IB Biology Unit 7: Carbohydrates and Lipids
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
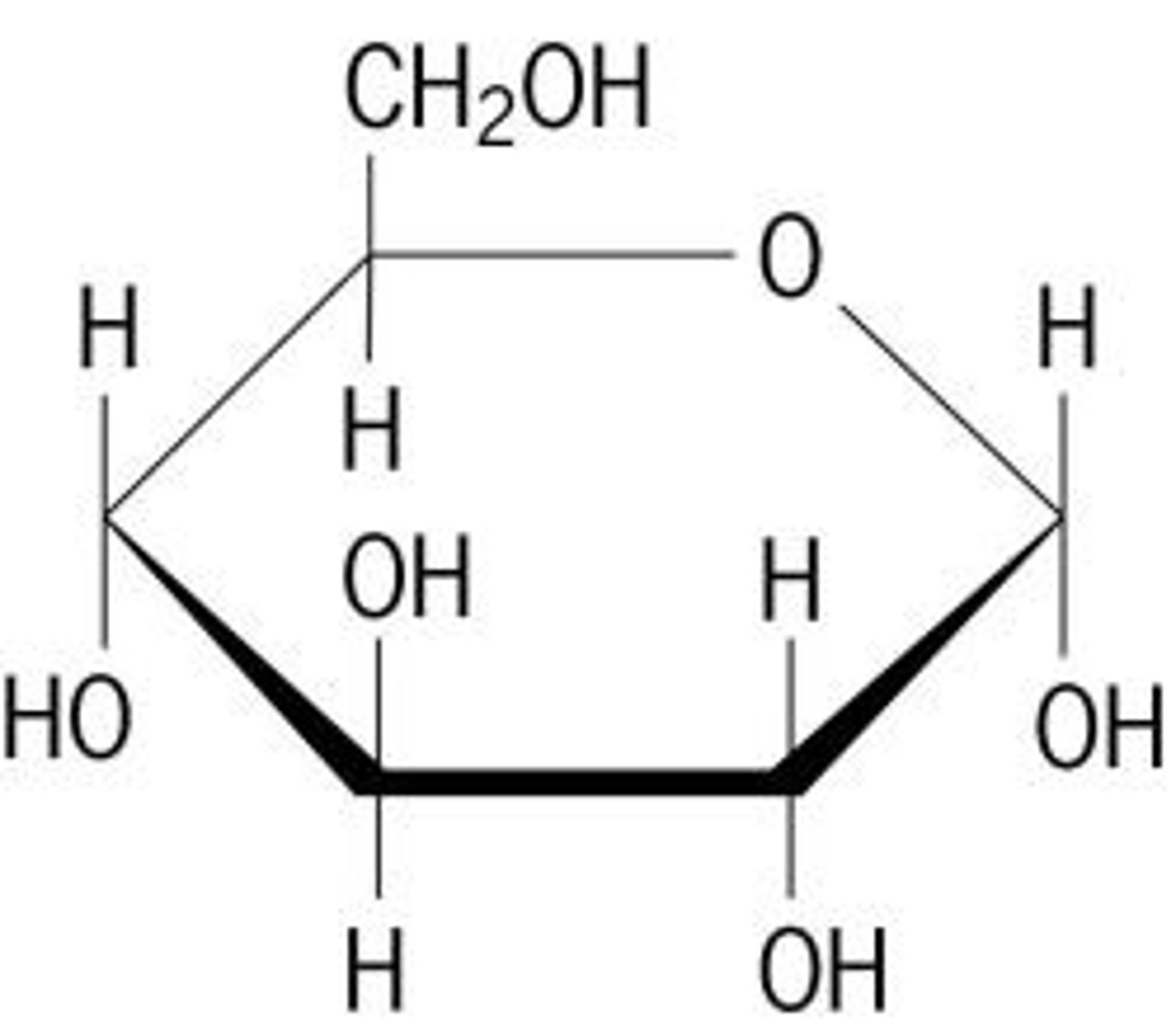
Draw the molecular diagram of glucose and ribose
*Search up for ribose if you don't remember!
