BIOL 251 Exam 3 Vaccines
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Which of the following statements concerning immunological memory is true?
The memory response involves only B cells.
The memory response is due to the production of long-lived memory cells.
Antibodies produced in reponse to a secondary infection are mostly IgM.
The memory response is usually faster, but not as strong as the primary response.
B
During a primary infection, some T cells and B cells become long-lived memory cells that persist in the body. When exposed to the same antigen again, the memory cells can produce a stronger and faster immune response.
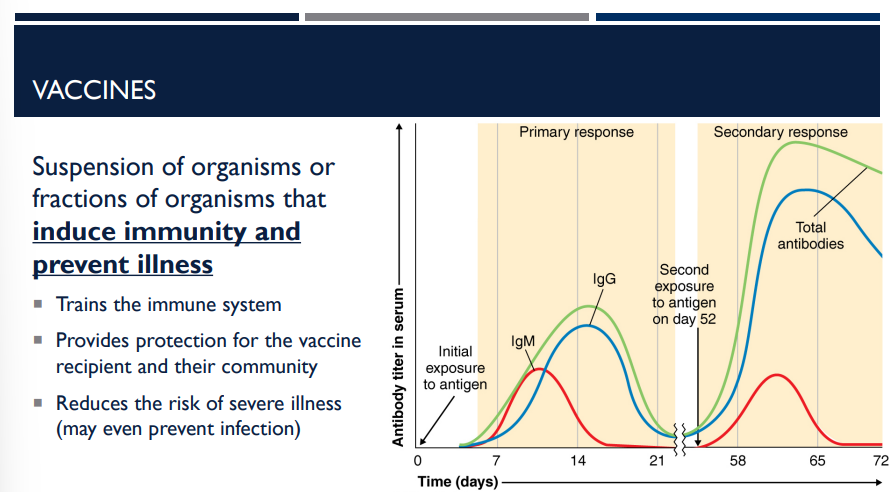
What are vaccines?
Suspension of organisms or fractions of organisms that induce immunity and prevent illness.
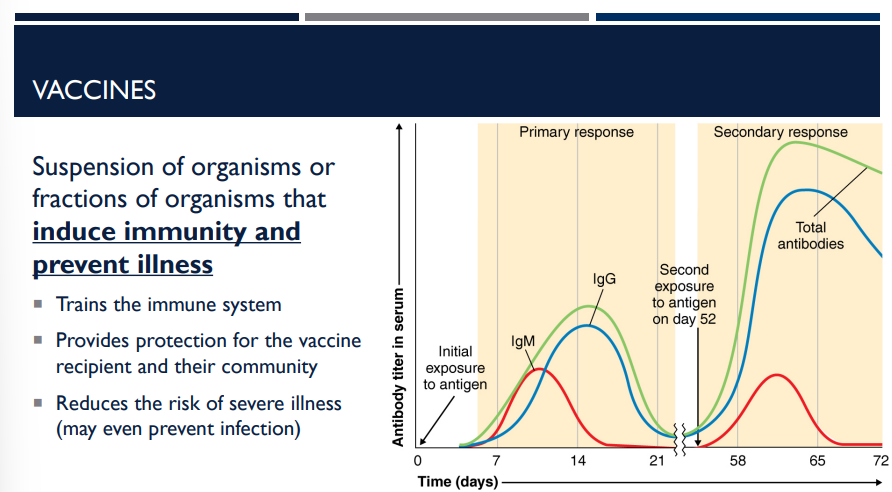
What are the benefits of vaccines?
Trains the immune system
Provides protection for the vaccine recipient and their community
Reduces the risk of severe illness (may even prevent infection)
![<p>[Smallpox] What was the fatality rate of variola minor and major? (idk if we need to know this tbh). When was the last natural case of smallpox? Why? </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2764c2e1-d9cd-4996-b617-3f76d043cf98.png)
[Smallpox] What was the fatality rate of variola minor and major? (idk if we need to know this tbh). When was the last natural case of smallpox? Why?
