Art and History of Madrid Midterm I
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
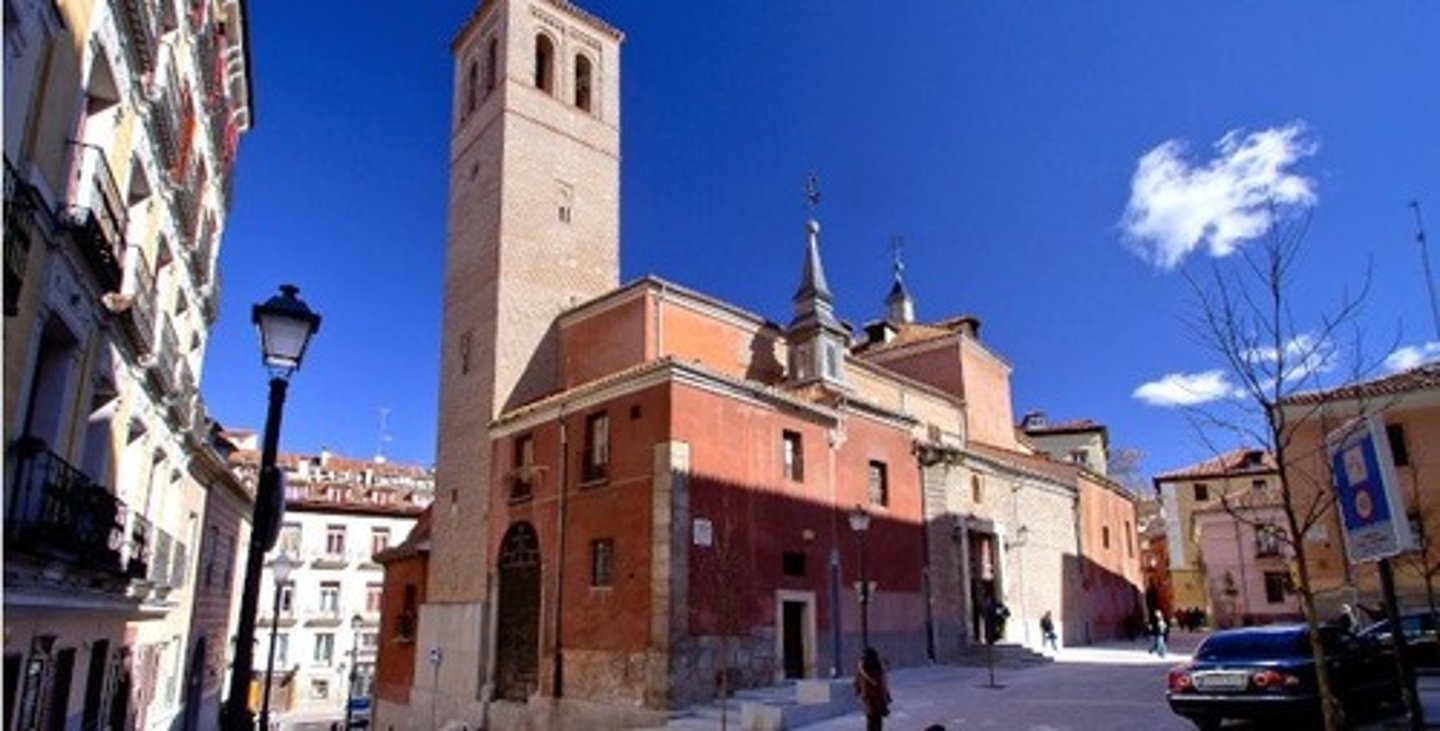
Church of San Pedro el viejo (St. Peter the elder)
Mudéar art, 14th century
One of the oldest churches in Madrid
Built over a mosque
Recycled bell tower once Christians took over
Renovated during 17th and 19th centuries
Bell tower resembles a minaret

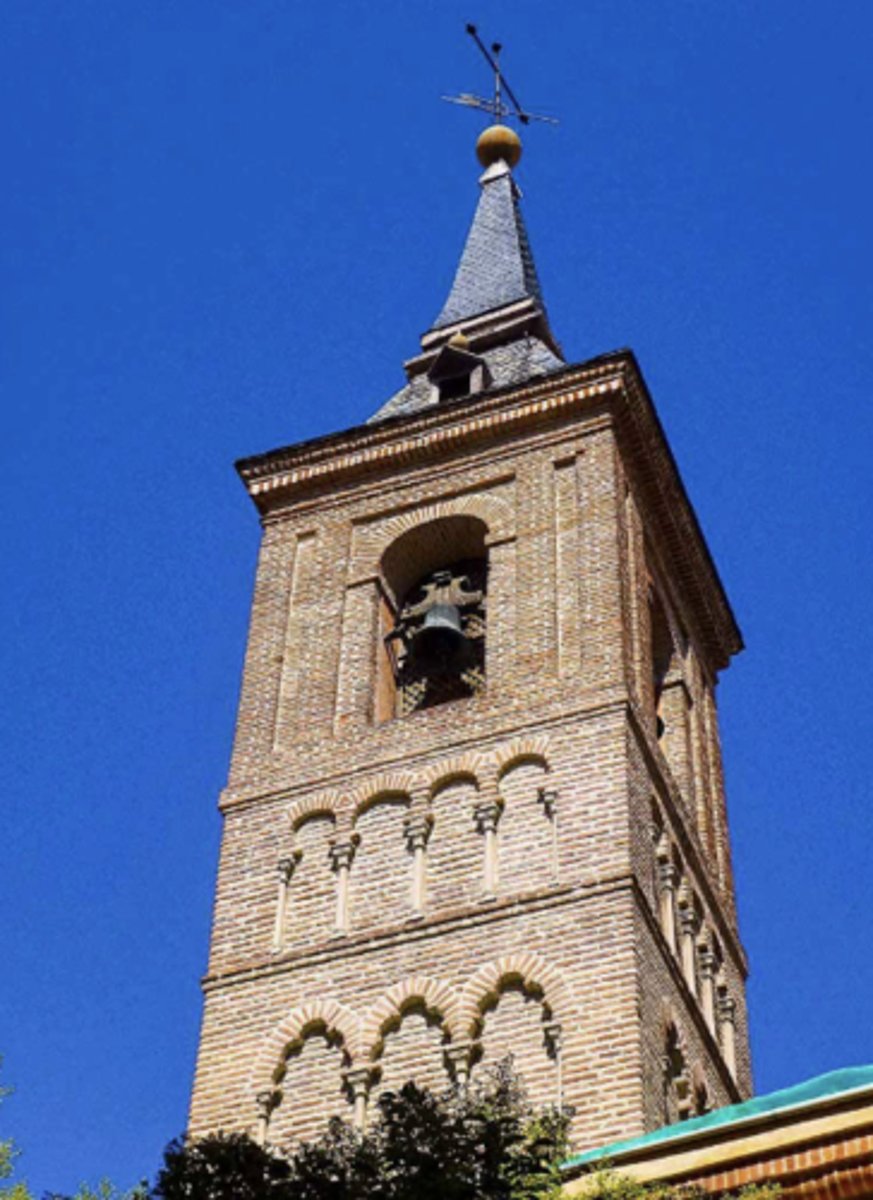
Tower of St. Nicholas.
Mudéar art, 12th century.
Oldest church in Madrid.
Rebuilt between 15th and 17th centuries.
Arches are decorative.
Located in south of Spain, Corrada.

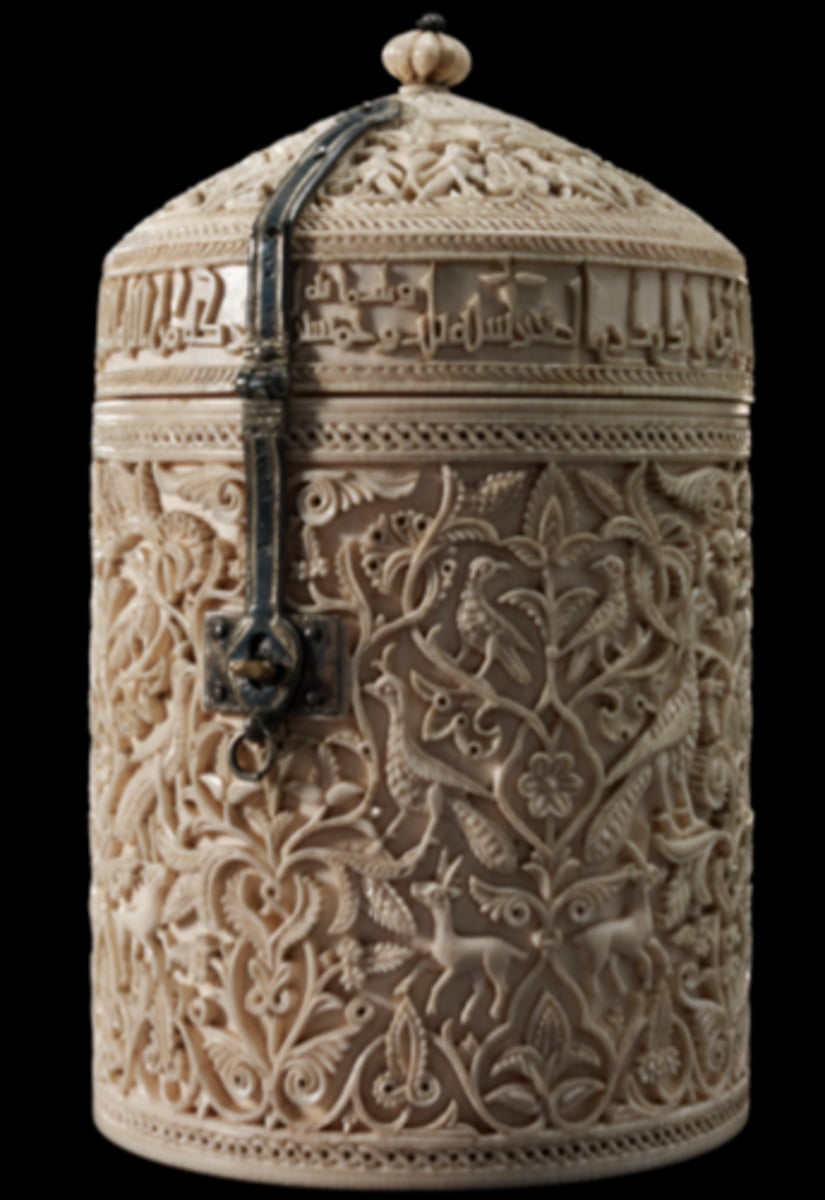
Pyxis of Zamora.
10th century, National Archeological Museum.
Ivory carving casket.
Commissioned by Al-Haken II for his concubine Subh.
Workshop of Madinat at Azahala.
Kufic inscription.
"Arabesque" decoration.
Ivory: elephant tusk.
Used for makeup, perfume, jewels.
Delicate material, hard to work with.
Islamic culture: gift giving is almost an art.
Madinat (city) al Azahara (of the orange tree place).
Peacocks: to Christians symbolism of God, sacrifice.

