Topic 9; Innovation and markets
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
pioneering strategy
being the first to market a new innovation
imitative strategy
developing products that are simialr to already existing products that are succesful
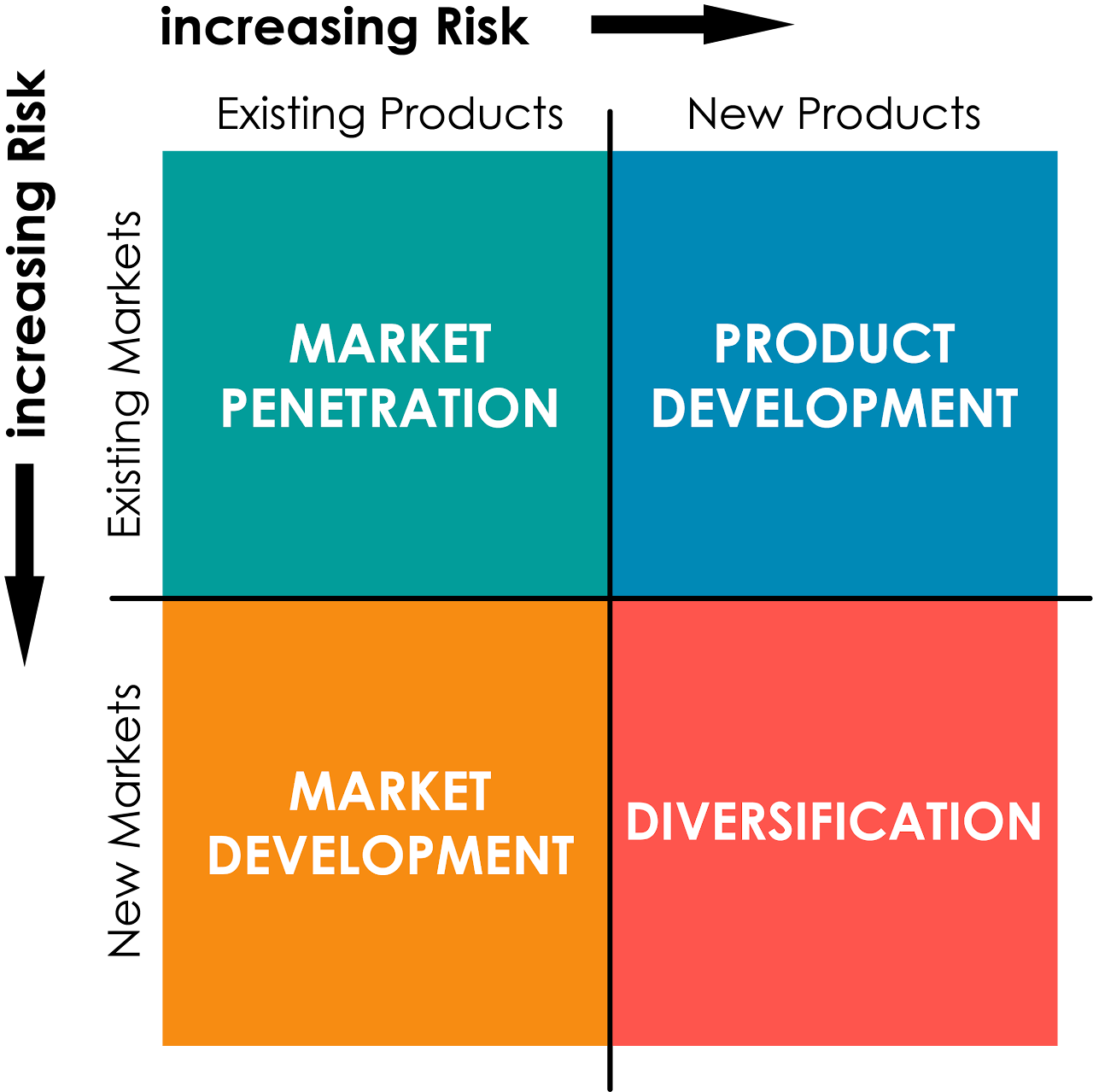
market penetration
finding more clients ot increasing sales on an already existing product; - aimed toincrease market shares.
product development
making new and updated products which are aimed at the company’s existing clientelle
market development
finding new ways to apply existing products to gain more market shares.
product diversification
selling new products in new markets (risky)
ansoff matrix
a tool that offers 4 product and market growth strategies for a business.
