MODULE 7: GESTALT THERAPHY
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Gestalt Therapy
The whole is greater than the sum of its parts
Max Wertheimer
published a paper demonstrating that individuals perceived motion in rapidly flickering static images—an insight that came to him as he used a child’s toy tachistoscope. The first Gestalt principles originated in the work of Max Wertheimer is a response to the structuralism of Wilhelm Wundt.
tachistoscope, structuralism of Wilhelm Wundt
Max Wertheimer published a paper demonstrating that individuals perceived motion in rapidly flickering static images—an insight that came to him as he used a child’s toy ___________. The first Gestalt principles originated in the work of Max Wertheimer is a response to the ____________
Wolfgang Köhler, Kurt Koffka, sensory stimuli
Wertheimer, and his assistants _____________ and _________ who later became his partners, believed that perception involved more than simply combining ___________
Christian von Ehrenfels
our experience is structured is a matter of certain special “Gestalt qualities” of complexes of data in a given experience, meaning each quality is determined by and is essentially dependent on the constituent elements of the complex with which it is associated.
Frederick (“Fritz”) S. Perls
______________, a German-born psychiatrist, founded Gestalt therapy in the 1940s with his wife, Laura Perls
Jacob Moreno
_______________ employed many approaches in his therapy, including psychodrama, sociatry, sociometry, and group psychotherapy.
Kurt Lewin
Social Psychology and Group Learning: ______________, a Gestalt psychologist, is often considered one of the founders of modern social psychology. His theories can be applied to group learning situations, where the dynamics of the group can significantly impact individual learning outcomes.
Gestalt therapy
__________ is an existential, phenomenological, and process-based approach created on the premise that individuals must be understood in the context of their ongoing relationship with the environment.
existential, phenomenological, and process-based approach
Gestalt therapy is an _________, ____________________, and ______________created on the premise that individuals must be understood in the context of their ongoing relationship with the environment.
GESTALT KEY CONCEPTS
Principle of Closure
Principle of Proximity
Principle of Continuity
Principle of Similarity
Principle of Figure to Ground
Principle of Pragnanz
Principle of Closure
In the logo of WWF, there is an image of a panda, and it has some missing spaces on its back and head. It is probably where the white fur of the panda would be. However, we are well aware of the shape and color of the panda; and so, we automatically and subconsciously fill the missing gaps.

Principle of Proximity
Happens when two or more elements are close to each other, the position of these elements portray the relationship between separate parts and render a specific meaning to that group.

Principle of Continuity
Whenever our eyes begin to follow something, they will continue to travel in that direction until they encounter another object. The eyes create momentum as they are compelled to move through one object and continue to another.

Principle of Similarity
We tend to perceive things that physically resemble each other as a part of the same object. There may be a similarity in any one of them, color, shape, texture, or any other element.

Principle of Figure to Ground
The human eye can differentiate an object from the surrounding. We perceive certain objects as being in the foreground and other objects as being in the background.

Principle of Pragnanz
Humans naturally perceive objects in the simplest form.

GESTALT THERAPY
is an experiential approach that stresses present awareness and the quality of contact between the individual and the environment.
The major focus is on assisting the client to become aware of how behaviors that were once part of creatively adjusting to past environments may be interfering with effective functioning and living in the present.
experiential approach, present awareness, quality of contact, individual and the environment
Gestalt therapy is an ___________that stresses ___________ and the ____________ between the __________.
aware
The major focus is on assisting the client to become ______of how behaviors that were once part of creatively adjusting to past environments may be interfering with effective functioning and living in the present.
Here and now
It is assumed that human beings perceive everything that happens to us as a unified experience.
Responsibility
Taking conscience of our own actions and styles of experiencing things also implies assuming the consequences of these choices.
It is essential to take note of what happens to oneself. Only in this way will it be possible to detect new ways of formulating the experience of the here and now in terms that bring us closer to self-realization.
Awareness
Holism
All of nature is seen as a unified and coherent whole, and the whole is different from the sum of its parts. Because Gestalt therapists are interested in the whole person, they place no superior value on a particular aspect of the individual. Gestalt practice attends to a client’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, body, memories, and dreams.