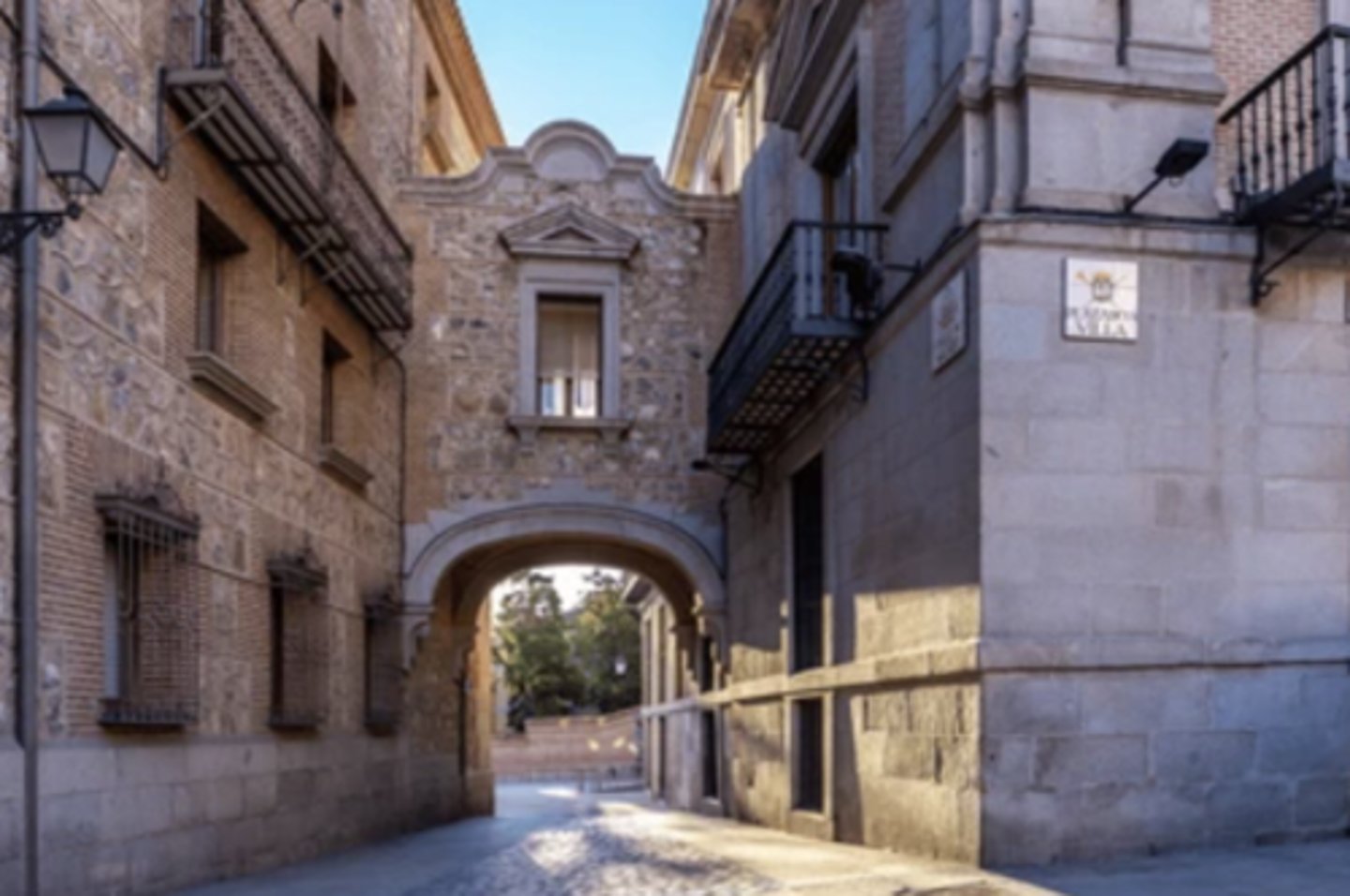
Mudéjar arch in Plaza de la Villa.
15th century.
Horseshoe arch, pointed, brick.
19th century revival.

Saint Dominic of Silos enthroned by a Bishop.
1474-1479.
Artist Bartolomé Bermejo.
Prado Museum.
Central panel of altar.
Surrounded by seven virtues.
Background: very thin gold.
Saint Peter on the left, Saint Catherine on the right.
Presence of gold is a connection to gothic art.
Clothing and realistic faces are Flemish characteristics.

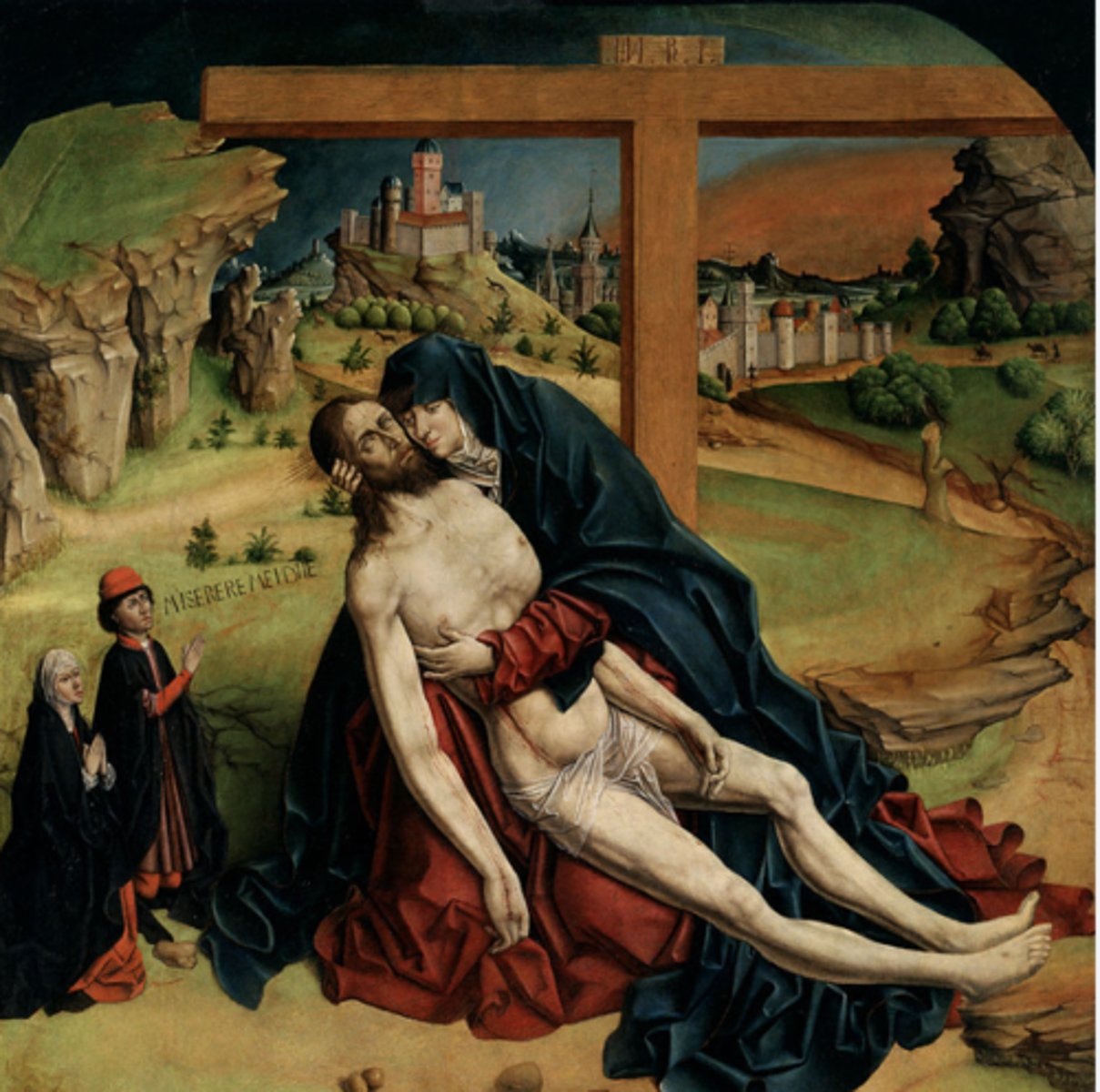
Pietá (Piedad).
Artist Fernando Gallego.
1465-1470.
Mixed method on pine panel.
118 x 111 cm.
San Jerónimo el Real.
16th century.
Royal chapel.
Connected to royalty since its founding site for investiture (formal ceremony) of the Kings.

