Guyton Unit IV Circulation
1/158
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
159 Terms
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure = 25 mm Hg
Capillary hydrostatic pressure = 25 mm Hg
Venous hydrostatic pressure = 5 mm Hg
Arterial pressure = 80 mm Hg
Interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure = −5 mm Hg
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure = 10 mm Hg
Capillary filtration rate = 150 ml/min
What is the capillary filtration coefficient (in ml/min/mm Hg) for this capillary wall?
A) 5
B) 10
C) 15
D) 20
E) 25
D) 20
Net filtration pressure = capillary
hydrostatic pressure − plasma colloid osmotic pressure
+ interstitial colloid osmotic pressure − interstitial
hydrostatic pressure.
A healthy 60-year-old woman with a 10-year history of hypertension stands up from a supine position. Which set of cardiovascular changes is most likely to occur in response to standing up from a supine position?
Sympathetic Nerve Activity; Cardiac Contractility; Heart Rate
Inc; Dec; Inc.
In an experimental study, administration of a drug decreases the diameter of arterioles in the muscle bed of an animal subject. Which set of physiological changes would be expected to occur in response to the decrease in diameter?
Vascular Conductance; Capillary Filtration; Blood Flow
E) Dec; Dec; Dec
A 60-year-old woman has experienced dizziness for the past 6 months when getting out of bed in the morning and when standing up. Her mean arterial pressure is 130/90 mm Hg while lying down and 95/60 while sitting. Which set of physiological changes would be expected in response to moving from a supine to an upright position?
Parasympathetic Nerve Activity; Plasma Renin Activity; Sympathetic Activity
G) Dec; Inc; Inc
A 35-year-old woman visits her family practitioner for an examination. She has a blood pressure of 160/75 mm Hg and a heart rate of 74 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has moderate aortic regurgitation. Which set of changes would be expected in this patient?
Pulse Pressure; Systolic Pressure; Stroke Volume
A) Inc. Inc. Inc
A healthy 27-year-old female medical student runs a 5K race. Which set of physiological changes is most likely to occur in this woman’s skeletal muscles during the race?
Arteriole Resistance; Tissue pH; Tissue CO2 Concentration
B) Inc; Dec; Inc
Cognitive stimuli such as reading, problem solving, and talking all result in significant increases in cerebral blood flow. Which set of changes in cerebral tissue concentrations is the most likely explanation for the increase in cerebral blood flow?
CO2; pH; Adenosine
B) Inc; Dec; Inc
Histamine is infused into the brachial artery. Which set of microcirculatory changes would be expected in the infused arm?
Capillary Water Permeability; Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure; Interstitial Hydrostatic Pressure
A) Inc; Inc; Inc
An increase in shear stress in a blood vessel results in which change?
A) Decreased endothelin production
B) Decreased cyclic guanosine monophosphate production
C) Increased nitric oxide release
D) Increased renin production
E) Decreased prostacyclin production
C) Increased nitric oxide release
A 65-year-old man with a 10-year history of essential hypertension is being treated with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Which set of changes would be expected to occur in response to the ACE inhibitor drug therapy?
Plasma Renin Concentration; Total Peripheral Resistance; Blood Pressure
D
Inc, dec, dec
The diameter of a precapillary arteriole is decreased in a muscle vascular bed. An increase in which of the following would be expected?
A) Capillary filtration rate
B) Vascular conductance
C) Capillary blood flow
D) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
E) Arteriolar resistance
E) Arteriolar resistance
A 55-year-old man with a history of normal health visits his physician for a checkup. The physical examination reveals that his blood pressure is 170/98 mm Hg. Further tests indicate that he has renovascular hypertension as a result of stenosis in the left kidney. Which set of findings would be expected in this man with renovascular hypertension?
Total Peripheral Resistance; Plasma Renin Activity; Plasma Aldosterone Concentration
Inc, Inc, Inc
Under control conditions, flow through a blood vessel is 100 ml/min with a pressure gradient of 50 mm Hg. What would be the approximate flow through the vessel after increasing the vessel diameter by 100%, assuming that the pressure gradient is maintained at 50 mm Hg?
A) 200 ml/min
B) 400 ml/min
C) 800 ml/min
D) 1600 ml/min
E) 700 ml/min
D) 1600
BF x 16= 100 × 16= 1600
Doubling the vessel diameter (while keeping pressure constant) increases blood flow sixteen-fold according to Poiseuille’s law.
A 24-year-old woman delivers a 6-lb, 8-oz baby girl. The newborn is diagnosed as having patent ductus arteriosus. Which set of changes would be expected in this baby?
Pulse Pressure; Stroke Volume; Systolic Pressure
Inc; Inc; inc
A 72-year-old man had surgery to remove an abdominal tumor.Pathohistological studies revealed that the tumor mass contained a large number of vessels. The most likely stimulus for the growth of vessels in a solid tumor is a decrease in which of the following?
