anatomy midterm
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
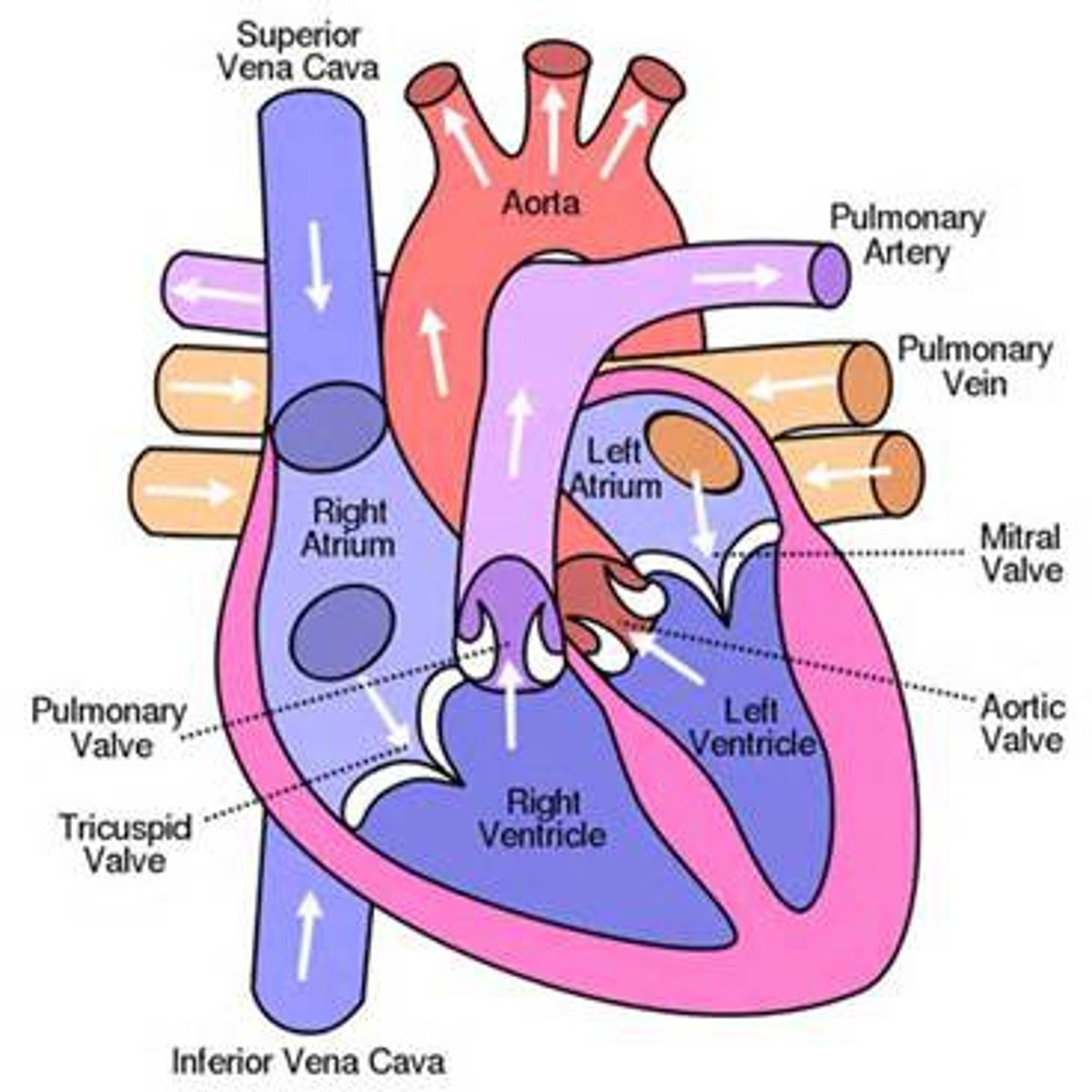
blood flow
1. superior/inferior vena cava into right atrium
2. from right atrium blood will pass through tricuspid valve into right ventricle
3. right ventricle contracts and sends blood to pulmonary artery
4. pulmonary artery will bring blood to lungs to be oxygenated
5. pulmonary veins will bring blood back to heart
6. blood will flow to left atrium
7. let atrium will send blood through bicuspid valve into left ventricle
8. left ventricle will contract and send blood through semilunar valve and into aorta then to rest of body
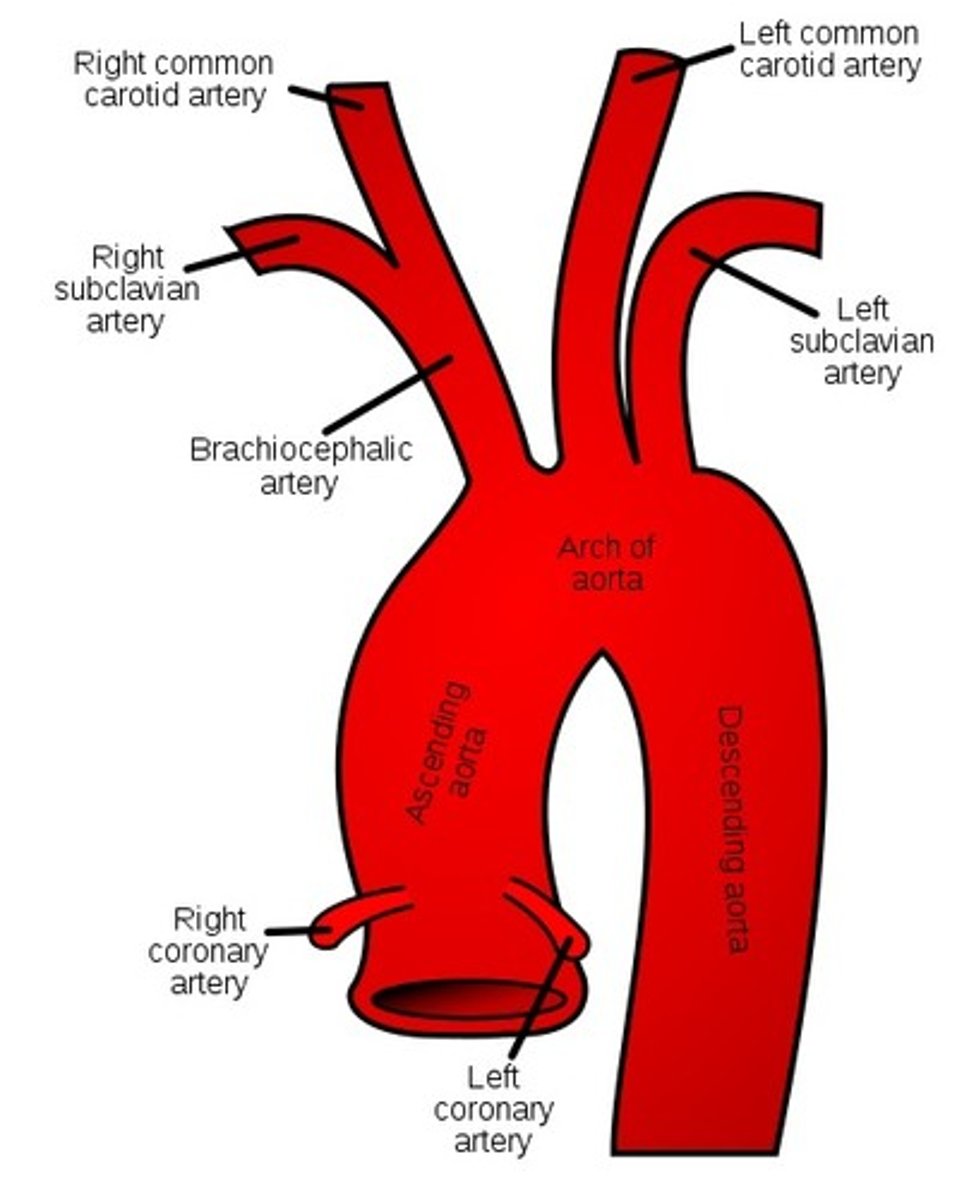
aortic arch branches
cervical spine
7 cervical vertebrae
1. occiput (C0)
2. atlas (C1)
3. axis (C2)
cervical vertebrae
-facet joints 45 degrees in relation to transverse plane
-smaller sized
-transverse foramen for vertebral artery C1-C6
-lordotic curve
-bifid spinous processes
-spinous process points posteriorly
cervical spine movements
allows movement in ALL directions
thoracic spine
-12 thoraces vertebrae
-T1-T4: transition from C -> T
-T5-T8: "typical" T spine vertebrae
-T9-T12: transition from T -> L
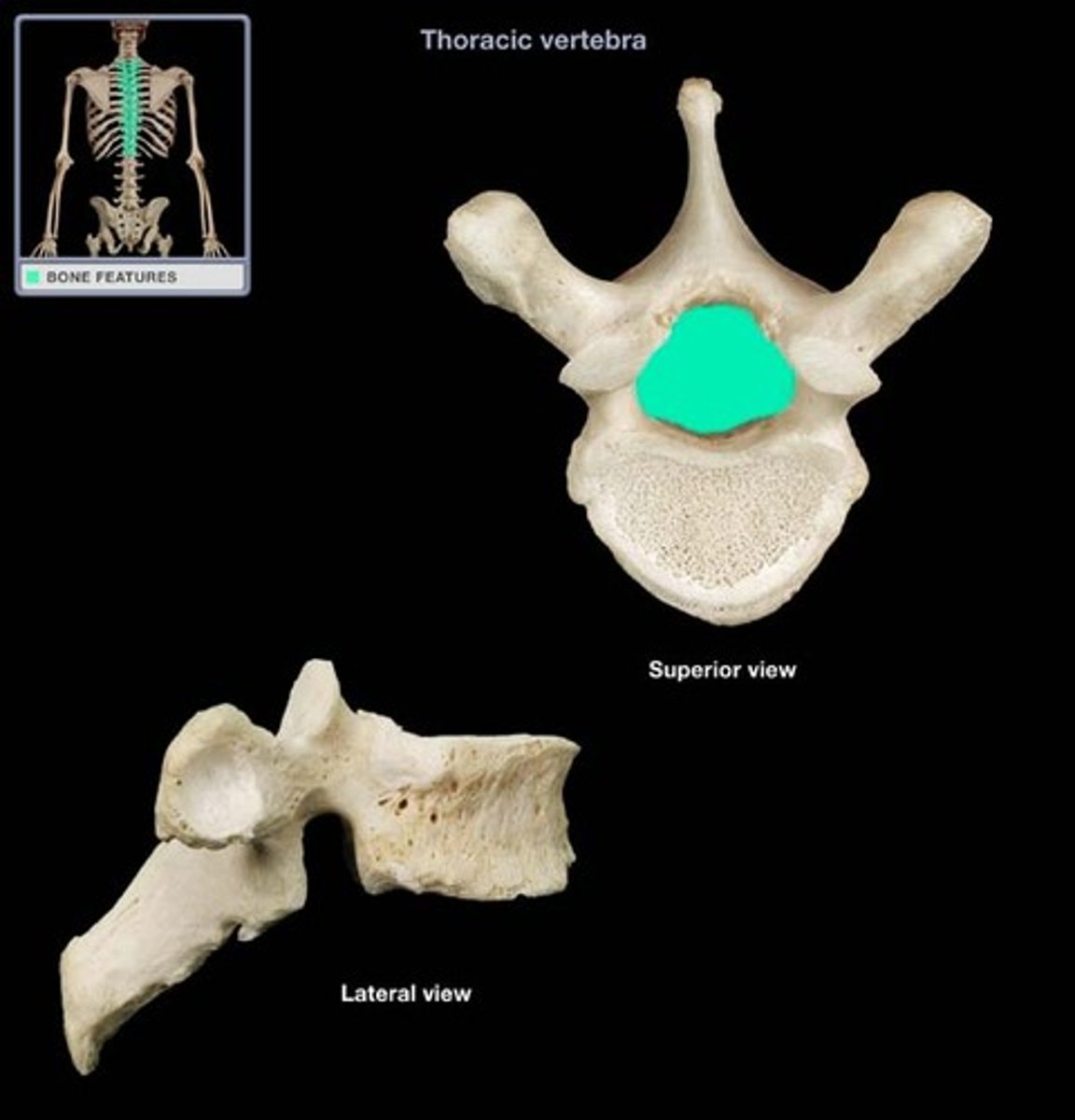
thoracic vertebrae
-facet joint angled 60 degrees from horizontal
-heart shaped body
-vertebral body taller posterior than anterior (kyphotic)
-spinous process point down (level above)
