Edexcel DT Timbers
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Examples of hardwoods
Beech, Mahogany, Oak, Balsa, Jelutong, Birch, Ash

Examples of softwoods
Pine, Cedar, Larch

Examples of manufactured timbers
MDF, Plywood, Chipboard

Physical properties of beech wood
Slight pink tint, close grain

Working properties of beech wood
Tough, durable and smooth to finish

Physical properties of mahogany wood
Dark-reddish colour, very close grain

Working properties of mahogany wood
Cuts and polishes easily, gives a fine finish, used for high-quality furniture

Physical properties of oak wood
Moderate-brown colour with unique and attractive grain markings

Working properties of oak wood
Tough and durable, polishes well, used for quality furniture

Physical properties of balsa wood
Pale and wide-spaced grain due to it being a fast-growing hardwood

Working properties of balsa wood
Very soft and easy to form, often used to make models

Physical properties of jelutong wood
Creamy yellow colour. Close and even grain.

Working properties of jelutong wood
Easy to cut and shape. Used for model making and vacuum forming moulds. Soft so not good for structural uses.

Physical properties of Birchwood
Even grain, range of different colours.

Working properties of Birchwood
Even grain so often used for veneers in furniture. Easy to cut and shape. Liable to rot and insect attacks.

Physical properties of Ash wood
Light coloured and smooth-grained. Straight grained.

Working properties of Ash wood
Finishes well. Strong and flexible. Used in ladders, tool handles, walking sticks and sports equipment such as oars. Liable to rot and insect attacks.

Physical properties of Pine wood
Pale coloured with aesthetically pleasing grain

Working properties of Pine wood
Lightweight, easy to form, used for construction and decking

Physical Properties of Cedar wood
Lightweight, pale colour with even texture

Working properties of Cedar wood
More expensive than pine but not as strong

Physical properties of Larch wood
Elegant gold colour
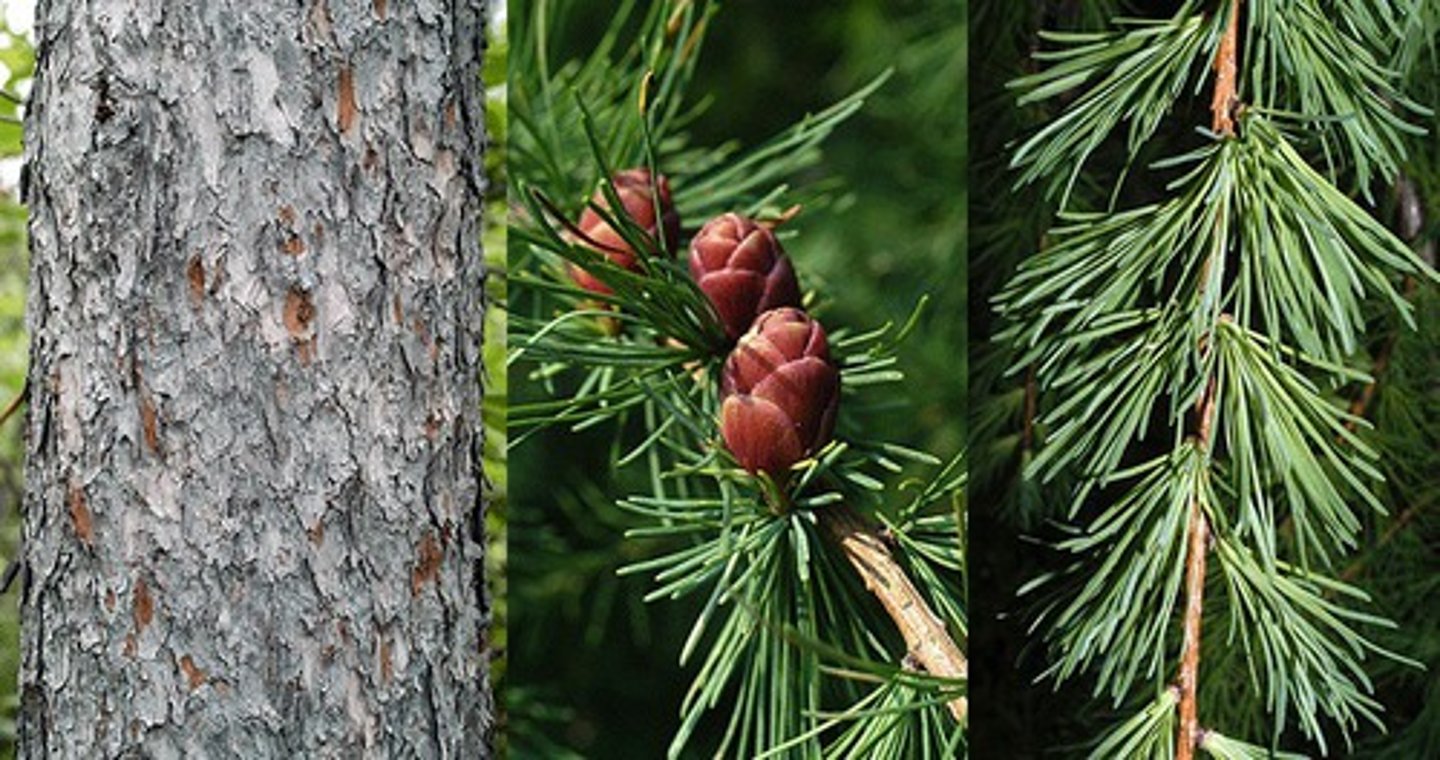

Working properties of Larch wood
Used in exterior cladding, small boats and for fence posts and is selected because it is durable and resistant to water. It is, however, more expensive than other softwoods.

