Microbio Final Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/319
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
320 Terms
1
New cards
Obligate pathogen
* Always causes disease
* T. pallidum, B. anthracis, etc
* T. pallidum, B. anthracis, etc
2
New cards
Opportunistic pathogen
* Normal flora causing disease due to immune status or getting somewhere it isn’t supposed to be
* NO Normal flora in sterile sites
* Normal flora in GI, GU, Skin, Oral cavity and Respiratory tract
* NO Normal flora in sterile sites
* Normal flora in GI, GU, Skin, Oral cavity and Respiratory tract
3
New cards
How can we tell if an organism is a contaminant vs true infection?
* Colony count (Few vs Many) and occurrence in repeat culture
\
\
4
New cards
Specimen - swabs
* Transport media to prevent drying
* Cotton can be toxic
* Cotton can be toxic
5
New cards
Specimen - urine
* Sterile cup or gray top tube(boric acid)
* Clean catch midstream; first morning
* Catheter line NOT bag
* Suprapubic
* Clean catch midstream; first morning
* Catheter line NOT bag
* Suprapubic
6
New cards
Specimen - syringe
NO NEEDLE
7
New cards
Specimen
Sterile cups
8
New cards
Specimen - stool
Non-sterile container OK
9
New cards
Specimen - blood culture bottles
Set = aerobic & anaerobic
10
New cards
Blood cultures
* 2+ sets can help us determine if infection vs contamination
* Disinfecting site is important!
* Common contaminants are P. acnes, S. epidermidis, Micrococcus species and Corynebacterium species
* Disinfecting site is important!
* Common contaminants are P. acnes, S. epidermidis, Micrococcus species and Corynebacterium species
11
New cards
Blood cultures - bottle
* ==1:10 ratio of blood to culture media==
* Anticoagulant (SPS, charcoal)
* Antibiotic removal device
* 10% sucrose :osmotic stabilizer
* Anticoagulant (SPS, charcoal)
* Antibiotic removal device
* 10% sucrose :osmotic stabilizer
12
New cards
Blood cultures - automated systems
* Detect CO2
* BACTEC FX
* BacT/ALERT
* VersaTREK
* BACTEC FX
* BacT/ALERT
* VersaTREK
13
New cards
Blood cultures - BACTEC FX
Fluorescence
14
New cards
Blood cultures - BacT/ALERT
Colormetric (pH)
15
New cards
Blood cultures - VersaTREK
Gas in headspace of bottle
16
New cards
Plating specimen
* Streak for isolation
* 4 quadrant streak allows for quantitation of organism growth
* How do we do CFU counts?
* Urine cultures BAP and MAC struck for isolation
* 0.001 calibrated loop, multiply colony by 1000
* Quantitate colony from BAP ONLY
* 4 quadrant streak allows for quantitation of organism growth
* How do we do CFU counts?
* Urine cultures BAP and MAC struck for isolation
* 0.001 calibrated loop, multiply colony by 1000
* Quantitate colony from BAP ONLY
17
New cards
Microaerophilic
Requires very little free oxygen
18
New cards
Capnophilic
Requires increased CO2
19
New cards
Anaerobic
Lives in the absence of free oxygen
20
New cards
Strict (obligate) anaerobe
Will die in the presence of oxygen
21
New cards
Facultative anaerobe
Aerobe that can grow without oxygen (anaerobic condition)
22
New cards
Aerotolerant
Anaerobe unaffected by oxygen
23
New cards
BSL 1
Agents not known to cause disease in healthy individuals
24
New cards
BSL 2
Associated with human disease
25
New cards
BSL 3
Negative pressure; agents with potential aerosol transmission
26
New cards
BSL 4
Dangerous agents; full body suit
27
New cards
Biosafety cabinet I
Specimen contamination possible, unfiltered air into cabinet
28
New cards
Biosafety cabinet II
Laminar flow: air is recirculated
29
New cards
Biosafety cabinet III
2 HEPA filters, gas tight
30
New cards
Chemical disinfection
Alcohol, aldehydes, halogens, chlorine, quaternary ammonium compounds, metals
31
New cards
Physical disinfection
Boil, Pasteurization, Inspissation
32
New cards
Chemical sterilization
Gas vapor sterilants (Ethylene oxide), Liquid gas sterilization
33
New cards
Physical sterilization
Steam – Autoclave, Dry Heat – Oven, Ionizing and nonionizing radiation
34
New cards
What is the most likely identification of a mucoid, lactose-fermenting colony isolated on MacConkey agar that is indole negative, citrate positive and nonmotile?