-facets limited by ribcage (limit some movement)
thoracic spine movements
-less mobile than cervical region
-allows lateral flexion and rotation primarily
-allows flexion but NOT extension
lumbar spine
-5 lumbar vertebrae
-L5 is largest vertebrae in body
lumbar vertebrae
-facet joints angled 90 degrees from horizontal
-massive vertebral body (kidney shaped)
-taller anteriorly (lordosis)
-vertebral foramen more triangular
-facets allow for for flexion and extension
-facet above can't glide on facet below; prevent anterior translation of vertebral bodies
lumbar spine movements
-allows flexion/extension
-some lateral bending
-very little to no rotation
sacrum
-5 fused vertebrae
-wedged shaped
sacrum vertebrae
-superior articular facet of sacrum articulates with L5 articular facet
-base: formed by superior surface of S1
-apex: inferior, articulates with coccyx
sacrum movements
-provides strength and stability of pelvic girdle
-transmits body weight to pelvic girdle
intervertebral discs
-allow movement of spine and shock absorber
-adheres to cartilaginous end plate
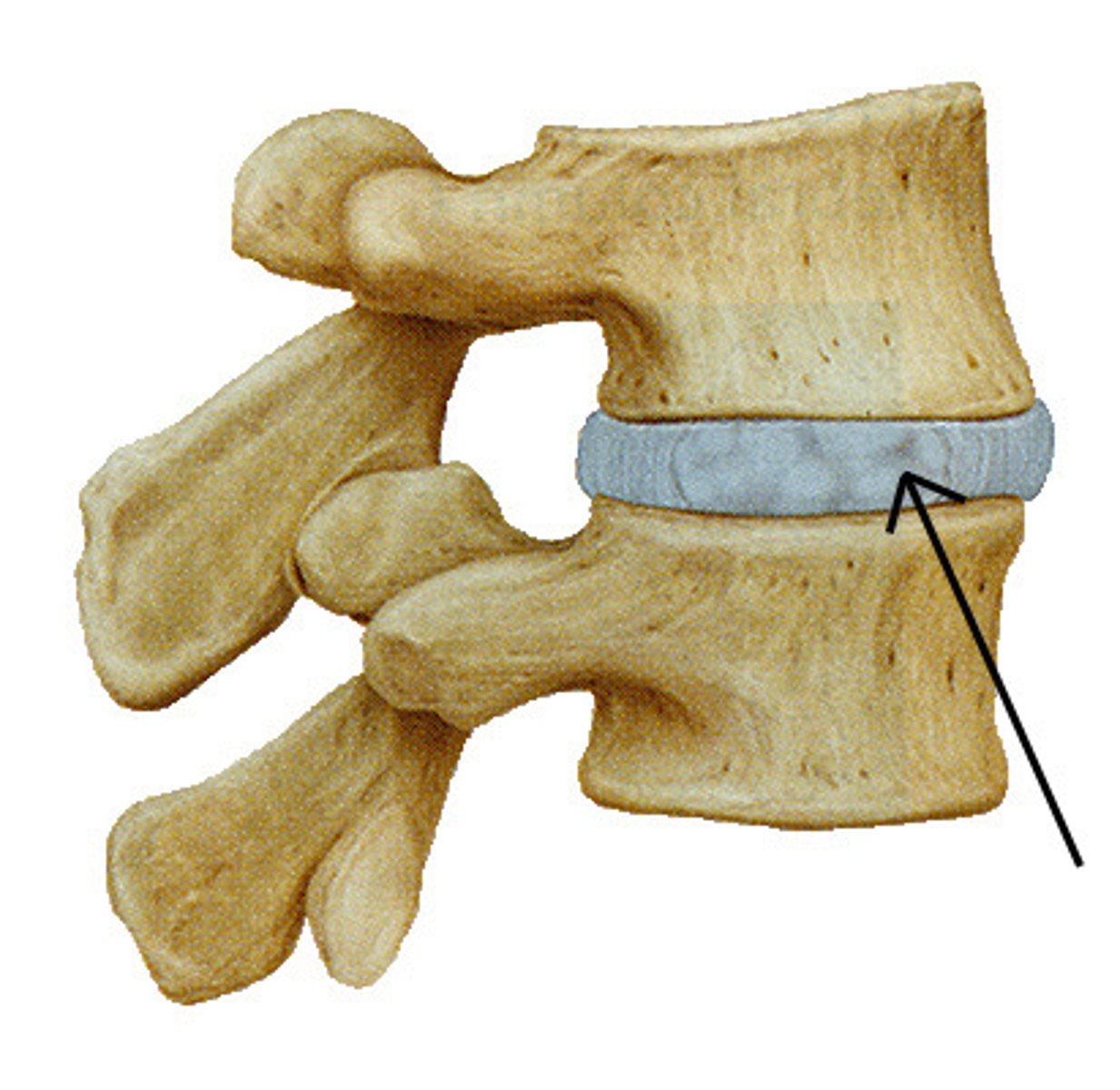
annulus fibrosis
-concentric lamellae of fibrocartilage
-outer 1/3 of IV disc
-vascular supply and sensory innervation
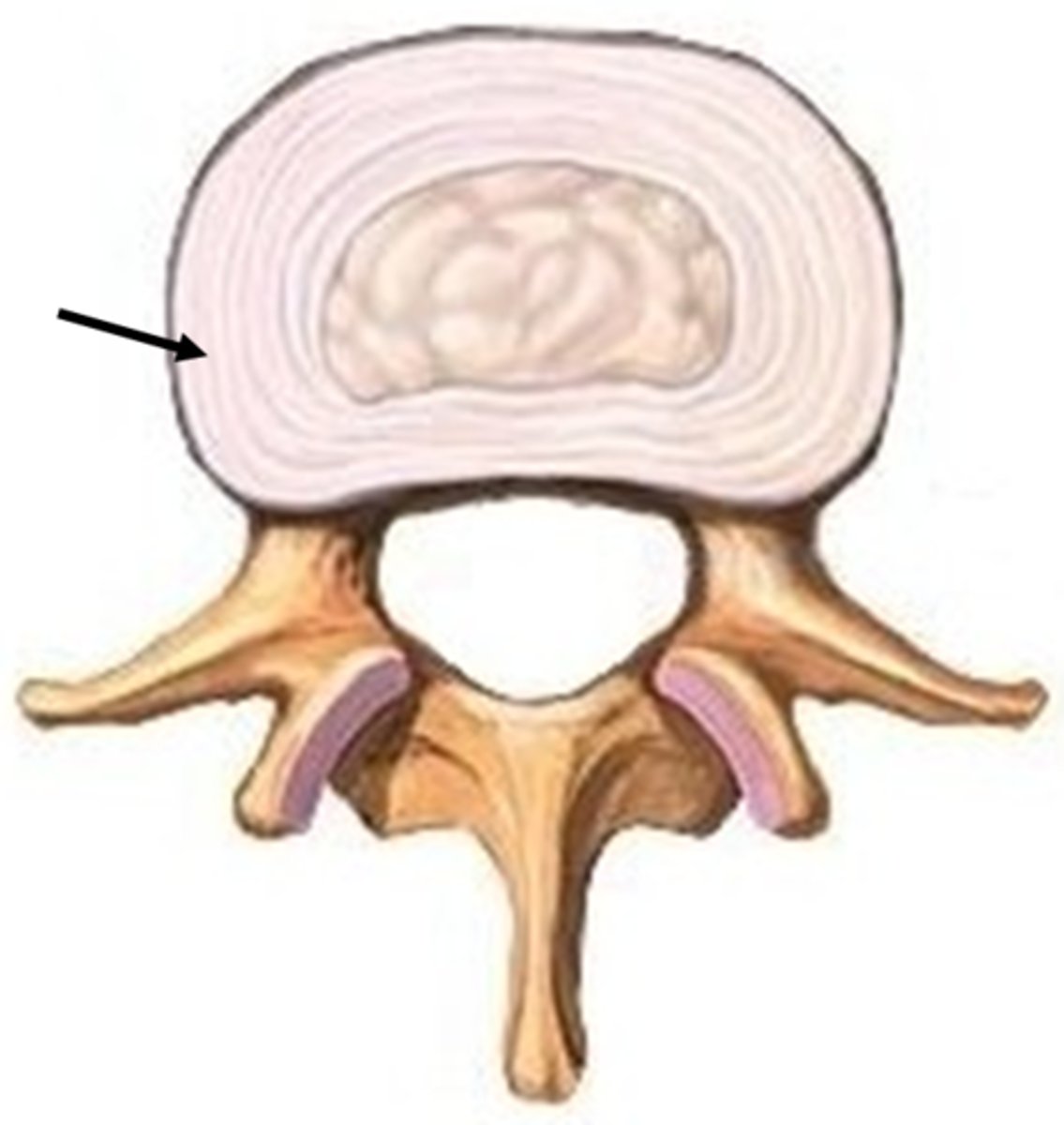
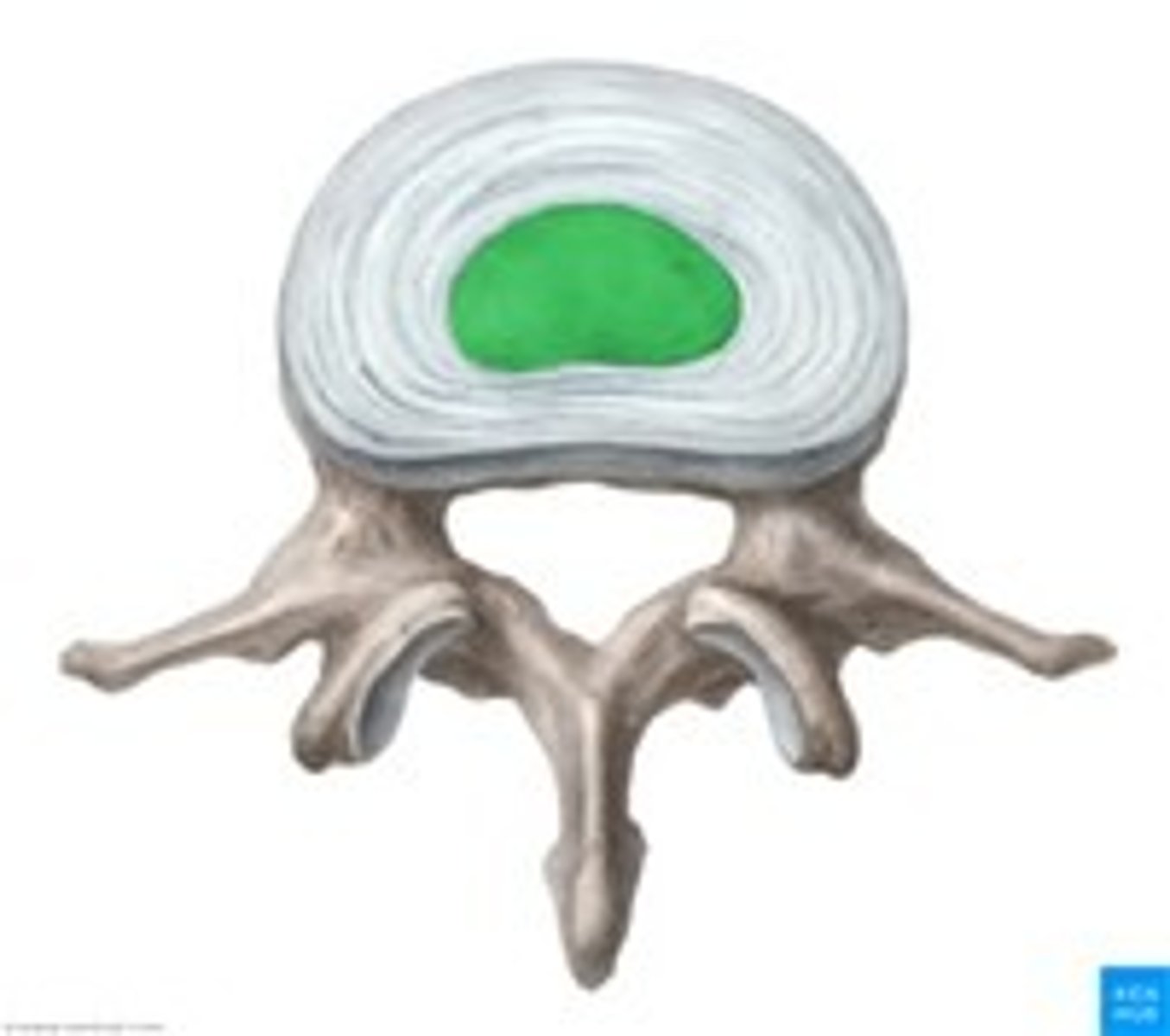
nucleus pulposis
-core of IV disc
-very hydrophilic
-no vascular supply
-posterolateral disc herniation common
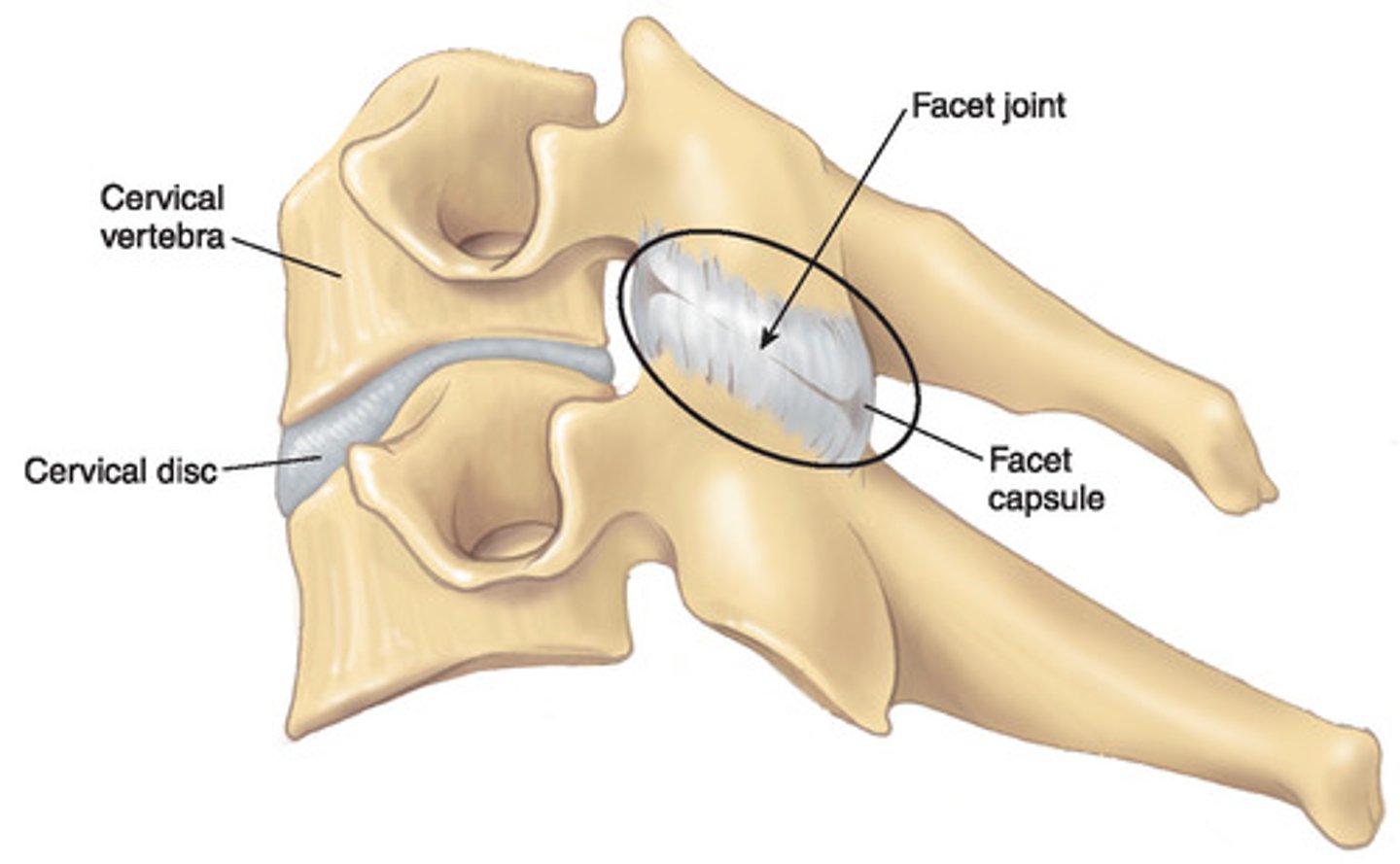
