Covalent bonding
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What is a covalent bond?
The electrostatic force of attraction between the negative shared pair of electrons & a positive nuclei
Covalent bonds are formed between…
Non-metal atoms that share electrons to obtain a full outer shell
Covalent bonds can be represented by…
Dot & cross diagrams
Displayed formula
Give a dot & cross diagram for hydrogen (H2)
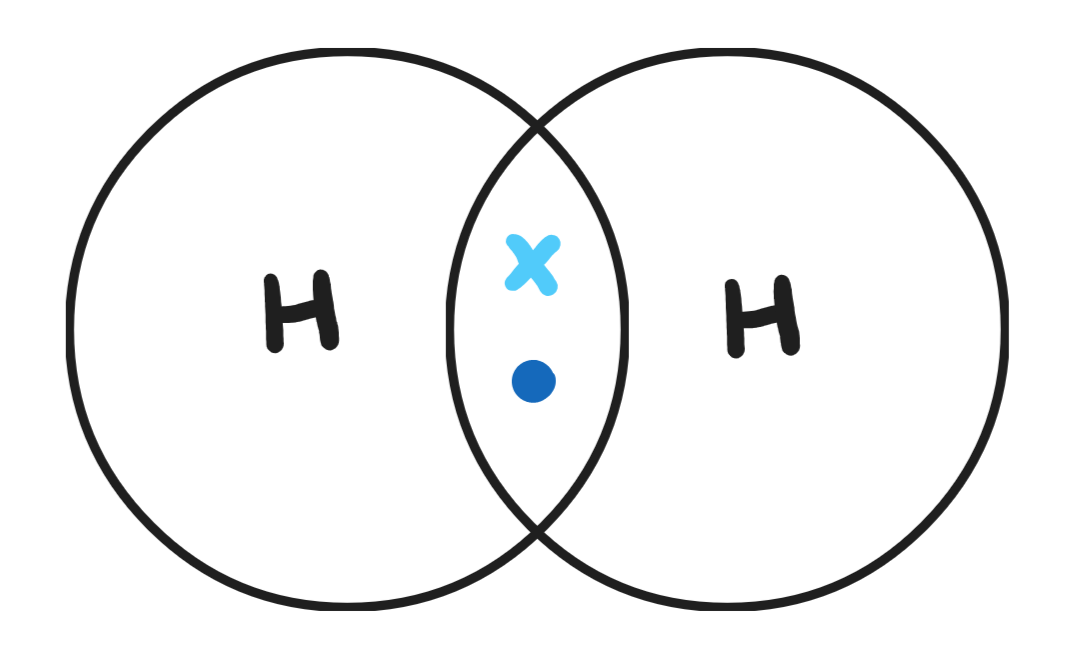
Give a dot & cross diagram for oxygen (O2)
