The Nursing Process
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
The nurse focuses on what?
promoting health and well-being, including the dignity and humanity of the clients, families, and communities
The art of being a nurse is illustrated as what?
a healthy nurse-patient relationship where communication skills are foundational and respect, acceptance, and caring are essential, and the science of nursing is founded in understanding the four nursing concepts of health, person, environment, and nurse.
The nursing process:
include assessment, analysis, planning, implementation, and evaluation and involve skills of critical thinking.
The nursing process clinical judgement skills:
Recognition and observation for data collection (both subjective and objective)
Analysis of what was observed to determine possible client needs, concerns, or problems
Determination of priorities of care based on client health problems
Generation of a solution by creating a plan for and with the client based on measurable goals
Action and implementation of the most appropriate nursing actions or interventions
Evaluation of the client’s response to interventions
The nursing process be impacted so the nurse should consider?
The whole person as well as the environmental and individual factors that may impact how they understand, interpret, or relate to the client
The nursing process is ongoing meaning?
It demonstrates how a nurse thinks and what actions a nurse will take, and most importantly, how the client responds.
Environmental studies to consider for the nursing process:
Setting, situation, and the physical environment: Consider the safety and surroundings.
Observations of client: Consider clinical manifestations, appearance, and age.
Resources: Does the nurse have the tools, staff, or equipment required for client care?
Health record: Review the medical records, client history, labs, and diagnostic tests.
Is there a time limitation? Such as STAT or change in client condition?
Cultural considerations
Task requirements: skills needed, number of staff required, complexity of tasks
Risk assessment: identifying, finding, and removing any risks for harm and promoting safety and well-being
Individual nurse factors
Nurse Specific: Consider needed knowledge, skill, or specialized training to address the client’s needs.
Nurse Characteristics: Consider self, including attitude, thoughts, bias in caring for this client, as well as level of experience.
Nurse Cognitive Load: Consider stress level, ability to problem-solve, and memory.
Steps of the Nursing Process & Correlating Clinical Judgment Functions
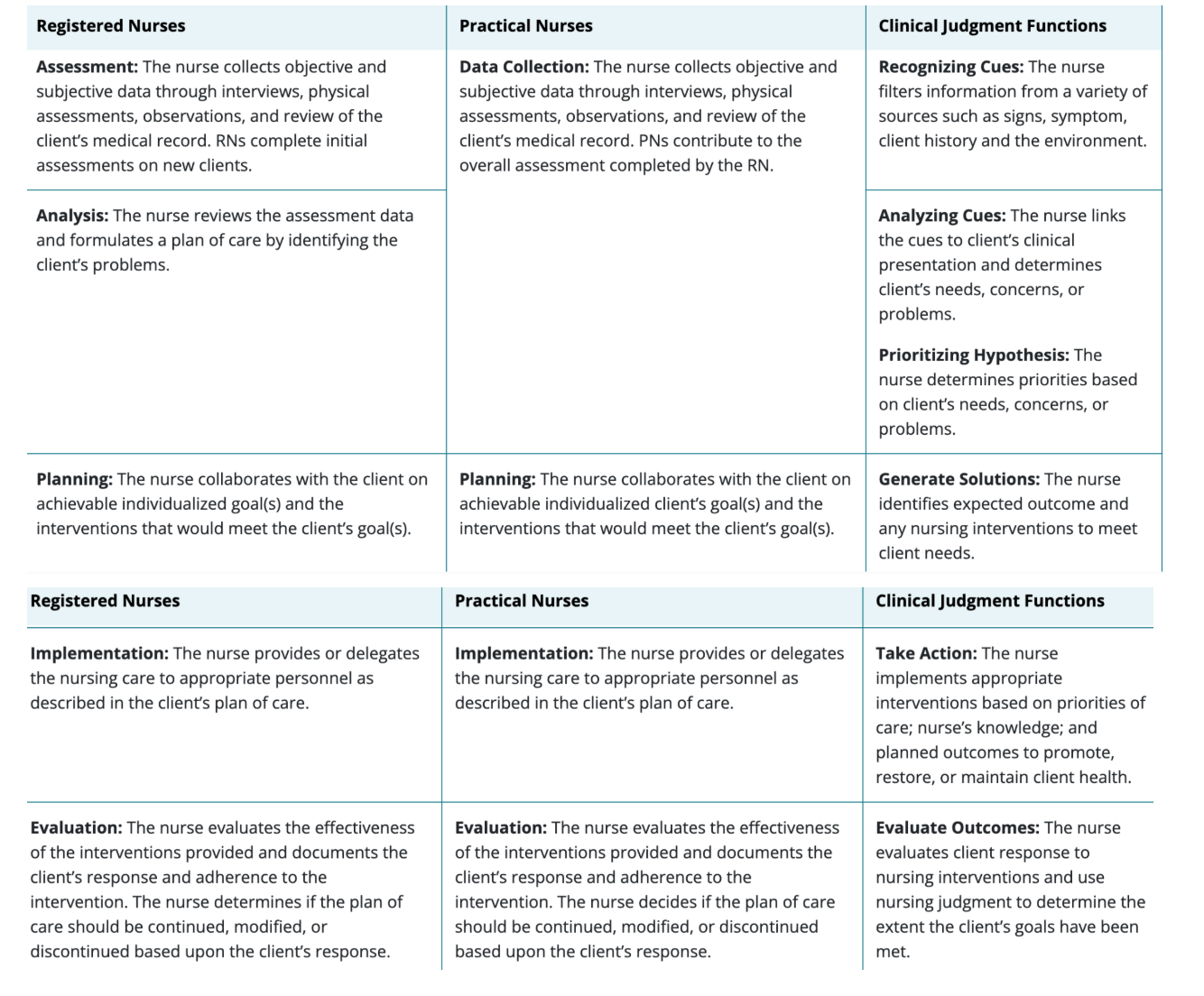
What is clinical judgement?
