AP Psychology - Biological Bases of Behavior, AP Psychology: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
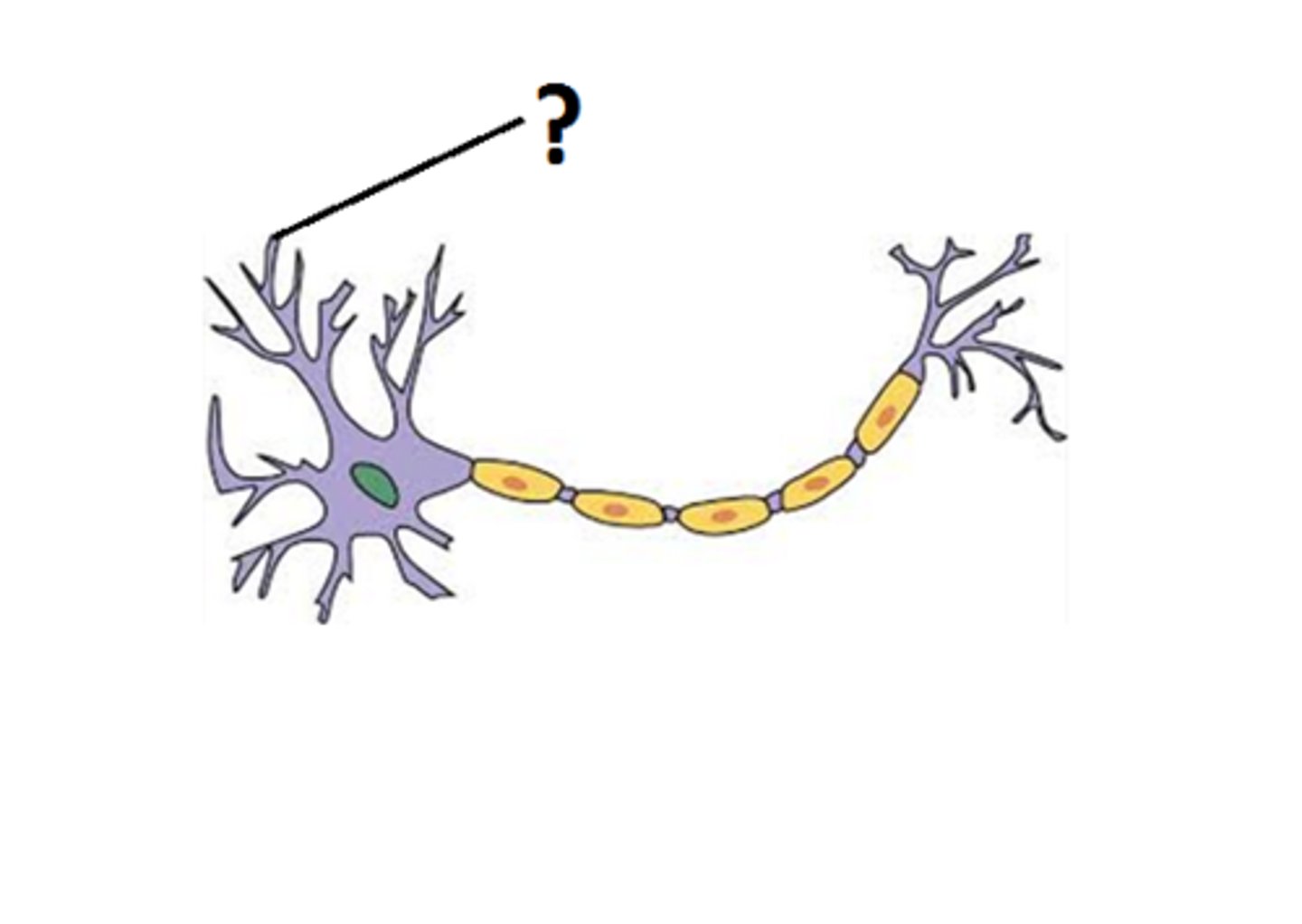
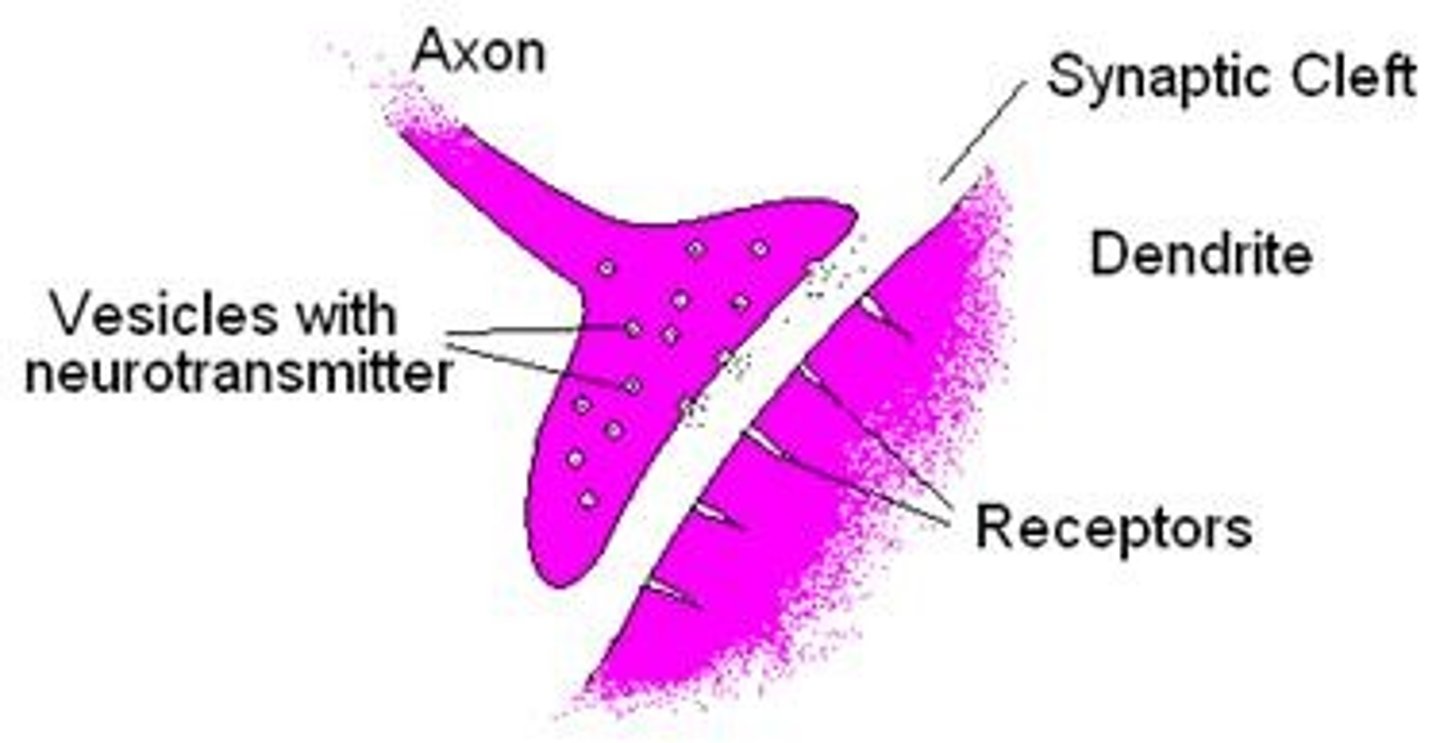
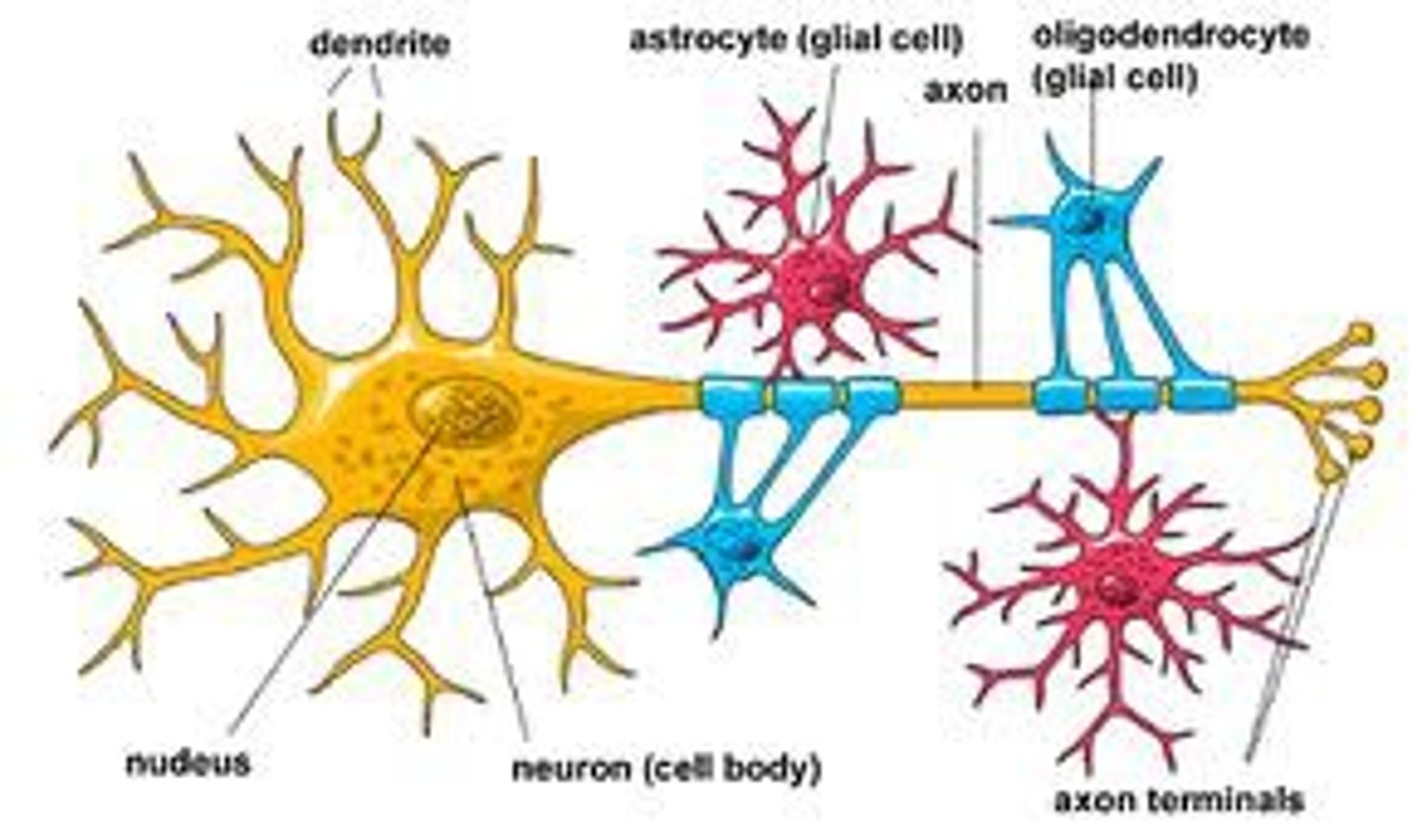
Dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
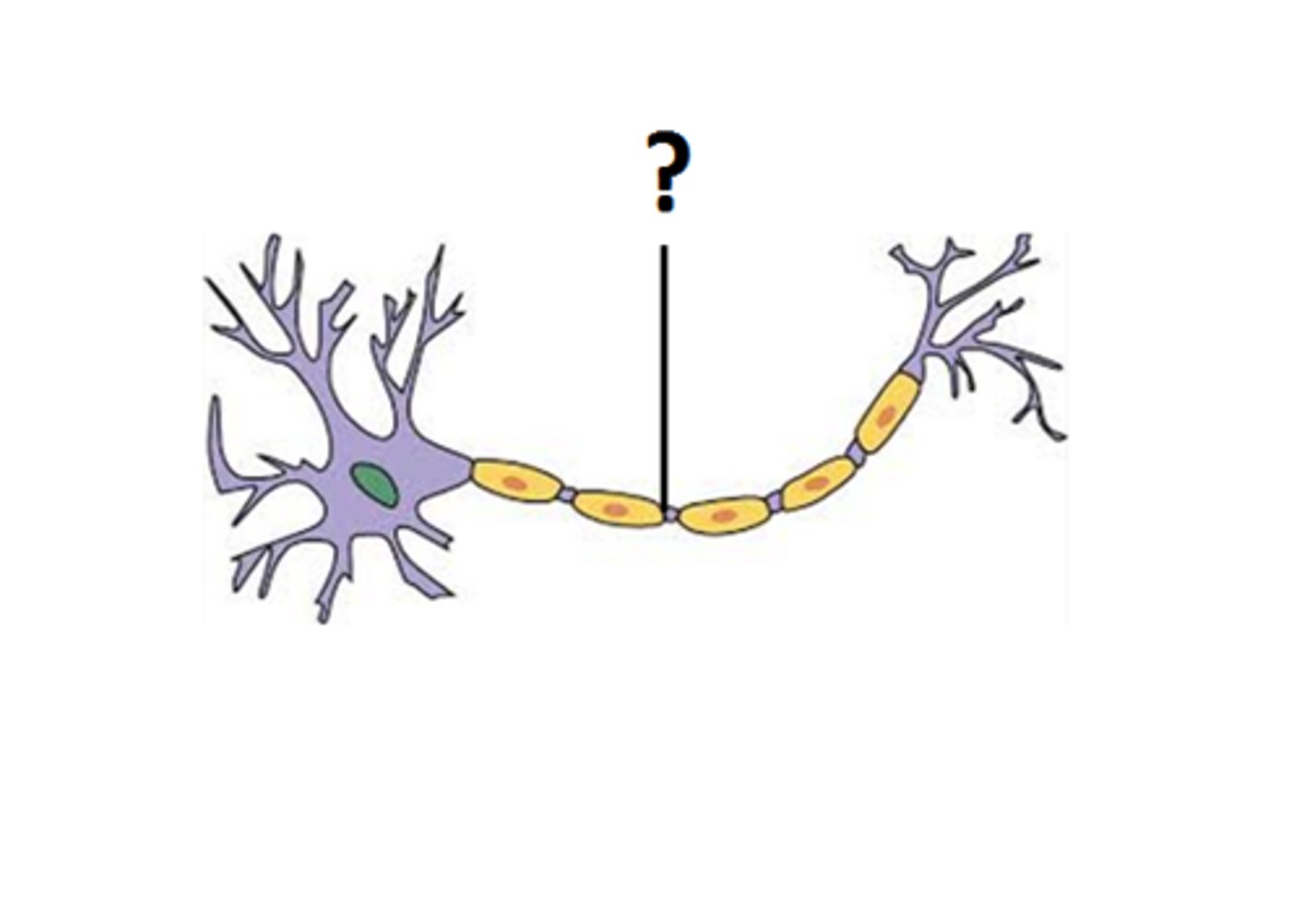
Axon
A threadlike extension of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
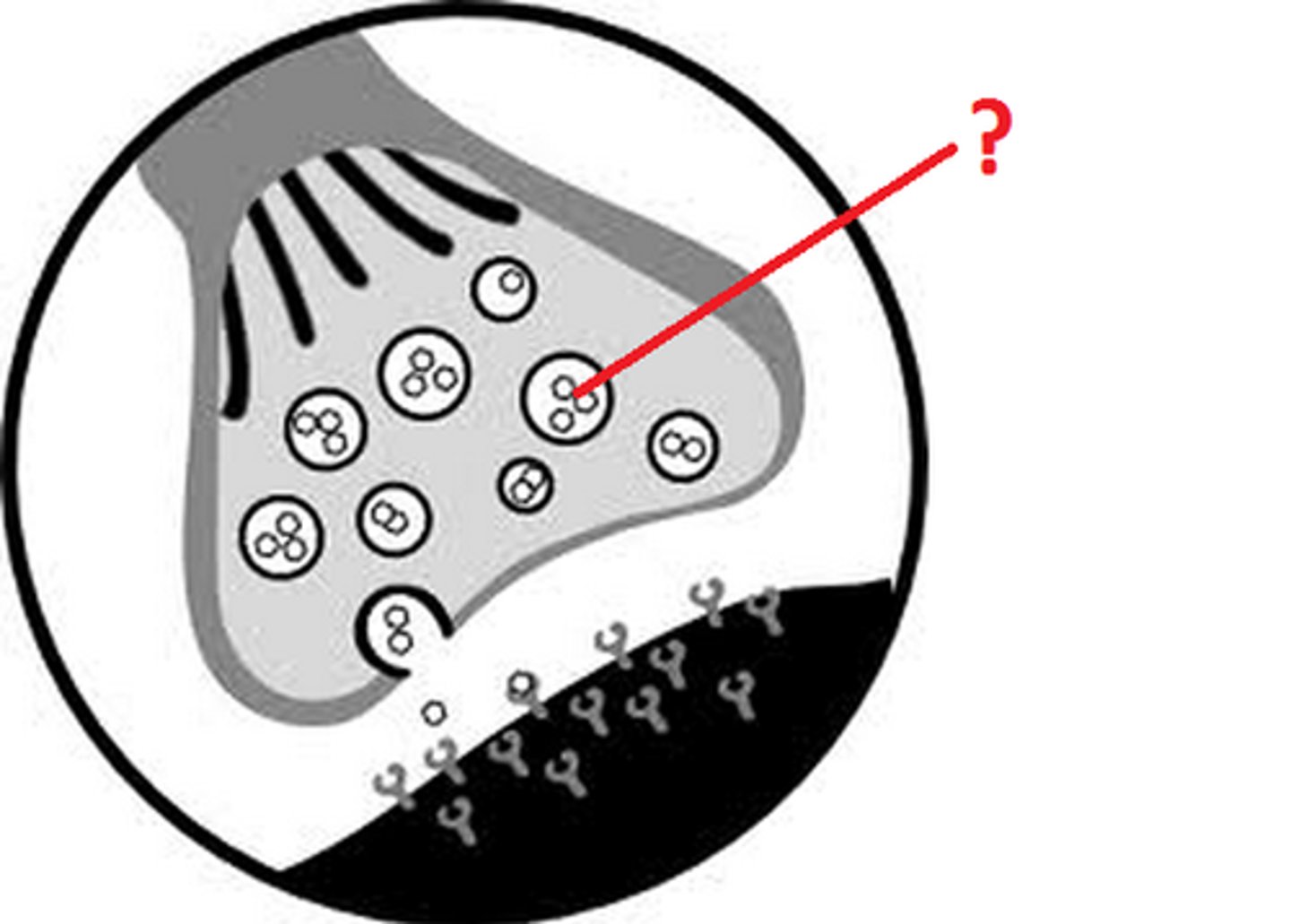
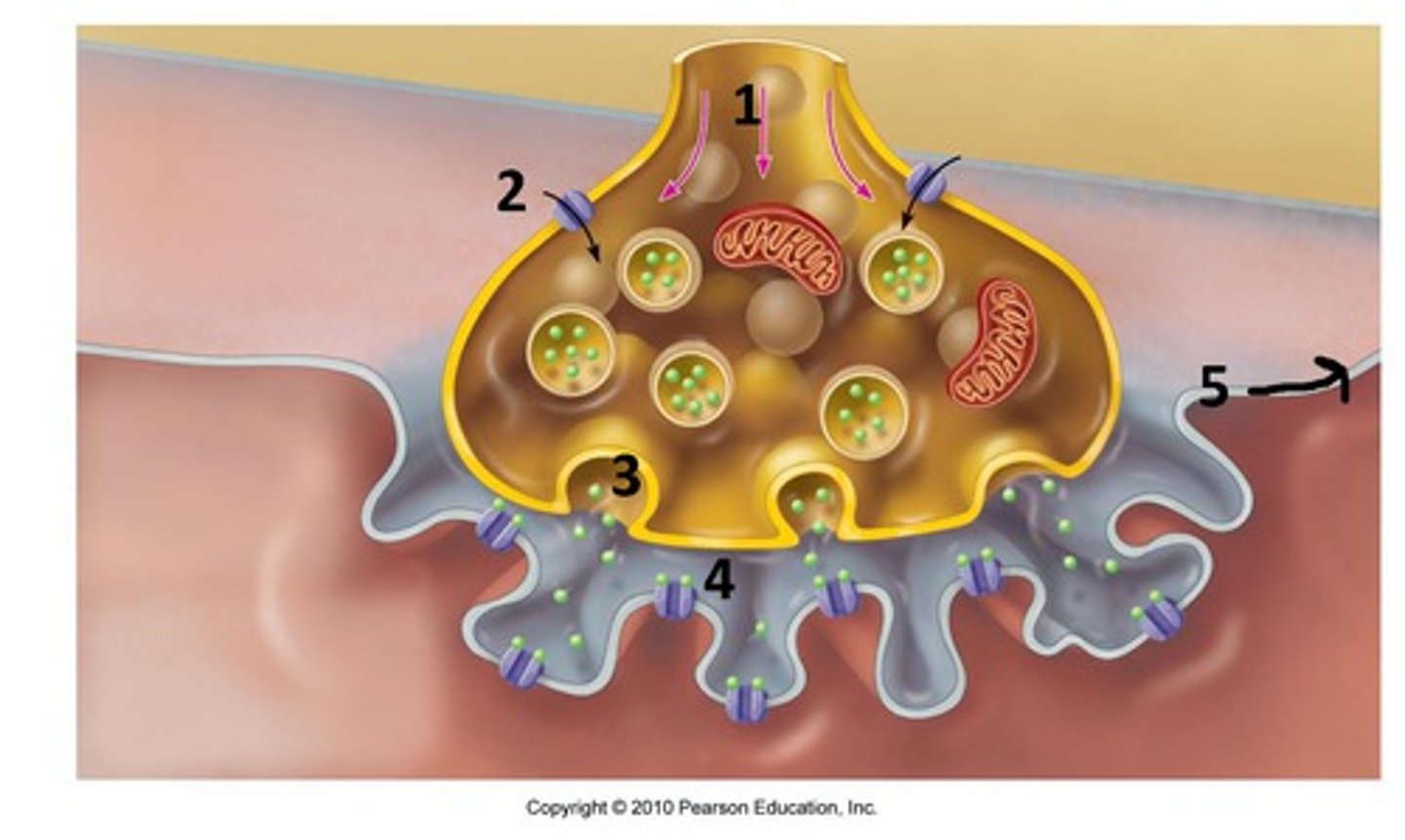
Synaptic vesicles
Tiny pouches or sacs in the axon terminals that contain chemicals called neurotransmitters.