A) Growth hormone
B) Plasma glucose concentration
C) Angiostatin growth factor
D) Vascular endothelial growth factor
E) Tissue oxygen concentration
D) Vascular endothelial growth factor
Which set of changes would be expected to cause the greatest increase in the net movement of sodium across a muscle capillary wall?
Wall Permeability to Sodium; Wall Surface Area; Concentration Difference Across Wall
A.
Inc, inc, inc
While participating in a cardiovascular physiology laboratory, a medical student isolates an animal’s carotid artery proximal to the carotid bifurcation and partially constricts the artery with a tie around the vessel. Which set of changes would be expected to occur in response to constriction of the carotid artery?
Heart Rate Parasympathetic Nerve Activity Total Peripheral Resistance
C. inc, dec, inc
A 35-year-old woman visits her family practice physician for an examination. She has a mean arterial blood pressure of 105 mm Hg and a heart rate of 74 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has moderate aortic valve stenosis. Which set of changes would be expected in this patient?
Pulse Pressure Stroke Volume Systolic Pressure
E
dec,dec, dec
A 60-year-old man visits his family practitioner for an annual examination. He has a mean blood pressure of 130 mm Hg and a heart rate of 78 beats/min. His plasma cholesterol level is in the upper 25th percentile, and he is diagnosed as having atherosclerosis. Which set of changes would be expected in this patient?
Pulse Pressure Arterial Compliance Systolic Pressure
B
inc, dec, inc
While participating in a cardiovascular physiology laboratory, a medical student isolates the carotid artery of an animal and partially constricts the artery with a tie around the vessel. Which set of changes would be expected to occur in response to constriction of the carotid artery?
Sympathetic Nerve Activity Renal Blood Flow Total Peripheral Resistance
B. inc, dec, inc
Which one of the following would tend to increase capillary filtration rate?
A) Decreased capillary hydrostatic pressure
B) Decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C) Decreased interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
D) Decreased capillary water permeability
E) Increased arteriolar resistance
B. Decreased plasma colloid osmotic pressure
A 72-year-old man had surgery to remove an abdominal tumor. Findings of pathohistological studies reveal that the tumor mass contains a large number of blood vessels. The most likely stimulus for the growth of vessels in a solid tumor is an increase in which of the following?
A) Growth hormone
B) Plasma glucose concentration
C) Angiostatin growth factor
D) Tissue oxygen concentration
E) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
E) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)
The diameter of a precapillary arteriole is decreased in a muscle vascular bed. Which change in the microcirculation would be expected?
A) Decreased capillary filtration rate
B) Increased interstitial volume
C) Increased lymph flow
D) Increased capillary hydrostatic pressure
E) Decreased arteriolar resistance
A) Decreased capillary filtration rate
A 50-year-old man has a 3-year history of hypertension. He reports fatigue and occasional muscle cramps. There is no family history of hypertension. The patient has not had any other significant medical problems in the past. Examination reveals a blood pressure of 168/104 mm Hg. Additional laboratory tests indicate that the patient has primary hyperaldosteronism. Which set of findings would be expected in this man with primary hyperaldosteronism hypertension?
Extracellular Fluid Volume; Plasma Renin Activity Plasma Potassium Concentration
C
Inc; Dec; Dec
A decrease in which of the following would tend to increase lymph flow?
A) Hydraulic conductivity of the capillary wall
B) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
D) Vascular conductance
E) B and D
E.
A decrease in plasma colloid osmotic pressure and vascular conductance would tend to increase lymph flow, as lower osmotic pressure would reduce fluid reabsorption into the capillaries, and decreased vascular conductance would enhance filtration.
In control conditions, flow through a blood vessel is 100 ml/min under a pressure gradient of 50 mm Hg. What would be the approximate flow through the vessel after increasing the vessel diameter to four times normal, assuming that the pressure gradient was maintained at 50 mm Hg?
A) 300 ml/min
B) 1600 ml/min
C) 1000 ml/min
D) 16,000 ml/min
E) 25,600 ml/min
E ) 25,600 ml/min
If the vessel diameter increases to four times normal, flow (at the same pressure gradient) increases by 256-fold, demonstrating the extreme sensitivity of flow to radius changes in laminar conditions per Poiseuille’s law.
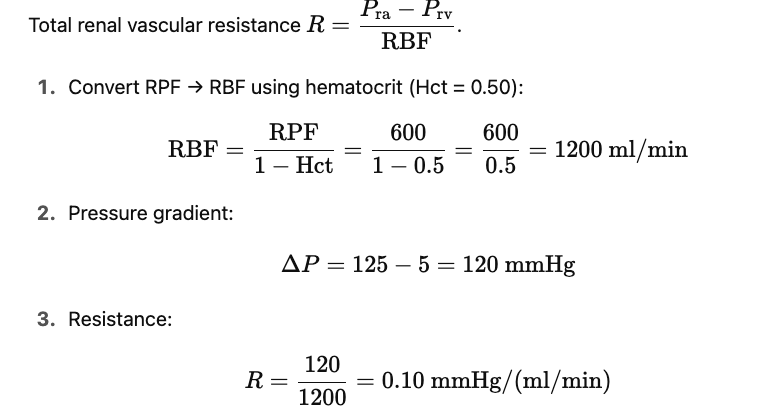
A 50-year-old woman has a renal plasma flow of 600 ml/min and hematocrit of 50. Her arterial pressure is 125 mm Hg and renal venous pressure is 5 mm Hg. What is the total renal vascular resistance (in mm Hg/ml/min) in this woman?