Physical properties of MDF
Smooth, light brown, can be veneered
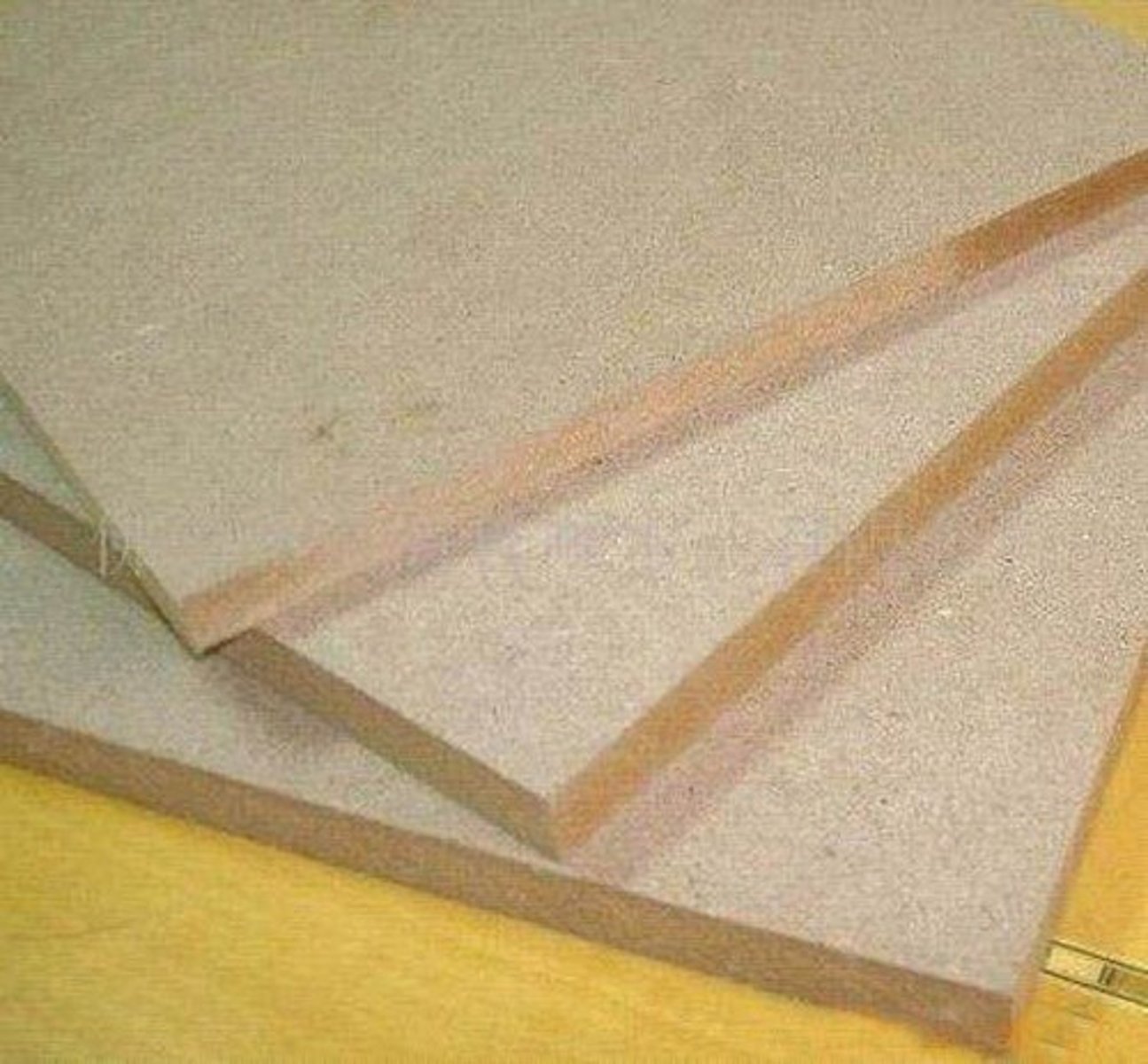

Working properties of MDF
Smooth and easy to finish, absorbs moisture so not suitable for outdoor use

