Psych 111 class 14 - Intelligence + IQ Testing
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is intelligence
Edward Boring: It’s whatever intelligence tests measure
Conceptualizing intelligence
Sensory capacity: the ability of our senses (sight, hearing, touch, taste, smell) to receive and process information
More than just good eyesight, hearing, and smell - Lilienfeld 2019
Origins of Intelligence Testing
Early 20th century Francy
Alfred Binet and Theodore Simon
What is intelligence?
Abilities to:
reason abstractly
learn to adapt to novel environmental circumstances
acquire knowledge
benefit from experience
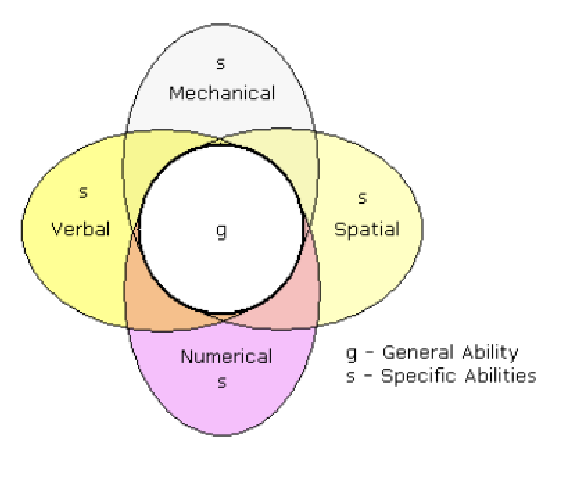
General vs. Specific Abilities
g = general intelligence
s = specific abilities
Theorized by Charles Spearman
Fluid and Crystallized Intelligence
Raymond Cattell and John Horn
Fluid Intelligence
Global capacity to reason
Ability to learn new things
Think abstractly and solve problems
Crystallized Intelligence
Prior learning and past experiences
based on facts
increases with age
Multiple Intelligences: Howard Gardner’s Frames of Mind
Linguistic
Logico-mathematical
Spatial
Musical
Bodily-kinesthetic
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Naturalistic
Sternberg’s Triarchic Theory
Analytical Intelligence - intelligence tests
Creative intelligence - adapting and generating novel ideas
Practical Intelligence - attaining a fit between oneself and their environment, or “street smarts”
Today’s most common intelligence assessments
The Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS - IV)
The Wechsler Intelligence Scare for Children (WISC - V)
Intellectual Disability
Characterized by deficits in intellectual functioning and adaptive functioning that occur in the developmental period
< 70 = Intellectual Disability
90 - 100 = Average
130 - 140 = Gifted
Genetic Influences
NATURE
family studies
twin studies
adoption studies
Environmental Factors
NURTURE
expectancy effects
poverty
flynn effect
Behavioral Genetic Designs
Family Studies: analysis of how characteristics run in intact families
Twin Studies: analysis of how traits differ in identical versus fraternal twins
Adoption studies: analysis of how traits vary in individuals raised apart from their biological relatives
Genetic influences on IQ
Family studies on IQ: relationship declines with increasing biological distance
Twin studies on IQ: correlation is higher for identical twins (MZ) (.7-.8) than fraternal twins (DZ) (.3-.4)
Environmental Influences on IQ: Teacher Expectancy Effects - Rosenthal & Jacobson, 1966
Administered IQ tests, gave results (bloomers), retested 1-year later
Robert Rosenthal and Lenore Jacobson's study showed that children's performance was enhanced if teachers were led to expect enhanced performance from children
Environmental Influences on IQ
Poverty
stress, nutrition, lead exposure, access to books, quality of education, etc can all impact an individuals IQ
Flynn effect
Average IQ scores are rising approximately 3 points per decade
Some of the possible explanations include increased schooling, greater educational attainment of parents, better nutrition, and less childhood disease. A particularly interesting explanation is that of more and better parental attention to children.