Cancer
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Allogeneic
What type of transplant is characterized by donor bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells?
Autologous
What type of transplant is characterized by receiving their own previously collected bone marrow or peripheral blood stem cells?
20-34 y/o male
Epistats for Hodgkin Lymphoma
Unknown (theoretically EBV but not conclusive)
Etiology for Hodgkin Lymphoma
B-cells mutate and become resistant to apoptosis (this affects the lymphoid tissues and organs where they live)
Patho for Hodgkin Lymphoma
painless lymph node swelling (starts in 1, usually cervical/supraclavicular), fever, night sweats, weight loss, pruritus, spleen/liver/lung/bone marrow involvement, Pel-Ebstein fever pattern (high fever 1-2 weeks, then no fever)
Clinical findings in Hodgkin Lymphoma
CBC (leukocytosis, eosinophilia, thrombocytosis), ESR (increased), LDH (increased), lymph node biopsy (reed-sternberg 🏆), PET/CT Chest/abdomen/pelvis
Diagnostics for Hodgkin Lymphoma
Reed sternberg cells
A large abnormal lymphocyte that may contain more than 1 nucleus
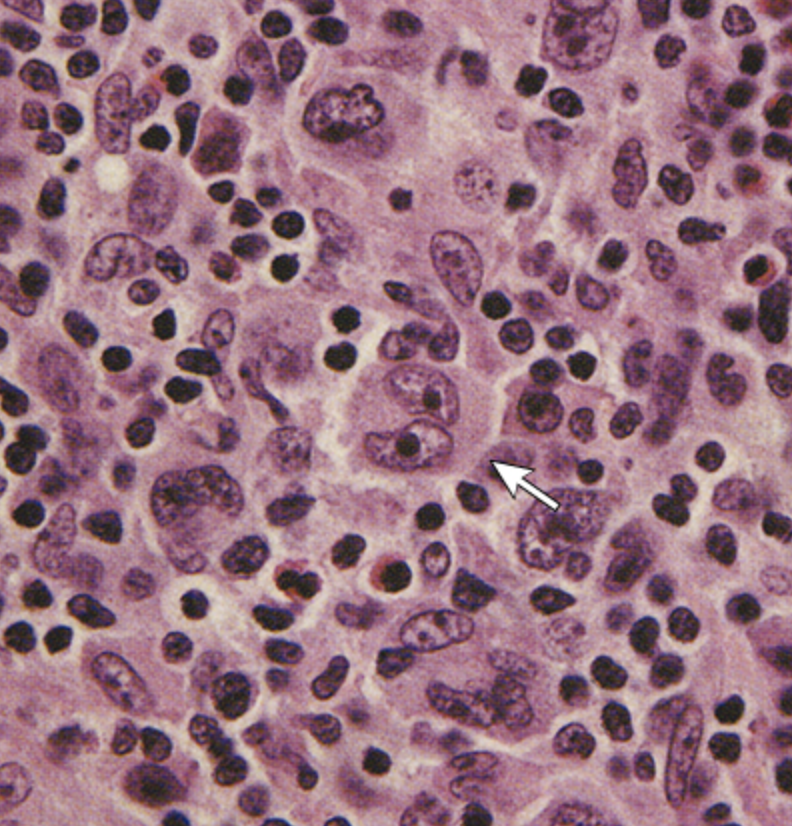
stage 1
What stage of Hodgkin Lymphoma is characterized by 1 lymph node region affected?
Stage II
What stage of Hodgkin Lymphoma is characterized by 2 or more lymph node regions involved, on 1 side of the diaphragm?
stage III
What stage of Hodgkin Lymphoma is characterized by lymph node regions involved on both sides of the diaphragm
stage IV
What stage of Hodgkin Lymphoma is characterized by disseminated disease with extranodal involvement?
Radiation therapy for initial
Management for stage IA Hodgkin Lymphoma
Chemo with radiation
Management for stage I-II Hodgkin Lymphoma
chemo, no radiation
Management for stage III-IV Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
A malignancy of lymphocytes that commonly affects Bs (85%), Ts (15%), or NK (under 1%) that leads to cytogenetic abnormalities?