Organismic Self-Regulation, (Latner, 1986)
The figure-formation process is intertwined with the principle of organismic self-regulation, a process by which equilibrium is “disturbed” by the emergence of a need, a sensation, or an interest. Organisms will do their best to regulate themselves, given their own capabilities and the resources of their environment (_____________, ________.)
becoming who or what we are not, the more we remain the same.
The Gestalt theory of change posits that the more we work at _______________________________________.
Arnie Beisser (1970)
Fritz’s good friend and psychiatrist colleague _____________ suggested that authentic change occurs more from being who we are than from trying to be who we are not.
authentic change occurs more from being who we are than from trying to be who we are not.
Fritz’s good friend and psychiatrist colleague Arnie Beisser (1970) suggested that ____________________________
paradoxical theory of change, should be, are
Fritz’s good friend and psychiatrist colleague Arnie Beisser (1970) suggested that authentic change occurs more from being who we are than from trying to be who we are not.
Beisser called this simple tenet the ________________.
We are constantly moving between who we “______” and who we “____”.
sensation - scanning
excitement/awareness - conceptualisation
mobilisation - commitment
action - movement
contact - change of boundaries
withdrawal - assessment
GESTALT CYCLE OF CHANGE
sensation - scanning
data:
Attend to environment
Assess needs
Identify key issues
Seek/share information
excitement/awareness - conceptualisation
image creation (intention)
Creation of image or reality
Development of common vision/compelling picture
mobilisation - commitment
energy mobilisation
Discuss potential directions for work
Establish levels of resources to commit
Establish experiment/pilot
action - movement
action
Action taken to impact environment
Energy used
contact - change of boundaries
change
Self and other impacted
Shift in reality occurs
withdrawal - assessment
closure
Evaluation of activity
Time for appreciation
CONTACT BOUNDARY DISTURBANCES
egotism, retroflection, projection, confluence, introjection
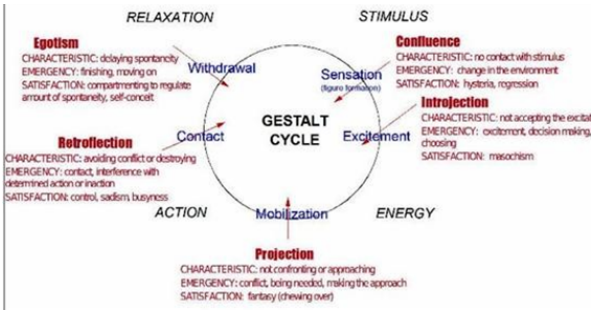
egotism
CHARACTERISTIC: delaying spontaneity
EMERGENCY: finishing, moving on
SATISFACTION: compartmenting to regulate amount of spontaneity, self-concept
retroflection
CHARACTERISTIC: avoiding conflict or destroying
EMERGENCY: contact, interference with determined action or inaction
SATISFACTION: control, sadism, busyness
projection
CHARACTERISTIC: not confronting or approaching
EMERGENCY: conflict, being needed, making the approach
SATISFACTION: fantasy (chewing over)
confluence
CHARACTERISTIC: no contact with stimulus
EMERGENCY: change in the environment
SATISFACTION: hysteria, regression
introjection
CHARACTERISTIC: not accepting the excitation
EMERGENCY: excitement, decision making, choosing
SATISFACTION: masochism
“contact boundary phenomena.”
Refer to the characteristic styles people employ in their attempts to control their environment through one of these channels of resistance.
Gestalt therapists talk about the two functions of boundaries: to connect and to separate. Both contact and withdrawal are necessary and important to healthy functioning.
to connect and to separate
Gestalt therapists talk about the two functions of boundaries: ________________. Both contact and withdrawal are necessary and important to healthy functioning.
