Economics Sem 1
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
What is the economic problem?
Problem of scarcity and choice.
What is scarcity?
There are not enough resources to satisfy an infinite number of want.
What is economics?
The study of how people allocate their scarce resources to satisfy their unlimited wants, everything with you buy that has a price is scarce.
What are the three basic questions of the economic problem of choice producers have to answer?
what to produce?
how to produce?
for whom to produce?
What are three types of resources?
natural resources
human resources
capital resources
What are natural resources?
Natural resources are “gifts from nature”- resources such as air, water,, minerals, energy resources such as coal and oil and soil and vegetation, any resource that is supplied from the natural environment.
What are human resources?
Human resources refers to the quantity and quality of the labour force.
What are human resources divided into?
Labour and enterprise
What is labour?
Labour is the physical or mental effort applied in the production of a good or service.
What is enterprise?
Enterprise: the coordination and management of production of a good or entrepreneur, it also represents the ideas and skills which are needed to create new goods and services.
What are capital resources?
Capital refers to the man-made resources which assists human resources in the production of goods and services, referring to the physical capital.
What is physical capital?
The ‘tools of trade’, the machinery and equipment that is required to produce goods and services.
What is social overhead capital?
The basic infrastructure of the economy, such as transport and communications, power and water supply, schools and hospitals, usually supplied by the government.
What is investment?
The creation of new capital goods, creation of new machinery, buildings and roads it’s seen as the ‘engine of economic growth’.
What is microeconomics?
Deals with the economic problem from an individual or ‘micro’ point of view, attempts to understand how consumers and producers make decisions, how market and prices work to allocate resources between all competing industries.
What is macroeconomics?
Deals with the economic problem from society’s point of view, the performance of the whole economy, it focuses on total economic activity in terms of total production, total employment and the overall price level, the most important theory of economic growth and business cycle’s.
What is ceteris paribus assumption?
Our hypotheses is valid only if other independent variables are kept constant. The latin term means ‘all other things constant’.
What are economic models?
simplified representation of economic reality showing the relationship between certain economic variables.
What is rational self-interest?
Means that economic decisions are based on a person following a logical process in order to compare the cost and benefits of decision.
What is positive economics?
Testing and developing economic theory, concerned with “what is in” the economy.Objective.
What is normative economics?
“What should be” which involves personal opinion and value judgments, economic policy involves normative economics. Subjectove.
What is a positive statement?
Can be proven true or false.
What is a normative statement:
An opinion or a value judgement.
Do free good’s exist?
No, everything has an opportunity cost.
What is opportunity cost?
The value of the best alternative foregone.
What is the principle of decreasing marginal benefit?
As you consume more of something the extra or additional benefit you get declines.
What is marginal analysis?
Compares the additional benefits derived from an activity with the extra cost incurred.
What is production possibility frontier (PPF) model?
Shows the maximum output for an economy given fixed resources and technology, the frontier illustrates scarcity, trade-offs and opportunity cost.
What are PPF model assumptions?
resources are fixed
technology is fixed
the economy produces just two goods
What does a straight frontier line in a PPF model represent?
Opportunity cost is constant.
What does a bowed outward frontier line in a PPF model represent?
Increasing opportunity cost.
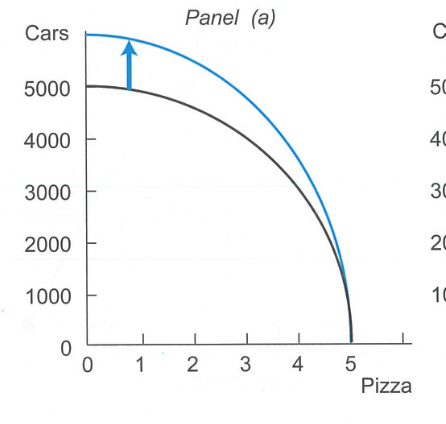
What does this shift show?
Increase in quantity of resources (labour and capital)
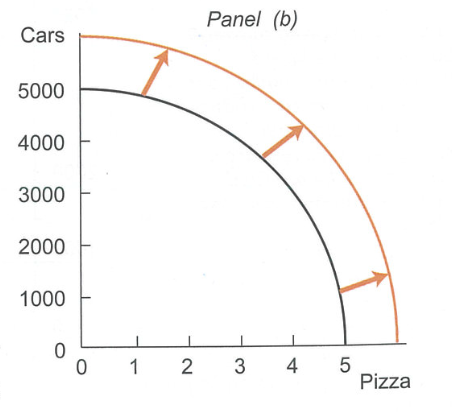
What does this shift show?
