motivational and humanistic theories
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
According to Murray’s motivational theory, what is a need, a motive, and environmental press?
Need: Physiochemical (biological) force in the brain that organizes perception/action to transform unsatisfying situation to more satisfying + strongest need → weakest need creates hierarchy of needs that characterizes personality
need is not consciously experienced
Need Types:
Viscerogenic (physiological; food, water) vs. Psychogenic (psychological; achievement)
Adience (approach; food) vs. Abience (avoidance; harm avoidance)
Reactive (react to a trigger; harm avoidance) vs. Proactive (spontaneous; food)
Motive: elicited by a need, directs thought and behaviour toward or away from objects, people, and goals
consciously felt
Environmental Press: environmental factor that increases or decreases motive expression and thus influences thought and behaviour
How are needs measured?
Thematic Apperception Test + picture story exercise:
present participants w/ images of ambiguous situations + assume participants ‘project’ their needs when interpreting
‘what has led up to event, what is happening, what characters are thinking/feeling, what is outcome’
Assesses implicit needs + dominant needs (Participants’ dominant needs form the defining characteristics of their personality)
Personality Research Form:
self-report measure
assesses explicit (self-attributed) needs
Multi-Motive Grid:
Combines both
projective test: images of ambiguous situations
self report measure that assesses the big 3 needs (achievement, affiliation, power)
assesses implicit and explicit needs
What are the primary assumptions of humanistic theories of personality?
Assumptions:
Humans have free will + can determine the course of events in their lives
Unlike behaviorist theories, evolutionary theories (sex differences are hardwired, biological deterministic), or Freuds psychoanalytic theory (id impulses drive behavior unconsciously and out of control)
Conscious experience is the primary determinant of behaviour and personality
More like nonanalytic than psychoanalytic
Humans are inherently good and innately strive for growth and improvement
According to Rogers’ person-centered theory, what is a fully functioning person?
roger’s person centred theory:
all motives are characterized by one ‘master motives’ which determines all other needs
The actualizing tendency (pattern of the active process of life - directional tendency toward growth) - can be thwarted and warped, but not removed
fully functioning person:
is engaged in self-actualization (as a process, not an “end state”)
exhibits personality characteristics that facilitate self- actualization:
openness to experience (doesn’t distort experience, sees reality as it is)
existential living (time competence)
organismic trust (trust of ones judgement; inner direction)
experiential freedom (autonomy in actions)
creativity (adapt to circumstance)
harmoniousness in relationships with others (minimal conflict, accept others as they are)
How does an individual become a fully functioning person?
becomes fully functioning if they:
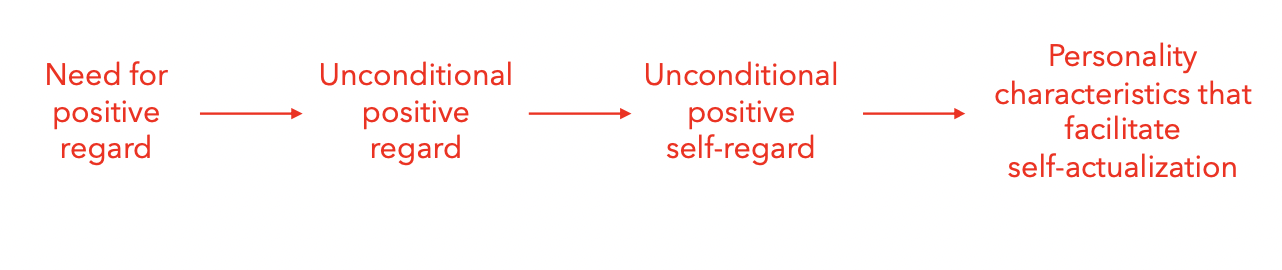
experience unconditional positive regard
Acceptance, love, and affection that are given without conditions
An individual who experiences unconditional positive regard in childhood develops unconditional positive self- regard: An ability to view the self favorably under all conditions
An individual with unconditional positive self-regard accepts personal experiences, trusts their judgments, and acts in accordance with their desires and wishes
an individual with unconditional positive self-regard develops personality characteristics that facilitate self-actualization
What needs did Maslow identify in his theory of self- actualization?