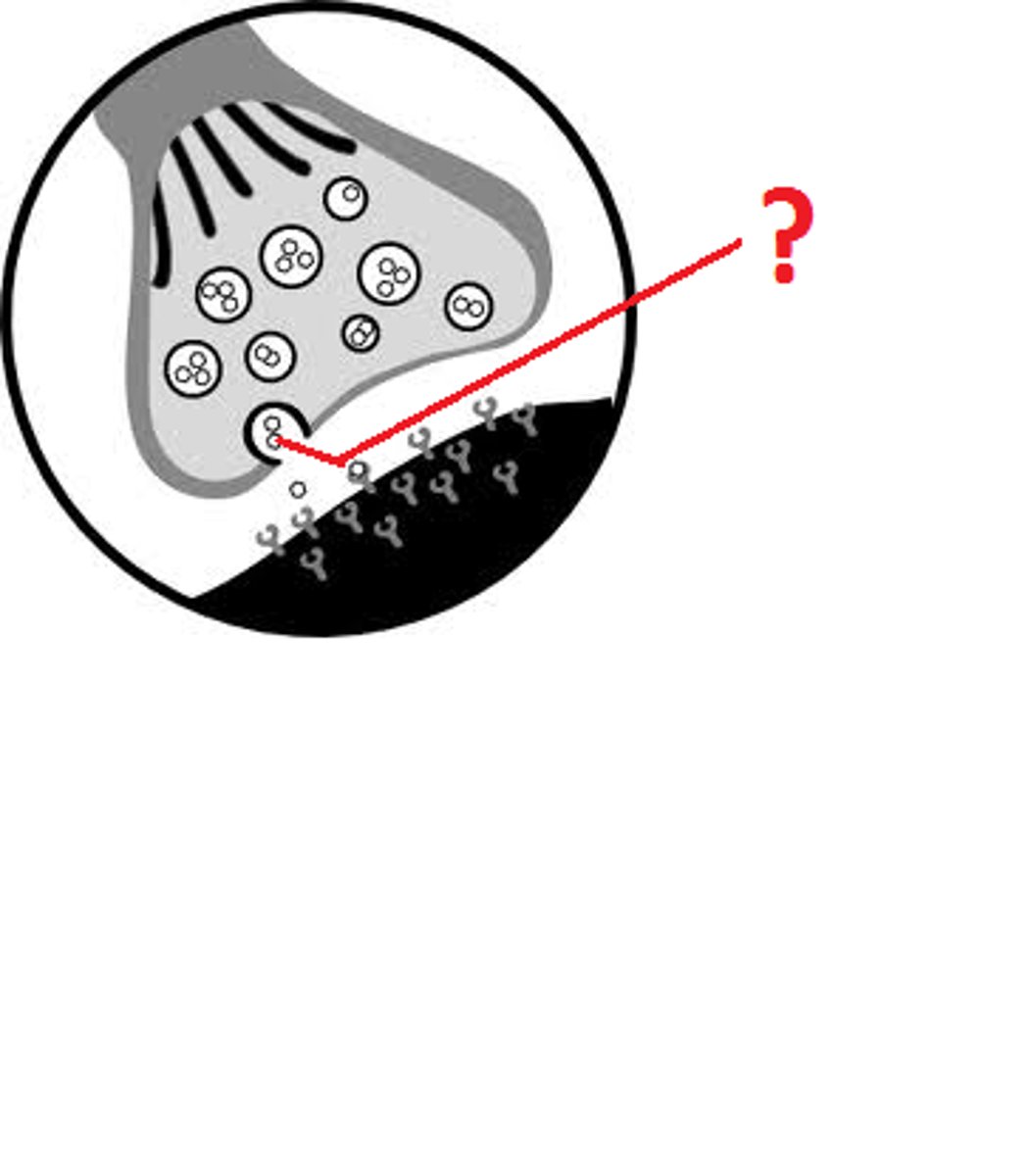
Neurotransmitter
Chemical messenger specialized for communication from neuron to neuron
Synapse
Space between two connecting neurons through which messages are transmitted chemically
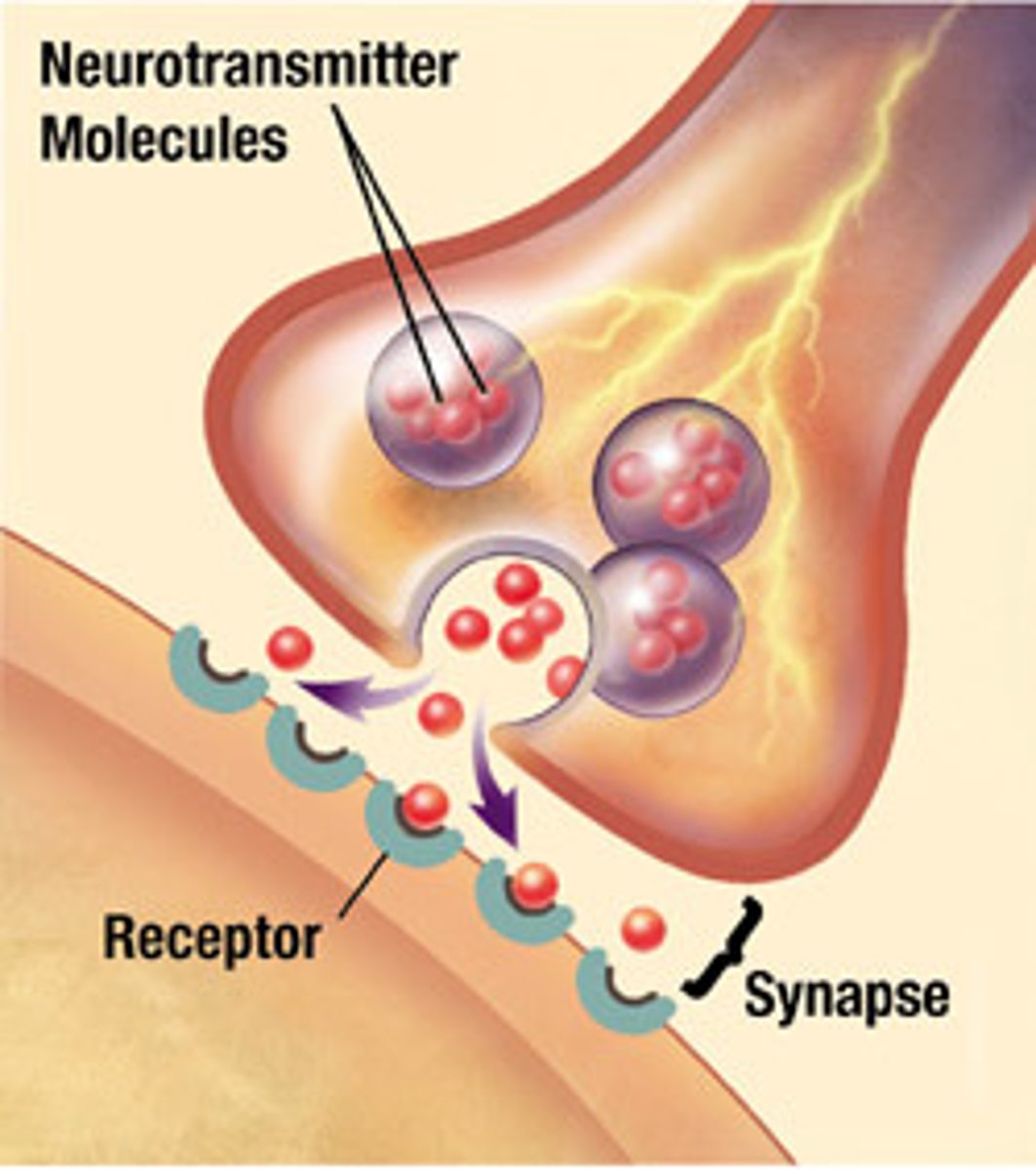
Synaptic cleft
A gap into which neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal
Glial cell
Cell in nervous system that plays a role in the formation of myelin and the blood-brain barrier, responds to injury, removes debris, and enhances learning and memory
Threshold
Membrane potential necessary to trigger an action potential.
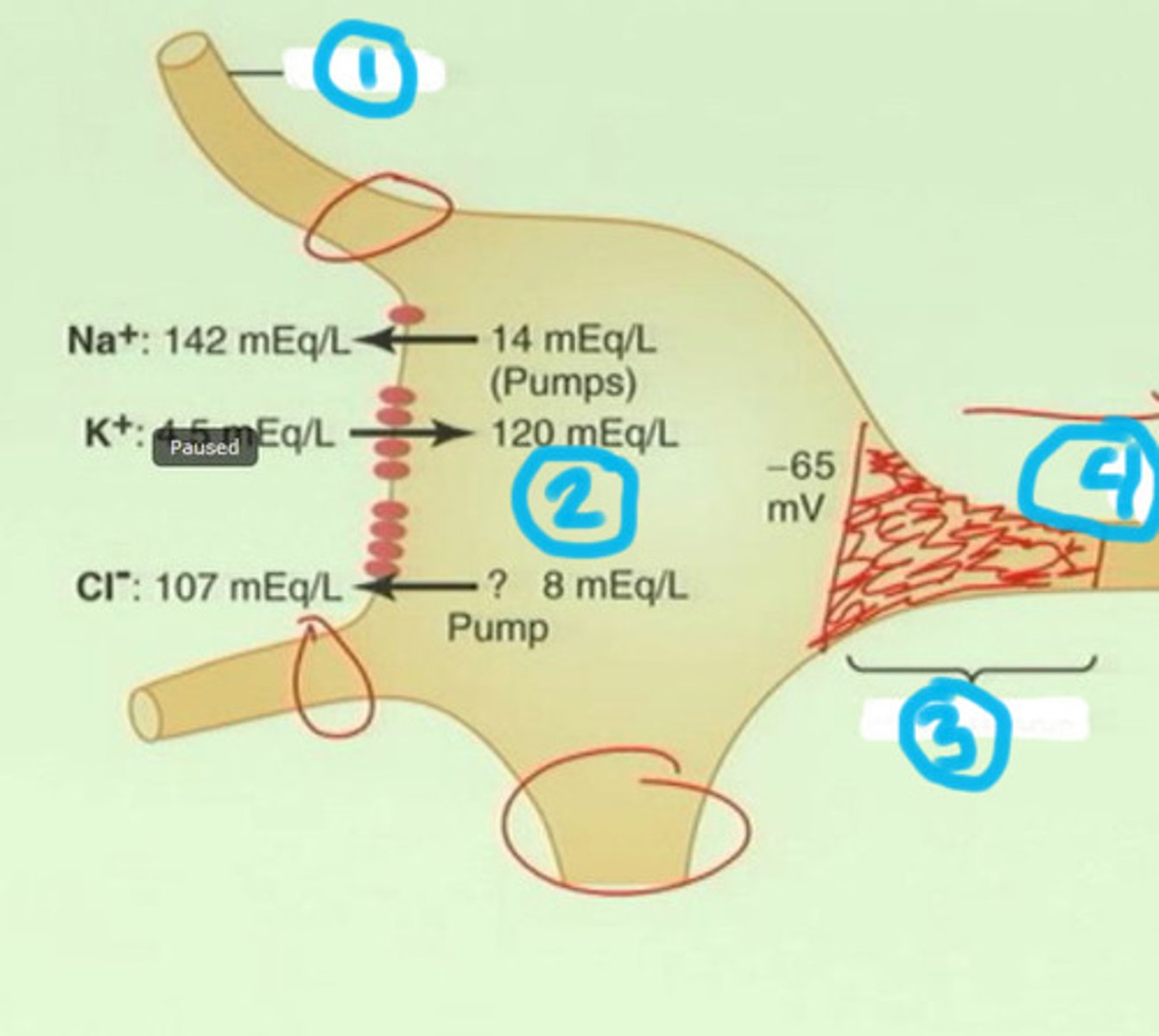
Absolute refractory period
Cardiac cells have not completely repolarized
Receptor site
Locations on a receptor neuron into which a specific neurotransmitter fits like a key into a lock.
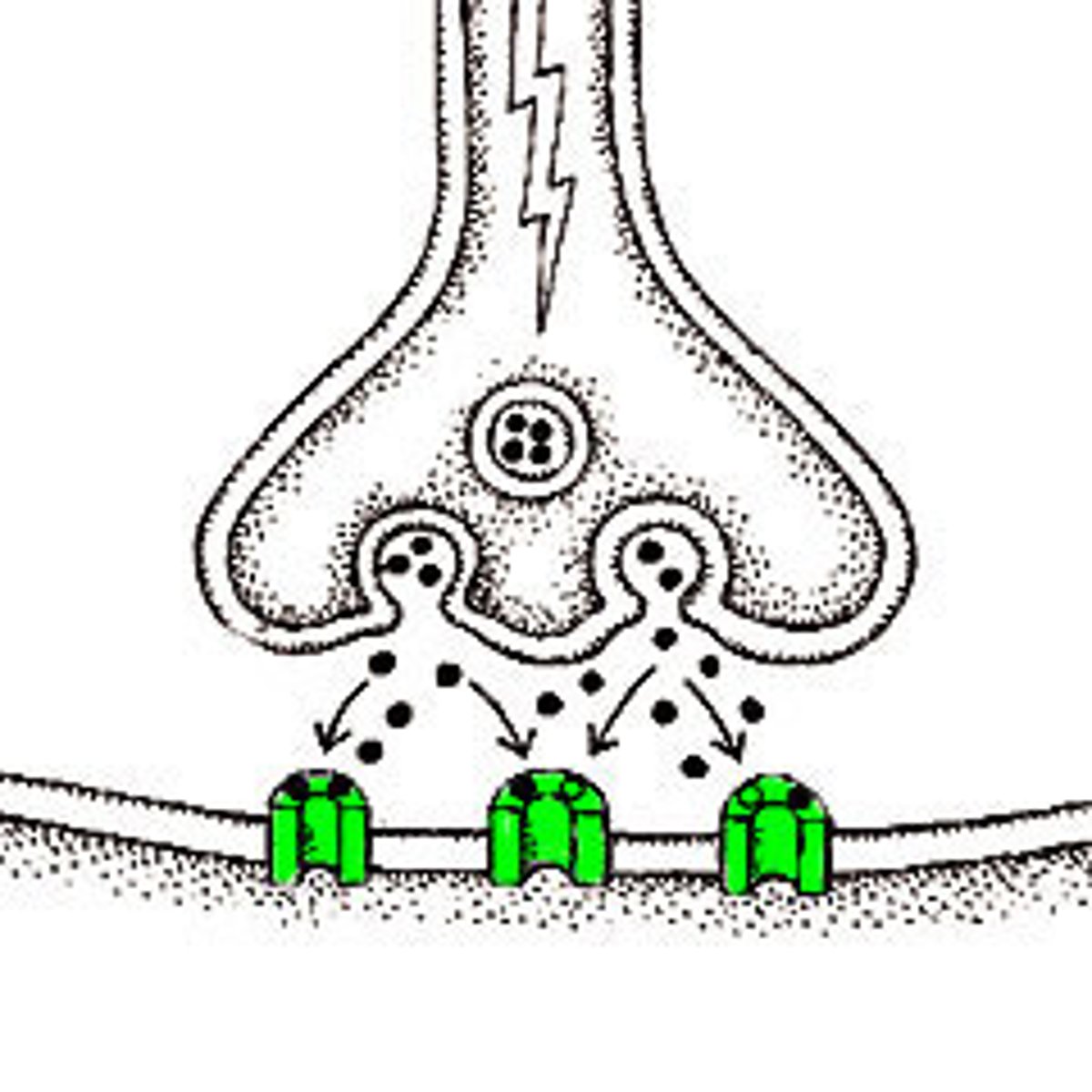
Reuptake
A neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
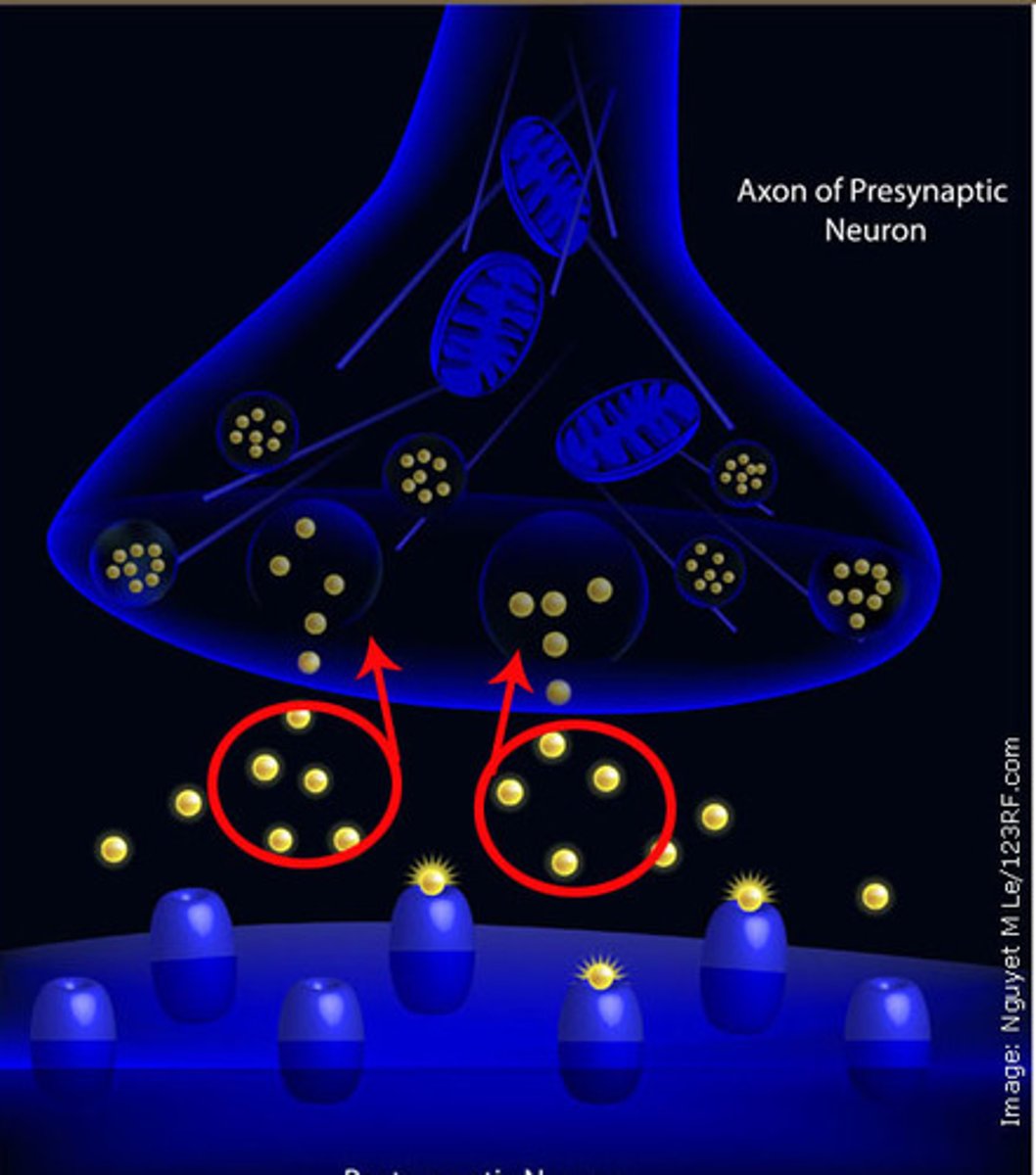
Endorphin
"Morphine within" - natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
Plasticity
Ability of brain tissue to modify itself and take on new functions.

Neurogenesis
Creation of new neurons in the adult brain

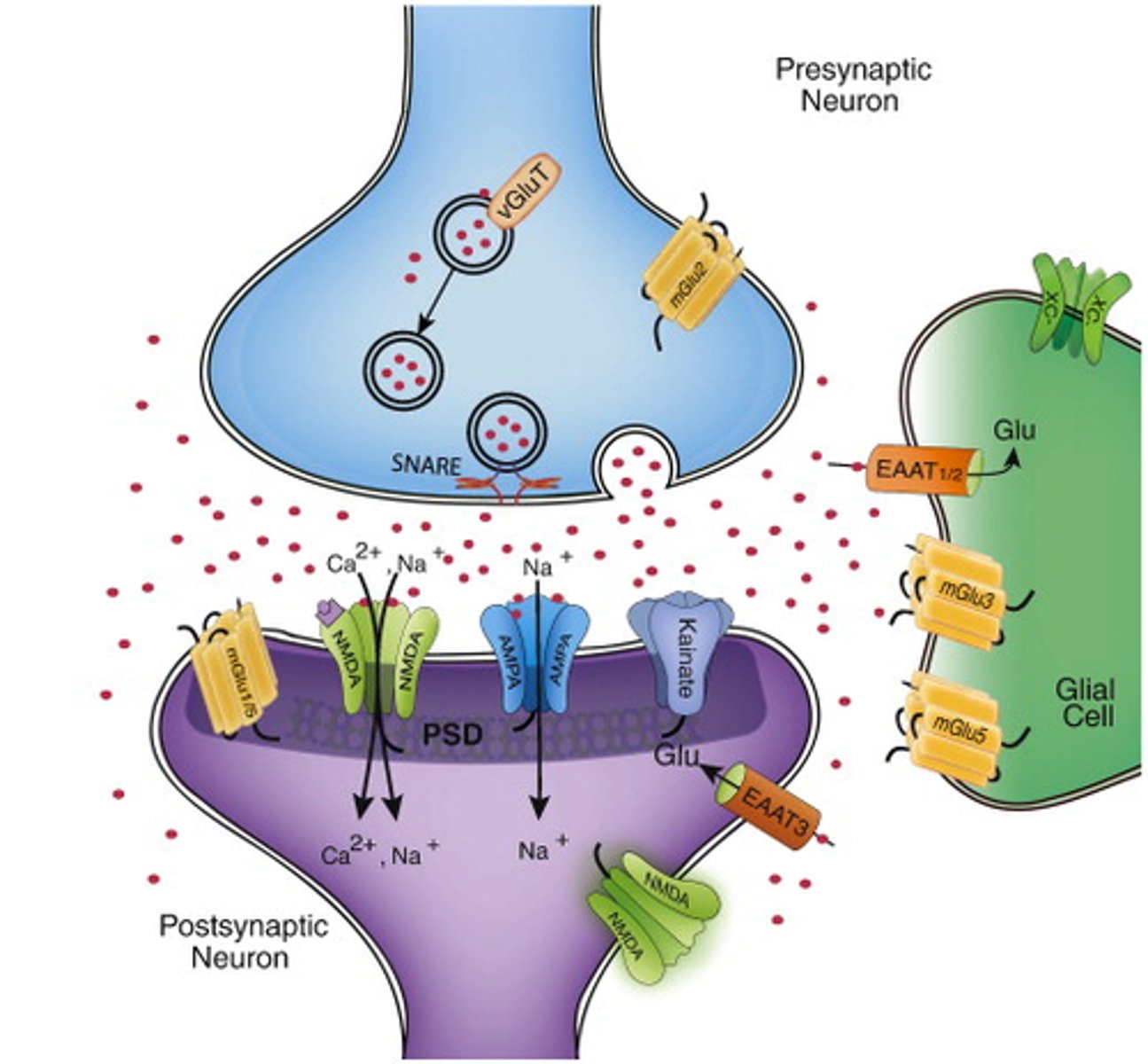
Glutamate
Main excitatory neurotransmitter in the nervous system; participates in relay of sensory information and learning
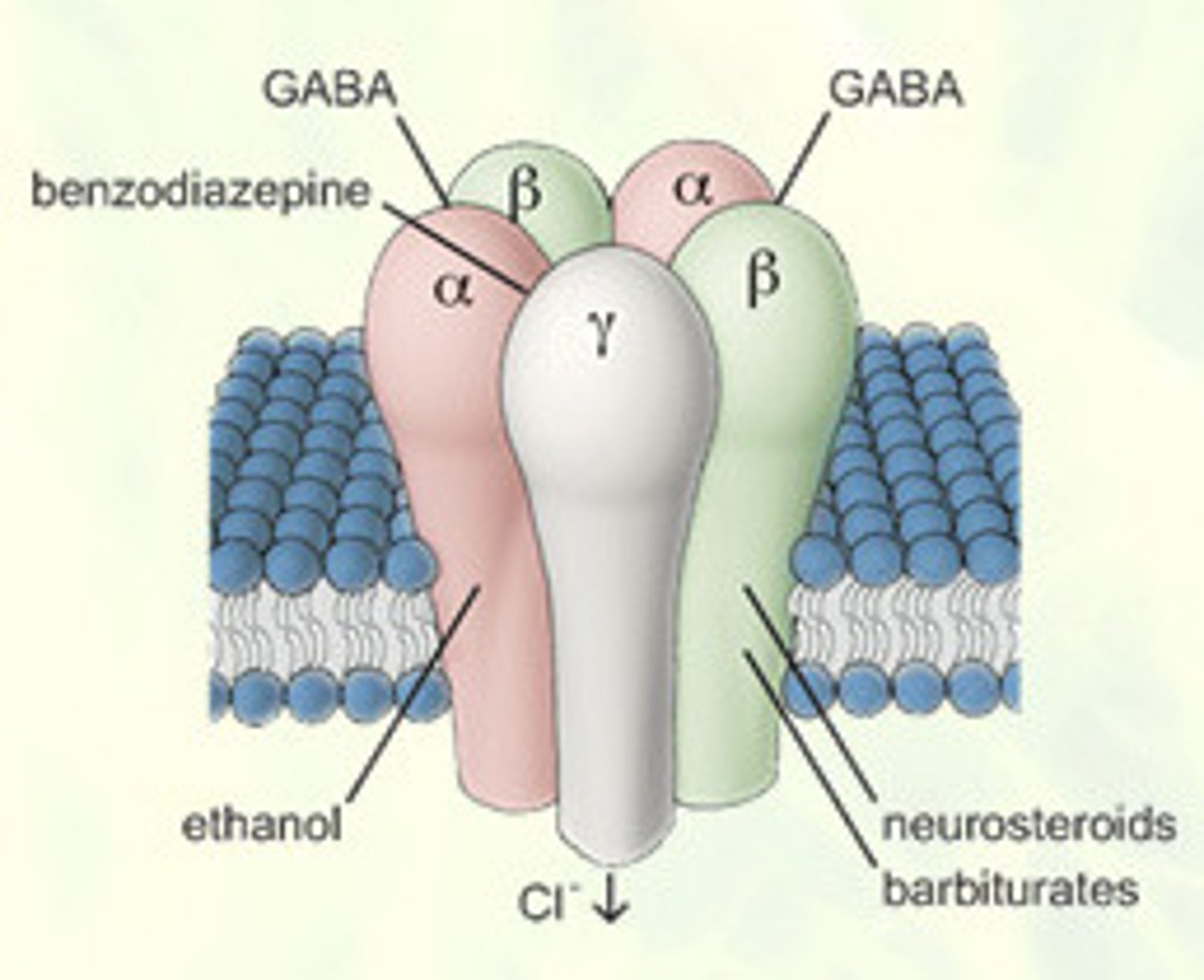
Gamma-aminobutyricvcacidc(GABA)
Main inhibitory neurotransmitter in the nervous system
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Muscle contraction (PNS) Cortical arousal (CNS)
Norepinephrine (NE)
Brain arousal and other functions like mood, hunger, and sleep

Dopamine
Motor function and pleasure reward

Serotonin
Mood and temperature regulation, happiness
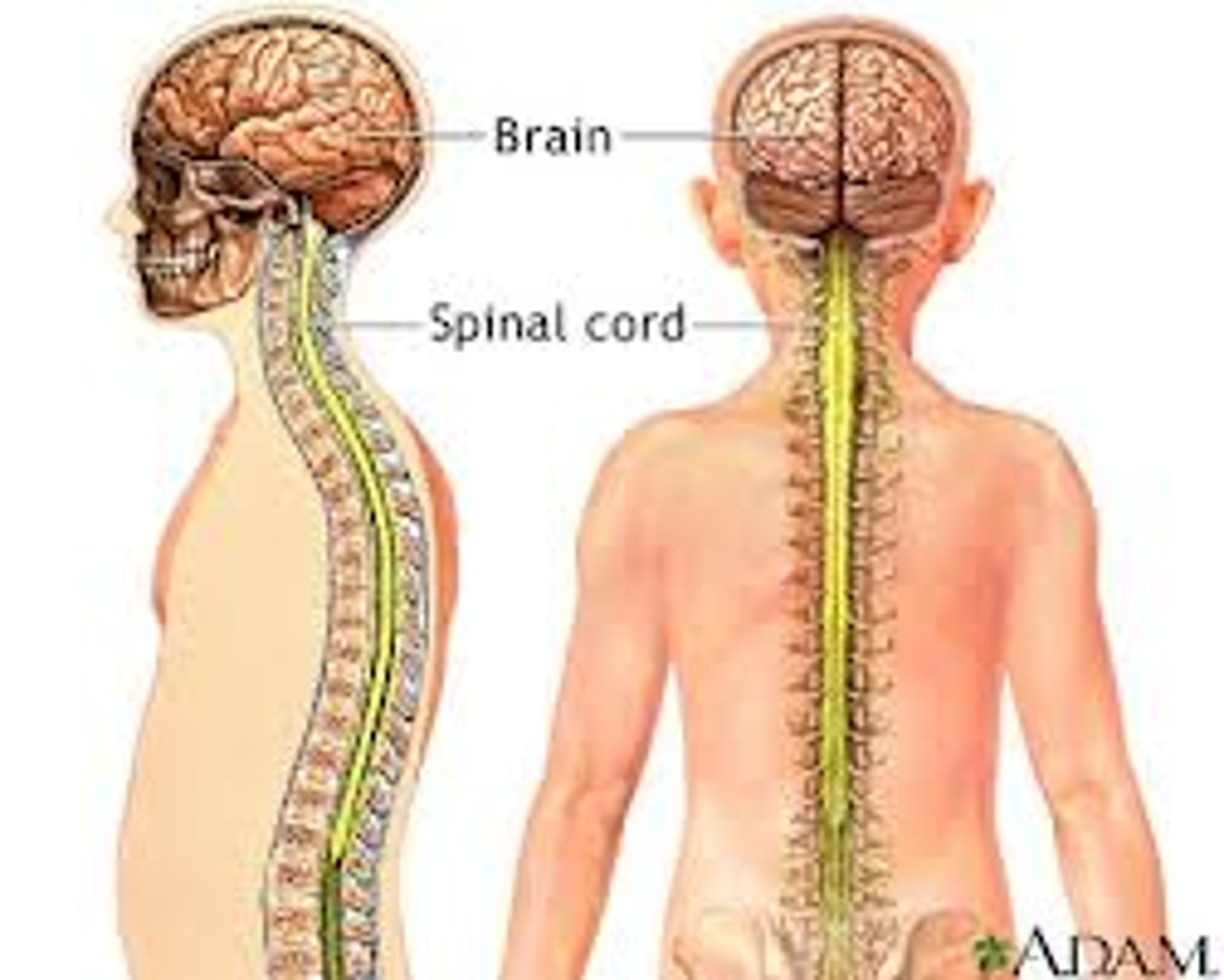
Central nervous system (CNS)
A system that includes the brain and spinal cord, controlling voluntary and involuntary acts
Peripheral Nervous System
nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord.