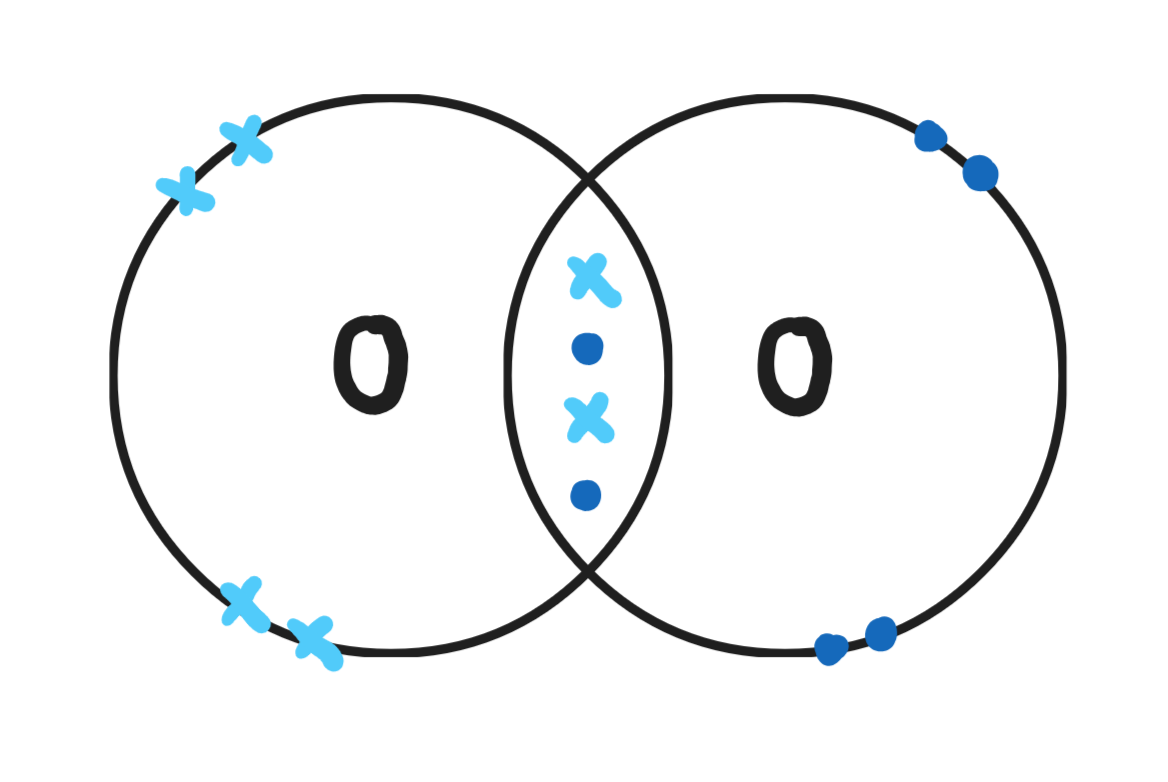
Give a dot & cross diagram for nitrogen (N2)
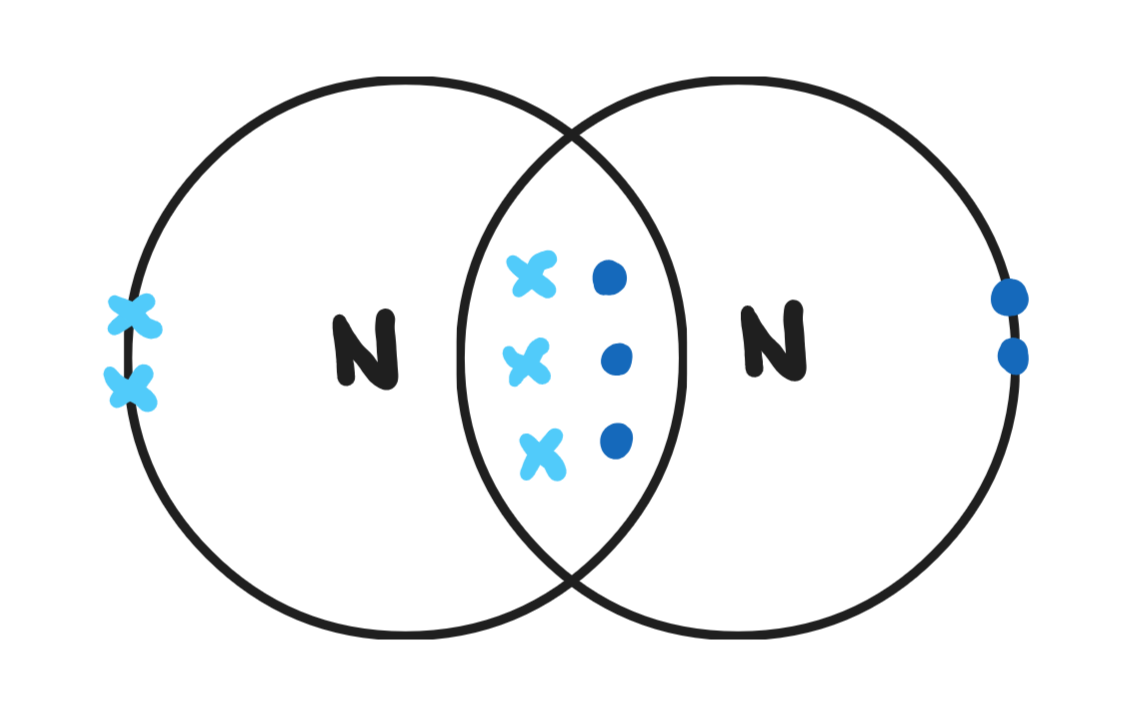
Give a dot & cross diagram for fluorine (F2)
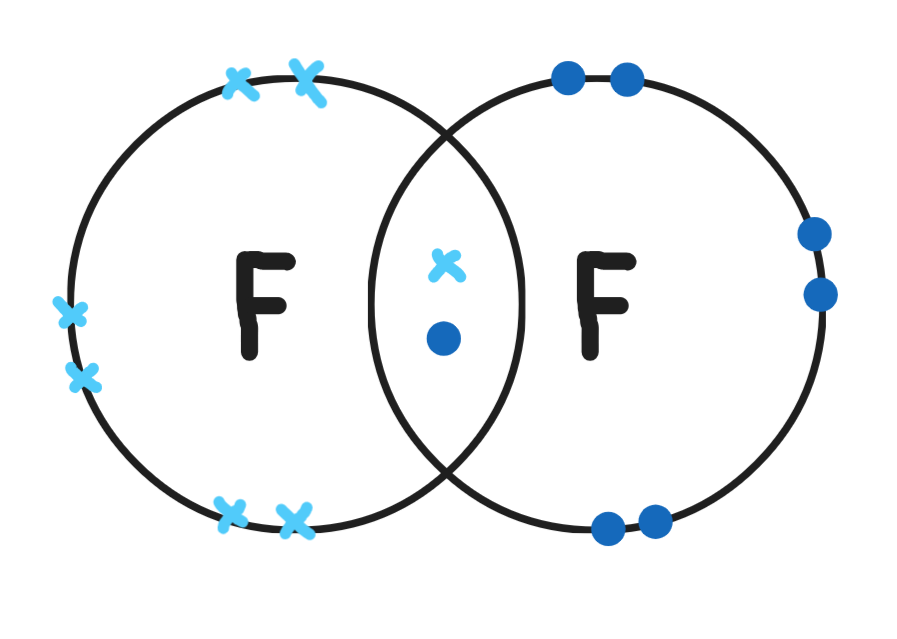
Give a dot & cross diagram for hydrogen chloride (HCl)
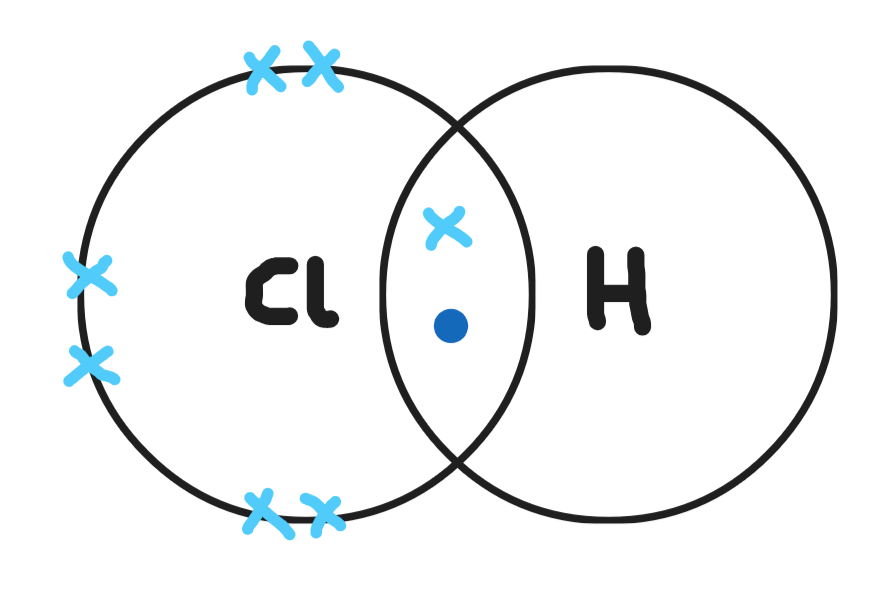
Give a dot & cross diagram for water (H20)
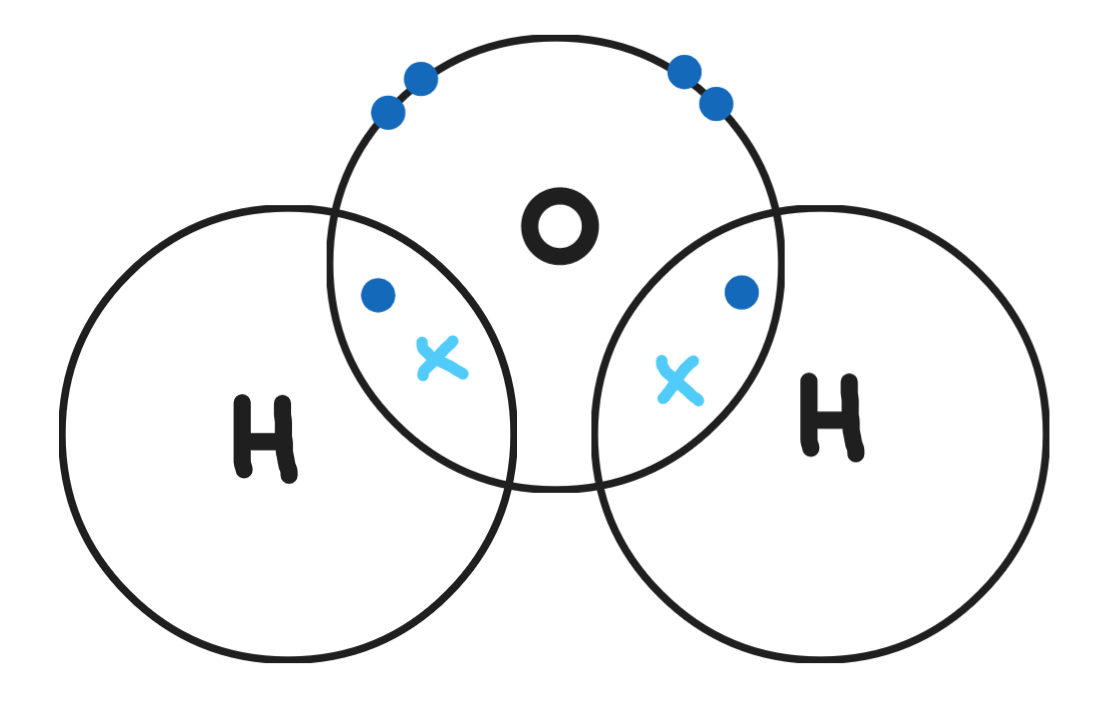
Give a dot & cross diagram for ammonia (NH3)
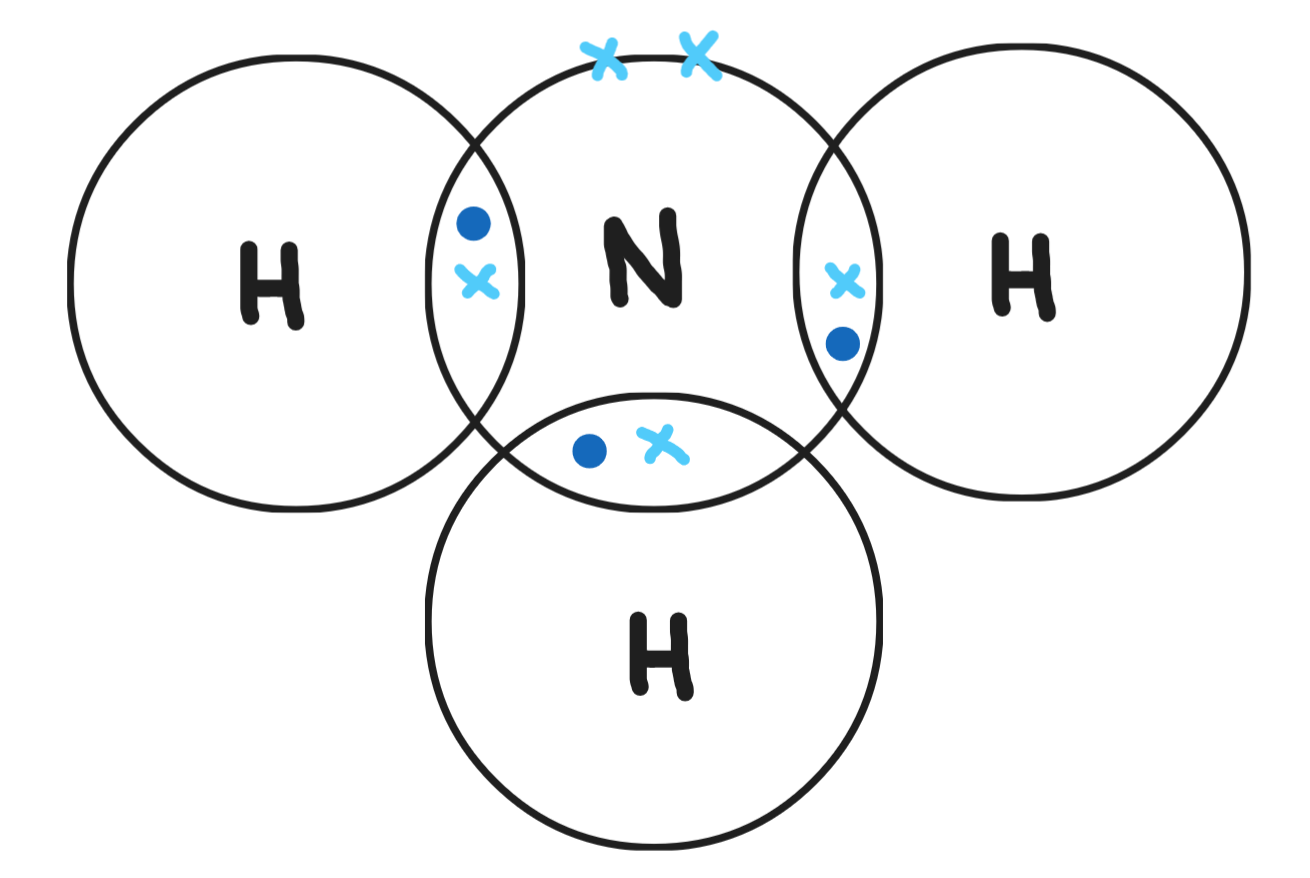