Corporate Social Responsbilty (CSR)
a form of self regulation for development through economic, social and environmental areas.
market sector
a broader way to categorize industries
geographical sectors
focus on value, culture and charachteristics of purchasing power of clients in a region
client-based sectors
focusing purely on the consumer
products in sectors
finding out which products fall under whhich sector to determine marketing strategy
market segements
the division of markets into smaller categories which target customers on shared charachteristics
categories of market segments
geographic, demographic, psychographic, and behavioural
product family
a group of products which similar classification criteria.
the marketing mix
4 factors identifies through market research to help the designer understand brief requirements of a product.
4 P’s of the marketing mix
product, place, price, promotion
pricing penetration
pricing products at very low prices to gain more market share.
competitor based pricing
depending on the market, prices are set based on competition; either low, equal or high.
psychological pricing
prices appear cheaper than they actually are to influence consumer perception (199 instead of 200)
cost plus pricing
adding a percentage on a product detemined by the cost of production (a product cost 100 to make, add 20% to sell for 120 and make a profit)
product line pricing
selling different versions of the same product based on quality or features at different prices to attract more customer segments.
demand pricing
starting with a high price for early buyers and gradually lowing the price to attract more consumers.
above the line promotion
using paid branding methods such as tv, radio or billboards.
below the line promotion
cheaper and more targetted branding methods such as PR, emails or packaging.
product standardisation
having the same (uniform) characteristics of a product.
gov/trading-area standardisation
products must meet specific national requirements to be legally sold in countries.
industry-wide standardisation
companies often adopt similar standards to ensure safety, quality and fair competition among the market.
component standardisation
using common parts like in tyres and USB’s to ensure convinience for consumers.
efficency and performance standardisation
the gov. creates laws to limit harmful production strategies to make products more efficent and environmentally friendly.
trigger products
products that achieve basic needs and tasks