Cerebral Cortex
outermost part of forebrain, responsible for
analyzing sensory processing and higher brain functions
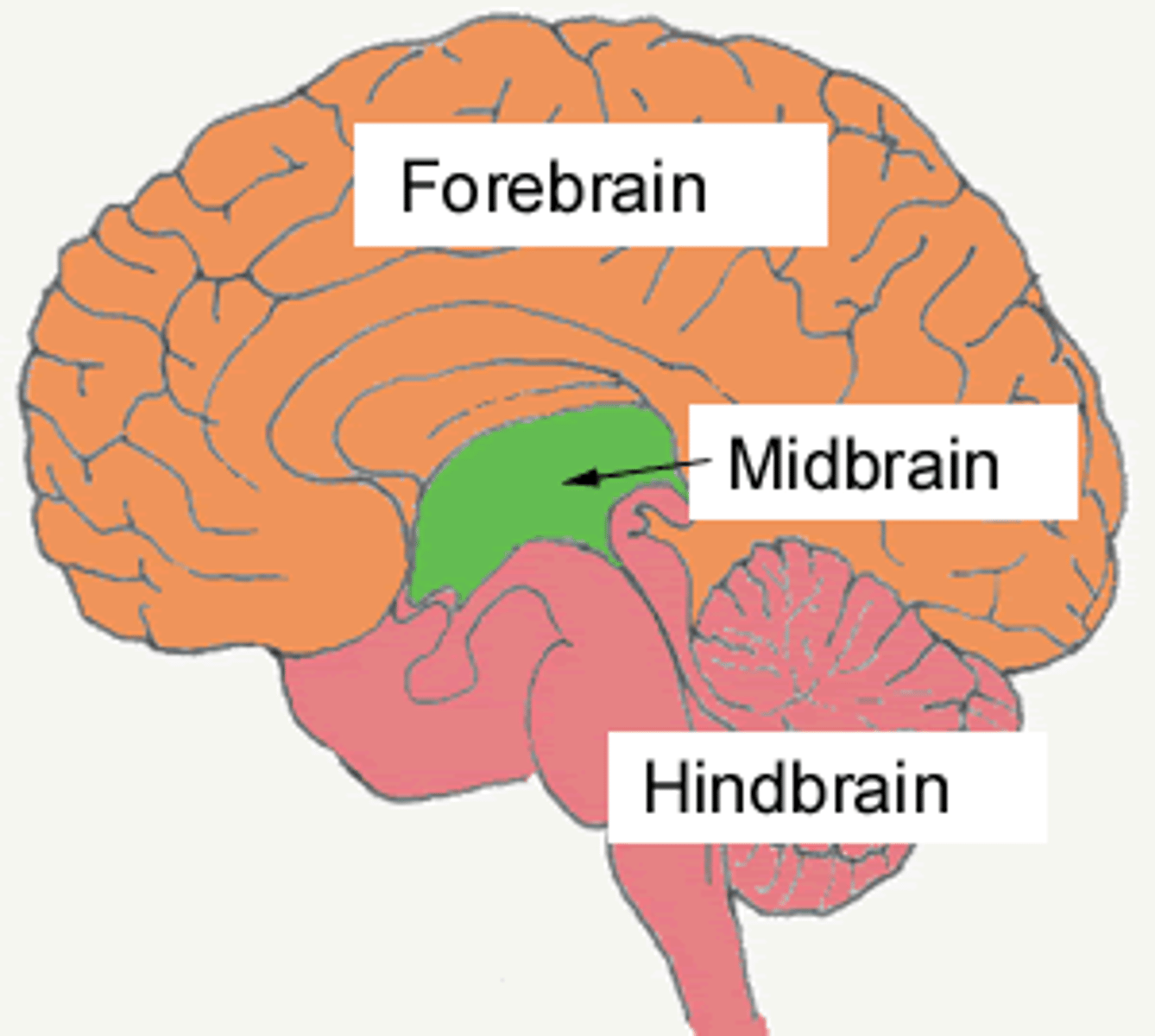
Forebrain (Cerebrum)
forward part of the brain that allows advanced intellectual abilities
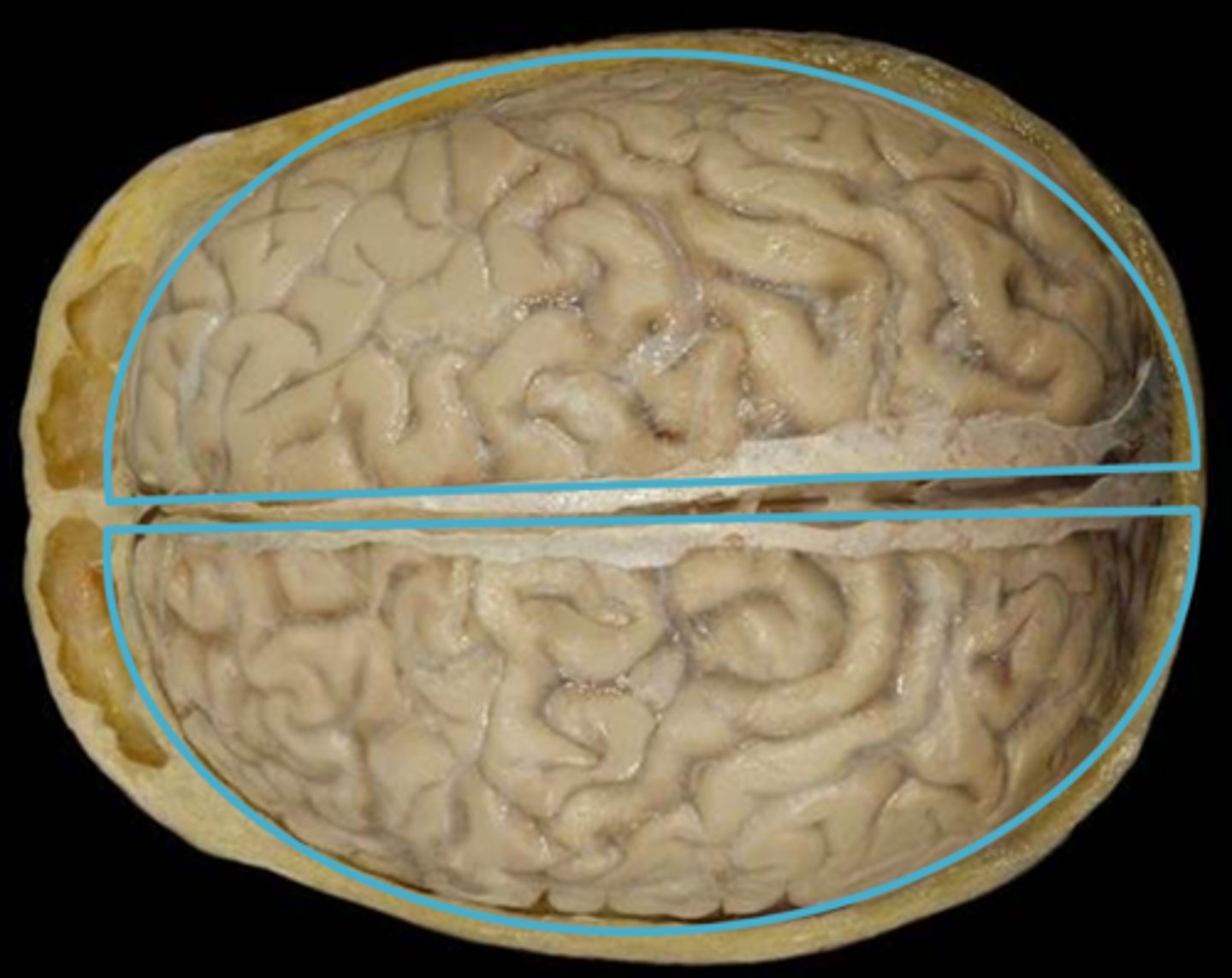
Cerebral Hemispheres
Divided into right and left by the cerebrum.
Corpus Callosum
A thick band of nerve fibers that connects large areas of the cerebral cortex on each side of the brain and supports communication of information across the hemispheres.
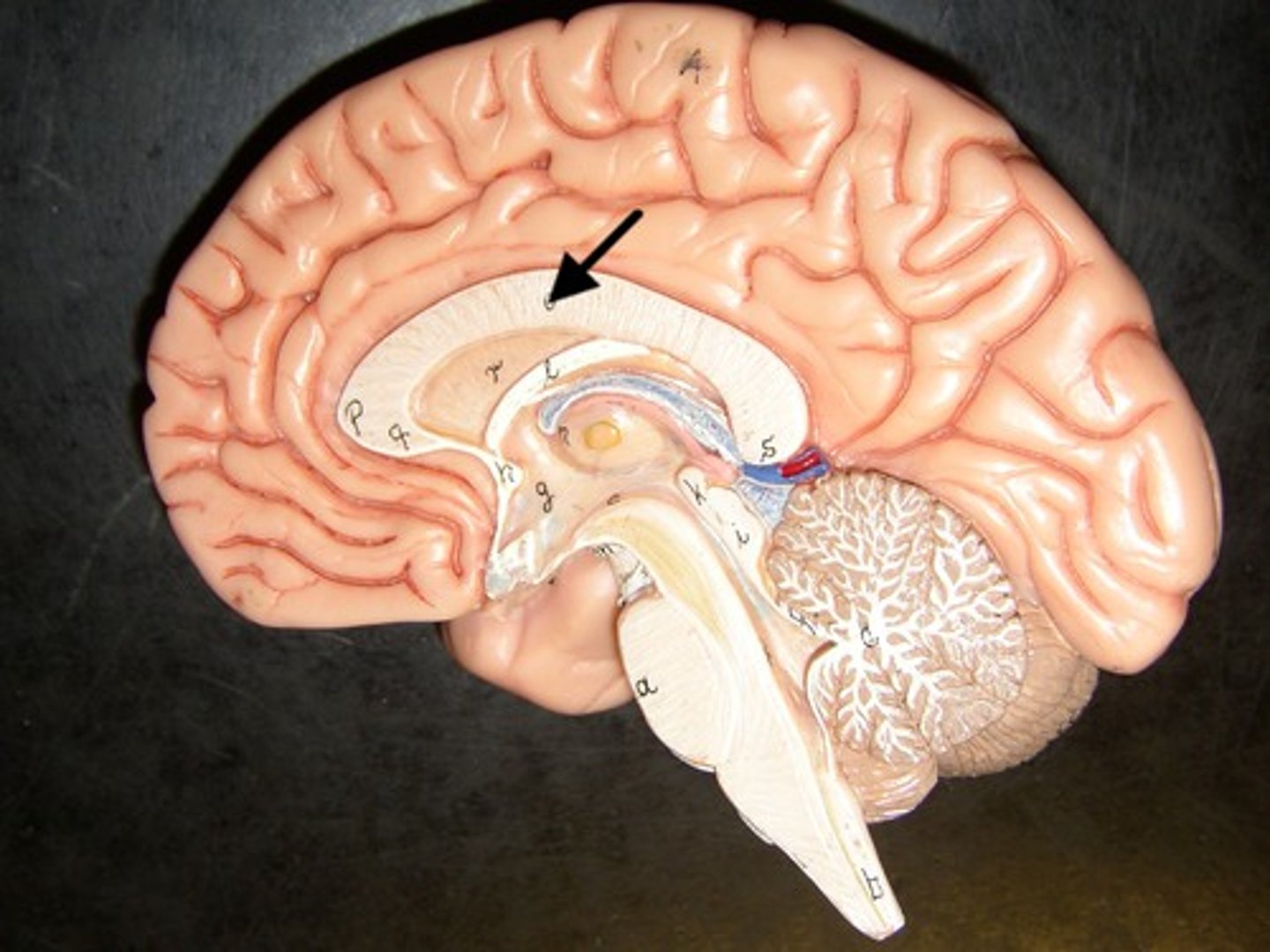
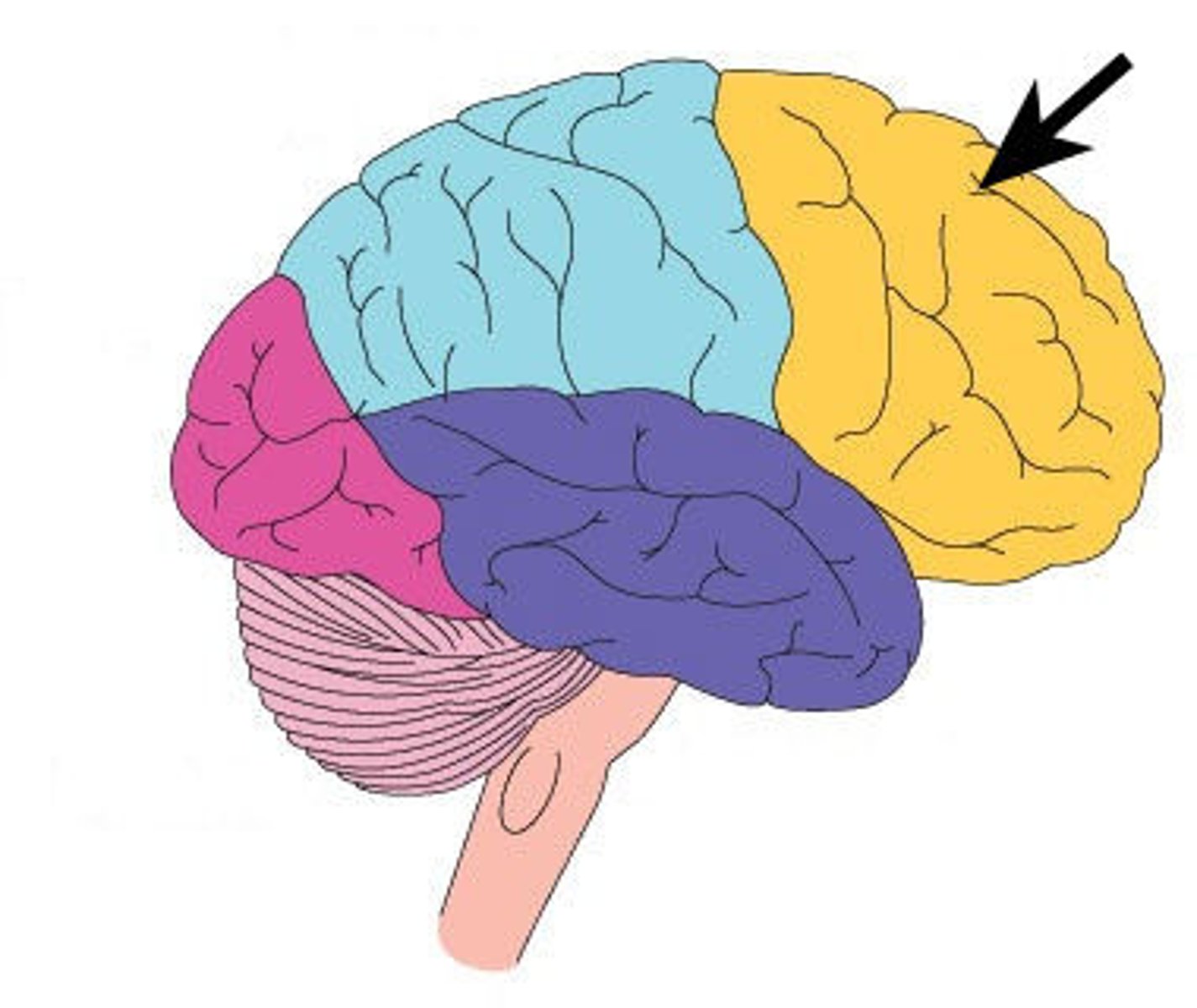
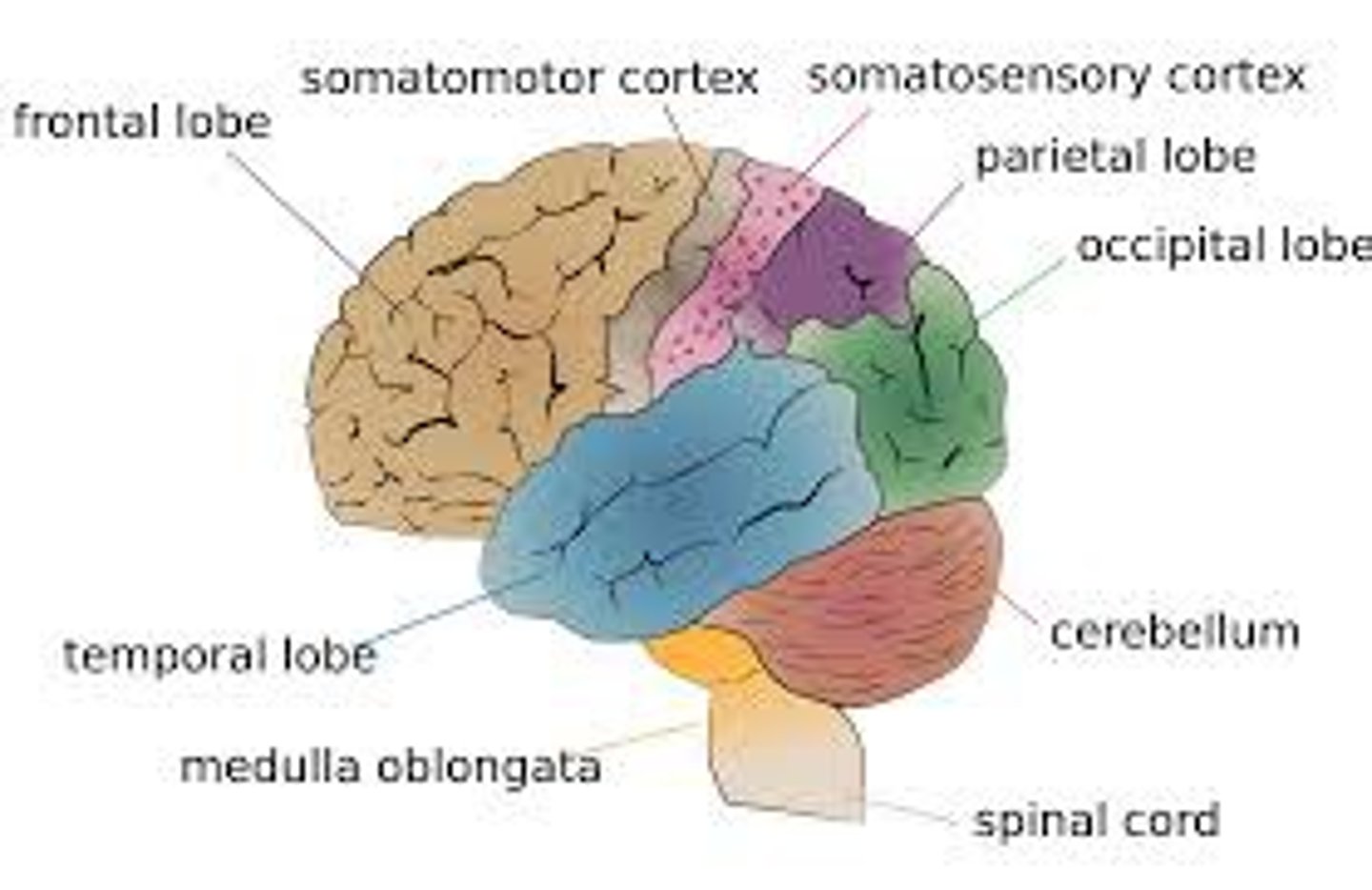
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
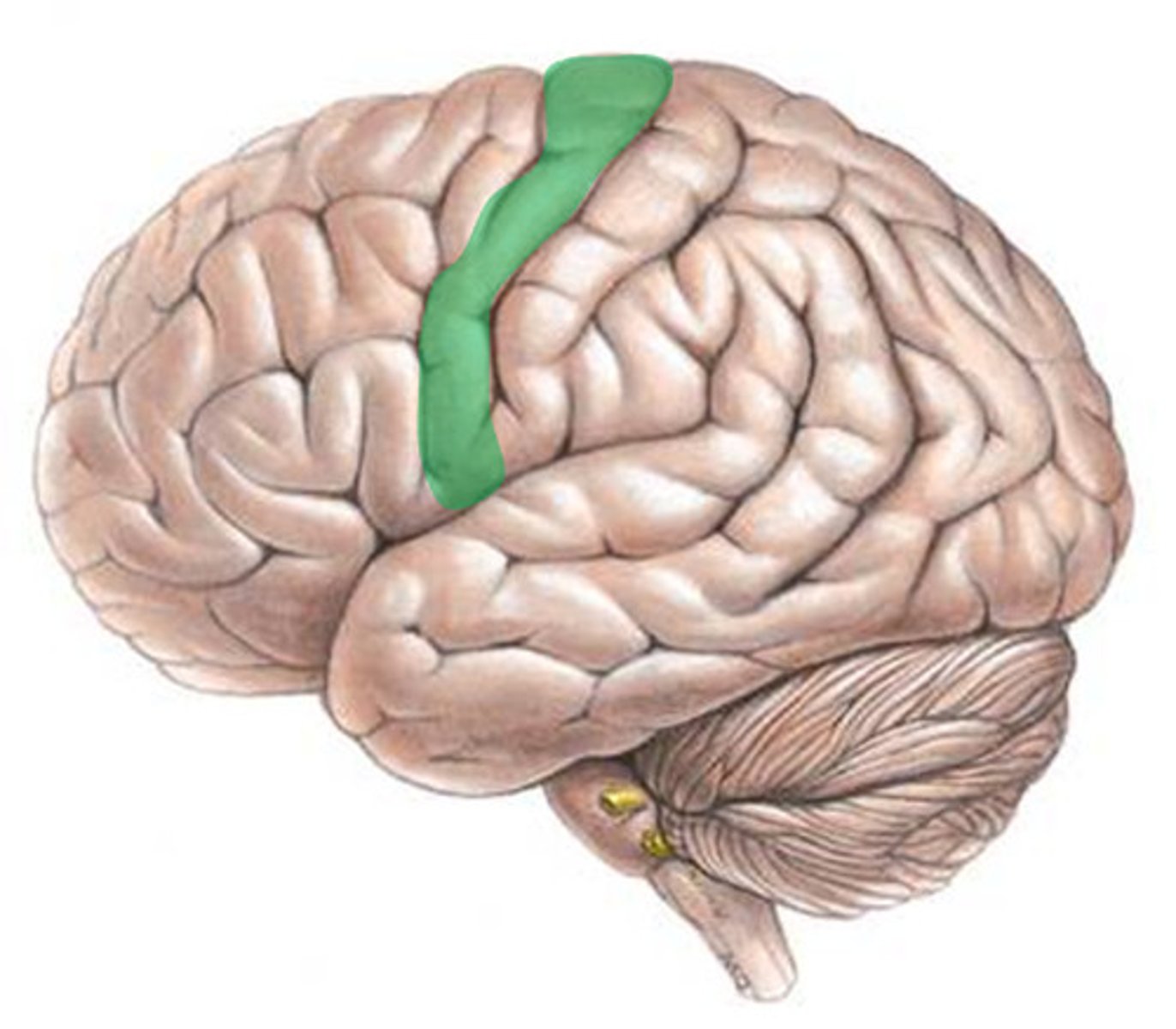
Motor cortex
An area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements
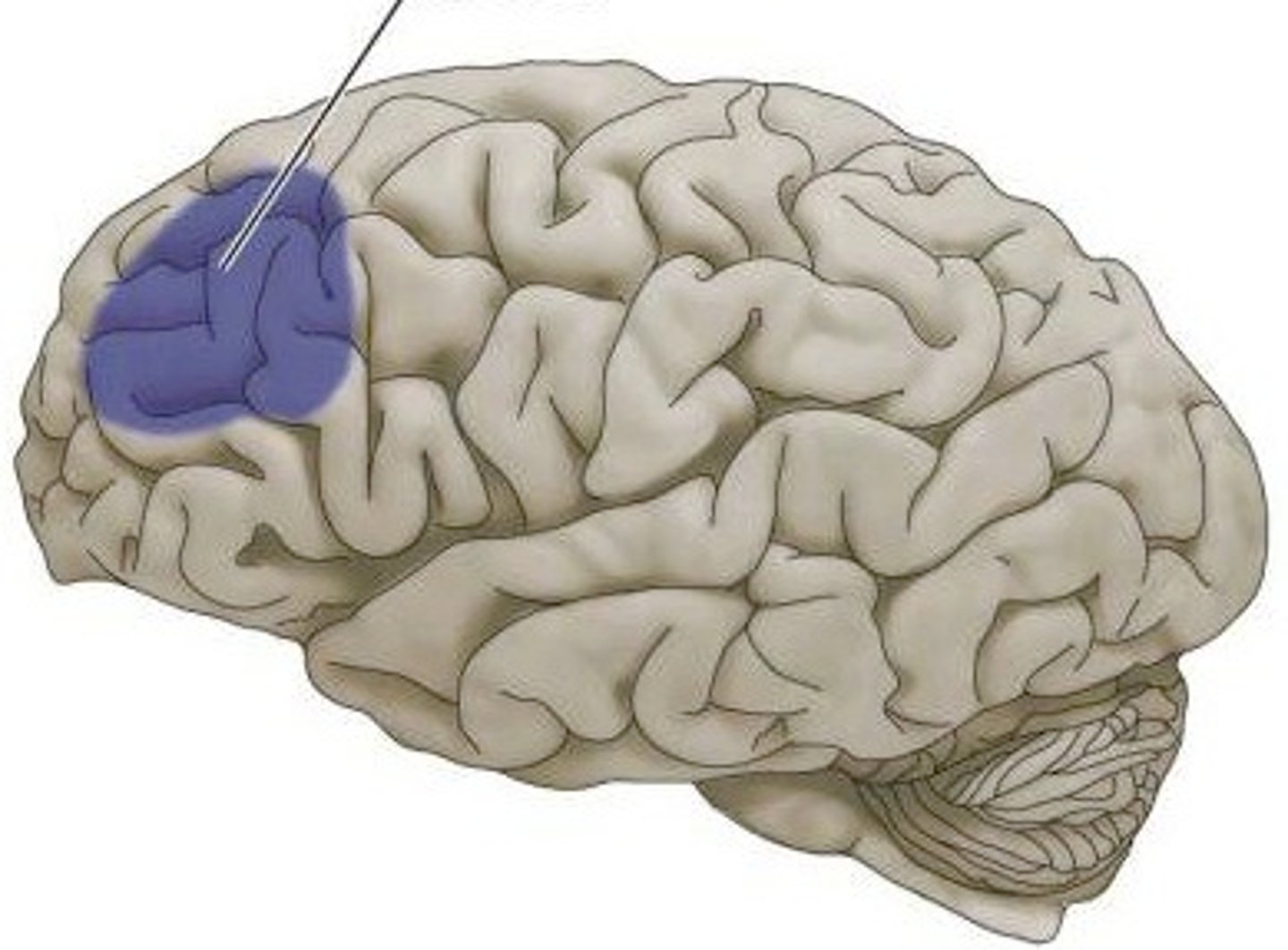
Prefrontal cortex
part of frontal lobe responsible for thinking, planning, and language
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