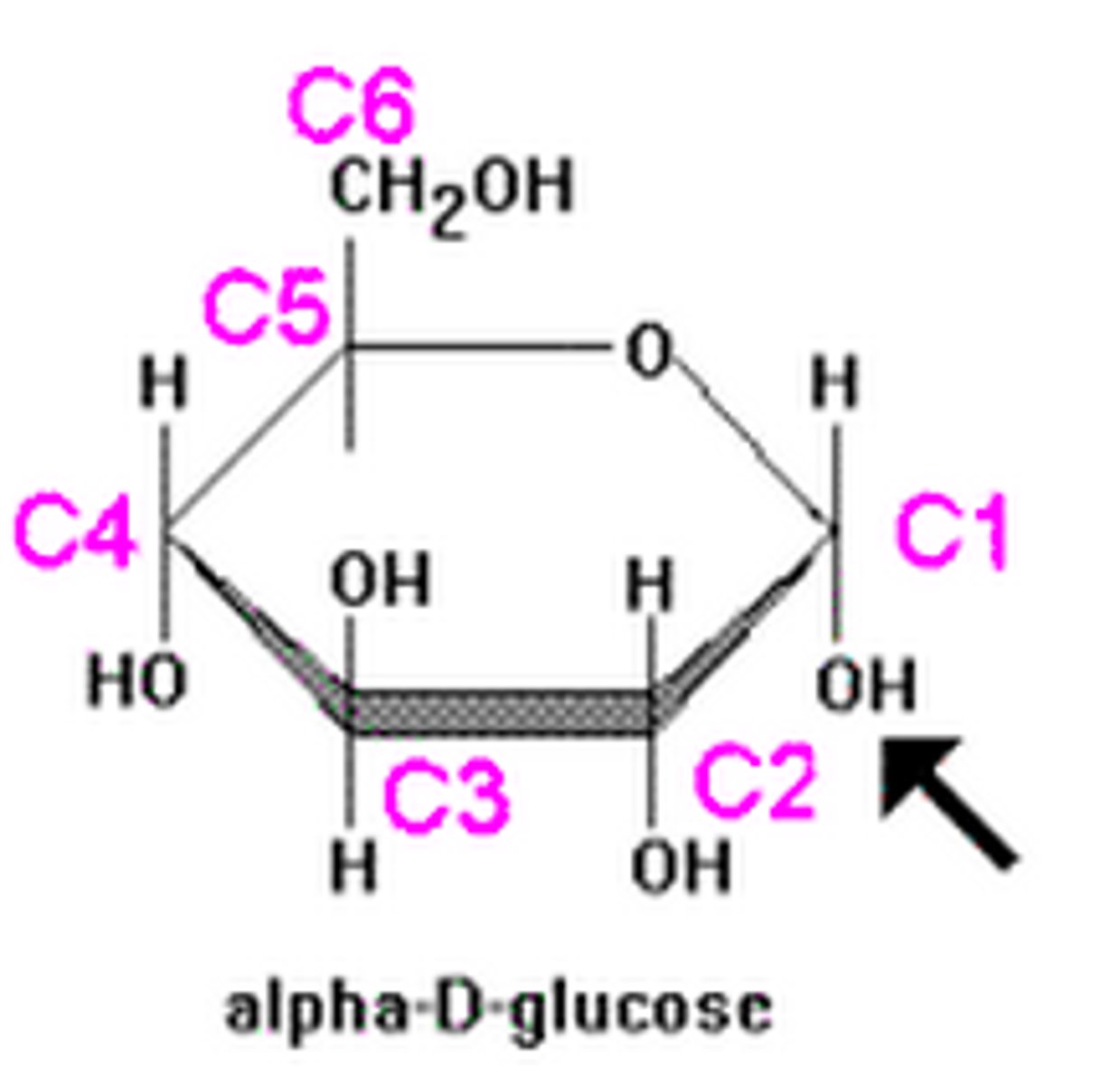
Draw the molecular diagram of alpha glucose
State the generalized chemical formula of the carbohydrates.
General formula: (CH2O)x (x being the # of carbons).
Eg. (CH2O)6 --> C6H12O6
Identifying the following molecular drawings
D-ribose, a-glucose, b-glucose, cellulose, amylose, amylopectin.
Define monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides
Monosaccharides: Refers to one single carbohydrate, "one sugar".
Disaccharide: Refers to the sugar formed when two monosaccharide are joined.
Polysaccharide: Refers to the longer chains of monosaccharides joined together.
List 3 examples of monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharides: Glucose, ribose and deoxyribose.
Disaccharides: Maltose, sucrose, and lactose
Polysaccharides: Starch-amylose, glycogen and cellulose.
Use molecular diagram to draw the formation of maltose from two glucose monomer.
