Business - 3.10
1/103
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A-level Business AQA Managing Change
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
104 Terms
causes for change (x5)
a need to replace and update current technology
number, nature and quality of human resources in a business e.g. skills, motivation etc.
issues about the organisational structure including lines of communication, management hierarchies etc.
growth vs retrenchment
objectives and vision of internal stakeholders
external change
changes in the external environment of a business or its competitive environment (must ensure the business can respond quickly to this)
incremental change
introducing many small, gradual changes in order to meet a goal e.g. improving quality = refining each component of a product
radical change
stepped change e.g. plan for the sudden automation of a production process as would be extremely disruptive to work practices
disruptive change
shift in the underlying forces of an industry or segment of an industry e.g. retailing or cameras on phones influencing market for cameras
managing change
the moving of individuals, teams and organisations from a current state to a future desired state (involves helping employees to understand, commit to and accept the need for change)
lewin’s force field analysis (x4)
identify and evaluate (score) the driving forces for change
do the same for restraining forces
chart and calculate the overall ranking
develop a strategy to strengthen driving forces or weaken restraining ones
driving forces
those seeking to promote change
restraining forces
those attempting to maintain current business operations
equilibrium
the balance between the driving and restraining forces (must be upset for change to occur)
value of change (x5)
maintain a competitive advantage
can take advantage of developing technologies
customers needs and wants constantly changing so must be prepared to meet their needs
change can lead to improved working conditions and greater job satisfaction
improve organisational structure (efficiency + productivity)
flexible organisations
to respond to change, businesses must be flexible so they can respond quickly
benefits of flexible organisations (x6)
respond quickly to market conditions
cut down costs, particularly labour ones
improved 24/7 customer service
subcontract and outsource non-core features
cut down business premise costs
improved motivation and productivity
restructuring
fundamental internal change to the organisational structure or systems of a business e.g. Ford
examples of restructuring (x4)
dismiss employees
eliminate whole departments
close retail or factory locations
outsource their manufacturing
advantages of restructuring (x4)
operational costs can be reduced
outsourcing can be less expensive
layers of management can be removed which can help communication and decision-making
new technologies may enable a competitive advantage
disadvantages of restructuring (x4)
can lose highly skilled workers
remaining staff may have to be retrained (costly)
insecurity and morale issues for remaining staff
employee responsibilities may change (temporary fall in production)
delayering
the removal of one or more levels of hierarchy within an organisation (producing a flatter organisational structure with managers having a wider span of control) e.g. Microsoft
advantages of delayering (x5)
can redesign jobs so greater delegation, empowerment and motivation
more authority is given lower down organisation
improved communication as messages pass through fewer layers
departmental rivalry is reduced
reduced costs and fewer managers who tend to be on higher salaries
disadvantages of delayering (x5)
not all organisations suit flatter structures as workers on the factory floor may not want more authority
motivation and security issues with remaining staff
period of disruption as employees learn their new roles
wider span of control can reduce communication
loss of ‘corporate knowledge’
flexible working contracts
give employees a choice over the actual times they are contracted to be at work e.g. Google
part-time working
employees are contracted to work less than full time hours
term time working
workers remain on full time contracts but can take time off during the school holidays
job sharing
two or more people share the responsibility of a job between them
flexitime
allows employees to choose, within certain time limits, when to start and finish work (as long as present at core times)
career breaks or sabbaticals
extended periods of leave, normally unpaid, from a few months to a few years
zero-hour contracts
individuals have no guarantee of a minimum number of working hours (only when required)
advantages of flexible working (x5)
employees have greater freedom
can reduce commuting time allowing for improved work-life balance for employees
can improve morale and reduce absences
reduction in overtime costs, late arrivals etc.
reduces unnecessary costs of paying employees when not needed
disadvantages of flexible working (x3)
administration of the scheme has significant costs
when premises are open longer there may be increased overheads
employees may not work at certain times which may not be suitable for all organisations
organic structures
flat or open structures typified by wide spans of control, decentralisation, low specialisation and formalisation, horizontal communication and loose departmental control e.g. Patagonia or Facebook
mechanistic structures
more traditional and highly inflexible structures typified by narrow spans of control, centralisation, high specialisation and formalisation as well as rigid departmentalisation e.g. McDonald’s
what does the structure a business chooses depend on? (x5)
industry → organic structures work best in a fluid, unpredictable business climate i.e. start ups
size of organisation (larger = mechanistic as clear lines of authority makes it simpler)
technology (mechanistic if tasks are routine etc.)
