CH 29: continuous wave doppler
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
The capabilities of continuous wave doppler includes its ability to evaluate for what 2 pathologies?
Deep venous system for obstruction
Venous incompetence
Complete the blanks of the 6 limitations of continuous wave doppler.
Fixed _________
No ______ resolution
No ability to place _____________ at a specific depth
No ________ image
Abnormal flow patterns can make differentiating patterns of __________________ and _________________ difficult
Paired ___________ veins in the calf make the diagnosis of _____________________ extremely difficult
Sample size
Range
Sample volume
Anatomic
Deep venous obstruction and extrinsic compression
Deep, isolated calf vein thrombosis
Because continuous waveforms provide no anatomic imaging, how is the exam interpreted? (2)
Seeing waveforms
Hearing the signals
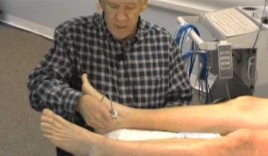
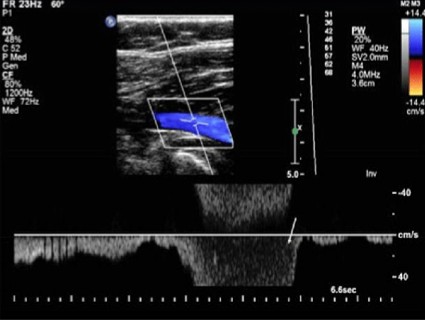
What exam is being performed here?
What probe is used here?
Ankle-Brachial Index
Continuous wave probe
Will continuous or pulsed wave dopplers have a more accurate measurement of high velocities?
Continuous wave
Will continuous or pulsed wave dopplers have a poor range resolution?
Continuous wave
Will continuous or pulsed wave dopplers have a good range resolution?
Pulsed wave
Will continuous or pulsed wave dopplers have limitations on maximum velocities?
Pulsed wave
List the 4 reasons for a false-positive study.
Extrinsic compression
Peripheral arterial disease
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Improper doppler angle/Probe pressure
Describe what a false-positive study is.
We said the patient has a disease, but they tested negative for disease
Describe what a false-negative study is.
We said the patient does not have a disease, but they tested positive for disease
List the 4 factors that can cause extrinsic compression.
Tight clothing
Tumors
Ascites
Pregnancy
Peripheral arterial disease can cause a decrease in what?
Venous filling
COPD can result in an elevated…
The elevation in this can alter…
And can reduce…
Central venous pressure
Pressure gradients
Venous flow patterns
An increase in probe pressure can (1)_________ venous flow and/or result in (2)____________ flow that may be misinterpreted as flow in a (3)_________ vessel.
Obliterate
Accelerated
Diseased
List the 3 reasons for a false-negative study.
Partial thrombosis
Collateral development
Duplicate deep veins
How many piezoelectric crystals does continuous wave doppler have?
2
With the 2 piezoelectric crystals, describe what they’ll each be doing?
One is continuously sending signals
The other is continuously receiving signals
What probe frequency is used for continuous wave doppler?
What angle should the probe be from the skin surface?
5 MHz
45 - 60 degrees
The deep veins are found _________ to the corresponding artery.
Adjacent
Because the deep veins are found adjacent to their corresponding artery, correct vessel identification depends on hearing the accompanying (1)_______ signal and then moving (2)________.
Arterial
Medial
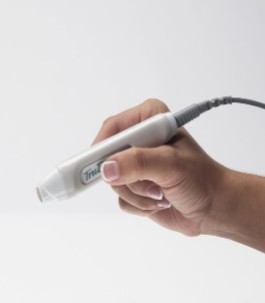
What kind of doppler does this probe perform?
What kind of exam is performed with this probe?
What kind of frequency will it have?
Continuous wave
ABI
5 MHz
The patient for a continuous wave doppler should be positioned similar to what other study?
Lower venous duplex
Having the patient in what position helps to facilitate venous filling?
Extremities lower than the level of the heart
OR reverse Trendelenburg
When the patient is positioned with their extremities lower than the level of the heart, what can that help facilitate?
Venous filling
Define the reverse Trendelenburg.
When the extremities are lower than the level of the heart
If abnormal venous signals are obtained, what 2 tips are essential to do before reaching a reliable conclusion?
Repositioning
Reevaluation
When performing a continuous wave doppler exam, we want to start with what side?
Asymptomatic side
With a continuous wave doppler exam, the probe will first be placed in what area?
While in this area, what vessel should the sonographer identify?