A) 0.05
B) 0.10
C) 0.50
D) 1.00
E) 1.50
B) 0.10
(Renal art Pressure -renal venous pressure) /RBF
convert RPF to RBF with hct. 600/ (1-0.5)= 1200
Find pressure gradient- 125-5=120
R= 120/1200 = 0.10
An increase in which of the following would be expected to decrease blood flow in a vessel?
A) Pressure gradient across the vessel
B) Radius of the vessel
C) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
D) Viscosity of the blood
E) Plasma sodium concentration
D) Viscosity of the blood
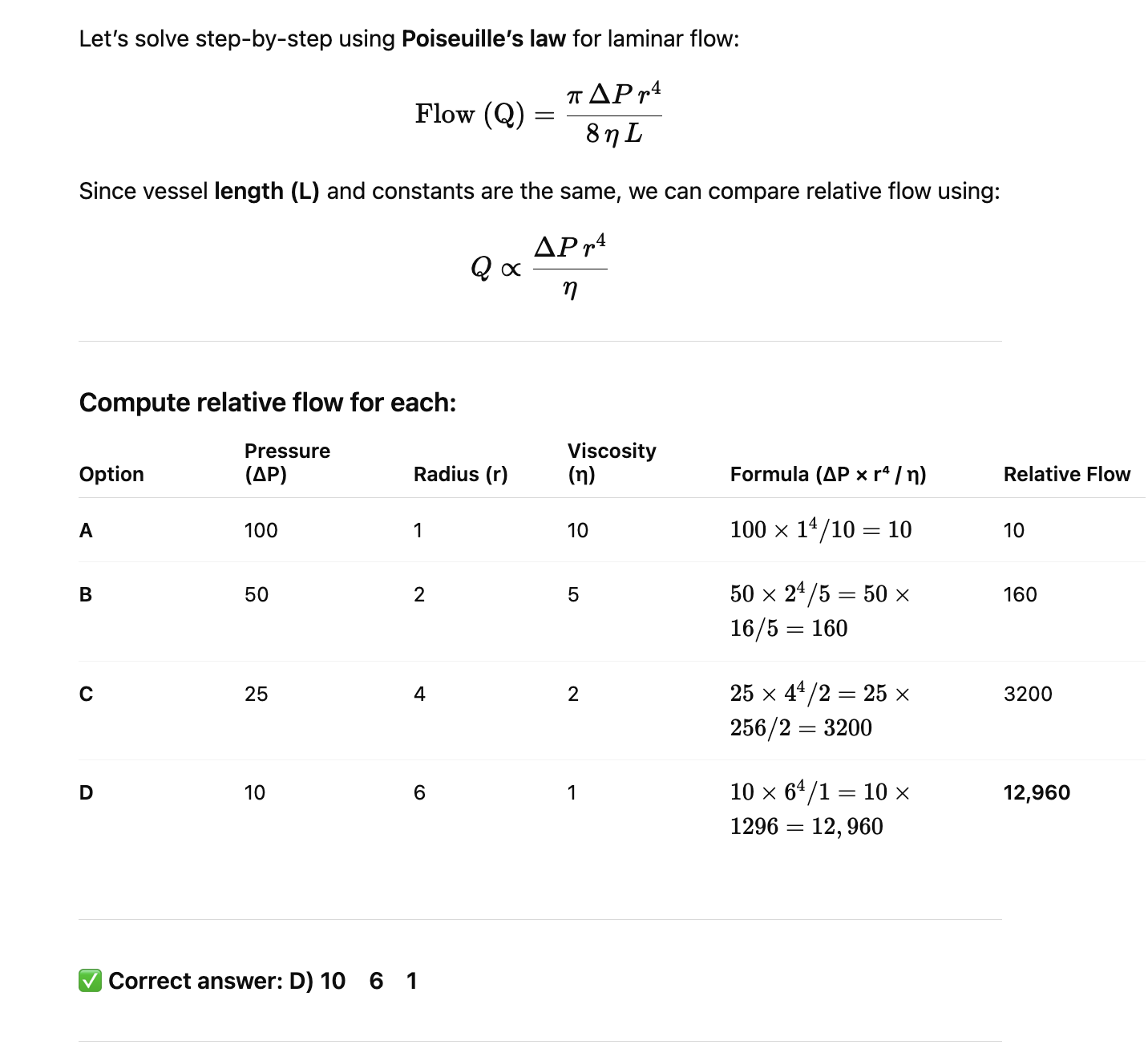
Assuming that vessels are the same length, which one has the greatest flow?