5 conative (basic) needs
physiological needs: biological maintenance (e.g. food, oxygen, sleep, water)
only needs that can be fully satisfied, even though they will re-occur
for survial
safety needs: physical security (e.g. protection, shelter, stability)
in chaotic environments, anxiety will occur
belonging needs: affiliation (e.g. friendships)
esteem needs: public recognition and self-esteem (e.g. prestige, status, self-respect)
avoids a sense of inferiority (can link to erikson conflict: industry v inferiority)
self-actualization needs: self-fulfillment (e.g. pursuit of intrinsic motivations)
for avoiding meta pathology (restlessness, frustration, and disintegration)
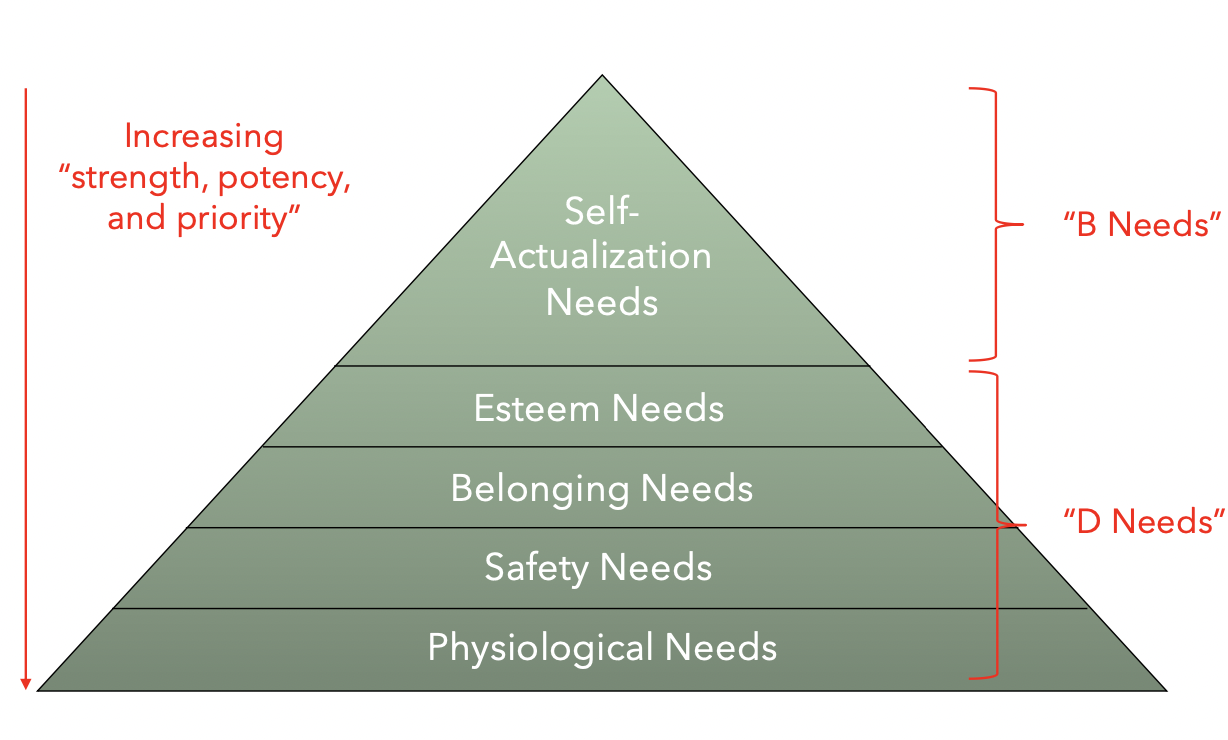
D needs (deficiency needs): belonging, safety, physiological
B needs (being needs): needs linked to growth; esteem, self actualization
A needs do not have to be fully met in order to begin meeting needs of a higher order
Is self-actualization universally achieved?