a complex decision-making process that combines nursing knowledge, client situations, and prioritization of client problems and concerns.
The clinical judgement model
developed as a way of understanding how the nurse is thinking and what cognitive actions the nurse is to be doing during each step of the nursing process.
Clinical judgment model six steps
recognize cues, analyze cues, prioritize hypotheses, generate solutions, take actions, and evaluate outcomes. Additional skills include noticing, interpreting, responding, and reflecting.
Nursing standard of practice includes:
assessment, diagnosis, outcome identification, planning, implementation, and evaluation.
To provide safe evidence therapeutic care the nurse uses:
The nursing process, clinical judgment, and standards of practice
Assessment and recognizing cues is the first steps which includes?
collection of information or data related to the client’s health or situation through objective, subjective data interviews, observations, physical examinations, and a review of the client’s medical record.
What information should the nurse collect from the client?
family history, past experiences including traumatic and/or abusive experiences, client’s attributes, abilities, resources, coping skills, past successes, and current goals.
Client centered care
Occurs when the nurse includes the client as an active participant and collaborates with the client to develop their treatment plan and goals.
Therapeutic involvement:
collaboration, teaching, empathy and trust.
The therapeutic relationship is what?
Foundational to the care of the individual and sometimes is known to be the actual treatment.
How should nurses approach clients?
Being aware of their own perceptions, attitudes, and approach. Also, promoting a nonreactive and nonjudgmental manner to maintain a therapeutic relationship.
Therapeutic communication includes:
Open-ended questions, clarification, closed-ended questions, and summarizing.
Open-ended questions allows what?
The client to tell their stories and allow the nurse to assess the client’s thought process.
When do we use closed-ended questions?
Clients with cognitive impairment may struggle to answer open-ended questions; helps with assessing a client’s risk of suicide or self-harming behaviors
Building Rapport and Trust
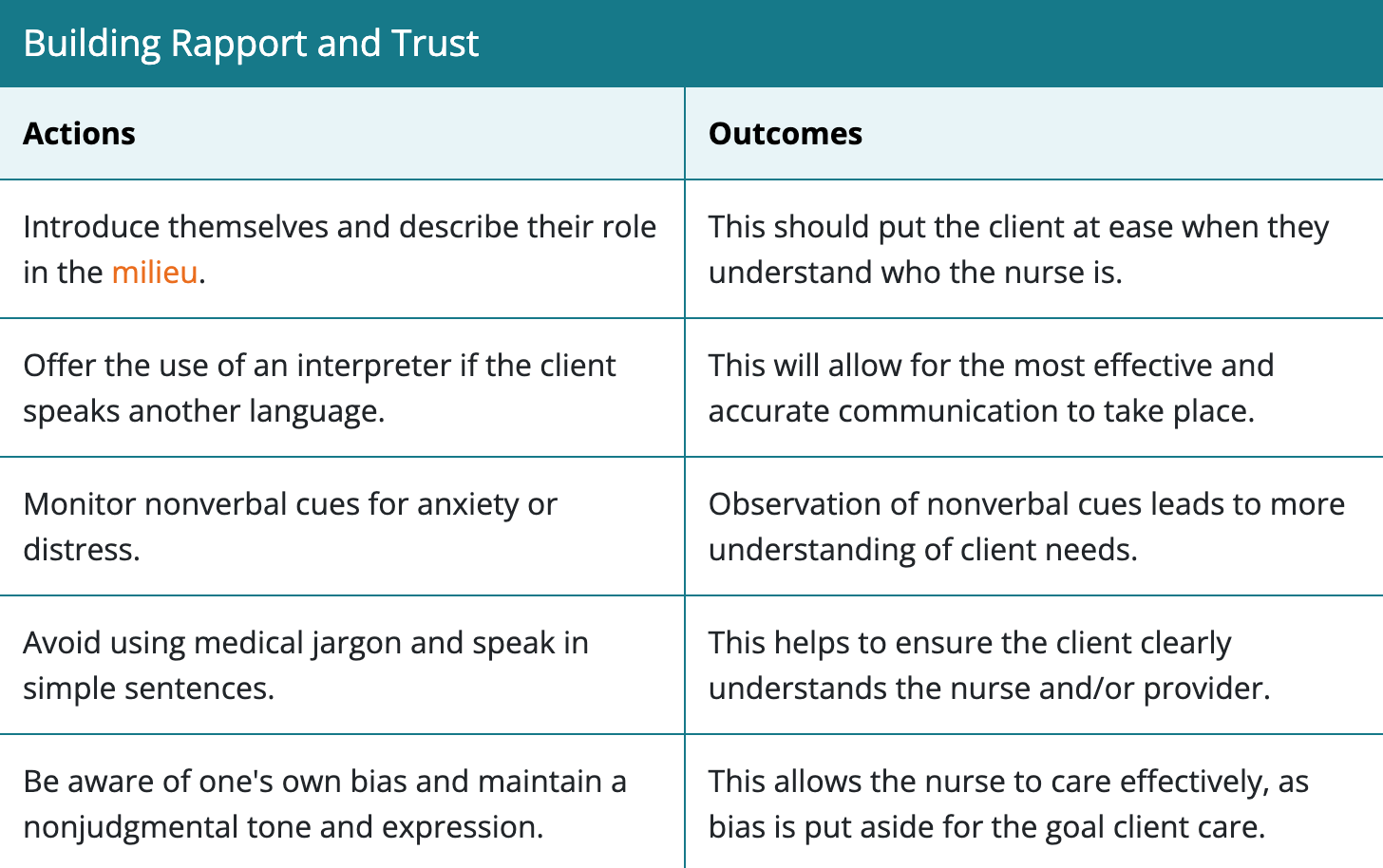
Other than the client’s response the nurse should also observe?
the affect, mood, orientation, behavior, speech, thought process, and cognition.
When caring for clients experiencing changes in their mental health, the nurse must use?
a holistic approach considering the client’s physical, emotional, psychological, intellectual, social, and spiritual aspects . This begins with observation.
What can affect a client’s status?
The client’s physiological status, sedated or in physical distress, limiting the amount of information that the nurse will be able to obtain.
Co-occuring disorder:
Is when a client has two or more mental health disorders or medical illnesses
What other factors should nurses consider?