Increases with age (median age 50 y/o)
Epistats for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
accumulation of gene alterations in the tumor genome, infection of the tumor clone by an oncogenic virus, stimulation and selection of tumor cells by an antigen, immunodeficiency
What are 4 main mechanisms of pathogenesis?
Painless lymph node enlargement (anterior cervical, retroperitoneum, mesentery, pelvis), affects the skin, GI tract, liver, and bone marrow; fever, night sweats, weight loss
Clinical findings in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Abdominal pain/fullness/obstruction, enlarged facial bones/thyroid/tonsils
Characteristics for Burkitt’s Lymphoma
Increased LDH, Increased ESR, mediastinal mass on CXR, lymph node biopsy 🏆 (presence of malignant lymphoid cells), lumbar puncture (if meningeal involvement is suspected), CT/PET chest, abdomen, pelvis
Diagnostics for Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Chemo 🥇
Management of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Multiple Myeloma (Plasma Cell Myeloma)
A malignant proliferation of plasma cells (anti-body producing B cells) originating in the bone marrow that leads to an abnormal amount of immunoglobulins (usually IgG) and/or light chain
Older adults (65-74), higher in black populations, slightly higher increased in males, increased BMI, agent orange exposure
Epistats for Multiple Myeloma
Bone pain (osteolytic lesions/pathologic fracture in the hips, spine, ribs), anemia symptoms, Mucosal bleeding, vertigo, nausea, visual changes, AMS, infections with encapsulated organisms (S. pneumonia, H. influenzae)
Clinical findings in multiple myeloma
Calcium elevation, renal insufficiency, Anemia (normochromic normocytic with rouleaux formation), Bone disease (osteoporosis and lytic lesions); Bence jone proteins on UA (M or light chains)
Diagnostics for Multiple Myeloma
SPEP (detects M protein), Immunofixation electrophoresis (identifies TYPE of protein), Free light chain assay (unbound kappa/lambda chains (light chain only)), Bone marrow biopsy 🏆 (10%+ clonal plasma cells), CBC, Ca2+. creatinine, Beta-2 microglobulin, LDH, skeletal survery
Specific labs for Multiple Myeloma
Biologics (lenalidomide, Bortezomib), Dexamethasone, Chemo, After chemo do a transplant of stem cells of you can, radiation (palliative), aggressive hydration, bisphosphonates
Treatment plan for Multiple Myeloma
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL)
The most common childhood malignancy that accounts for 80% of childhood leukemias
Peaks 4-5 (75% of cases occur before age of 15), then again in adults 50+
Epistats for ALL