incremental products
products that have add-ons to the basic achieving product to make it more innovative.
market research
systemic gathering of data about consumers using statistical data.
it is timely and constly but vital for product ideas
literature market research strategy
using consumer reports, newspapers, magazines to conduct research.
user trial market research strategy
observing how people use the product and gaining feedback
expert appraisal market research strategy
relying on the skill of an expert in the field
user research market research strategy
obtaining user responses through surveys or interviews.
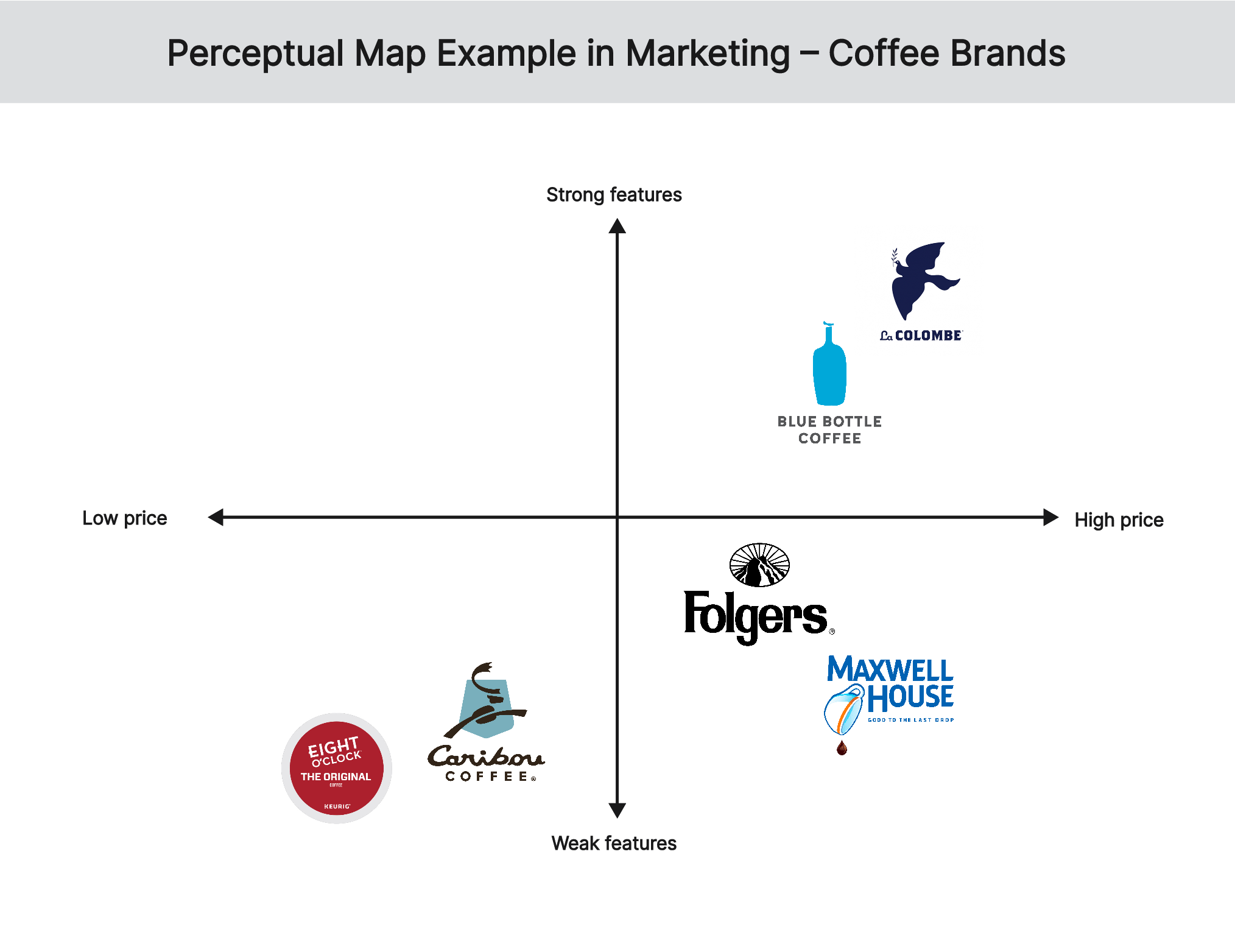
perceptual mapping
a graphical tool to visually comapre how products appear across markets, relative to competitors.
environmental scanning
analyzing trends to identify threats and opportunities for a business
innovative consumer response (2.5%)
take high risks and are first to adopt new innovations
early adopter consumer response (13.5%)
quickly mebraces new innovations and influence others to do so as well.
early majority consumer response (34%)
rely on feedback from early adopters and adopt innovations after careful consideration
late majority consumer response (34%)
adopt only after there is proof on the goodness of the innovation
laggard consumer response (16%)
they avoid risk as they prefer tradition and thus are the very last to adopt innovations.
green motivated consumer response (10%)
commited greens are strongly pro-environment and are prepared to sacrifice economically for natures benefit.
bright green consumer response (34%)
believe that tech and social innovation are the best paths to achieve sustainability .
green hypocrite consumer response (26%)
promote a green image publicly but dont follow through genuine action
green ignorant consumer response (19%)
not interested in environmental issues and dont make sacrifices for sustainability
dull green consumer response (11%)
support environmental ideas but are less consistent in practicing green behaviour.
brand loyalty
when a consumer commits to a brand and repeats purchases.
hard core loyals
those who buy only from the one brand all the time
split loyals
those who are loyal to 2-3 brands
shifting loyals
those who move from one brand to another
switchers
those who aren’t loyal and always looking for a bargain
trademark
a legally protected recognizable sign which identifies a brand.
registered design
a legally protected visual feature of a product