zygapophyseal (facet) joints
-synovial joint
-formed by: inferior articular process of SUPERIOR vertebrae; superior articular process of INFERIOR vertebrae
-create IV foramen: spinal nerves run through here
-change shape and size as we travel down spine
Atlanto-occipital joint
-occipital condyles (C0) and superior articular facets (C1)
-allows tilting and head nodding
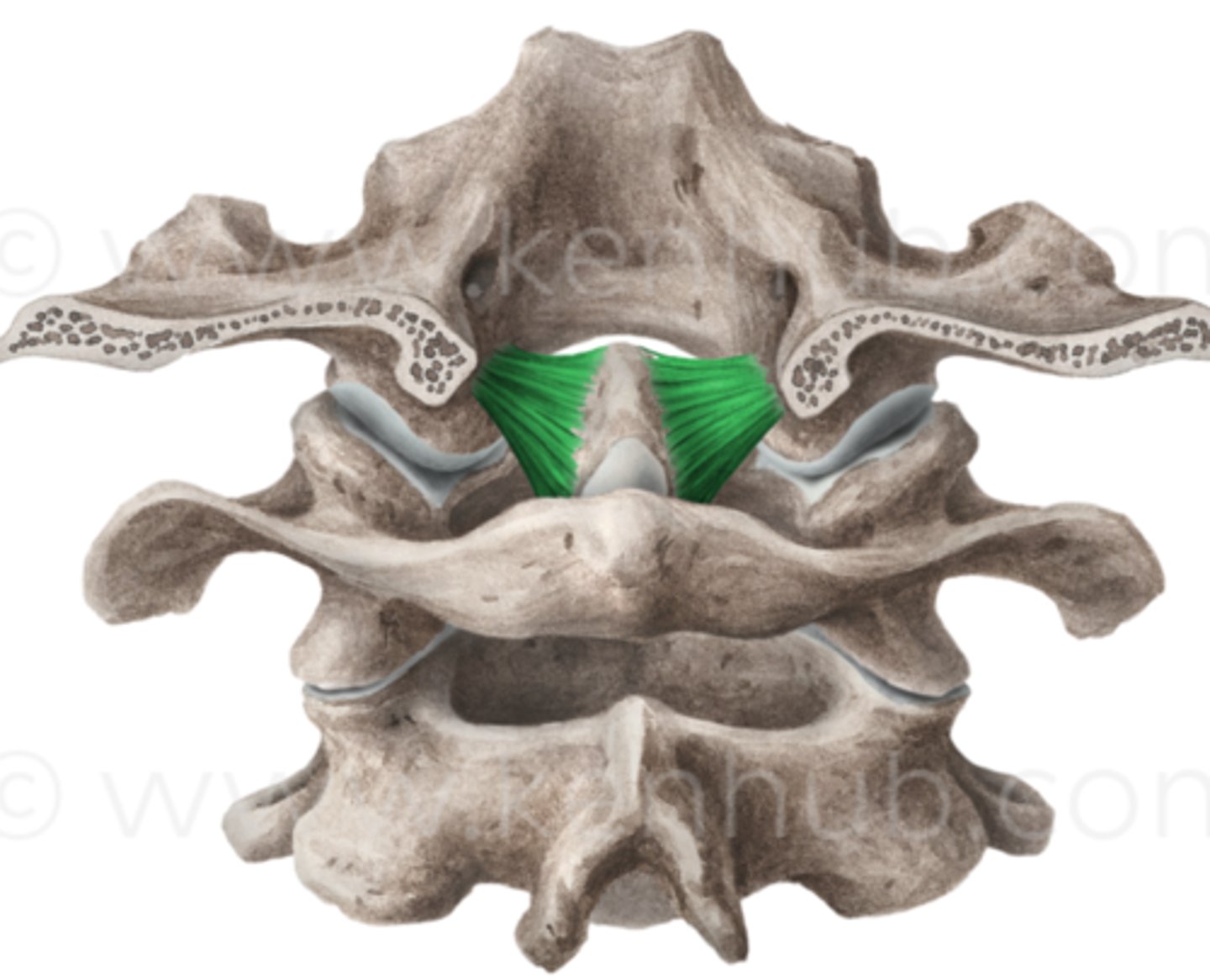
Atlanto-axial joint (C1-C2)
-R/L
-median
-transverse ligament of atlas
-atlas moves on axis
-1/2 of all cervical rotation through this joint
posterior spine: superficial muscles
-trapezius
-lat dorsi
-levator scapulae
-rhomboid major/minor
posterior spine: intermediate spine
-serratus posterior superior
-serratus posterior inferior
posterior spine: deep (superficial)
-splenius capitus
-splenius crevicus
posterior spine: deep (intermediate)
erector spinae group
-iliocostalis
-lomgissimus
-spinalis
posterior spine: deep (major)
transversospinalis group
-semispinalis
-multifidus
-rotatores
posterior spine: deep (minor)
proprioception
-interspinales
-intertransversarri
-levator costourm
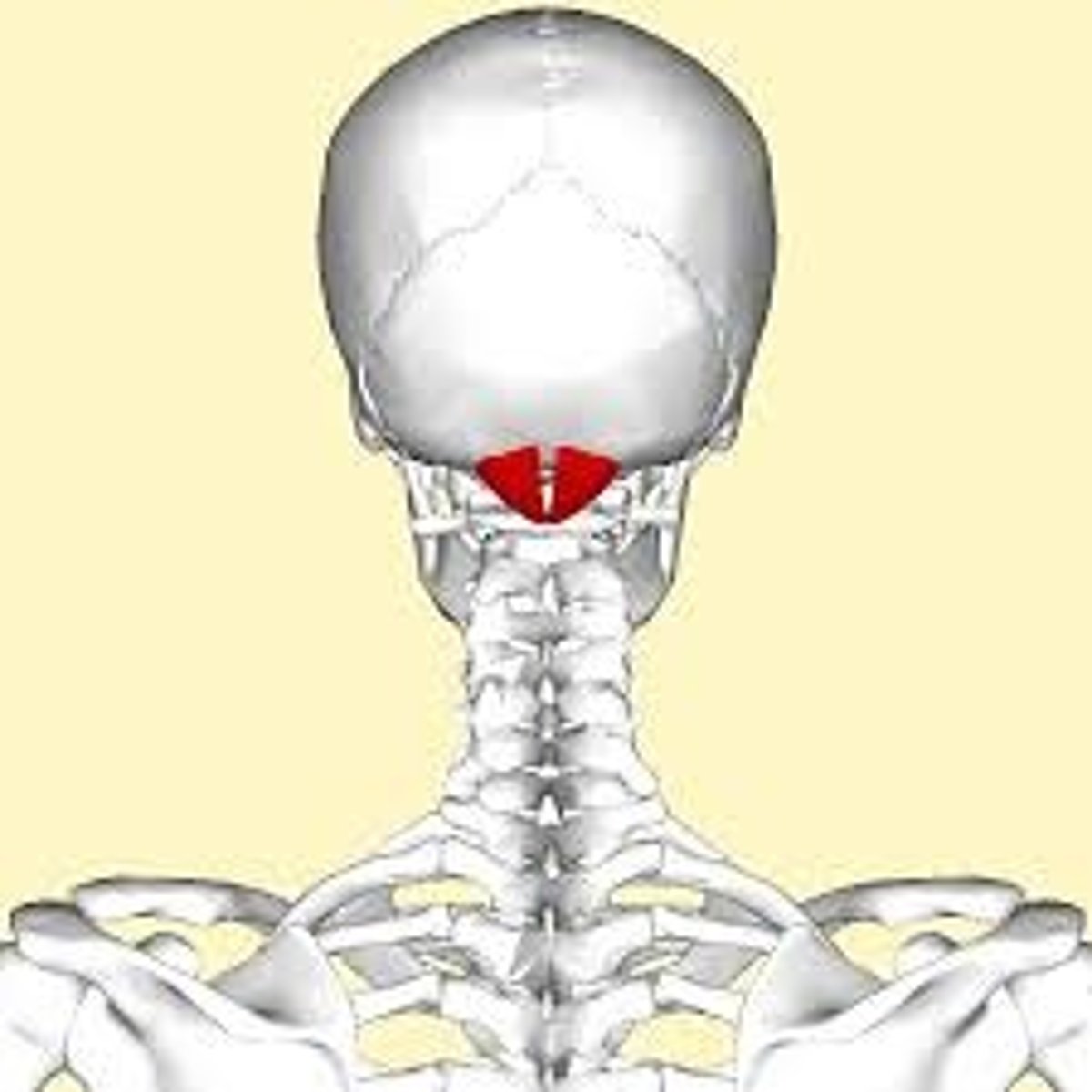
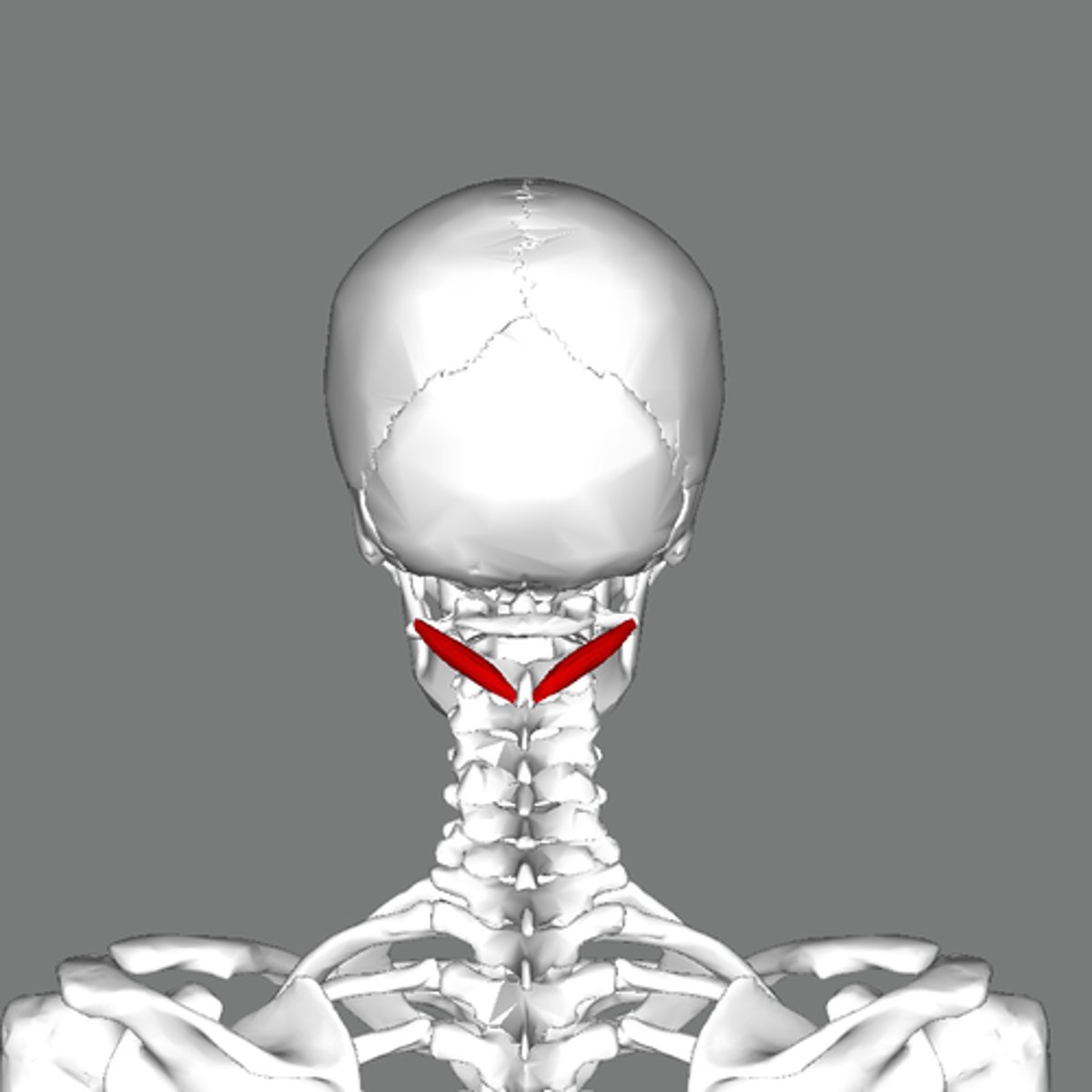
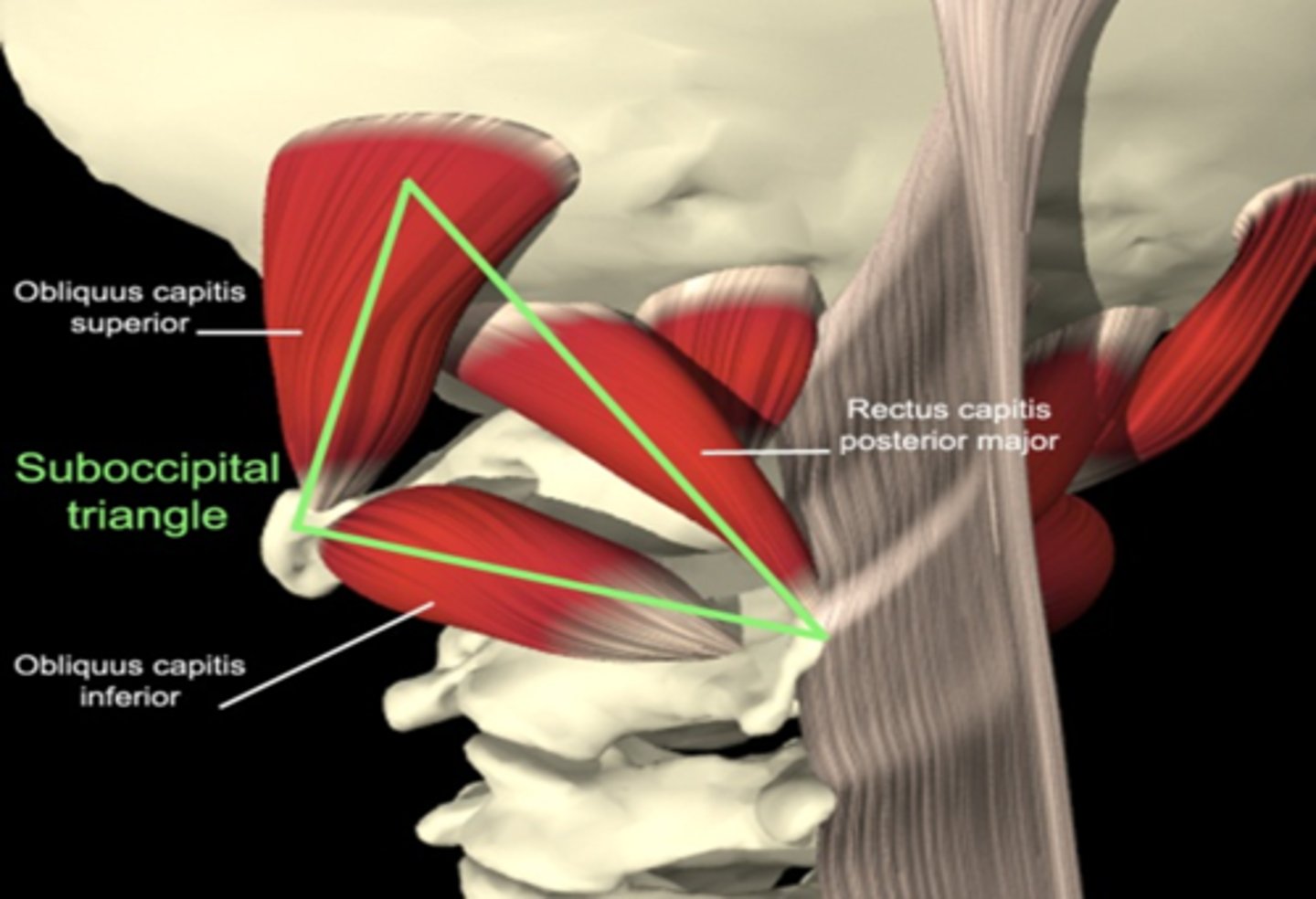
suboccipital triangle
-innervated by suboccipital nerve (C1)
-obliquis captits superior
-obliquis capitus inferior
-rectus captious posterior major
-rectus capitus posterior minor
-contains vertebral artery