Variola major: 20-60% fatality rate
Variola minor: 1% fatality rate
Last natural case in 1977 thanks to vaccination!
No animal resorvoir, meaning the virus only infected humans, so stopping human transmission eliminated it completely.
What is herd immunity?
reduces the number of susceptible hosts, thereby reducing the total number of infections
T/F: All vaccines are 100% effective.
F!!! No vaccine is 100% effective (most are 90%+)
T/F: No vaccine is 100% effective.
T. Most are 90%.
What are the characteristics of live attenunated vaccines?
Suspension of weakened pathogen
Closely mimics an actual infection by allowing pathogen to replicate within the host without causing the disease
Stimulates cellular and humoral immunity
Usually results in lifelong immunity
Attenuated pathogen may revert to pathogenic form (Sabin vaccine for polio)
What type of vaccine closely mimics an actual infection by allowing pathogen to replicate within the host without causing the disease?
Live attenuated vaccines
What type of vaccine stimulates cellular and humoral immunity
Live attenuated vaccines
What type of vaccine usually results in lifelong immunity?
Live attenuated vaccines
Attenuated pathogens may revert to what form?
pathogenic form (Sabin vaccine for polio)
What are the characteristics of inactivated vaccines?
Whole microbes are inactivated or killed (usually by chemical methods)
What type of vaccine is when whole microbes are inactivated or killed (usually by chemical methods)?
Inactivated vaccines
What type of vaccine has a pathogen that cannot replicate in the host?
Inactivated vaccines
What type of vaccine is considered safer?
Inactivated vaccines
What type of vaccine requires booster doses?
Inactivated vaccines
What type of vaccine induces mostly humoral immunity?
inactivated vaccines
Influenza Polio (Salk) Pneumococcal pneumonia, are types of ______ vaccines
inactivated vaccines
What are the characteristics of subunit vaccines?
Contain only antigenic fragments that induce the best immune response (isolated protein, part of the bacteria capsule, fragments of viral capsid).
What are polysaccharide vaccines, a type of subunit vaccine? Name an example.
composed of components of the bacterial capsule (meningitis)
What are conjugated vaccines, a type of subunit vaccine? Name an example.
Bacterial polysaccharides (capsule) combined with protein to stimulate a stronger immune response (Haemophilus influenzae type B [Hib])
What are virus-like particles, a type of subunit vaccine? Name an example.
viral capsid with no genetic material (human papilloma virus [HPV])
What are toxoids, a type of subunit vaccine? Name an example.
inactivated form of a toxin (tetanus)
What are recombinant vaccines, a type of subunit vaccine? Name an example.
genetic engineering allows antigens to be produced by other organisms (hepatitis B viral protein produced by yeast)
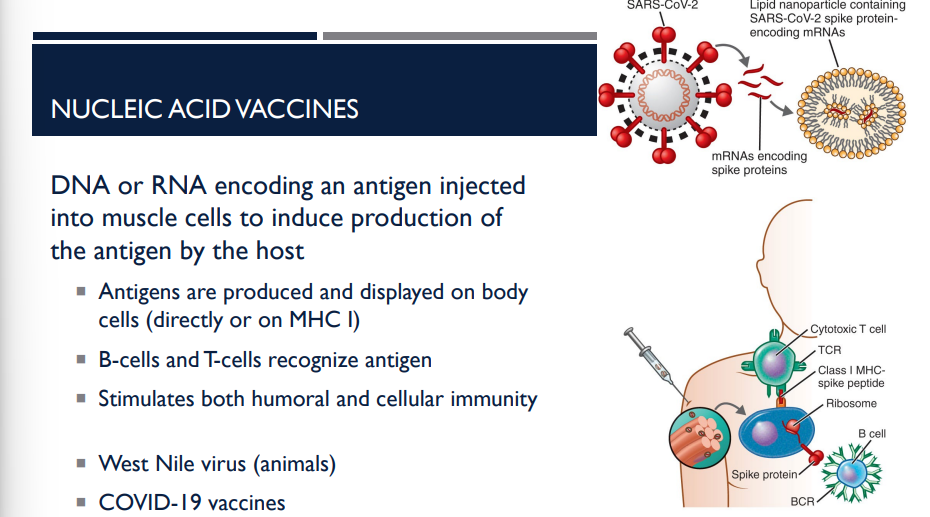
What are the charcteristics of a nucleic acid vaccine?