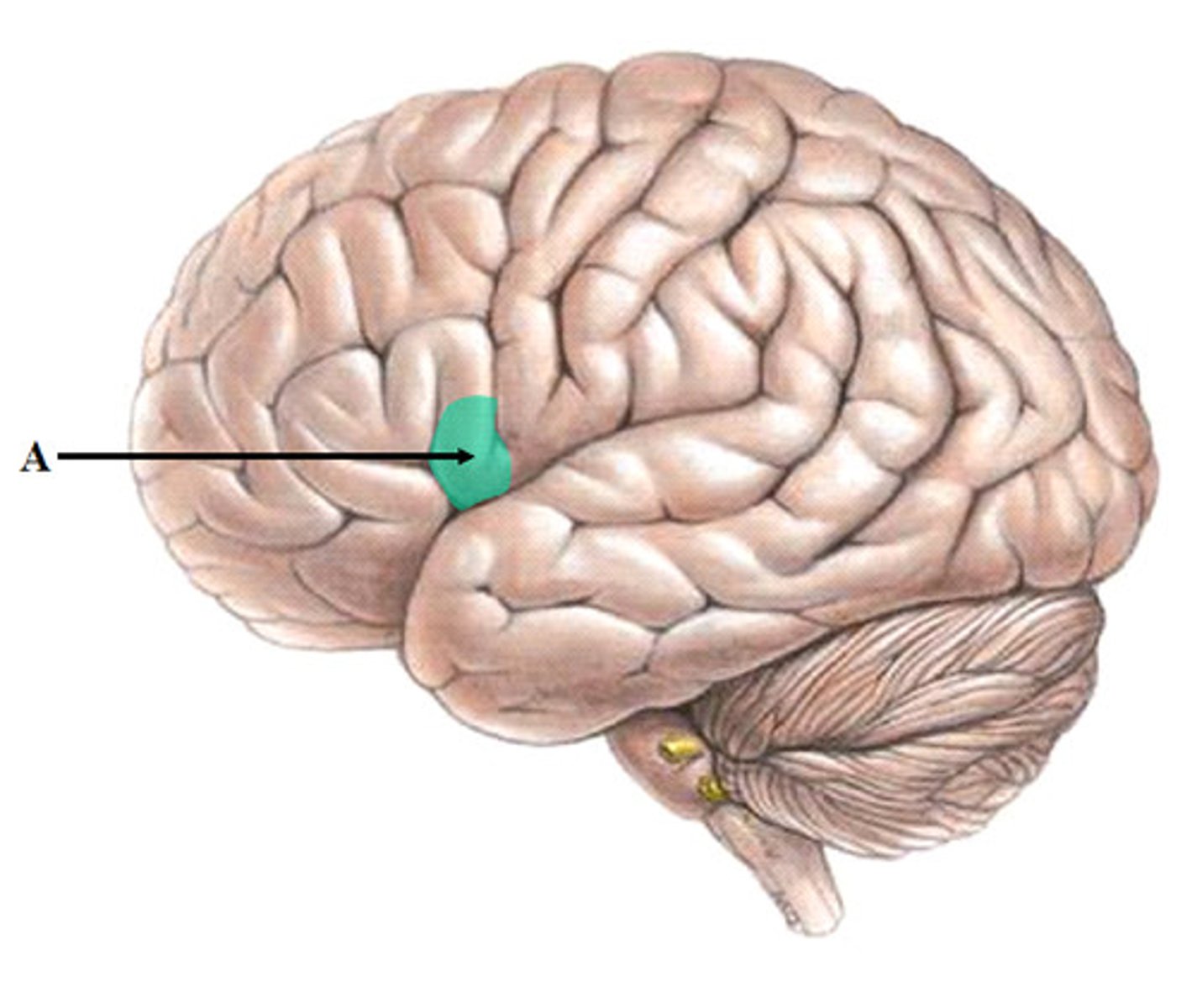
Parietal Lobe
upper middle part of the cerebral cortex lying behind the frontal lobe that is specialized for touch and perception
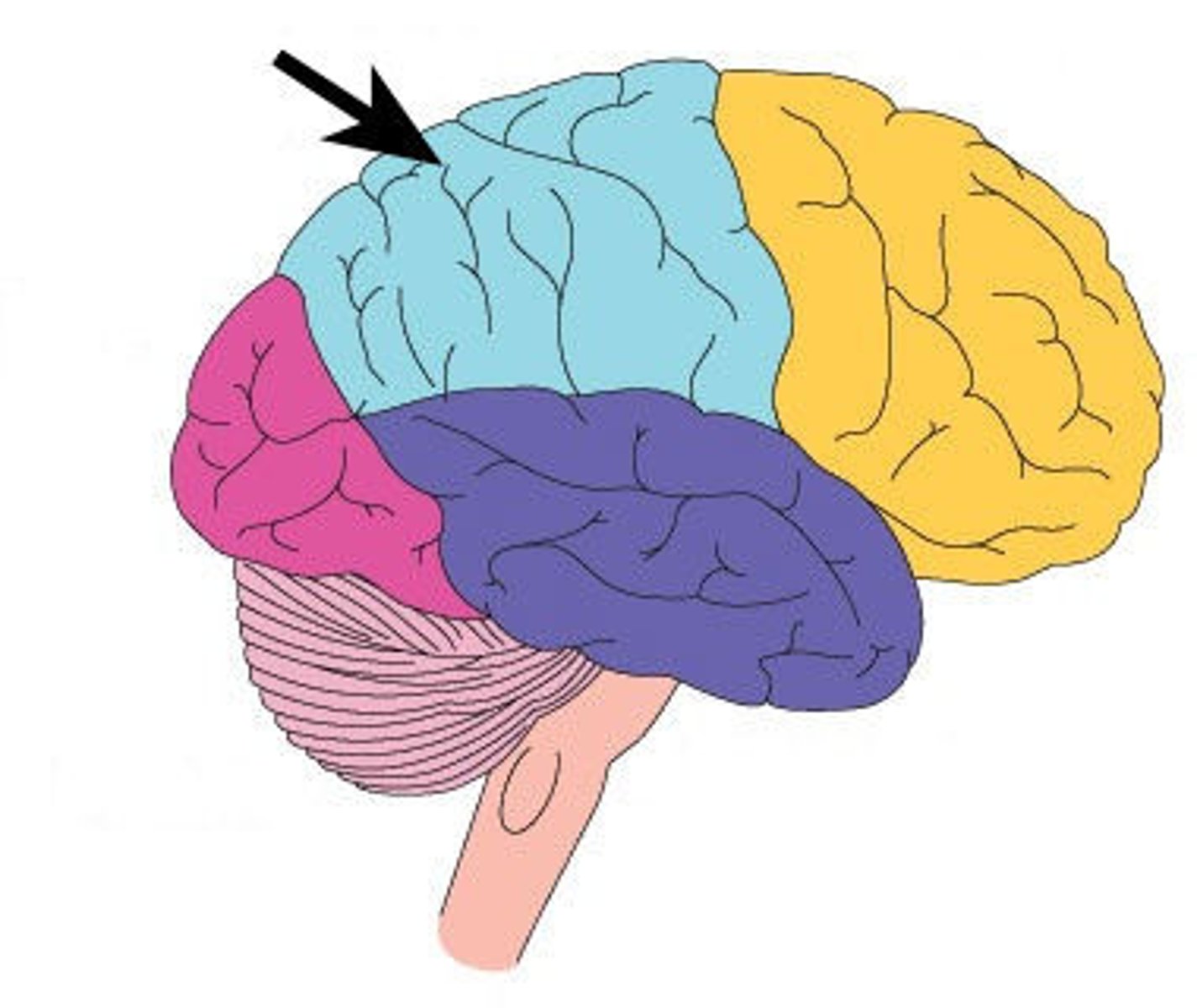
Temporal lobe
lower part of cerebral cortex that plays roles in hearing, understanding language, and memory
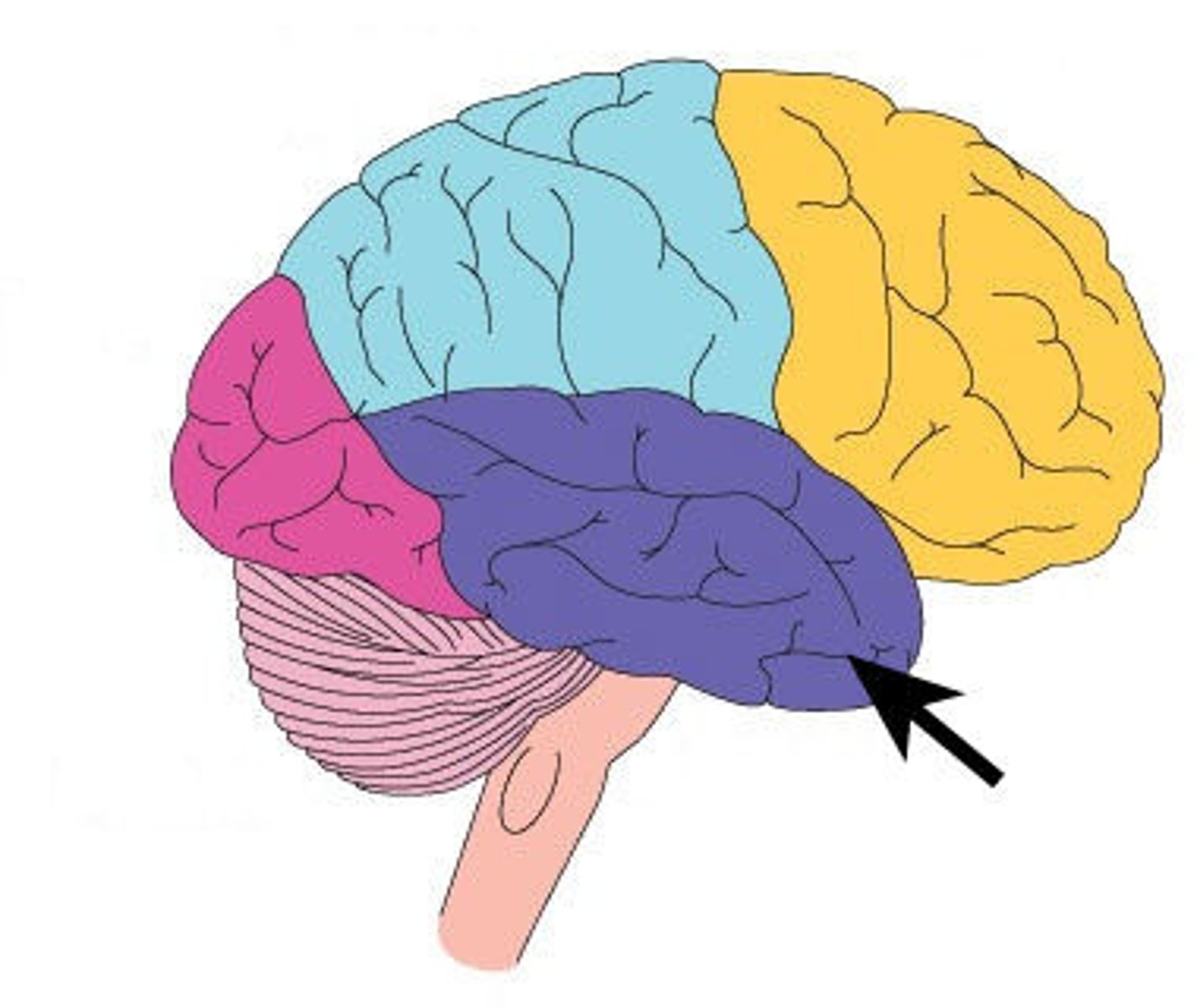
Wernicke's Area
part of the temporal lobe involved in understanding speech
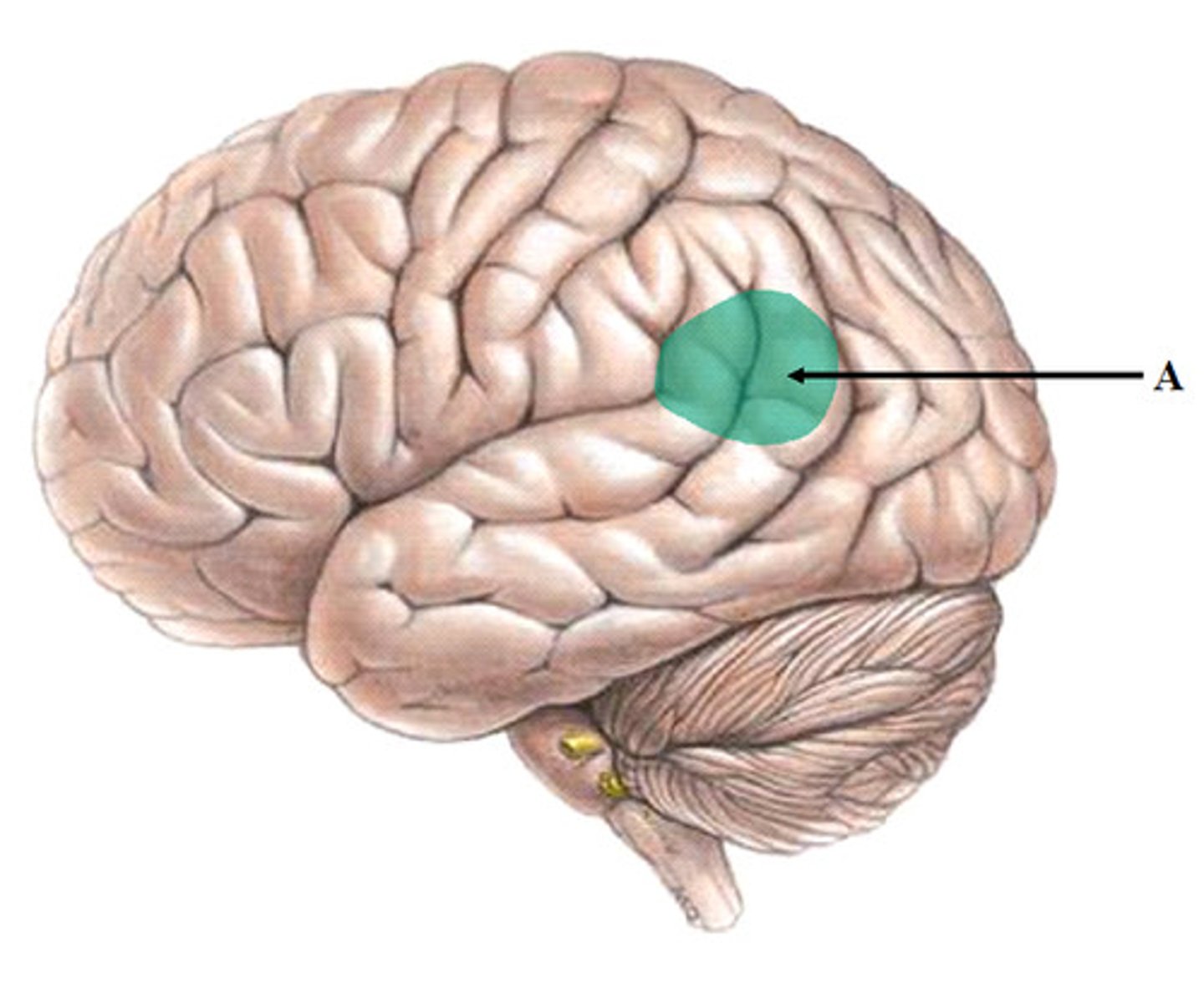
Occipital Lobe
back part of cerebral cortex specialized
for vision
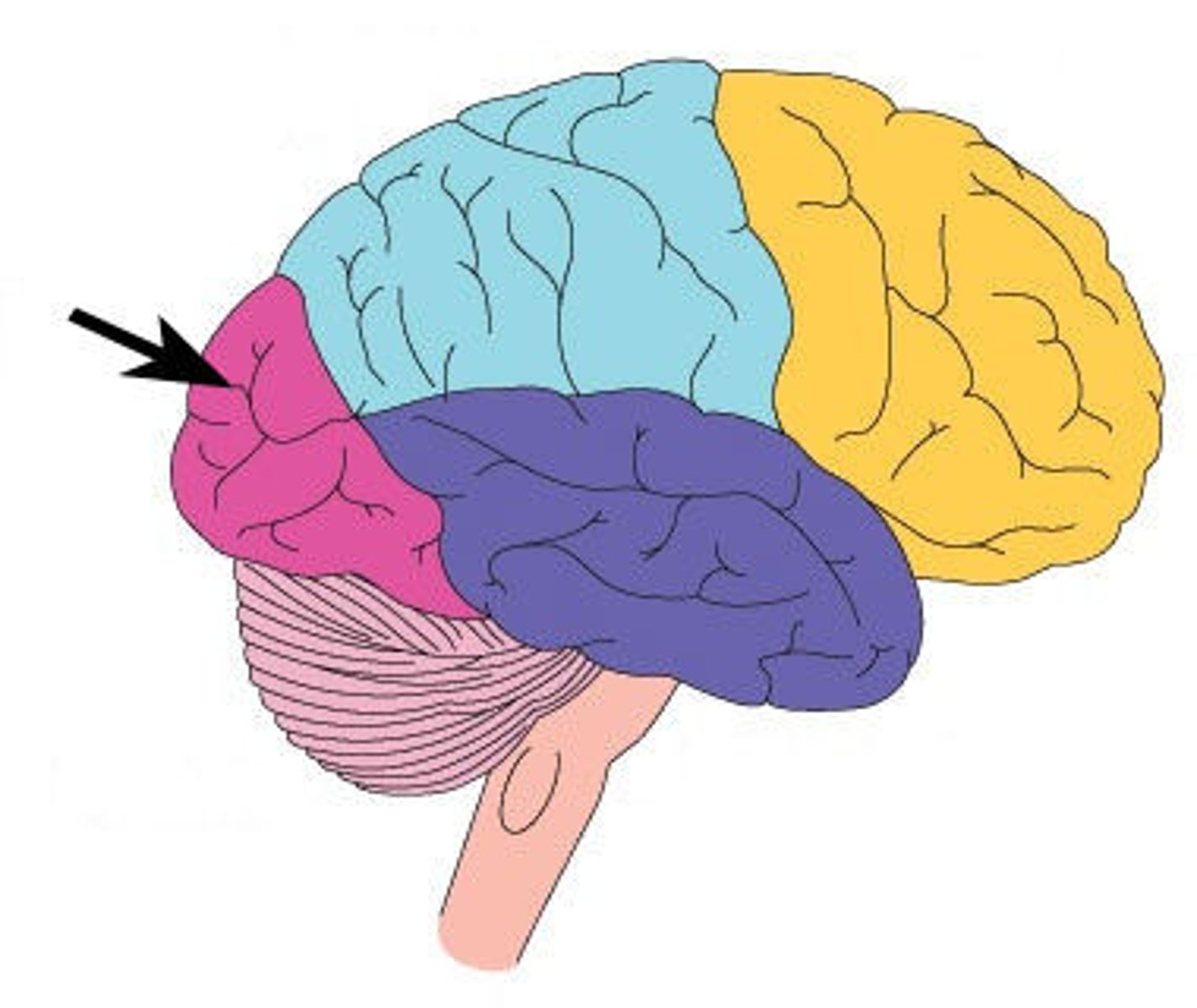
Primary Sensory Cortex
regions of the cerebral cortex that initially
process information from the senses
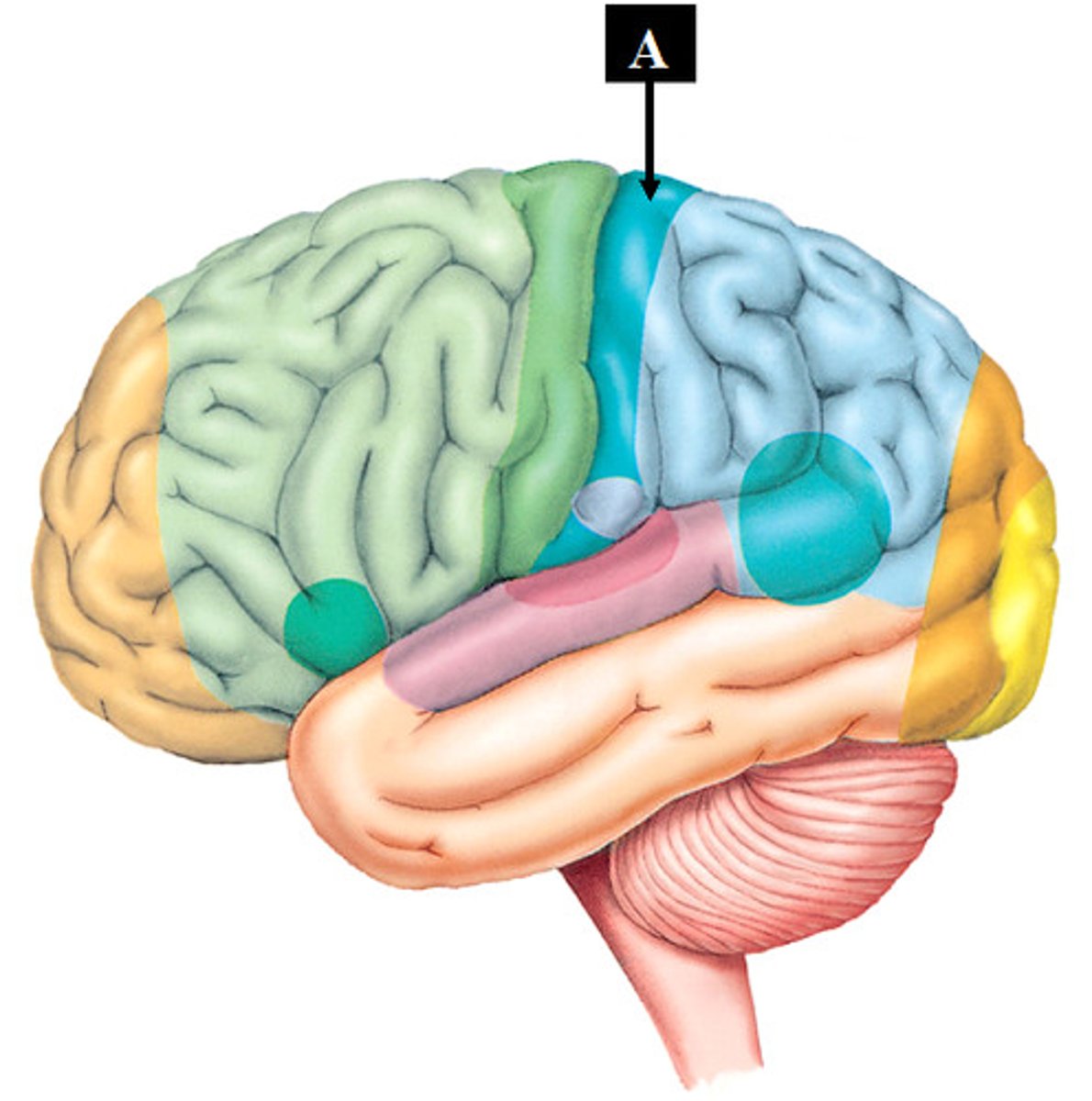
Limbic System
emotional center of brain that also plays roles in smell, motivation, and memory
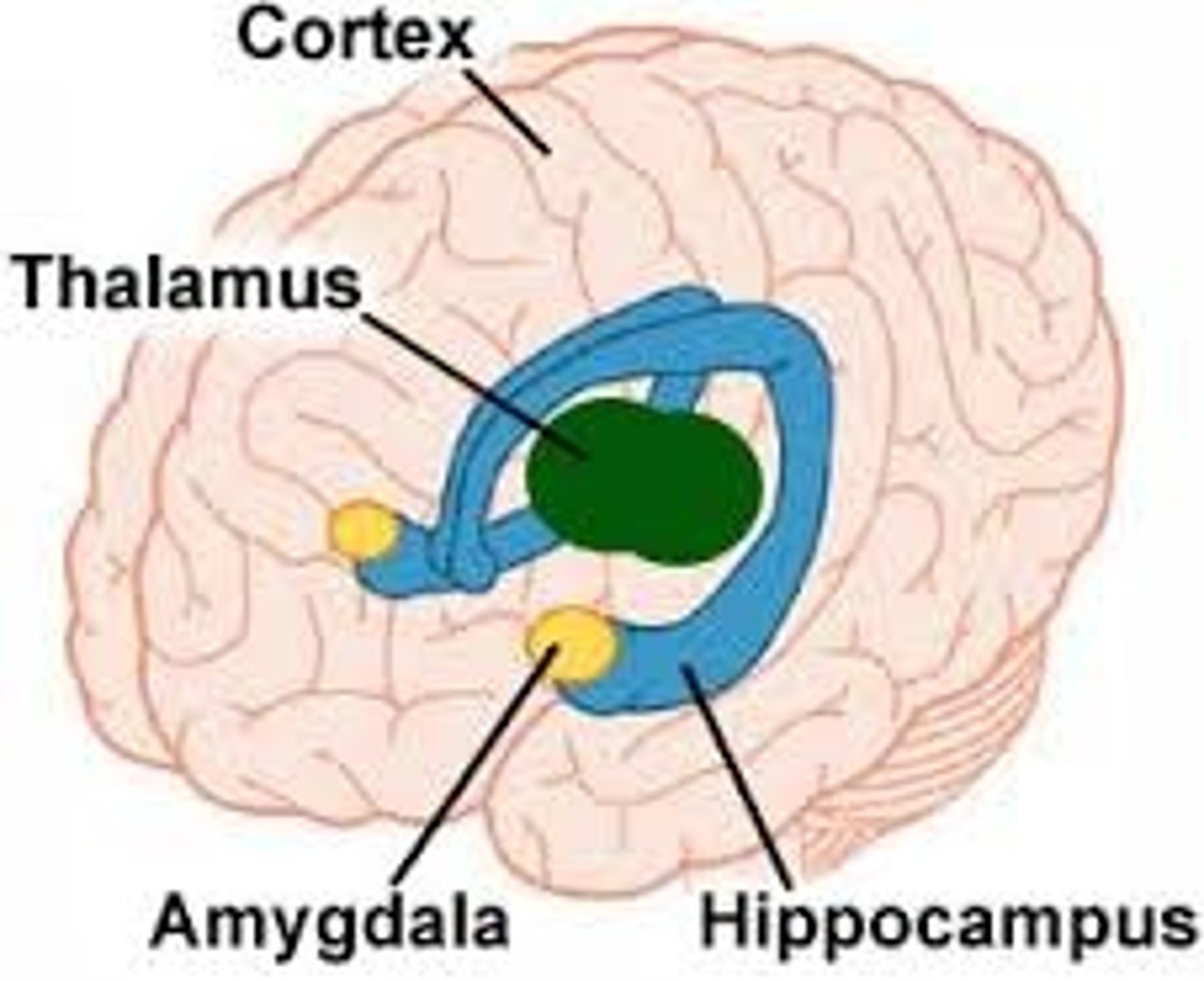
Thalamus
A forebrain structure that processes sensory information for all senses, except smell, and relays it to the cerebral cortex.