Pressure Gradient; Radius; Viscosity
A) 100 1 10
B) 50 2 5
C) 25 4 2
D) 10 6 1
D) 10 6 1
A 22-year-old man enters the hospital emergency department after severing a major artery in a motorcycle accident. It is estimated that he has lost approximately 700 ml of blood. His blood pressure is 90/55 mm Hg. Which set of changes would be expected in response to hemorrhage in this man?
Heart Rate Parasympathetic Nerve Activity Plasma Renin Activity
A
Increase Decrease Increase
A healthy 28-year-old woman stands up from a supine position. Moving from a supine to a standing position results in a transient decrease in arterial pressure that is detected by arterial baroreceptors located in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses. Which set of cardiovascular changes is most likely to occur in response to activation of the baroreceptors?
Mean Circulatory Filling Pressure; Strength of Cardiac Contraction; Sympathetic Nerve Activity
A
Increase; Increase; Increase
An ACE inhibitor is administered to a 65-year-old man with a 20- year history of hypertension. The drug lowered his arterial pressure and increased his plasma levels of renin. Which mechanism would best explain the decrease in arterial pressure?
A) Inhibition of angiotensin I
B) Decreased conversion of angiotensinogen to angiotensin I
C) Decreased plasma levels of bradykinin
D) Decreased plasma levels of prostacyclin
E) Decreased formation of angiotensin II
E) Decreased formation of angiotensin II
A 25-year-old man enters the hospital emergency department after severing a major artery during a farm accident. It is estimated that he patient has lost approximately 800 ml of blood. His mean blood pressure is 65 mm Hg, and his heart rate is elevated as a result of activation of the chemoreceptor reflex. Which set of changes in plasma concentration would be expected to cause the greatest activation of the chemoreceptor reflex?
Oxygen; CO2; Hydrogen
G
Dec; Inc; Inc
Under normal physiological conditions, blood flow to the skeletal muscles is determined mainly by which of the following?
A) Sympathetic nerves
B) Angiotensin II
C) Vasopressin
D) Local metabolic factors
E) Capillary osmotic pressure
D) Local metabolic factors
A healthy 22-year-old female medical student has an exercise stress test at a local health club. An increase in which of the following is most likely to occur in this woman’s skeletal muscles during exercise?
A) Vascular conductance
B) Blood flow
C) Carbon dioxide concentration
D) Arteriolar diameter
E) All the above
E) All the above
Which of the following segments of the circulatory system has the lowest velocity of blood flow?
A) Aorta
B) Arteries
C) Capillaries
D) Veins
C) Capillaries
Listed below are the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures within a microcirculatory bed.
Plasma colloid osmotic pressure (πp)= 25 mm Hg
Capillary hydrostatic pressure (Pc)= 25 mm Hg
Venous hydrostatic pressure = 5 mm Hg
Arterial pressure = 80 mm Hg
Interstitial hydrostatic pressure (Pif) = −5 mm Hg
Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure (πif)= 5 mm Hg
Filtration coefficient (Kf)= 15 ml/min/mm Hg
What is the filtration rate (ml/min) of the capillary wall?
A) 100
B) 150
C) 200
D) 250
E) 300
B) 150
Net Filtration Pressure= Pc-Pif- πp+πif
(25- (-5) -25 +5= 10
filtration rate= kf x NFP
15 × 10= 150
Which blood vessel has the highest vascular resistance?
Blood Flow (ml/min) Pressure Gradient (mm Hg)
A) 1000 100
B) 1200 60
C) 1400 20
D) 1600 80
E) 1800 40
A) 1000 100
100/1000= 0.10
60/1200-0/05
20/1400= 0.014
80/1600= 0/05
40/1800=0.022
A 2-fold increase in which of the following would result in the greatest increase in the transport of oxygen across the capillary wall?
A) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
B) Intercellular clefts in the capillary wall
C) Oxygen concentration gradient
D) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
E) Capillary wall hydraulic permeability
C) Oxygen concentration gradient
A balloon catheter is advanced from the superior vena cava into the heart and inflated to increase atrial pressure by 5 mm Hg. Which of the following would be expected to occur in response to the elevated atrial pressure?
A) Decrease atrial natriuretic peptide
B) Increased angiotensin II
C) Increased aldosterone
D) Decreased renal sympathetic nerve activity
A) Decrease atrial natriuretic peptide
Which of the following vessels has the greatest total cross- sectional area in the circulatory system?
A) Aorta
B) Small arteries
C) Capillaries
D) Venules
E) Vena cava
C) Capillaries
An increase in atrial pressure results in which of the following?
