Physics - Forces and Motion + Energy Resources and Transfers
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Energy Store
Energy Transfer
Kinetic
Moving objects have energy in their kinetic store
Gravitational
Objects gain energy in their gravitational potential store when they are lifted through a gravitational field
Elastic
Objects have energy in their elastic potential store if they are stretched, squashed or bent
Magnetic
Magnetic materials interacting with each other have energy in their magnetic store
Electrostatic
Objects with charge (like electrons and protons) interacting with one another have energy in their electrostatic store
Chemical
Chemical reactions transfer energy into or away from a substance’s chemical store
Nuclear
Atomic nuclei release energy from their nuclear store during nuclear reactions
Thermal
All objects have energy in their thermal store, the hotter the object, the more energy it has in this store
Mechanical Working
When a force acts on an object (eg. pulling, pushing, squashing, stretching)
Electrical Working
A charge moving through a potential difference (eg. current)
Heating (by particles)
Energy is transferred from a hotter object to a colder one (eg. conduction)
(Heating by) radiation
Energy transferred by electromagnetic waves
Principle of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred from one store to another
Formula for Efficiency
efficiency = (useful energy output/total energy input) x100
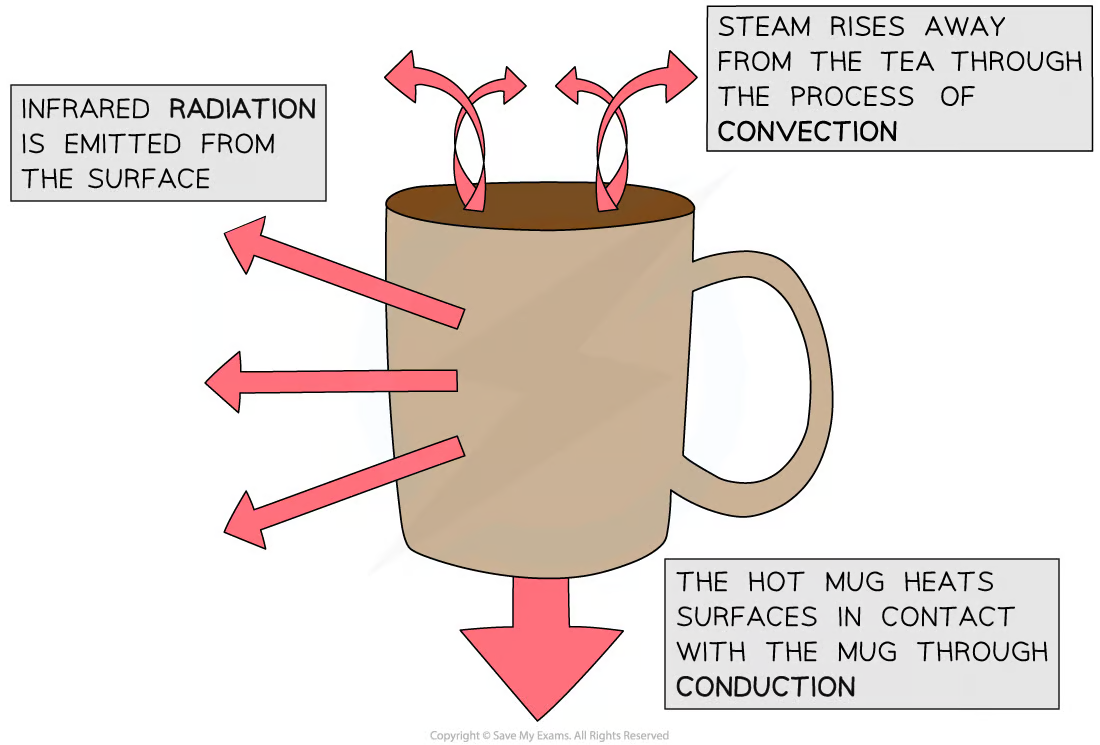
Conduction
The main method of energy transfer by heating in solids
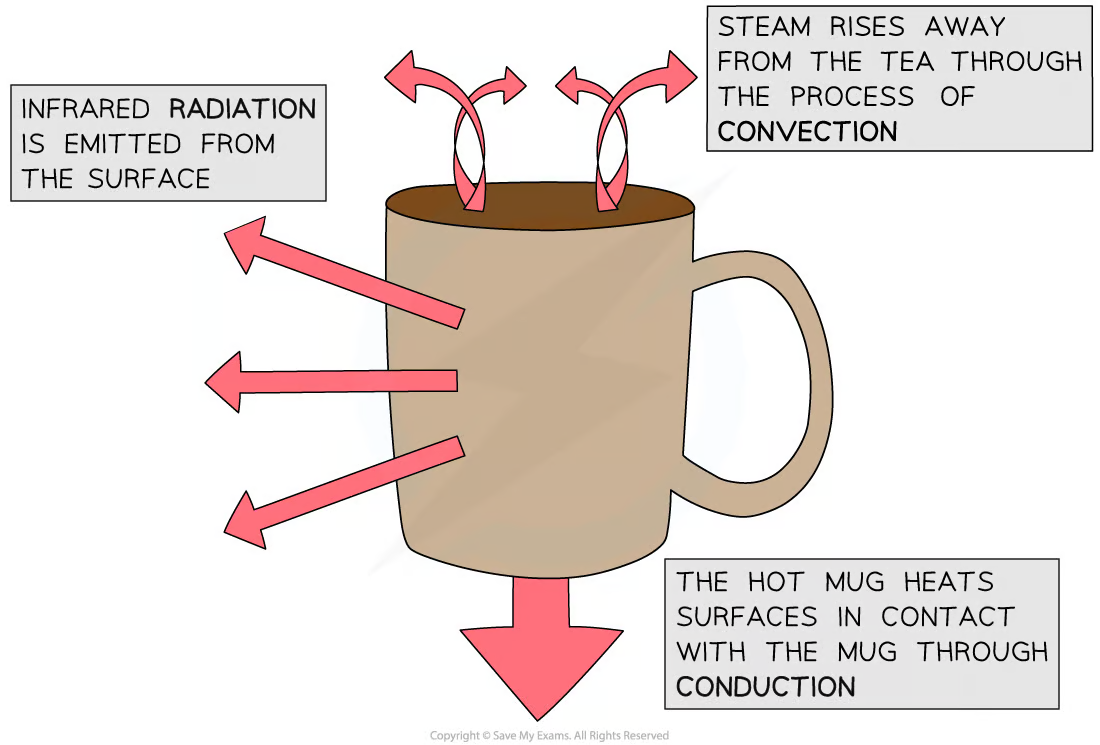
Convection
The main way that thermal energy is transferred through liquids and gases
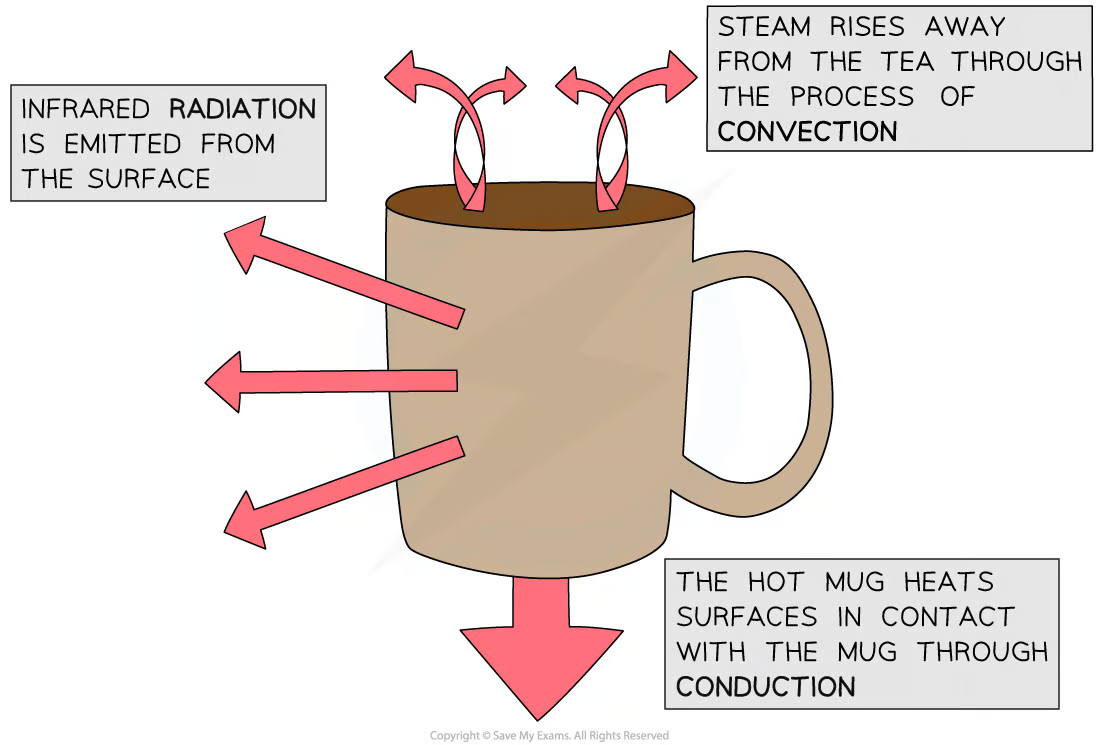
Radiation
All bodies (objects), no matter what temperature, emit infrared radiation
The hotter object, the more infrared radiation it radiates in a given time
Effect of Black on absorbing and emitting ability
Absorbing: Good
Emitting: Good