The Garden of Earthly Delights.
Artist Bosch.
Triptych (a picture or relief carving on three panels, typically hinged together vertically and used as an altarpiece).
1490-1500.
Grisallie and oil on oak panel.
2.2 m x 3.89 m.
"For he spoke and it was done and For he commanded, and they were created" (Psalms 33:9 and 148:5).

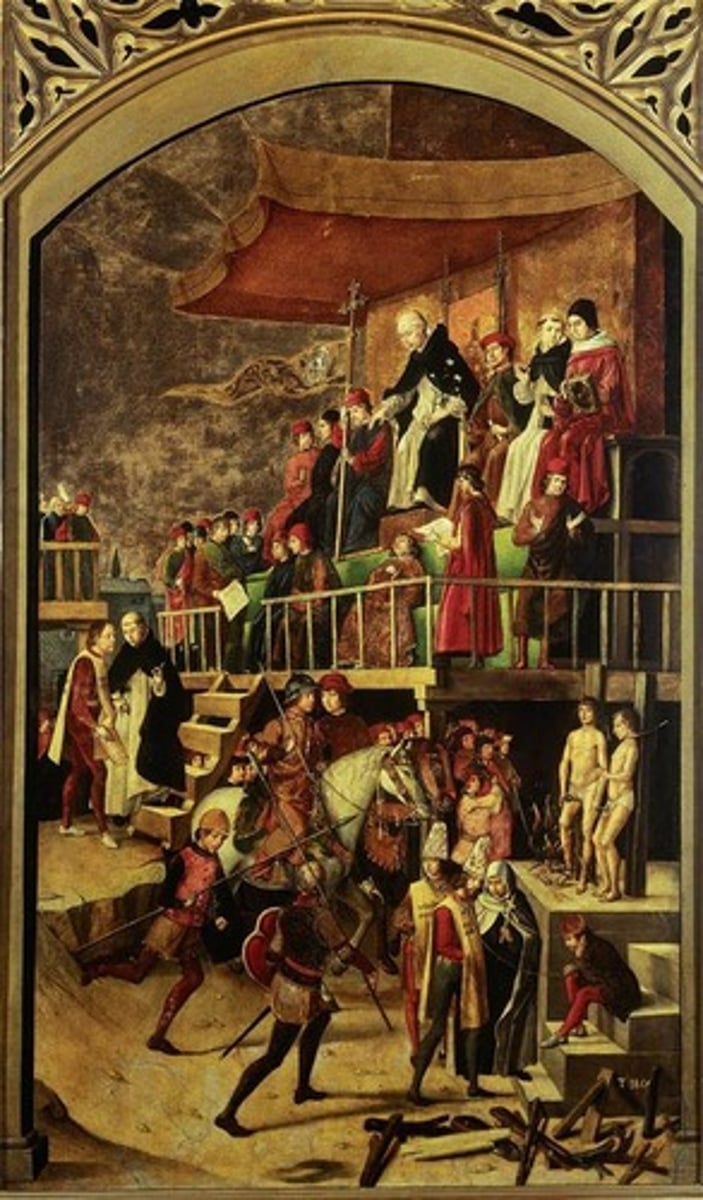
Saint Dominic Presiding over an Auto-da-fe
Artist Pedro Berruguete.
1495.
"Action", narrative.
Linear perspective.
Anatomy, human body, movement (man running, sleeping).

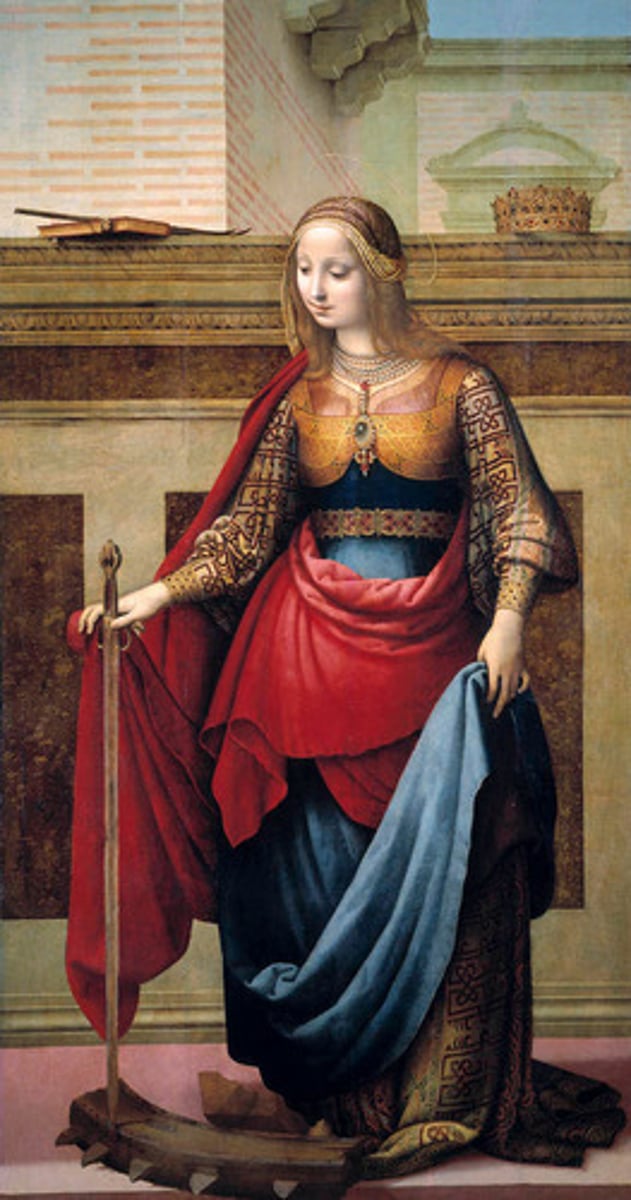
Saint Catherine
Artist Fernando Yañez de la Almedina.
Oil on wood.
c. 1506.
Colors are bright.
Focused on one person.
Composition: crown, book, sword, wheel.
Clothing is natural.
Elegant, self-control facial expression.
Sfumato (Fumo in Spanish = smoked, smoke, I smoke), technique used by Leonardo Da Vinci for a more naturalistic face.
Idealization: ideal version of beauty.

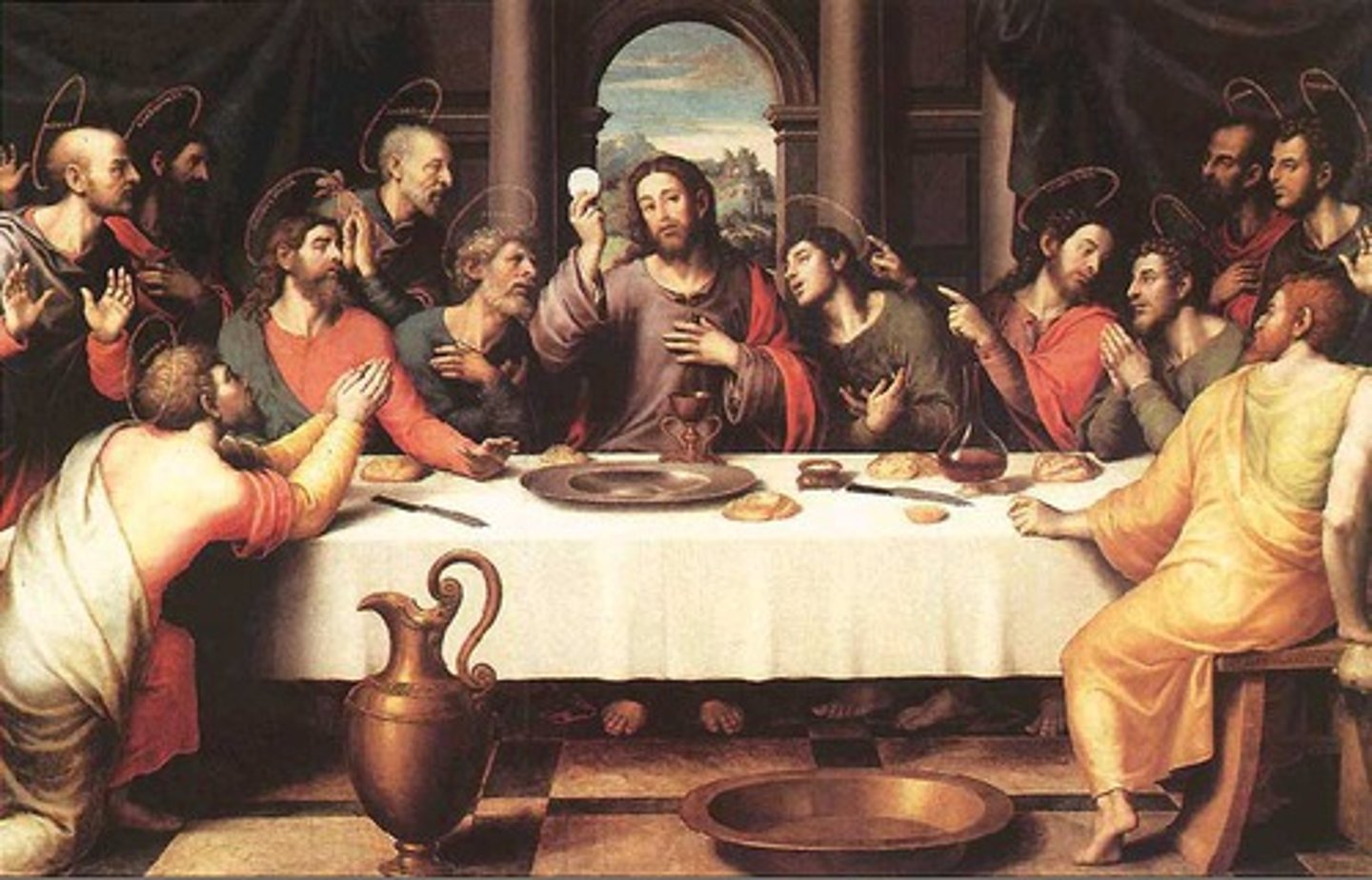
Last Supper
Artist Juan de Juanes
c. 1560-1565.
Oil on wood.
Commissioned by church of Valencia.
Cup included on painting is a pretend relic the church owns.
Centered on Jesus, six people each side, round arch emphasizing his holiness.
Colors inspired by Raphael, death in 1520 causes many artists to imitate his style.
Figures inspired by Michelangelo.