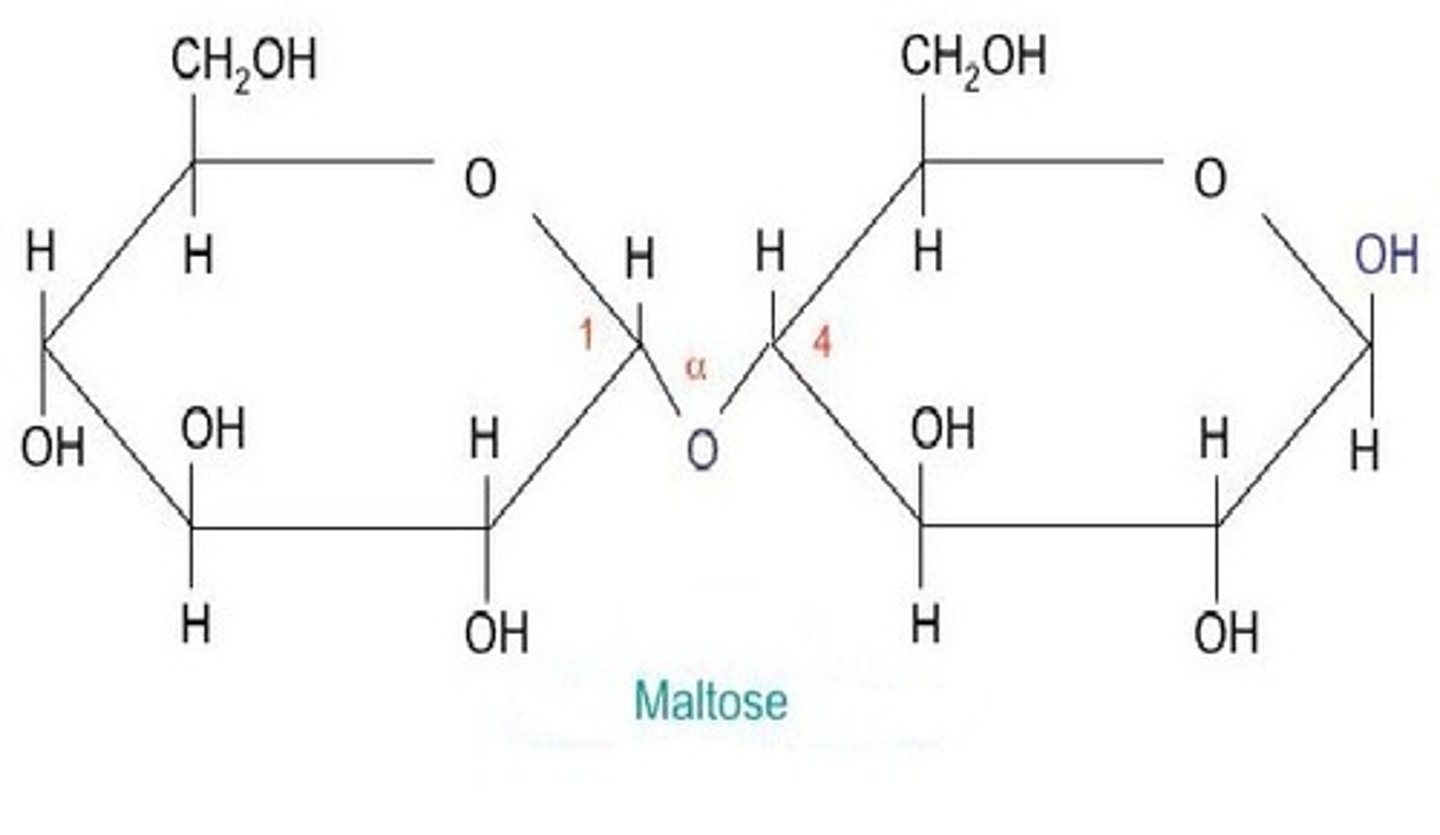
Explain a condensation reaction connecting two monosaccharides in the formation of a disaccharide.
Condensation is a chemical reaction in which two molecules are joined to form a larger molecule with the loss of water.
_(-H from carbon 1 hydroxyl (-OH) group combines with carbons 4's hydroxyl group. Combines to form water, with bonds C-O-C bridge forming between the monosaccharides.)_
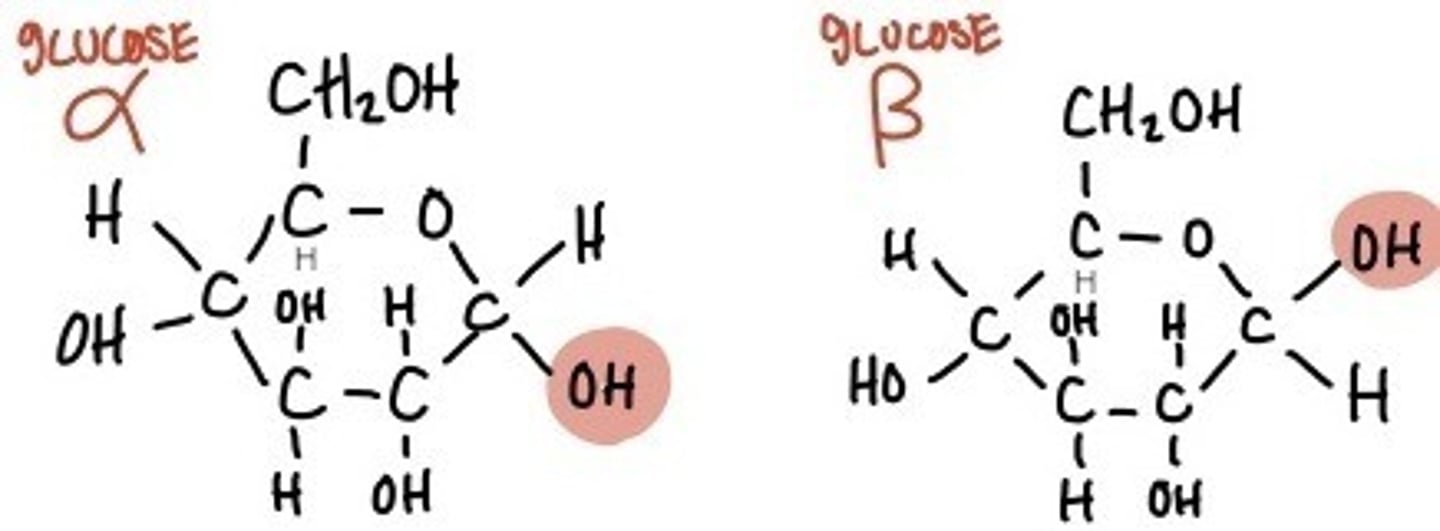
State the difference between alpha and beta glucose.
