Lec week 9 Mismatch Negativity, P3 family, N2pc
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
oddball paradigms
a deviant stimulus (oddball) presented infrequently with a frequent standard stimulus
can be 2 stimuli or 3 stimuli
can be auditory, visual
2 types of deviant stimuli
task-relevant/target stimulus
irrelevant/nontarget stimulus
what can a deviant stimulus for a visual oddball paradigm be varied
novel deviant (ex: a different picture for every deviant stimulus)
3 advantages to 3 stimulus oddball paradigm
deviants (nontarget and target) are equally frequent → equal signal to noise ratio
controls for attention, motor responses
can make a deviant ‘novel’
are different cognitive processes involved in discriminating target and nontarget deviants?
yes
P3a = nontarget deviant
P3b = target deviant
is attention involved in processing deviant stimuli
yes, the deviant can demand attentional focus.
are there special processes for novelty detection
novelty detection is not entirely special because it is observed as P3a, which responds to difficult target and standard discrimination. This is not limited to just novel stimulus.
which modality of MMN is the true MMN
auditory
mismatch negativity arises from either 2 things
sensory memory trace (compare new stimulus w old one in memory)
expectancy deviation (what u expect)
3 ERP components elicited by oddball paradigm
mismatch negativity (MMN)
N2 family
P300 family
what is MMN
generated in auditory cortex near N1 peak
second generator in frontal cortex (right lateralized) → may signal need for attention shift to deviant stimulus
product of comparision between stimulus and representation of a recent stimulus in the sensory memory
components of N2 family
N2b/anterior N2
N2c/posterior N2
which component of N2 family occurs first
N2b occurs after N2a, while N2c occurs later
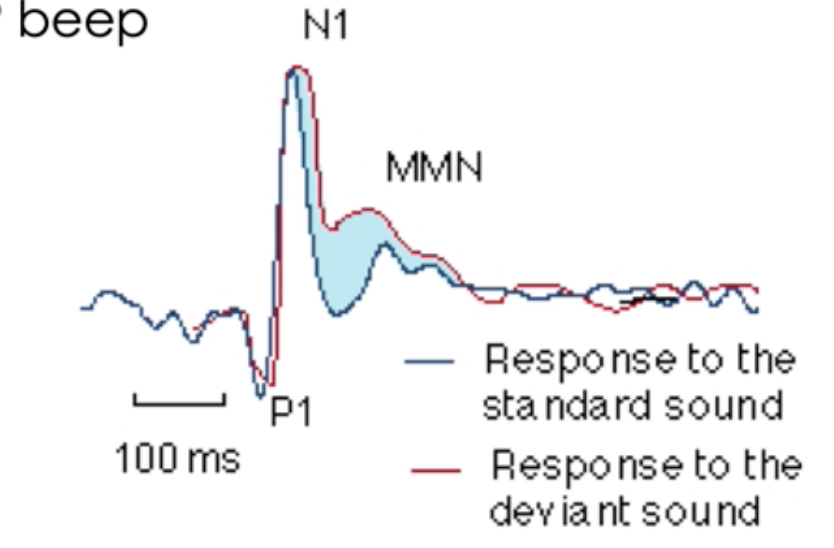
MMN elicited by
elicited by an infrequent and discriminable change (deviant) in a frequent auditory stimulus
discriminable change includes:
frequency/amplitude: beep, beep, boop
intensity (loudness): beep BEEP
when does MMN start
at peak of N1 component or area between the deviant minus standard difference wave
where is MMN found on the scalp? why?
MMN found on the fronto-central scalp, although its neural source is in the temporal lobe. This is due to volume conduction (electric fields picked up away from neural source)
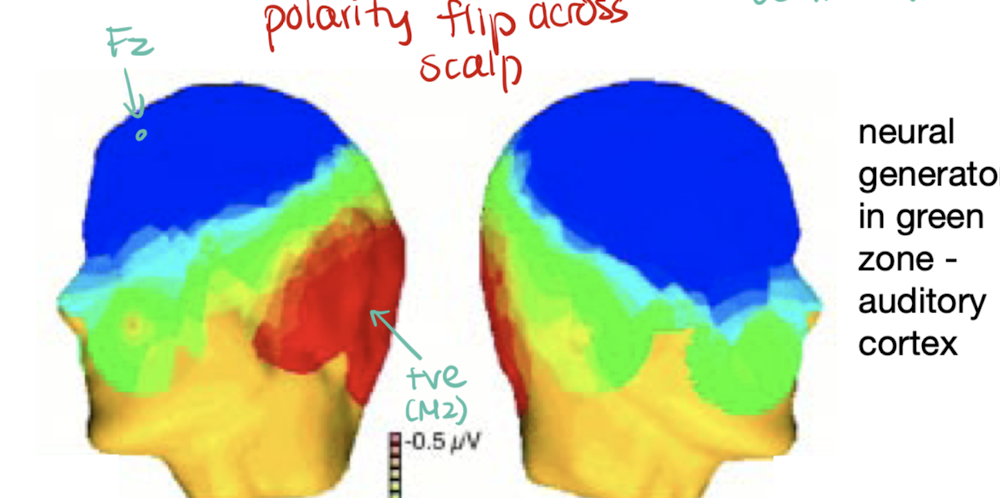
what does the blue and red in a MMN indicate
the blue is negatvitiy, which is one side of the dipole, theerefore the red is the other end of the dipole. This is called a polarity flip. The neural source is found in the auditory cortex which is in green, and the dipole is towards the fronto-central scalp, explaining why MMN is found there.
difference between fMRI vs EEG of MMN activity
fMRi - bilateral frontal generator, bilateral auditory generator
EEG - right lateralized frontal generator, bilateral auditory generator
is EEG or MEG better for determining neural source
MEG because less volume conduction, thus better able to pinpoint neural source
whats the sensory memory model
standard stimuli is placed into echoic memory (short term) and compared with what you hear. If it is a deviant, it generates a mismatch negativity
is there MMN to repeated tones?
yes but this is due to predictor error rather than mismatch
P3 family
a positivity around 300 ms elicited from a infrequent stimulus
P3 family components
P3b
P3a/novelty P3
No-go P3
P3b
positivty at 300ms elicited by the target stimulus
midline -parietal scalp distribution
occurs later than P3a
often prominent in Pz electrode