Perls (p.225)
Clients have to grow up, stand on their own two feet, and “deal with their problems themselves”
unfinished business
When figures emerge from the background but are not completed and resolved, individuals are left with _____________________, which can be manifested in unexpressed feelings such as resentment, rage, hatred, pain, anxiety, grief, guilt, and abandonment. Unacknowledged feelings create unnecessary emotional debris that clutters present-centered awareness.
impasse, stuck point
The _______, or ______, occurs when external support is not available or the customary way of being does not work. The therapist’s task is to accompany clients in experiencing the impasse without rescuing or frustrating them. The counselor assists clients by providing situations that encourage them to fully experience their condition of being stuck.
energy
In Gestalt therapy special attention is given to where _______is located, how it is used, and how it can be blocked.
Blocked energy
_________is another form of defensive behavior. It can be manifested by tension in some part of the body, by posture, by keeping one’s body tight and closed, by not breathing deeply, by looking away from people when speaking to avoid contact, by choking off sensations, by numbing feelings, and by speaking with a restricted voice, to mention only a few.
Anxiety
“_______is excitement without the breath”
Depression or mood disorders like bipolar disorder
Anxiety disorders or general stress and anxiety
Relationship problems or interpersonal conflicts
Behavioral problems like gambling disorder
Self-esteem issues or a lack of confidence
● Negative self-talk
● Identity crisis
● Improving self-awareness
Gestalt therapy has been used to treat issues like:
The Internal Dialogue Exercise
Gestalt therapists pay close attention to splits in personality function.
A main division is between the “top dog” and the “underdog,” and therapy often focuses on the war between the two
The Empty-Chair Technique, empty chair
Jacob Moreno, the founder of psychodrama, originated the __________ which was later incorporated into Gestalt therapy by Perls
The ________is a vehicle for the technique of role reversal, which is useful in bringing into consciousness the fantasies of what the “other” might be thinking or feeling. Essentially, this is a role-playing technique in which all the parts are played by the client. In this way the introjects can surface, and the client can experience the conflict more fully.
Future Projection Technique
an anticipated event is brought into the present moment and acted out. This technique, often associated with psychodrama, is designed to help clients express and clarify concerns they have about the future.
Making the Rounds
is a Gestalt exercise that involves asking a person in a group to go up to others in the group and either speak to or do something with each person.
The purpose is to confront, to risk, to disclose the self, to experiment with new behavior, and to grow and change.
The Reversal Exercise
The theory underlying the ________is that clients take the plunge into the very thing that is fraught with anxiety and make contact with those parts of themselves that have been submerged and denied.
This technique can help clients begin to accept certain personal attributes that they have tried to deny
The Rehearsal Exercise
When clients share their rehearsals out loud with a therapist, they become more aware of the many preparatory means they use in bolstering their social roles. They also become increasingly aware of how they try to meet the expectations of others, of the degree to which they want to be approved, accepted, and liked, and of the extent to which they go to attain acceptance
The Exaggeration Exercise
One aim of Gestalt therapy is for clients to become more aware of the subtle signals and cues they are sending through body language. Movements, postures, and gestures may communicate significant meanings, yet the cues may be incomplete.
In this exercise the person is asked to exaggerate the movement or gesture repeatedly, which usually intensifies the feeling attached to the behavior and makes the inner meaning clearer.
Some examples of behaviors that lend themselves to the exaggeration technique are trembling (shaking hands, legs), slouched posture and bent shoulders, clenched fists, tight frowning, facial grimacing, crossed arms, and so forth. If a client reports that his or her legs are shaking, the therapist may ask the client to stand up and exaggerate the shaking. Then the therapist may ask the client to put words to the shaking limbs.
Staying With the Feeling
At key moments when clients refer to a feeling or a mood that is unpleasant and from which they have a great desire to flee, the therapist may urge clients to stay with their feeling and encourage them to go deeper into the feeling or behavior they wish to avoid.
Facing and experiencing feelings not only takes courage but also is a mark of a willingness to endure the pain necessary for unblocking and making way for newer levels of growth.
A strong therapeutic relationship built on trust and nonjudgmental acceptance fosters the safety needed for clients to stay with these unpleasant feeling
The Gestalt Approach to Dream Work
The Gestalt approach does not interpret and analyze dreams. Instead, the intent is to bring dreams back to life and relive them as though they were happening now.
The dream is acted out in the present, and the dreamer becomes a part of his or her dream.