alcohol, drug use, multiple risk factors such as client that choose to self-medicate with drugs or alcohol, or have changes that occur in the brain as they move into adolescence leading to an increased risk for mental illness in adulthood.
A client with a history of psychological trauma:
-The nurse should be aware that trust and safety are essential in the initial interactions with the client.
Trauma-informed milieu
is a large part of the trauma-informed approach that will facilitate the client’s ease in sharing important details in the assessment. This milieu or environment includes the mental health nurse and the relationships with staff, other clients, visitors, and family and the physical space in which these relationships take place.
Information to include in a client’s history:
Demographic data: name, age, gender, race/ethnicity, developmental stage, relationship status, employment status, and advance directives.
History of present illness: why the client is seeking care, duration, and severity of current manifestations.
Health history and current health status: past illnesses, past surgical interventions, and psychiatric history including time frames, diagnosis, hospitalizations, and current treatments. Allergies to medications, environment, and food. Current medications, including over-the-counter, supplements, and herbal remedies. Past or current alcohol or substance use. Current adherence levels and health goals of the client.
Coping abilities: coping strategies, support system, and the client’s strengths.
Cultural, spiritual, and religious beliefs.
Persons with serious mental illness:
Are at great risk for developing physical illness; comprehensive physical assessment should include an assessment of all body systems should be done.
Specific areas of concern for the client with mental illness are:
dental health, vision/eye health, sexual and reproductive health, substance use disorders, and metabolic syndrome.
Clients living with long-term physical condition
are at greater risk of also developing a mental health condition.
THINC-MED offers a way to consider mental illness which includes?
T – Tumors
H – Hormones
I – Infection or infectious diseases such as uremia or sepsis
N – Nutritional deficits
C – Central nervous system disturbances such as neurological conditions or head injury
M – Miscellaneous medical conditions
E – Electrolyte disturbances or environmental toxins
D – Drugs and substances use or polypharmacy
Why may clients with a mental illness have oral health issues?
fears regarding dental visits, greater incidence of gum disease, inadequate nutrition, drug or alcohol use, tobacco use, and medication side effects.
Vision can be impacted by?
psychotropic medications, while others are contraindicated if the client has been diagnosed with visual disorders like glaucoma
Client’s with mental illness, manic episodes, substance abuse have also a great risk for what?
developing sexually transmitted diseases, becoming a victim of sexual violence, and reproductive health issues due to a lack of impulse control.
Psychotropic medications
directly affect a client’s sexual functioning or may be contraindicated during pregnancy
Tobacco use leads to what?
Respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and worsening diabetes
Tobacco use has been associated with what?
Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, or psychosis. Smoking cessation should be initated.
Alcohol/ substance use disorder
Mental illness clients are at great risk developing this which can cause cancer, diseases of the liver, heart disease, gastrointestinal tract health issues, and nutrition-related issues.
Metabolic syndrom
characterized by increased waist circumference, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and hyperglycemia, which can complicate the care of a client with mental illness.
The mental status exam
an important part of a structured assessment regarding the client’s cognitive and behavioral functioning.
Mental status exam nine domains:
Appearance: How the client looks, including grooming, hygiene, and attention to detail.
Alertness: What is the client’s level of consciousness? Are they arousable or can they focus on the conversation? What is their attention span like?
Behaviors: What is the client’s level of activity? Are they cooperative? Aggressive or agitated? What is their interaction with the nurse/staff like? Cooperation?
Motor: Any abnormal movements? Psychomotor retardation, gait, catatonia?
Speech: What is their speech like including tone, rate, clarity, volume, and amount?
Mood: What is their overall emotional state? (Such as happy or sad) Is this mood appropriate for the current situation?
Affect: How does their expression of feelings appear to the nurse? Such as angry, calm, agitated, fearful, hopeless, hostile, or flat (unchanged or without emotions)?
Thought process: This is the way the client thinks. Are thoughts orderly and logical or disorganized and illogical?
Though content: Describe what the client is thinking about. Does the client have thoughts of self-or other-directed harm?
Perception or insight: Does the client understand their current situation, medical or mental health condition? Is there any evidence of delusions or hallucinations?
Cognition: Is the client oriented to self, others, place, location, or situation? What is the client's intellectual capacity for understanding?
Judgment: Determining if the client can make appropriate decisions or problem solve.
Mental Status Examination Thought Process and Speech Patterns considerations:
Thought blocking: An interruption in the flow of speech due to the intrusion of distracting thoughts
Looseness of associations: Lack of clarity of logical connection between one thought and the next
Perseveration: Persistence of a single word or phrase in response to various questions
Echolalia: Repeating exactly whatever is heard
Neologism: The coinage of new words, each of which has a special meaning for the person
Flight of ideas: Rapid verbal skipping from one idea to the next
Tangentially: Loss of goal direction in communication; failure to address the original point
Circumstantiality: Inclusion of many nonessential details in a response
Clang association: Client responding by rhyming, e.g., play ball, call, fall, tail
Word salad: Mixture of words and phrases that lack comprehensive meaning or logical coherence
Executive functioning
Ability to order and use specific cognitive functions to perform tasks necessary for day-to-day functioning.
-Is tested by the Mini-Mental Examination and the Montreal Cognitive Assessment
The MMSE assesses 12 areas within six domains:
orientation, attention, language, visuo-constructional skills, verbal memory, and calculation.
The Montreal Cognitive Test assesses 14 areas within six domains:
Visuo-constructional within language and executive functioning, attention, orientation, and conceptual thinking.
Visuo-constructional
Involves drawing two- and three-dimensional objects; also often involves a recall exercise of drawing they completed earlier in the assessment.
Psychosocial assessment
Identify client-specific information.
Age, gender identification, languages preferred
Describe the client’s presenting problem and clinical manifestation.
Provide mental and physical health history.
Current or past diagnosis
Childhood illnesses
Experiences of trauma
Current clinical manifestations
Impact on daily living
Hospitalizations
Current treatment
Allergies
Medications
Nonprescribed or over the counter
Describe the client’s employment and education history.
Employment background
Education background
Describe the client’s relationships and social patterns.
Current relationships
Marriage status
Abuse or neglect history
Sexual identification
Sexual patterns
Sexual concerns
Provide family history of medical and mental health conditions.
Physical
Mental
Provide current and past substance use and/or abuse.
Tobacco
Alcohol, last drink, history of use, history of withdrawal, history of treatment
Other
Describe the client’s current health habits.
Coping practices
Interests, hobbies, leisure practices
Social support
Exercise
Dietary
Sleep
Describe the clients’ spiritual preferences or practices.
Current practices
How impacts care during difficult times
Determine safety and risk assessment.
Self-harm, including suicidal ideations
Other directed harm
History of abuse or trauma
Psychosocial assessment environment:
The environment should be free of unnecessary noise and interruptions. Active listening, proper eye contact, posture, and positioning (sitting up engaged in conversation and positioning oneself at eye-level with the client), appropriate use of silence, open-ended questions, and maintaining empathy throughout the interview support the client in sharing personal information.