Amyglada
part of limbic system that plays key roles in
fear, excitement, and arousal
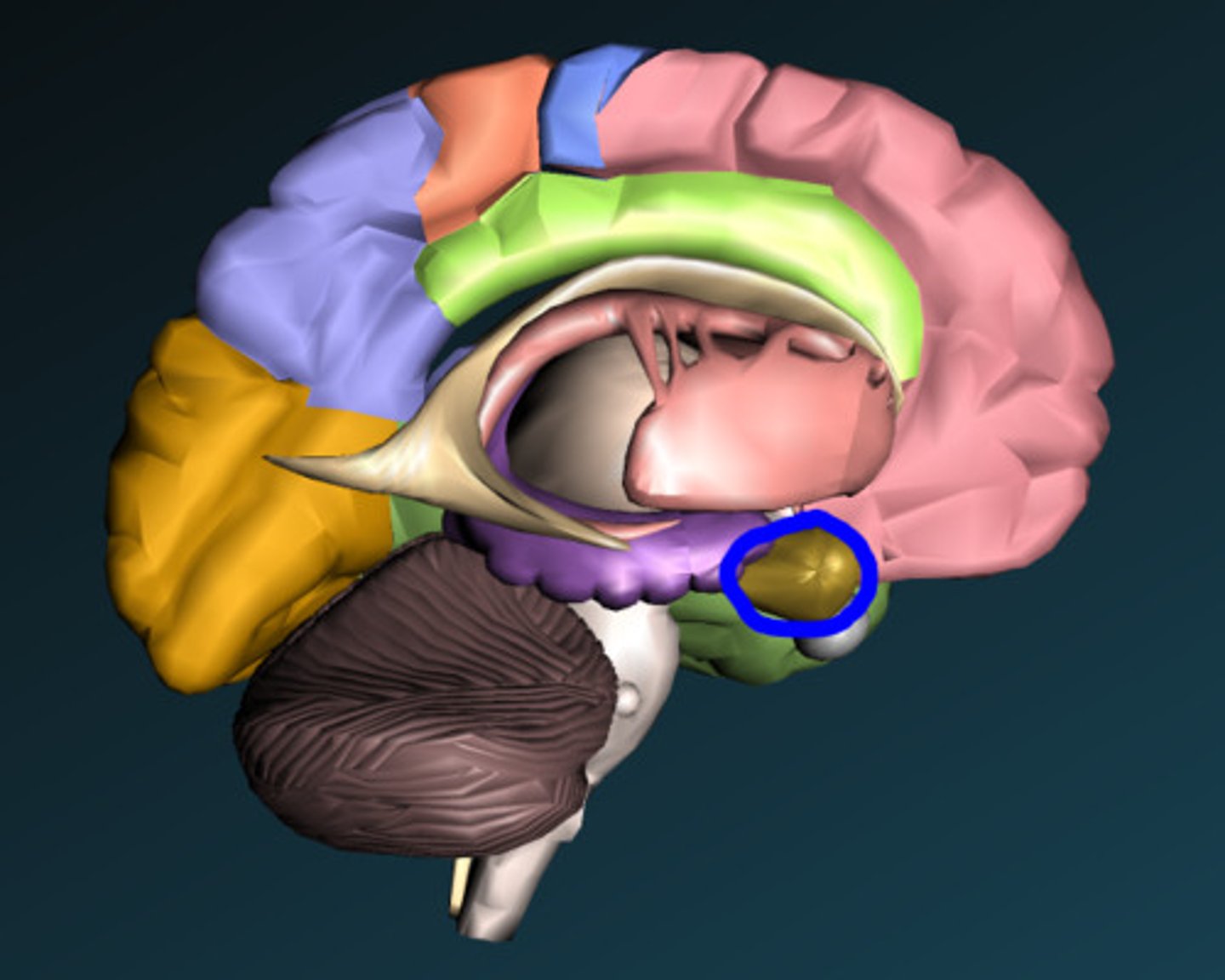
Hippocampus
part of the brain that plays a role in spatial
memory
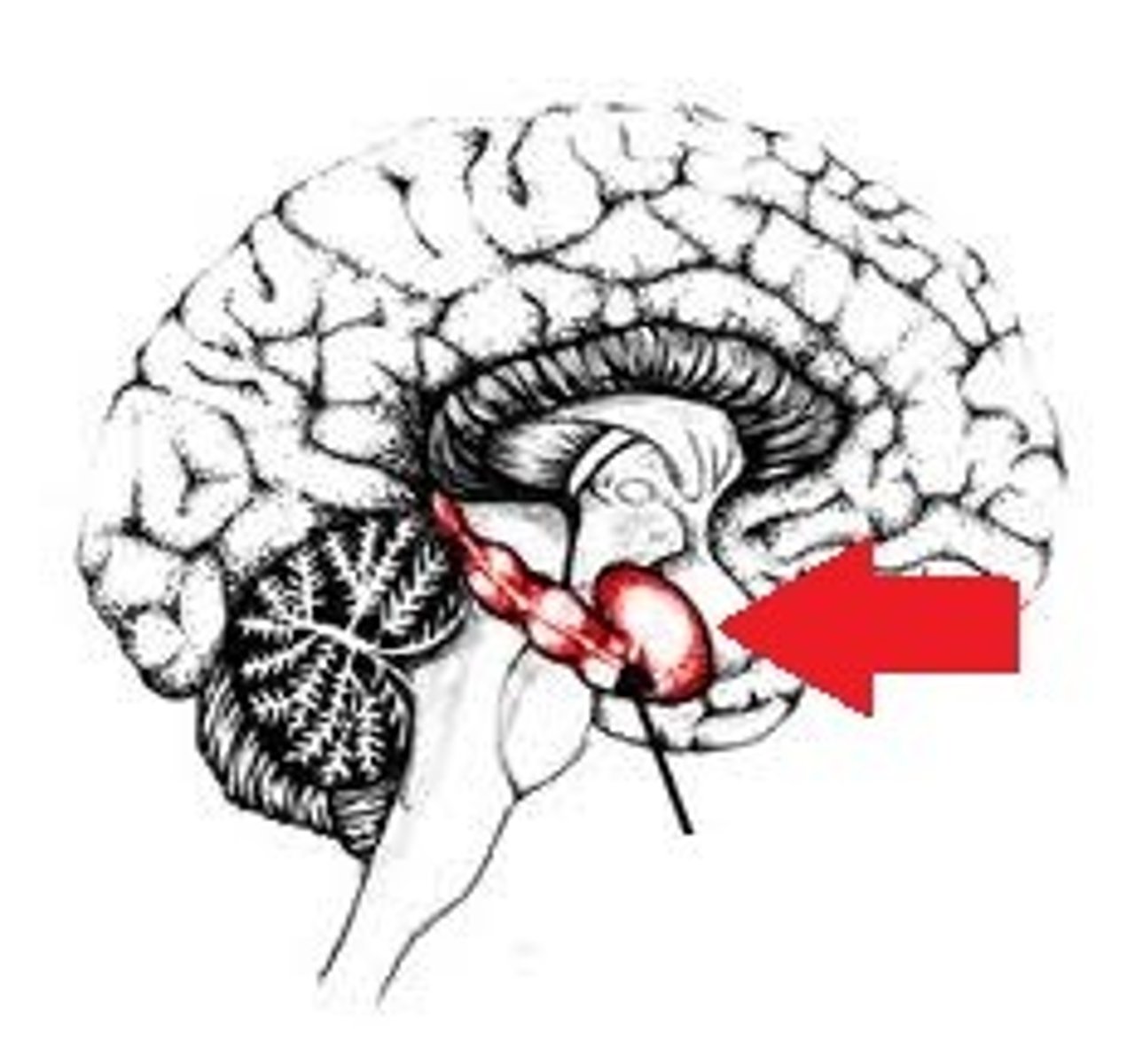
Brain Stem
part of the brain between the spinal cord and cerebral cortex that contains the midbrain, pons, and medulla
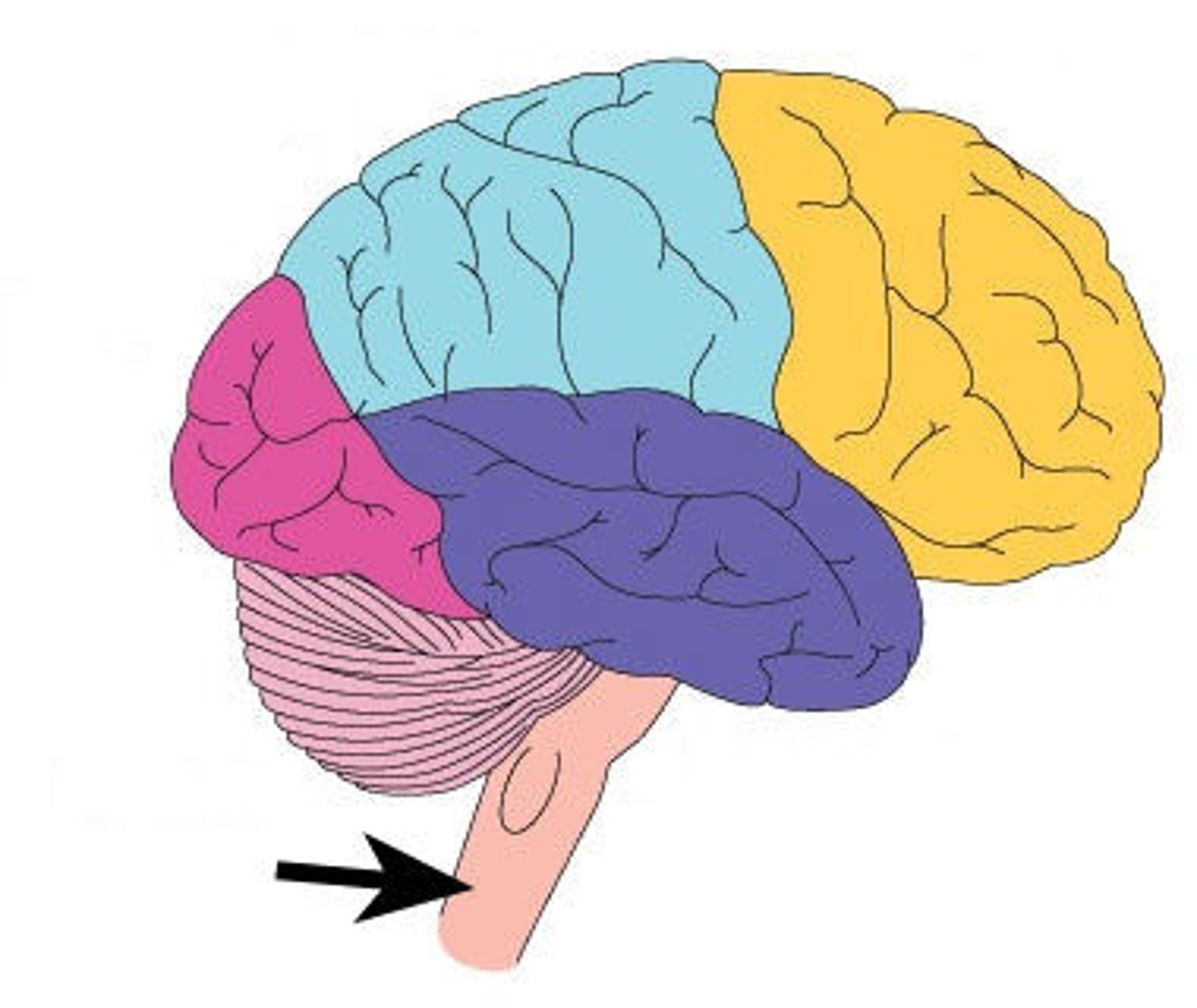
Midbrain
part of the brain stem that contributes to
movement, tracking of visual stimuli, and
reflexes triggered by sound
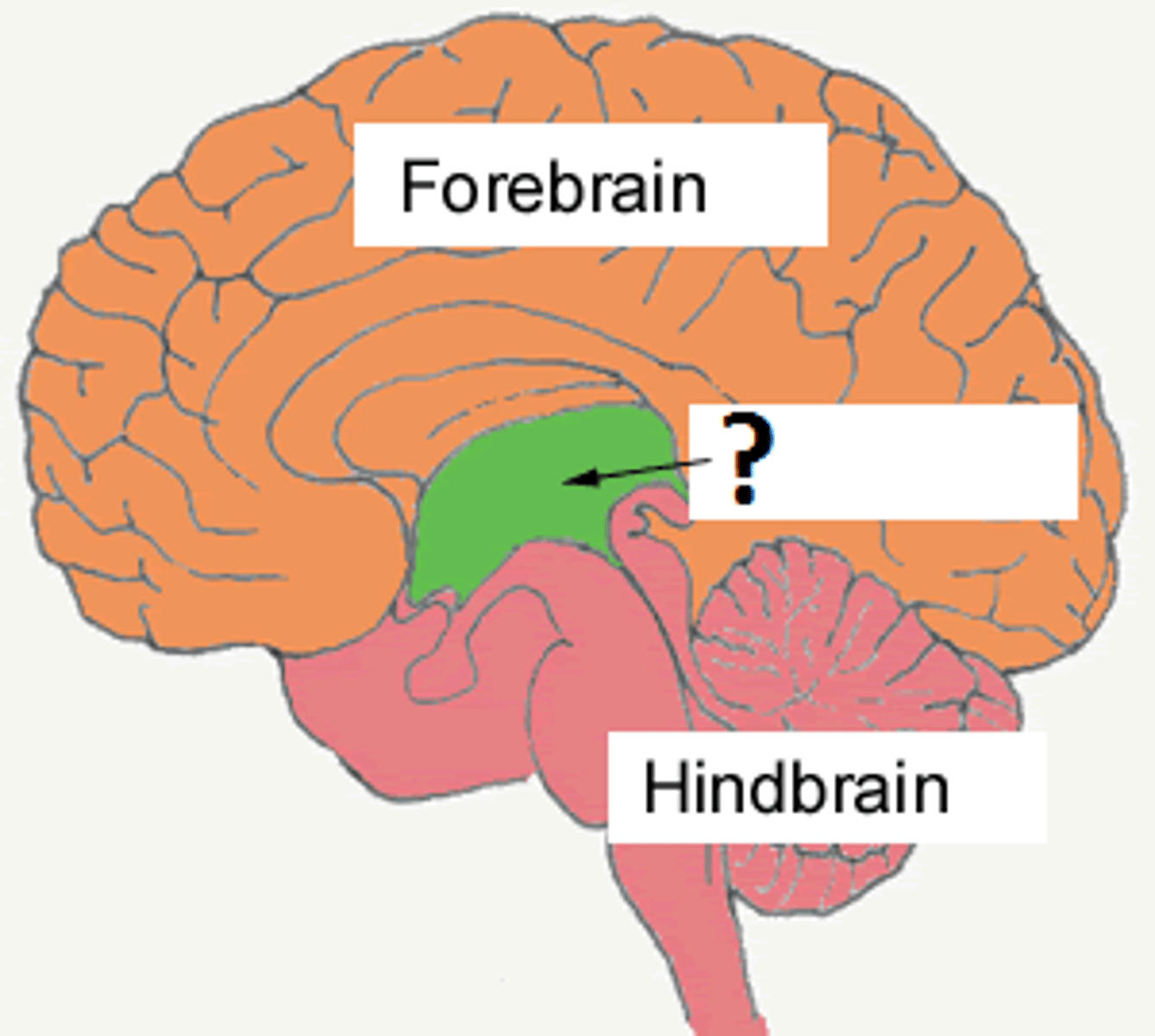
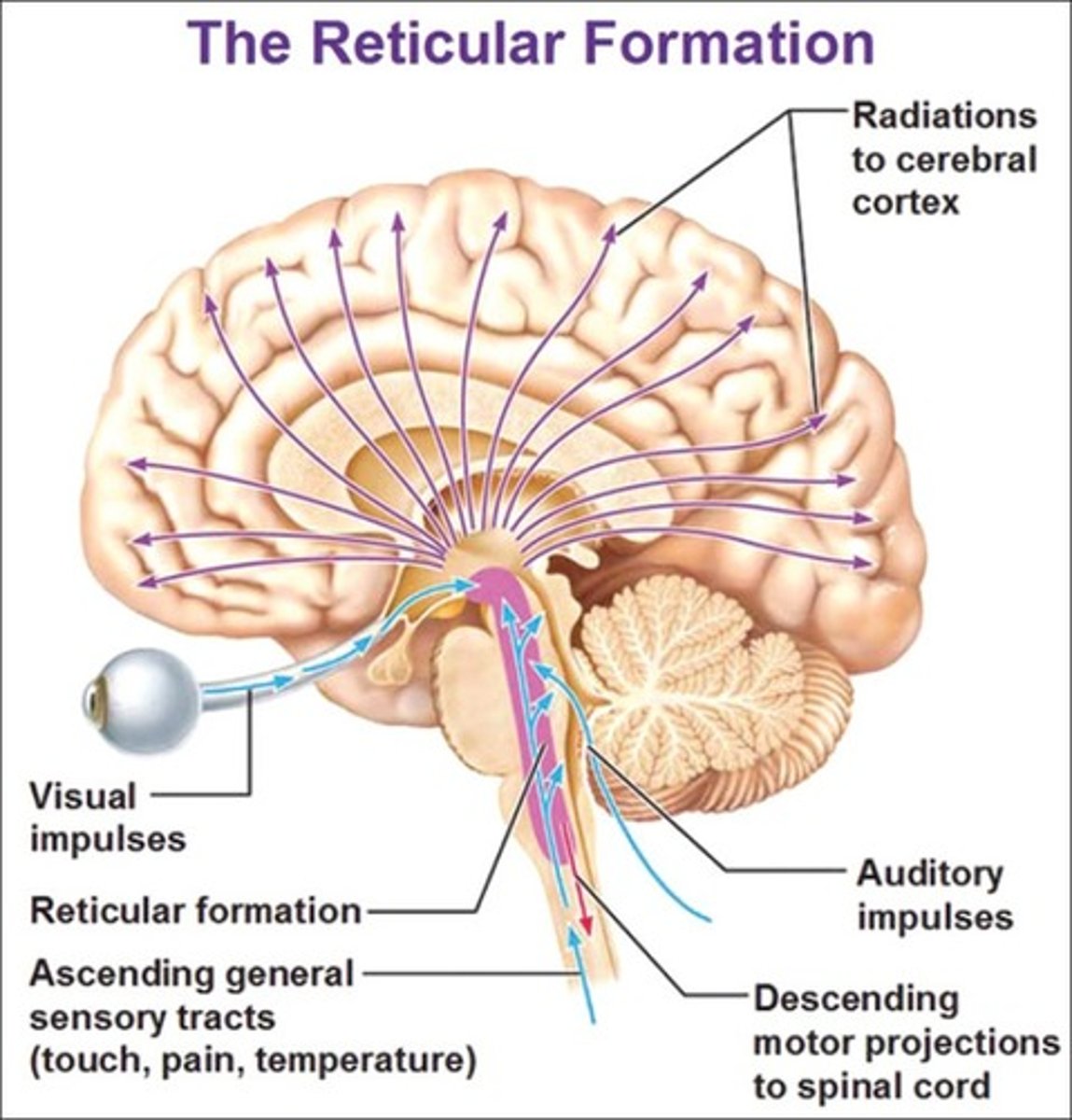
reticular activating system (RAS)
brain area that plays a key role in arousal
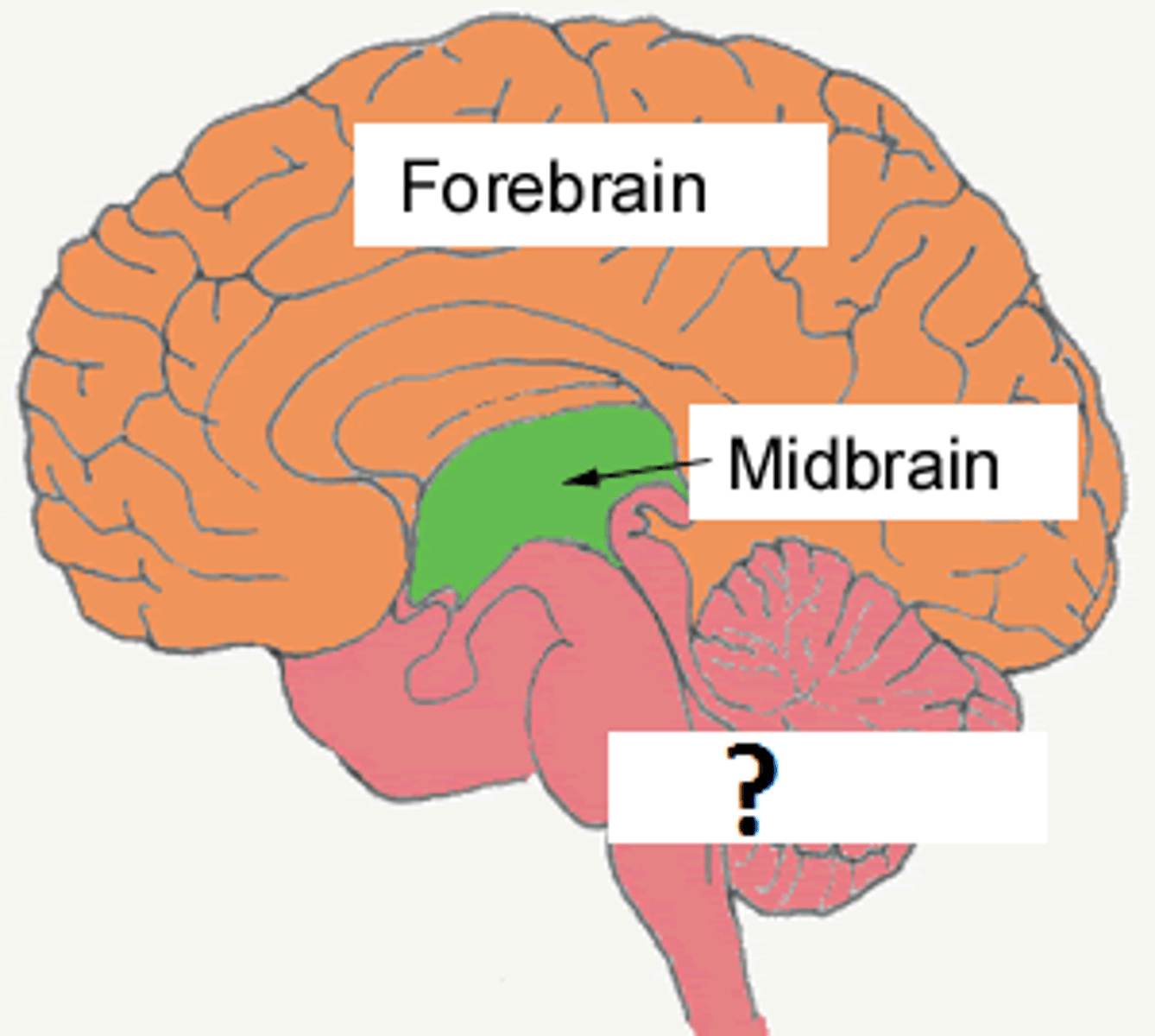
Hindbrain
region below the midbrain that contains the
cerebellum, pons, and medulla
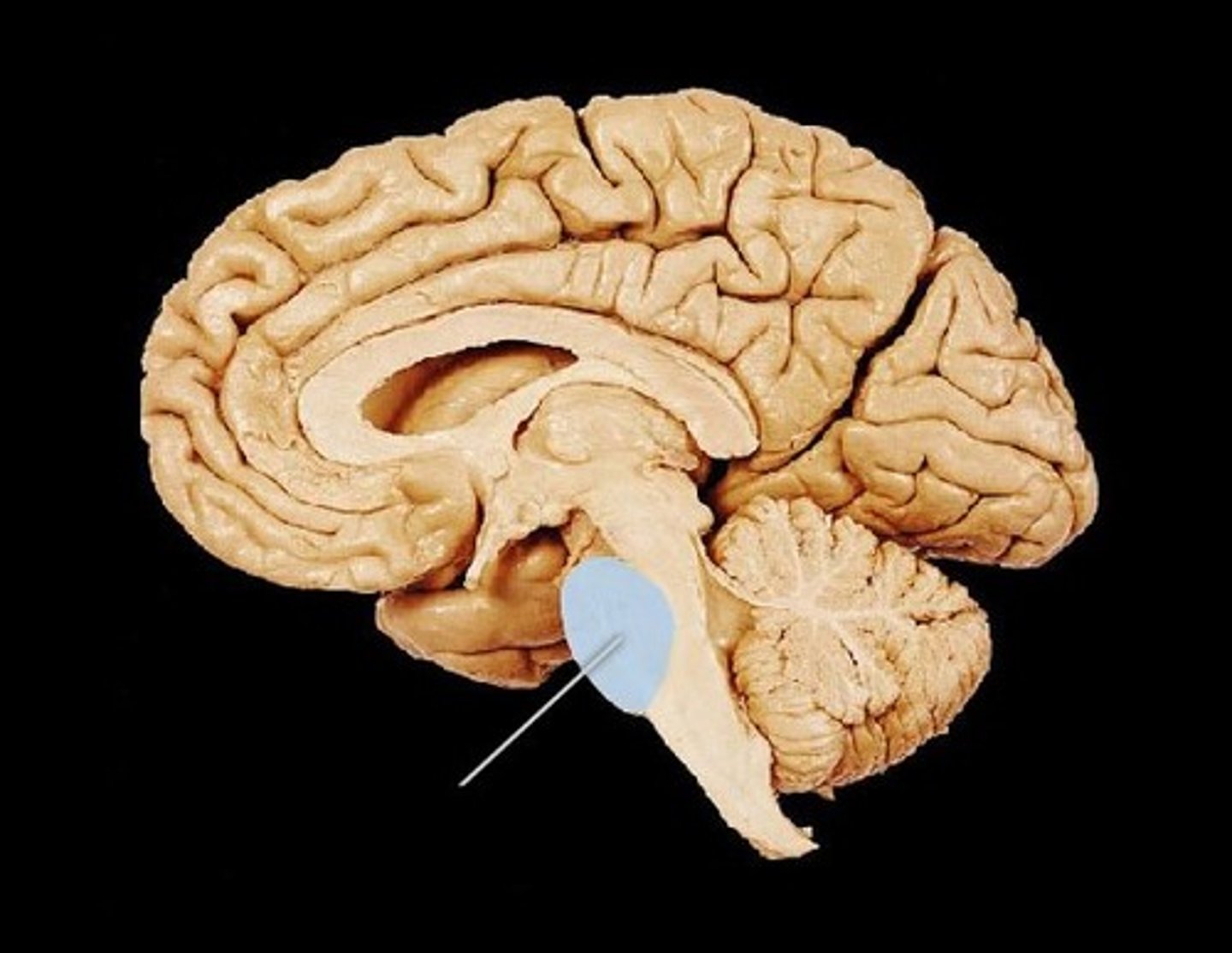
Pons
part of the brain stem that connects the
cortex with the cerebellum
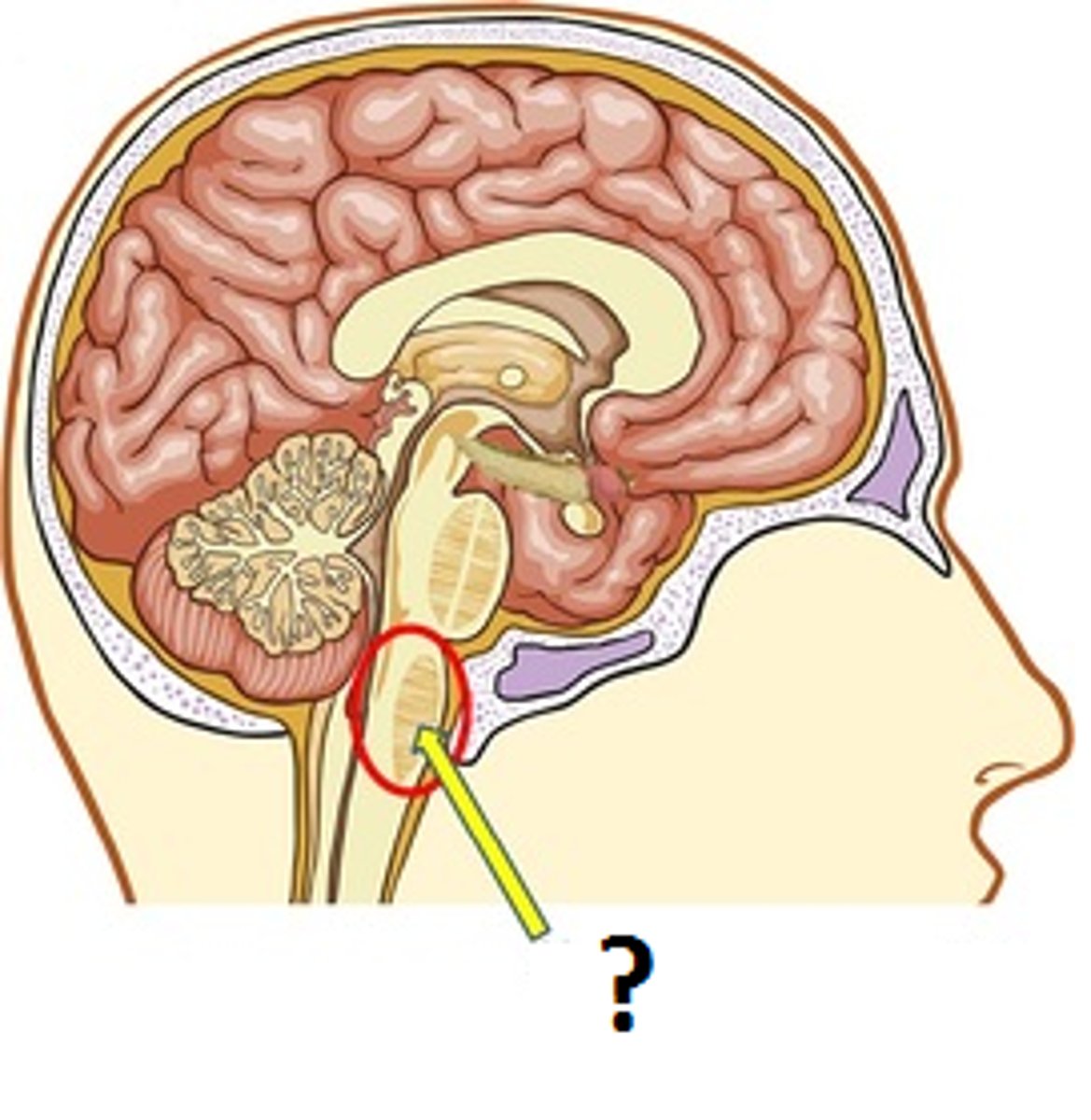
Medulla
part of brain stem involved in basic functions, such as heartbeat and breathing
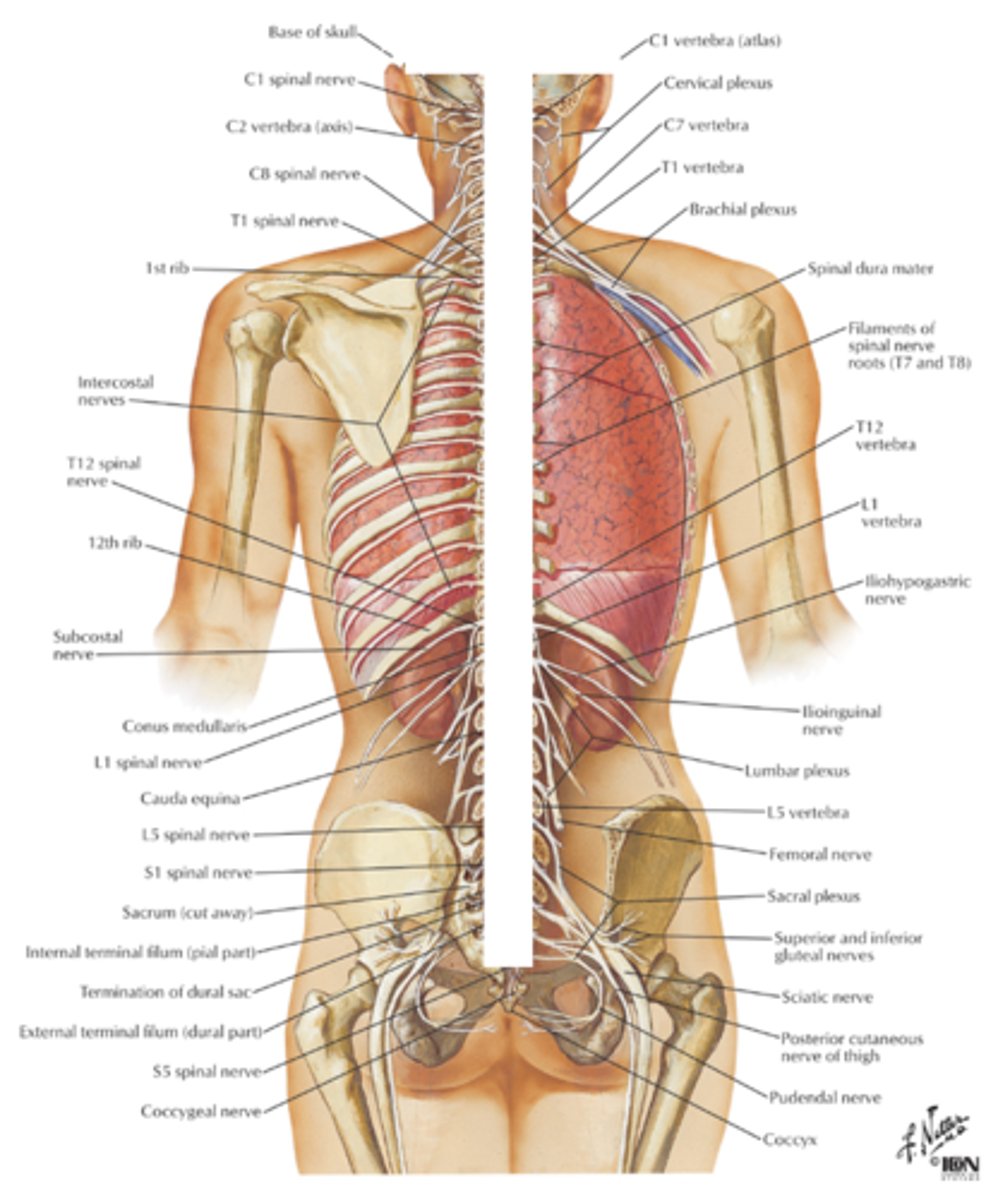
Spinal Cord
thick bundle of nerves that conveys signals
between the brain and the body
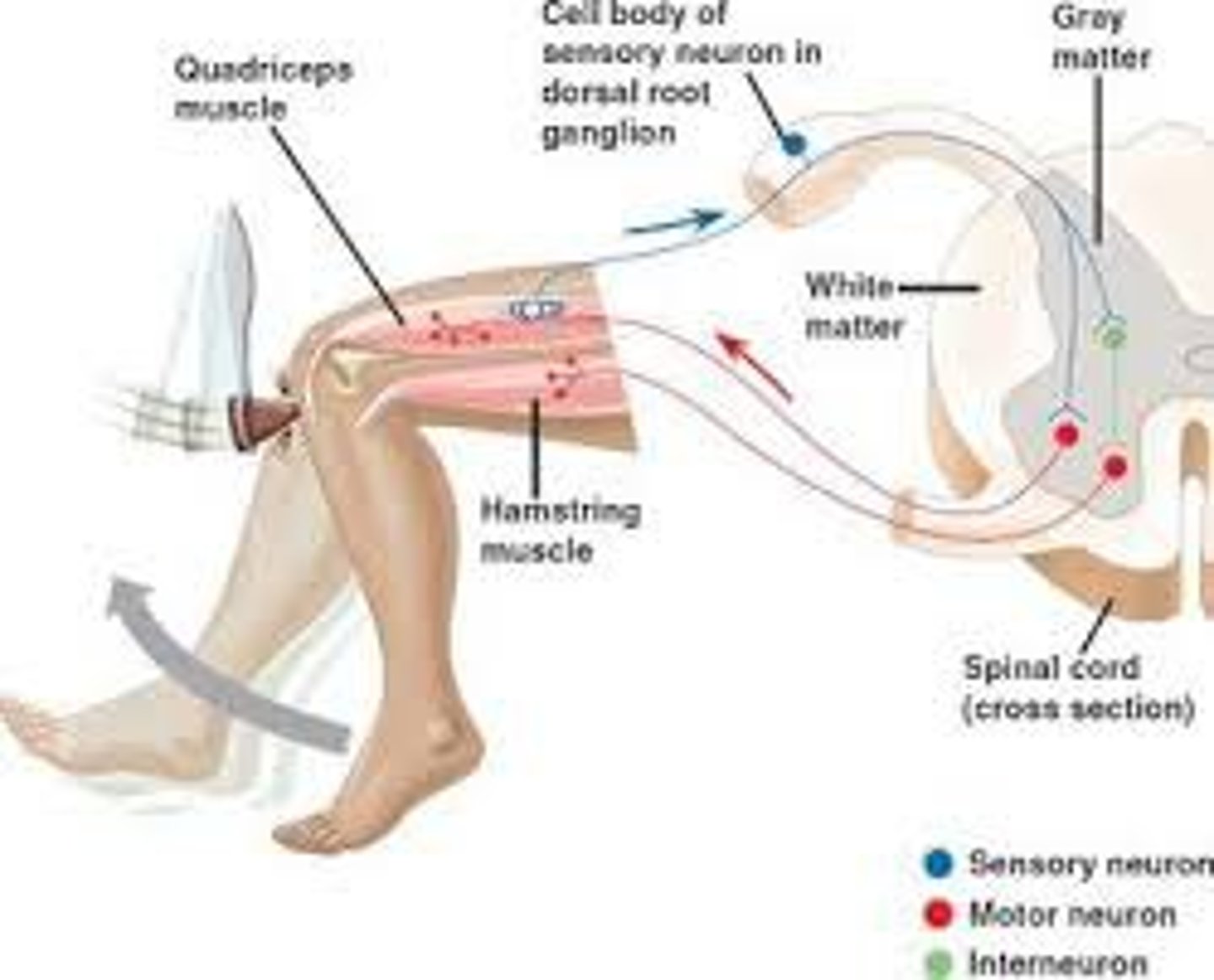
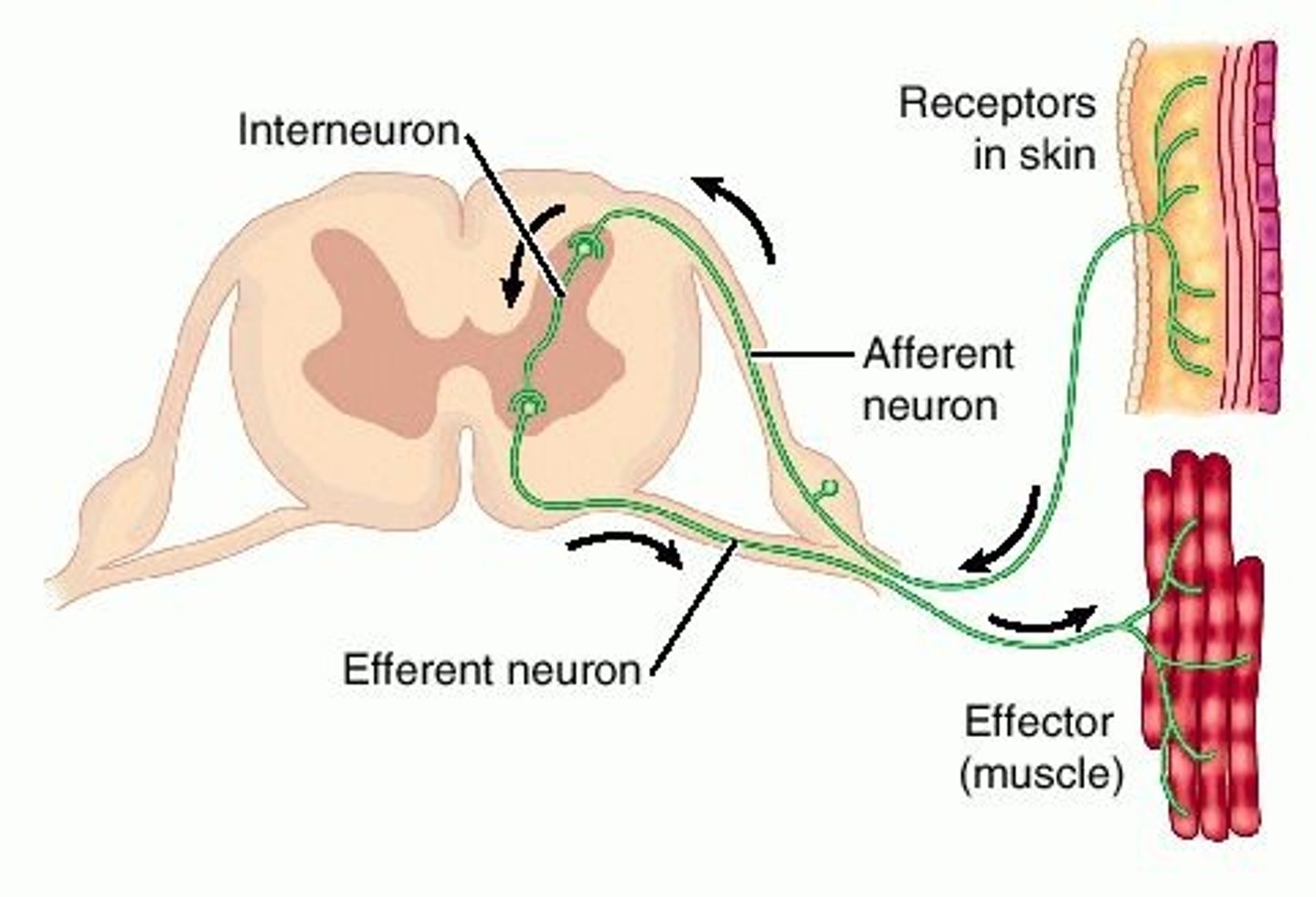
Interneuron
neuron that sends messages to other neurons nearby
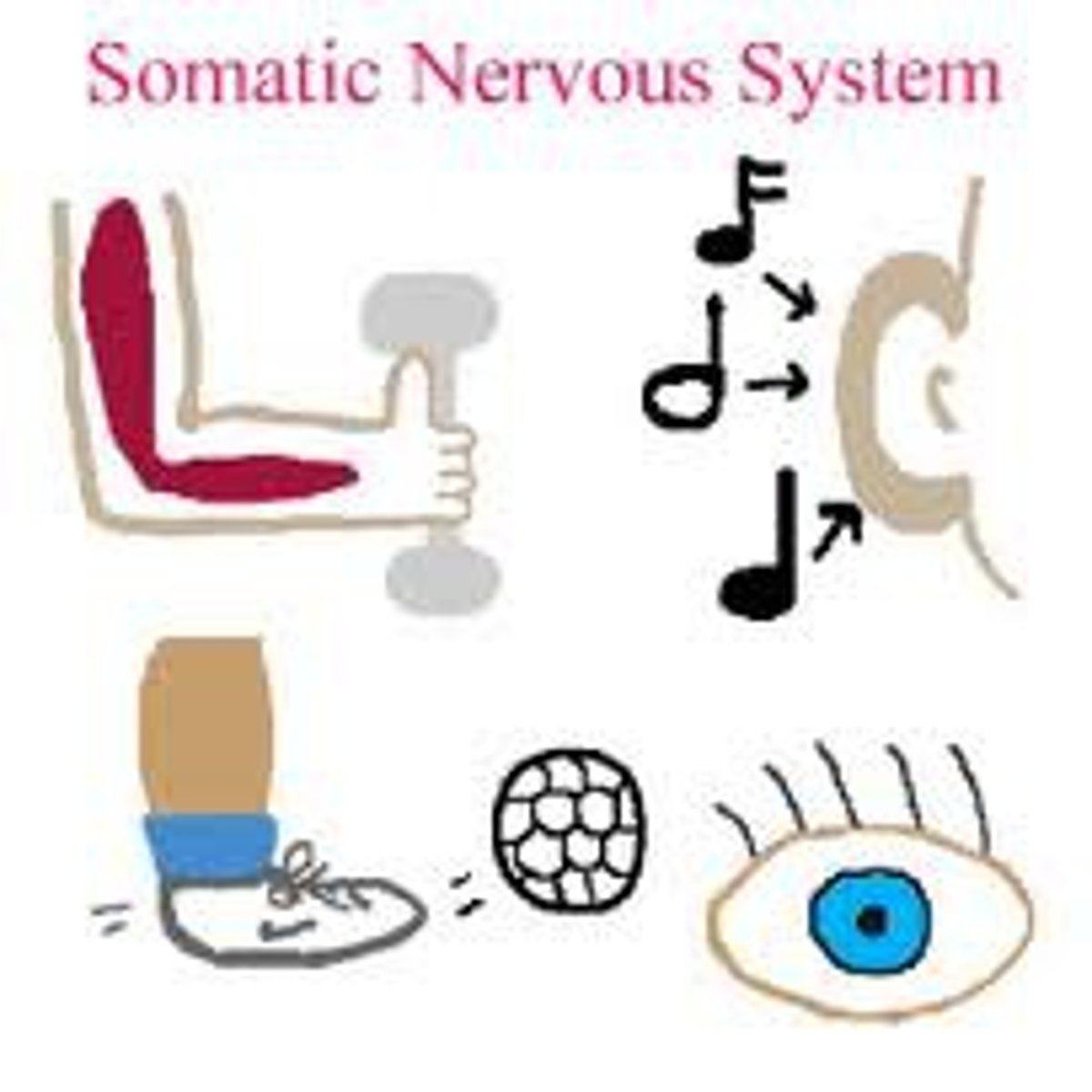
somatic nervous system
part of the nervous system that conveys
information between the CNS and the
body, controlling and coordinating voluntary
movement
autonomic nervous system
part of the nervous system controlling the
involuntary actions of our internal organs and glands, which (along with the limbic system) participates in emotion regulation
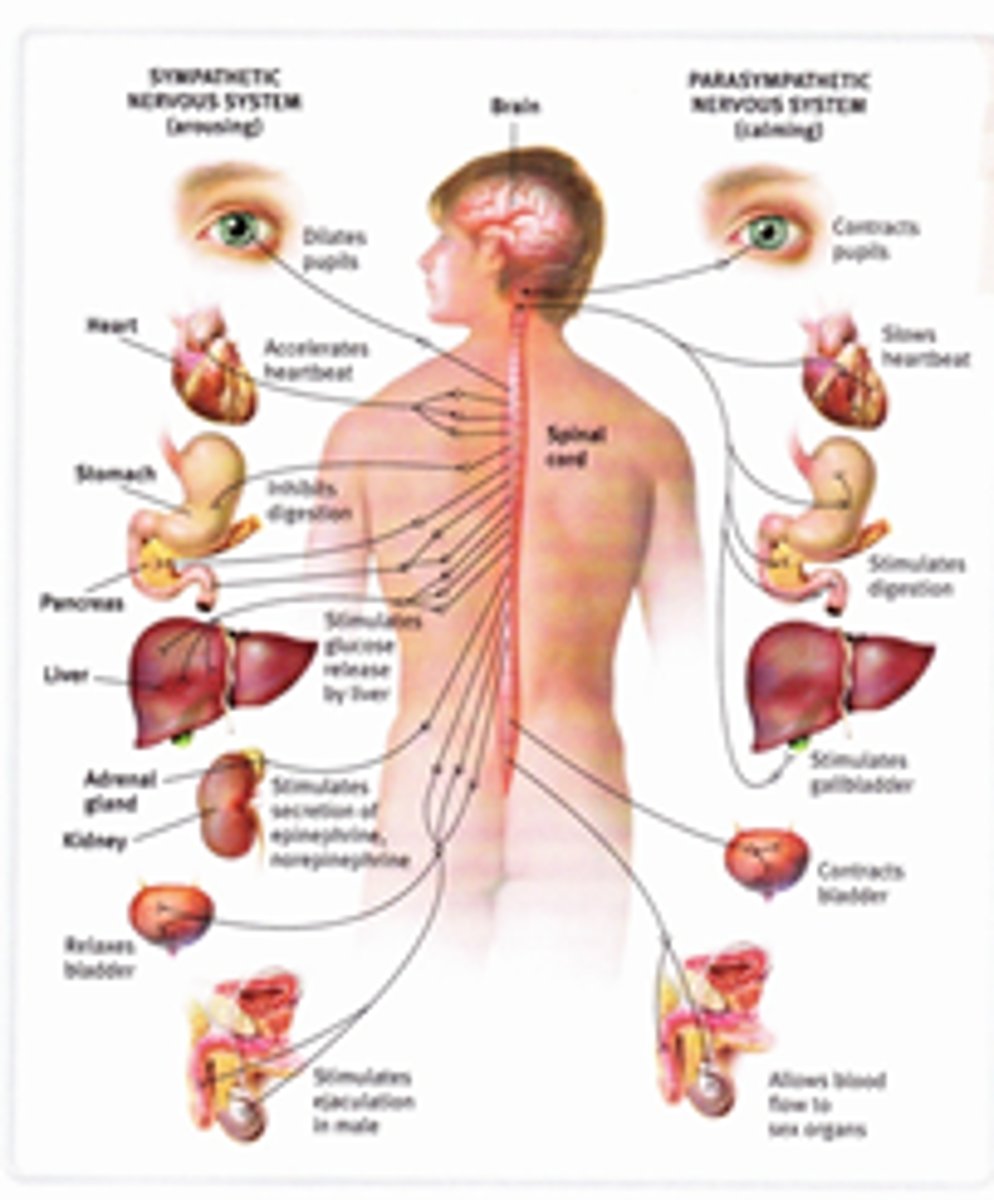
sympathetic nervous system
division of the autonomic nervous system
engaged during a crisis or after actions
requiring fight or flight
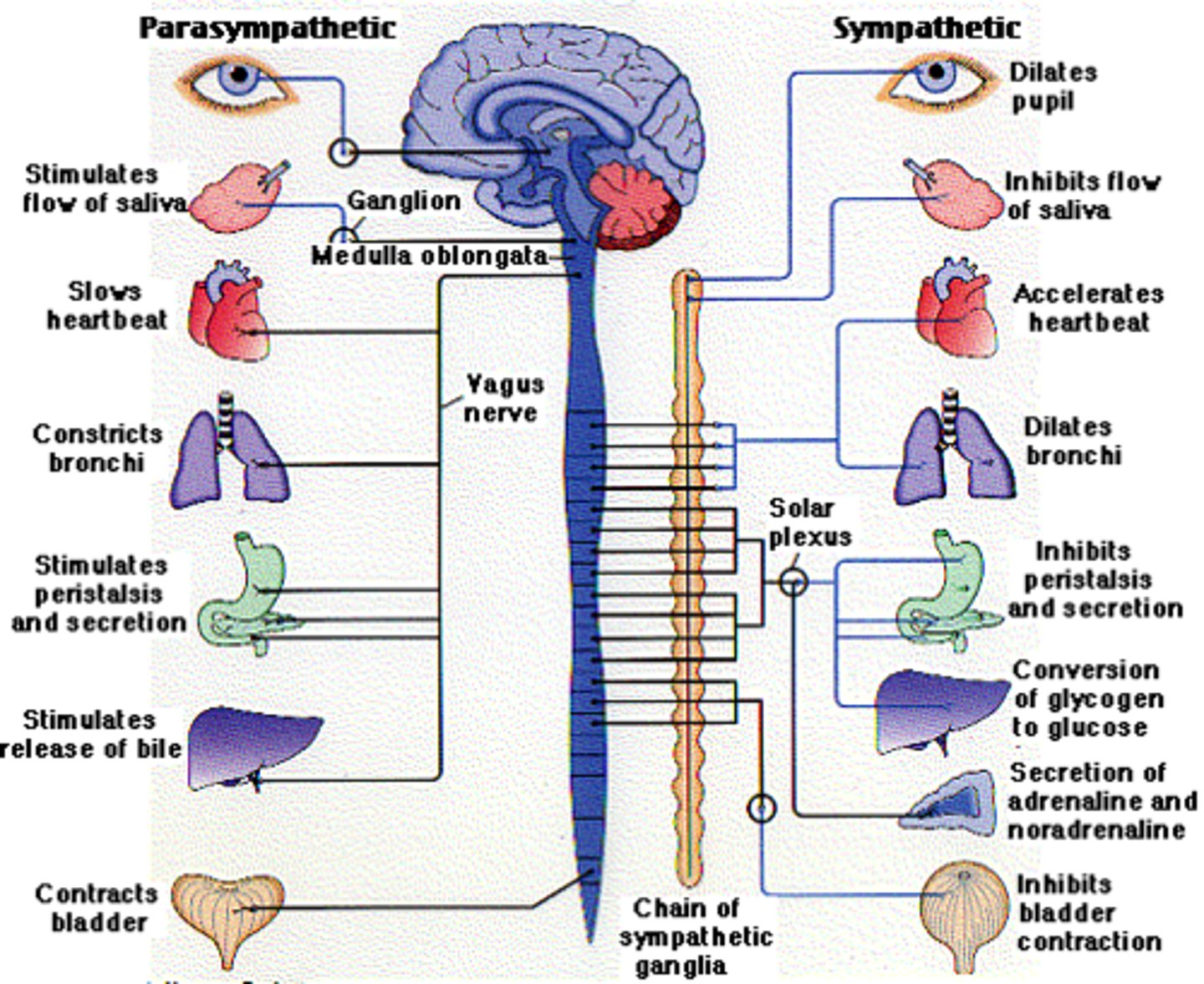
parasympathetic nervous system
division of autonomic nervous system that
controls rest and digestion