true ribs
-1-7
-attach directly to sternum
false ribs
-8-10
-attach to 7th costal vertebrae
floating ribs
-11-12
-no attachment
C1 (atlas)
-holds up occiput
-occiput flexion and extension because of facet joints
-minimal spinous process
-vertebral foramen
-sits on axis
C2 (axis)
-facet joints articulate with atlas
-dens articulate with C1
-C1 and C2 allow for rotation
-ligaments stabilize C1 on C2 (without ligaments can bump into spinal cord)
upper motor neurons
brain and spinal cord
lower motoneurons
peripheral (body)
intervertebral foramen
-space between vertebrae; more lateral
-spinal nerves exit (lower MN)
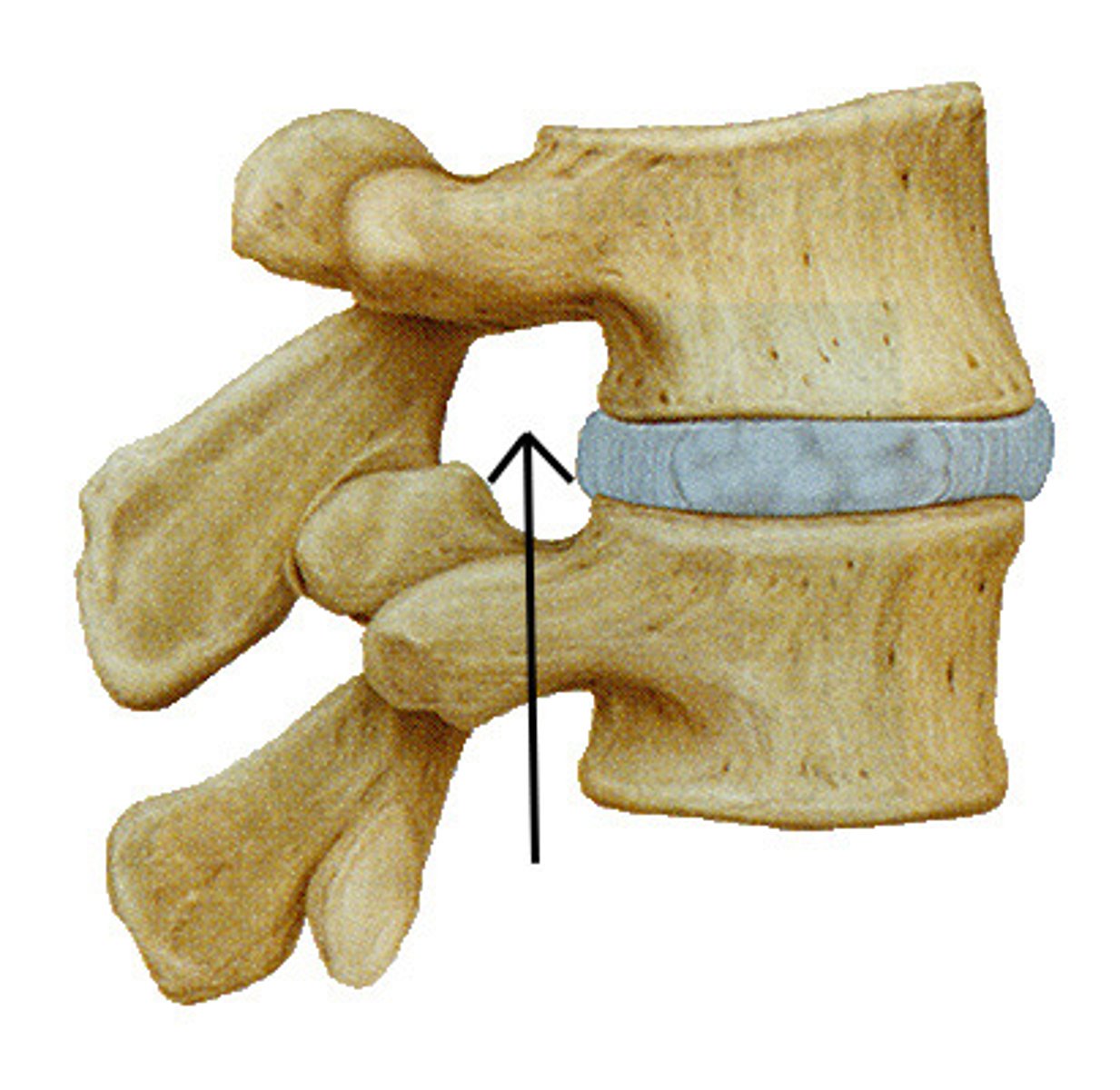
vertebral foramen
spinal cord (upper MN)
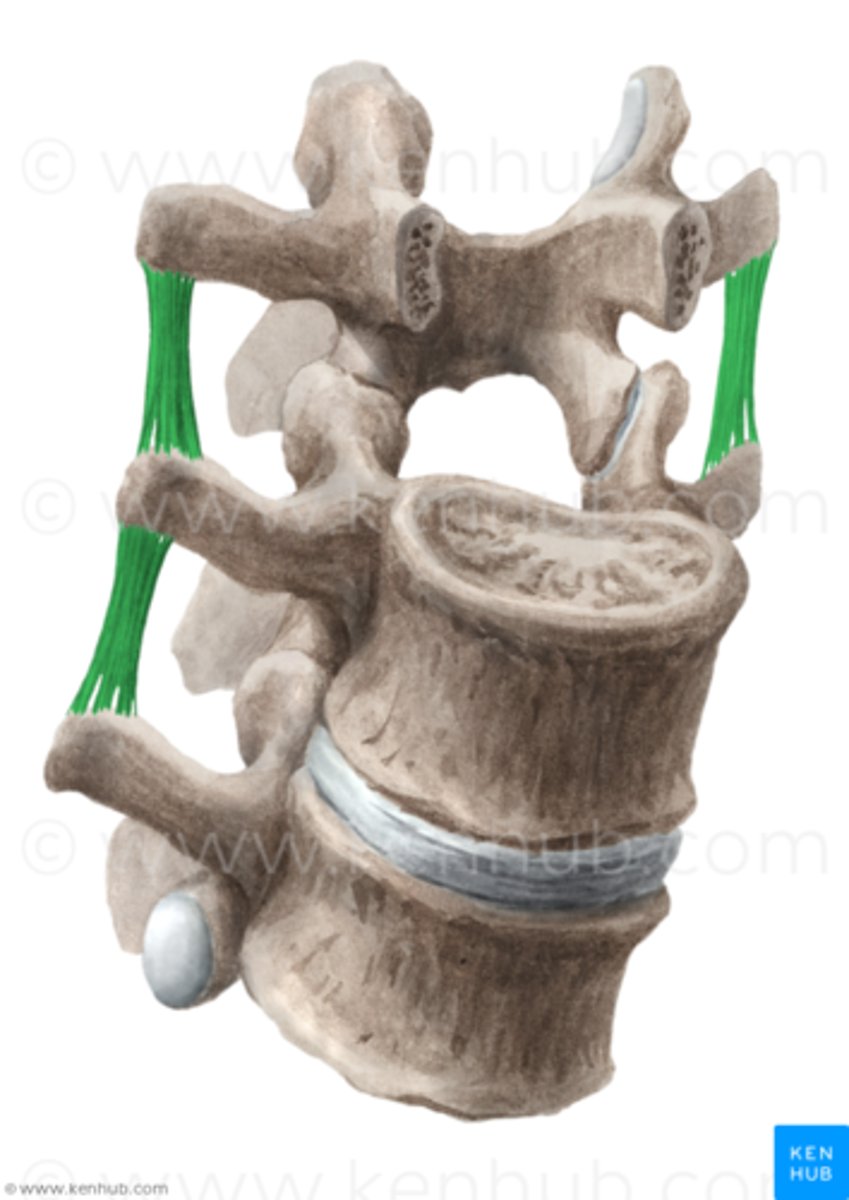
intertransverse ligament
transverse process to transverse process; restrict side bending
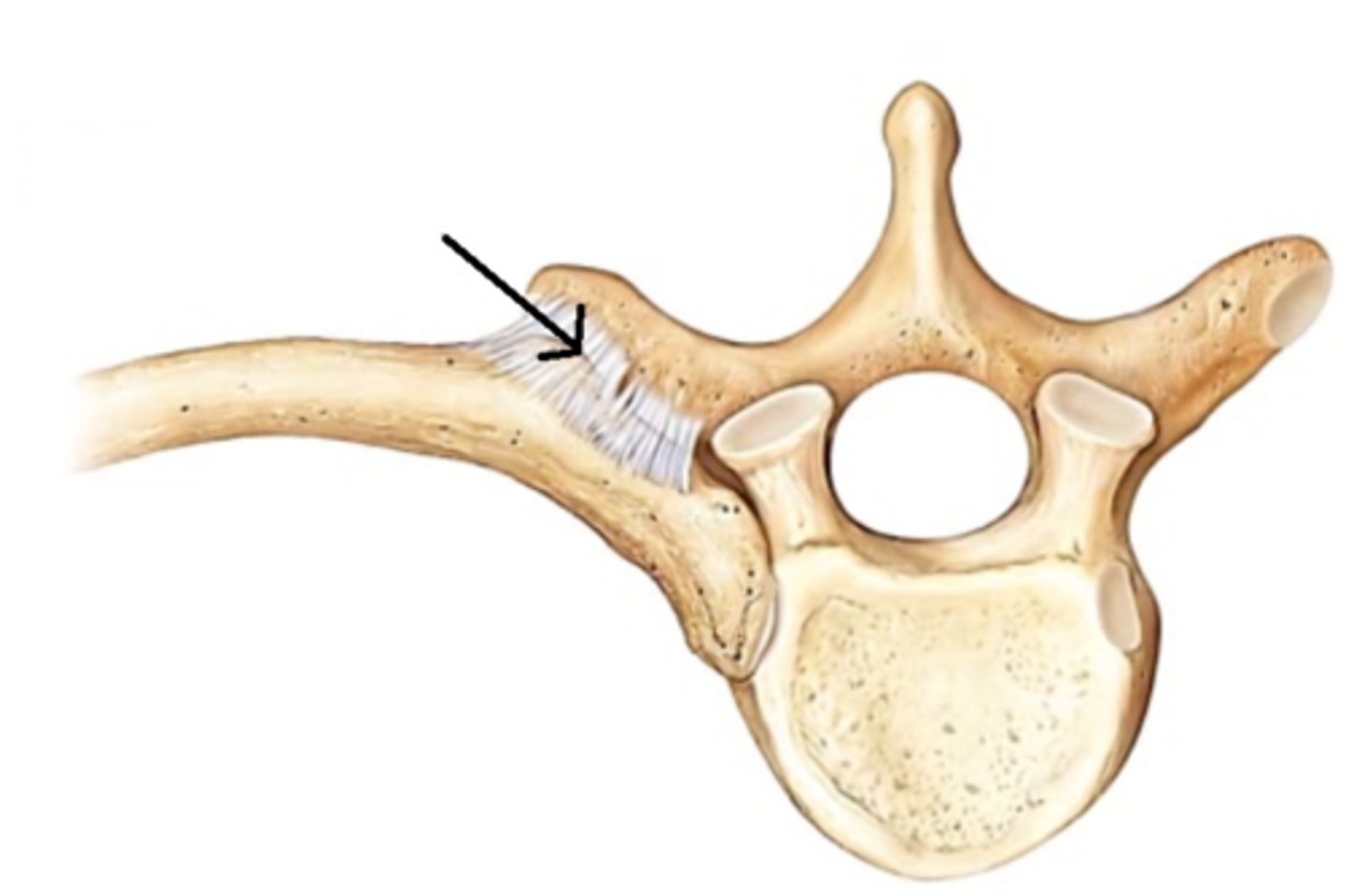
costotransverse ligament
rib to transverse process
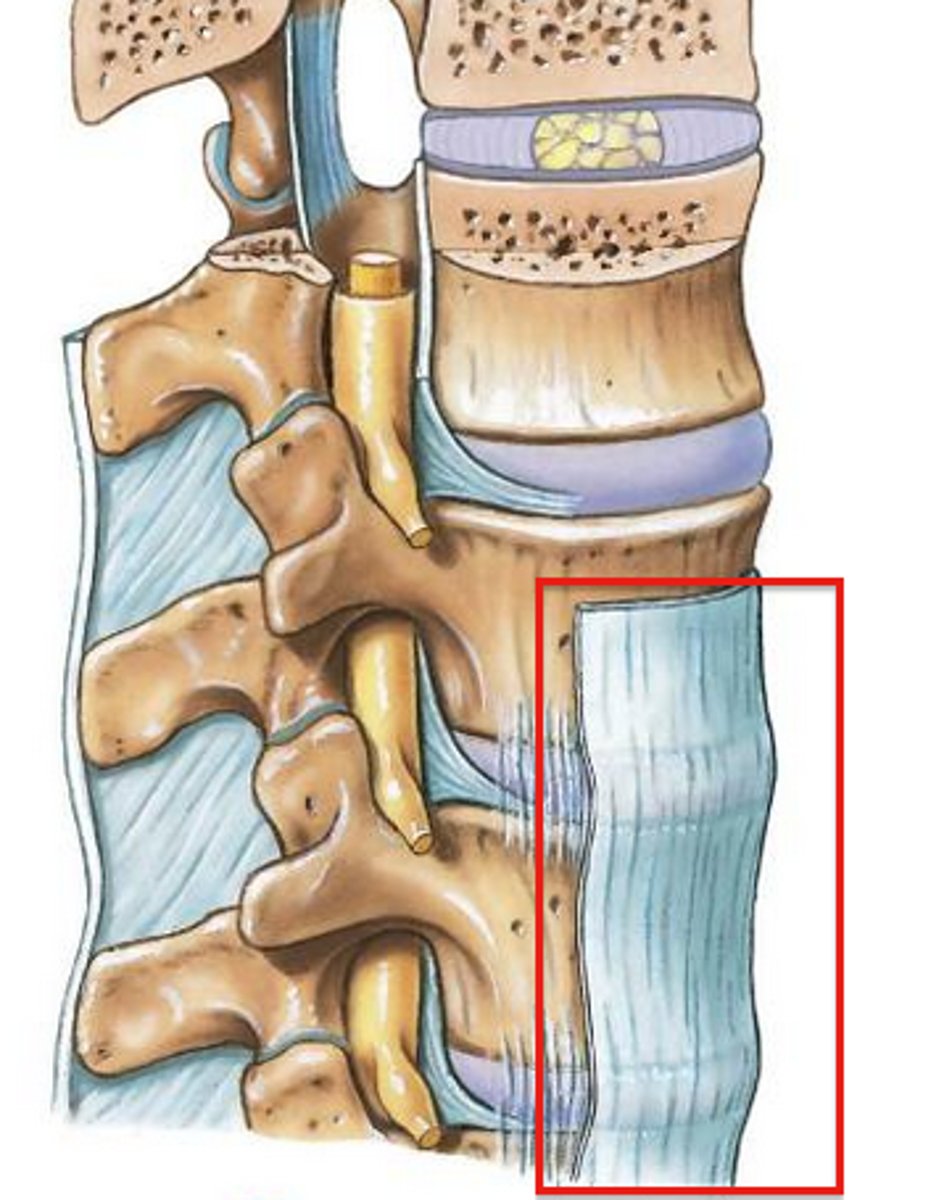
anterior longitudinal ligament
runs down spine; resists extension
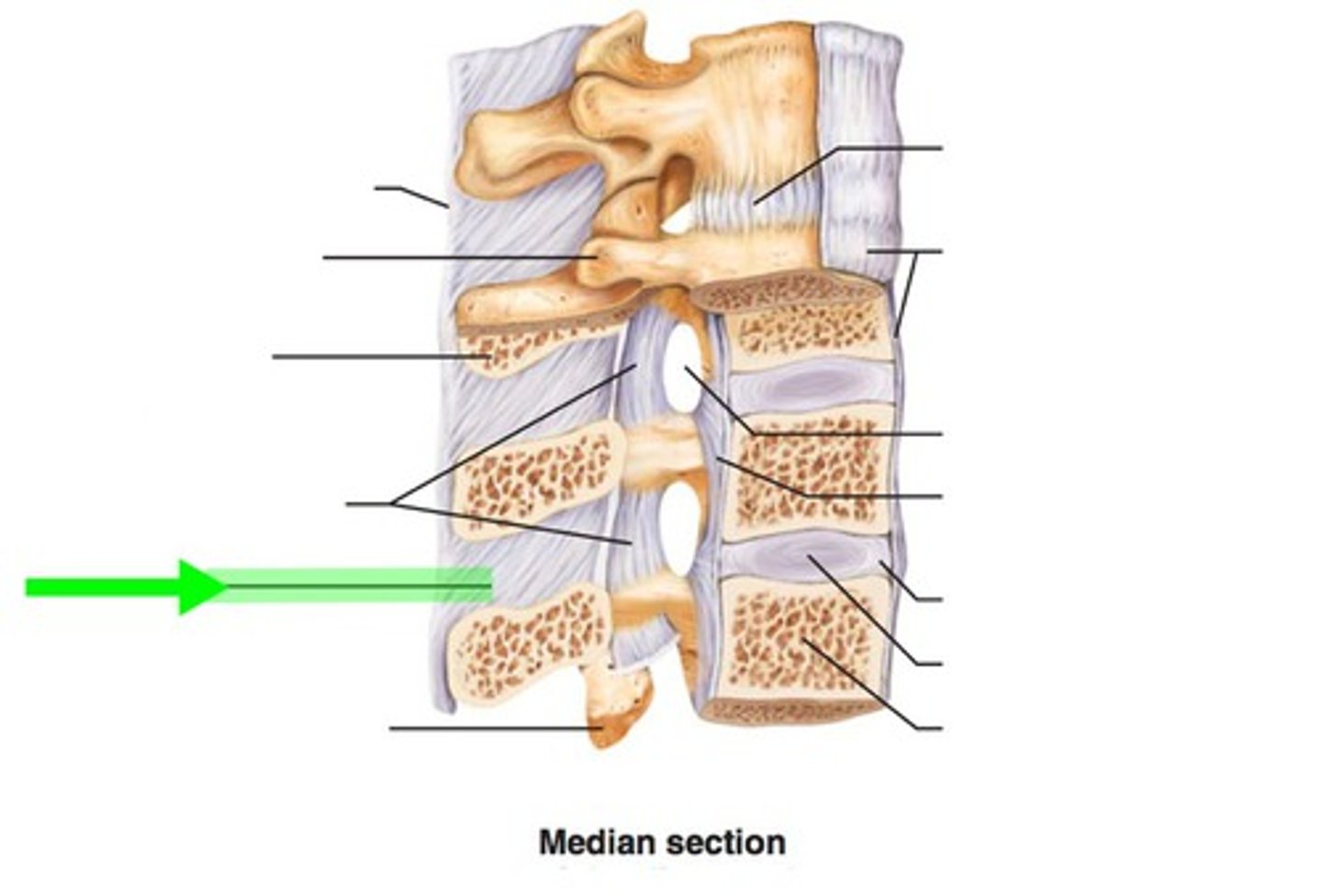
interspinous ligament
connect adjacent spinous processes
ligamentum flavum
yellow color; cervical; highest elastic content; vertebral to vertebral; prevent flexion
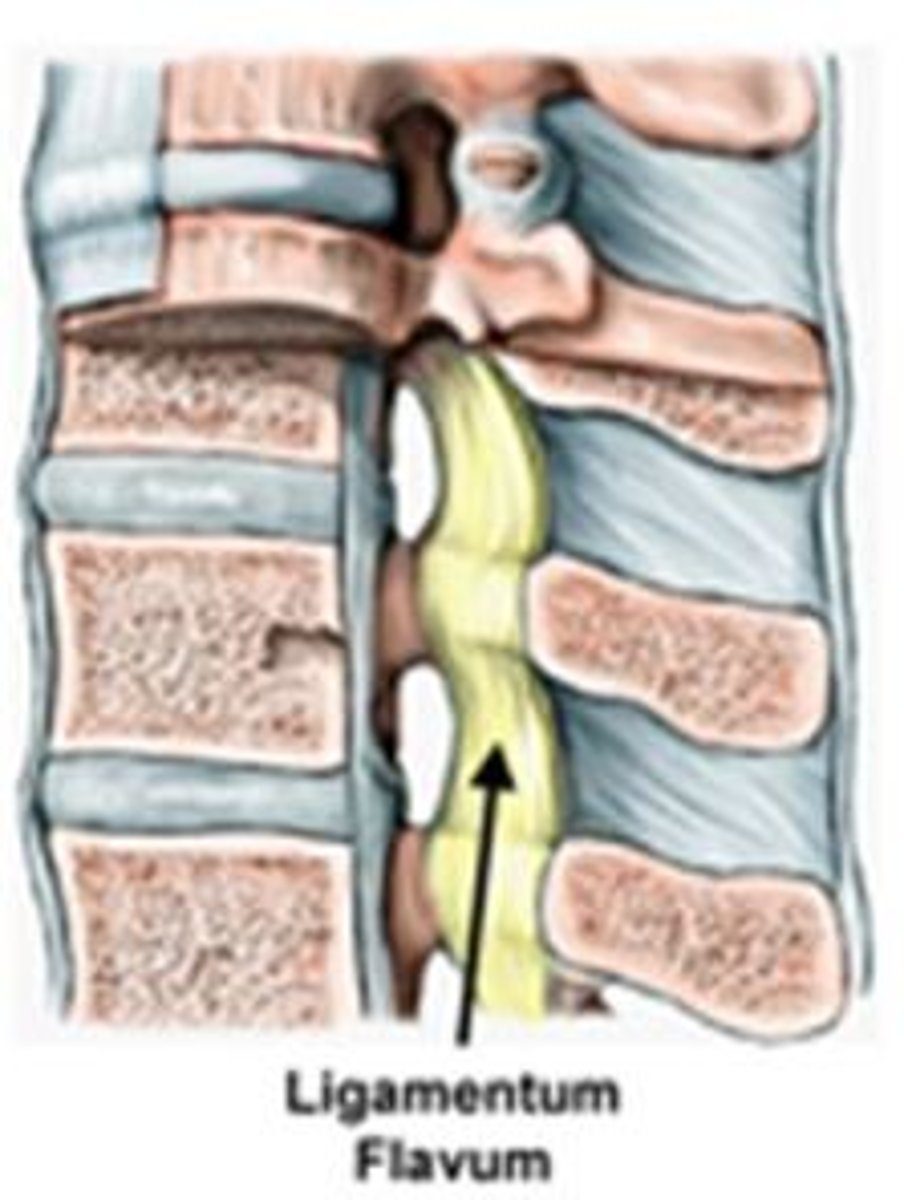
posterior longitudinal ligament
runs up and down entire spine
tectorial membrane
runs inside vertebral formamen
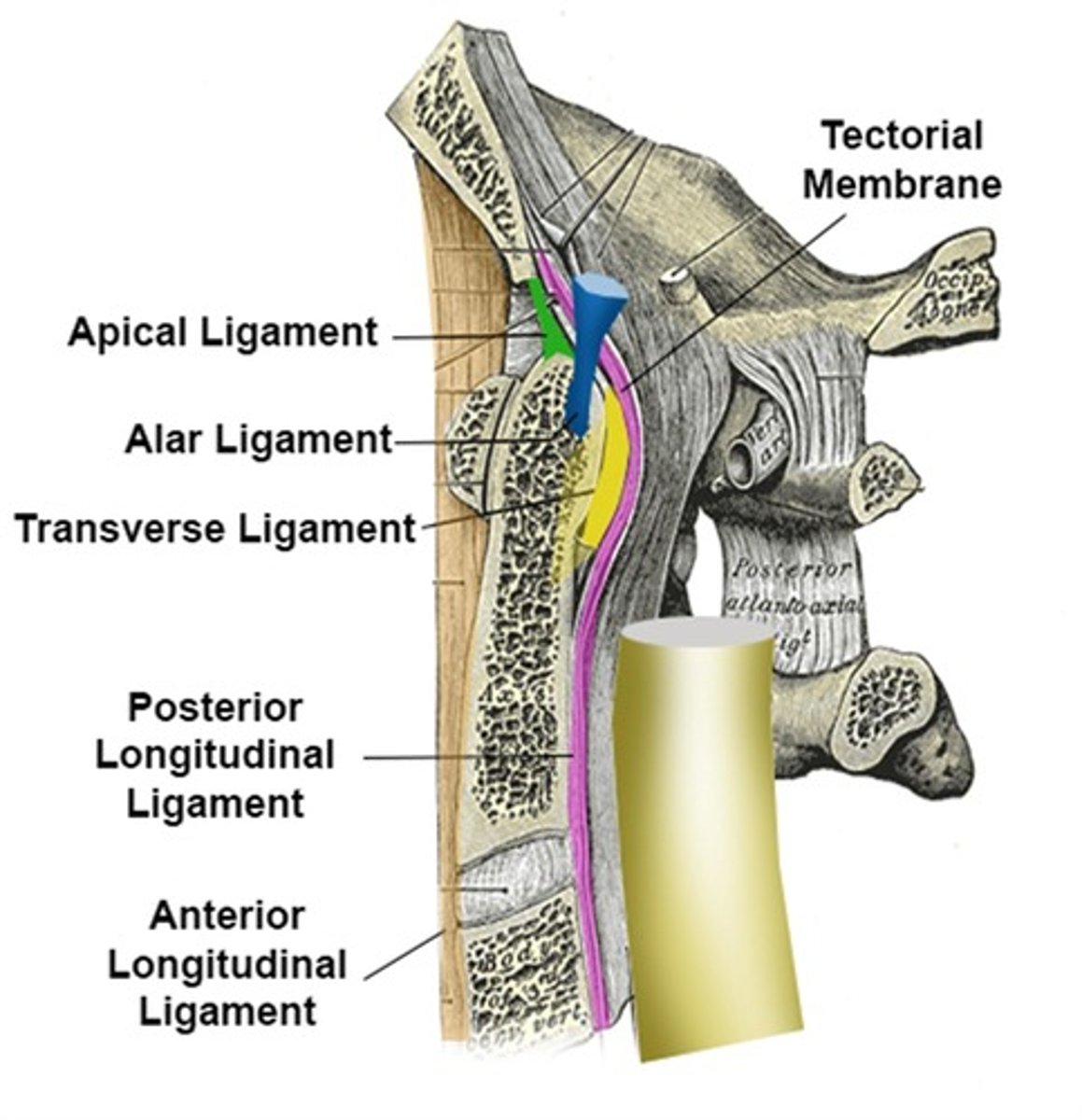
alar ligament