Effect of Dull/dark surfaces on absorbing and emitting ability
Absorbing: Reasonable
Emitting: Reasonable
Effect of White on absorbing and emitting ability
Absorbing: Poor
Emitting: Poor
Effect of Shiny surfaces on absorbing and emitting ability
Absorbing: Very poor
Emitting: Very poor
Ways of reducing unwanted Conduction
Use materials of low conductivity (INSULATORS)
Ways of reducing unwanted Convection
Prevent convection currents from forming
The fluid must be prevented from moving
Insulation
Reduces thermal conductivity
The more dense the insulator the more conduction can occur - in denser material, the particles are closer together so they can transfer energy to one another more easily
The thicker the material the better it will insulate
Energy Resources
Large stores of energy that can be used to generate electricity and heat homes and businesses
Energy transfers involved in generating electricity using Wind and Water
A turbine is turned which turns a generator which generates electricity
Energy in the kinetic store of the flowing wind/water is transferred to the kinetic store of the turbine, then to the kinetic store of the generator and transferred electrically to the National Grid
Energy transfers involved in generating electricity using Fossil Fuels
Can be combusted to heat water and the steam produced can be used to turn turbines
Energy from the chemical store of the fuel is transferred to the thermal storeof the water, which is then transferred to the kinetic store of the turbine, and then transferred to the kinetic storeof the generator and then transferred electrically to the National Grid
Energy transfers involved in generating electricity using Nuclear Power
Can also be used to heat water to produce steam to turn turbines
Nuclear store of fuel → thermal store of water → kinetic store of turbine → kinetic store of generator
Energy transfers involved in generating electricity using Geothermal Resources