There is a different orientation of the hydroxyl group (-OH) relative to carbon 1.
Contrast the structure and function of cellulose, amylose and amylopectin and glycogen.
Cellulose: forms the plant cell walls and is a polymer of the b-glucose.
Glycogen: energy storage in animals, branched polymer of a-glucose.
Amylose: Starch, is an unbranched polymer from a-glucose as a storage unit in plants.
Amylopectin: starch, is a branched polymer of a-glucose as a storage unit in plants.
Demonstrate the use of JMol to view molecular structures.
JMol is a software which allows us to view molecules, rotate it, zoom in and manipulate it.
Identify carbon, hydrogen and oxygen by colours.
Carbon: black
Hydrogen: white
Oxygen: red
Draw the molecular diagram of a saturated fatty acid and identify the carboxyl and methyl groups.
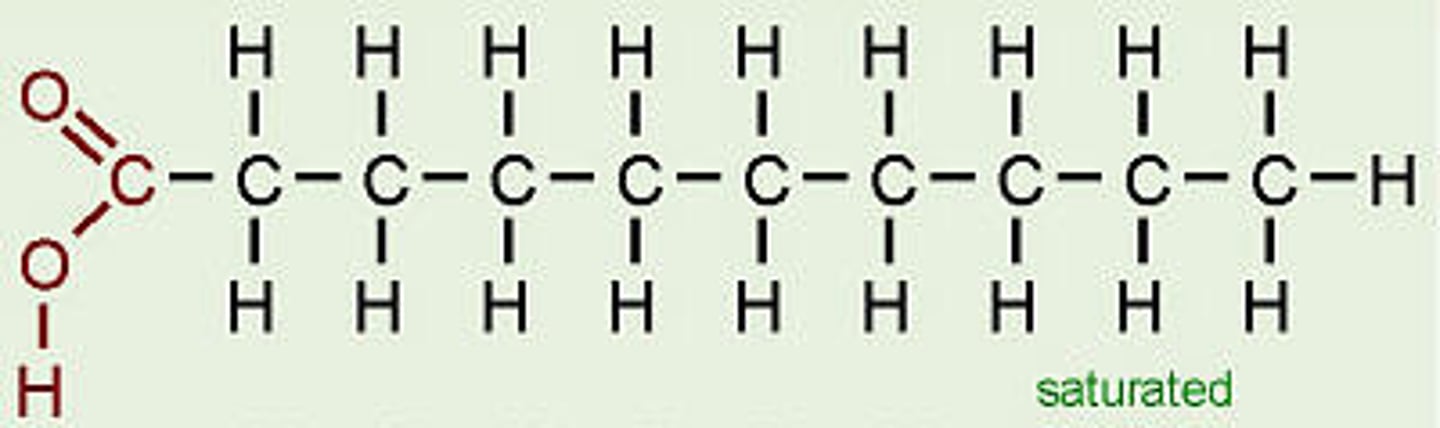
Compare the relative amount of oxygen atoms in lipids to the amount in carbohydrates
Lipids are mostly hydrocarbons. It has relatively less oxygen than carbohydrates. Hence why carbohydrates can dissolve in water.
Draw the following molecules: triglyceride, phospholipid and sterols.
Check google you dumb.
Describe the difference between saturated and unsaturated (mono- and poly-) fatty acids.
Saturated: They have only single carbon to carbon bonds.
Unsaturated: they have one or more double carbon-to-carbon bonds.