DNA or RNA encoding an antigen injected into muscle cells to induce production of the antigen by the host
Antigens are produced and displayed on body cells (directly or on MHC I)
B-cells and T-cells recognize antigen
Stimulates both humoral and cellular immunity
West Nile virus (animals)
COVID-19 vaccines
are what type of vaccine?
nucleic acid vaccines — DNA or RNA encoding an antigen injected into muscle cells to induce production of the antigen by the host
Why did the COVID-19 vaccine seem rushed?
Research into mRNA vaccines has been going on for decades
Multiple phases at the same time
Easier to recruit volunteers
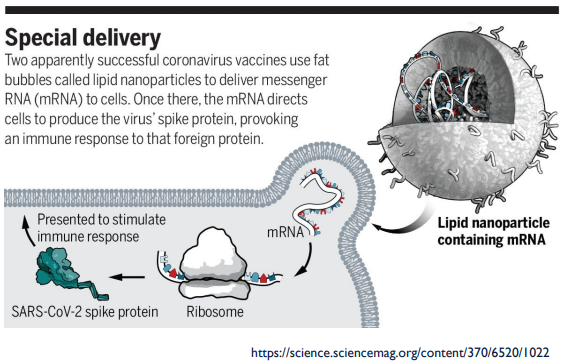
Why is the claim that the COVID-19 vaccine will change someone’s DNA is false?
The vaccine contains mRNA that encodes the viral spike protein.
The mRNA does NOT enter the nucleus of your cells
T/F: Vaccines have no risk of side effects.
F. ALL vaccines have a risk of side effects, like:
Dangerous allergic reactions
Myocarditis
Blood clots
Risks are higher following a COVID-19 infection
Risks of side effects of vaccines are higher when
following a COVID-19 infection. This is your immune system responding!
T/F: It has been shown that the COVID-19 vaccine has long term side effects.
F. No evidence of long-term side effects. First trials started in March 2020.
mRNA lasts a few days in the body
Spike protein last a few weeks in the body
Cells regulate activity by degrading mRNA and proteins that are no longer needed
T/F: It has been shown that the COVID-19 vaccine has no long term side effects.
T. First trials started in March 2020.
mRNA lasts a few days in the body
Spike protein last a few weeks in the body
Cells regulate activity by degrading mRNA and proteins that are no longer needed
How long does mRNA last in the body? What about spike proteins? How do cells regulate activity in a vaccine?
a few days; a few weeks; Cells regulate activity by degrading mRNA and proteins that are no longer needed
Does the COVID-19 vaccine cause infertility?
No evidence that the vaccine causes infertility.
In the Pfizer vaccine trial, 23 participants became pregnant
1 miscarriage was reported in an individual who received the placebo
Rate of miscarriage in vaccinated individuals is similar to the rate in the general population
T/F: Every vaccine is 100% effective!
F!!! No vaccine is 100% effective.