Malignant proliferation of immature lymphoid stem cells (B or T) that originate in the bone marrow
Patho for ALL
More common
Characteristics of B-cell ALL
more aggressive, mediastinal mass (T cells mature in the thymus)
Characteristics of T-cell ALL
hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, pallor, fever, bruising, “sick” for days/weeks, bleeding, weight loss, fatigue, irritability, anorexia, bone pain, arthralgia, HA, stiff neck, vision disturbances, lymphadenopathy, CN palsies, seizures, AMS
Clinical findings of ALL (usually nonspecific)
CBC (anemia, leukocytosis due to leukemic blast cells, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia), CXR (mediastinal mass if T cell), Bone marrow biopsy (30%+ lymphoblast and hypercellular), Philly chromo on karyotype
Diagnostics for ALL
Chemo (maintenance for 2-3 yrs), CNS prophylaxis (intrathecal chemo/cranial irradiation), bone marrow transplant (relapsed)
Management of ALL in children - 70% will be cured with 98% reaching remission within 4 weeks
Chemo (maintenance for 2-3 yrs), CNS prophylaxis (intrathecal chemo/cranial irradiation), bone marrow transplant - allogeneic, stem cell transplant (autologous or allogeneic)
Management of ALL in adults - 60-90% remission rate, 30-40% cure rate
Philly chromo, 60+ y/o, long time to remission, leukocytosis at the time of diagnosis
Red flags for reduced survival in ALL
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
A malignancy of lymphocytes that is more common in adults (50+) - unknown cause linked to hereditary and cytogenetic factors
Proliferation of mature looking lymphocytes (usually B), infiltrates the bone marrow, spleen, lymph nodes
Patho for CLL
Unintentional weight loss, fever, night sweats, fatigue, lymphadenopathy, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, leukemia cutis
Features of CLL
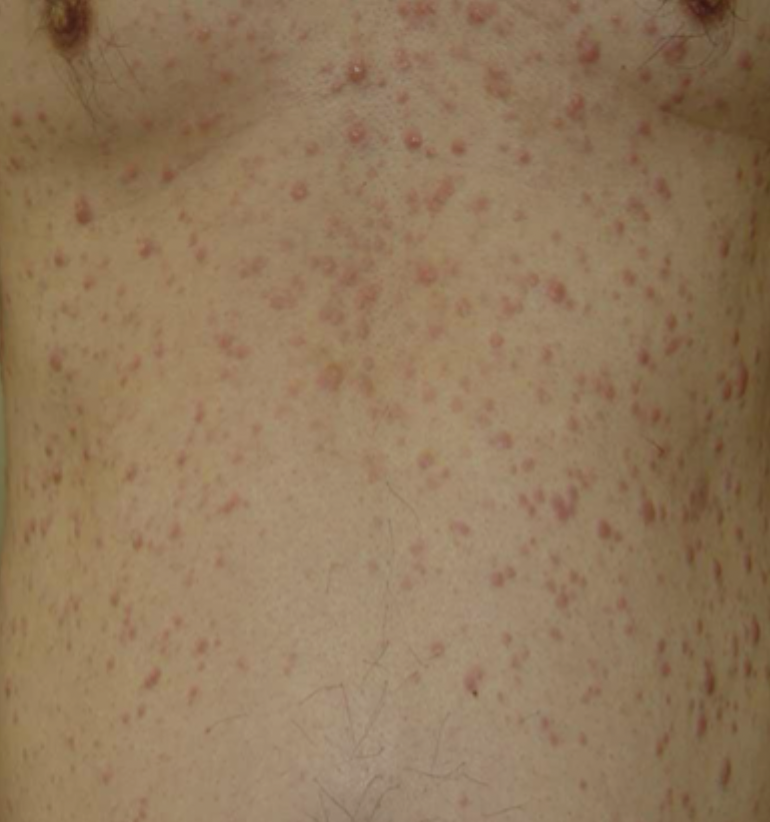
Leukemia Cutis
Flesh-colored-to-violaceous papules, plaques, or nodules
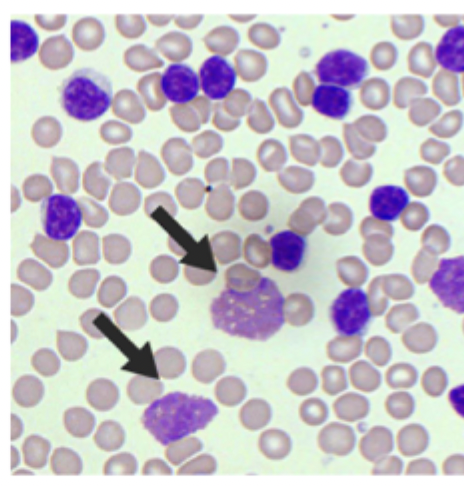
Lymphocytosis (WBCs over 20K), Peripheral blood smear (smudge cells, mature lymphocytes), Anemia, thrombocytopenia (splenic sequestration, bone marrow infiltration)
Diagnostics for CLL
Lymphocytosis ONLY (0), lymphadenopathy (I), organomegaly (II), Anemia (III), thrombocytopenia (IV)
CLL staging (modified RAI classifications - 0-I is low risk, II is intermediate, III-IV is high)
No treatment for early stages, chemo with immunotherapy is 1st line 🥇, local radiation (painful lymphadenopathy), allogeneic stem cell transplant (high risk or refractory)
Management for CLL
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
The most common leukemia in adults (80% of acute cases) that usually affects adults over 60?