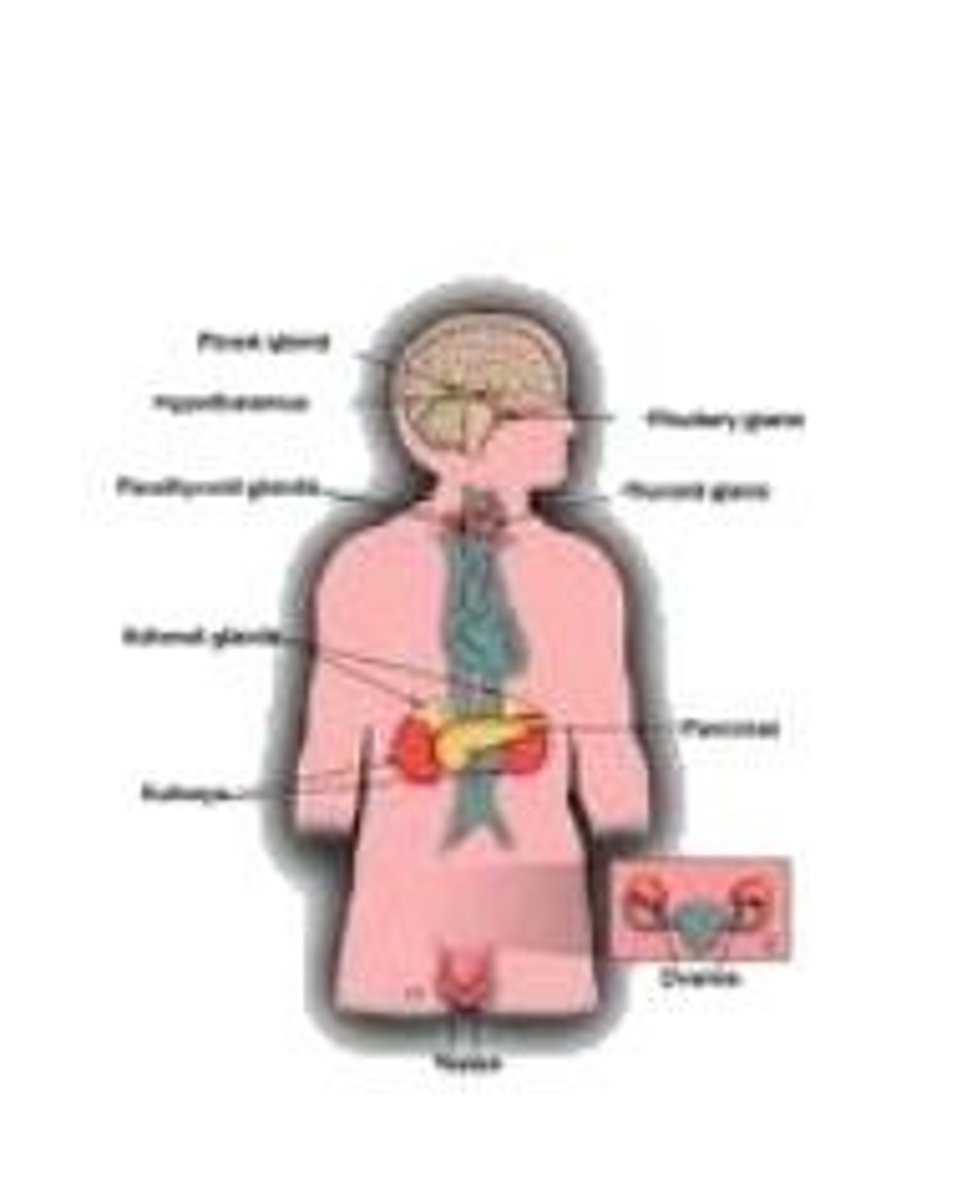
endocrine system
system of glands and hormones that
controls secretion of blood-borne chemical
messengers
Hormone
chemical released into the bloodstream that
influences particular organs and glands
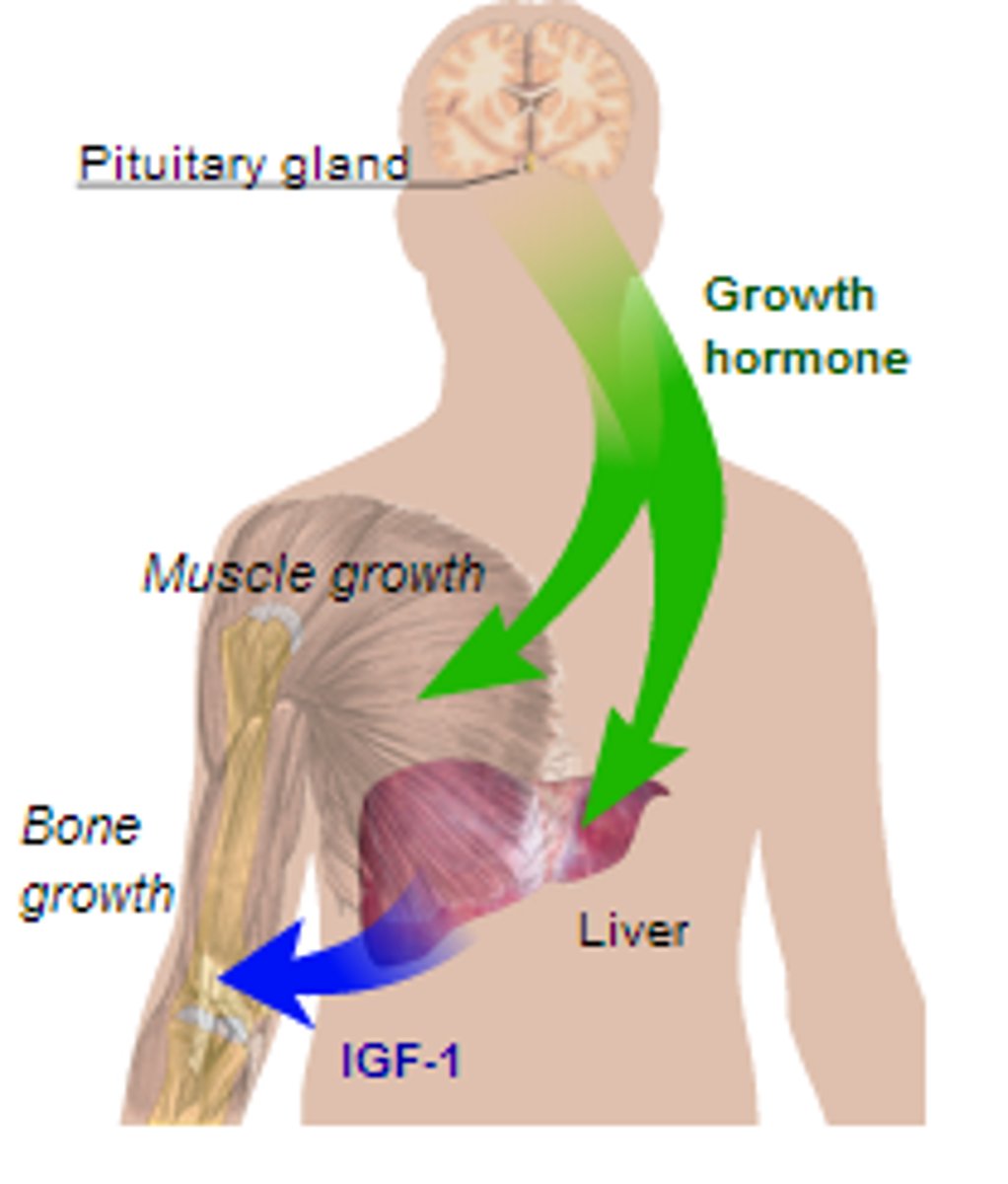
Pituitary Gland
master gland that, under the control of the
hypothalamus, directs the other glands of
the body
adrenal gland
tissue located on top of the kidneys that
releases adrenaline and cortisol during states of emotional arousal

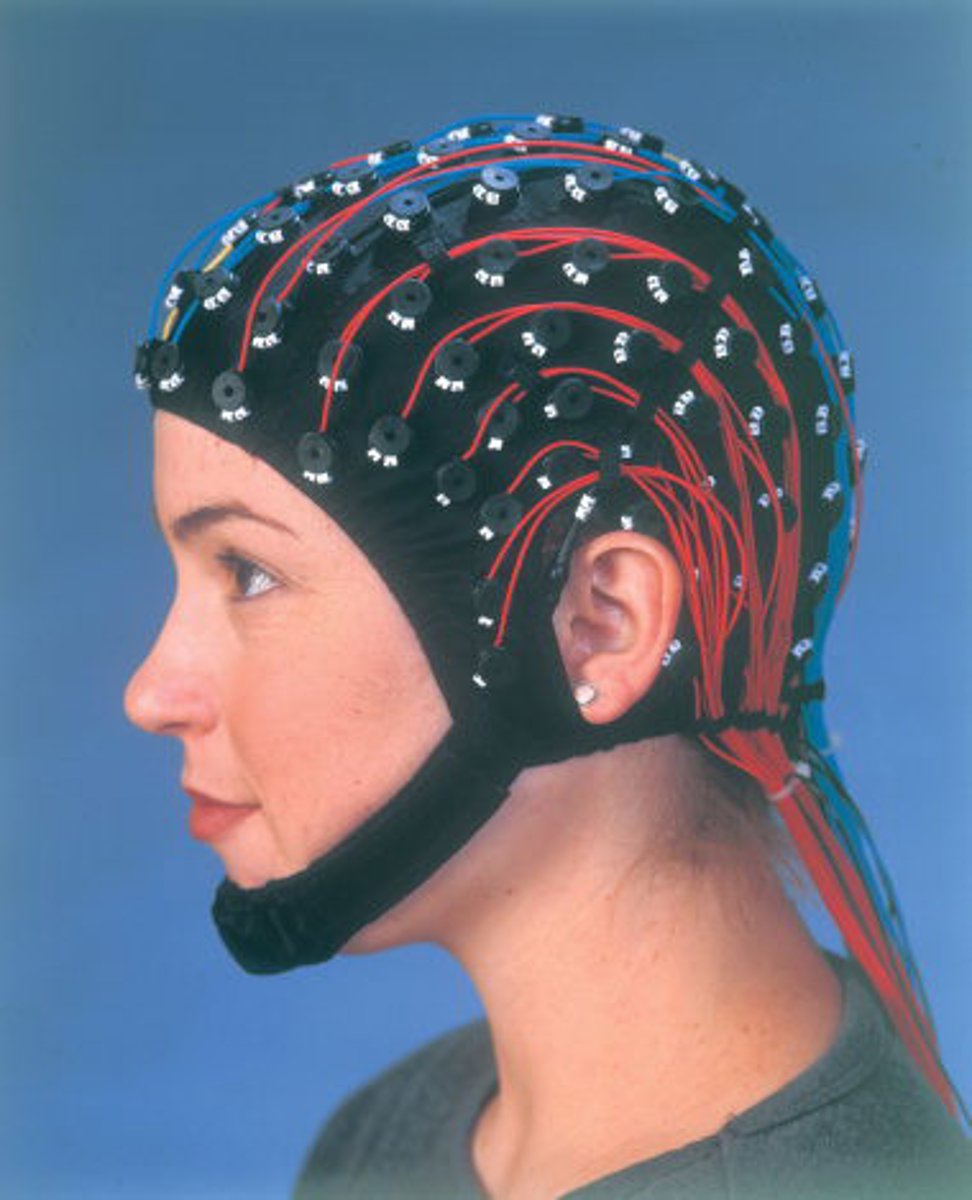
electroencephalograph (EEG)
recording of brain's electrical activity at the
surface of the skull
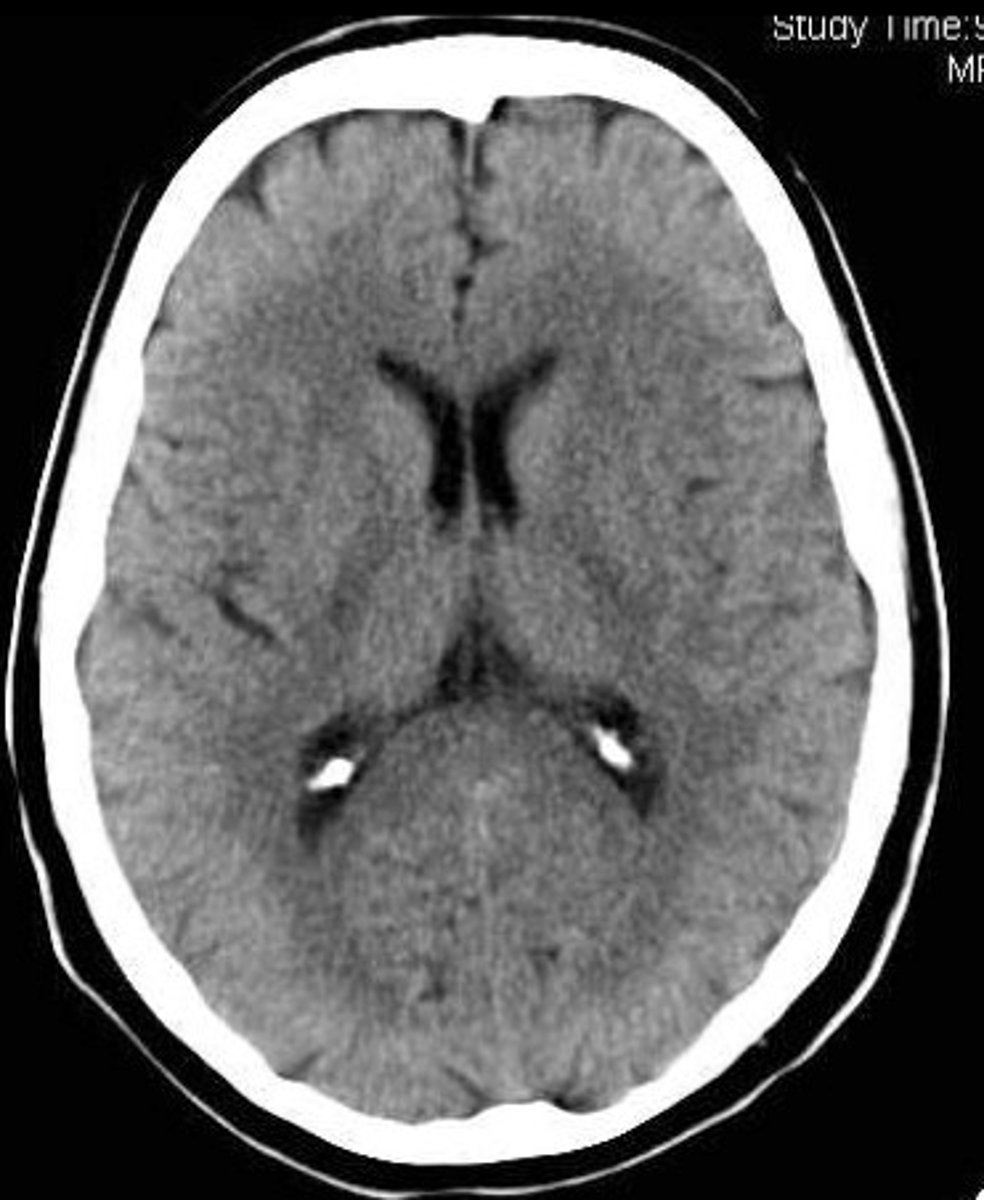
computed tomography (CT)
(CAT scan) a scanning technique using multiple X-rays to construct three-dimensional images
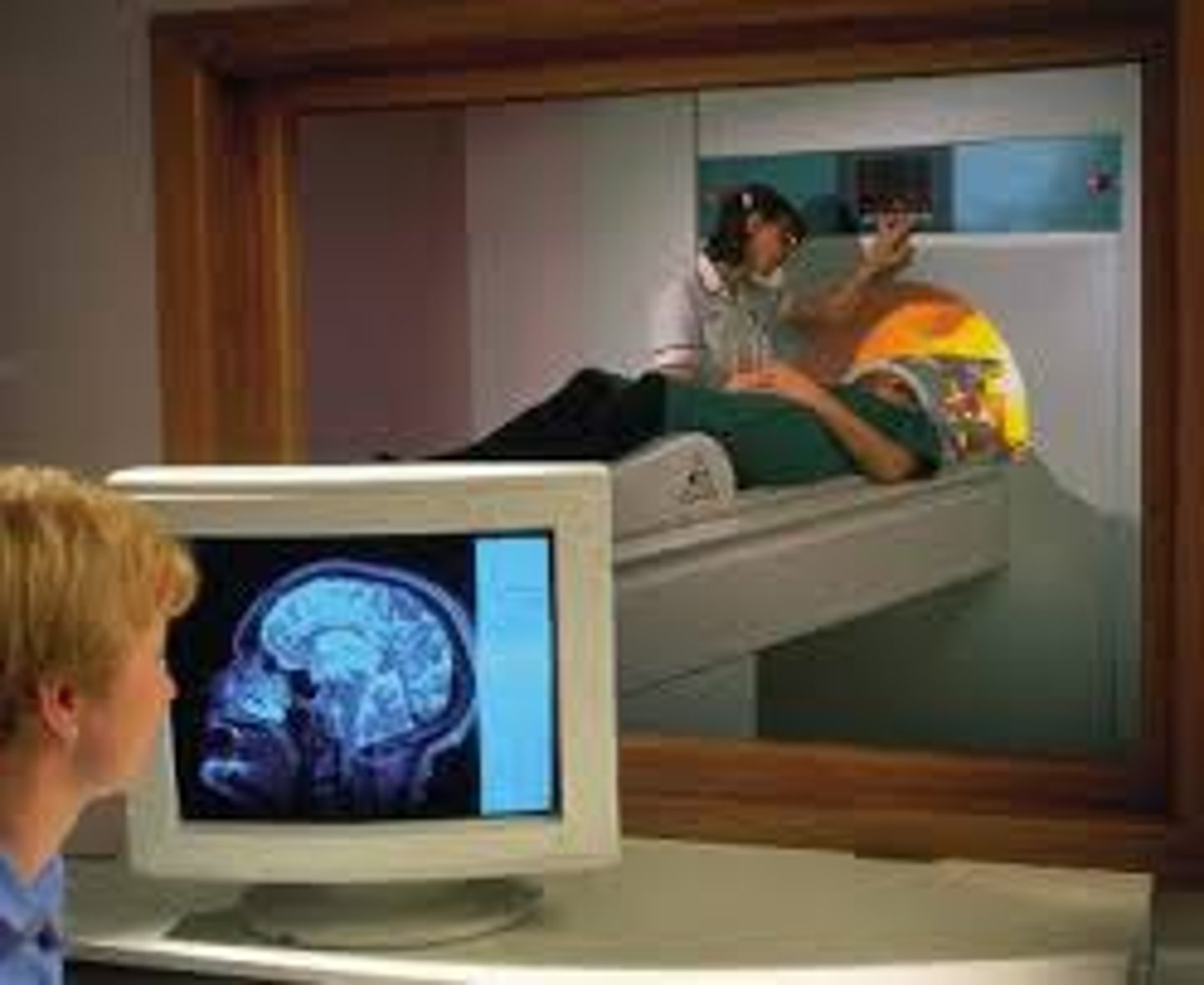
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
technique that uses magnetic fields to
indirectly visualize brain structure
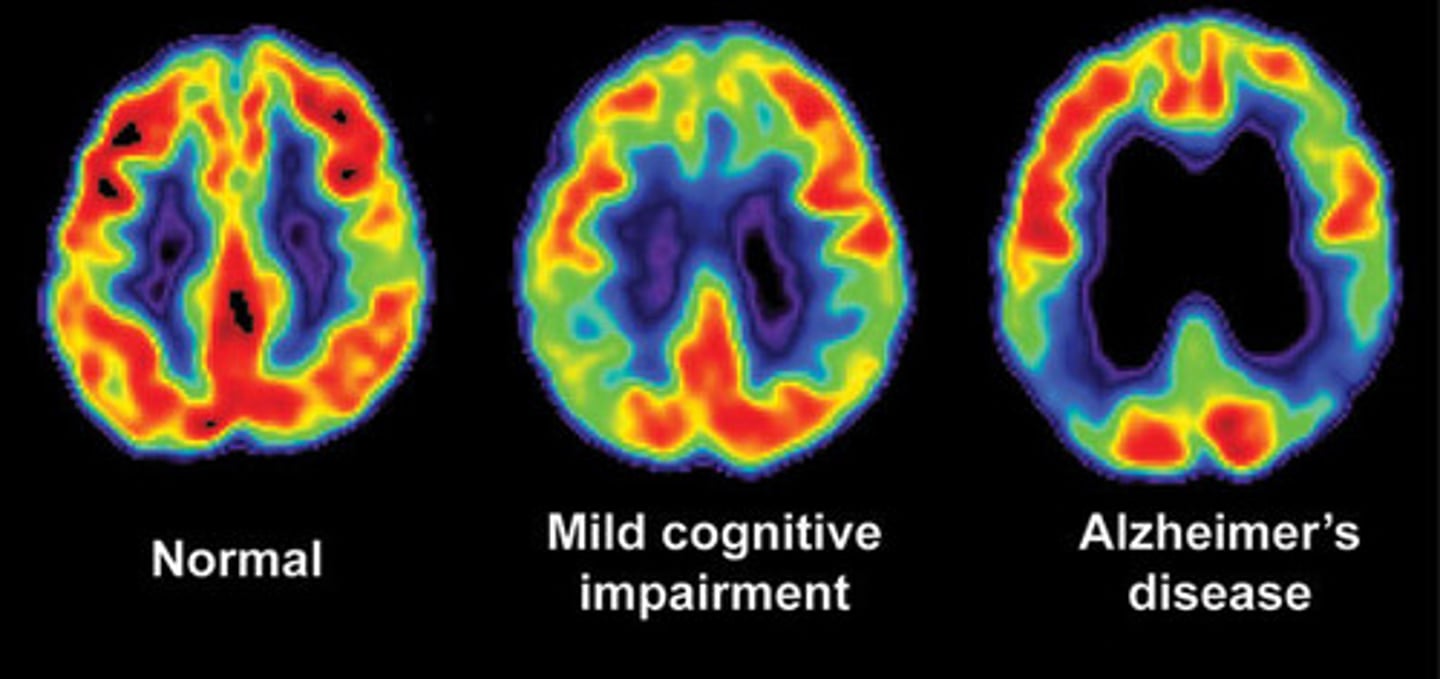
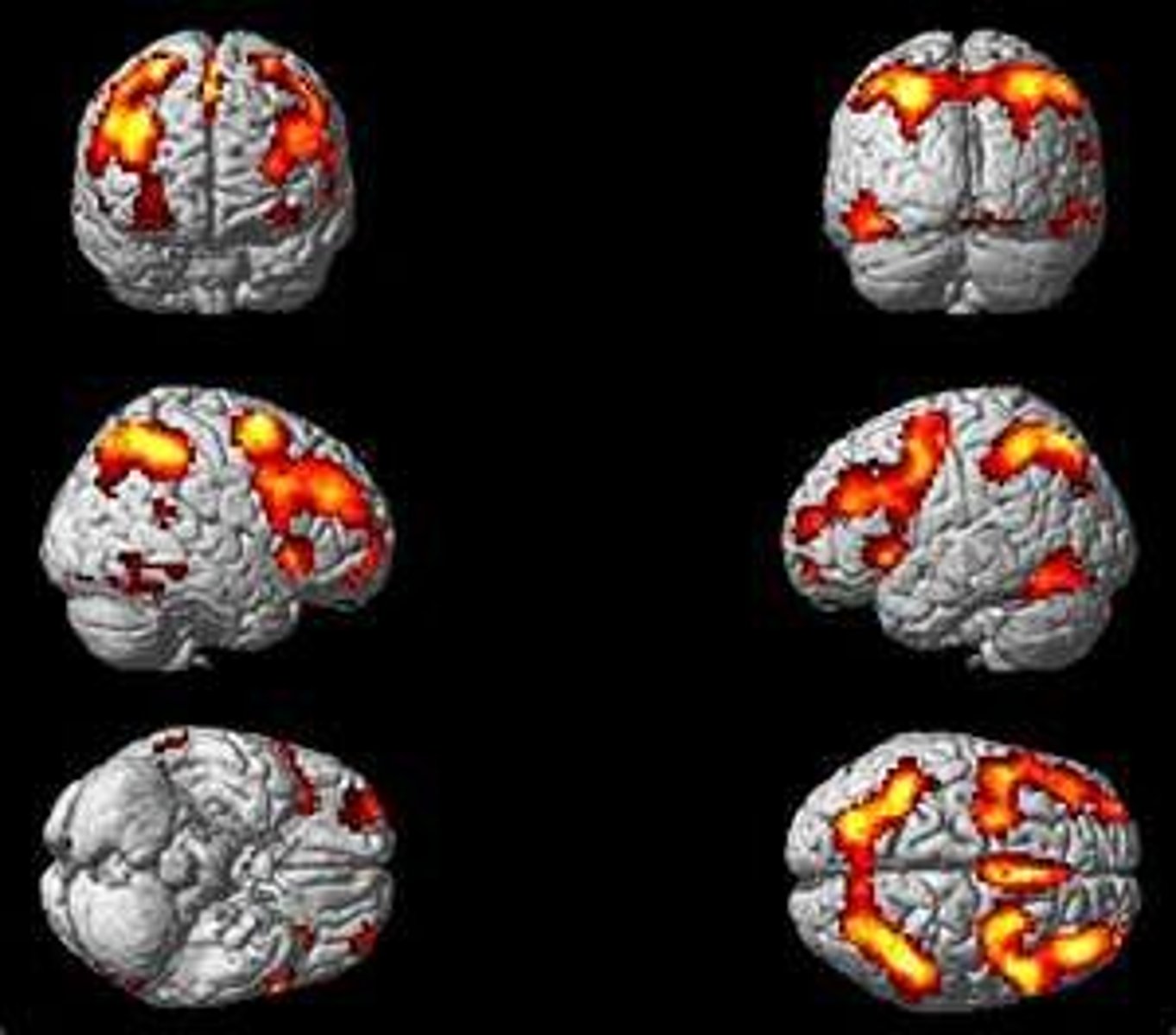
positron emission tomography (PET)
imaging technique that measures consumption of glucose-like molecules, yielding a picture of neural activity in different regions of the brain
functional MRI (fMRI)
technique that uses magnetic fields to visualize brain activity using changes in blood oxygen level
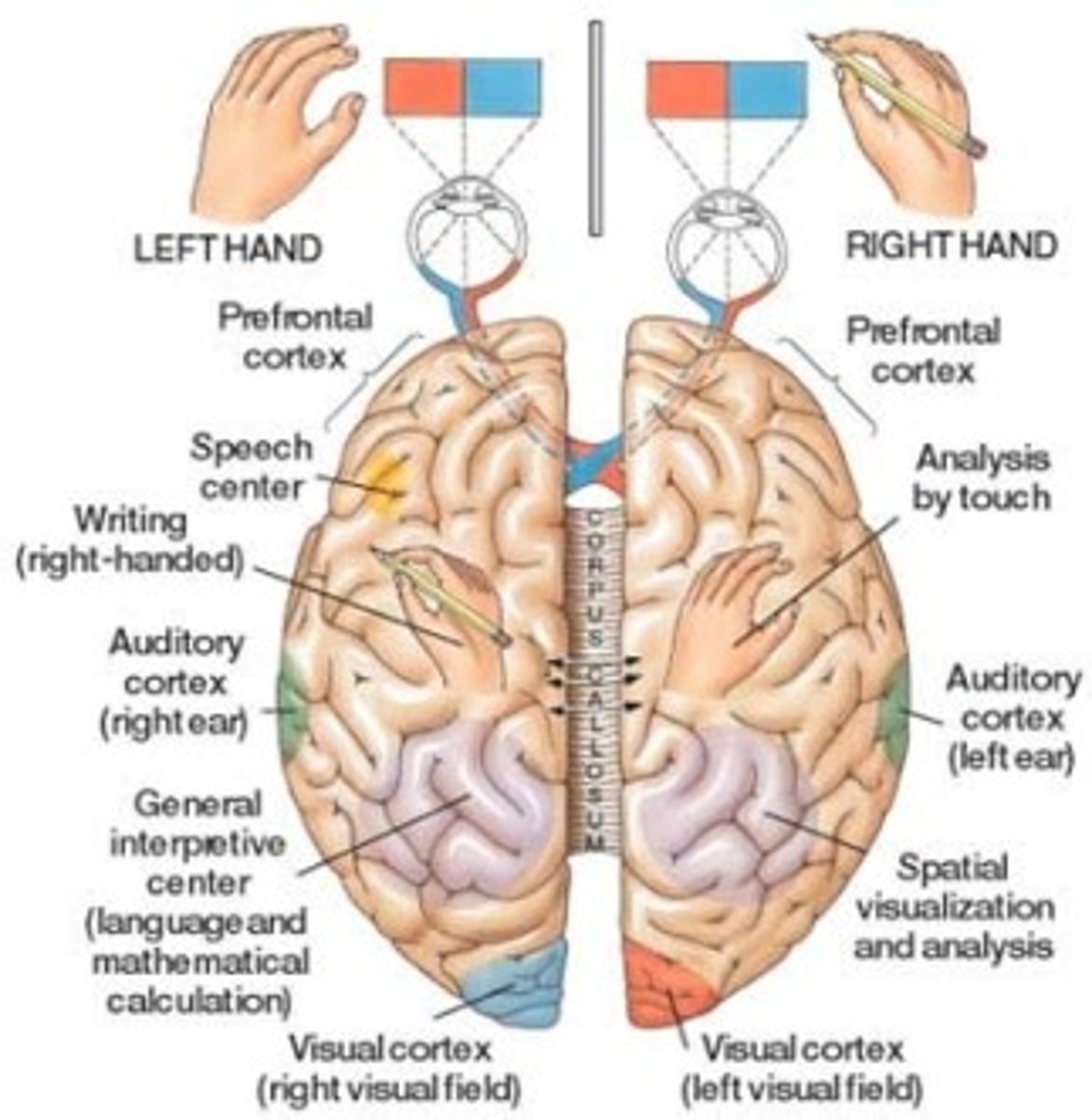
split-brain surgery
procedure that involves severing the corpus callosum to reduce the spread of epileptic seizures
Afferent Neurons
neurons that send signals to the brain
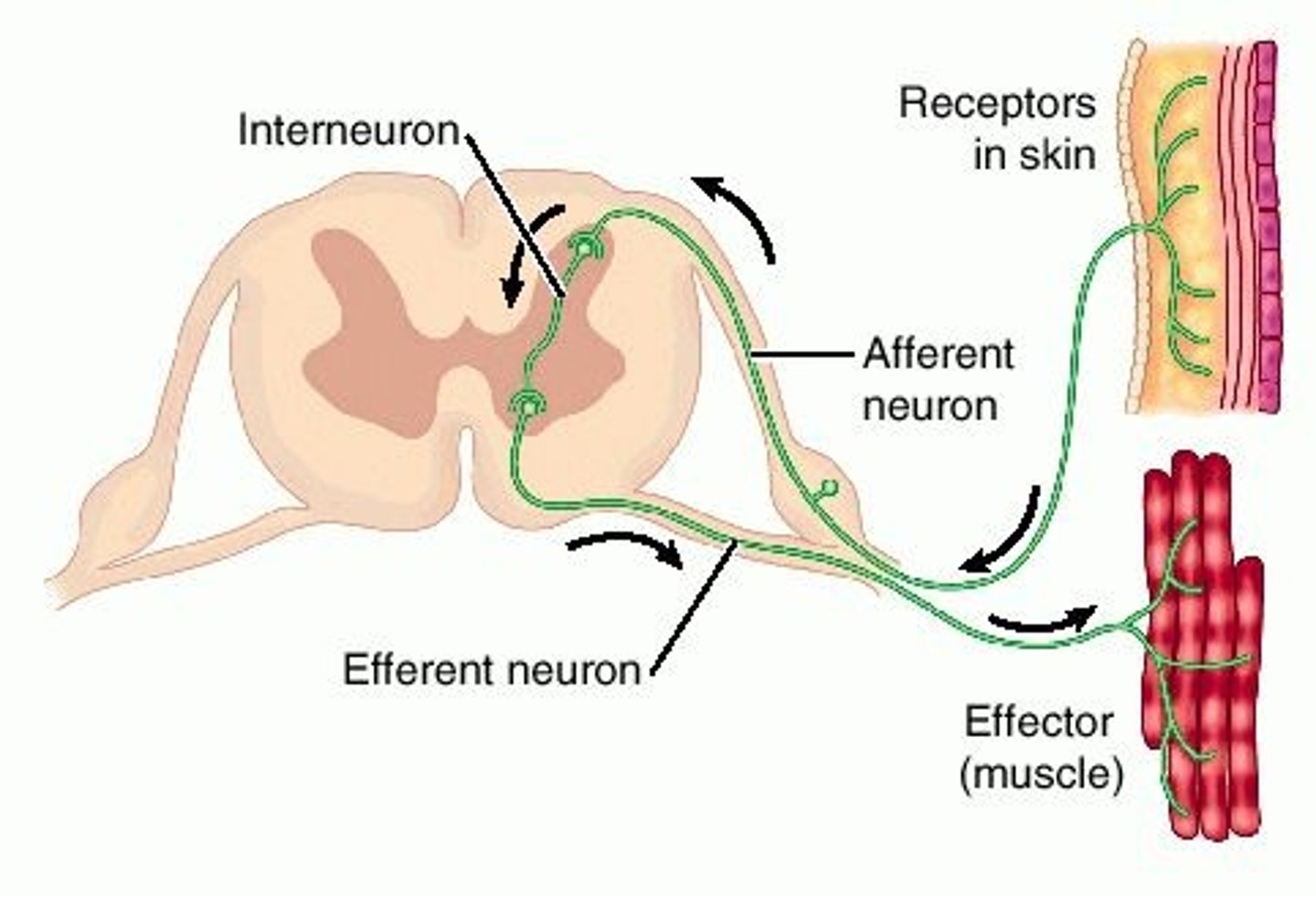
Efferent Neurons
neurons that send signals away from the brain
All-or-Nothing Principle
a neuron can release all of its neurotransmitters or none

Antagonist
locks into a receptor site like the neurotransmitter it mimics

Agonist
blocks a neurotransmitter

Sensory Cortex
portion of the brain which interprets body sensations
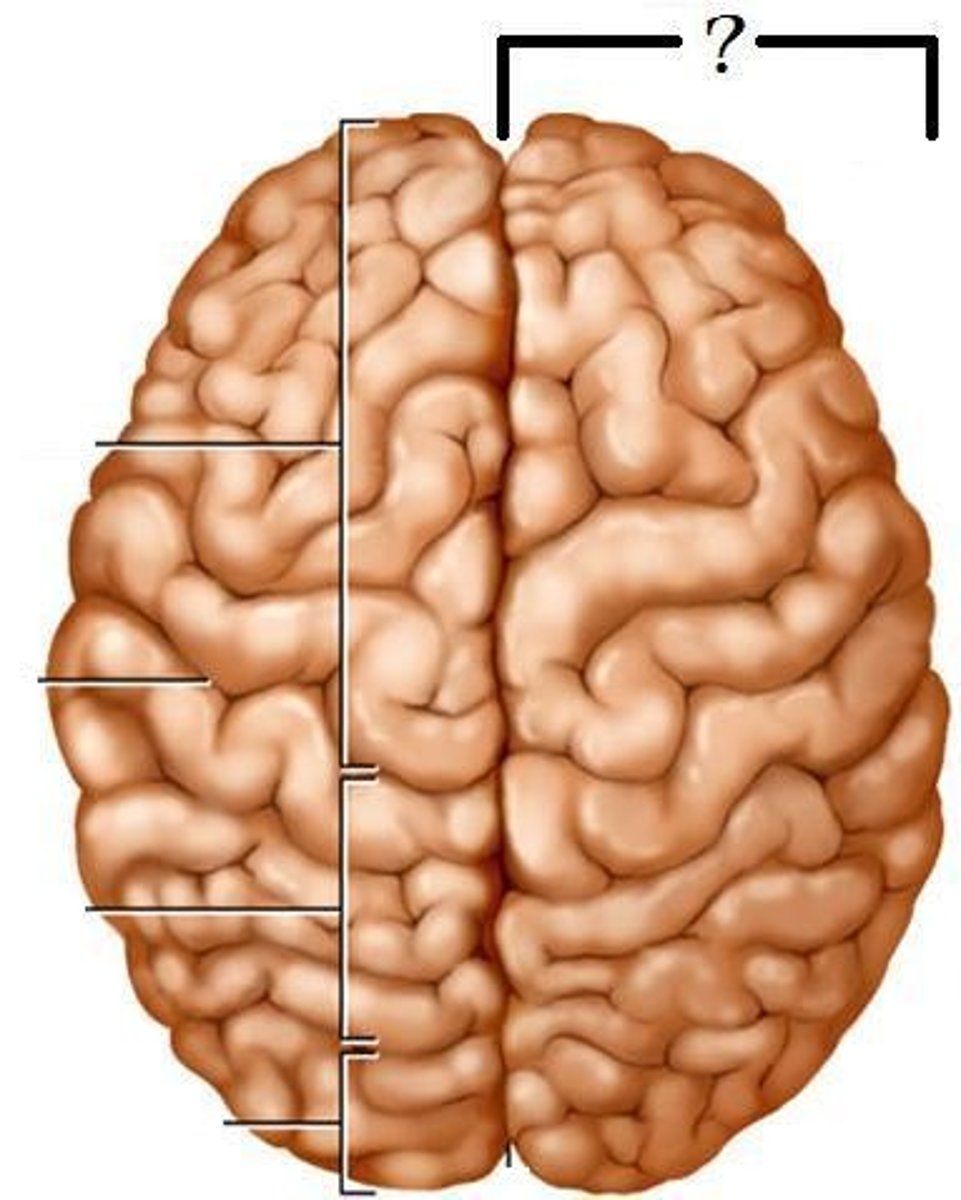
Right Hemisphere
part of the brain responsible for logic, spatial and holistic