Vaccinated individuals can still get COVID-19, but they are less likely to get sick
Symptoms are less severe in vaccinated
Less likely to be hospitalized
Less likely to have a fatal case
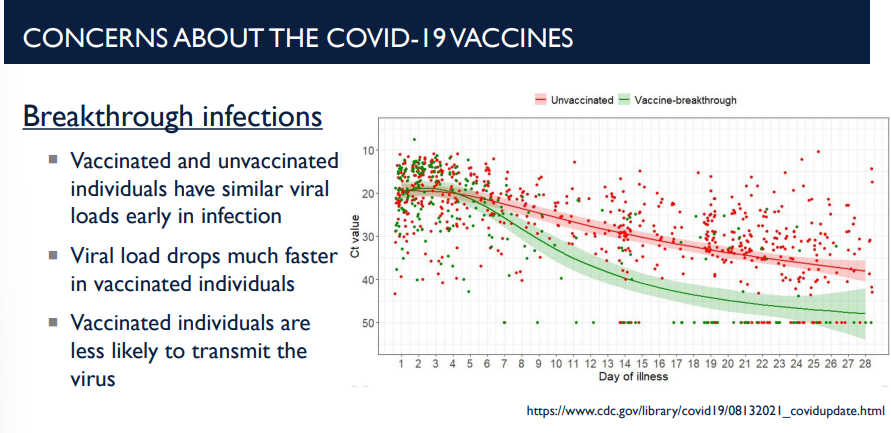
Describe breakthrough infections. How is viral load affected in unvaccinated vs vaccinated individuals?
A breakthrough infection is an illness caused by a pathogen in a person who has been fully vaccinated against that specific disease.
Vaccinated and unvaccinated individuals have similar viral loads early in infection
Viral load drops much faster in vaccinated individuals
Vaccinated individuals are less likely to transmit the virus.
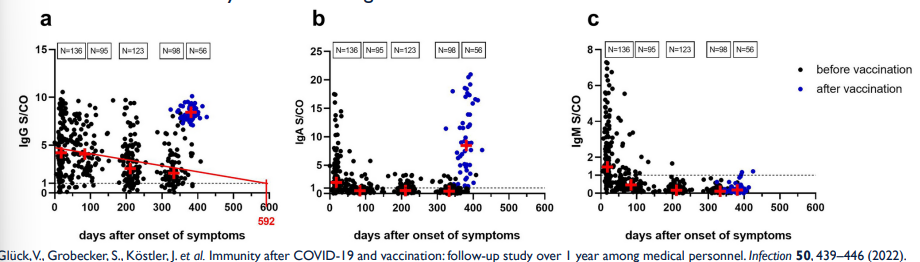
T/F: Natural infection of COVID-19 may offer some immune protection.
T, BUT natural immunity is more variable and may not last as long
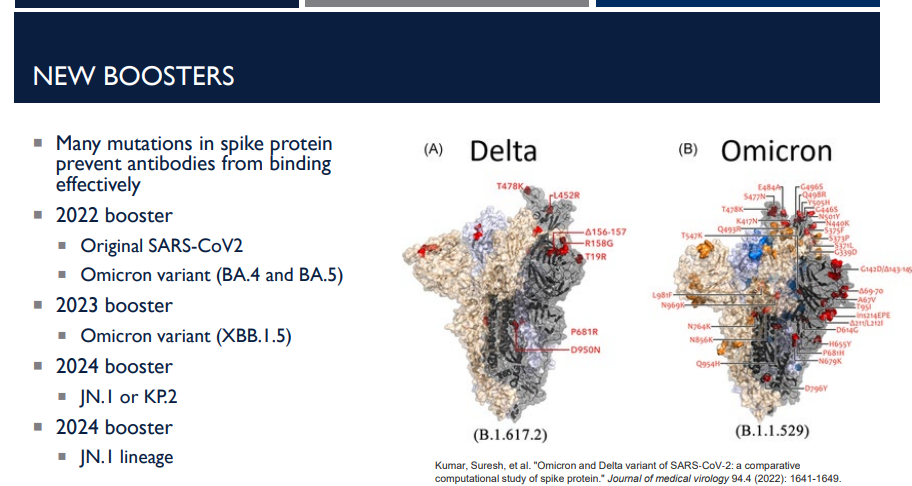
What do boosters do?
Annual COVID-19 boosters are updated to match circulating variants, especially changes in the spike protein, ensuring antibodies can still effectively recognize and neutralize the virus.