Klebsiella pneumoniae
35
New cards
A gram negative rod was isolated from a stool culture. It produced colorless colonies on EMB and red colonies on XLD. In TSI, it produced a yellow butt and a pink slant with no gas or H2S. It was nonmotile, negative for indole, VP, citrate, urea and phenylalanine deaminase. It was positive for methyl red. What is the presumptive identification?
Shigella
36
New cards
O/F Media - What is in the tube?
* Glucose
* Peptones – smaller concentration to help determine oxidizer since they produce weak acids; prevents the use of peptones to prevent seeing pH change
* pH indicator
* Peptones – smaller concentration to help determine oxidizer since they produce weak acids; prevents the use of peptones to prevent seeing pH change
* pH indicator
37
New cards
TSI - what sugars?
* Lactose, glucose and sucrose; lactose and sucrose 10:1 to glucose
38
New cards
TSI - what can we detect?
H2S, Gas and Sugar fermentation
39
New cards
TSI
Aerobic slant & anaerobic butt
40
New cards
TSI - K/A
Glucose fermenter only
41
New cards
TSI - A/A
Glucose AND lactose or sucrose
42
New cards
TSI - hydrogen sulfide
ONLY seen if the butt of the tube is acidic (==YELLOW==)
43
New cards
TSI - E. coli
A/A with gas
44
New cards
TSI - Shigella
K/A
45
New cards
TSI - Salmonella
K/A with H2S
46
New cards
TSI - P. aeruginosa
K/K
47
New cards
LIA slant
* Determines lysine decarboxylation; glucose fermentation at the butt of the tube and if organism decarboxylates lysine the butt turns ==purple== (alkaline pH)
* Remember the enzyme needs an anaerobic AND acidic environment to decarboxylate
* Lysine deamination results in a ==wine slant==
* For H2S to be seen, the butt of the tube has to be ALKALINE (==purple==)
* Remember the enzyme needs an anaerobic AND acidic environment to decarboxylate
* Lysine deamination results in a ==wine slant==
* For H2S to be seen, the butt of the tube has to be ALKALINE (==purple==)
48
New cards
LIA - Proteus
W/Y
49
New cards
LIA - Salmonella
K/K with H2S
50
New cards
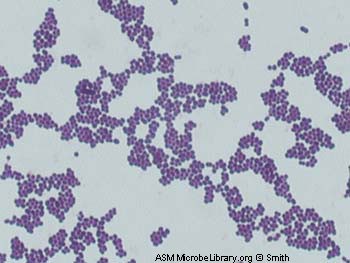
GPC
51
New cards
S. aureus
* Coagulase positive
* Staph latex positive
* Protein A and clumping factor
* MSA agar: yellow
* Test for VISA/VRSA
* Vancomycin Screen agar: Confirm with broth microdilution
* Test for MRSA
* Oxacillin screening agar
* Cefoxitin
* mecA: PBP2a
\
* Staph latex positive
* Protein A and clumping factor
* MSA agar: yellow
* Test for VISA/VRSA
* Vancomycin Screen agar: Confirm with broth microdilution
* Test for MRSA
* Oxacillin screening agar
* Cefoxitin
* mecA: PBP2a
\
52
New cards
CNS
* Coagulase negative
* Staph latex negative
* MSA: Red
* S. epidermidis
* Contaminant
* Catheter/indwelling device infections - Biofilm
* Nosocomial UTI
* Source: Urine
* Novobiocin for S. saprophyticus
* Staph latex negative
* MSA: Red
* S. epidermidis
* Contaminant
* Catheter/indwelling device infections - Biofilm
* Nosocomial UTI
* Source: Urine
* Novobiocin for S. saprophyticus
53
New cards
S. aureus
Skin and wound infections
54
New cards
S. aureus - Exfoliative toxin
Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
55
New cards
S. aureus - TSST-1
* Toxic shock syndrome
* Tampons
* Tampons
56
New cards
S. aureus - enterotoxin
* Food poisoning
* Occurs 2-8 hours after consumption
* Occurs 2-8 hours after consumption
57
New cards
S. aureus - cytolytic toxins
* Alpha, beta, gamma, and delta
* Alpha and beta lyse RBC’s
* Gamma associated with Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL) : prevents phagocytosis of PMNs
* Alpha and beta lyse RBC’s
* Gamma associated with Panton-Valentine leucocidin (PVL) : prevents phagocytosis of PMNs
58
New cards
S. aureus - Protein A
Binds Fc region of IgG, neutralizing antibody
59
New cards
S. aureus - Enzymes
facilitate spread
60
New cards
GPC - Rothia species
* Sticky!