Funnel Approach to questioning
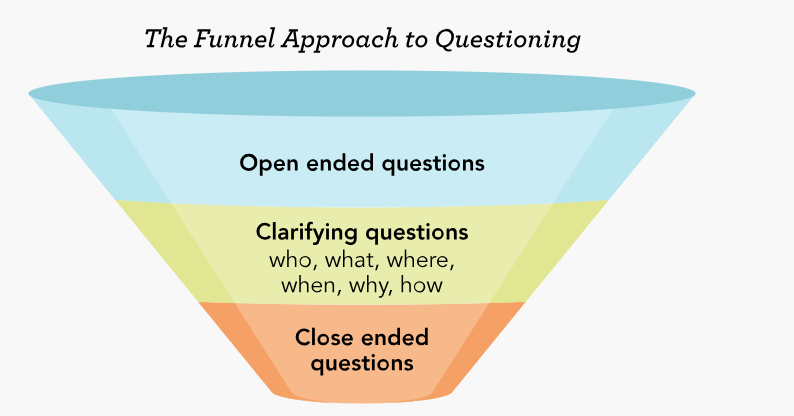
Family functioning
Involves the ability of the family unit to manage life, deal with disagreements, and live within a determined set of boundaries effectively
Family Assessment Device (FAD)
Used for children who are facing critical illnesses and helps to determine the level of psychosocial risk for the child. The FAD is useful for psychiatric clients, clients without psychiatric diagnoses, and family members who are caring for pediatric clients.
Also known as the McMaster Family Assessment Device with a Likert scale (scoring 1 to 5) responses for about 60 questions
FAD Six Domains:
Problem solving, communication, behavior control, affect-involvement, responsiveness, and roles within the family.
Community-based participatory assessment
Uses the actual community in working through the assessment, highlights the positive aspects of the community, has staff that is part of the community of population, and reports information to all involved.
Spiritual well being
a protective factor for clients, resulting in decreased stress, pain, negative emotions, and a lower risk for depression and suicide. This includes the client’s religious/spiritual preference and level of participation in spiritual/religious activities.
FICA (spiritual tool) to collect data
faith, importance/influence, community, address
Cultural assessment
Essential because it allows the nurse a view of the client’s cultural background and facilitates culturally sensitive care.
DSM-5-TR Cultural Formation Interview (CFI) Domains & Questions
Domain 1: Cultural definition of the mental health concern
What brought you here today?
Some people describe their concerns to their family, friends, or community in different ways. How would you describe your concern?
What is most concerning to you?
Domain 2: Cultural perception of cause, context, and support
Why do you think you are experiencing this? What do you think is the cause?
What do others (family, friends, community) think the cause is?
Domain 3: Cultural factors affecting self-coping and what worked in the past
Is there any specific support for your concern that makes you feel better? (Include further inquiry to family, friends, or community members.)
Sometimes aspects of a person’s background (the family or group the client identifies with) can make the concern feel worse or better. For you, what is the most important aspect of your background (or identity)?
Is there any aspect of your background or identity that cause concern or difficulty for you?
Domain 4: Cultural factors which affect currently seeking help
Sometimes individuals have various ways of dealing with their concerns. What have you done to cope with your concern?
Often people seek help or support from others such as doctors or healers. What kinds of help or treatments have you found useful?
Is anything preventing you from getting the assistance you need?
What kind of help or assistance would you find the most useful?
Is there any kind of help your family (group or community) has suggested that you would find helpful?
Sometimes doctors or persons providing care and the client misunderstand each other because they have different backgrounds. Do you have any concerns about this, and is there anything we can do to provide the help you need?
Situational assessment
conducted immediately upon entering the client’s room or in a situation where an urgent or immediate response is needed and involves the nurse observing the client’s behavior and the environment.
Situational awareness includes what?
the nurse’s continual attention, perception, and analysis of what is currently taking place and what may take place in the future to plan for safety, especially when interacting with clients who are angry or violent.
Situational plan includes:
strong communication between the staff
not wearing clothing or accessories or any item that could be used to harm the nurse or staff member
having a clear pathway to an exit/door
choosing to position themselves close to the door so that staff will not be hindered from leaving
having easy and quick access to security
having the ability to confidently use de-escalation techniques, if necessary.
Examples of cues suggesting a mental health crisis:
Client personal care changes with lack of hygiene, unwillingness, or unable to provide self-care, including bathing or oral care.
Rapid mood changes from being ecstatic excitement to being withdrawn or depressed.
Client has increased agitation with self or others, including verbal threats and destroying property. They appear to be out of control.
Client is demonstrating self- or other-directed harm.
Client has increased isolation from family and friends. This may include not going to work or school.
Client is out of touch with reality with increased or new onset of hallucinations.
Client has increased paranoia and distrust.
Why does the nurse analyze?
To determine the priority problems and the primary areas that require intervention. The client should be a part of this process.
Consider the following questions for analysis of cues discovered during assessment.
How do the client’s clinical manifestations compare to evidence-based resources (DSM-5-TR criteria)? Consider how the client’s clinical presentation is a result of pathophysiological changes.
Based on the assessment, how did the client’s behaviors, cognitions, attitude, affect, and mood (items found in MSE) affect the client’s daily functioning?