A) Increased plasma atrial natriuretic peptide
B) Increase in plasma angiotensin II concentration
C) Decrease in plasma aldosterone concentration
D) Decrease in sodium excretion
E) A and C
E) A and C
Autoregulation of tissue blood flow in response to an increase in arterial pressure occurs as a result of which of the following?
A) Decrease in vascular resistance
B) Initial decrease in vascular wall tension
C) Excess delivery of nutrients such as oxygen to the tissues
D) Decrease in tissue metabolism
C) Excess delivery of nutrients such as oxygen to the tissues
Which component of the circulatory system contains the largest percentage of the total blood volume?
A) Arteries
B) Capillaries
C) Veins
D) Pulmonary circulation
E) Heart
C) Veins
Which set of changes would be expected to occur 2 weeks after a 50% reduction in renal artery pressure?
Plasma Renin; Plasma Aldosterone; GFR
Inc, Inc, Dec,
Plasma renin concentration will increase, leading to an elevation in plasma aldosterone concentration and a decrease in glomerular filtration rate.
An increase in which of the following tends to decrease capillary filtration rate?
A) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
B) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C) Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
D) Venous hydrostatic pressure
E) Arteriolar diameter
B) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
A decrease in which of the following would be expected to occur in a person 2 weeks after an increase in sodium intake?
A) Angiotensin II
B) Sodium Excretion
C) Aldosterone
D) Atrial natriuretic peptide
E) A and C
D) ANP
Which of the following would tend to increase lymph flow?
A) Increase capillary hydrostatic pressure
B) Increased plasma colloid osmotic pressure
C) Increased interstitial volume
D) Decreased arteriolar diameter
E) A and C
C) Increased interstitial volume
An increase in the production of which of the following would most likely result in chronic hypertension?
A) Aldosterone
B) Prostacyclin
C) Angiotensin II
D) Nitric oxide
E) A and C
D) Nitric oxide
Which of the following capillaries has the highest capillary permeability to plasma albumin?
A) Glomerular
B) Liver
C) Muscle
D) Intestinal
E) Brain
E. Brain
Which of the following would be expected to occur during a Cushing reaction caused by brain ischemia?
A) Increase in parasympathetic activity
B) Decrease in arterial pressure
C) Decrease in heart rate
D) Increase in sympathetic activity
D) Increase in sympathetic activity
Which of the following tends to increase the net movement of glucose across a capillary wall?
A) Increase in plasma sodium concentration
B) Increase in the concentration difference of glucose across the wall
C) Decrease in wall permeability to glucose
D) Decrease in wall surface area without an increase in the number of pores
E) Decrease in plasma potassium concentration
B) Increase in the concentration difference of glucose across the wall increases the net movement of glucose through facilitated diffusion and concentration gradients.
A 65-year-old man has congestive heart failure. He has a cardiac output of 4 l/min, arterial pressure of 115/85 mm Hg, and heart rate of 90 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has a right atrial pressure of 10 mm Hg. An increase in which of the following would be expected in this patient?
A) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
B) Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
C) Arterial pressure
D) Cardiac output
E) Vena cava hydrostatic pressure
E) Vena cava hydrostatic pressure
Which set of changes would be expected to occur in response to a direct increase in renal arterial pressure in kidneys without an intact tubuloglomerular feedback system?
Glomerular Filtration; Sodium Excretion; Water Excretion
Increase Increase Increase
Which part of the circulation has the highest compliance?
A) Capillaries
B) Large arteries
C) Veins
D) Aorta
E) Small arteries
C) Veins have the highest compliance due to their ability to stretch and accommodate varying volumes of blood.
A decrease in which of the following tends to increase pulse pressure?
A) Systolic pressure
B) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
C) Arterial compliance
D) Stroke volume
E) A and D
C) Arterial compliance
Which set of physiological changes would be expected to occur in a person who stands up from a supine position?
Venous Hydrostatic Pressure in Legs; HR; Renal Blood Flow
Inc; Inc; Dec
Which one of the following compensatory physiological changes would be expected to occur in a person who stands up from a supine position?
A) Increased parasympathetic nerve activity
B) Increased sympathetic nerve activity
C) Decreased heart rate
D) Decreased heart contractiltiy
B) Increased sympathetic nerve activity
Blood flow to a tissue remains relatively constant despite a reduction in arterial pressure (autoregulation). Which of the following would be expected to occur in response to the increases in arterial pressure?
A) Increased conductance
B) Increased tissue oxygen concentration
C) Decreased vascular resistance
D) Increased arteriolar diameter
D) Increased arteriolar diameter
Which of the following would have the slowest rate of net movement across the capillary wall?
A) Sodium
B) Albumin
C) Glucose
D) Oxygen
B) Albumin
An increase in which of the following tends to increase capillary filtration rate?
A) Capillary wall hydraulic conductivity
B) Arteriolar resistance
C) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
D) Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
E) Plasma sodium concentration
A) Capillary wall hydraulic conductivity
The tendency for turbulent flow is greatest in which of the following?