* Seen in respiratory cultures
* Opportunistic pathogen
* Seen in respiratory cultures
* Opportunistic pathogen
61
New cards
GPC - Micrococcus species
* YELLOW colony
* Microdase test (modified oxidase test)
* Gram Stain: tetrads
* Normal flora, contaminant
* Microdase test (modified oxidase test)
* Gram Stain: tetrads
* Normal flora, contaminant
62
New cards
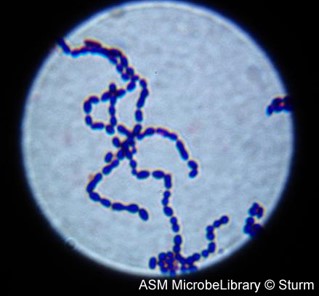
63
New cards
Streptococcus
* Treat with Penicllin
* Erythromycin if allergic
* Increased CO2 enhances growth
* Hemolysis?
* Alpha, beta, gamma hemolysis
* Gamma
* PYR(quicker!), 6.5% Nacl and BEA determine if Viridans streptococci or Enterococcus
* Erythromycin if allergic
* Increased CO2 enhances growth
* Hemolysis?
* Alpha, beta, gamma hemolysis
* Gamma
* PYR(quicker!), 6.5% Nacl and BEA determine if Viridans streptococci or Enterococcus
64
New cards
Enterococcus
* Nosocomial infections: UTI, bactermia
* PYR, BEA, 6.5% NaCl (+)
* VRE
* Vancomycin screen agar
* CHROMagar: PINK (E. faecium) or BLUE (E. faecalis if catalase negative)
* Serious infections treated with an aminoglycoside and penicillin - synergistic
* PYR, BEA, 6.5% NaCl (+)
* VRE
* Vancomycin screen agar
* CHROMagar: PINK (E. faecium) or BLUE (E. faecalis if catalase negative)
* Serious infections treated with an aminoglycoside and penicillin - synergistic
65
New cards
Streptococcus - Alpha hemolysis
* P disc or Bile solubility
* S. pneumoniae vs Viridans streptococcus
* “S” and soluble vs “R” not soluble
* Could it be Enterococcus?
* PYR, 6.5% NaCl, Bile Esculin
* Weird ones:
* Aerococcus: GS=more tetrads than chains but looks alpha
* Leuconostoc and Pediococcus: Intrinsically resistant to Vancomycin
* S. pneumoniae vs Viridans streptococcus
* “S” and soluble vs “R” not soluble
* Could it be Enterococcus?
* PYR, 6.5% NaCl, Bile Esculin
* Weird ones:
* Aerococcus: GS=more tetrads than chains but looks alpha
* Leuconostoc and Pediococcus: Intrinsically resistant to Vancomycin
66
New cards
S. pneumoniae
* Lancet-shaped
* Mucoid or dimpled (autolysis)
* Capsule most important virulence factor
* Pneumonia - #1 cause; otitis media; meningitis; bacteremia
* Bile soluble (+) and Optochin (S)
* Mucoid or dimpled (autolysis)
* Capsule most important virulence factor
* Pneumonia - #1 cause; otitis media; meningitis; bacteremia
* Bile soluble (+) and Optochin (S)
67
New cards
Viridans streptococci
* #1 cause of bacterial endocarditis
* Normal flora
* Can cause oral infections
* Hemolysis: alpha or gamma
* PYR (=) and P disk (R)
* Normal flora
* Can cause oral infections
* Hemolysis: alpha or gamma