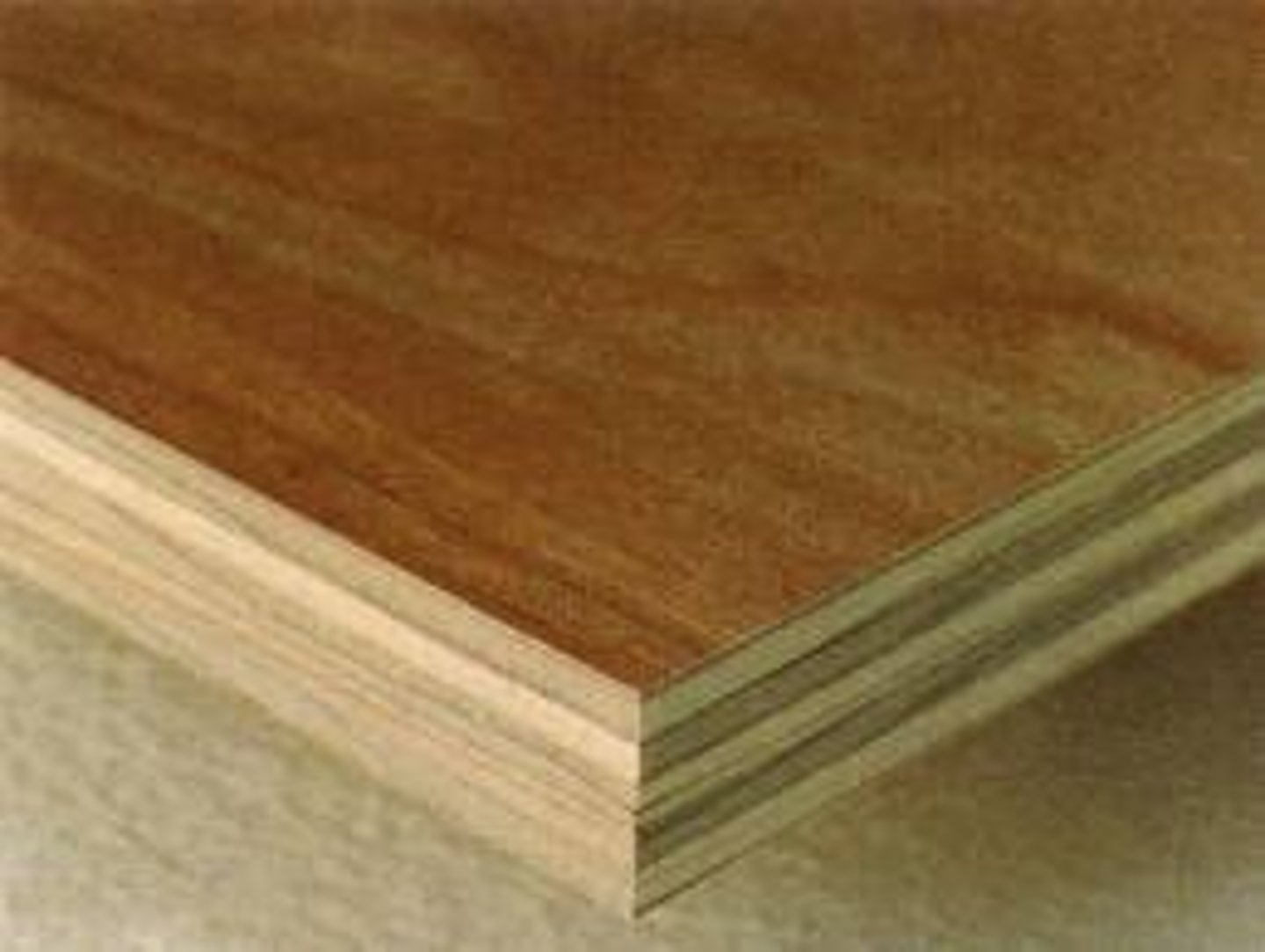
Physical properties of Plywood
Layers of veneer glued at 90 degree angles for strength, aesthetically pleasing outer layer
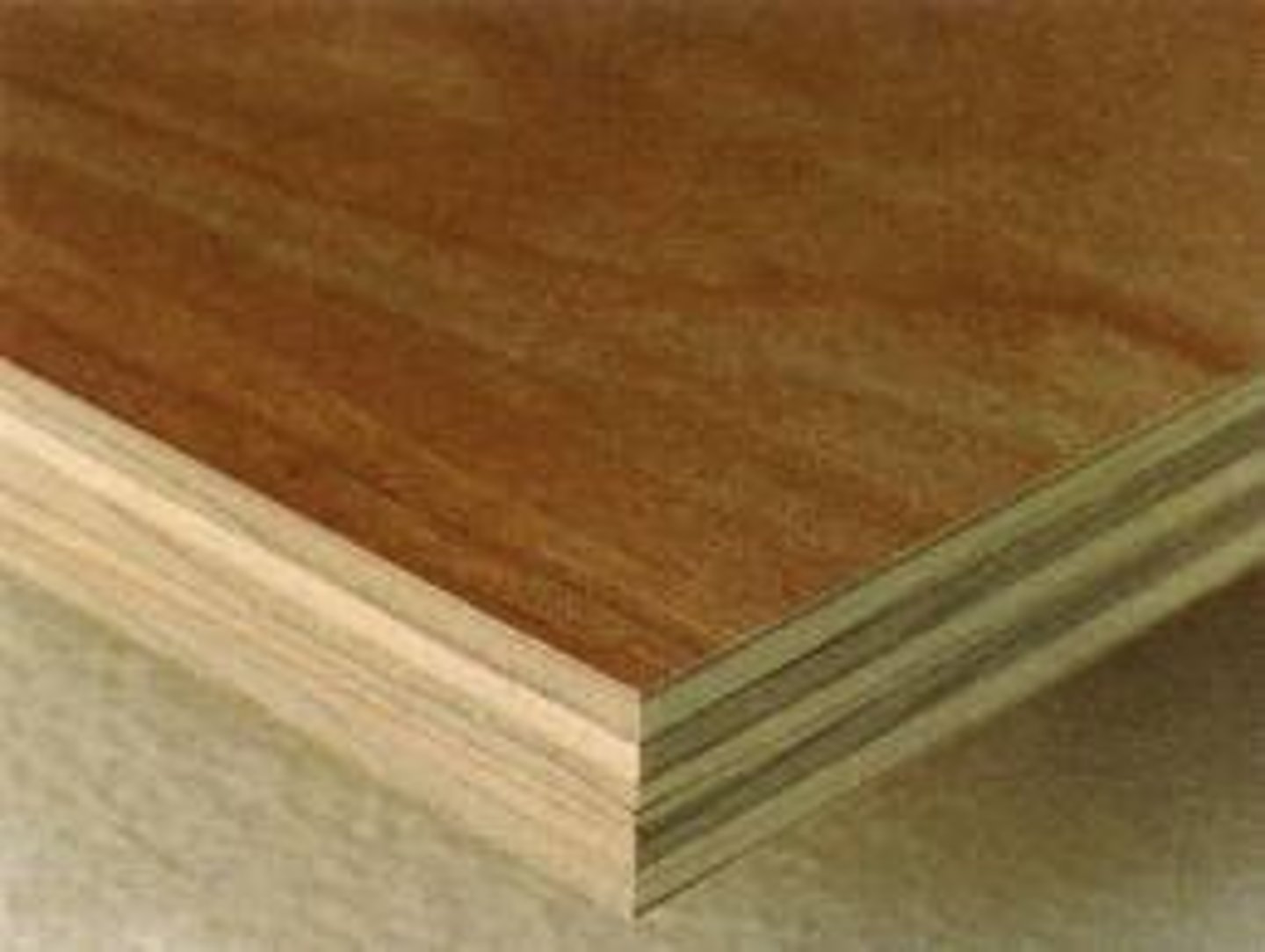