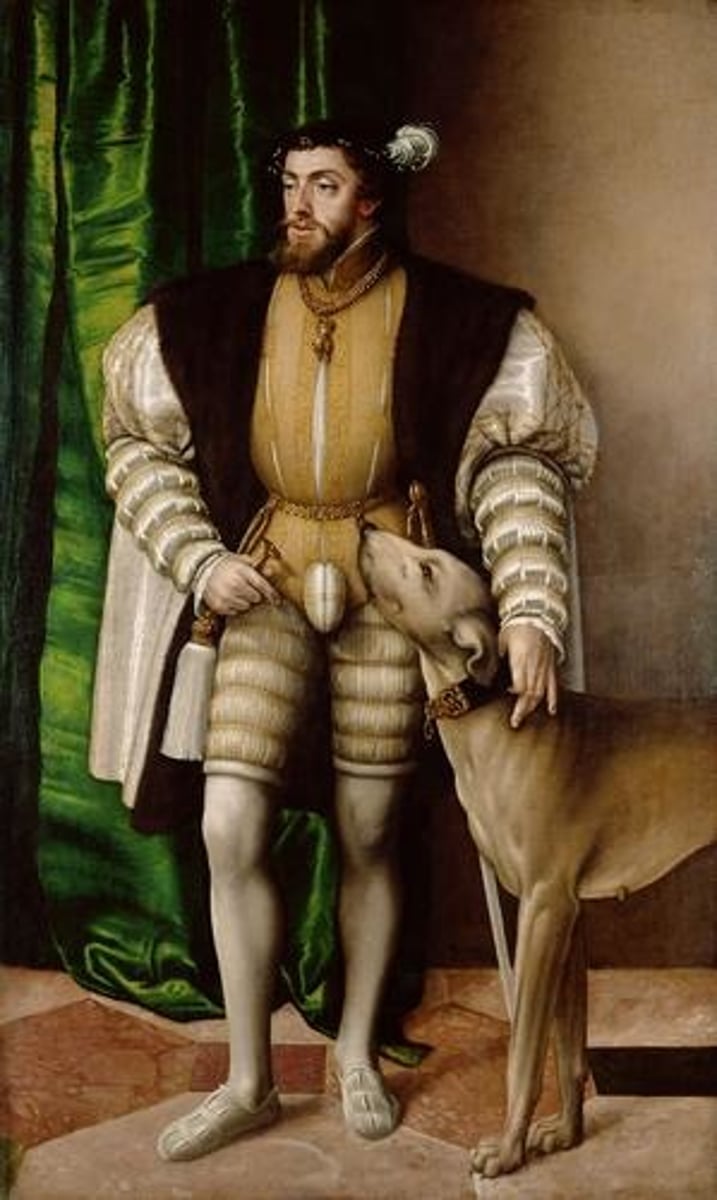
Charles V.
Artist Titian.
1532-1533.
Portraiture.
First portrait of a King where he is represented with his full body.

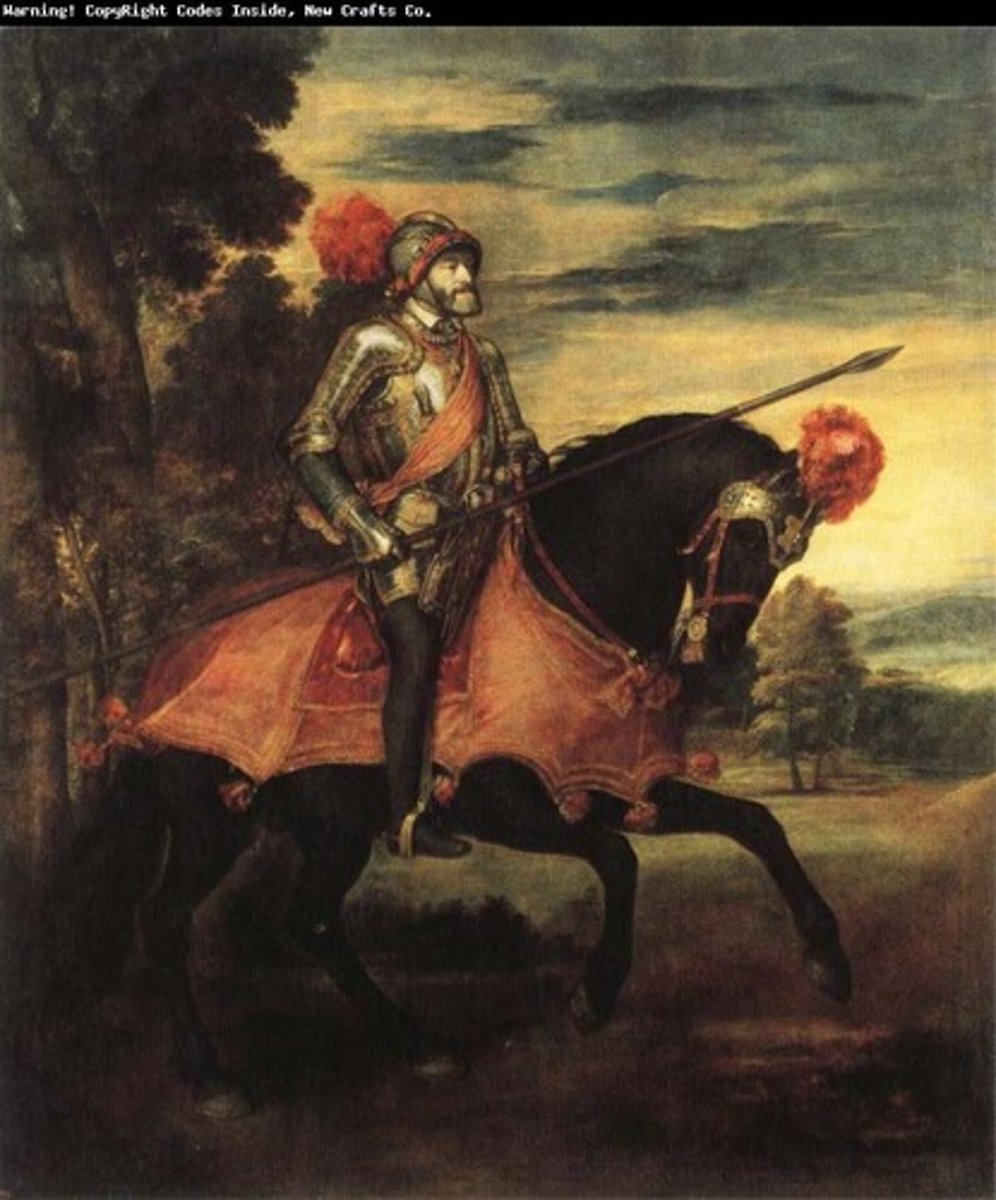
Equestrian Portrait of Charles V at Mühlberg.
Artist Titian.
1548.
King coming back from war.

