Exam 1 pt 1
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
state the 3 domains of life
bacteria
archaea
eukarya
representative microorganism for bacteria domain
representative microorganism for archaea domain
representative microorganism for eukarya domain
gram positive cell structure
thick peptidoglycan layer (multiple layers), no outer membrane
teichoic acids
narrow/absent perplasmic space
components of cell structure unique to gram positives
teichoic acids (attached to peptidoglycan), lipoteichoic acids (attached to cell membrane)
gram negative cell structure
thin peptidoglycan layer, both inner and outer membranes present
wide periplasmic space
lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
porins
components of cell structure unique to gram negatives
outer membrane
lipopolysaccharides (LPS)
porins
what type of bacteria has an outer AND inner membrane?
gram negative bacteria
what is peptidoglycan
strong, mesh-like molecule that forms the main structure of the bacterial cell wall
name of sugars: NAG, NAM
sugars in the peptidoglycan
NAG, NAM
function of peptidoglycan
gives the cell shape
protects the bacterium from bursting due to water pressure
is the target of some antibiotics (like penicillin), which weaken it and kill the bacteria
periplasmic space
the area between the inner (plasma) membrane and the outer structures of a bacterial cell wall
wide in gram-
narrow in gram+
porins
protein channels found in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
tiny holes that allow certain molecules to pass through the outer membrane
gram+ don’t have bc they dont have outer membranes
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
it’s a large molecule found only in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria ; has 3 parts
lipid A
core polysaccharide
o-antigen
lipid A
the toxic part of the lipopolysaccharide (lps) molecule found in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
released when bacteria die and break apart
can cause fever, inflammation, and even septic shock
why are gram- infections more dangerous?
bc they have endotoxins that are released when they break down and die
structures involves in bacterial attachment
pili, fimbriae, flagella,
pili
thin, hair-like protein structures that stick out from the surface of many bacteria, especially gram-negative bacteria.
fimbriae (shorter, more numerous, for attachment)
sex pili (longer, fewer, for gene transfer)
fimbriae
short, hairlike proteins for attachment and biofilm formation
structures involves in bacterial chemotaxis (movement)
flagella
flagella
structure used for motility
structures involves in bacteria horizontal gene transfer
conjugative (sex) pili, bacteriophages
conjugative (sex) pili
long protein appendages (pili) that join bacteria for horizontal transfer of genetic information
L forms
bacteria that have lost their cell wall, either partially or completely
can arise from gram+ or gram-
L-forms that arise from gram+
protoplasts
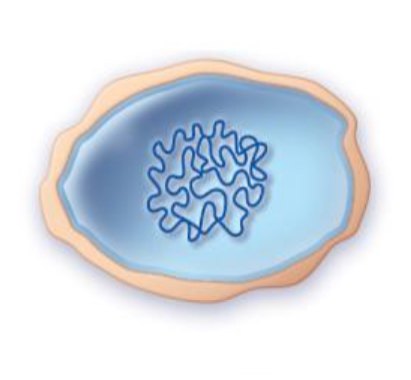
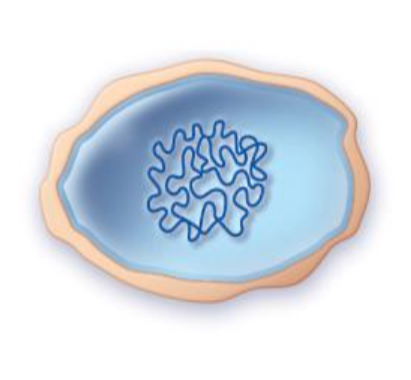
structure of protoplasts
• no cell wall at all
• only have the cell membrane
• round or irregular in shape
• very fragile because they lack the thick peptidoglycan layer
L-forms that arise from gram-
spheroplasts
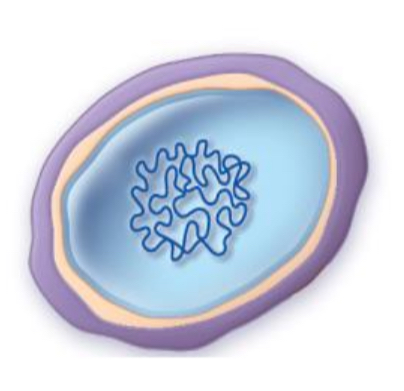
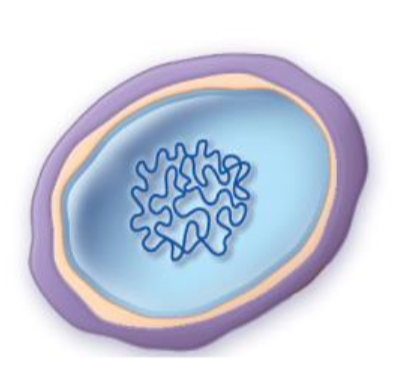
structure of spheroplasts
partially lost cell wall
outer membrane is still present
more stable than protoplasts due to the remaining outer membrane