Working properties of Plywood
Easy to cut and finish, can be stained or painted

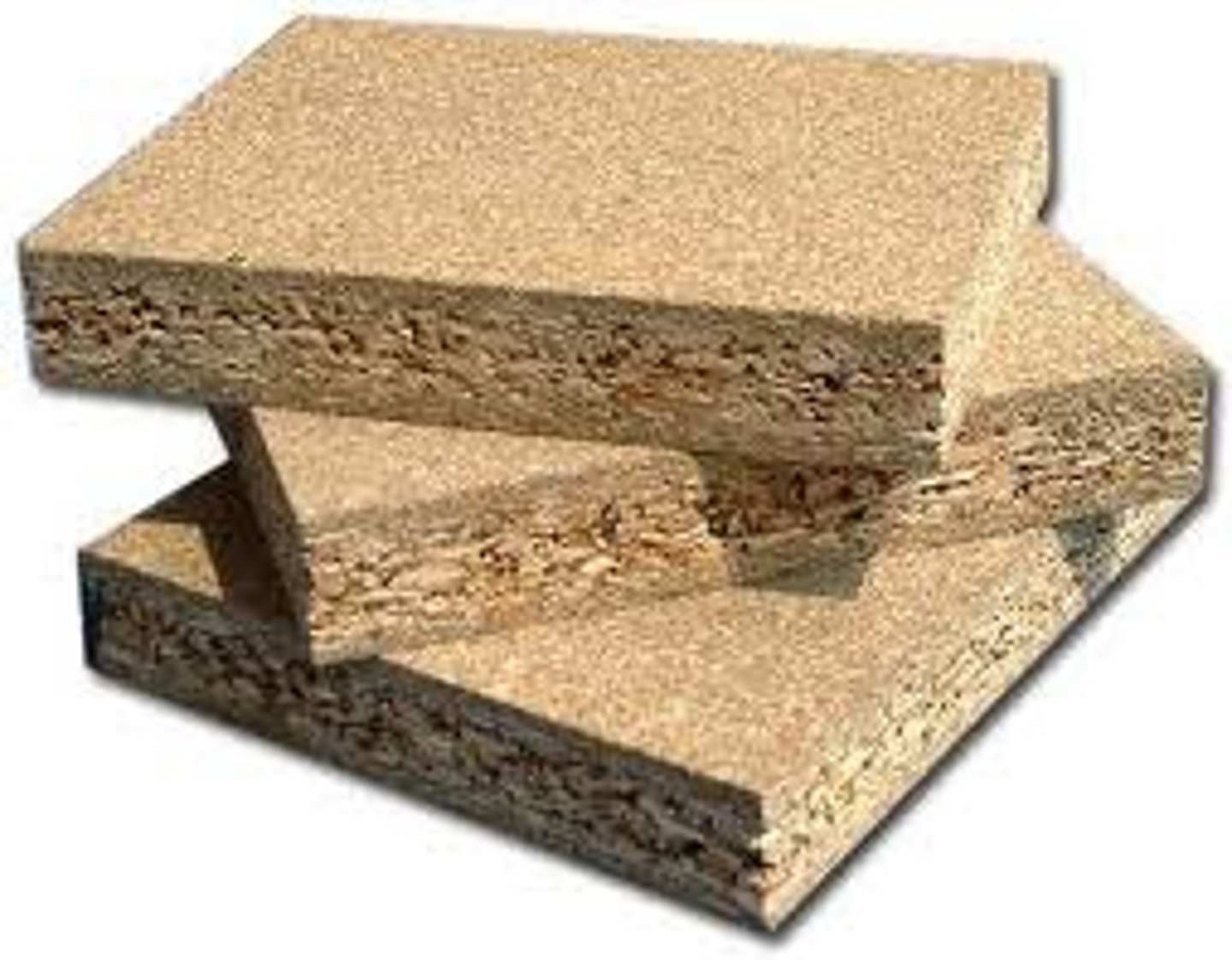
Physical properties of chipboard
Large and visible chips of wood.
Working properties of chipboard
Commonly used in kitchen worktops and flat-pack furniture because it is inexpensive to produce as it is made from waste timber. It is commonly covered using a real wood veneer or melamine sheet so it is not on show. Covering the chipboard provides a layer of protection - if chipboard is exposed to moisture it will swell up and fall apart.
What kind of trees do hardwoods come from?
Deciduous trees
How long does it take to grow a hardwood tree?
Often, it takes around 60 years for a hardwood tree to grow, but this can be as high as 100 years.
Are hardwoods cheap or expensive, and why?
Hardwoods tend to be more expensive than softwoods and manufactured timbers as they take a long time to grow.
Where do hardwoods grow?
The majority of hardwoods grow in tropical regions, such as Amazonian climates, while others grow in temperate climates such as Europe.
What type of wood is beech?
Hardwood
What type of wood is mahogany?
Hardwood
What type of wood is oak?
Hardwood
What type of wood is balsa?
Hardwood
What type of wood is jelutong?
Hardwood
What type of wood is birch?
Hardwood
What type of wood is ash?
Hardwood
What type of trees do softwoods come from?
Coniferous trees
What types of leaves do softwood trees tend to have?
Coniferous trees tend to have needle-like leaves that normally stay on during the winter, with the exception of larch.
Where do softwoods grow?
Softwoods naturally grow in colder regions such as Alpine climates.
How long does it take softwoods to grow?
It typically takes 20-30 years for a softwood tree to grow enough for its timber to be used. As a result, they are cheaper than hardwoods.
What type of wood is pine?
Softwood
What type of wood is cedar?
Softwood
What type of wood is larch?
Softwood
What are manufactured timbers made from?
Manufactured timbers can be made from leftover wood such as sawdust and wood chippings.
Are manufactured timbers expensive?
No - manufactured boards tend to be cheaper than both hardwoods and softwoods.
Why can manufactured timbers be larger than hardwoods and softwoods?
Because they are not restricted to the size of a tree trunk.

What is a knot?
A knot is where a branch would have once been attached to a tree trunk.
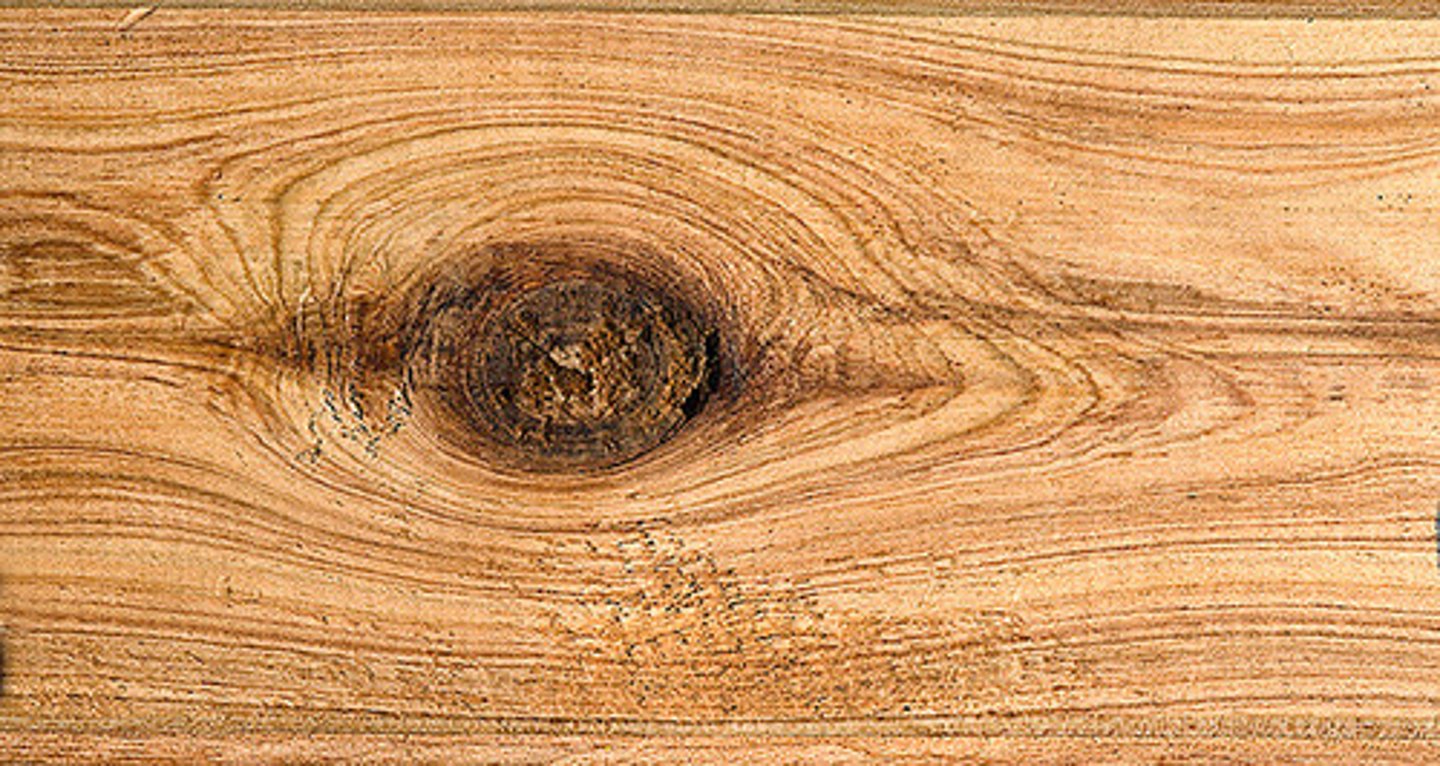