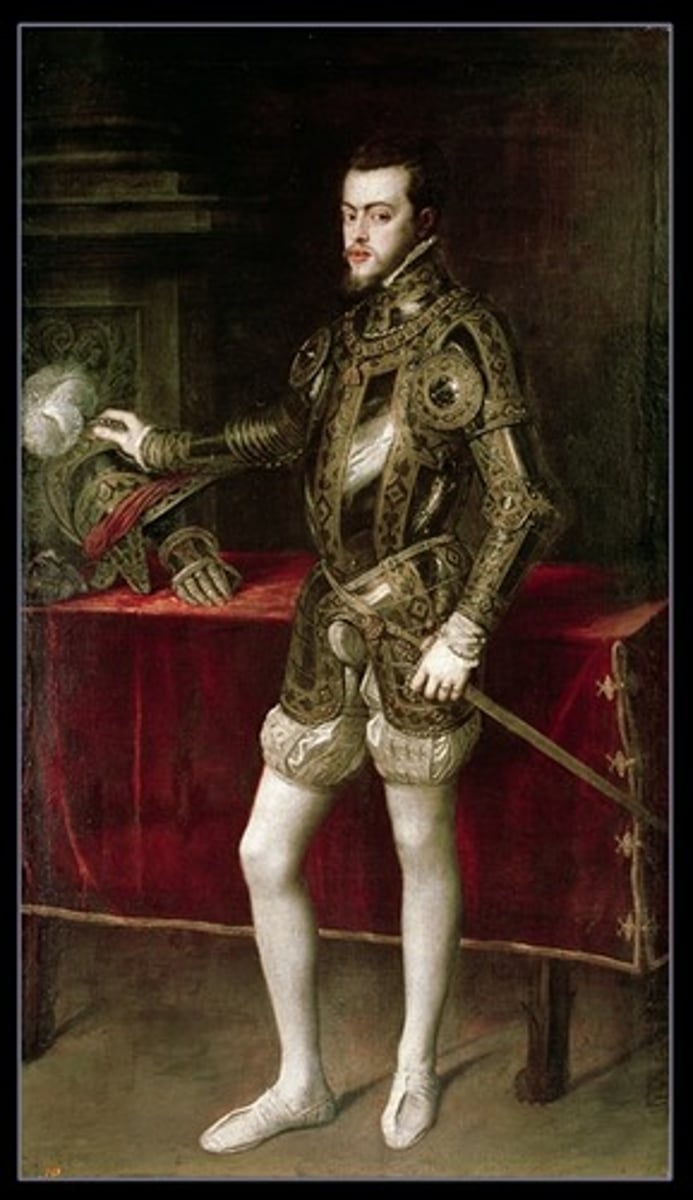
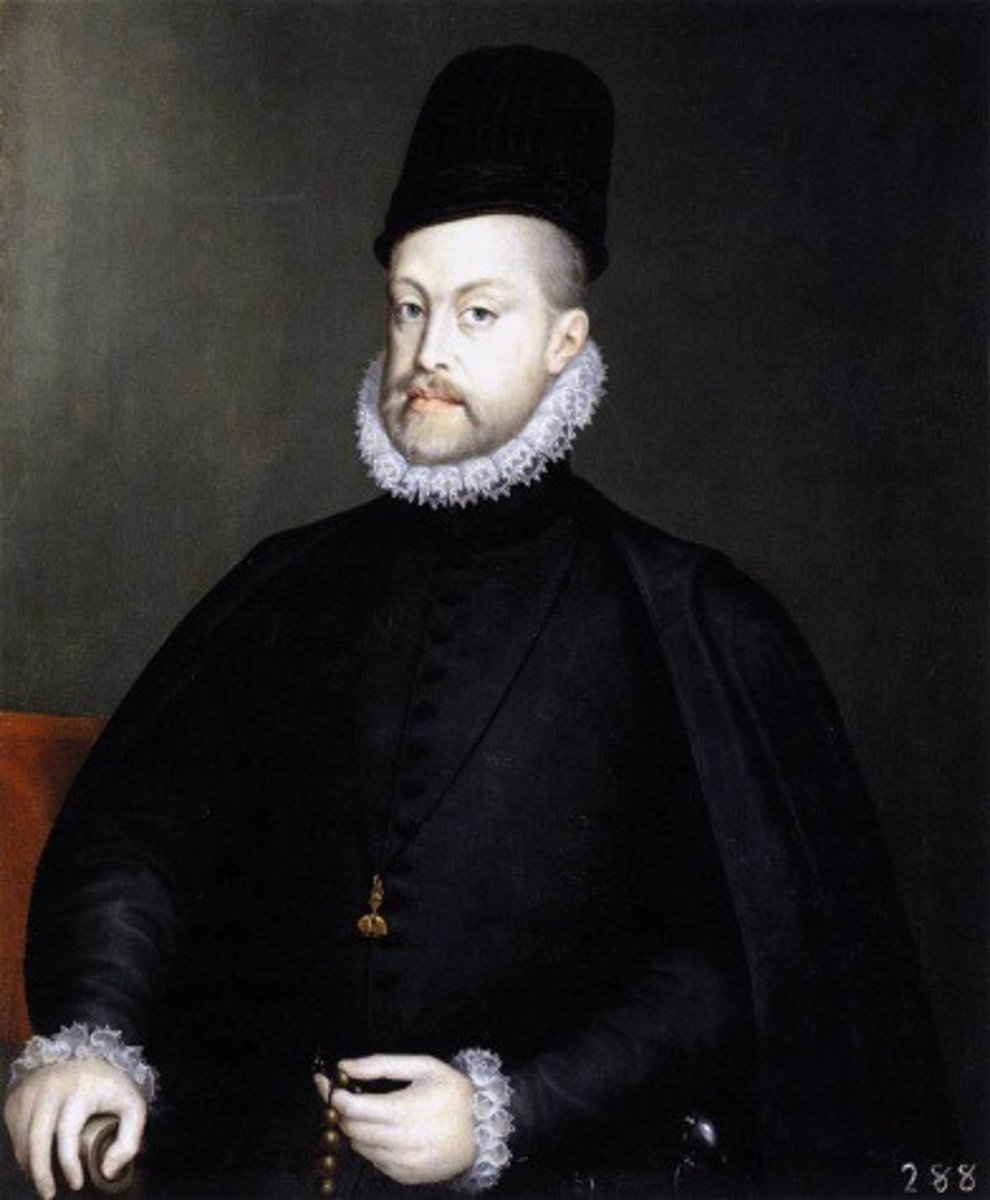
Portrait of Philip II.
1551.
Prado Museum.
193 x 111 cm.
A king at work, wearing armor.
Sets this iconography.
Artist Titian.

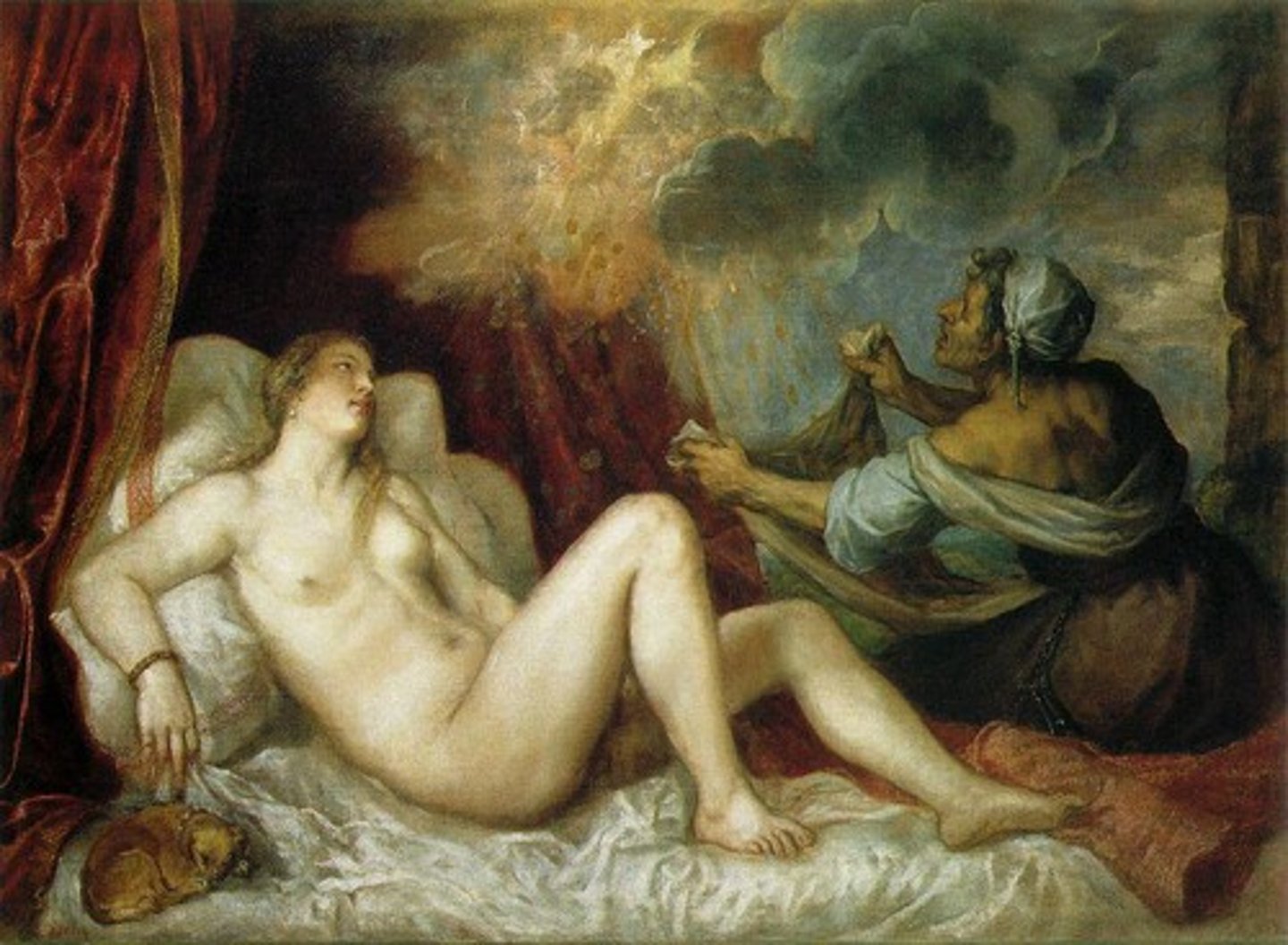
Danaë and the Shower of Gold.
Artist Titian.
16th century.
Princess, prophecy her son will dethrone her grandfather so she is locked in tower.
Prioritizing color and light.
Tonal painting, using different tones to create texture/volume.

Portrait of Philip II.
Artist Sofonisba Anguissola.
16th century.
Female artist, her and her sisters became artists and writers.
Kings and queens were painted separately, that way if one of them died, the other portrait could still be used.
Holding a rosary was new for the time and showed that he was a good Catholic and very religious.
Artist was not allowed to be the head artist because of gender roles but she did travel and work for the royal family.
Wearing a Golden Fleece to showcase his royalty.

