Cytoskeleton & cell mobility
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture notes 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
How does cytoskeleton affect cellular function?
It affects attachment, migration, mitosis, shape and function. It affects tissue formation and shape
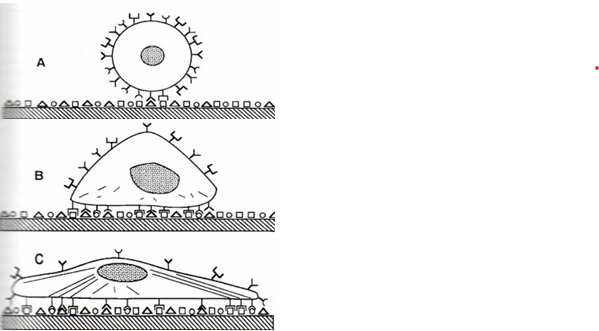
Why is it important to understand cytoskeletal function and formation?
By understanding it, we can possibly help manipulate cells through tissue engineering.
What is neurite extension?
It is the process by which projections from a nerve cell, called neurites, grow and elongate to form connections in the nervous system.
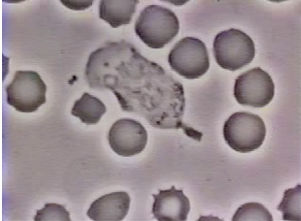
Describe this picture
Neutrophil ‘chasing’ a bacteria

Describe this picture
Neurite extensions from a neuron in culture. Such cellular extensions are made possible by cytoskeletal polymerization/ extension.
What is neutrophil?
It is a type of white blood cell that is the first to arrive at the site of an infection or injury to fight off pathogens like bacteria and fungi.
Function of cytoskeleton
Actin filaments (microfilaments), Intermediate filaments, Microtubules, Intracellular transport (‘railroad”), Contractility/mobility (phagocytosis, migration, etc) and Spatial organisation.
What are the several ways to study cytoskeleton?
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Light / fluorescence imaging coupled with antibodies to stain proteins of interest
Mutant cells with over / under-expression of proteins associated
Why are microtubles tubular and hollow?
They have 13 protofilaments (rows of globular proteins) that are held together noncavalenty.