Was the client a risk to themselves or someone else?
What possible protective or risk factors does this client have?
How do the client's cultural factors influence the illness? Well-being? Plan of care?
What does the client say their mental health needs are? Does this correlate with client behaviors? What client needs or concerns have been identified through observation, subjective and objective data? Are there any complications or potential risks for this client in the next hour? Next 4 hr? During the next shift?
Recognizing and analyzing cues is part of forming what?
a hypothesis; prioritizing hypotheses and generating solutions is part of refining a hypothesis.
Specific tasks designed for the analysis of cues
Recognize patterns.
Link cues.
Determine what is concerning.
Determine if additional information is needed.
Mental health assessment clues
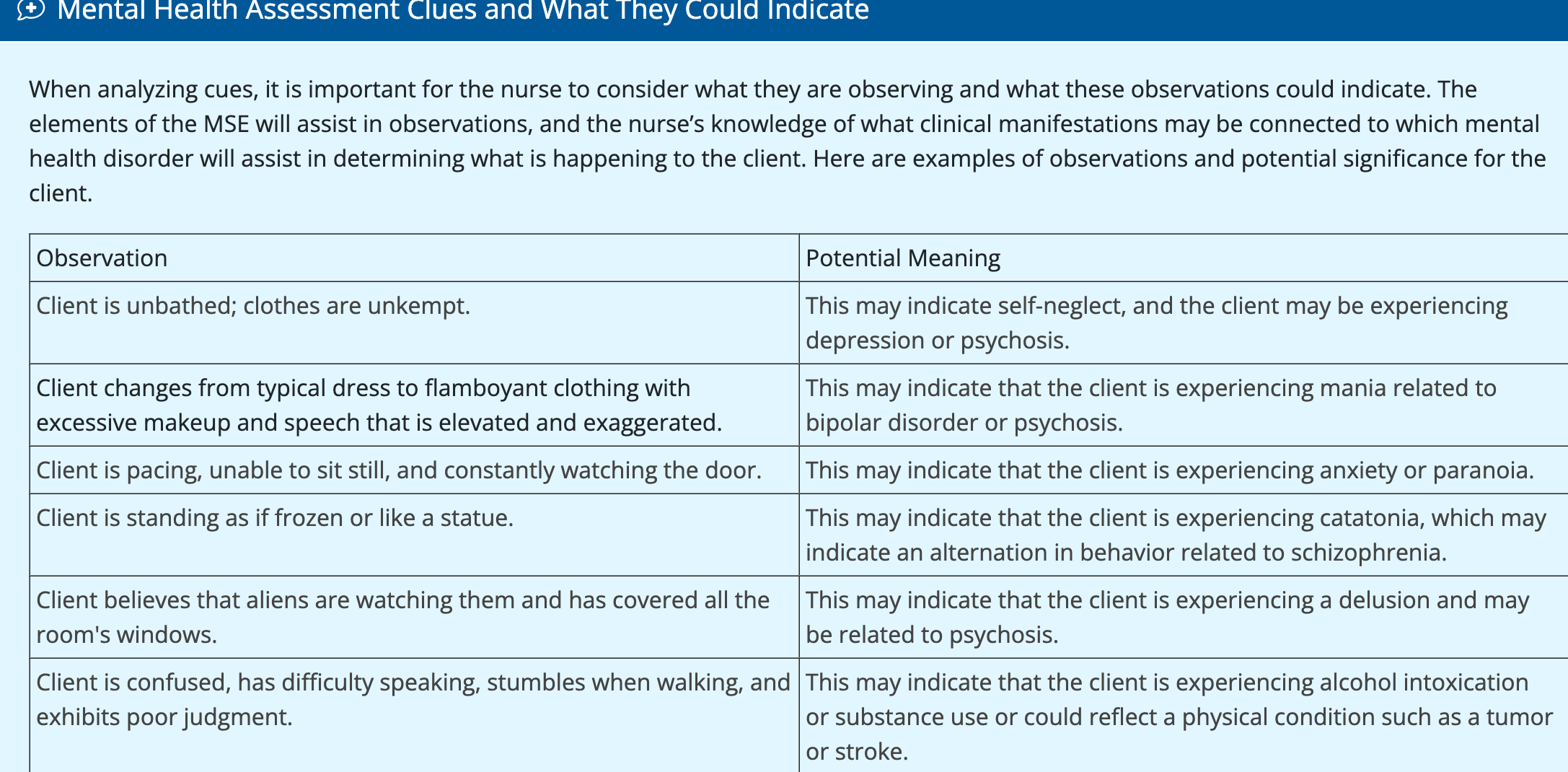
Prioritization of problem uses the ABCDE approach which includes?
Cluster information.
Narrow possibilities.
Determine the order of priorities.
Determine risk for action or inaction.
Provide evidence for the hypothesis.