A) Arterioles
B) Capillaries
C) Small arterioles
D) Aorta
D.) Aorta
A 60-year-old man has a mean arterial blood pressure of 130 mmHg, a heart rate of 78 beats/min, a right atrial pressure of 0 mm Hg, and a cardiac output of 3.5 L/min. He also has a pulse pressure of 35 mm Hg and a hematocrit of 40. What is the approximate total peripheral vascular resistance in this man?
A) 17 mm Hg/l/min
B) 1.3 mm Hg/l/min
C) 13 mm Hg/l/min
D) 27 mm Hg/l/min
E) 37 mm Hg/l/min
E) 37 mmHg/L/min
Total peripheral vascular resistance = arterial pressure
− right atrial pressure ÷ cardiac output. In this example,
total peripheral vascular resistance = 130 mm
Hg ÷ 3.5 L/min, or approximately 37 mm Hg/L/min.
Which pressure is normally negative in a muscle capillary bed in the lower extremities?
A) Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
B) Capillary hydrostatic pressure
C) Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
D) Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
E) Venous hydrostatic pressure
C) Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
What would tend to increase a person’s pulse pressure?
A) Decreased stroke volume
B) Increased arterial compliance
C) Hemorrhage
D) Patent ductus
E) Decreased venous return
D) Patent ductus
Movement of solutes such as Na+ across the capillary walls occurs primarily by which process?
A) Filtration
B) Active transport
C) Vesicular transport
D) Diffusion
D) Diffusion
What would decrease venous hydrostatic pressure in the legs?
A) Decrease in right atrial pressure
B) Pregnancy
C) Decreased movement of leg muscles
D) Abdominal compression of vena cava by a solid tumor in the abdomen
E) B and D
C) Decreased movement of leg muscles
Movement of the leg muscles causes blood to flow toward the vena cava, which reduces venous hydrostatic pressure. An increase in right atrial pressure would decrease venous return and increase venous hydrostatic pressure. Pregnancy and the presence of ascitic fluid in the abdomen would tend to compress the vena cava and increase venous hydrostatic pressure in the legs.
A nitric oxide donor is infused into the brachial artery of a 22- year-old man. Which set of microcirculatory changes would be expected in the infused arm?
Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure Interstitial Hydrostatic Pressure Lymph Flow
Inc, inc, inc
What often occurs in decompensated heart failure?
A) Increased renal loss of sodium and water
B) Decreased mean systemic filling pressure
C) Increased norepinephrine in cardiac sympathetic nerves
D) Orthopnea
E) Weight loss
D) Orthopnea
Which condition often occurs in progressive hemorrhagic shock?
A) Vasomotor center failure
B) Increased urine output
C) Tissue alkalosis
D) Decreased capillary permeability
E) Increased mean systemic filling pressure
A) Vasomotor center failure
A 50-year-old woman received an overdose of furosemide, and her arterial pressure decreased to 70/40. Her heart rate is 120, and her respiratory rate is 30/min. What therapy would you recommend?
A) Whole blood infusion
B) Plasma infusion
C) Infusion of a balanced electrolyte solution
D) Infusion of a sympathomimetic drug
E) Administration of a glucocorticoid
C) Infusion of a balanced electrolyte solution
A 30-year-old woman comes to a local emergency department with severe vomiting. She has pale skin, tachycardia, an arterial pressure of 70/45, and trouble walking. What therapy do you recommend to prevent shock?
A) Infusion of packed red blood cells
B) Administration of an antihistamine
C) Infusion of a balanced electrolyte solution
D) Infusion of a sympathomimetic drug
E) Administration of a glucocorticoid
C) Infusion of a balanced electrolyte solution
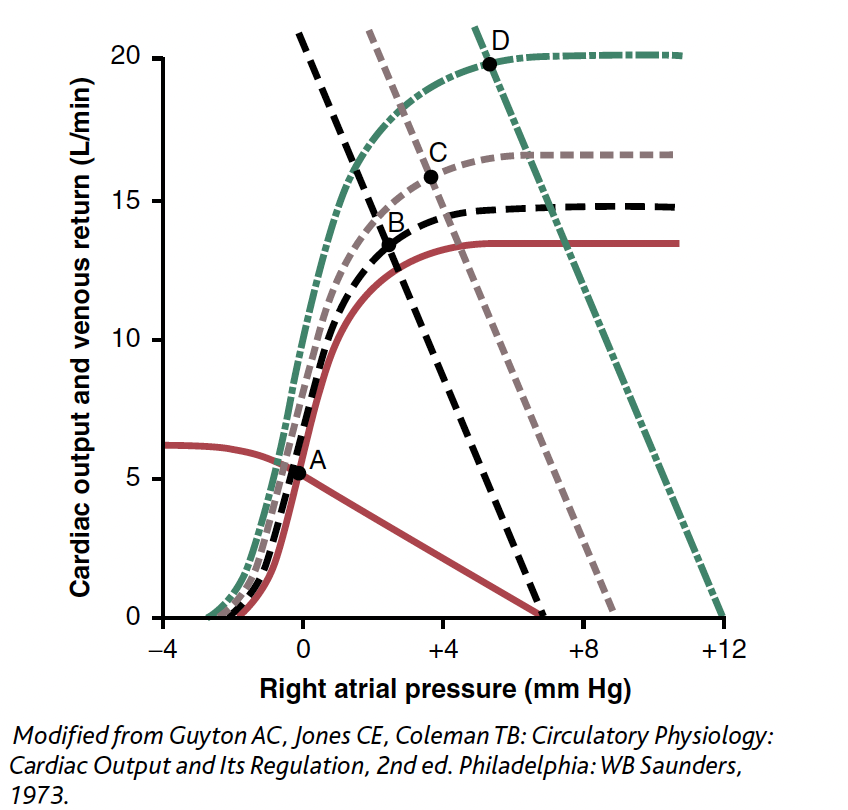
In the above figure, for the cardiac output and venous return
curves defined by the solid red lines (with the equilibrium at A), which of the following options is true?
