or purple because bats are colour blind
Exude a strong musty odor at night
Large and tough with lots of pollen and nectar (bats don’t land gracefully compared to butterflies or bees)
Plants pollintaed by bats include Bananas(Musa), Baobab, and Agave
What was Darwin’s first prediction?
The star orchid is an orchid endemic (commonly found) to Madagascar that has an extremely long nectar tube
Darwin predicted that in Madagascar, there must be moths with proboscis capable of extension to a length of between ten and eleven inches
No animal existed though
Darwins prediction (2)
in 1904 (41 years later) Xanthopan morganii praedicta was described and discovered by Karl Jordan and Lord Walter Rothschild
Study this
Wind-pollinated flowers produce many more
pollen grains per ovule than animal-pollenated
plants. True or False
True
Characteristics of Wind-pollinated flowers
Small
Colorless
Odorless
Lacking in nectar
Lacking petals or having petals reduced to small scales
Flowers or inflorescences are positioned to dangle or wave in the open
Grasses and sedges position their flowers well above the leaves so they are exposed to wind currents
Some trees produce flowers before new leaves emerge in the spring
Pollen grains are generally smaller, smoother, and drier
Shape is often frisbee-like to improve aerodynamic form
stigmatic surfaces are enlarged and elaborate, often extending
architecture of the flower and the inflorescence
creates vortices that trap pollen and permit the
grains to settle onto stigmas at a rate greater than
predicted by chance
Pollen development
Surrounded by elaborate cell walls
Contain Sporopollenin
Sporopollenin
a highly resistant biopolymer that forms the protective outer layer (exine) of plant spores and pollen grains.
a very hard material that resists decay and makes pollen grains good fossil
What is the main life cycle phase in the Angiosperm Life Cycle
Adult (sporophyte stage) -
What contributed to the Angiosperms evolutionary success
Miniaturization of the seed plant gametophyte
Angiosperms are heterosporous - what does that mean?
Land plants that produce two different types of spores: smaller male microspores that will generate pollen grains as the male gametophytes, and larger female megaspores, which will form an ovule that contains female gametophytes
What are anthers usually made of?
four elongated tubes called pollen sacs
each pollen sac contains a mass of dividing cells called microsporocytes
What do microsporocytes do?
Each microsporocyte divides by meiosis to form four haploid (n) microspores
The nucleus of each microspore divides by mitosis to form a two-celled pollen grain, which contains a tube cell and a smaller generative cell
What is the role of the two-celled haploid male gametophyte that was divided by mitosis
Produce sperm cells for fertilization
How much fertilization do flowers go though
2 - double fertilization
What does germination of a pollen grain produce?
A pollen tube which grows down though the stigmas and style and enters the ovary
What is germination?
The process when a dormant seed begins to grow and develop into a young plant or seedling
Many pollen grains may germinate and their pollen tubes may grow through the pistil, but only one pollen tube usually enters the ovule and its embryo sac - true or false?
true
Where is the growth of the pollen tube directed?
Down the style and to the embryo sac by molecules produced by the style and embryo sac tissues
During pollen tube growth what happens to the generative cell
it divides by mitosis to form two sperm cells
The two sperm pass through a synergid cell to effect what
Double fertilization: one fuses with the egg cell and the other fuses with the central cell (polar nuclei)
What does the sperm (n) and egg cell (n) fuse together to create
A diploid zygote (2n) which will grow into the embryo
The sperm nucleus fusion (n) with the two polar nuclei (n) of the central cell forms what
triploid (3n) nucleus which divide to become a reserve tissue called the endosperm
The antipodals and synergids usually degenerate after the formation of a triploid (3n) - true or false
true
Seed and fruit development are intiated by what
fertilization