Why are knots difficult to work with?
Knots are difficult to work with because they are much harder than the rest of the wood. They can also fall out when the wood expands and contracts.
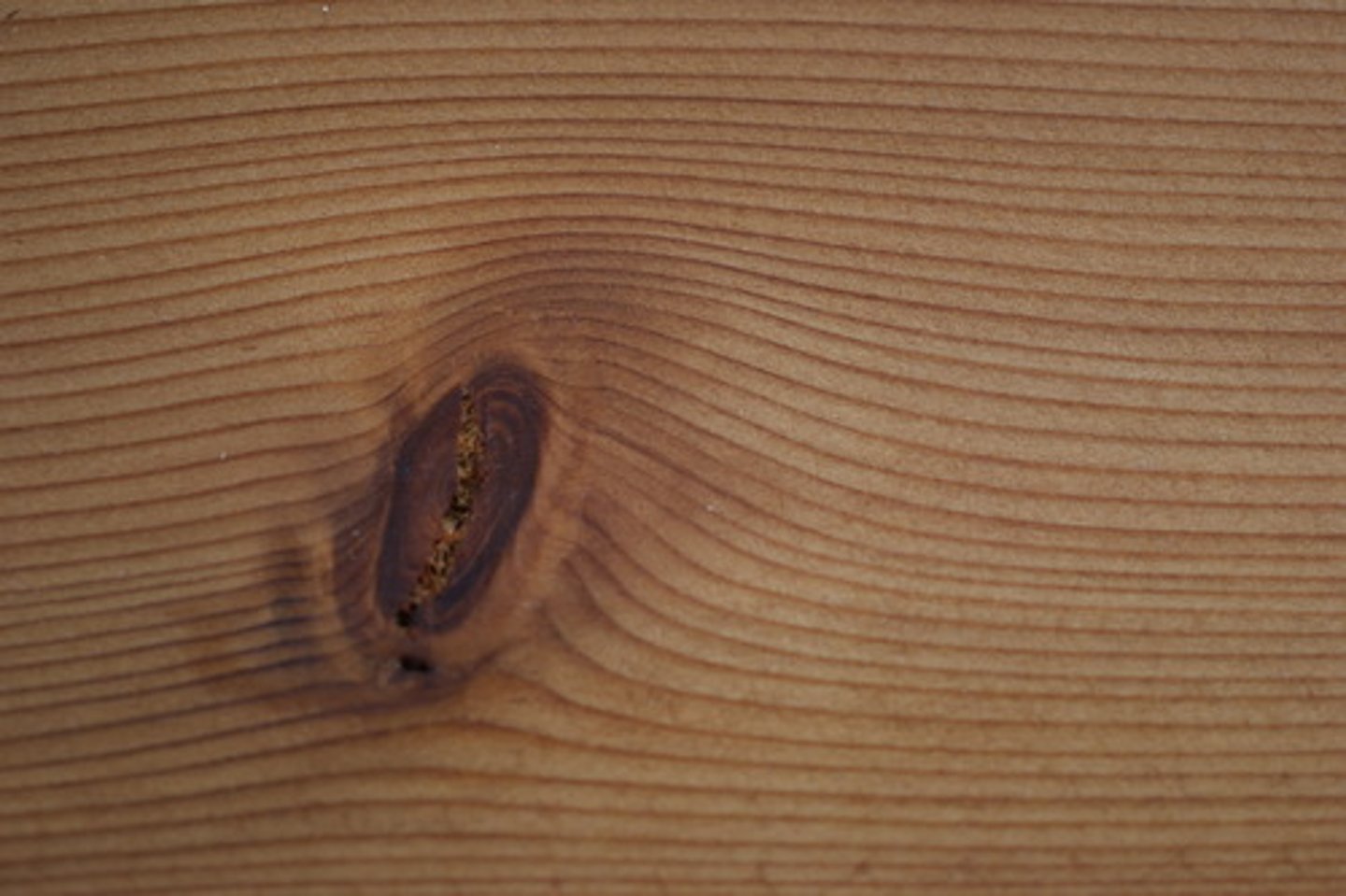