only 1-2% of NAmericans ahceive self-actualization due to
sociocultural constraints
self constraints (self-imposed restraint, dear of success)
measures of self-actualization:
characteristics of self-actualization scale
personal orientation inventory
short-index of self-actualization
note: Contemporary research suggests that self actualization is not associated with age, unlike what Maslow suggested
What therapeutic approach did Rogers develop to help people become fully functioning
Client-centered therapy (aka nondirective therapy)
the therapist creates an environment in which the patient is able to solve their own problem
idea behind it:
Argued that all individuals experience incongruity between self-concept and actual experience. This generates anxiety.
To minimize anxiety, individuals attempt to reduce the incongruities b/w self-concept and experience
Fully functioning person does this by incorporating new experience into their self-concept
Non-fully functioning people reduce anxiety through the use of defence mechanisms
Exemplifies an inaccurate perception of reality, undermining openness to experience (one of rogers 6 key attributes of aa fully functioning person)
not effective for ppl who are:
Collectivistic cultures (unconditional positive self regard is not a corner stone to psychological and social functioning, instead self criticism)
Authoritarian
Unable to verbalize emotions (alexithymia - cant connect to or communicate their emotions)
Low in tolerance for ambiguity
effective for:
Depression, bipolar, GAD, PTSD
What is happiness
Positive psychologists study “positive subjective experience, positive individual traits, and positive institutions to improve quality of life and prevent pathologies”
Positive psychologists distinguish between two forms of happiness
Hedonic happiness:
High satisfaction with life, high positive affect, low negative affect
Eudaimonic happiness:
Self-actualization (e.g., fulfillment of potential, pursuit of intrinsic motivations, experience of meaning in life)