Prior chemo/radiation, exposure to benzene or ionizing radiation, congenital disorders, preceded by chronic myeloid disorders
Risk factors for AML
malignant proliferation of blast cells, failure to differentiate (accumulation of blast in the marrow and blood), normal hematopoiesis is suppressed
Pathophys for AML
Anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia (easy bruising/bleeding), bone pain, hepatosplenomegaly, gingival hypertrophy (less common), Blurred vision, respiratory distress, priapism (leukostasis leads to microvascular obstruction)
Clinical findings of AML - develop of days to weeks
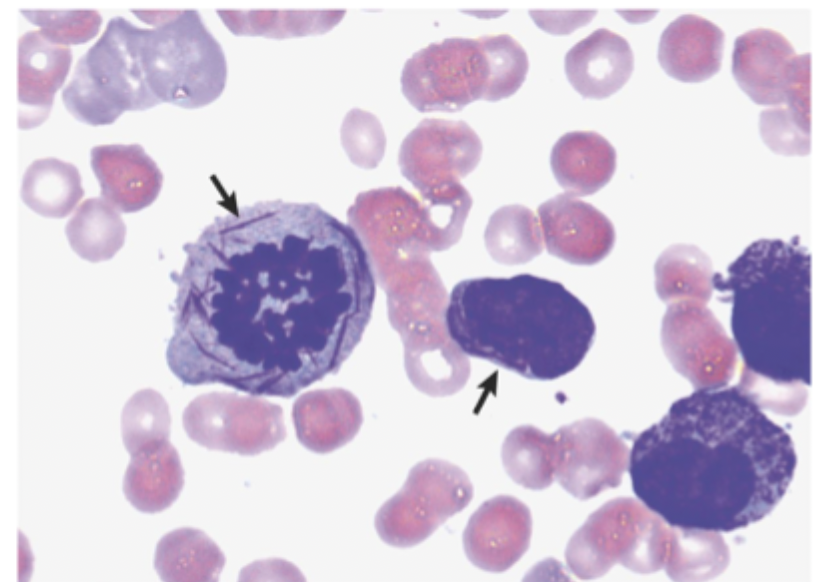
CBC (normocytic/normochromic anemia, thrombocytopenia, neutropenia, variable WBCs), Peripheral blood smear (myeloblast, Auer rods 🏆)
Diagnostics for AML
induction chemo 🥇, Allogeneic bone marrow transplant (not achieving remission), bone marrow/stem cell transplant (relapse)
Management of AML
older age, unfavorable cytogenetics (monosomy 5/7, complex karyotypes), prior toxin/chemo, secondary AML
Poor prognostic factors for AML
CML
Which myeloid malignancy occurs due to a translocation of the 9th and 22 chromosome which forms the BCR-ABL gene and activates tyrosine kinase, which promotes uncontrolled myeloid cell proliferation?
Unknown in most cases, benzene exposure, ionizing radiation
Etiology of CML
low blast in peripheral blood/bone marrow, asymptomatic or mild symptoms, bone marrow function is preserved, neutrophils can still do their job
Chronic phase findings of CML
5-30% blast, increased anemia/thrombocytopenia, worsening symptoms (fatigue, weight loss, splenomegaly), reduced response to therapy
Accelerated phase findings of CML
30%+ blast, transformation into acute leukemia, Severe symptoms (bleeding, infections, bone pain), often resistant to treatment
Blast crisis phase findings of CML
night sweats, fever, weight loss, fatigue, pallor, weakness, DOE, splenomegaly, bone pain
CML clinical findings - usually asymptomatic
CBC (increased granulocytes, normocytic normochromic anemia, thrombocytosis), Bone marrow biopsy (left shift myelopoiesis), Philly chromo (90%), BCR-ABL fusion gene on PCR (blood or marrow) 🏆
Diagnostics for CML
tyrosine kinase inhibitors (imatinib, dasatinib, nilotinib) 🥇, allogeneic bone marrow transplant (only curative option for young patients, accelerated cases, TKI resistance)
Treatment plan for CML
average survival is 3 months w/o treatment
Prognosis of CML blast crisis (resembles acute leukemia)