Give a dot & cross diagram for carbon dioxide (CO2)
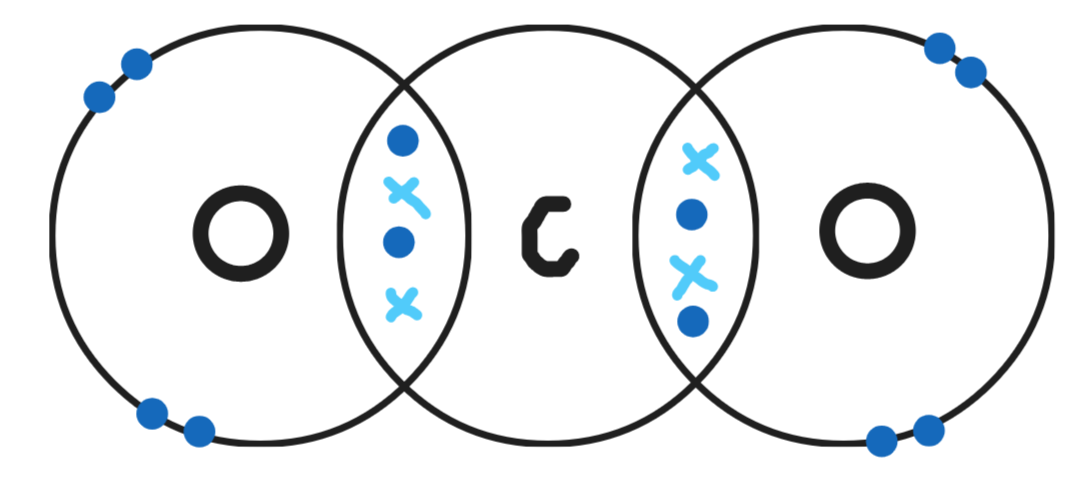
Give a dot & cross diagram for methane (CH4)
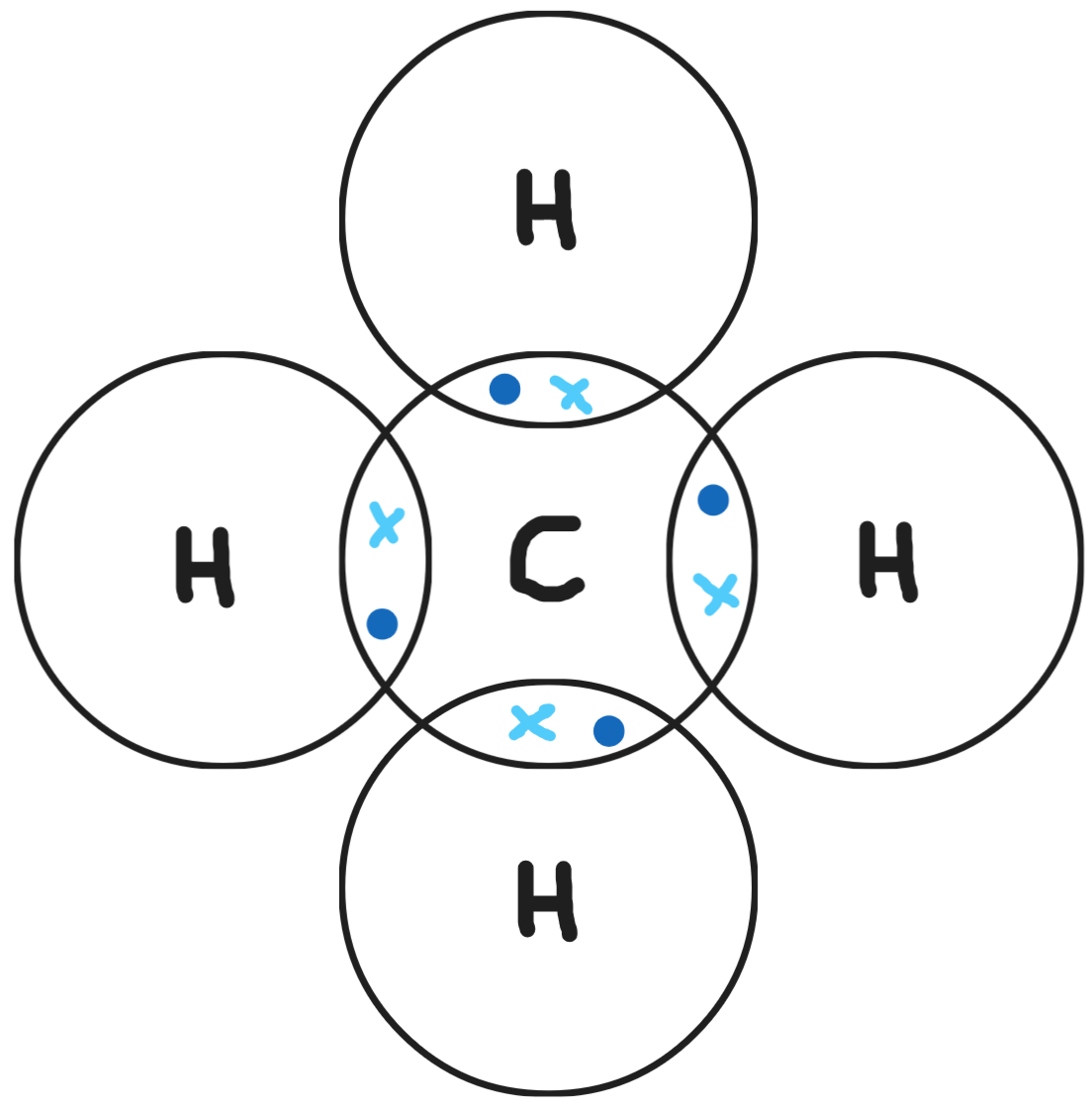
Give a dot & cross diagram for ethane (C2H6)
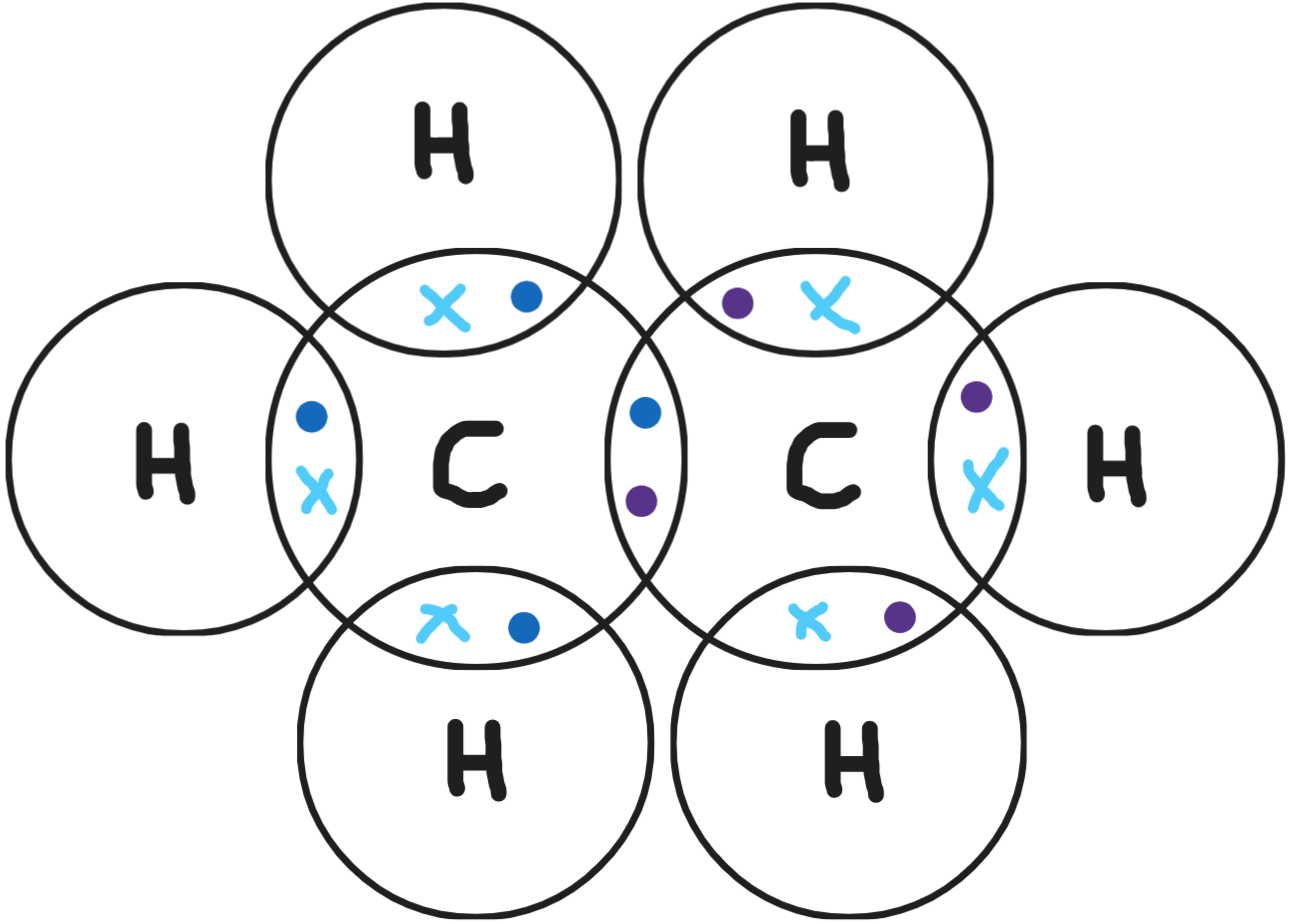
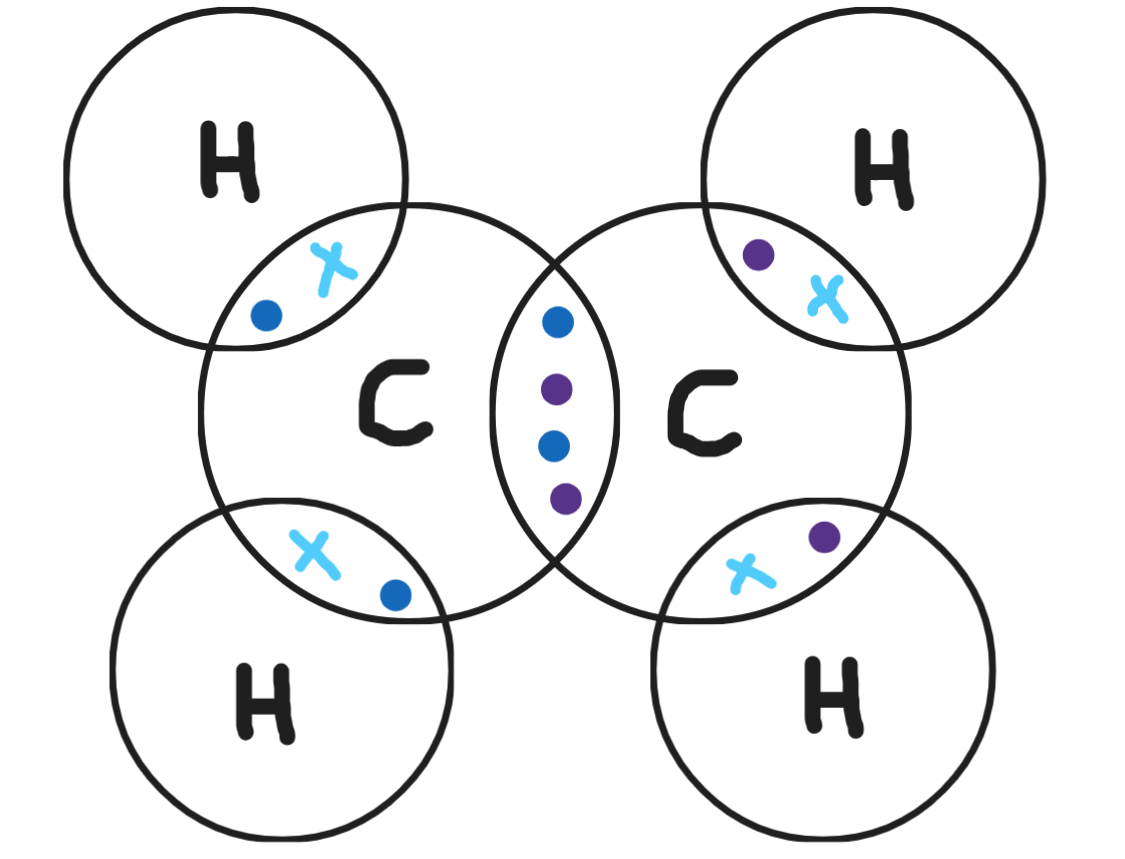
Give a dot & cross diagram for ethene (C2H4)
Why do simple molecular substances have low melting & boiling points?
Because the intermolecular forces of attraction are weak which means that little energy is required to separate them & therefore only low temperatures are needed