dens to occiput; prevents rotation of occiput on atlas
cruciform ligament
transverse; atlas; maintain articulation between dens and atlas
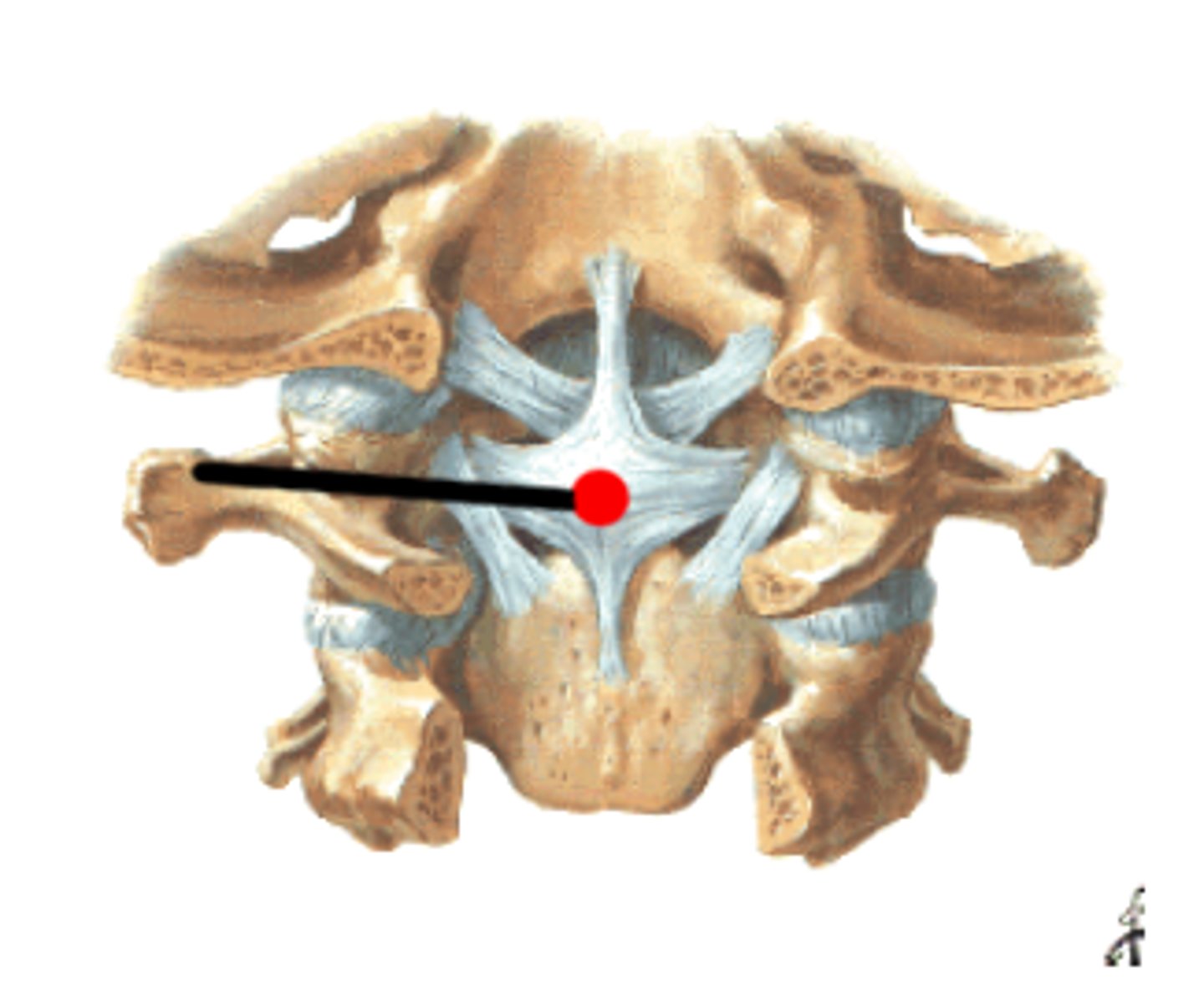
greater occipital nerve
-compressed = numbness, tingling, headaches
-above occiput
suboccipital nerve
below occiput
cervical verve roots
-8 cervical nerve roots but 7 vertebrae
-8th nerve between C7 and T1; comes out below C7
atypical ribs
1, 2, 10, 11, 12
typical ribs
-3-9
-Have a head, neck, tubercle, and body.
spinal cord
white and gray mater
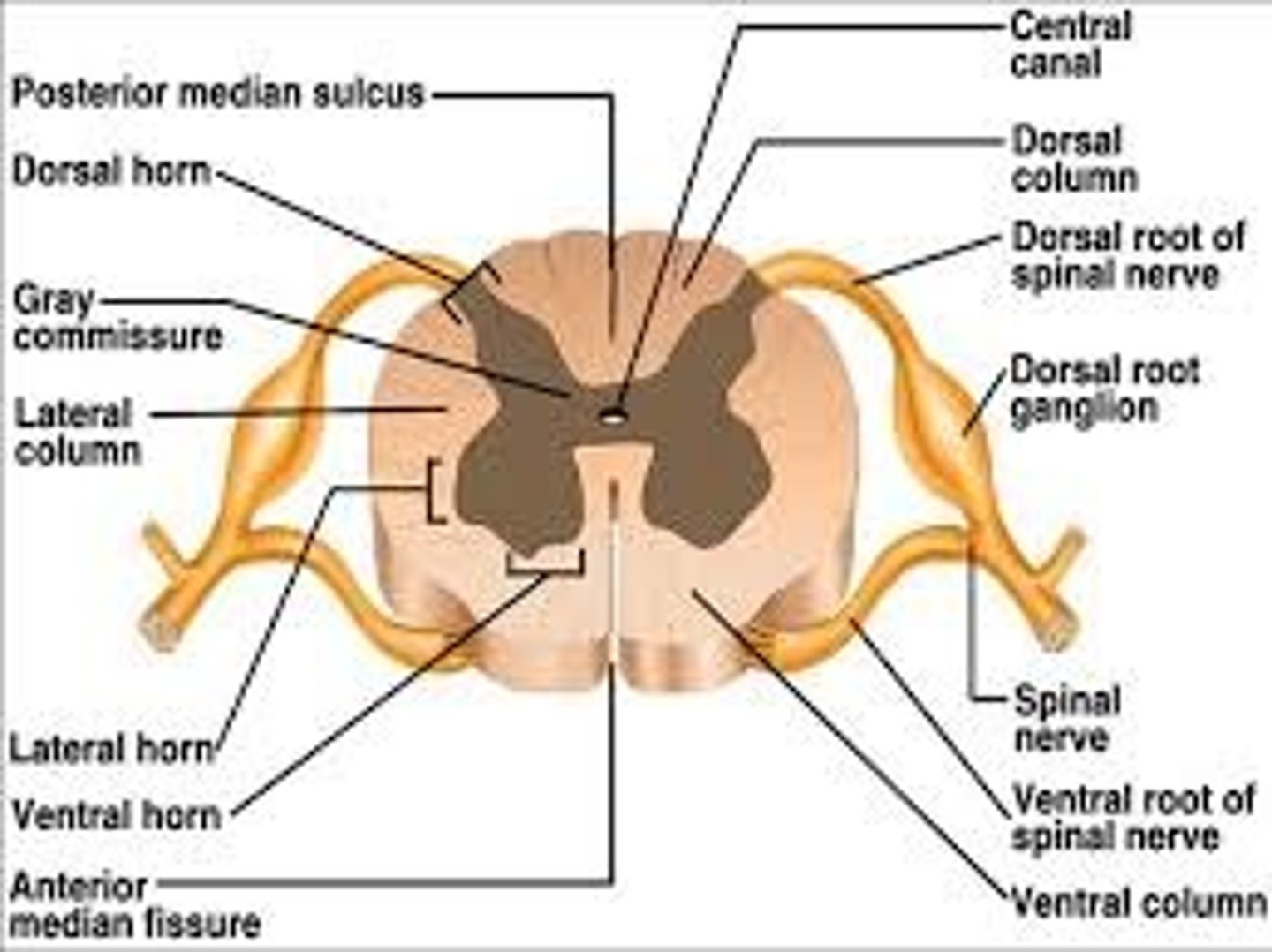
meniges
-dura mater (outer)
-aranchoid mater (middle)
-pia mater (right on spinal cord)
denticular ligament
allows meninges to maintain contact
end of spinal cord
-L1 and L2
-nerves continue to come out
conus medullaris
tapered end of spinal cord
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
filum terminale
-anchors spinal cord to coccyx (S5-coccyx)
-pia mater
-connective tissue
-rootlets -> roots -> spinal nerve
sensory nerves
-afferent
-goes in posteriorly to brain
motor nerves
-efferent (exit)
-anteriorly out to body
xiphisternal joint
-point where sternal body and xiphoid process fuse
- attaches to inferior border of heart
thorax
creates rigid cage for lungs
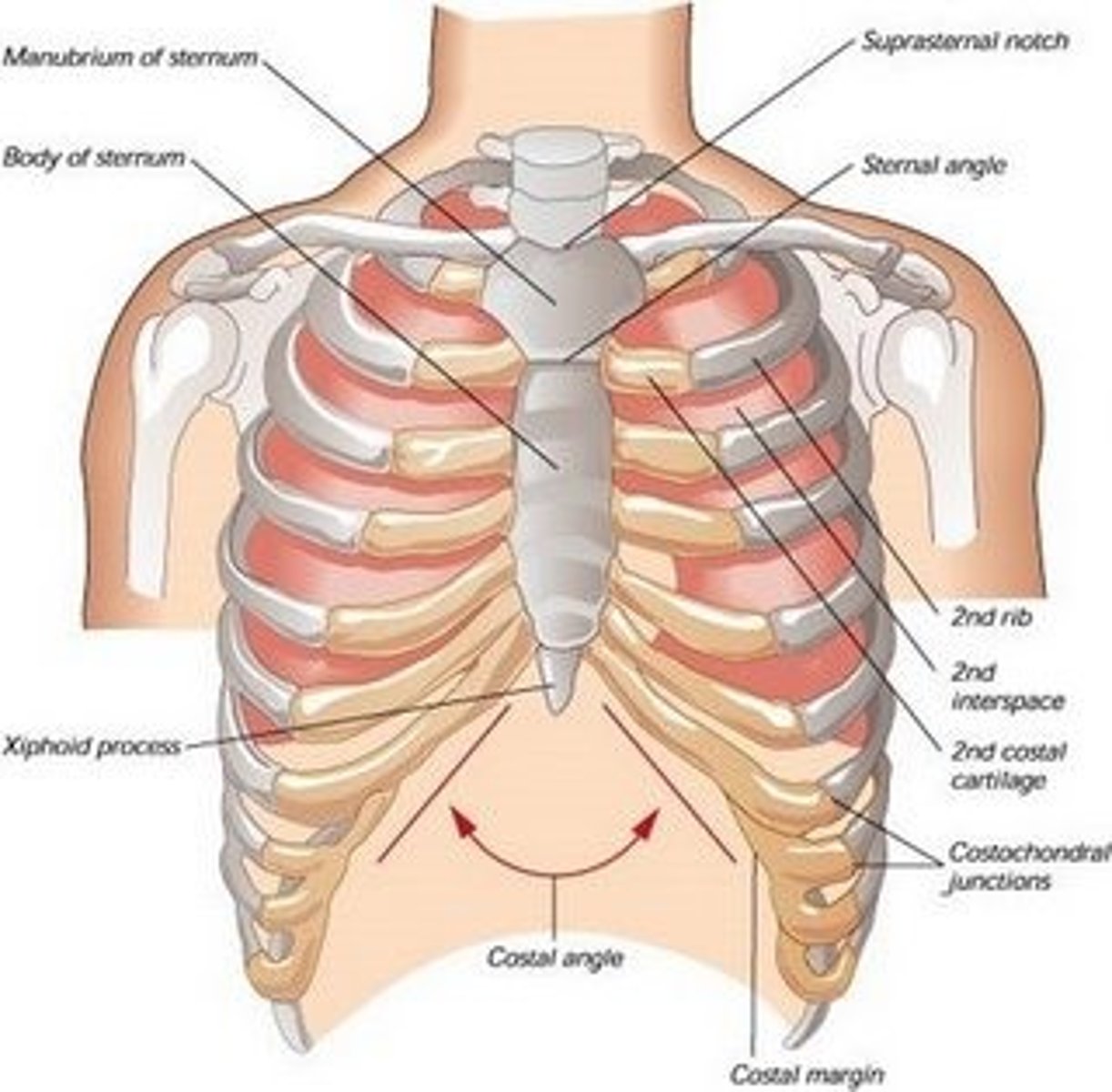
sternum
-manibrium
-sternal angle/manibrosternal joint: 2nd rib attaches
-xiphoid process
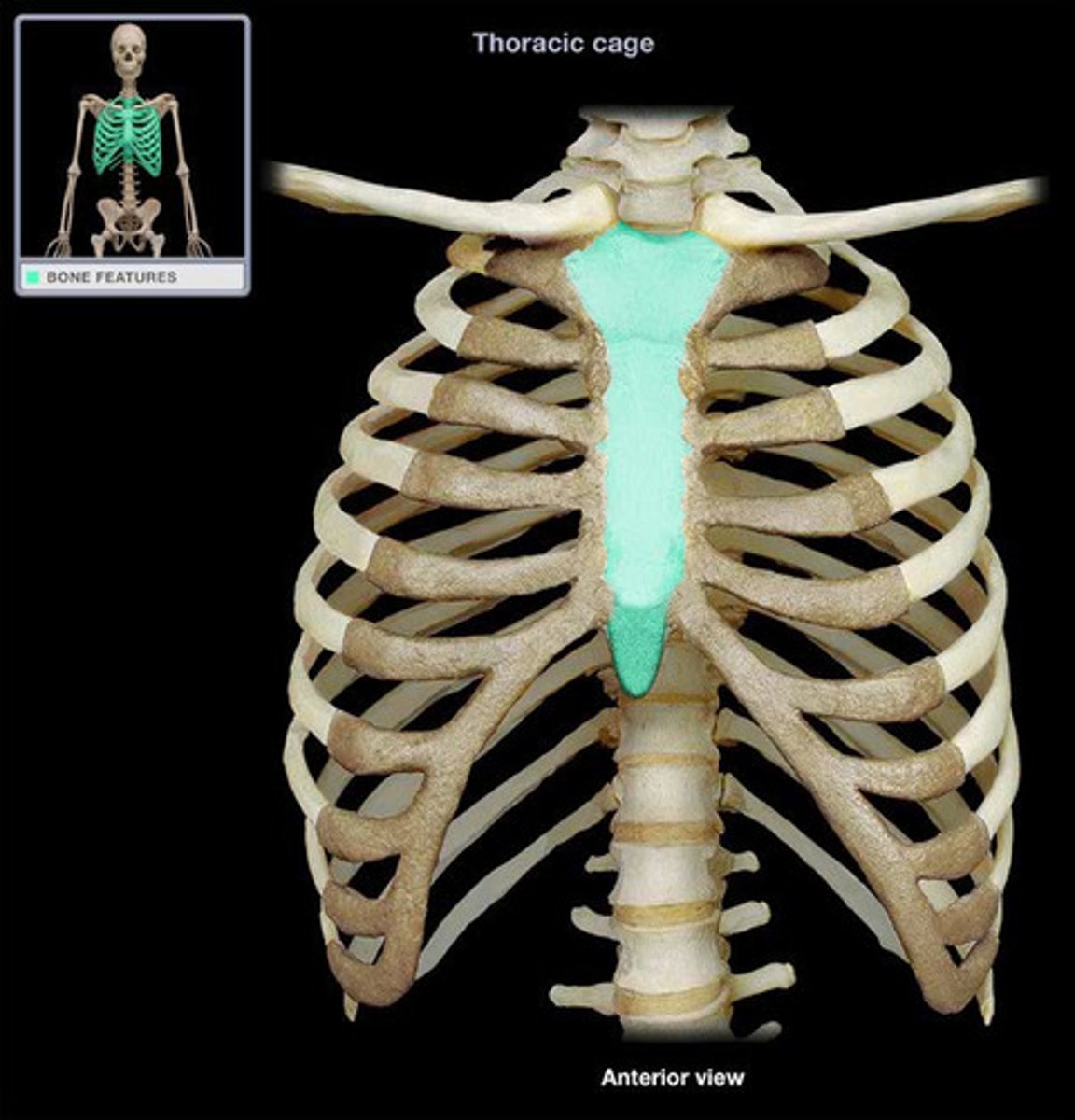
categorizing ribs