Improvement in production technology (capital resource)
How is economic growth in PPF model represented?
shift to the right
What is an economic system?
The way in which a country’s resources are allocated to deal with the economic problem.
What are the characteristics of a free enterprise or capitalist economy (Market Economy)?
Resources are owned privately and all decisions are made by the owners of resources acting in their own self-interest, they thrive on competition, boosting innovation and economic growth.
What is a command or Planned Economy?
An economy in which resources are owned by the state and decisions are made by a planning authority.
What happens in a mixed economy?
Both government and the private sector determine the allocation of resources.
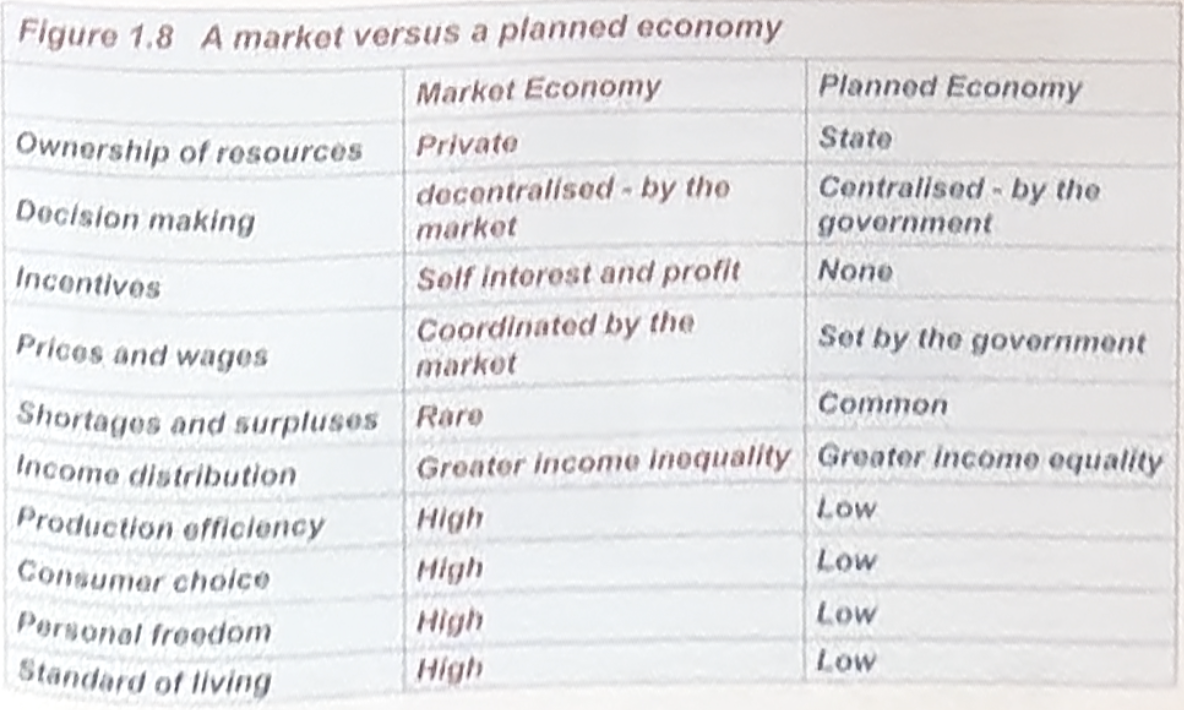
Compare and contrast market & planned economies.
What is a product market?
Where buyers and seller exchange goods and services?
What are factor market?
deal in the buying and selling of factors of production or resources such as labour market, the capital market and selling to housholds
What are competitive markets?
price is determined by the interactions between buyers and sellers, no individual buyer or seller can influence market price: this means there’s no market power
How is competitive market categorised?
large number of buyers and sellers
firms are price takers
very similar (homogeneous) products
easy entry into the market (no barriers to entry or exit)
What are price takers?
firms
What is an imperfect market?
any market with a large number of relatively small firms selling very similar goods and/or services and with easy entry conditions
How are imperfect markets categorised?
small number of firms
product differentiation
firms are price setters: have market power
entry into market is restricted
What is a monopoly market?
An extreme type of imperfect market with just one dominant firm.
What is an oligopoly market?
An extreme type of imperfect market with a few dominant firm.
Who are price makers?
Firms with market power.