Many mutations in spike protein prevent antibodies from binding effectively.
The MMR vaccine contains a weakened version of the measles virus. What type of vaccine is this?
live attenuated
killed inactivated
nucleic acid
subunit
conjugated
toxoid
Answer
A
A live-attenuated vaccine contains a weakened form of the pathogen. This means that the pathogen can replicate in the host body, but will not cause symptoms. Live-attenuated vaccines closely mimic infections and usually provide life-long immunity.
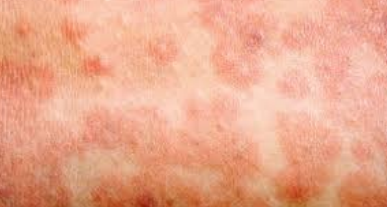
The following patient comes with these symptoms. What could they have?
Fever Rash Cough Runny nose Sore throat
Measles
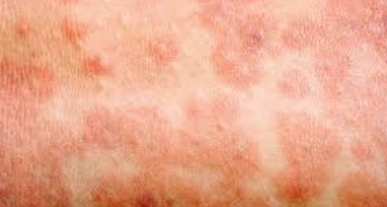
What are the long term effects of measles?
Disables the immune system
Infects macrophages
Secondary infections
Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis
Fatal within 1-3 years
Blindness
Deafness
T/F: Measles is eradicated.
F, we only have a potential to eradicate measles. We have had a recent outbreak in the US in 2025. In 2000, we eliminated measles in the USA but we nearly lost that status in 2019.
What were the context and problems with the Wakefield study?
Context
MMR vaccine
1998 -Wakefield study
Claimed that autism symptoms appeared very close to administration of the MMR vaccine
Also claimed to link autism and the vaccine to gastrointestinal issues
“Autistic enterocolitis”
Problems
Paper was eventually retracted
Andrew Wakefield lost his medical license
Small sample size (12 patients)
No control subjects
Selection bias
Claims were based on parents reporting the first recognized symptoms of autism
Ignored tests that did not detect measles virus
Problems with informed consent
“callous disregard for the distress and pain of children”

T/F: andrew wakefield was anti-vaccine.
F. Lead author was not anti-vaccine.
Promoted a single measles vaccine
In 1997, Wakefield filed a patent for an alternative measles vaccine
Working with a lawyer for parents who claimed their children were harmed by vaccines
Needed to show vaccine caused “a distinct and specific clinical syndrome”
Started a company to research and produce a test to detect “autistic enterocolitis”
Estimated £3,300,000 - £28,000,00 annually
What is thimerosol? What is its relevance to vaccines and autism?
Thimerosol – antibacterial compound used in some vaccines
50% ethylmercury
As a precaution, it was recommended that mercury be removed from vaccines (1999)
Misinterpretation
Autism and mercury poisoning exhibit different symptoms
No link between thimerosol and autism has been found

T/F: Vaccinated and unvaccinated children show similar susceptibility to other infections
T. Infection with measles can weaken the immune system MMR vaccine does not.
What was one of the fears towards adminstration regarding vaccines?
Fear that administration of too many vaccines simultaneously can weaken the immune system. This is not true btw.

What is the composition of the influenza vaccine?
Influenza vaccines are typically inactivated (killed) vaccines produced in eggs or cell culture. Production takes several months, which is why it must begin well before flu season.The vaccine targets two major viral surface proteins:
Hemagglutinin (H): helps the virus attach to host cells.
Neuraminidase (N): helps newly formed viruses exit host cells.
Inactivated vaccine produced in eggs or cell culture
Takes several months to produce
Does not protect against all strains of the flu
Hemagglutinin (H)
Neuraminidase (N)

Why are new vaccines for the flu required each year?
They do not protect against all strains because influenza viruses constantly change.
New vaccines are required each year due to changes in viral antigens:
Antigenic drift: small, gradual mutations in H and N proteins that reduce antibody recognition.