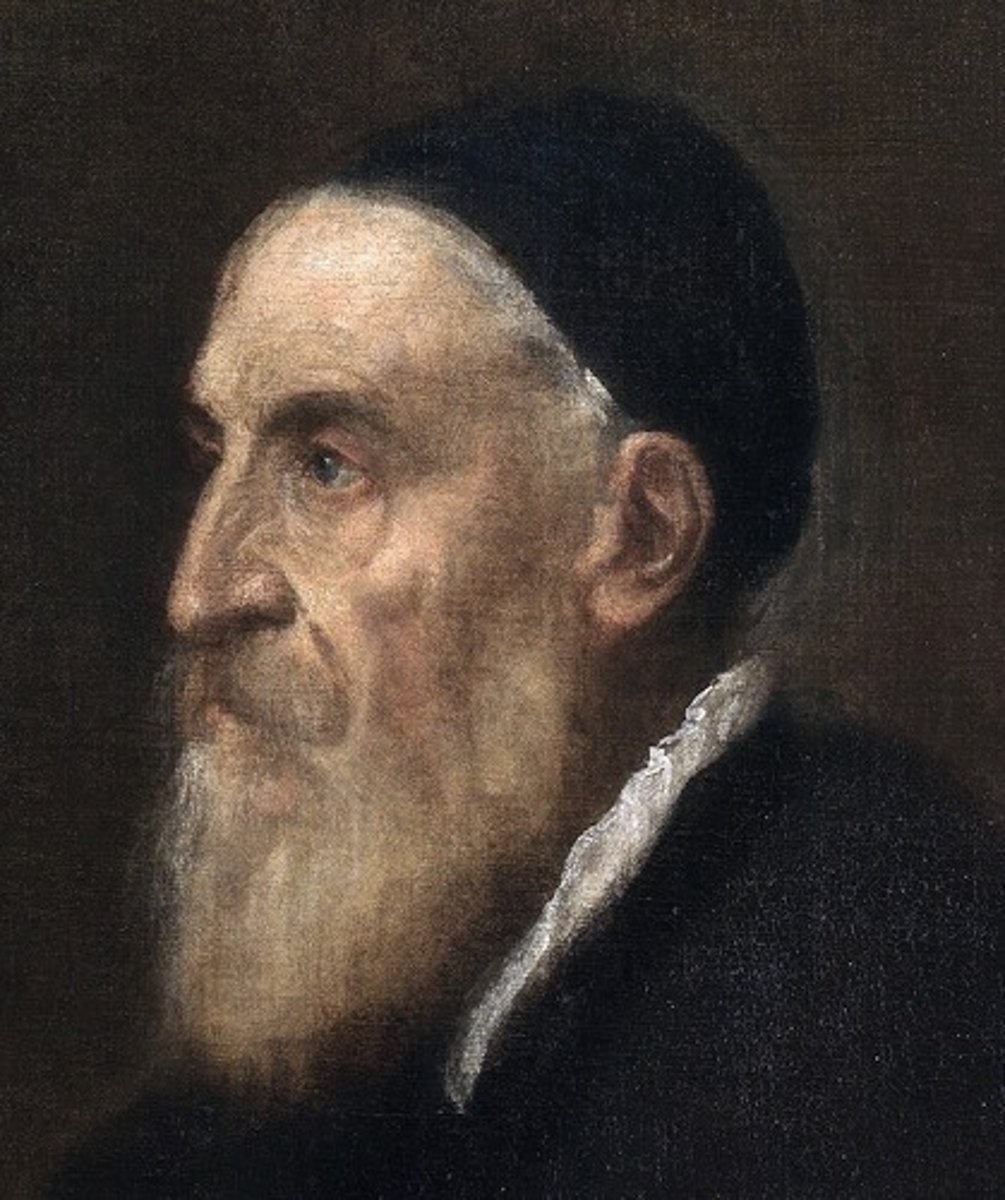
Self-portrait.
Artist Titian.
16th century.
Depicting himself as an old man and successful artist through clothing (fur, double golden chains).

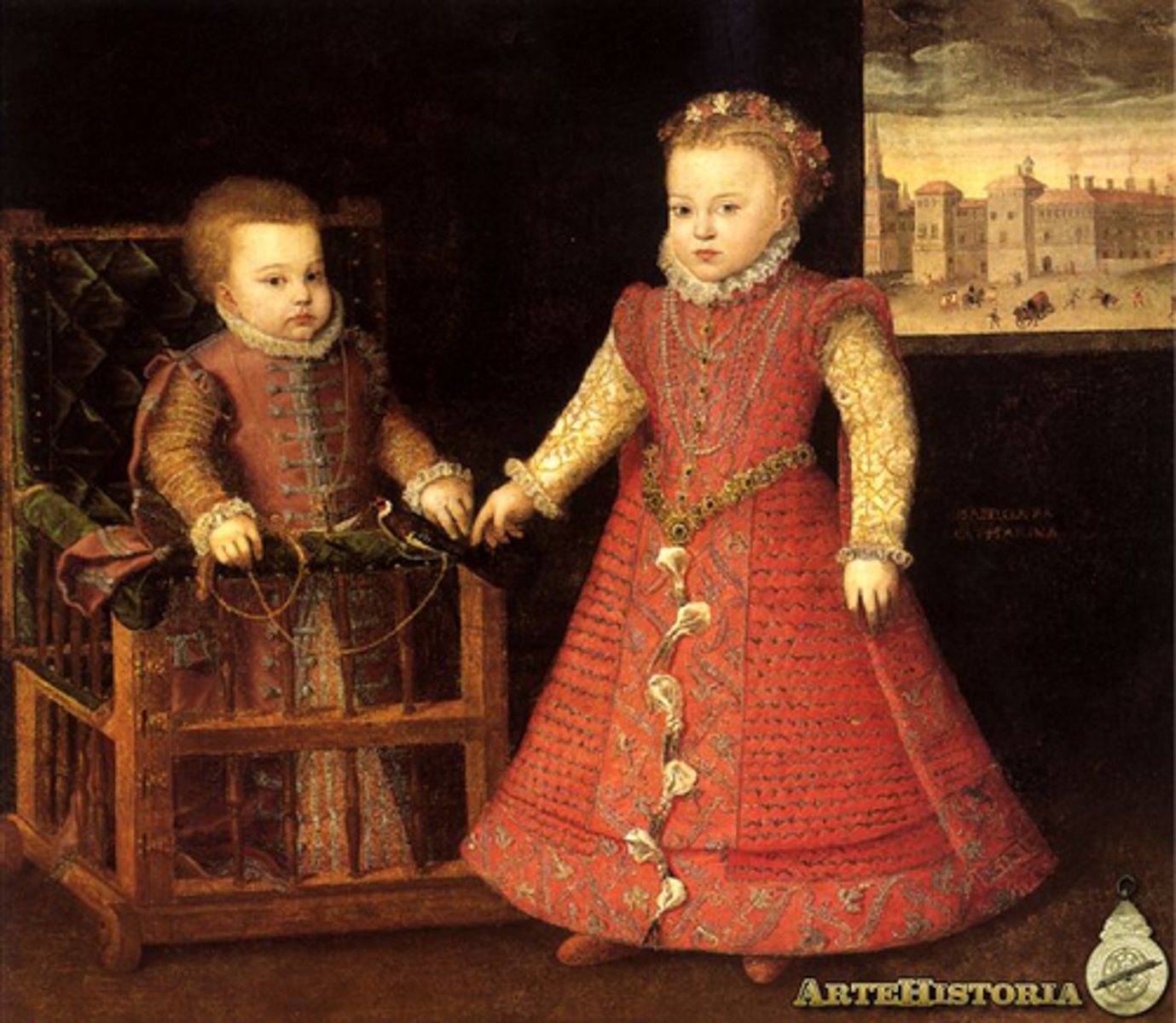
Portrait of the Infanta Isabel Clara Eugenia and Magdalena Ruiz.
Artist Alfonso Sánchez Coello.
16th century.
Daughter of Philip II.
Magdalena Ruiz, someone who accompanies the royal family and served Charles V which was a privilege at the time.
Golding the broach of Philip II, "cameo".
Colors on dress, coral beads, and monkeys symbolize the annex of Portugal.

The infantas Isabel Clara Eugenia and Catalina Micaela.
Artist Alfonso Sánchez Coello.
16th century.
Window shows alcazar, fortress, and royal palace.
Words that start with "al" are from the Islamic period.

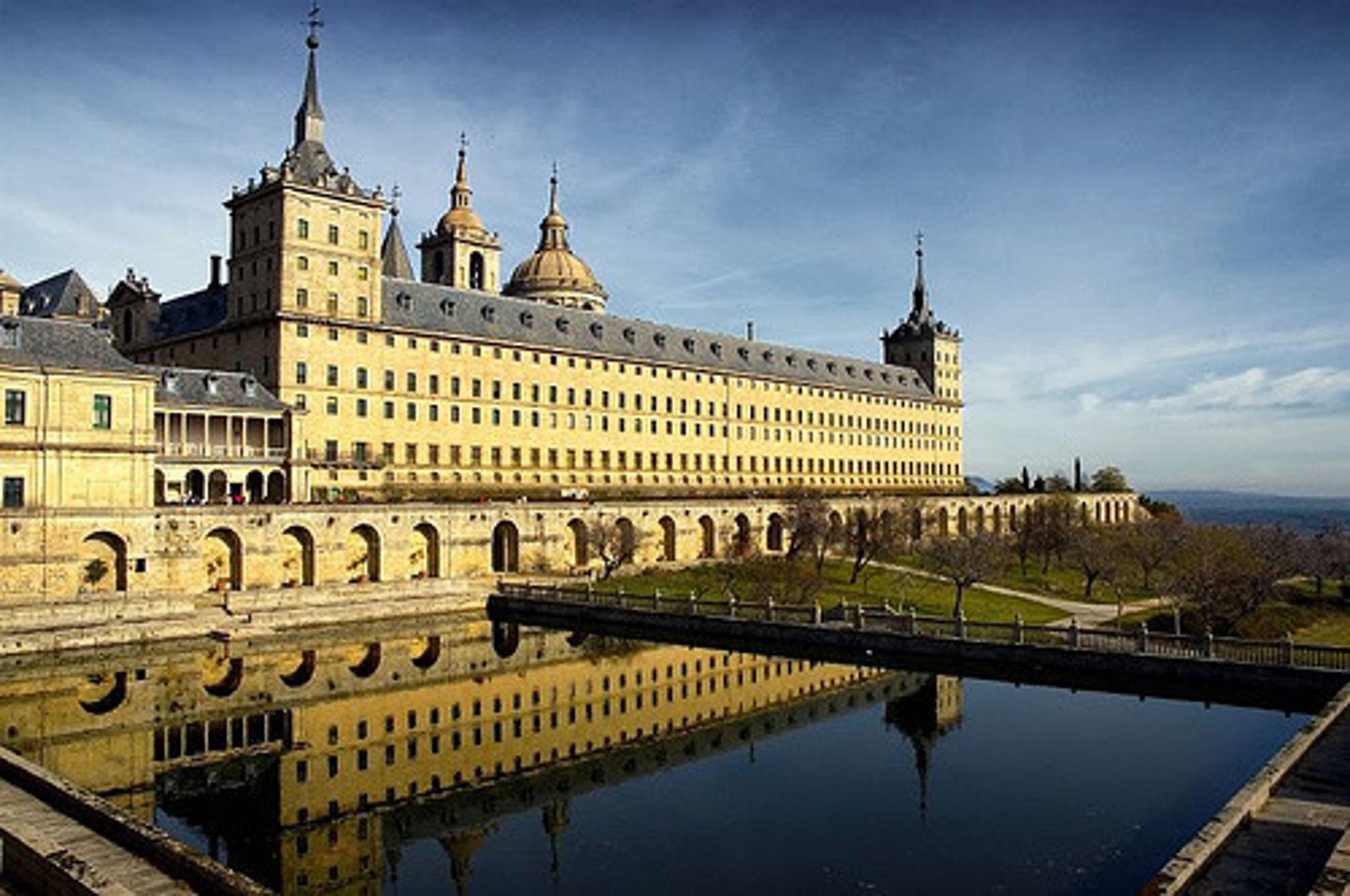
El Escorial: Floor map, Façade, Library, Courtyard of Kings, Basilica major altarpiece.
16th century.
Geometry, ratio, proportion, Renaissance ideal.
Eucharist is at the center, the vanishing point.
Importance of nature showed Islamic influence.