Why aren't knots in manufactured timbers.
Manufactured timbers are made from wood scraps, so knots can be found and removed from the mixture.
What are growth rings?
Every year, a tree produces a new layer under their bark. This is called a growth ring. They are close together for hardwoods and further apart for softwoods.
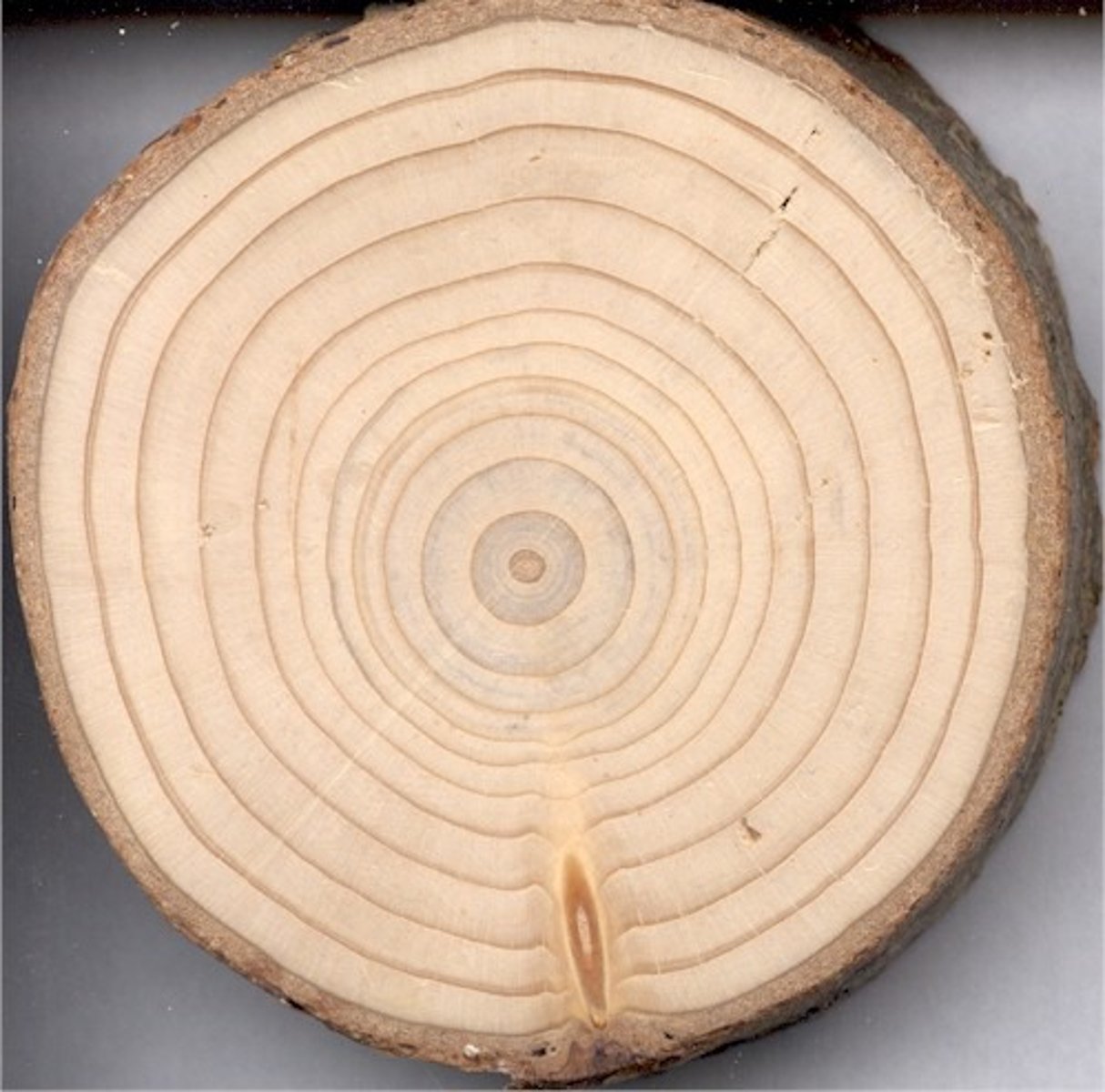