Once this vessel has been identified, where should the probe move to insonate the CFV?
Inguinal ligament
CFA
Medially
Once the sonographer has scanned the asymptomatic side, what vessel will the sonographer evaluate on the symptomatic side?
What 2 things will the sonographer look for on the symptomatic side?
CFV
Same flow patterns
Responses to compression maneuvers
On the symptomatic side, aside from the CFV, which 3 other vessels will also be evaluated?
Femoral veins
Popliteal veins
PTVs
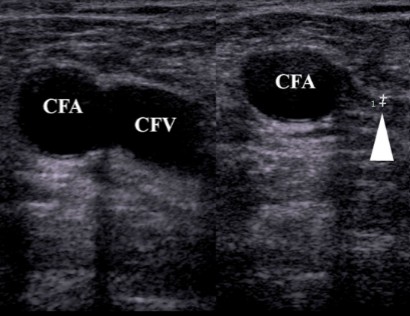
What is occurring in the image on the right?
CFV compression
The flow characteristics evaluated with CW doppler are also evaluated when using (1)_____ doppler with (2)_______ scanning.
PW
Duplex
Define spontaneity.
Spontaneous flow without augmentation
Spontaneity is when the venous signal is clearly heard at all sites, with the exception at what 3 vessels?
Tibial veins
GSVs
Radial/Ulnar veins
Vasoconstriction occurs when the veins are… (3)
Vasoconstriction will reduce what?
Cold
Nervous
In pain
Venous flow
With vessels that typically show spontaneity, if signals are only becoming evident AFTER performing distal compression, what can that be an indication of?
Abnormal
Define patency.
Spontaneous flow following distal augmentation
Which vessels are considered ‘patent’? (3)
Tibial veins
Radial veins
Ulnar veins
Distal augmentation provides documentation that the vessel is…
Patent
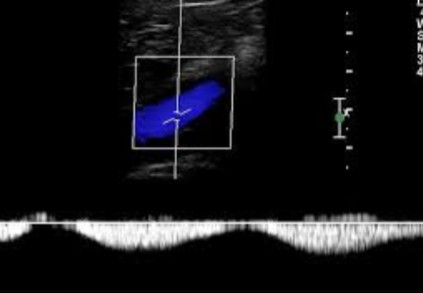
Does this doppler waveform show a vessel that displays spontaneity or patency?
Spontaneity
Does this doppler waveform show a vessel that displays spontaneity or patency?
Patency
Lower extremity venous signals are normally ______ with respiration.
Phasic
When is it normal to see a continuous flow pattern of the veins in the upper or lower extremity?
It is abnormal to see a continuous flow pattern of the veins in the upper or lower extremity with what pathology?
With patients who have shallow breathing
Proximal venous obstruction
Define phasicity.
Flow changes with respiration
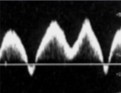
This is a respiratory flow pattern.
How would this flow type be labeled?
Rapid
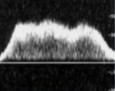
This is a respiratory flow pattern.
How would this flow type be labeled?
Slow
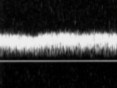
This is a respiratory flow pattern.
This flow type can be seen with what medical condition?
Apnea
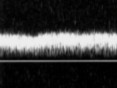
Seeing this continuous flow pattern in the lower or upper extremities can be an indication for what 2 conditions?
Normal, shallow respirations
OR
Proximal venous obstruction
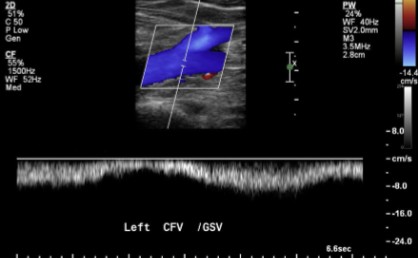
This flow pattern can be described as…
Phasic
Describe what the sonographer does for augmentation with distal compression.
Manual compression is applied distal to the transducer
Distal compression should _______ the venous signal.
Augment
Augment on doppler will show a…
Increase
The absence of augmentation during distal compression is consistent with…
An obstruction
Normally, when the sonographer releases from distal compression, what should venous flow do?
Move forward
After the sonographer releases from a distal compression, reversed doppler signals are seen/heard. What does this finding suggest?