Christ Healing the Blind.
Artsit El Greco
c. 1567.
Venice before 1567.
Inspired by TIntoretto The Washing of the Feet because of the colors
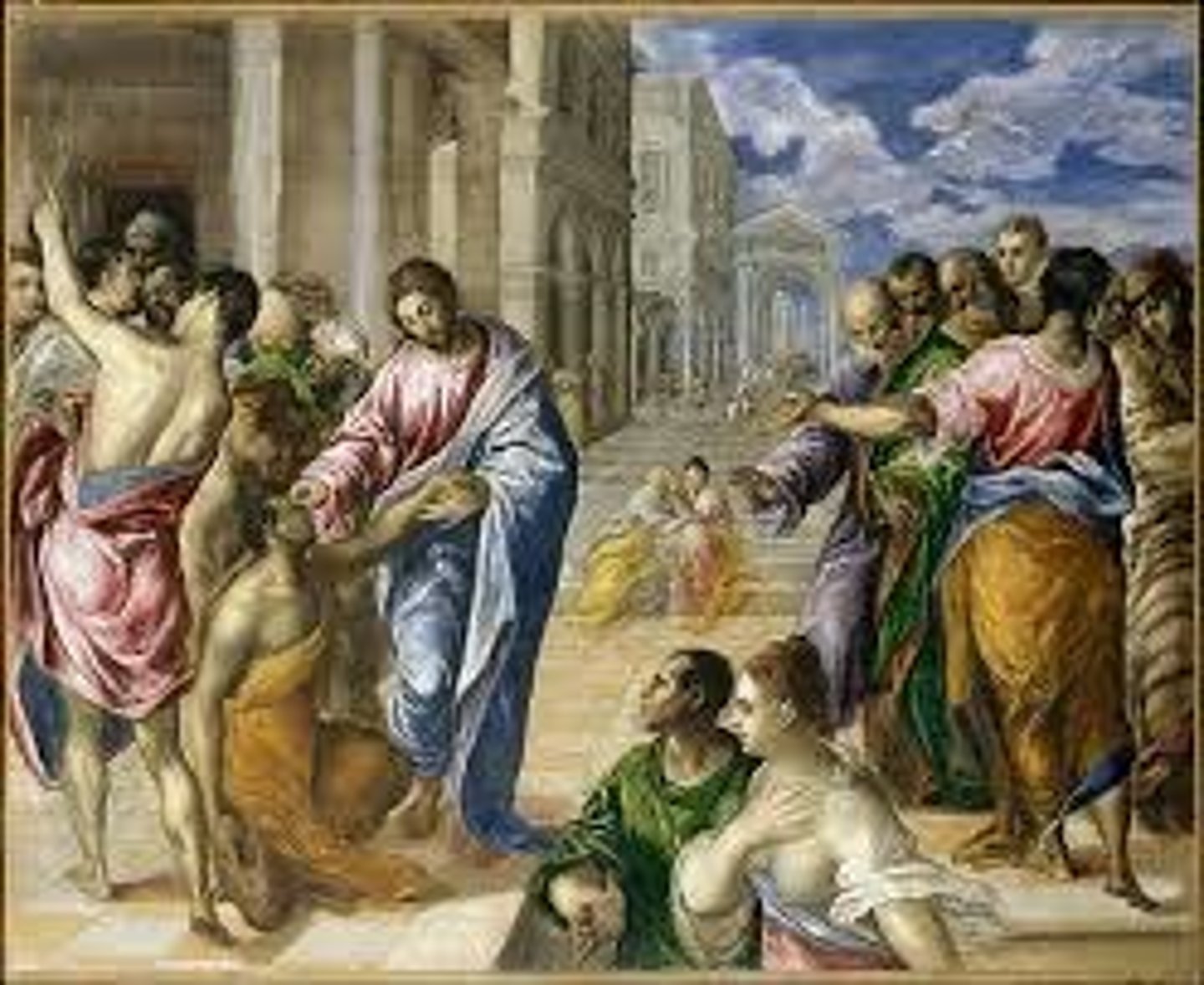

Annunciation.
Artist El Greco.
c. 1576.
Oil on canvas.
117 x 98 cm.
Thyssen Bomemizsa Museum.
Figure of angel is inspired by Michelangelo because he is floating, s-shape, twisted, and contorted.
Linear perspective.

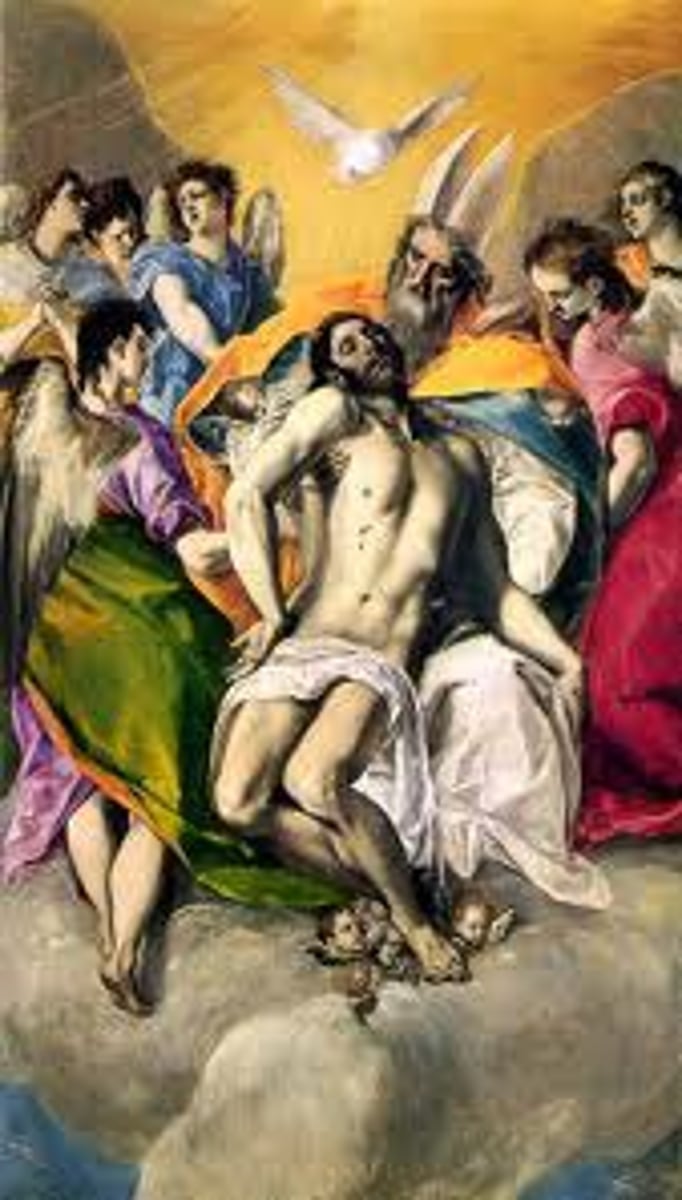
Holy Trinity.
Artist El Greco.
c. 1577.
Mature style.
Body of Christ is very present and you can see physicality (emphasis on Christ being a human being).
Important because Protestants did not believe that the bread became the body of Christ.
Michelangelo influence because of shape of bodies.
Emphasis on emotions.
God the father holding Jesus showed a new masculinity because he showed emotions and it was the first time he was depicted holding Jesus.