Although theoretically distinct, hedonic and eudaimonic happiness are highly positively correlated (up to .7)
Most focus on H and assume that being high in H will mean high in E
What factors predict happiness?
three broad sources of happiness:
set point (abt 50%)
a level of happiness we return to despite deviaitons in our lives (after abt 3 months) → hedonic treadmill/ hedonic adaptation of habituating to life circumstances (exceptions are long term unemployment + bereavement
hertiability= .4 and .5 (i.e. ‘trait’ happiness being stable)
circumstance (abt 10%)
(income, educational attainment, martial status, parental status, religiousity, health)
income improves H until 60K threshold. then limited increases after
negatively correlated with parenthood
intentional activity (abt 40%)
connecting with others, physical activity, ‘savouring’, learning, giving
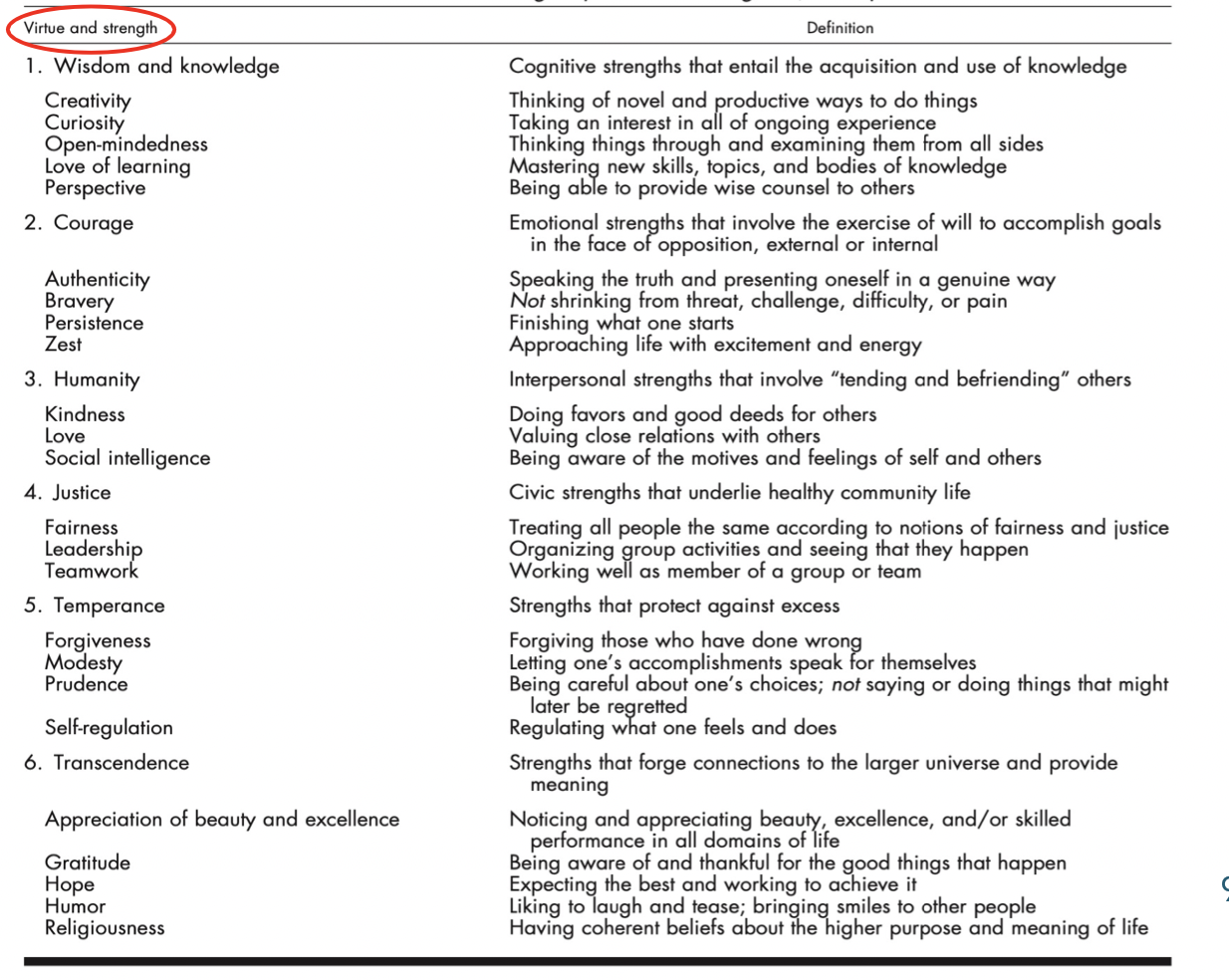
character strengths
6 virtues:
wisdom and knowledge
courage
humanity
justice
termpance
transcendence
identify defense mechanisms that are used by individuals who are not fully functioning
denial and distortion
describe the three conditions that are necessary for therapeutic change in client-centered therapy
Therapist congruence
Therapist is genuine and authentic in their therapeutic interactions with the client
Unconditional positive regard
Communicate that there are no conditions of worth, no accepting/rejection actions
Empathetic understanding
Communicated by restating comments and feelings shared by the patient (validation)
Allows client to listen to their own remarks, clarify them for the therapist, reflect and solve their own problems
distinguish between implicit and explicit (i.e., self- attributed) needs
implicit needs
unconscious motivational tendencies that influence spontaneous behavior and long-term goals.
influence naturalistic behavior in ambiguous or unstructured situations (e.g., creative tasks, social interactions)
Rooted in early developmental experiences
explicit needs
Conscious motivational values that reflect how people see themselves and what they believe motivates them.