-short
-long
-typical
-atypical
upper ribs (inhale)
move up anteriorly (pump)
lower ribs (inhale)
move inwards (bucket)
intercostal muscles innervation
intercostal nerves
external intercostals
-fibers inferior and anterior
-rib above to rib below
-contract and come up
internal intercostals
-fibers run interior and posterior
-depress ribs
innermost intercostals
-fibers run inferior and posterior
-between all pairs of ribs
inside posterior ribs
-subcostals: depress ribs
-levator costorum: transverse cross to ribs below; elevate ribs
inside anterior ribs
transverse throacis: depress ribs; support thorax and ribcage anteriorly; stabilize actual rib (attachment); innervated by intercostal nerves
intercostal nerves and arteries
-posterior
-deep to ribs and interior to surface
-supply blood to intercostal muscles
-arteries come from thoracic aorta
interior thoracic arteries (both sides)
-comes from anterior part of intercostal artery
-comes from subclavian artery
pleura
-covering of lungs
-outside: parietal (ribs)
-inside: viscera (lungs)
pleural effusion
extra fluid inside layers of pleura
trachea split into
right and left bronchi
right lung
-superior, middle, inferior lobes
-horizontal fissure
-oblique fissure
left lung
-superior and inferior lobes
-oblique fissure
-cardiac notch
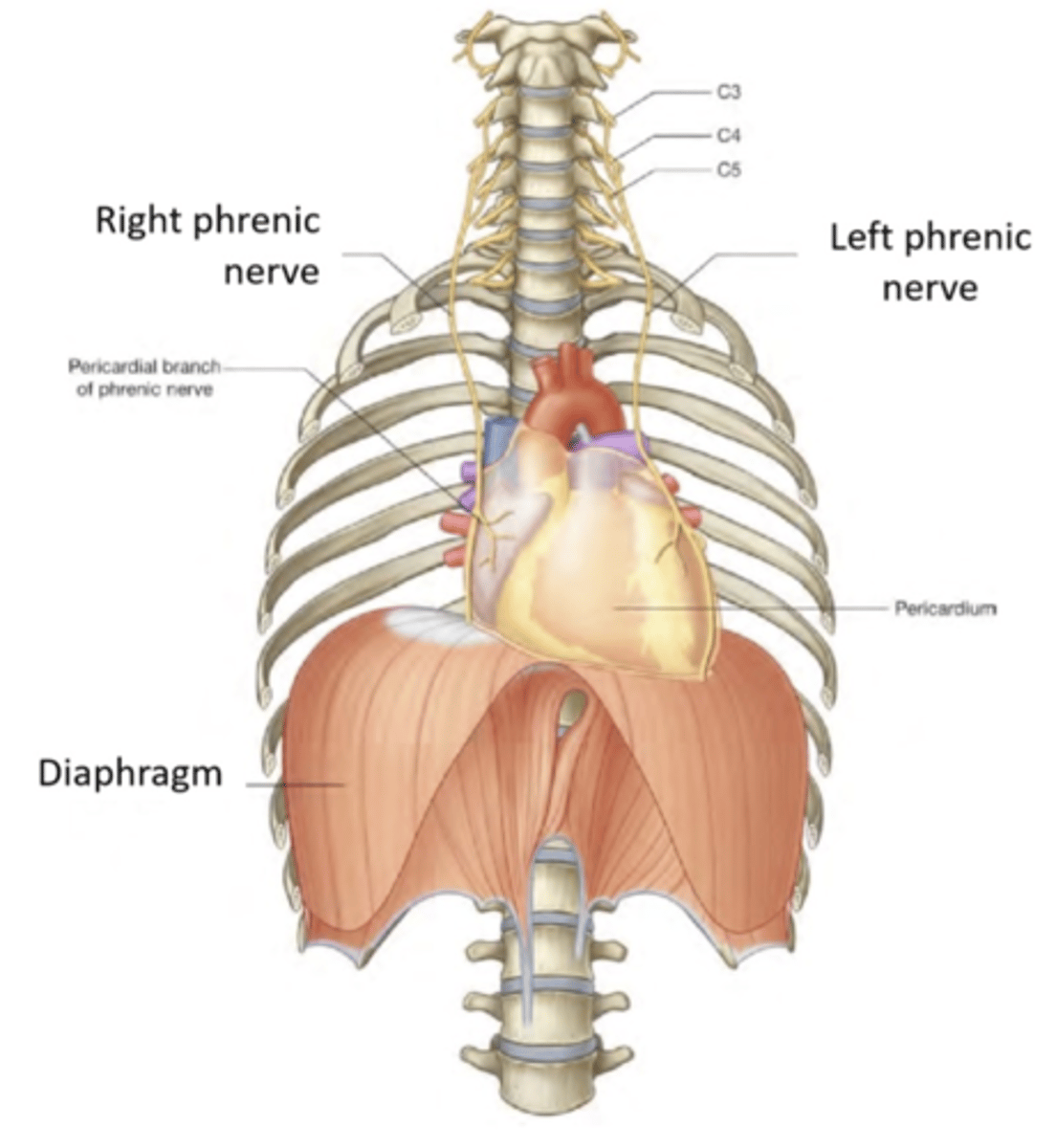
diaphragm innervation
C3-5 phrenic nerve
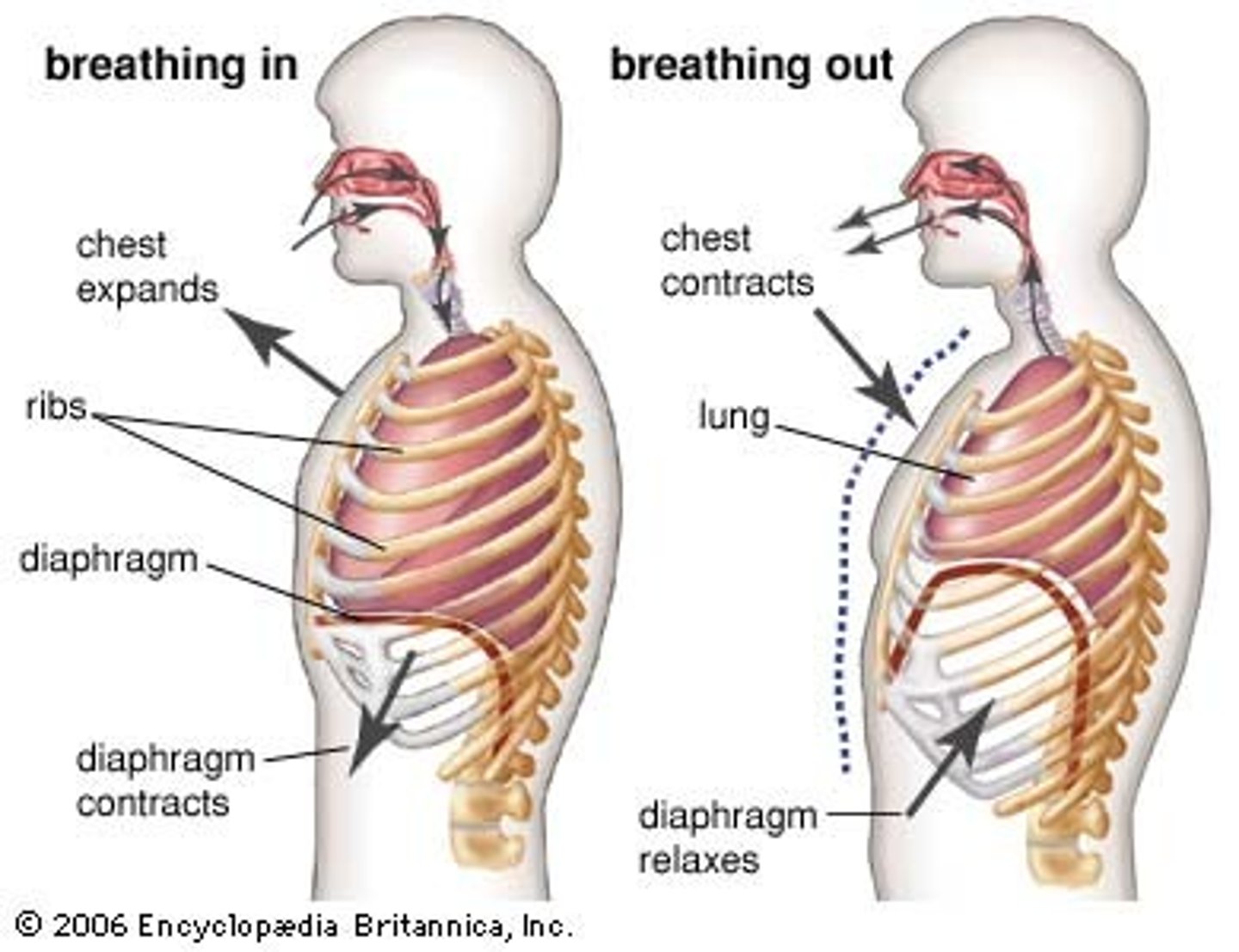
diaphragm contracts