Geothermal energy is another way to produce the steam that turns the turbines
Water is pumped down to the hot rocks and returns through a fissure as steam
Advantages and disadvantages of methods of large-scale electricity production from various renewable and non-renewable resource
Energy resource | Renewable? | Advantages | Disadvantages |
Fossil fuels | No | Reliable. Can produce large amounts of energy consistently. Can respond to changes in demand. | Produces carbon dioxide (CO2) which contribute to global warming, and sulphur dioxide, which causes acid rain |
Nuclear | No | Reliable. Produces large amounts of energy consistently. Produces no pollution or CO2. Large amounts of energy are produced from small amounts of fuel. | Produces radioactive waste that takes thousands of years to decay and must be safely disposed of. Nuclear power stations are expensive to build and maintain, and take many years to build. Can not be turned on and off quickly so cannot respond to changes in demand. |
Bio fuels | Yes | The CO2released from combustion is balanced by the CO2 absorbed in photosynthesis, so could be considered carbon neutral | Land and resources used to grow crops are needed to grow food crops |
Wind | Yes | Produces no pollution or CO2. Are cheap to build and maintain | Non-reliable. Only generate electricity when the wind is blowing in a certain direction. Some people consider them visual pollution (they spoil the view) |
Hydroelectric | Yes | Reliable. Can respond to meet changes in demand. No pollution or CO2 produced (unless a pump is used to return the water as this uses fossil fuels). | Can involve flooding large areas to build reservoirs which destroys habitats and displaces wildlife |
Tidal | Yes | Tides are very predictable, so energy can be produced at regular intervals | Few suitable locations (estuaries). Can harm aquatic life and disrupt shipping |
Geothermal | Yes | Reliable | Not many suitable locations. Can release methane (a greenhouse gas) in the extraction process. |