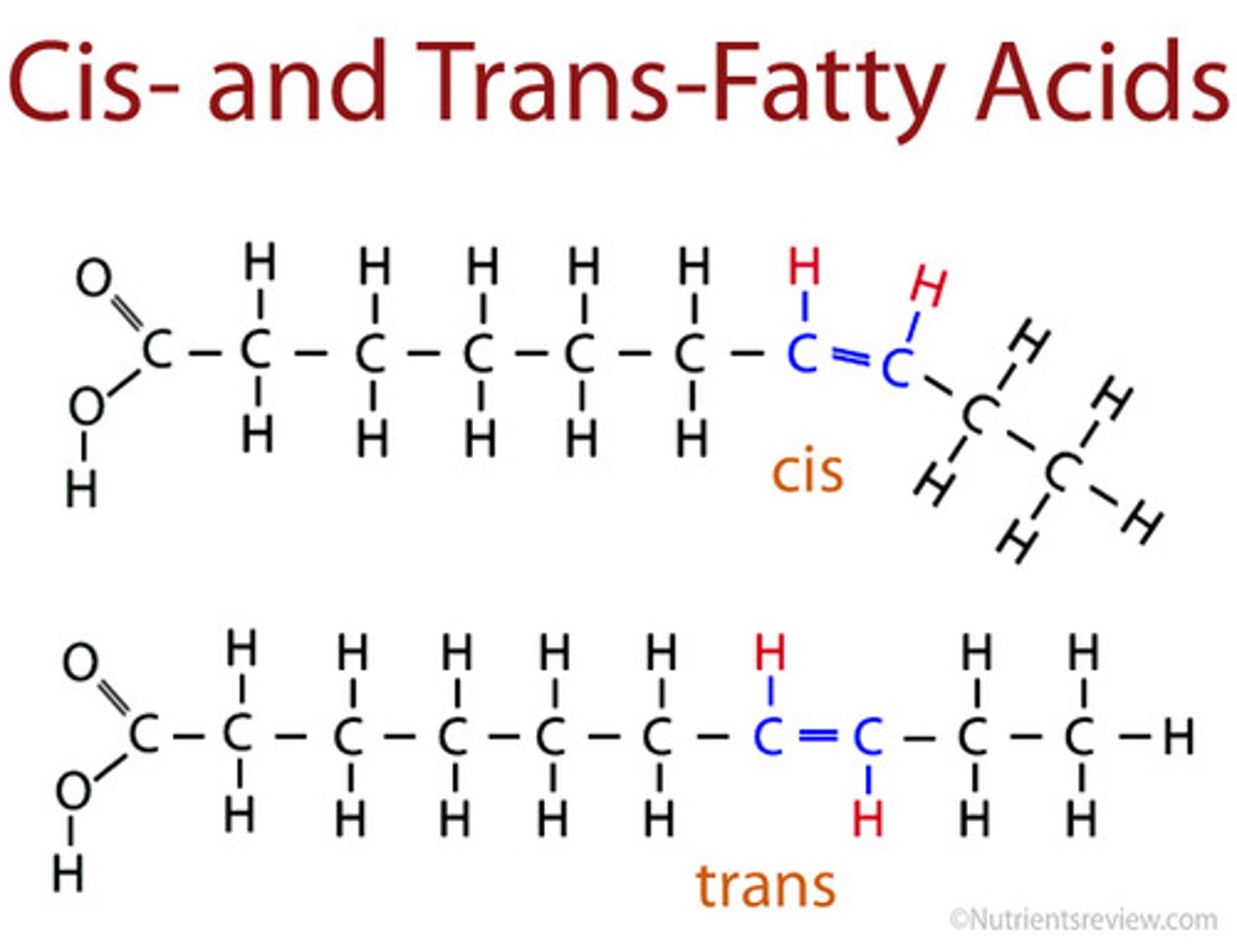
Describe the difference between cis- and trans- fatty acids.
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula but a different structure. Eg. Cis- and Trans-
Cis- has their hydrogen on the same side whilst trans- has their hydrogen on opposite sides.
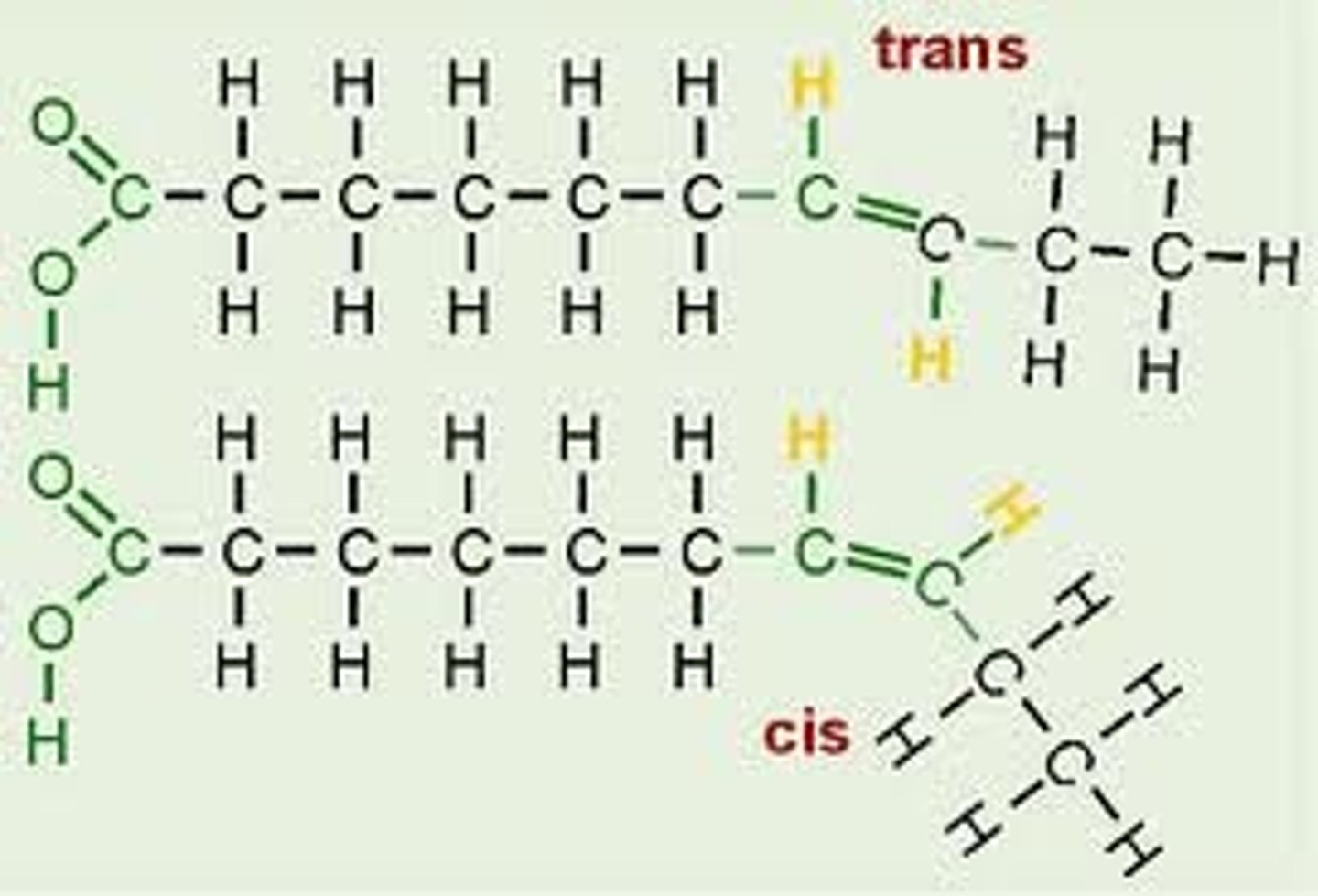
Outline the difference between fats and oils
FATS: Solid at room temp (24), saturated fatty acids, mostly from animals.
OILS: Liquid at room temp (24), unsaturated fatty acids, mostly from plants.
Explain a condensation reaction connecting fatty acids and glycerol to form a triglyceride.
1 glycerol is present to combine with 3 fatty acids. Each bond with the 3 fatty acids results the removal of 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen. Since there's 3, that means there will be 3 water molecules are produced as the byproduct.
State two functions of triglycerides
Water proofing, energy storage.
Others: source of energy, thermal insulation, protection.
Use a computer application to keep a record of food consumed in a day.
There are a lot of databases to record our food intake. MyFitnessPal etc.
Compare the tracked food intake to the recommended intake of nutrients.
Often people intake more: calories, sugar, fats and salt. But not enough: fiber and vegetables.
(I personally eat too much carbs.)
Discuss the relationship between saturated fatty acids and unsaturated fatty acids (cis and trans) and the rates of coronary heart disease
*There has been a a strong positive correlation between the intake of saturated fats and transunsaturated fats with he following problems:
•All causes of mortality
•Cardiovascular diseases and associated with mortality
•Strokes
•Type II diabetes.
Discuss how the effect of lipids on health can be assessed scientifically
• Scientific investigations, labs and reports.
-Determine the correlation of lipids and health effects by using large data bases of population statistics.
-Performing controlled experiments with human volunteers or animal models.
Define evaluation in respect to evidence from and the methods of research.
A systematic determination of significance of a claim against a set of standards.
Outline the manner in which the implication of research can be assessed.
Implication: does the result of the research support the claim strongly, moderately or not at all?
-How strong is the correlation
-Is the result significant or by change, use the statistical test.
-How much variation is there between people?
Outline the manner in which the limitations of research can be assessed.
Limitation: was the investigation well designed or might there be weaknesses?
-Is there a large sample size?
-Are the relevant variables controlled.
-How accurate are the measurement tools and/or techniques?