Influence deliberate choices and responses in structured settings (e.g., interviews, academic tasks)
Shaped by social norms and self-concept
discuss common criticisms of measures of needs
TAT + picture story exercise
Poor inter-rater reliability (high subjectivity for the scoring)
Internal consistency across 20 cards is very poor (they say its to be expected because of the pressure they feel not to be redundant, creative, variable images)
personality research form:
Does not assess implicit (unconscious) needs
multi-motive grid
constrained to only 3 needs
distinguish between conative and neurotic needs
neurotic needs:
contribute to a dysfunctional lifestyle, foster stagnation,
contribute to pathology
are reactive; develop in an attempt to compensate for unsatisfied conative needs
identify the correlates of self-actualization
Time competence (live in the present, can connect past present and future for a sense of time continuity)
Inner directed (motivated by own principles motivations and morals )
Internal locus of control (feel that they are in control of outcomes of their life) and a higher environmental mastery (they can change their environment)
Higher A,C, E, O
Lower N
Higher school/ workplace satisfaction
Higher self-acceptance and esteem
Higher purpose in life and life satisfaction
More self-transcendent experience
define Jonah complex
fear of realizing one’s full potential, of becoming the best version of oneself, and the anxiety or avoidance that can arise when we come close to profound growth, success, or creative achievement.
fear of the demands^
review the conditions that are necessary to become a non-fully functioning person
an individual does not become fully functioning if they experience conditional positive regard:
Acceptance, love, and affection that are given under conditions (i.e., conditions of worth)
An individual who experiences conditions of worth in childhood develops conditional positive self-regard:
An inability to view the self favorably under all conditions
An individual with conditional positive self-regard
distorts personal experiences, disregards their judgments, and acts in accordance with the desires and wishes of othersAccordingly, an individual with conditional positive self- regard develops personality characteristics that hinder self-actualization
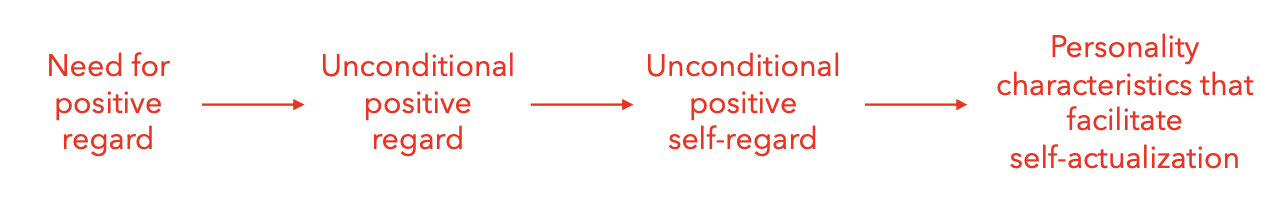
define conditions of worth
Acceptance, love, and affection that are given under conditions
identify personality characteristics that are related to happiness
Five-factor model → extraverion, neuroticism (negatively related with hedonic affect), agreeablility (connect w/ other people), O (related to intelligence, learning), C (eudaimonic happiness/ meaning
optimism → dispositional optimism (trait stable across situations, biological determined), optimisitc attributional style (can be used, not biological)
Attribute success to internal stable and global factors
Attribute failure to external, unstable, specific factors
autotelic personalty → characterised by pursuit of intrinsic motivations
demonstrates curiosity, inherent enjoyment of activities, narrow concentration, need to achieve, persistence, cooperation, and independence
define autotelic personality and flow
autotelic personalty → characterised by pursuit of intrinsic motivations
demonstrates curiosity, inherent enjoyment of activities, narrow concentration, need to achieve, persistence, cooperation, and independence
reports frequent occurrence of ‘flow’
intense involvement in moment-to-
moment activity, focused attention, optimal functioning → Associated with clear goals, a sense of control, distortion of time, and balance between challenge and skill
describe virtues and character strengths
consider research findings on interventions to enhance happiness
participants received individualzed feedback abt their top 5 (signature) strengths + asked to use one of these top strengths in a new and different way every day for one week
result: long-term improvement occured participants in the using signature strengths in a new way condition
participants in the truncated identifying signature strengths condition showed an effect only at the immediate posttest but not thereafter.”
explain how signature strengths may be used to increase happiness
must use signature strengths in a new way
must implement them, not just identify them
factors that may account for self-actualization in the absence of lower-order need satisfaction
prior need satisfaction (a temporal factor)
perceived competence to satisfy lower-order needs (a cognitive factor
percieved competences emerges from (a) material competence (in due time) and (b) cognitive competence