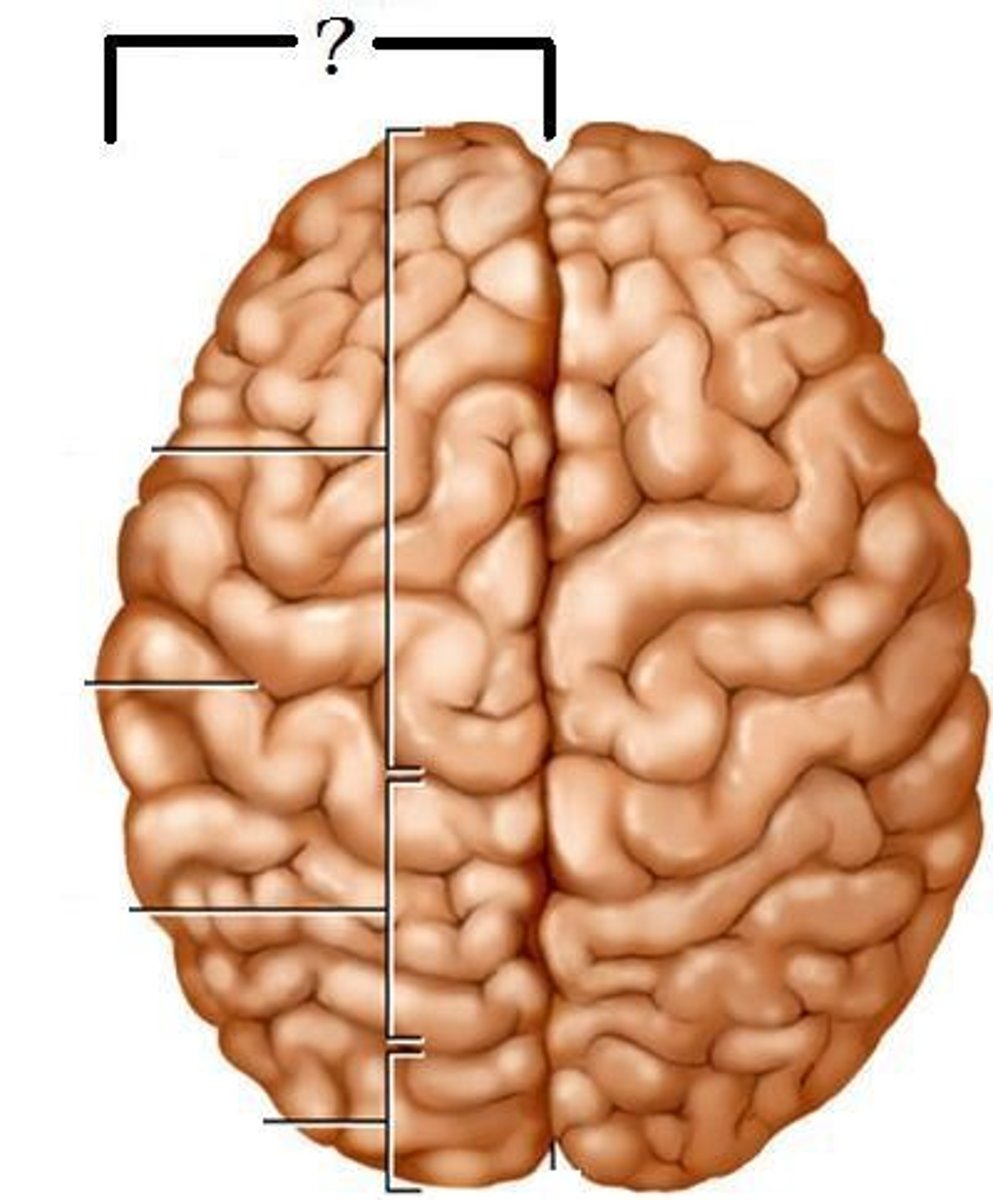
Left Hemisphere
part of the brain responsible for language, math and analyzing
Biological psychology
A branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior.
Neuron
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
Myelin sheath
A layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the next.
Action potential
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon. The action potential is generated by the movement of positively charged atoms in and out of channels in the axon's membrane.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers that traverse the synaptic gaps between neurons. When released by the sending neuron, neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a neural impulse.
Acetylcholine (Ach)
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction.
Endorphins
"Morphine within"—natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and to pleasure.
Nervous system
The body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems.
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The sensory and motor neurons that connect the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body.
Nerves
Neural cables containing many axons. These bundled axons, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, connect the central nervous system with muscles glands, and sense organs.
Sensory neurons
Neurons that carry incoming information from the sense receptors to the central nervous system.
Motor neurons
Neurons that carry outgoing information from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands.
Interneurons
Central nervous system neurons that internally communicate and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs.
Somatic nervous system
The division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the bod's skeletal muscles. Also called the skeletal nervous system.
Autonomic nervous system
The part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
Sympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations.