-moves inferiorly
-inhalation
-makes cavity bigger; negative pressure
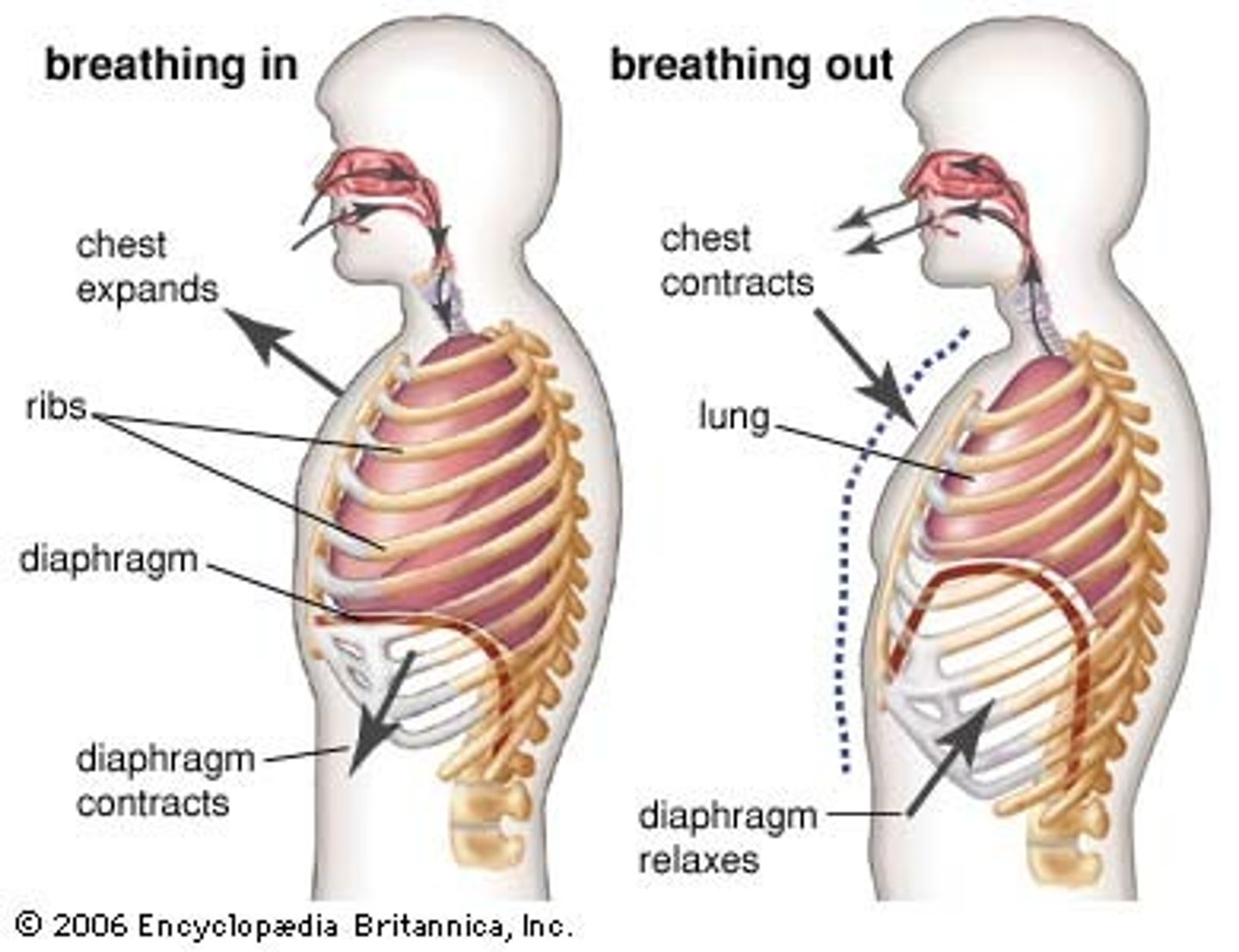
diaphragm relaxes
-pushes back up
-exhalation
-positive pressure
heart innervation
-vagus nerve
-gives parasympathetic innervation (slows HR)
pericardium
-surrounds heart
-outer layer: fibrous pericardium (inelastic)
pericardial effusion
build up of fluid (pericardium won't stretch/expand)
coronary arteries
-supply blood to hearty
-right coronary and left coronary
-left coronary -> left anterior descending artery (massive heart attack)
median/sagittal plane
-divides body into right and left sides
-around transverse axis
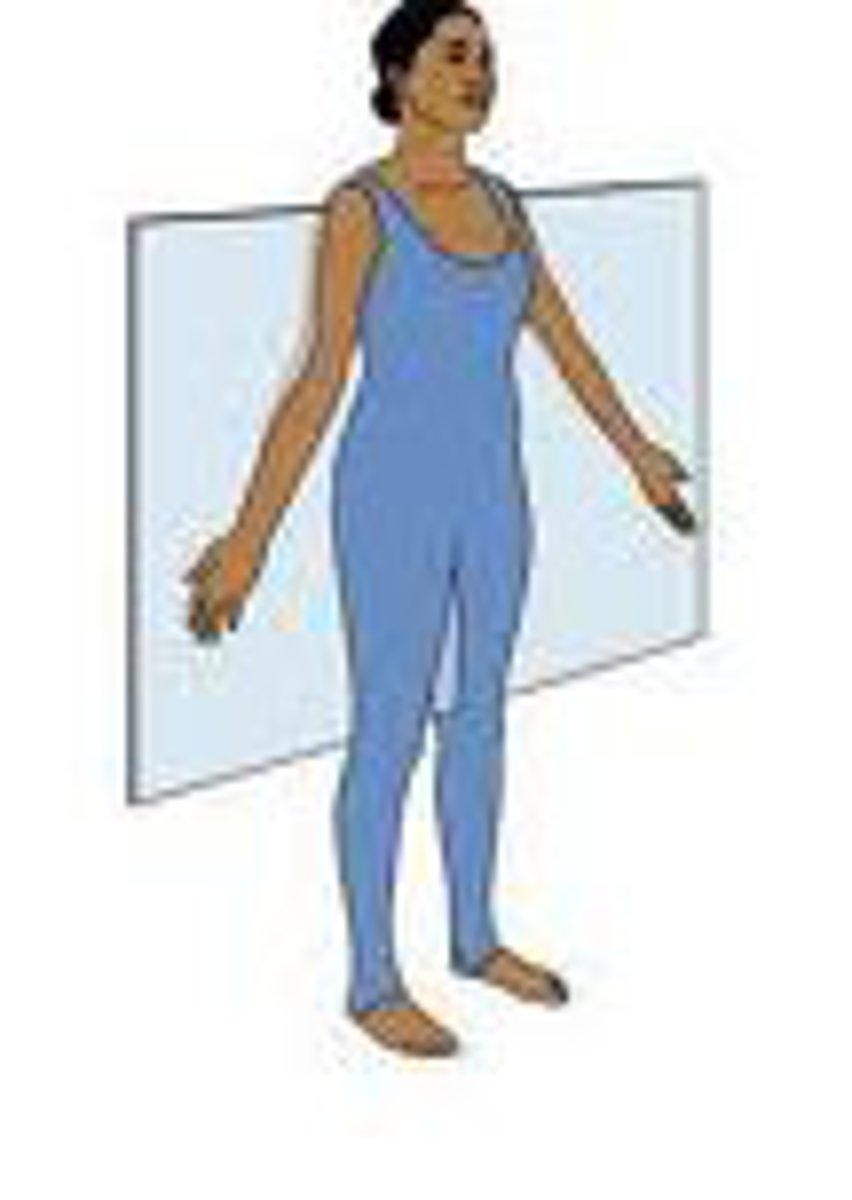
coronal/frontal plane
-divides the body into anterior and posterior portions
-around anterior posterior axis

transverse/horizontal plane
-divides body into superior and inferior portions (upper and lower)
sagittal plane movements
flexion and extension
frontal plane movements
-abduction/adduction
-fingers and toes have different midline (3rd finger, 2nd toe)
-lateral flexion
transverse plane movements
rotation
anterior compartment of thigh
-hip flexors (pectineus, iliopsoas, iliacus, psoas major/minor, sartorius)
-knee extensors (quad femoris, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius)
-femoral nerve and ventral rami of L1 and L2
anterior compartment of foot
-extensor hallicus longus (extension 1)
-extensor digitorum longus (extension 2-5)