What happens to the melting & boiling point of simple molecular substances as relative molecular mass increases?
Melting & boiling point increases as relative atomic mass increases
This is because the intermolecular forces of attraction are stronger & therefore more energy is required to separate them
Do covalent substances conduct electricity?
No
(except graphite & graphene)
Why do most covalent substances not conduct electricity?
Because they do not have an overall charge or particles that are free to move
What are giant covalent substances?
Atoms that are covalently bonded together in a giant lattice
(e.g. diamond, graphite, silicon dioxide/silica)
Why do giant covalent substances have high melting & boiling points?
Because all the atoms in the giant structure are linked together by very strong covalent bonds
This means that a lot of energy is required to break the bonds & therefore high temperatures are needed
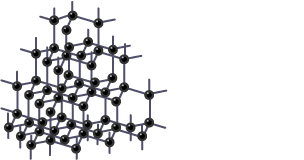
Describe the structure & bonding of diamond
Each carbon atom is joined to 4 other carbon atoms by covalent bonds
The carbon atoms form a tetrahedral structure
There are no free/delocalised electrons
What are the properties of diamond?
- Very hard
- Has a very high melting & boiling point
- Does not conduct electricity
- Useful for cutting tools
Describe the structure & bonding of graphite
Each carbon atom is joined to 3 other carbon atoms by covalent bonds