* PYR (=) and P disk (R)
68
New cards
Streptococcus - Beta hemolysis
* PYR (quicker!) and/or Bacitracin (A disk) help us determine GAS or not
* GDS associated with colon cancer
* PYR and 6.5% NaCl (=)
* GDS associated with colon cancer
* PYR and 6.5% NaCl (=)
69
New cards
S. pyogenes
* Toxins and infections
* Bacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis (strep throat)
* Skin infections: Impetigo, Erysipelas & Cellulitis
* Scarlet fever – Spe’s
* Necrotizing fasciitis “flesh-eating”
* Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
* Sequelae
* Rheumatic fever: damage to heart valves
* Acute glomerulonephritis
* Bacterial pharyngitis and tonsillitis (strep throat)
* Skin infections: Impetigo, Erysipelas & Cellulitis
* Scarlet fever – Spe’s
* Necrotizing fasciitis “flesh-eating”
* Streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
* Sequelae
* Rheumatic fever: damage to heart valves
* Acute glomerulonephritis
70
New cards
S. pyogenes - M protein
most important virulence factor
71
New cards
S. pyogenes - Streptolysin O
* oxygen labile
* anaerobic
* highly immunogenic (ASO test)
* anaerobic
* highly immunogenic (ASO test)
72
New cards
S. pyogenes - Streptolysis S
oxygen stable – see hemolysis of RBCs in agar
73
New cards
S. agalactiae - Capsule
most important virulence factor
74
New cards
S. agalactiae
* Newborn infections: pneumonia, sepsis, meningitis
* Lim broth
* Carrot broth
* Lim broth
* Carrot broth
75
New cards
S. pyogenes
* Large hemolysis and small colony
* A disk “S”
* PYR (+)
* CAMP(=)
* BEA (=)
* Latex A (+)
* A disk “S”
* PYR (+)
* CAMP(=)
* BEA (=)
* Latex A (+)
76
New cards
S. agalactiae
* Small zone of hemolysis compared to colony size
* A disk “R”
* PYR (=)
* CAMP (+)
* Hippurate hydrolysis (+)
* Latex B (+)
* A disk “R”
* PYR (=)
* CAMP (+)
* Hippurate hydrolysis (+)
* Latex B (+)
77
New cards
Nutritionally deficient strep
* Abiotrophia and Granulicatella
* Gram Stain: GPC in chains in a blood culture but does not grow on BAP
* Grows on CHOC
* Satellite test
* Gram Stain: GPC in chains in a blood culture but does not grow on BAP
* Grows on CHOC
* Satellite test
78
New cards
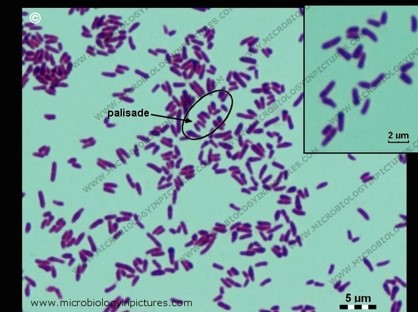
79
New cards
B. cereus
* Infections
* food poisoning (8-16 hours) diarrheal enterotoxin OR emetic enterotoxin (Fried rice)
* Ocular infections
* Ground glass, beta hemolysis, motile
* food poisoning (8-16 hours) diarrheal enterotoxin OR emetic enterotoxin (Fried rice)
* Ocular infections
* Ground glass, beta hemolysis, motile
80
New cards
B. anthracis
* Infections – how do spores enter?