What are the two types of long vessels that run the length of hardwood trees?
Fibres and pores
Give examples of working properties of woods.
Elasticity, Tensile strength, Compressive strength
What is elasticity?
The ability of a material to stretch and return to its original shape.
What is tensile strength?
The ability of a material to withstand being pulled by a certain amount of force
What is compressive strength?
The ability of a material to withstand being crushed by a certain amount of force
How does the density of a wood effect its compressive strength?
The higher the density, the higher the compressive strength.
What is deforestation?
When a clearing is made by chopping down trees
What re some environmental issues of deforestation?
Harms wildlife habitats, causes soil erosion that can lead to landslides. Less trees means an increase in global warming.
How can you minimise the environmental impact of deforestation?
Plant more trees than you cut. This system is often found in 'managed forests'.
Why can't manufactured timbers be recycled?
Because they are held together by glue which is not recyclable.
How can the supplying of timber be bad for the environment?
- transportation often involves burning fossil fuels, adding to the carbon footprint of the timber
- wastage of small branches and leaves are often burned, releasing carbon dioxide
- processes such as kiln drying use energy, adding to the ecological footprint of the timber
What are the 6 Rs?
Reduce, Reuse, Recycle, Rethink, Refuse, Repair
What are the 6 Rs used for?
The 6 Rs can be considered by the designer, the manufacturer and the consumer to reduce the negative impact on the environment.
What factors are considered when purchasing timbers?
- How they look
- What they are commonly used for
- How they can be manufactured
- How they perform in use
- What makes them unique - are they the most durable, the lightest etc?
How can the aesthetic of a timber be changed?
- Staining
- Varnishing
- Oiling
- Waxing
- Painting
- Laminating
How is expensive wood often made cheaper?
Quite often medium-density fibreboard (MDF) is laminated with a single sheet of a hardwood veneer to give the impression that solid hardwood has been used to make a product, but at a fraction of the cost.
What is genetically engineering trees for?
Genetic engineering could make trees that could grow faster or have a resistance to particular diseases. The long-term effects of genetic engineering are unknown, which causes some people to be wary of using it.
What is seasoning for?
When a tree is initially cut it is extremely wet, with 85 per cent water content. The timber is often dried to 10-12 per cent for indoor use through a process called seasoning. Seasoning increases strength, stability and resistance to decay.
What are the two types of seasoning?
Air seasoning, kiln drying
What is air seasoning?
Leaving planks of wood outside for a few years to dry them until they are only 18% water
What is kiln drying?
Pumping steam and warm dry air around wooden planks to dry them until they are only 10% water
How can timbers be treated for specific purposes?
- Polymer veneers make timber look more expensive than it is - used in furniture.
- Flame-retardant chemicals can be sprayed onto timbers used within house constructions to slow the spread of fire
What are some social factors of selecting timbers?
Personal preference, age, background, finances, and interests.
What is timber that has been cut by a sawmill referred to as?
Once timber has been cut at a sawmill, it is referred to as 'rough cut'
What does 'PSE' mean?
PSE is a term used to indicate that the timber has a 'planed square edge'. This means that one edge will be planed smooth.
What does 'PAR' mean?
This means that one edge will be planed smooth. PAR is a term used to indicate that the timber is planed all round, meaning that both the edges and sides have been planed.
What are the stock shapes/sizes of timbers?
- Regular sections
- Mouldings
- Dowels
- Sheets
What is a 'regular section'?
Regular sections and sheets refer to the proportional dimensions of the timber
What is a 'moulding'?
Moulding refers to a decorative pattern (in wood) that has been cut using a spindle moulder
What are some uses of moulded timbers?
Skirting boards and dado rails.
What is a dowel?
A dowel is a cylindrical-shaped piece of wood. They can be purchased in different diameters.
What is the most common size of manufactured boards?
2440 mm x 1220 mm
What is shear force?
Forces acting across a material
What is 'kerfing'?
Adding slots to a material to allow it to bend.
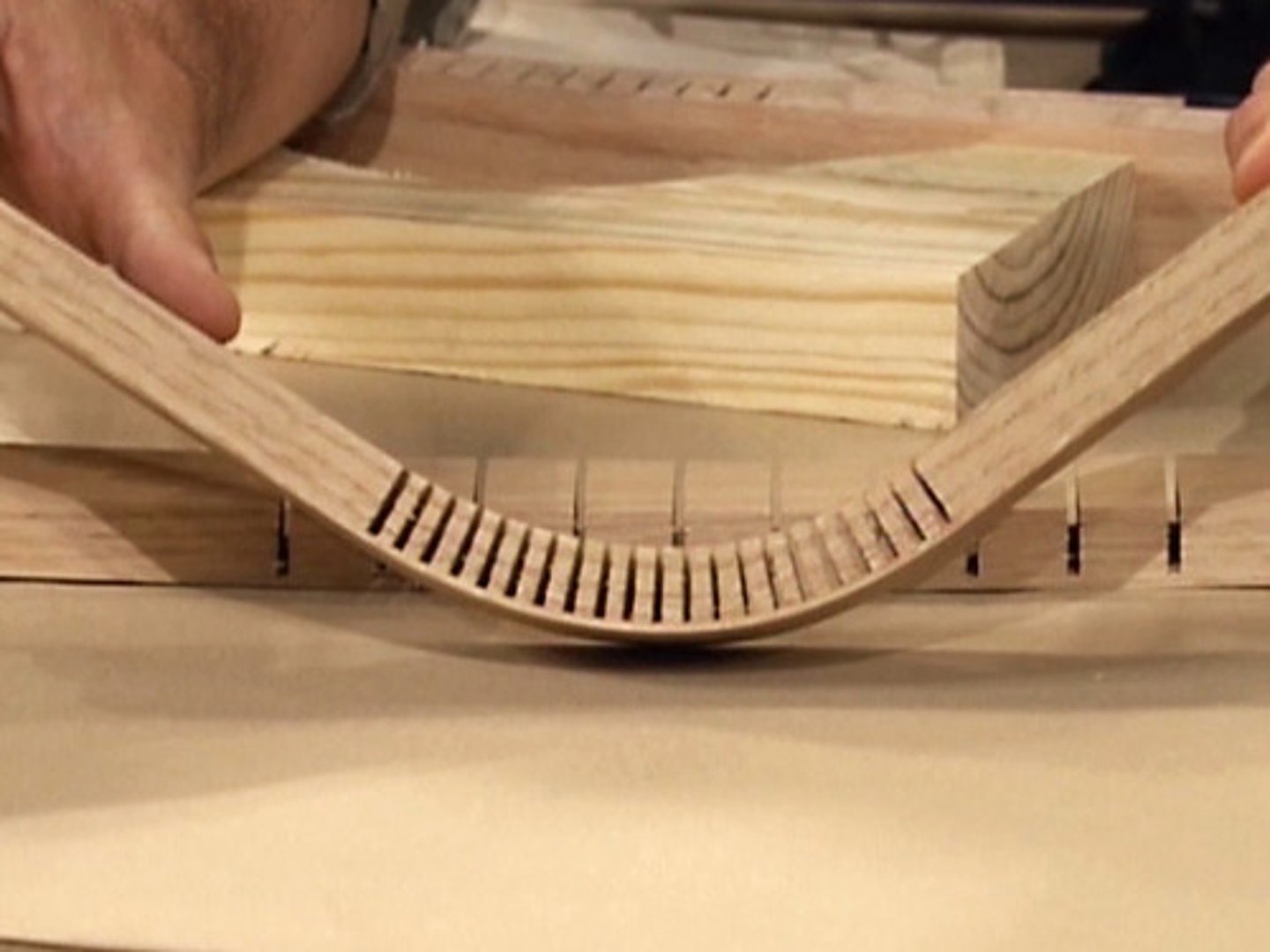
What is a strut?
A beam that is used in structures to resist compressive forces.
What is lamination?
Gluing multiple layers of material together. This creates a laminate.
Why is plywood glued at 90 degrees?
To increase its cross-sectional stability