A) Mean systemic filling pressure is 12 mm Hg
B) Right atrial pressure is 2 mm Hg
C) Resistance to venous return is 1.4 mm Hg/l/min
D) Pulmonary arterial flow is approximately 7 l/min
E) Resistance to venous return is 0.71 mm Hg/l/min
C) Resistance to venous return is 1.4 mm Hg/l/min
A 30-year-old man is resting, and his sympathetic output increases to maximal values. Which set of changes would be expected in response to this increased sympathetic output?
Resistance to Venous Return; Mean Systemic Filling Pressure; Venous Return
A
inc, inc, inc
If a patient has an oxygen consumption of 240 ml/min, a pulmonary vein oxygen concentration of 180 ml/l of blood, and a pulmonary artery oxygen concentration of 160 ml/l of blood units, what is the cardiac output in l/min?
A) 8
B) 10
C) 12
D) 16
E) 20
C) 12
O2 consumption/AV O2 difference
240/(180-160)
240/20= 12
What normally causes the cardiac output curve to shift to the right along the right atrial pressure axis?
A) Changing intrapleural pressure to −1 mm Hg
B) Increasing mean systemic filling pressure
C) Taking a patient off a mechanical ventilator and allowing normal respiration
D) Decreasing intrapleural pressure to −7 mm Hg
E) Breathing against a negative pressure
A) Changing intrapleural pressure to −1 mm Hg
What normally causes the cardiac output curve to shift to the left along the right atrial pressure axis?
A) Surgically opening the chest
B) Severe cardiac tamponade
C) Breathing against a negative pressure
D) Playing a trumpet
E) Positive-pressure breathing
C) Breathing against a negative pressure
Several factors can cause the cardiac output to shift
to the right or to the left. Among those are surgically
opening the chest, which makes the cardiac output
curve shift 4 mm Hg to the right, and severe cardiac tamponade, which increases the pressure inside the
pericardium, thus tending to collapse the heart, particularly
the atria. Playing a trumpet or positive pressure
breathing tremendously increases the intrapleural pressure,
thus collapsing the atria and shifting the cardiac
output curve to the right. Breathing against a negative
pressure will shift the cardiac output curve to the left.
What will elevate the plateau of the cardiac output curve?
A) Surgically opening the thoracic cage
B) Connecting a patient to a mechanical ventilator
C) Cardiac tamponade
D) Increasing parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
E) Increasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart
E) Increasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart
What is normally associated with an increased cardiac output?
A) Increased parasympathetic stimulation
B) Atrioventricular (A-V) fistula
C) Decreased blood volume
D) Polycythemia
E) Severe aortic regurgitation
B) Atrioventricular (A-V) fistula
Which condition would be expected to decrease mean systemic filling pressure?
A) Norepinephrine administration
B) Increased blood volume
C) Increased sympathetic stimulation
D) Increased venous compliance
E) Skeletal muscle contraction
D) Increased venous compliance
A 35-year-old man undergoes several cardiac test during exercise.
The following measurements are made:
Right atrial pressure = +2 mm Hg
Left atrial pressure = +7 mm Hg
Left ventricular end diastolic pressure = +10 mm Hg
Mean systemic filling pressure = +12 mm Hg
Cardiac output = 10 l/min
What is the resistance to venous return (mm Hg/l/min) in this individual?
A) 0.1
B) 0 .5
C) 1.0
D) 1.4
E) 2.0
C) 1.0
Resistance to venous return= mean systemic filling pressure- RAP/ venous return
(12-2) /10= 1
In which condition would you expect a decreased resistance to venous return?
A) Anemia
B) Increased venous resistance
C) Increased arteriolar resistance
D) Increased sympathetic output
E) Obstruction of veins
A) Anemia
Which of the following would decrease cardiac output?