Calculate BMI using the formula
Formula: weight in Kg/(height in meter)^2
Determine BMI using a monogram
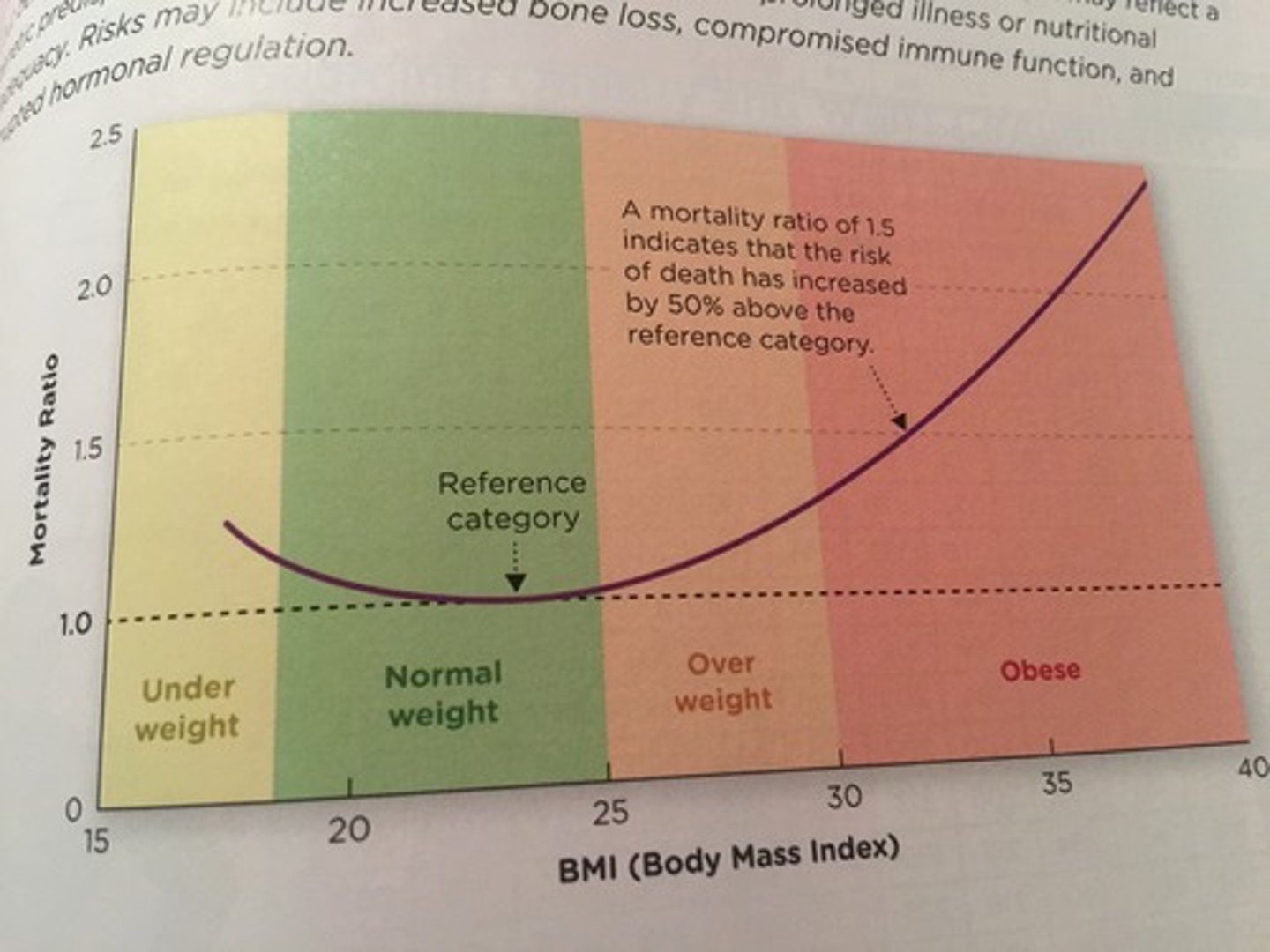
Outline the effects of a BMI that is too high or too low.
High BMI can indicate possible health problems such as: type II diabetes, Gallstone, hypertension or heart disease.
Low BMI can indicate malnourishment.
However, BMI has limitations such as it doesn't not take into account fat to muscle ratio, and a healthy person can occur obese when they're not, and vice versa.
Explain the energy storage of lipids compared to that of carbohydrates
Lipids:
-slow release of energy
-able to store chemical energy for long-term
-has 2x the amount of energy per gram compared to carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates:
•Fast release of energy
•Quick and short-term energy
•1/2 of energy per grams compared to lipids.
Explain how a calorimeter can be used to determine the energy content in food.
-Calorimeters can be used to determine the energy content of food by burning the food and measuring by temperature of water in calorimeter.