Antigenic shift: sudden, major changes (often from reassortment) that can produce new viral subtypes.
New vaccines required each year because viral antigens have changed
Antigenic shift
Antigenic drift
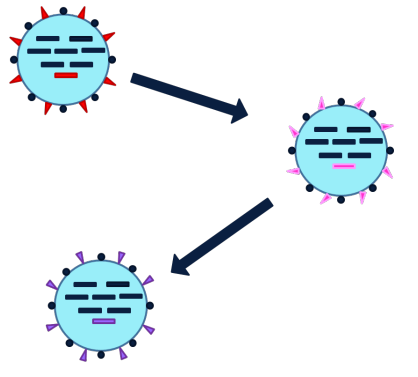
What is antigenic drift?
Slow accumulation of genetic mutations that alter the antigens on the surface of the virus
No proofreading mechanism for viral RNA
Antigenic drift over time allows viruses to evade the host immune system
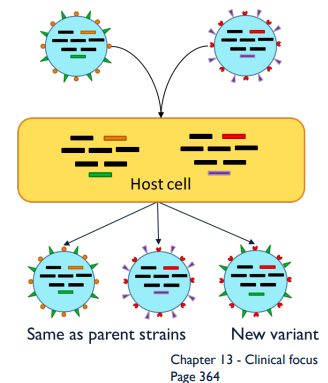
What is antigenic shift?
Shuffling of segmented viral genome
Causes large, rapid changes in viral antigens
Host cell is infected by multiple strains of the virus
Different RNA segments may be packaged together
New combinations of antigens
May allow virus to infect other organisms
Evade immune system
What (antigenic shift or drift) is often associated with pandemics?
Anitgenic shift
True or false? Both antigenic shift and drift contribute to the need for new flu vaccines each year.
A - true
Antigenic shift and drift can both alter the antigens presented on the surface of the virus. These changes mean that different strains of the virus will predominate in different year. Thus, different vaccines must be developed every year to account for the different antigens.
Antigenic shifts are larger changes that are often associated with pandemics due to new combination of antigens being presented on the virus.
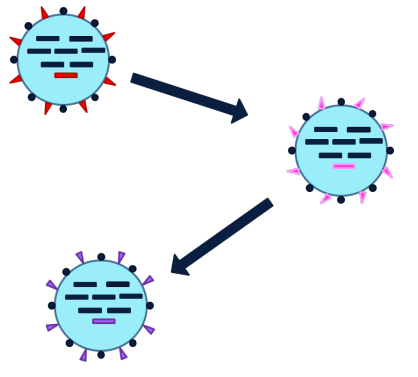
What is the Slow accumulation of genetic mutations that alter the antigens on the surface of the virus a characteristic of (antigenic drift or shift)?
antigenic drift

Is it antigenic shift or drift if there is No proofreading mechanism for viral RNA?
Antigenic drift
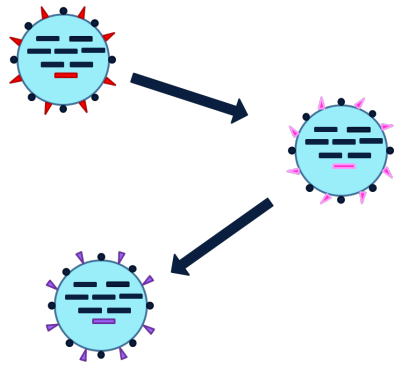
Antigenic drift over time allows viruses to
evade the host immune system
What is the Shuffling of segmented viral genome a characteristic of (antigenic drift or shift)? what does it cause?
antigenic shift. it causes large, rapid changes in viral antigens.
What is it called when the Host cell is infected by multiple strains of the virus (antigenic drift or shift)?
Antigenic shift
What is it called when Different RNA segments may be packaged together (antigenic drift or shift)?
antigenic shift.
New combinations of antigens
May allow virus to infect other organisms
Evade immune system
Which one (antigenic shift or drift) is often associated with pandemics?
antigenic shift