management style
employee skills (organic requires versatility)
knowledge management
the process of capturing, developing, sharing and effectively using organisational knowledge
uses of knowledge management (x2)
allows predictions, associations and predictive decisions as found in connections, conversations, experienced based intuition and ability to compare (personality)
providing insight, guidance, experience and know-how for the purpose of decision making and effective action
information management
the provision of the right information to the right people at the right time (processed and factual data easily expressed in written form)
e.g. big data and data mining
benefits of knowledge and information management (x7)
sustainable competitive advantage as can exploit it
sharing of information between employees means knowledge doesn’t leave with employees
substantial savings as more easily brought ‘up to speed’ with valuable knowledge
lead to greater innovation
help a ‘global team’ of management coordinate and share knowledge and ideas (avoid managerial diseconomies)
decrease in labour turnover and increase in productivity
helps to ensure faster and more accurate decision making as utilises skills of all employees
barriers to change (x6)
lack of clear objectives or sense of mission and purpose
inappropriate and insufficient resources to assist change
inappropriately trained staff with non-relevant experience
resistance to change in relation to impact on employees
nature of organisaton
external factors such as competitors’ actions
Kotter + Schlesigner’s reasons for resistance to change (x4)
parochial self-interest = a desire not to lose something of value in terms of implications of change
misunderstanding and lack of trust
different assessments as employees don’t think it makes sense
low tolerance of change as fear not able to develop new skills
education and communication to overcome barriers to change
one to one discussions, presentations or group reports etc.
especially relevant if resistance based upon a lack of understanding and change requires resistors help
participation and involvement to overcome barriers to change
especially important if initiators for change don’t have all knowledge, skills and information so can use other employees (making them more committed and ‘buy in’ to change)
facilitation and support to overcome barriers to change
providing practical and emotional support to employees who have difficulty dealing with change including training in new skills or offering mentoring and counselling services
negotiation and agreement to overcome barriers to change
giving resistors incentives to either adapt or leave e.g. higher wages for no industrial action etc.
manipulation and cooperation to overcome barriers to change
co-opting an individual or a leader to become involved for their cooperation and influence on other employees (not fully informed)
explicit and implicit coercion to overcome barriers to change
suggest it may result in a loss of their jobs, being transferred or a loss of promotion prospects
organisational culture
the behaviour of people within an organisation and the meaning that they attach to those behaviours (based on values of founders, senior managers and core people who direct the organisation)
culture
organisation’s vision, values, norms, systems, symbols, language, assumptions, beliefs and habits
culture of Google (x5)
teamwork and creativity central to the design (to boost productivity and satisfaction)
staff treated as friends with access to various facilities e.g. gyms, hair salons etc.
20% of time spent on external projects
on-sight solar panels to meet energy needs sustainably
free food to meet all dietary preferences/needs
culture of Innocent (x4)
family atmosphere and strong culture to motivate employees based on entrepreneurial traits
lots of trust (viewed as a motivator)
engaged workforce
receive feedback constantly
how is culture demonstrated within a business (x6)
aims
behaviours of senior staff (+ in response to risk)
recruitment and training procedures
the way visitors and guests are looked after
degree of delegation
speed of decision
importance of organisational culture (x5)
creates distinctions between one organisation and another, differentiating
provides a sense of identity for employees and members
helps to generate commitment to something larger than self-interest
helps to hold organisations together by providing appropriate standards for what to do/say
guides and shapes the attitudes and behaviours of employees by defining rules etc.