The carbon atoms form a hexagonal layered structure
Each carbon atom has 1 delocalised electron between the layers
The layers have weak intermolecular forces so they can slide over each other
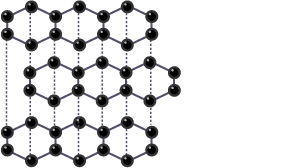
What are the properties of graphite?
- Soft
- Conducts electricity
- Still has a high melting & boiling point
- Useful for pencils & electrodes
What is graphene?
A single layer of graphite
Its properties make it useful for electronics & composites
Describe the structure & bonding of Fullerene (C60)
Fullerene has a simple molecular structure
Each carbon atom is joined to 3 other carbon atoms by covalent bonds
The carbon atoms form a spherical shape
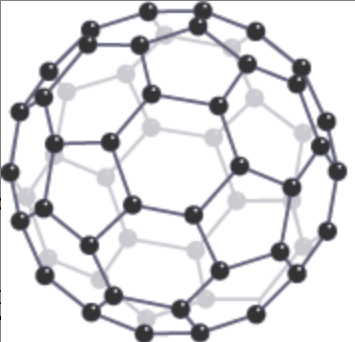
What are the properties of Fullerene (C60)
- Soft
- Low melting & boiling point
- Does not conduct electricity
What are nanotubes?
Cylindrical fullerenes with very high ratios of length : diameter
Their properties make them useful for nanotechnology & electronics