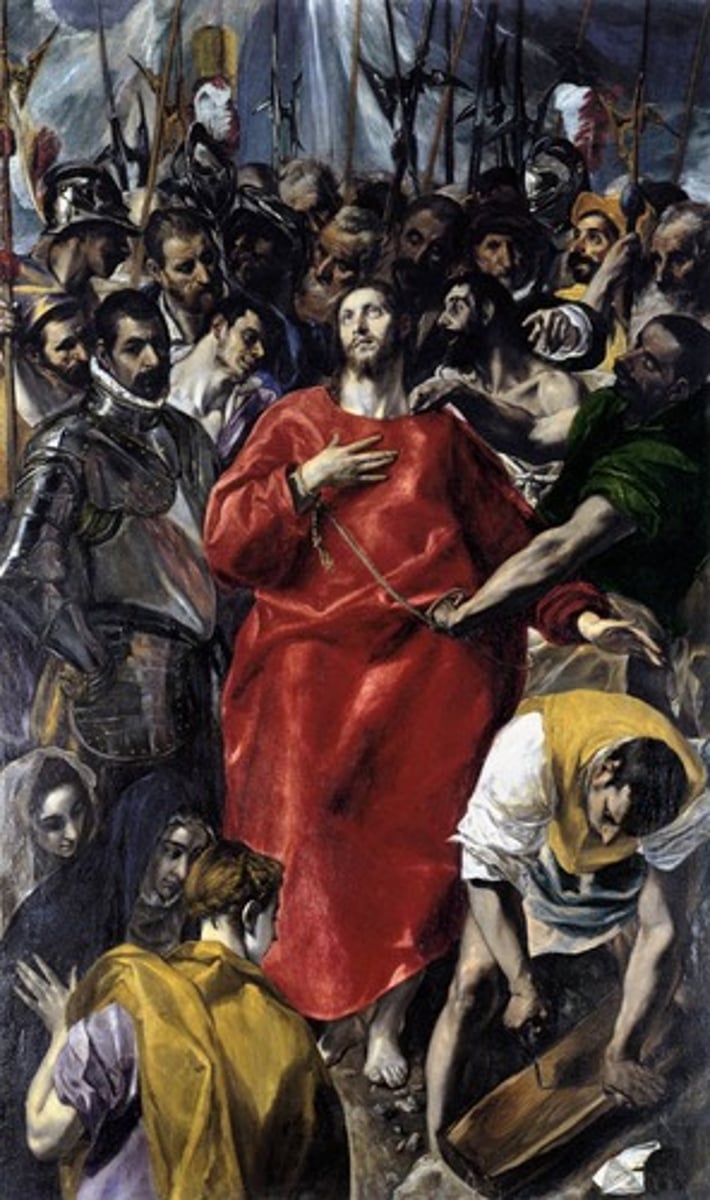
The Disrobing of Christ.
c. 1577-79.
Artist El Greco.
Commissioned by the Cathedral of Toledo for the Sacristy room.
Dean of the church did not like the painting because it showed Three Mary's not in the Bible, people were above Christ, and clashed with the decorum of the Catholic Church.
Dean of the church sued El Greco.
Red tunic symbolizes blood.

St. Maurice Martydom.
Artist El Greco.
1580-1582.
Commissioned for San Lorenzo del Escorial.
Roman solider, forced to participate in religious acts he doesn't believe in, is decapitated for standing up for his faith (Catholicism).
Painting took 2 years, King Philip II didn't like it because it was "too artistic".
King Philip II did not like that the message was more hidden.
Paid El Greco but kept the painting hidden.

Burial of the Count of Orgaz.
Artist El Greco.
1586-1588.
Oil on canvas.
480 x 360 cm.
For Santo Tomé Church in Toledo.
Family of Count of Orgaz was Catholic and he died in the 14th century.
Saints came down to assist with burial.
The group showcases important people in Toledo.
Red Cross showed highest nobility.
Texture of clothing is detailed.
Two different scenes: burial and heaven.
Figures in heaven are elongated and have a different lighting.
Contemporary and saintly figures.

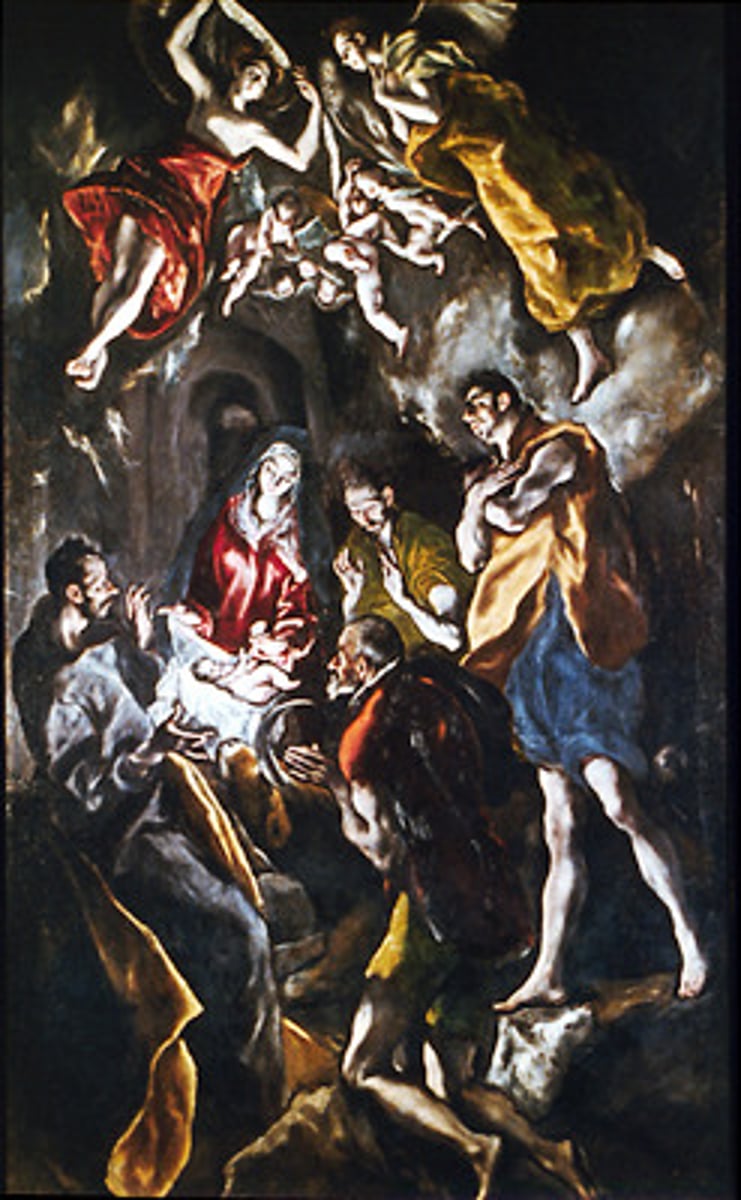
Adoration of the Shepherds.
Artist El Greco.
c. 1613.
Prado Museum.
Very elongated figures.
Setting is confusing but the figures matter.
Mannerism but start of Baroque period (light, emotions).

How is Spanish art unique within its European context?
Spanish art has Roman, Islamic, and Flemish influences.
Explain the Islamic past of the city of Madrid. Is there any artistic evidence of the presence of the Muslim peoples in the capital of Spain?
rabe
rdoba Eight centuries Iberian Peninsula under Muslim rule.
Al-Ándalus: When Spain was under Muslim rule.
Bell tower in Church of San Pedro el viejo looks like a minaret and was built over a mosque. It was made by Islamic architects but paid for by the Christians and they took inspiration from Islamic artists.
Beginning of 8th century, Muslims started occupying the Iberian Peninsula and it took about 800 years for the Christians to begin taking over. In 1492 no Muslims were left because the Catholic Kings expelled them, which is the reconquest.
8th century: Ummayads arrive from Damascus.
Evidence:
- La casa encendida
- La casa árabe
- Las ventas bullfighting
- Church of Santa Cristina
- School "El Recuerdo"
- Matadero de Madrid
Briefly explain the foundations of Islamic art and architecture.
Muslim religion is not humanistic at the center, you are a tiny speck of dust in comparison to God.
Geometry, religion, and plants for decoration.
Most important part of the mosque: Mihrab is empty.
Complicated arches in a decorative way.
Macsura cupola decorated with mosaic. Octagonal dome above the mihrab flanked by columns with interlaced multi-lobed arches.
Geometry: synchrony, perfect, represents God.
Describe Madrid in the time of Catholic Kings and mention any royal commission created at the time.
5th to 15th centruy
Mainly feudal and rural, people were attached to their land.
A period of territorial and religious wars, famine, and disease.
People traveled during the Iberian Peninsula and took the word of God to the "end of the world".
Relics had a very important role in the economy, spiritually, and with people's curiosity which caused churches, towns, and cities to try and get the best relics to get people to visit.
Roman Empire society, political system, and economy had slavery at its core.
Theocentric society, Christianity spread.
Land was given free of charge to Christians who chose to establish themselves in the city of Madrid to increase population, located between Segovia and Toledo.
Commissioned work:
- Portrait of Philip II by Titian
- Equestrian Portrait of Charles V at Mühlberg by Titian
How was the art produced in the time of Charles V? Explain subjects, influences, and main artists.
Subjects: Infanta Isabel Clara Eugenia, Philip II, Charles V, Venus in mythological paintings
Influences: Raphael, Michelangelo
Artists: Titian, Alonso Sánchez Coello
The art was commissioned by churches and the royal family.
Explain the different stages in the art and architecture in the Spanish Renaissance with all its particularities.
What is Titian's role in Spanish art?
Titian worked closely with the royal family to create portraits, such as Charles V and Philip II. He also created mythological paintings including Danaë and the Shower of Gold.
Explain Philip II's role as an art patron specifying the art portrayed at El Escorial.
El Escorial is what Philip II is recognized for and the geometry, ratio, and proportion reflected the idealism of the Renaissance. Patronage was important during the Renaissance.
Which were El Greco's influences before his arrival to Spain? Elaborate.
El Greco was born in Crete and spent 10 years in Italy as an artist. He associated himself with Venetian artists and was influenced by them. The colors he used, creating more tonal paintings where the colors were tinted by other tones, was from the influence of Venetian artists. Some of his work was influenced by Michelangelo because of the shape of the figures, which is shown in his painting Annunciation. He was also inspired by Tintoretto and the Mannerist style, which emphasized elongated forms and dramatic compositions.
Explain El Greco's connection to the Counter Reformation: was he an important figure in such process?
El Greco was an important figure to the Counter Reformation because he was commissioned to create artwork depicting religious symbolism. One of these artworks in Saint Maurice Martyrdom. This artwork depicted a saint who was forced to participate in a religious act he didn't believe in, so when he stood up for his faith in Catholicism, he was decapitated. Also his painting Holy Trinity shows the body of Christ and there is emphasis on Christ being a human being.