With prioritization, safety is a critical consideration. Questions to consider include:
Which of the problems is most critical to client safety/risk of compromise and needs immediate action?
Is there a risk of suicide or self-harm or a risk of harm to others?
Milieu Therapy
Based in creating and maintaining an environment of safety emphasizing trauma-informed therapeutic relationships that actively engage the clients in their recovery.
-The nurse's coordination, planning, and implementation of client care are built upon a therapeutic milieu.
-Educating the client and the family about the specifics of the hospital and the environment, as well as client rights and expectations, are all important features of this type of therapy.
Generate Solutions Planning The Nurse Will:
Determine desired outcomes.
Determine the best solution based on evidence.
Prioritizing nursing care and the awareness of possible negative effects of chosen interventions.
Being able to update nursing priorities as the client’s condition worsens or improves.
Determine what resources are needed (e.g., people, equipment, medications).
Collaborate with the interprofessional team in caring for the client.
Collaborate with the client and family to ensure that the care is client-centered
Client Problem
Connected to the reason they are seeking medical or mental help. Often this is related to an illness, clinical manifestation, or improving well-being. When considering a client's problem, the use of the DSM-5-TR criteria for mental health disorders may be helpful.
Nursing actions for a mental health client can include
monitoring, supervising activities, providing teaching or instruction, promoting recovery, or a specific task such as taking blood pressure prior to administration of medication. Additionally, the nurse will determine what supplies, equipment, or personnel (aides, techs, providers, social workers) may be needed.
Planning nursing actions
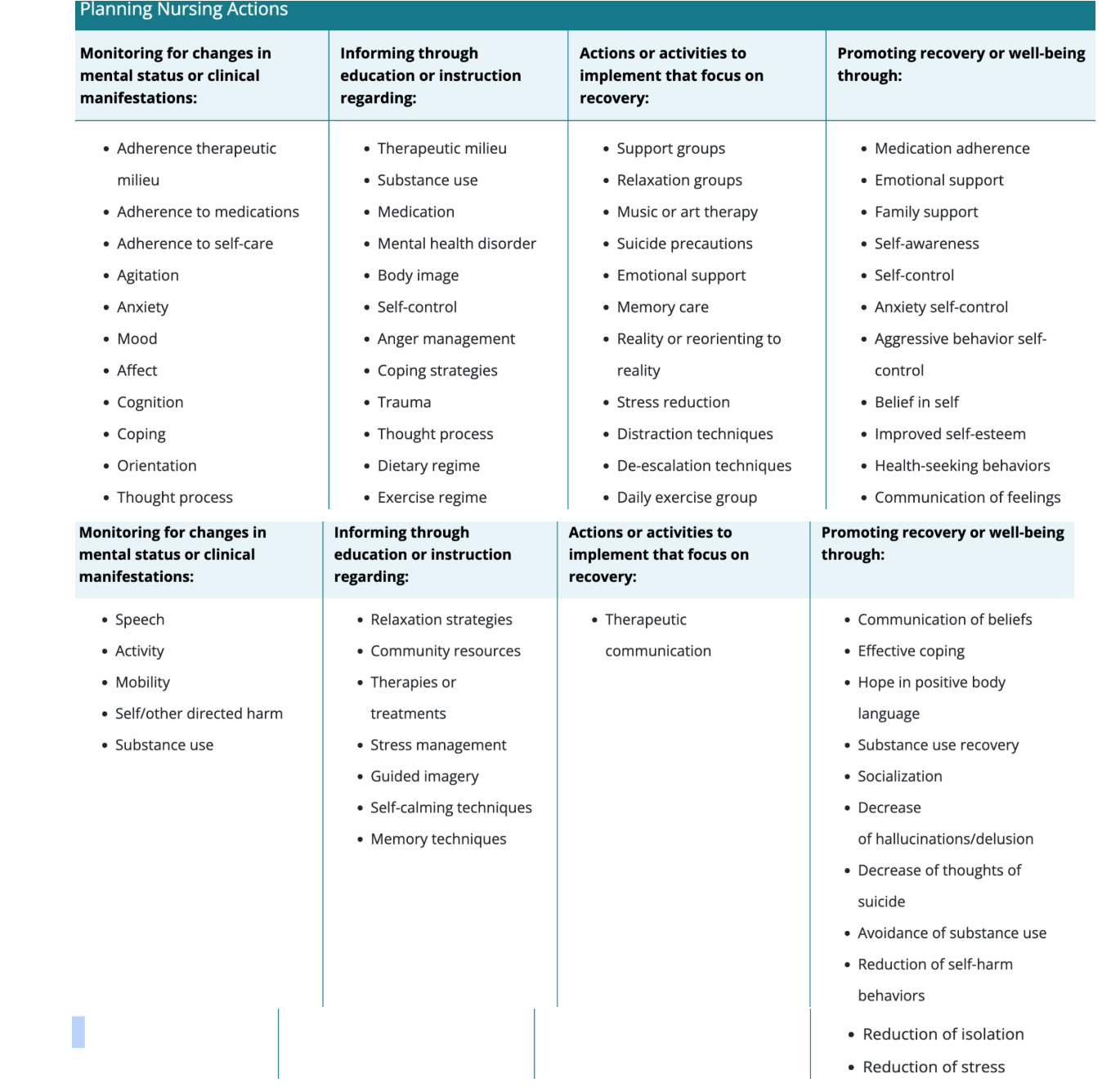
Interdisciplinary Treatment Plan
Effective interdisciplinary treatment plans are generally written by an identified team member such as a therapist, social worker, or provider and include input from the entire team.