* Cutaneous anthrax – (eschar)
* Inhalation anthrax – (woolsorter’s disease)
* Gastrointestinal anthrax
* Toxins
* PA + EF = Edema toxin
* PA + LF = Lethal toxin
* Egg-white/medusa head, non-motile, gamma hemolysis
* Cutaneous anthrax – (eschar)
* Inhalation anthrax – (woolsorter’s disease)
* Gastrointestinal anthrax
* Toxins
* PA + EF = Edema toxin
* PA + LF = Lethal toxin
* Egg-white/medusa head, non-motile, gamma hemolysis
81
New cards
GPR - Corynebacterium
* C. diphtheriae - Diphtheria toxin
* Gray pseudomembrane
* Elek tests for toxin
* C. urealyticum – urea positive; found in urine
* Pallisading, Chinese letters, Catalase (+)
* Gray pseudomembrane
* Elek tests for toxin
* C. urealyticum – urea positive; found in urine
* Pallisading, Chinese letters, Catalase (+)
82
New cards
GPR - Listeria
* Listeriosis – contaminated food products
* Pregnant women, newborns, immunocompromised
* Beta hemolysis, Tumbling/Umbrella motility, BEA (+), CAMP (+), Hippurate hydrolysis (+), Catalase (+)
* Pregnant women, newborns, immunocompromised
* Beta hemolysis, Tumbling/Umbrella motility, BEA (+), CAMP (+), Hippurate hydrolysis (+), Catalase (+)
83
New cards
GPR - Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
* Infection by a cut
* Fish handlers disease - Erysipeloid
* H2S+, Catalase =, can look alpha, ppt colony
* Fish handlers disease - Erysipeloid
* H2S+, Catalase =, can look alpha, ppt colony
84
New cards
GPR - G. vaginalis
* Bacterial vaginosis – clue cells
* PPT colony, Catalase =
* PPT colony, Catalase =
85
New cards
GPR - Branching
* Nocardia – Partial PAF, chalky colony
* Streptomyces – PAF =, waxy colony
* Streptomyces – PAF =, waxy colony
86
New cards
GPR - Rhodococcus
Pink mucoid colonies
87
New cards
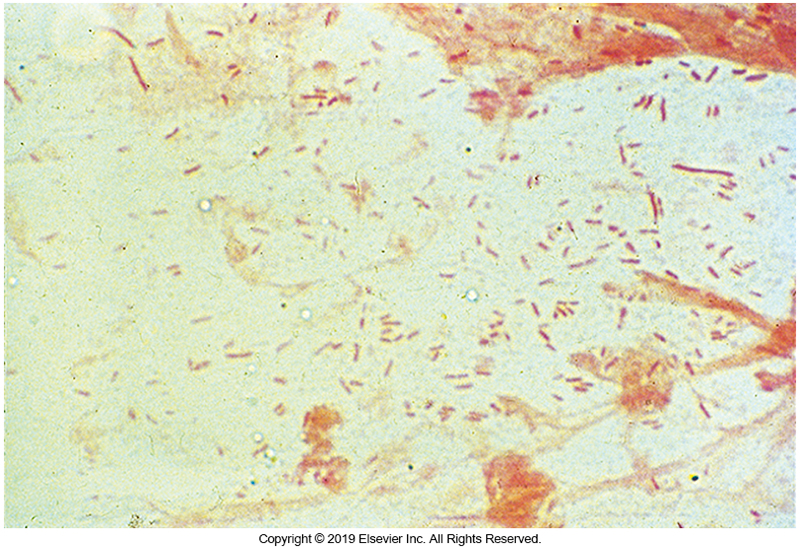
88
New cards
Cardinal Rules for Enterobacteriaceae
* Gram negative rods
* All ferment glucose
* All reduce nitrate to nitrites
* All are oxidase negative
* Except Plesiomonas
* All motile at body temperature except
* Shigella
* Klebsiella
* Yersinia
* All ferment glucose
* All reduce nitrate to nitrites
* All are oxidase negative
* Except Plesiomonas
* All motile at body temperature except
* Shigella
* Klebsiella
* Yersinia
89
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae - H antigen
* Flagellar antigen
* Responsible for motility; heat stable
* Responsible for motility; heat stable
90
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae - O antigen
* Somatic antigen
* Heat stable antigen located in the cell wall (LPS)
* Heat stable antigen located in the cell wall (LPS)
91
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae - K antigen
* Capsular antigen
* Heat labile: Add heat if isolate didn’t type and try again
* K1 antigen of E. coli, Vi antigen of Salmonella typhi
* Heat labile: Add heat if isolate didn’t type and try again
* K1 antigen of E. coli, Vi antigen of Salmonella typhi
92
New cards
E. coli
* IMVC: ++- -
* Motile
* Motile
93
New cards
E. coli - UTI, GI - Enterotoxigenic
* travelers diarrhea
94
New cards
E. coli - UTI, GI - Enterohemorrhagic
* EHEC 0157:H7 associated with Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS) and Shiga toxigenic E. coli (STEC)
95
New cards
Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia
* IMVC: - - + +
96
New cards
Klebsiella
* Not motile
* Mucoid
* ==K. oxytoca: indole positive==
* ODC =
* Mucoid
* ==K. oxytoca: indole positive==
* ODC =
97
New cards
Enterobacter
* Motile
* Can also be mucoid
* ODC +
* Can also be mucoid
* ODC +
98
New cards
Serratia
DNAse +
99
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae - Morganella morganii
* UTI
* PAD +
* PAD +
100
New cards
Enterobacteriaceae - Providencia
PAD +