What is the difference between a brace, a tie bar and a strut?
A brace is similar to a strut; it is a bar that is added to strengthen a material or product. They usually go diagonally across a material to make triangle shapes. A tie bar is used in a similar manner and holds the frame in shape. While a strut resists compression, a tie bar resists tension. In construction, a tie bar sits across the structure where the roof meets the walls and acts to resist the weight of the roof. Diagram: https://bam.files.bbci.co.uk/bam/live/content/zkh8nrd/medium
What is a router?
A router can be hand-held, mounted to a table or even computer controlled. All routers work by rotating a cutting bit at high speed. As the cutting tool passes over or along the edge of the timber, a cut or profiled shape is made. Routers can plunge into a material to cut holes. They can follow jigs or patterns, for example kitchen fitters might follow a pattern to join worktops together.
What are sawing machines for?
Sawing machines help cut timbers quickly. The circular saw and bandsaw are commonly found in workshops.
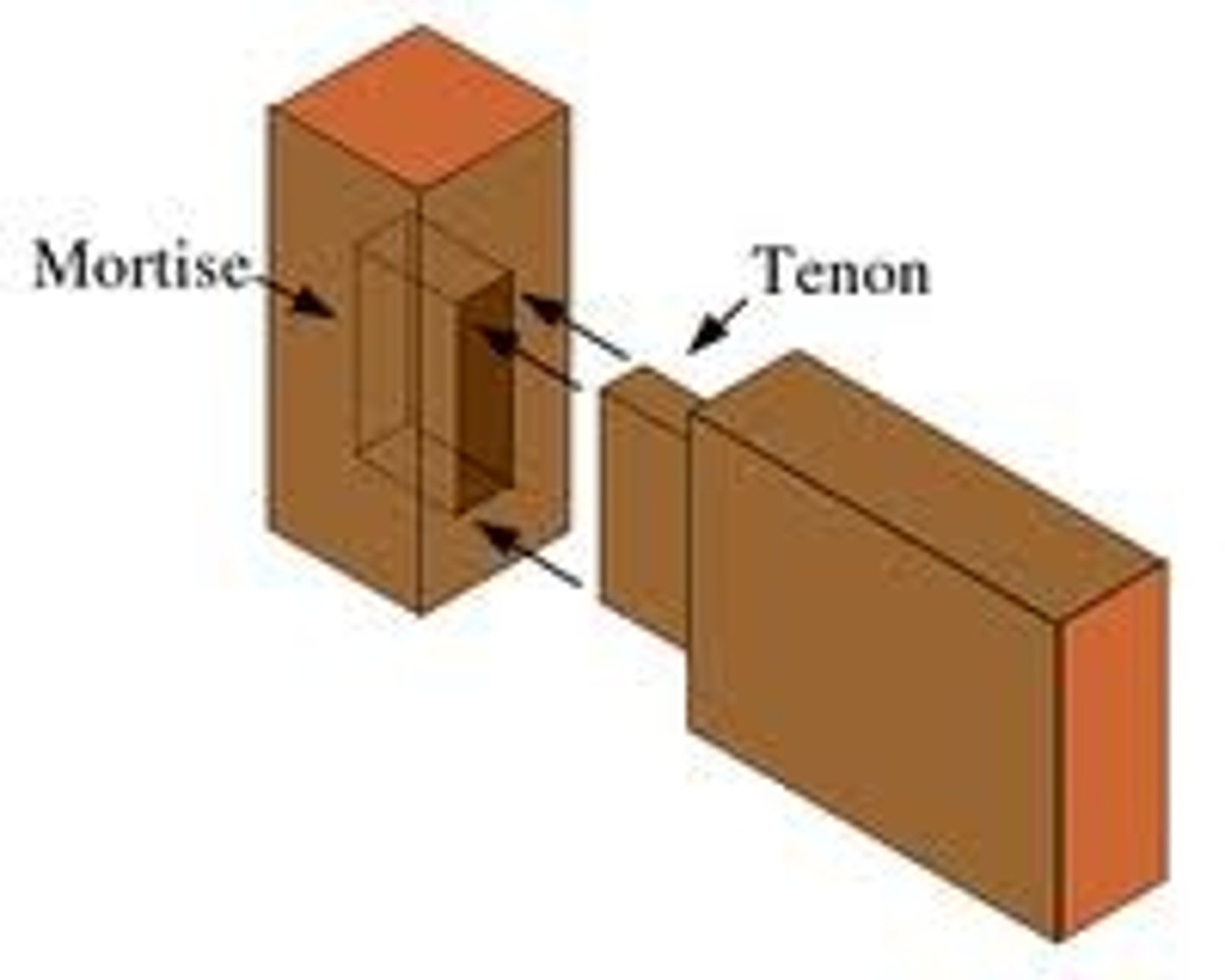
What is a mortiser for?
A mortiser makes a square hole for a mortise and tenon joint.
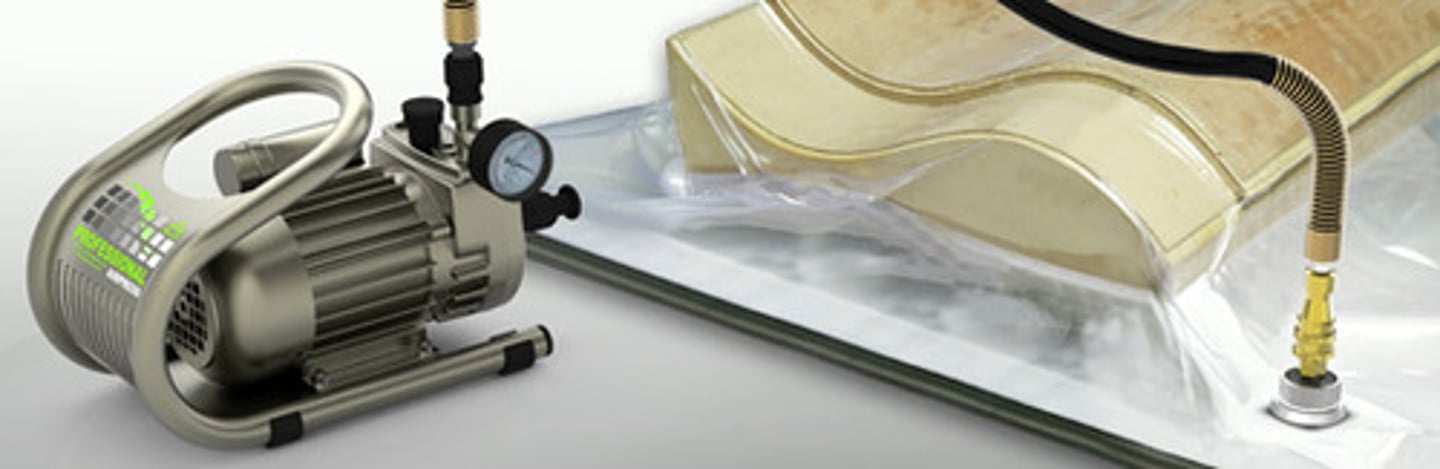
What is a bag press?
A bag press is often used to create curved shapes in laminated timber veneers. The bag is sealed and the air is sucked out while the glue dries between the veneers.

What is a jig?
Used to guide a drill or saw to cut in exactly the same place each time on every piece of timber - reduces marking out time thus increasing the efficiency of the manufacturing process
What is a fixture?
Holds the piece of timber in place whilst it is being worked on
What is a template?
Made out of paper, card, thin metal or wood, these are drawn around to mark out the same shape repetitively, with the aim of speeding up the marking-out process and decreasing the chance of an error occurring
What is a pattern?
A collection of templates that go together to make a part, or all, of a product