Client history, assessment, and demographic information
Reason client is seeking treatment
Treatment agreement of who is responsible for what aspect of care. This can be formally or informally agreed upon.
Treatment goals, including objectives or steps that are measurable.
Planned interventions
Progress toward outcomes
The client should be part of their goals and outcomes, what should it reflect?
client’s choices, beliefs, and values, and the nurse facilitates the process of working to achieve a recovery-oriented focus. Client participation results in increased motivation and focuses on meeting goals.
How should the nurse offer guidance?
ensure that the goals are realistic, recovery-oriented, and achievable through evidence-based interventions.
Goals should be SMART
specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timely.
Both short- and long-term goals should be a part of the plan which is?
Short-term goals may be created for one day, while long-term goals might address the time of discharge and beyond.
Example short-term behavioral goal:
The client will verbalize using a relaxation breathing technique when anxious one time during the current shift.
Example long-term behavioral goal:
The client will report having fewer than three panic attacks in the next 14 days.
Goals for clients who have mental health disorders are?
Behavioral
Considerations for planning:

Consideration of safety for mental health is considered when?
The client is at increased risk for a mental health crisis as there is increased potential for harm to themselves or another person. Therefore, the physiological needs are considered based on psychological risk for harm and safety, the essential prioritizing hypotheses.
-Safety needs often require that the nurse remain aware of the milieu and manage the environment accordingly (safe and therapeutic milieu for all clients).
Goals of discharge planning
-Remember discharge begins at admission and its more complex for patients with chronic illnesses

Implementation of the plan of care includes:
Working with client and family to execute the plan of care in a time-oriented fashion.
Prioritizing the therapeutic relationship.
Identifying and use of evidence-based nursing actions.
Using technology and community resources to carry out the plan of care.
Focusing on holistic care that is person-centered instead of focused on the disorder.
Championing for the best care for the client.
Identifying needs of groups across the lifespan.
Overseeing ancillary staff.
Joining forces with nursing co-workers and others to execute the plan of care.
Accurately documenting the implementation of the plan of care.
Using new knowledge to bring about changes.
Handling psychiatric crisis emergencies.
Nursing intervention that can have a profound effect on clients:
Spending time with the client so that they know they are not alone.
Client and family teaching:
It is essential.
Teaching medication information during hospitalization, in outpatient settings, and at discharge is critical to ensure that the client understands their prescribed medications.
Educating the family about the client’s disorder and what behaviors to expect or how to respond to behaviors is important as well.
One specific issue that should be included in client teaching is the signs that may arise leading to relapse and what steps to take to prevent a relapse.
Mental health teaching

Community resources
As a nurse having an awareness of what mental health resources are available in your community is essential.
The CDC provides links to the national suicide prevention lifeline, assistance for those who are experiencing abuse or domestic violence as well as assistance for finding treatment.
The social worker connects patients and families to support groups, researches and relays information on health care options, and refers them to appropriate legal agencies
Follow Up and Continuum of Care
The continuum of care involves the community services and resources available to promote the recovery of a client.
This continuum ranges from offices/clinics to outpatient services, partial hospitalization programs, crisis centers, and psychiatric hospitals.
Adolescents who have been diagnosed with a serious mental illness and have access and receive consistent follow-up care with their primary providers have improved outcomes during young adulthood.
Documentation
Client records are legal documents. Documentation provides a record of the continuity, quality, and safety of client care. Additionally, mental health documentation provides a record of the nurse’s awareness of the client’s behaviors and mental status.
An ongoing record of client care should include the following.
Client condition physical and mental health
Interventions and care provided
Client response to interventions
Client’s progress toward goals
Progress notes
provide a narrative record of the client’s situation.
They are used to describe any significant changes in a client’s mental or physical status, what interventions were provided, how the client responded in response to the interventions, and what plan or follow-up for the client has been determined.
Method of Progress Note BIRP:
Behavior – objective and subjective data of the client’s situation and behavior
Intervention – specific interventions including such as redirection, relaxation techniques used, or medications
Response – following the intervention, how did the client respond—provide both objective and subjective data
Plan – describe what will happen next in the client’s care

Nursing care along the continuum of mental health and mental illness includes?
health promotion, health maintenance, and care for clients requiring mental health rehabilitation or recovery