Thermoregulation
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
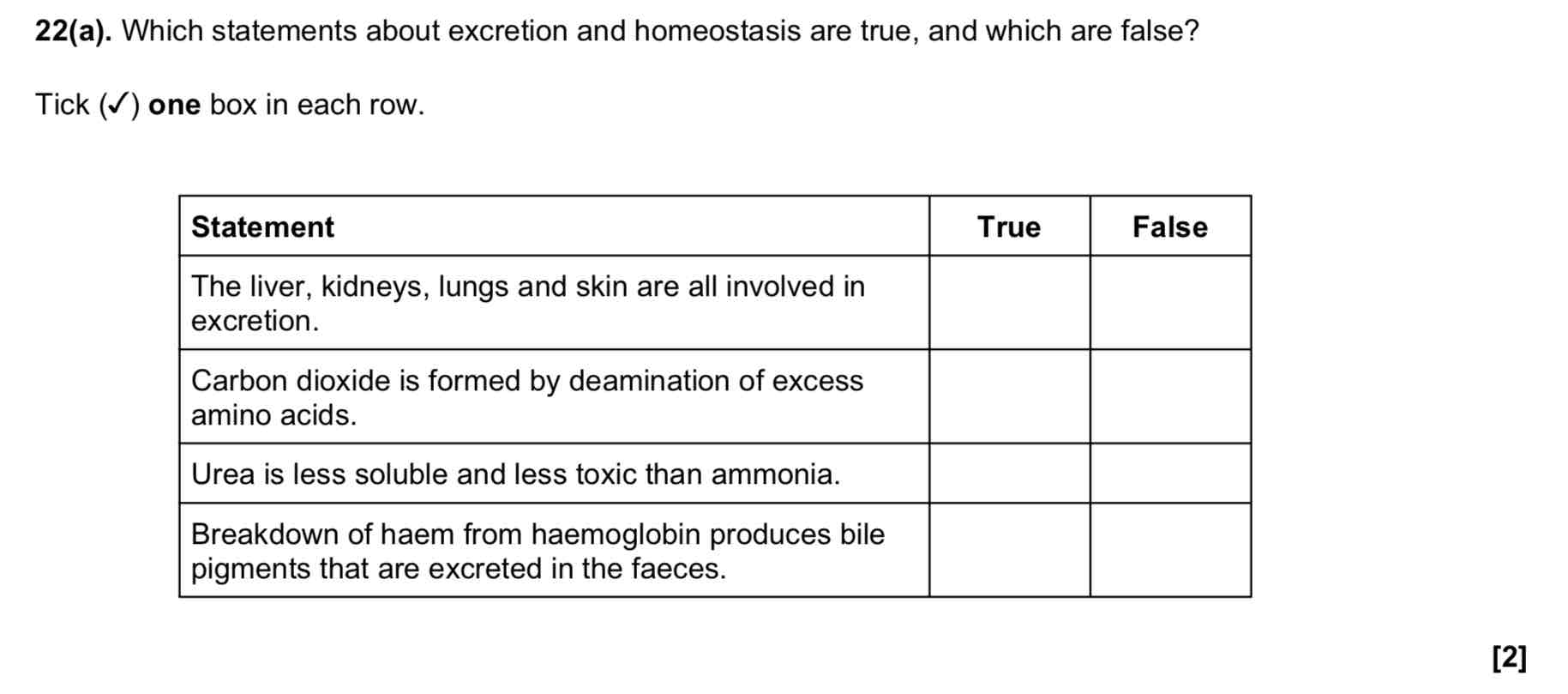
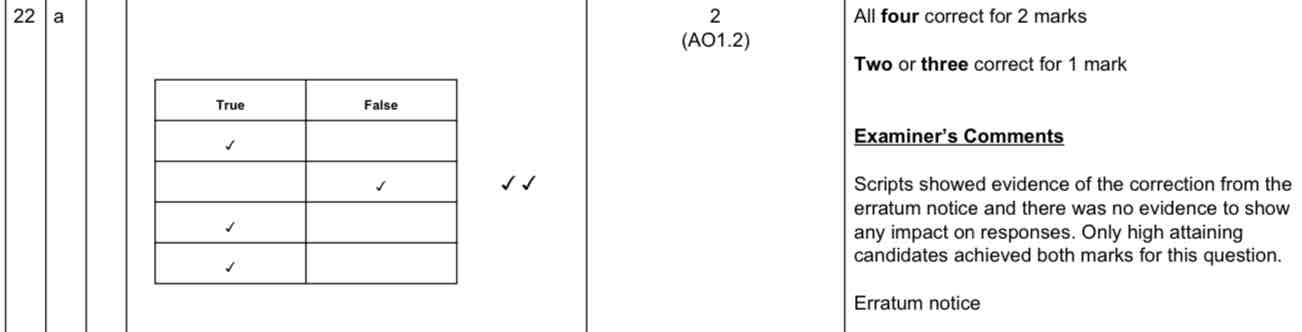
Why do multicellular organisms need communication systems? [2]
To respond when their internal and external environment changes
To coordinate function
What is cell signalling?