Solar | Yes | Produces no pollution or greenhouse gases. Good for electricity production in remote areas. |
Newton’s 1st Law
An object will remain at a constant velocity unless acted upon by a net external force
Newton’s 3rd Law
For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
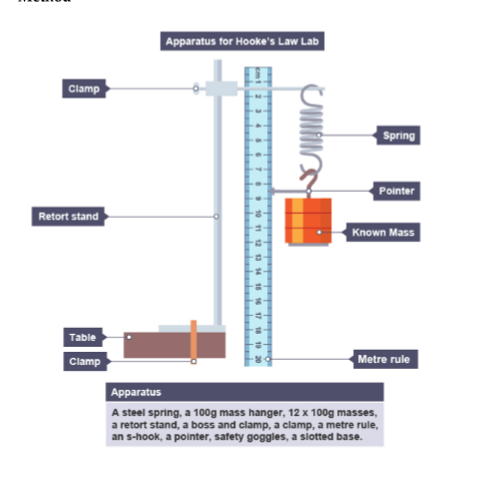
Hooke’s Law
force = spring constant x extension (f=kx)
Practical: Investigate how extension varies with applied force for helical springs, metal wires and rubber bands
What is the initial linear region of a force-extension graph associated with?
Hooke’s Law
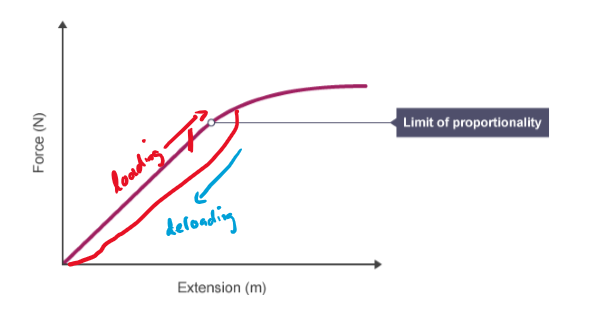
Definition of: Elastic Behaviour
The ability of an object to recover to its original shape after the forces causing deformation have been removed
Safety Features Associated with Momentum
In a car:
Seatbelts: brings the person to rest more slowly
Airbags: brings the person to rest more slowly
Crumple zones: A crumple zone increases the time-taken to come to rest for a given change in momentum here since F = Δp/t, the force decreases.
Definition of: Power
The rate of transfer of energy or the rate of doing work
Where does the weight of a body act through?
It’s centre of gravity
Principle of Moments
If an object is balanced, the total clockwise moment about a pivot is equal to the total anticlockwise moment about that pivot.
Equation Linking: Momentum, Mass and Velocity
p(kgm/s) = mv: p(momentum), m(mass), v(velocity)
Equation Linking: Force, Change in Momentum and Time Taken
F= Δp/t
Equation Linking: Moment of Force, Force and Distance to Pivot
M = Fd
Equation Linking: Work Done, Force and Distance Moved in Direction of Force
W = Fd
Formula for Calculating: Kinetic Energy
KE = 1/2 mv2
Formula for Calculating: Change in GPE
GPE = mgh: m(mass), g(gravitational field strength), h(height)
Formula for Calculating: Power
P = W/t
Formula for Calculating: Efficiency
efficiency = useful energy transferred/ total energy input