Incompetent valves (reflux)
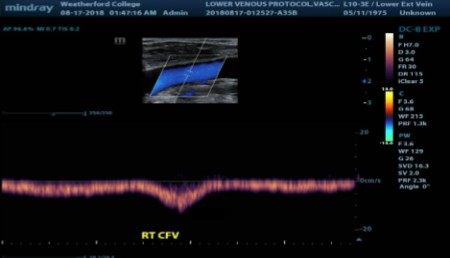
What has been done for the waveform to appear this way?
Augmentation with distal compression
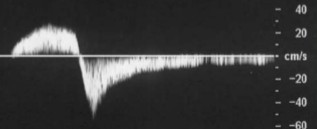
Does this waveform appear normal or abnormal?
If abnormal, what about the waveform indicates that?
If abnormal, what pathology could this waveform be an indication of?
Abnormal
Reversed doppler signals
Incompetent valves (reflux)
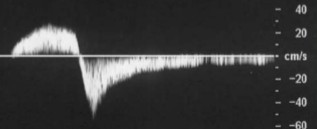
What is abnormal about this waveform? (2)
Reversed doppler signals
Does not resume in same direction
Proximal compression can also be done through what maneuver?
Valsalva
With maximal proximal compression, venous flow should be…
Halted
The effect of proximal compression on venous flow is similar to that of what movement?
Valsalva Maneuver
What can be used to substitute for Valsalva Maneuver?
Proximal compression
When performing valsalva or proximal compression, if the waveform augments, is that normal?
No
When performing valsalva or proximal compression, if the waveform halts, is that normal?
Yes
A waveform that augments during proximal compression/valsalva is indicative of what pathology?
The pathology form question 1 signifies what other pathology?
Valvular incompetence
Venous reflux
Upon release of proximal compression/valsalva, what should be seen on the venous doppler waveform?
Augmentation
What is abnormal to see upon release of proximal compression/valsalva?
Seeing this can be indicative for what pathology?
No doppler signals
Obstruction
What should be seen on the venous doppler waveform during proximal compression/valsalva to indicate a competent vein?
Halted flow
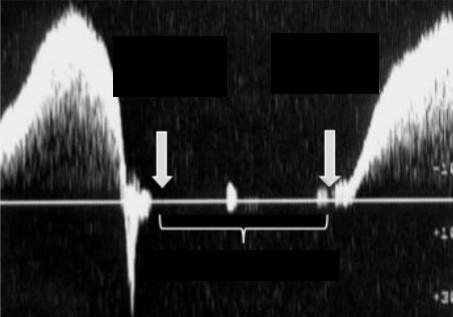
What movement is being performed for the waveform to appear this way?
Does this show if the vein is competent or incompetent?
Proximal compression OR Valsalva maneuver
Competent
Define extrinsic compression.
Pressure on the vessels from surrounding tissues nad/or structures
List 3 examples that can cause extrinsic compression.
Tumors
Pregnancy
Ascites
Extrinsic compression can ______ normal flow patterns.
Alter
What flow type is commonly and normally heard in the subclavian vein?
Why is this?
Pulsatile flow
Close proximity to the heart
What kind of venous flow is not normal to see in the lower extremities?
Pulsatile
If pulsatile venous flow is evident in the lower extremities, what 3 pathologies can it be indicative of?
Fluid overload
Chronic venous insufficiency
Increased venous pressure
Increased venous pressure is due to what pathology?
CHF (congestive heart failure)
Venous flow is also related to _________________ resistance.
Arterial peripheral
Venous flow can be affected by changes in ___________ tone.
Venomotor
List the 2 areas of venomotor tone.
Vasodilation
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation may result in more (1)__________ flow with less (2)___________ variation.
Continuous
Respiratory
Will this be vasodilation or vasoconstriction?
“Results in more continuous flow with less respiratory variation.”
Vasodilation
Vasoconstriction occurs from what 4 factors?
Trauma
Pain
Anxiety
Need to conserve body heat
Vasoconstriction may result in markedly _________ venous flow signals.
Decreased
Will this be vasodilation or vasoconstriction?
“May result in markedly decreased venous flow signals.”
Vasoconstriction
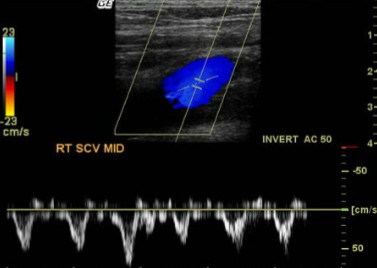
*SCV= Subclavian Vein
Is this flow type continuous or pulsatile?
Based on the vessel scanned, is this waveform normal or abnormal?
Pulsatile
Normal