According to Perls, it represents an unfinished situation, but every dream also contains an existential message regarding oneself and one’s current struggle. Everything can be found in dreams if all the parts are understood and assimilated; dreams serve as an excellent way to discover personality voids by revealing missing parts and clients’ methods of avoidance.
Perls (1969a) suggested that “we start with the impossible assumption that whatever we believe we see in another person or in the world is nothing but a projection”
person-to-person
As an existential brand of therapy, Gestalt practice involves a ___________ relationship between therapist and client.
(Wheeler & Axelsson, 2015)
However, therapists need to be thoughtful about when and what to share. When a difficulty in a client’s life is being enacted in the therapeutic relationship, the therapist invites the client to explore this issue (_____________)
clients’ body language
An important function of Gestalt therapists is paying attention to_______________
nonverbal cues
These _________ provide rich information as they often represent feelings of which the client is unaware. The therapist needs to be alert for gaps in attention and awareness and for incongruities between verbalizations and what clients are doing with their bodies.
here-and-now experience
By focusing on language, clients are able to increase their awareness of what they are experiencing in the present moment and of how they are avoiding coming into contact with this _____________
“You” talk
language tends to keep the person hidden. The therapist often points out generalized uses of “you” and invites the client to experiment with substituting “I” when this is what is meant.
“It” talk
when clients say “it” instead of “I,” they are using depersonalizing language. The counselor may ask them to substitute personal pronouns for impersonal ones so that they will assume an increased sense of responsibility. For example, if a client says, “It is difficult to make friends,” he could be asked to restate this by making an “I” statement: “I have trouble making friends.”
Questions
have a tendency to keep the questioner hidden, safe, and unknown. Gestalt therapists often ask clients to experiment with changing their questions into statements. In making personal statements, clients begin to assume responsibility for what they say.
Language that denies power
Some clients have a tendency to deny their personal power by adding qualifiers or disclaimers to their statements. The therapist may also point out to clients how certain qualifiers sub- tract from their effectiveness. Experimenting with omitting qualifiers such as “maybe,” “perhaps,” “sort of,” “I guess,” “possibly,” and “I suppose” can help clients change ambivalent messages into clear and direct statements.
Listening to clients’ metaphors
In his workshops, Erving Polster (1995) emphasizes the importance of a therapist learning how to listen to the metaphors of clients. By tuning into metaphors, the therapist gets rich clues to clients’ internal struggles.
Listening for language that uncovers a story.
Polster (1995) also teaches the value of what he calls “fleshing out a flash.” He reports that clients often use language that is elusive yet gives significant clues to a story that illustrates their life struggles. Effective therapists learn to pick out a small part of what someone says and then to focus on and develop this element.
Gestalt, dialogue
The general orientation of __________therapy is toward _______, an engagement between people who each bring their unique experiences to that meeting
I/Thou Relationship
contemporary relational gestalt therapy stresses dialogue and the I/Thou relationship between client and therapist.
Therapists emphasize the therapeutic relationship and work collaboratively with clients in a search for understanding (Wheeler & Axelsson, 2015; Yontef & Schulz, 2013).
Following the lead of Laura Perls and the “Cleveland school” when Erving and Miriam Polster and Joseph Zinker were on the faculty in the 1960s and 1970s, this model includes more support and increased sensitivity and compassion in therapy than the confrontational and dramatic style of Fritz Perls (Yontef, 1999).
The majority of today’s Gestalt therapists emphasizes support, acceptance, empathy, respect, and dialogue as well as confrontation
(Wheeler & Axelsson, 2015; Yontef & Schulz, 2013).
Therapists emphasize the therapeutic relationship and work collaboratively with clients in a search for understanding (___________, _____)
Yontef, 1999)
Following the lead of Laura Perls and the “Cleveland school” when Erving and Miriam Polster and Joseph Zinker were on the faculty in the 1960s and 1970s, this model includes more support and increased sensitivity and compassion in therapy than the confrontational and dramatic style of Fritz Perls (_______, _____.)
support, acceptance, empathy, respect, dialogue, confrontation
The majority of today’s Gestalt therapists emphasizes ______________ as well as ________
Oprah Winfrey
“The whole point of being alive is to evolve into the complete person you were intended to be”