Parasympathetic nervous system
The division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy.
Reflex
A simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response.
Neural networks
Interconnected neural cells. With experience, networks can learn, as feedback strengthens or inhibits connections that produce certain results. Computer simulations of neural networks show analogous learning.
Endocrine system
The body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream.
Hormones
Chemical messengers, mostly those manufactured by the endocrine glands, that are produced in one tissue and affect another.
Adrenal glands
A pair of endocrine glands just above the kidneys. The adrenals secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress.
Pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
Lesion
Tissue destruction. A brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue.
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
An amplified recording of the waves of electrical activity that sweep across the brain's surface. These waves are measured by electrodes placed on the scalp.
PET (positron emission tomography)
A visual display of brain activity that detects where a radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain performs a given task.
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
A technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain.
fMRI (functional MRI)
A technique for revealing blood flow and, therefore, brain activity by comparing successive MRI scans show brain anatomy; fMRI scans show brain function.
Brainstem
The oldest part and central core of the brain, beginning where the spinal cord swells as it enters the skull; the brainstem is responsible for automatic survival functions.
Reticular formation
A nerve network in the brainstem that plays an important role in controlling arousal.
Cerebellum
The "little brain" attached to the rear of the brainstem; its functions include processing sensory input and coordinating movement output and balance.