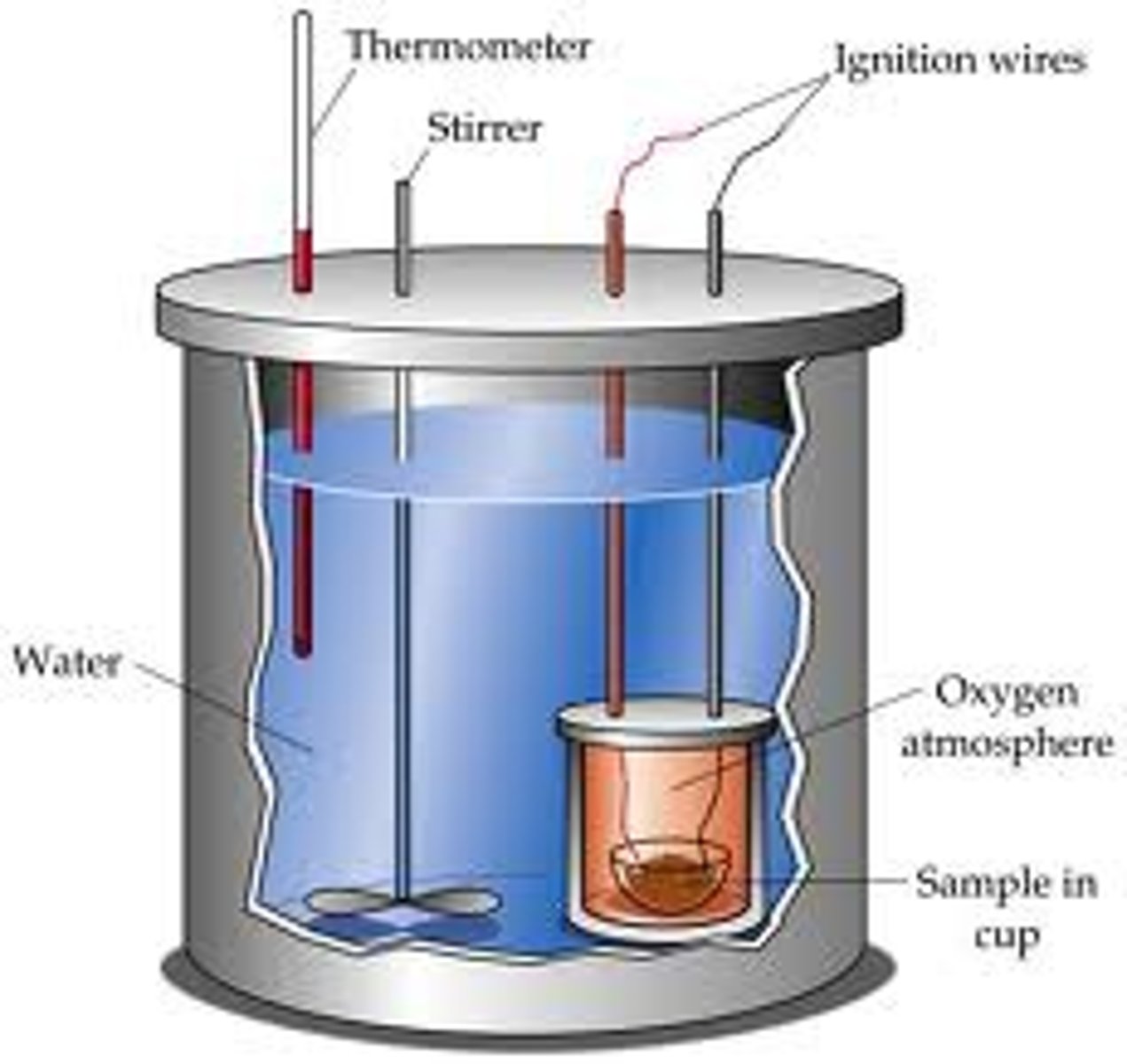
Calculate the energy content of a food sample using calorimetry data.
Calories: mass of water • specific heat of water (cal/g^oc) • change of water temp.
What is the function of alpha and beta-glucose?
Primary source of energy for living organisms that is naturally occurring or found in fruits.
What is the function of ribose and deoxyribose?
Important component required for DNA, RNA, ATP. Building block for nucleic acid.
What is the function of Maltose?
Energy for germinating seeds. Helps with digestion.
What is the function of sucrose?
Transport form of sugar by plants and harvested by humans for food.
What is the function of lactose?
Found in milk and it is a sugar that nourish baby animals.
What is the function of amylose, amylopectin and glycogen?
Energy storage
Distinguish between the structures of amylose and amylopectin.
Both are polymers of alpha glucose. Amylose has no branching whilst amylopectin has branching every 30 glucose. This results in the structural spiraling of amylose.
What is the function and structure of cellulose?
It is a polymer of beta-glucose, which makes it ribbon-like. Beta-glucose flips as they create bonds. It's function is to provide structure.
Why is cis-fats good for you?
It decreases LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, whilst increasing HDL (good cholesterols) which decreases risks of heart diseases.
State the energy per 1 gram for carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
17kJ, 38 kJ, 17 kJ
Name 2 examples of steroids
Cholesterol and testerone
Draw a cis-unsaturated fatty acid and a trans-unsaturated fatty acid.
What is glucose and fructose?
Sucrose
What is glucose and galactose?
Lactose
Name whether these are mono-, di- or polysaccharides: fructose, ribose, cellulose, glucose, sucrose, glycogen, starch and maltose.
mono, mono, poly, mono, di, poly, poly, di
Briefly describe the process of the hydrolysis reaction for carbohydrates.
When water is added, the shared O atom would bond with one of the H from water, and the left over OH group would join the other carbohydrate that didn't take the O with it.
What is the function of lipids?
Nutrition, storage, water proofing, thermal insulation, hormones, protection, cell membrane, water repellant.
Name examples of steroids.
Cholesterol, cortlsol, testosterone, aldosterone
Where is the energy stored?
Liver, fats.