task culture (+ examples)
project teams complete set tasks e.g. innovative businesses like Google
‘getting the task done’ so often when environment is rapidly changing and product life cycle is short
involves team working which ensures skills of individuals are exploited fully
role culture (+ examples)
clearly delegated authorities with a highly defined structure e.g. schools or the NHS
controlled by procedures and role descriptions (so coordination is from the top)
value predictability and consistency so difficult to adjust to change
power culture (+ examples)
control radiate from the centre with power concentrated with few individuals e.g. family business or Virgin (Richard Branson = charismatic leader)
decisions made quickly but success depends upon skills of those ‘at the top’
performance judged upon results so can be accompanied by low morale or high labour turnover
person culture (+ examples)
people (with similar training, background and expertise) believe themselves to be superior to the business e.g. firm of architects
exists when individuals dictate the firm’s policies and strategies to gain personal benefits
difficult to manage as strong sense of how they want to work (but bring own expertise)
reasons for changing organisational structure (x4)
if there is a new leader who wants to do things differently
if society’s values change e.g. ethical/environmental policies
if performance of the business is deteriorating
if there are new owners with different objectives (= culture clash w. mergers and takeovers)
problems of changing organisational culture (x3)
change may be challenging and existing employees may resist
beliefs may be deeply held so may instead cause questions on how they view their job
may involve extensive training and education which may need heavy investment
strategic implementation
creating a framework for carrying out the strategy agreed at both corporate and functional levels by assigning responsibilities and operational targets (about 70% of strategic plans are never implemented)
method of strategic implementation (x4)
identify the mission and goals of the organisation
use a SWOT analysis before the strategies are put together to analyse internal and external environment
formulate strategies
implement strategies and evaluate results
external factors affecting strategy (x2)
changes in the external environment may affect strategic plans and their implementation e.g. economic cycle
changes in the firms competitive environment may affect implementation as competitor’s actions may change chance of success
internal factors affecting strategy (x8)
leadership styles need to be in support of strategy so actions align
organisational structure and culture
communication can overcome resistance
timing
adequate resources
network analysis for planning
monitoring to review progress and ensure accountability of meeting targets etc.
reviewing and evaluating for alternatives
value of leaders (x3)
likely to be involved in setting, communicating and implementing the strategy
if leaders do not invest time, it is unlikely to be successful
need to help employees understand how the company could benefit from change
value of communication (x3)
usually developed by senior leaders and managers so reason and benefits for change must be communicated to get employees ‘on board’
essential to overcoming resistance
must reach every level of the organisation
importance of organisatonal structure (x3)
determined by culture, size of business, leadership and management, type of product and market
structure must fully reflect the organisation’s mission, objective and strategy (e.g. increasing sales requires expansion)
broken up into functional plans so a clear organisatonal structure with clear functional responsibility would assist strategy
value of network analysis (x2)
involves planning the different elements, working out the order and identifying the key activities to ensure efficiency
can understand where resources need to be allocated for different tasks to be completed in a set time
nodes
circles representing the beginning and end of an activity split into:
left hand side = number of node
top segment is earliest start time
lower segment is latest finish time
activities
events or tasks that consume time and are shown as lines or arrows that link the nodes (a letter or description is above)
duration
length of time that it takes to complete an activity and shown beneath the line representing the activity
EST
depends on the completion of the previous activity and always starts as 0 for activity 1
work forward from left to right by adding the duration of activities on the path leading to the node
if more than one path, highest total is taken
LFT
work backwards from right to left as the final node must equal the EST
deduct the duration of the activity when going backwards
if multiple, take the lowest possible value
method of creating a network (x5)
draw a node to represent the start of the network
identify any activities that don’t have any prerequisites (don’t rely on the completion of another activity) and draw lines from left to right
identify the activity line by placing a letter and the duration
move on to the first activity
carry on until complete
critical path
sequence of activities that cannot be delayed without delaying overall completion
those activities where the ESTs and LFTs are the same
non-critical activities can be delayed without delaying the completion time
total float
the amount of time that non-critical activities can be delayed without delaying the completion of the project as a whole
float calculation
LFT - EST - duration
benefits of network analysis (x8)
allows a business to improve efficiency of resources
helps the business know when activities are scheduled, assisting resource planning and stock ordering
can use CPA to divert resources from non-critical activities to critical ones
can help monitor and review project
forces managers to undertake planning
can identify impacts of delays
can be used alongside lean production
helps reduce risk and cost of complex projects
problems of network analysis (x7)
managers may be inflexible and rigidly stick to timing in CPA, missing opportunities to reduce overall time
any delay can have serious consequences if employed contractors etc. as can’t wait
complex activities may be difficult to represent accurately
based on time estimates that may not be accurate
doesn’t guarantee success
resources may not actually be as flexible as management hope
too many activities may make it too complicated
strategic planning process
the study of a range of choices available to the business in order to gain a competitive advantage over their competitors
why can strategic planning be high risk?
outcomes tend to be unknown as often involve a company moving into new areas which require additional resources, procedures and retraining
strategic implementation
the stage in the corporate planning process when the agreed strategy is put into effect, creating a framework of action plans and targets at a functional level
why is strategic implementation difficult?
