Unit 10: Managing Strategic Change – Key Terms
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Kotter's Four Resistances to Change
1.Self-interest (employees fear personal loss from change)
2. Misunderstanding (Lack of trust or poor communication)
3. Different assessments (Disagreements on the necessity of change)
4. Low tolerance for change (Preference for stability)
Kotter & Schlesingers 6 methods of overcoming change
Education & Communication: Explaining the benefits of change.
Participation & Involvement: Engaging employees in decision-making.
Facilitation & Support: Providing training and resources.
Negotiation & Agreement: Offering incentives for acceptance.
Manipulation & Co-option: Persuading key individuals to influence others.
Explicit & Implicit Coercion: Using authority to enforce change.
Handy's Cultural Model
A framework developed by Charles Handy to categorize organizational cultures into four types:
Power Culture: Decisions are made by a central figure, commonly seen in small firms.
Role Culture: A bureaucratic and structured hierarchy where roles define behavior.
Task Culture: Focuses on teamwork and collaboration to achieve objectives.
Person Culture: Prioritizes the personal goals of employees over organizational objectives.
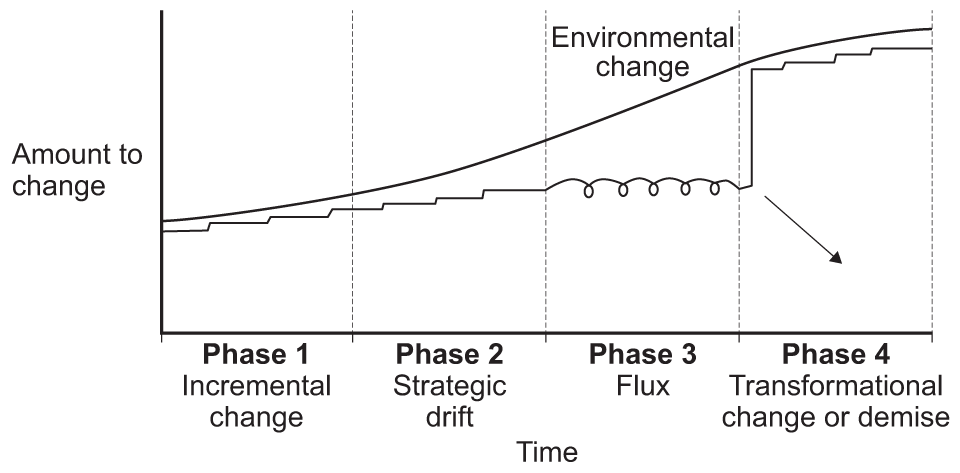
strategic drift
when a company responds too slowly to changes in the external environment and continue with a strategy that is no longer suited to the current situation
critical path analysis
the technique for planning the sequencing of activities to complete a project in the shortest time possible
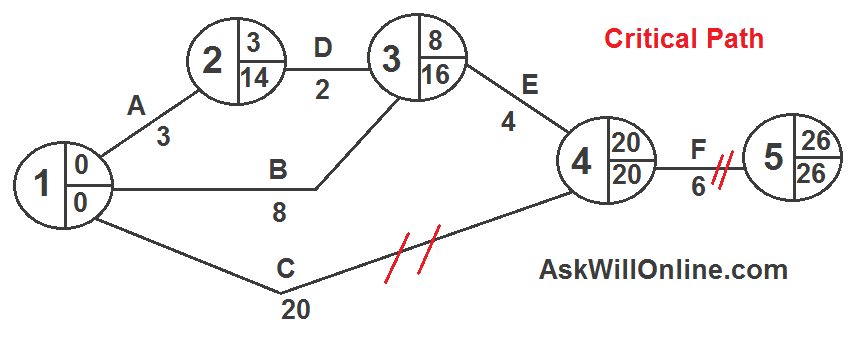
critical pathway
the sequence of activities which have no float time and are essential to complete in time to not delay the project
float time
the amount of time a task can be delayed without it delaying the projects overall completion time