A) Increased stroke volume
B) Increased heart rate
C) Increased mean systemic filling pressure
D) Increased resistance to venous return
E) Increased venous return
D) Increased resistance to venous return
In which condition would you normally expect to find a decreased cardiac output?
A) Hyperthyroidism
B) Beriberi
C) A-V fistula
D) Increased muscle mass
E) Hypothyroidism
E) Hypothyroidism
Which of the following sets of changes would tend to increase coronary blood flow?
Coronary Arteriole
Resistance
Cardiac Adenosine
Concentration
Coronary Vascular
Conductance
Cardiac
Workload
B
What will usually increase the plateau level of the cardiac output curve?
A) Myocarditis
B) Severe cardiac tamponade
C) Decreased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
D) Myocardial infarction
E) Mitral stenosis
C) Decreased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
If a person has been exercising for 1 hour, which organ will have the smallest decrease in blood flow?
A) Brain
B) Intestines
C) Kidneys
D) Nonexercising skeletal muscle
E) Pancreas
A) Brain
A 35-year-old man has been diagnosed with a vitamin B1 deficiency. Oxygen consumption in this man is 400 ml/min. In addition, pulmonary vein oxygen concentration is 200 ml/l of blood, and pulmonary artery oxygen concentration is 150 ml/l of blood. What is the cardiac output (l/min) in this man?
A) 4.0
B) 5.0
C) 6.0
D) 7.0
E) 8.0
E. 8.0
CO=O2 consumption/ (AV O2 difference)
200-150=50
400/50= 8
Which vasoactive agent is usually the most important controller of coronary blood flow?
A) Adenosine
B) Bradykinin
C) Prostaglandins
D) Carbon dioxide
E) Potassium ions
A) Adenosine
What will elevate the plateau of the cardiac output curve?
A) Surgically opening the thoracic cage
B) Connecting a patient to a mechanical ventilator
C) Cardiac tamponade
D) Increasing parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
E) Increasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart
E) Increasing sympathetic stimulation of the heart
The most likely cause of cardiac pain in acute ischemic coronary disease is an increase in the extracellular concentration of the following:
A) Adenosine
B) Potassium
C) Nitric oxide
D) ATP
E) Lactic acid
A) Adenosine
Which condition normally causes arteriolar vasodilation during exercise?
A) Decreased plasma potassium ion concentration
B) Increased histamine release
C) Decreased plasma nitric oxide concentration
D) Increased plasma adenosine concentration
E) Decreased plasma osmolality
D) Increased plasma adenosine concentration
At the onset of exercise, the mass sympathetic nervous system strongly discharges. What would you expect to occur?
A) Increased sympathetic impulses to the heart
B) Decreased coronary blood flow
C) Decreased cerebral blood flow
D) Reverse stress relaxation
E) Venous dilation
A) Increased sympathetic impulses to the heart
A sudden occlusion that occurs in larger coronary arteries causes an increase in the following:
A) Dilation of small anastomoses in cardiac tissue
B) Increase collateral blood flow
C) Increase production of adenosine
D) All of the above
E) Only A and C
D) All of the above
A 70-year-old man with a weight of 100 kg (220 lb) and a blood pressure of 160/90 mm Hg has been told by his doctor that he has angina caused by myocardial ischemia. Which treatment would be beneficial to this man?
A) Increased dietary calcium
B) Isometric exercise
C) A beta-1 receptor stimulator
D) Angiotensin II infusion
E) Nitroglycerin
E) Nitroglycerin
Which event normally occurs during exercise?
A) Arteriolar dilation in exercising muscle
B) Decreased sympathetic output
C) Venoconstriction
D) Decreased release of norepinephrine by the adrenals
E) A and C
C) Venoconstriction
Which of the following is (are) responsible for the increase in stroke volume in response to increased venous return?
A) Stretch of right atrium initiates a nervous reflex called the Bainbridge reflex
B) Stretch of the sinus node in the wall of the right atrium has a direct effect on the rhythmicity of the node to increase the HR
C) Frank-Starling law of the heart
D) All of the above
E) A and C
b?
A 60-year-old man sustained an ischemia-induced myocardial infarction and died from ventricular fibrillation. In this patient, what factor was most likely to increase the tendency of the heart to fibrillate after the infarction?
A) Low potassium concentration in the heart extracellular fluid
B) A decrease in ventricular diameter
C) Increased sympathetic stimulation of the heart
D) Low adenosine concentration
E) Decreased parasympathetic stimulation of the heart
C) Increased sympathetic stimulation of the heart
A 60-year-old man has been told by his doctor that he has angina caused by myocardial ischemia. Which treatment would be beneficial to this man?
A) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition
B) Isometric exercise
C) Chelation therapy such as ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)
D) Beta receptor stimulation
E) Increased dietary calcium
A) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition
What is one of the major causes of death after myocardial infarction?
A) Increased cardiac output
B) A decrease in pulmonary interstitial volume
C) Fibrillation of the heart
D) Increased cardiac contractility
C) Fibrillation of the heart