research tends to show that the people who are charged with the implementation strategies have often been left out of the planning stages meaning they may not be well informed of rationale or links to overall objectives
planned strategy
the strategy that the organisation hopes or intends to implement and is described in detail in the organisation’s strategic plan
what do planned strategies tend to involve
strategic analysis, choice and implementation BUT only appropriate if the internal and external environment is stable and predictable
benefits of planned strategies (x5)
provide a structured means of analysis and thinking about complex strategic thinking
it can encourage a longer term view
used as a means of control by reviewing progress
useful means of coordination, involving people
can be communicated effectively as fixed and known
emergent strategy
a business is constantly learning and adapting strategies to the environment they face. It is unplanned and emerges in responses to internal and external changes that were not envisaged when the original planned strategy was formulated
why is emergent strategy helpful (x2)
fast paced and constantly changing business environment means don’t have to waste time formulating plans for 2-5 years ahead
allows the business to be more flexible (noting internal and external environment)
realised strategy
the part of the planned strategy that the business achieves over time and actually happens in practice, including the emergent strategy responding to change
unrealised strategy
the part of the planned strategy that needs to be abandoned and forgotten due to events developing in unexpected ways
strategic drift
the company responds too slowly to change in its external and competitive environment, leading to its eventual demise as it continues with a strategy which may have served it well in the past but is no longer suited to current circumstances e.g. Nokia, Blockbuster etc.
reasons for strategic drift (x6)
organisational culture restricts the ability of the firm to change at a necessary rate
leaders continue to persist with obsolete or largely redundant policies
a company simply reacts to changes in the environment rather than being proactive
the strategic plan may not be reviewed regularly to check if it is well aligned to what is happening in the external environment
the organisation is not keeping pace with changes in technology
competitive actions
phases of strategic drift
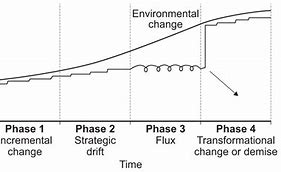
phase 1 of strategic drift
the firm makes incremental changes that are part of its planned strategy to change in line with external changes so remains ahead of the market and they develop or retain a competitive environment
phase 2 of strategic drift
rate of change in the external environment speeds up, but the firms approach of gradual incremental change means strategic drift begins and the firms starts to get left behind
phase 3 of strategic drift
leaders recognise the decline in the business performance and that there is a gap between what the market expects and what the business it provides
leaders try to respond by doing what they have always done, resulting in flux, and then strategies may change but disagreement about appropriateness
phase 4 of strategic drift
the business either falls completely and the firm closes or, if it survives, it undergoes transformational change to align its strategies with the market, and so begins to operate successfully again
transformational nature of overcoming strategic drift
includes a change in the underlying strategy and processes that an organisation has used in the past
occurs across the whole organisation and takes place over time as it addresses ALL the causes of strategic drift
evaluating strategic performance (x4)
evaluation and review of strategy will involve regular performance measurements against planned targets using KPIs
involves ongoing monitoring and reviewing of internal and external issues that may affect it
continual corrective actions need to be made to ensure that the strategy is appropriate to current conditions
should guard against strategic drift by identifying issues and allowing time to then adapt
stages of strategic planning (x5)
defining the mission and objectives
SWOT analysis
decides on choices available, with broad corporate plans emerging which an be interpreted into meaningful functional plans and targets
strategic implementation
control and evaluation to determine success in its implementation, and if it requires changing includes defining goals, analysing market conditions, formulating strategies, implementing plans, and evaluating outcomes
value of strategic planning (x4)
an organisation can improve business outcomes and avoid taking on unanticipated risks
provides direction and ensures everyone knows where it is heading, and how it intends to get there
leaders have a solid understanding of organisation and how the environment is changing
valuable learning tool to ensure managers are well informed and make decisions about required strategy quickly and appropriately
contingency planning
planning for the unexpected, reducing the risks and costs of unexpected events on the organisation as it may threaten the well-being or survival of the firm
examples where contingency plans are necessary (x8)
physical destruction from natural disasters
environmental disasters e.g. BP oil spillage
impact on foot and mouth disease on farming industry
major customers withdrawing custom or going into liquidation
pressure group activists or unwelcome media attention
workers going on strike
competitions launching a new product
severe recession or changes in exchange rates
crisis management
responds to a sudden event that poses a significant threat which normally involves damage limitation strategies and places heavy emphasis on PR and media relationships