Communication between cells, electrical signals carried by neurones or chemical signals as hormones
What are the three types of cell signalling?
Endocrine
Paracrine
Autocrine
What is endocrine signalling used for?
Long distance
What is Paracrine signalling used for?
Signalling between adjacent cells occurs directly or aided by extracellular fluid
What is autocrine signalling?
Cell releases signals to stimulate its own receptors and triggers a response within itself
What is homestasis?
Internal environment is maintained within set limits around an optimum
Define negative and positive feedback
Negative feedback: Self regulatory mechanisms that reverse a change in internal environments
Positive feedback: A change in internal environment is furthered by actions in the body
What are receptors and effectors?
Receptors: specialised cells located in sense organs that detect a specific stimulus
Effectors: Usually muscles or glands which enable a physical response to a stimulus
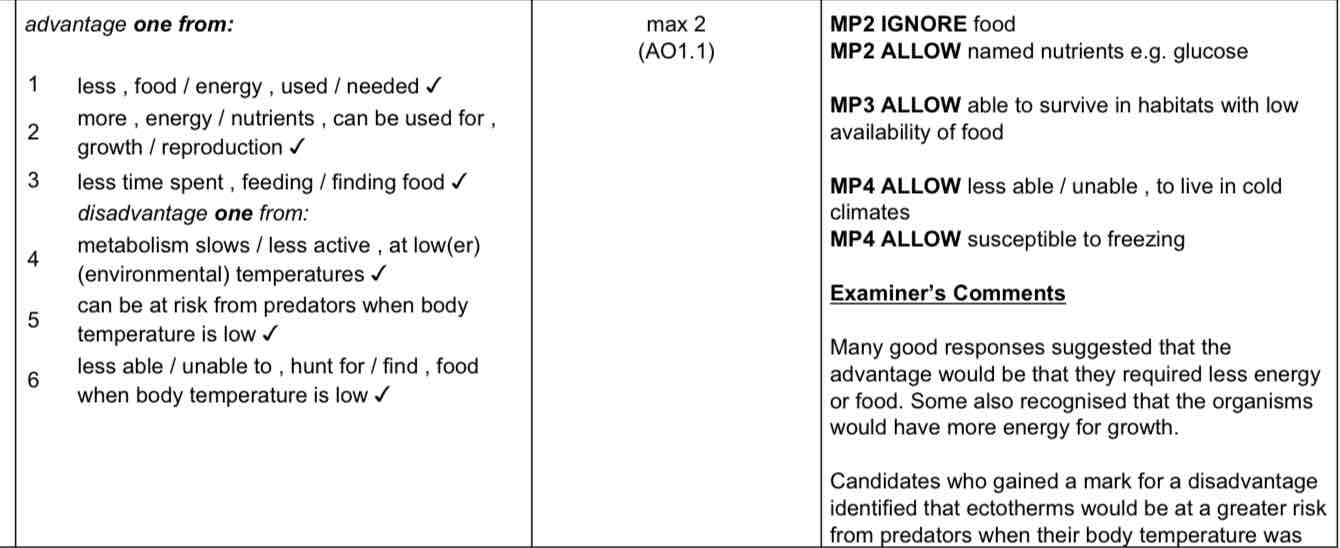
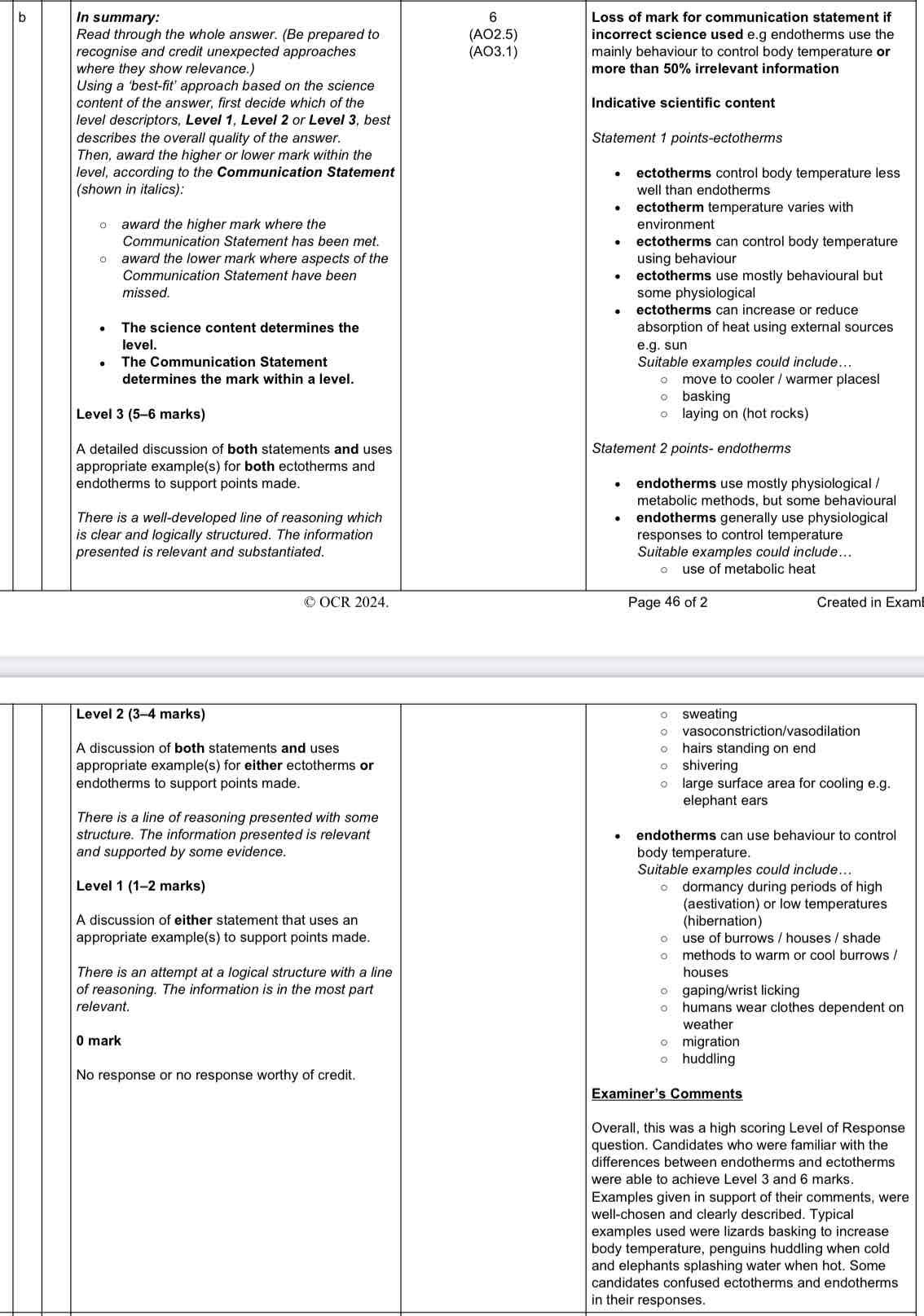
What is an ectotherm?
An organism that relies on external sources to regulate its body temperature
What is an endotherm?
Organism that can regulate their own body temperature via internal physiological or behavioural responses.
Outline behavioural methods endotherms use to regulate their body temperature
Baking in the sun
Pressing against warm surfaces
Digging burrows
Hibernation
Panting
How does the autonomic nervous system enable endotherms to Thermoregulate? [4]
Via negative feedback
Peripheral thermoreceptors detect changes in skin temperature
Thermoreceptors in hypothalamus detect changes in blood temperature
Hypothalamus sends impulses to effectors in skin and muscles
Explain the role of the skin in Thermoregulation [3]
Vasodilation/Constrction of arterioles supplying skin capillaries controls heat loss to skin surface
Hair erector muscles contract and follicles protrude to trap air for insulation
Evaporation of swear cools skin surface
Give an example of positive feedback
Blood clotting/Childbirth
Give an example of negative feedback
The control of blood glucose concentration