-tibialis anterior (inversion)
-fibularis tertius (eversion)
-innervation: deep fibular nerve
-dorsiflexion
superficial posterior compartment leg/foot
-gastroc (knee flexion, PF when knee extended)
-soleus (PF)
-plantaris (PF)
-innervation: tibial nerve
lateral compartment of foot
-fibularis longus
-fibularis brevis
-action: eversion, PF
-innervation: superficial fibular nerve
deep posterior compartment of leg/foot
-tiblias posterior
-flexor hallicus longus
-flexor digitorum longus
-innervation: tibial nerve
- PF, support medial longitudinal arch
-popliteus (innervation: finial nerve; action: unlock tibia, weak knee flexion)
medial compartment of thigh
-adductor muscle group -adductor longus
-adductor bevis
-adductor Magnus
-gracilis
-obutrator externus
-obtruator nerve
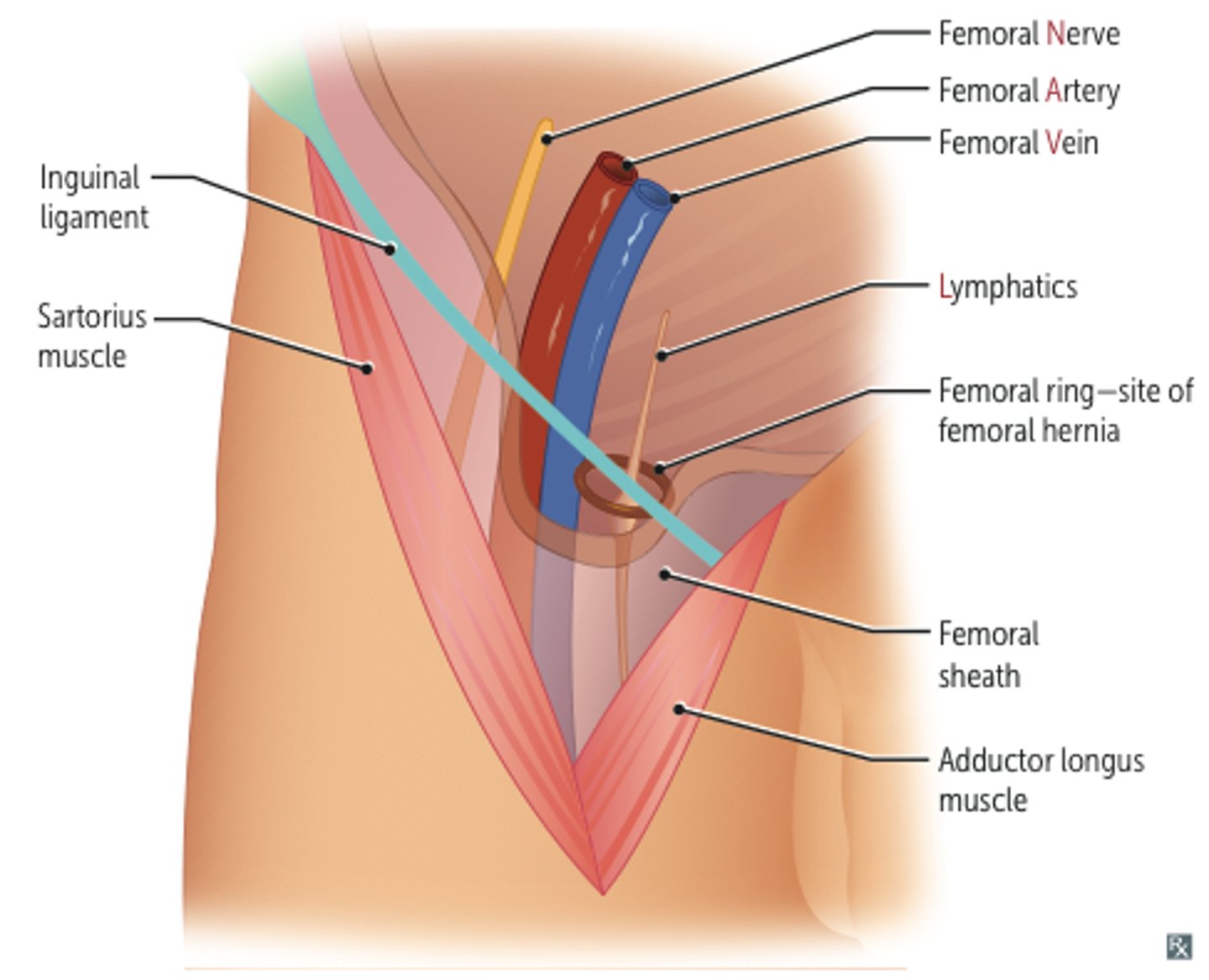
femoral triangle
-superior: inguinal ligament
-medial: lateral border of adductor longus
-lateral: medial border of sartorius
-floor: iliopsoas
-roof: fascia latae, subcutaneous tissue and skin
posterior compartment of thigh
-semitendinous
-semimembranosus
-biceps femoris long head
-innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve
-biceps femoris short head (common fibular division of sciatic nerve)
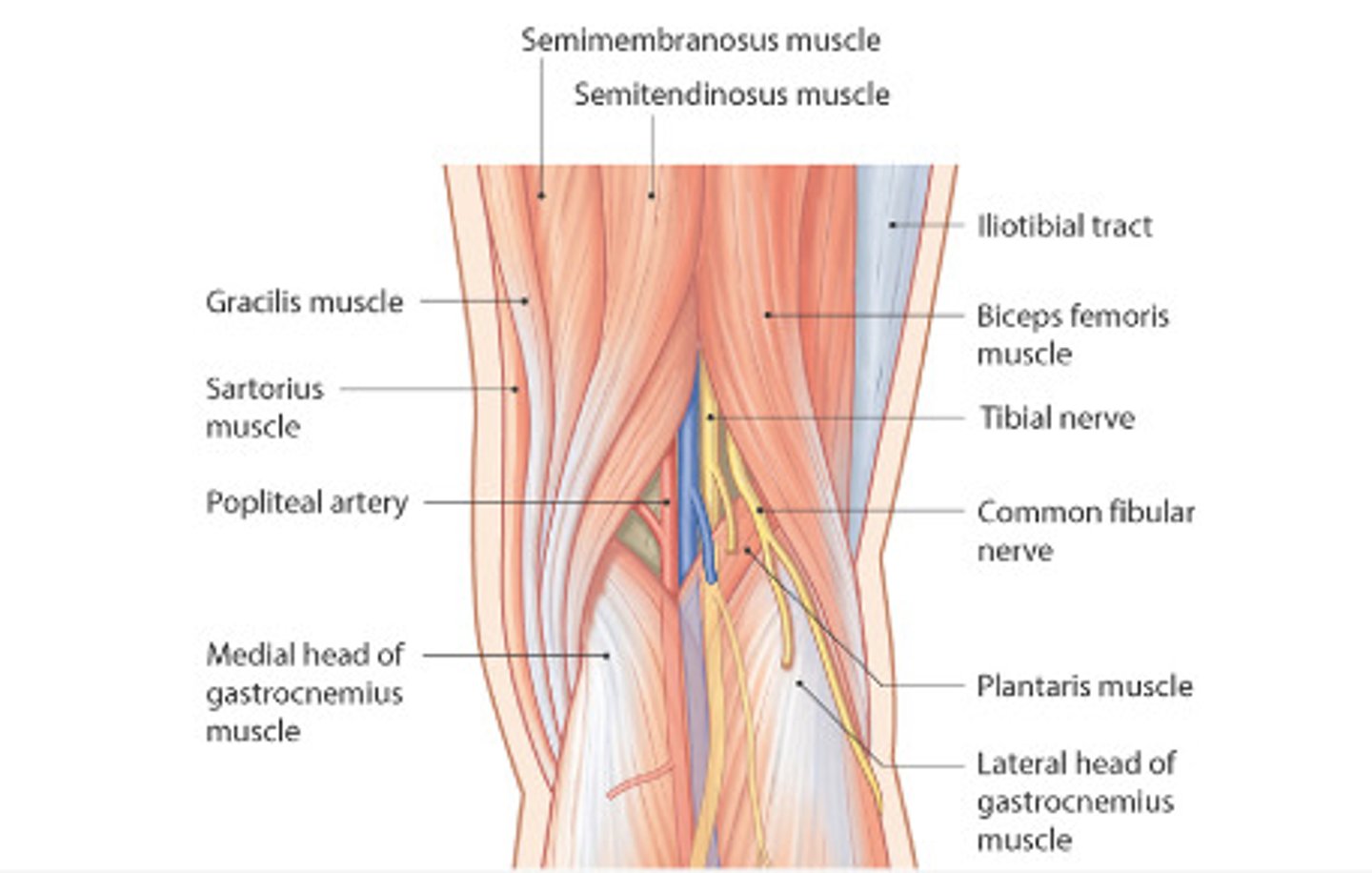
popliteal fossa
-small saphenous vein termination
-popliteal vein and artery
-tibial nerve
-common fibular nerve
-post cutaneous nerve of thigh
-lymph nodes and vessels